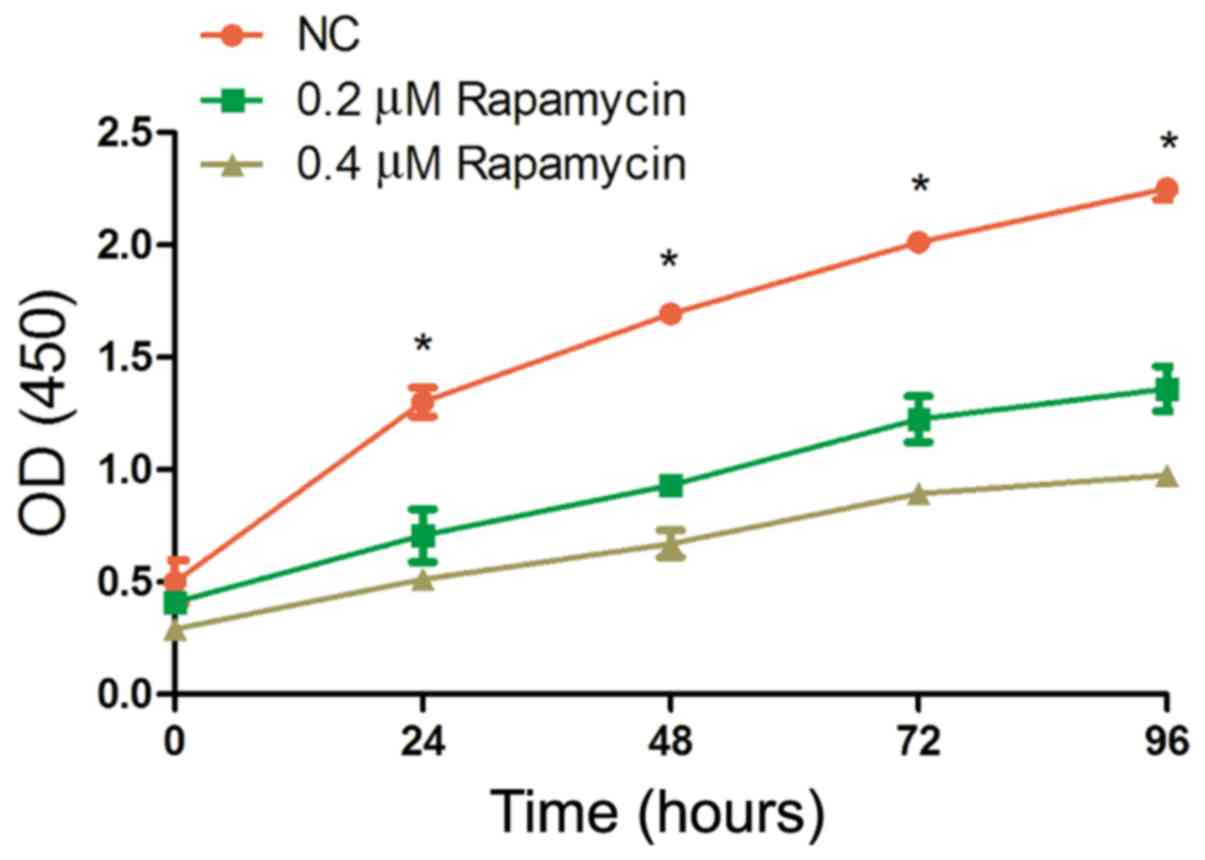
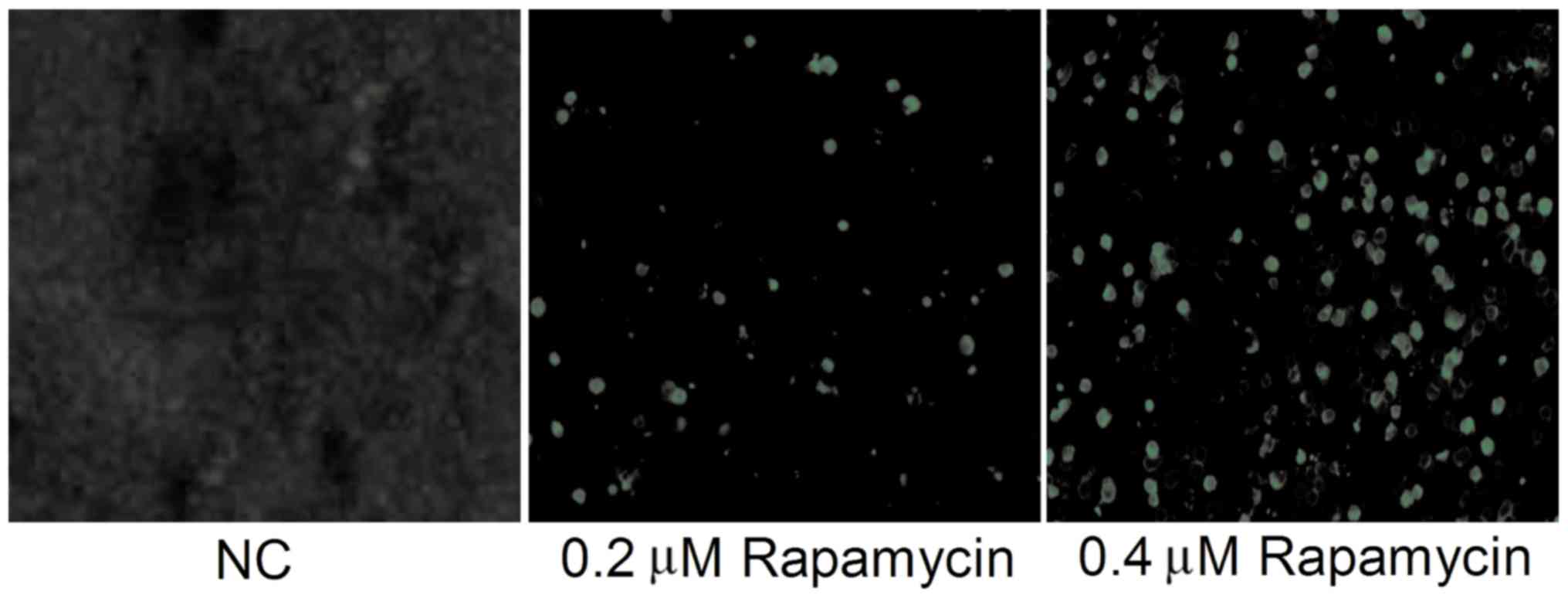
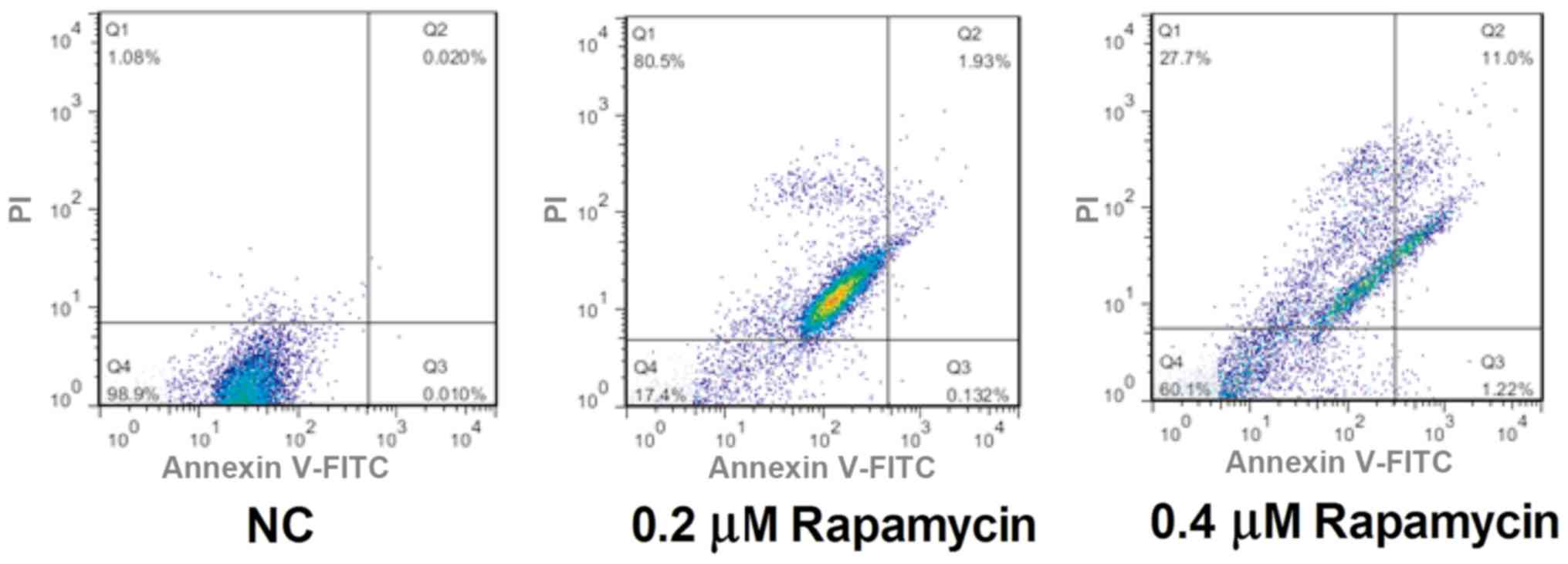
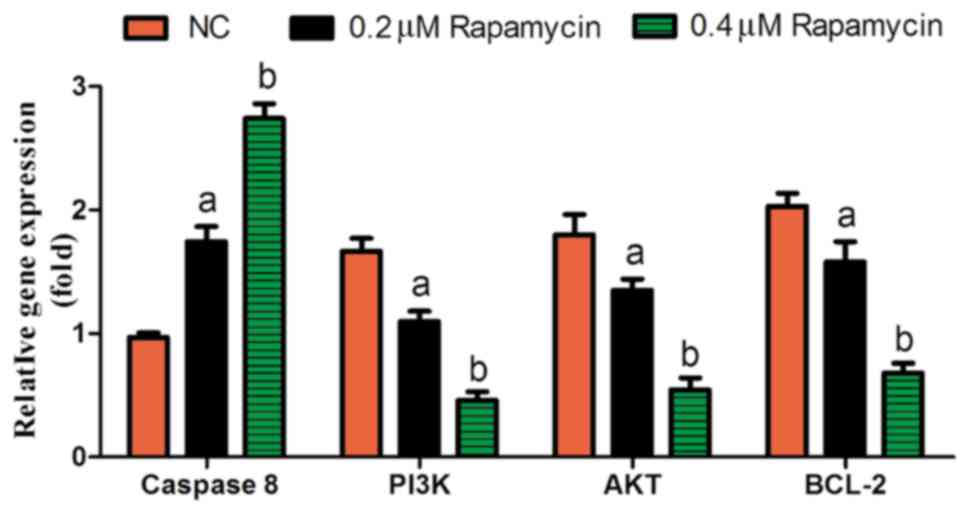
|
1
|
Bi LL, Han F, Zhang XM and Li YY: LncRNA
MT1JP acts as a tumor inhibitor via reciprocally regulating
Wnt/β-Catenin pathway in retinoblastoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
22:4204–4214. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Broaddus E, Topham A and Singh AD:
Survival with retinoblastoma in the USA: 1975–2004. Br J
Ophthalmol. 93:24–27. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yin L, Sun Z, Ren Q, Su X and Zhang D:
Methyl eugenol induces potent anticancer effects in RB355 human
retinoblastoma cells by inducing autophagy, cell cycle arrest and
inhibition of PI3K/mTOR/Akt signalling pathway. J BUON.
