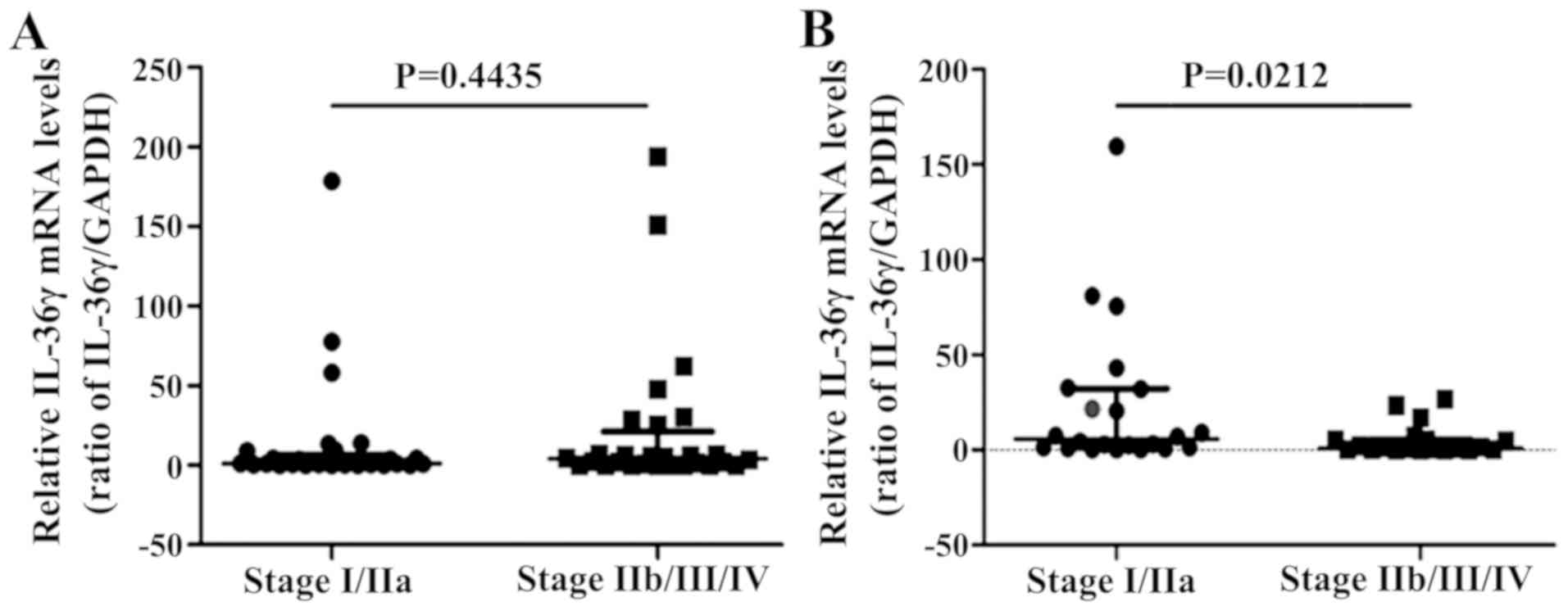
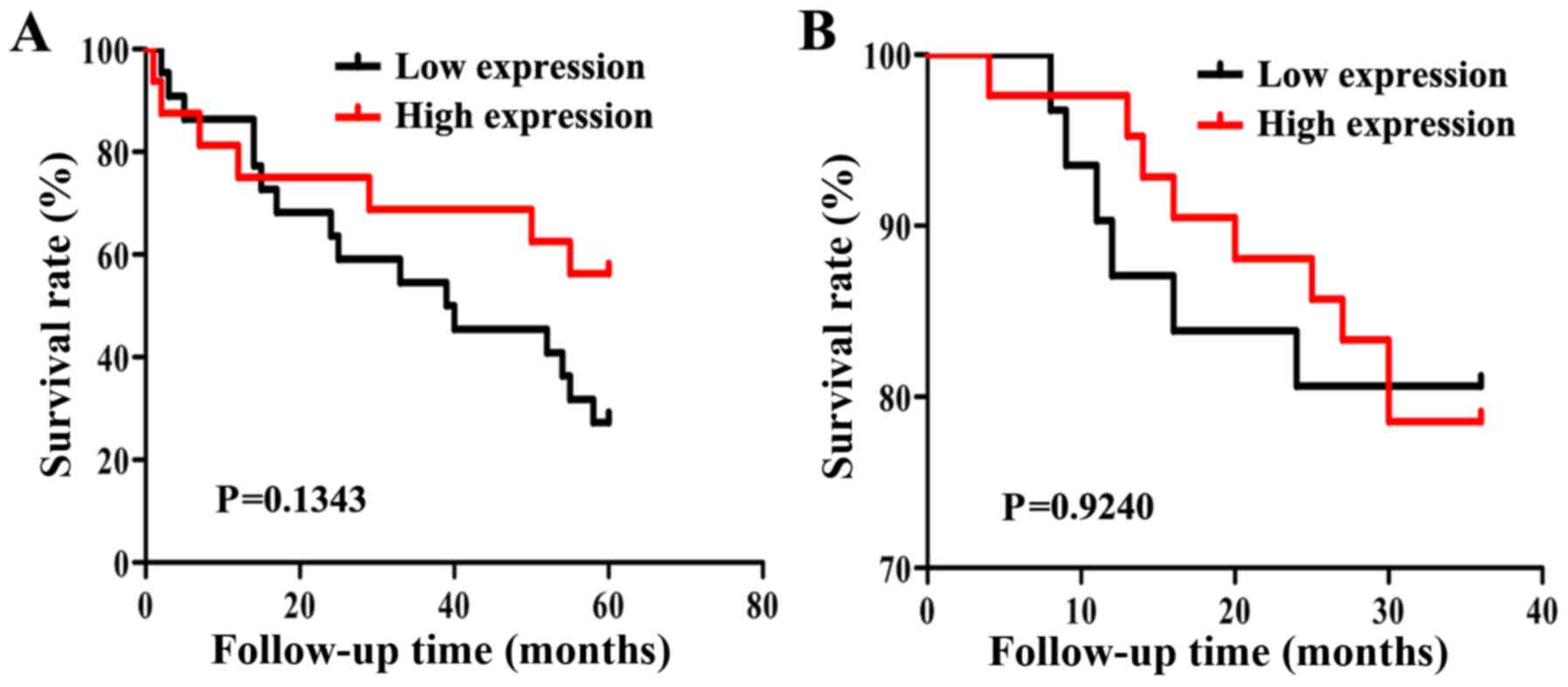
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miura Y and Sunaga N: Role of
immunotherapy for oncogene-driven non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 10:E2452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Burnet M: Cancer; A biological approach.
I. The processes of control. Br Med J. 1:779–786. 1957. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schreiber RD, Old LJ and Smyth MJ: Cancer
immunoediting: Integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression
and promotion. Science. 331:1565–1570. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sugie T: Immunotherapy for metastatic
breast cancer. Chin Clin Oncol. 7:282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mellman I, Coukos G and Dranoff G: Cancer
immunotherapy comes of age. Nature. 480:480–489. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X, Zhao X, Feng C, Weinstein A, Xia
R, Wen W, Lv Q, Zuo S, Tang P, Yang X, et al: IL-36γ transforms the
tumor microenvironment and promotes type 1 lymphocyte-mediated
antitumor immune responses. Cancer Cell. 28:296–306. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lippitz BE: Cytokine patterns in patients
with cancer: A systematic review. Lancet Oncol. 14:e218–228. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gresnigt MS and van de Veerdonk FL:
Biology of IL-36 cytokines and their role in disease. Semin
Immunol. 25:458–465. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bassoy EY, Towne JE and Gabay C:
Regulation and function of interleukin-36 cytokines. Immunol Rev.
281:169–178. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qin X, Liu M, Zhang S, Wang C and Zhang T:
The role of IL-36γ and its regulation in eosinophilic inflammation
in allergic rhinitis. Cytokine. 117:84–90. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ramadas RA, Li X, Shubitowski DM, Samineni
S, Wills-Karp M and Ewart SL: IL-1 receptor antagonist as a
positional candidate gene in a murine model of allergic asthma.
Immunogenetics. 58:851–855. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Blumberg H, Dinh H, Trueblood ES,
Pretorius J, Kugler D, Weng N, Kanaly ST, Towne JE, Willis CR,
Kuechle MK, et al: Opposing activities of two novel members of the
IL-1 ligand family regulate skin inflammation. J Exp Med.
204:2603–2614. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Johnston A, Xing X, Guzman AM, Riblett M,
Loyd CM, Ward NL, Wohn C, Prens EP, Wang F, Maier LE, et al:
IL-1F5, -F6, -F8, and -F9: A novel IL-1 family signaling system
that is active in psoriasis and promotes keratinocyte antimicrobial
peptide expression. J Immunol. 186:2613–2622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chustz RT, Nagarkar DR, Poposki JA,
Favoreto S Jr, Avila PC, Schleimer RP and Kato A: Regulation and
function of the IL-1 family cytokine IL-1F9 in human bronchial
epithelial cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 45:145–153. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gresnigt MS, Rosler B, Jacobs CW, Becker
KL, Joosten LA, van der Meer JW, Netea MG, Dinarello CA and van de
Veerdonk FL: The IL-36 receptor pathway regulates aspergillus
fumigatus-induced Th1 and Th17 responses. Eur J Immunol.