23:1174–1178. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang HF, Zheng SF, Chen Y, Zhou ZY and Xu
J: Correlations between claudin-1 and PIGF expressions in
retinoblastoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:4196–4203.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zheng Q, Zhang Y, Ren Y, Wu Y, Yang S,
Zhang Y, Chen H, Li W and Zhu Y: Antiproliferative and apoptotic
effects of indomethacin on human retinoblastoma cell line Y79 and
the involvement of β-catenin, nuclear factor-κB and Akt signaling
pathways. Ophthalmic Res. 51:109–115. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vézina C, Kudelski A and Sehgal SN:
Rapamycin (AY-22,989), a new antifungal antibiotic. I. Taxonomy of
the producing streptomycete and isolation of the active principle.
J Antibiot (Tokyo). 28:721–726. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Milani BY, Milani FY, Park DW, Namavari A,
Shah J, Amirjamshidi H, Ying H and Djalilian AR: Rapamycin inhibits
the production of myofibroblasts and reduces corneal scarring after
photorefractive keratectomy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
54:7424–7430. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ocana A, Vera-Badillo F, Al-Mubarak M,
Templeton AJ, Corrales-Sanchez V, Diez-Gonzalez L, Cuenca-Lopez MD,
Seruga B, Pandiella A and Amir E: Activation of the PI3K/mTOR/AKT
pathway and survival in solid tumors: Systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 9:e952192014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Moirangthem DS, Laishram S, Rana VS, Borah
JC and Talukdar NC: Essential oil of Cephalotaxus griffithii
needle inhibits proliferation and migration of human cervical
cancer cells: Involvement of mitochondria-initiated and death
receptor-mediated apoptosis pathways. Nat Prod Res. 29:1161–1165.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwon SJ, Lee JH, Moon KD, Jeong IY, Yee
ST, Lee MK and Seo KI: Isoegomaketone induces apoptosis in SK-MEL-2
human melanoma cells through mitochondrial apoptotic pathway via
activating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Oncol. 45:1969–1976. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang Z, Fang S, Di Y, Ying W, Tan Y and Gu
W: Modulation of NF-κB/miR-21/PTEN pathway sensitizes non-small
cell lung cancer to cisplatin. PLoS One. 10:e01215472015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY and Yang SL:
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance
to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:12061–12070. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dobbin ZC and Landen CN: The importance of
the PI3K/AKT/MTOR pathway in the progression of ovarian cancer. Int
J Mol Sci. 14:8213–8227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sarbassov DD, Guertin DA, Ali SM and
Sabatini DM: Phosphorylation and regulation of Akt/PKB by the
rictor-mTOR complex. Science. 307:1098–1101. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heavey S, O'Byrne KJ and Gately K:
Strategies for co-targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in NSCLC.
Cancer Treat Rev. 40:445–456. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Z, Yang L, Liu Y, Tang A, Li X, Zhang
J and Yang Z: LY294002 and Rapamycin promote coxsackievirus-induced
cytopathic effect and apoptosis via inhibition of PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem. 385:169–177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang YD, Su YJ, Li JY, Yao XC and Liang
GJ: Rapamycin, a mTOR inhibitor, induced growth inhibition in
retinoblastoma Y79 cell via down-regulation of Bmi-1. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:5182–5188. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Al-Malki AL: Oat attenuation of
hyperglycemia-induced retinal oxidative stress and NF-κB activation
in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2013:9839232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Valero T: Mitochondrial biogenesis:
Pharmacological approaches. Curr Pharm Des. 20:5507–5509. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ashkenazi A: Targeting the extrinsic
apoptotic pathway in cancer: Lessons learned and future directions.
J Clin Invest. 125:487–489. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang YD, Su YJ, Li JY, Yao XC and Liang
GJ: Rapamycin, an mTOR inhibitor, induced apoptosis via independent
mitochondrial and death receptor pathway in retinoblastoma Y79
cell. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:10723–10730. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sheppard K, Kinross KM, Solomon B, Pearson
RB and Phillips WA: Targeting PI3 kinase/AKT/mTOR signaling in
cancer. Crit Rev Oncog. 17:69–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Markman B, Dienstmann R and Tabernero J:
Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway - beyond rapalogs. Oncotarget.
1:530–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|