43:416–426. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Vigne S, Palmer G, Martin P, Lamacchia C,
Strebel D, Rodriguez E, Olleros ML, Vesin D, Garcia I, Ronchi F, et
al: IL-36 signaling amplifies Th1 responses by enhancing
proliferation and Th1 polarization of naive CD4+ T
cells. Blood. 120:3478–3487. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weinstein AM, Chen L, Brzana EA, Patil PR,
Taylor JL, Fabian KL, Wallace CT, Jones SD, Watkins SC, Lu B, et
al: Tbet and IL-36γ cooperate in therapeutic DC-mediated promotion
of ectopic lymphoid organogenesis in the tumor microenvironment.
Oncoimmunology. 6:e13222382017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang M, Feng Y, Yue C, Xu B, Chen L, Jiang
J, Lu B and Zhu Y: Lower expression level of IL-33 is associated
with poor prognosis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. PLoS One.
13:e01934282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Feng SH and Yang ST: The new 8th TNM
staging system of lung cancer and its potential imaging
interpretation pitfalls and limitations with CT image
demonstrations. Diagn Interv Radiol. 25:270–279. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen C, Qu QX, Xie F, Zhu WD, Zhu YH and
Huang JA: Analysis of B7-H4 expression in metastatic pleural
adenocarcinoma and therapeutic potential of its antagonists. BMC
Cancer. 17:6522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun J, Chen LJ, Zhang GB, Jiang JT, Zhu M,
Tan Y, Wang HT, Lu BF and Zhang XG: Clinical significance and
regulation of the costimulatory molecule B7-H3 in human colorectal
carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 59:1163–1171. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liew FY, Pitman NI and McInnes IB:
Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1
family. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:103–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Lv Q, Feng Y, Gu Y, Xia R, Ma J, He
H and Zhu Y: Interleukin-33, a potential cytokine expressed in
tumor microenvironment involves in antitumor immunotherapy through
facilitates CD8(+) T cells. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 38:491–499.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhao X, Chen X, Shen X, Tang P, Chen C,
Zhu Q, Li M, Xia R, Yang X, Feng C, et al: IL-36β promotes CD8(+) T
cell activation and antitumor immune responses by activating
mTORC1. Front Immunol. 10:18032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Boutet MA, Bart G, Penhoat M, Amiaud J,
Brulin B, Charrier C, Morel F, Lecron JC, Rolli-Derkinderen M,
Bourreille A, et al: Distinct expression of interleukin (IL)-36α, β
and γ, their antagonist IL-36Ra and IL-38 in psoriasis, rheumatoid
arthritis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 184:159–173. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tomuschat C, O'Donnell AM, Coyle D and
Puri P: Altered expression of IL36γ and IL36 receptor (IL1RL2) in
the colon of patients with Hirschsprung's disease. Pediatr Surg
Int. 33:181–186. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gardner JK and Herbst-Kralovetz MM: IL-36γ
induces a transient HSV-2 resistant environment that protects
against genital disease and pathogenesis. Cytokine. 111:63–71.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiaoling Y, Chao W, Wenming W, Feng L and
Hongzhong J: Interleukin (IL)-8 and IL-36γ but not IL-36Ra are
related to acrosyringia in pustule formation associated with
palmoplantar pustulosis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 44:52–57. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wein AN, Dunbar PR, McMaster SR, Li ZT,
Denning TL and Kohlmeier JE: IL-36γ protects against severe
influenza infection by promoting lung alveolar macrophage survival
and limiting viral replication. J Immunol. 201:573–582. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen Y, Sun J, Huang Y, Liu Y, Liang L,
Yang D, Lu B and Li S: Targeted codelivery of doxorubicin and
IL-36γ expression plasmid for an optimal chemo-gene combination
therapy against cancer lung metastasis. Nanomedicine. 15:129–141.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huynh J, Scholz GM, Aw J, Kwa MQ, Achuthan
A, Hamilton JA and Reynolds EC: IRF6 regulates the expression of
IL-36γ by human oral epithelial cells in response to porphyromonas
gingivalis. J Immunol. 196:2230–2238. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Foster AM, Baliwag J, Chen CS, Guzman AM,
Stoll SW, Gudjonsson JE, Ward NL and Johnston A: IL-36 promotes
myeloid cell infiltration, activation, and inflammatory activity in
skin. J Immunol. 192:6053–6061. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vigne S, Palmer G, Lamacchia C, Martin P,
Talabot-Ayer D, Rodriguez E, Ronchi F, Sallusto F, Dinh H, Sims JE
and Gabay C: IL-36R ligands are potent regulators of dendritic and
T cells. Blood. 118:5813–5823. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|