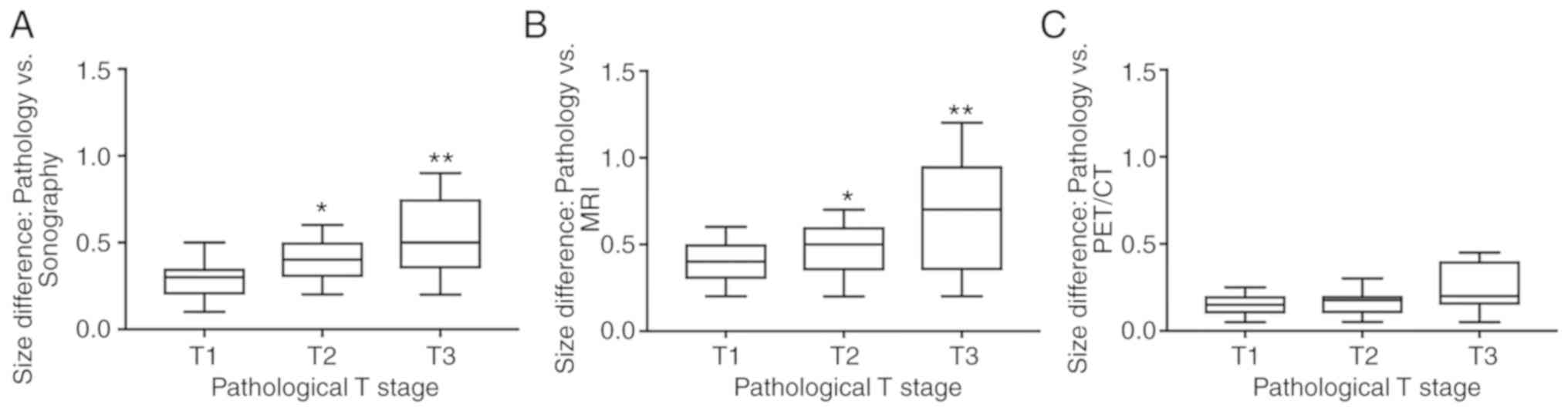
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ghoncheh M, Pournamdar Z and Salehiniya H:
Incidence and mortality and epidemiology of breast cancer in the
world. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 17((S3)): 43–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
McGhan LJ, Wasif N, Gray RJ, Giurescu ME,
Pizzitola VJ, Lorans R, Ocal IT, Stucky CC and Pockaj BA: Use of
preoperative magnetic resonance imaging for invasive lobular
cancer: Good, better, but maybe not the best? Ann Surg Oncol. 17
(Suppl 3):255–262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pop CF, Stanciu-Pop C, Drisis S,
Radermeker M, Vandemerckt C, Noterman D, Moreau M, Larsimont D,
Nogaret JM and Veys I: The impact of breast MRI workup on tumor
size assessment and surgical planning in patients with early breast
cancer. Breast J. 24:927–933. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miller AB, Baines CJ, To T and Wall C:
Canadian National Breast Screening Study: 1. Breast cancer
detection and death rates among women aged 40 to 49 years. CMAJ.
147:1459–1476. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Don S, Choi E and Min D: Breast mass
segmentation in digital mammography using graph cuts. Convergence
and Hybrid Information Technology. Lee G, Howard D and Ślęzak D:
Vol. 206:Springer. (Berlin, Heidelberg). 88–96. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Brem RF, Ioffe M, Rapelyea JA, Yost KG,
Weigert JM, Bertrand ML and Stern LH: Invasive lobular carcinoma:
Detection with mammography, sonography, MRI, and breast-specific
gamma imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 192:379–383. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sarno A, Mettivier G and Russo P:
Dedicated breast computed tomography: Basic aspects. Med Phys.
42:2786–2804. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Onesti JK, Mangus BE, Helmer SD and Osland
JS: Breast cancer tumor size: Correlation between magnetic
resonance imaging and pathology measurements. Am J Surg.
196:844–848; discussion 849-850. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Narod SA: Age of diagnosis, tumor size,
and survival after breast cancer: Implications for mammographic
screening. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 128:259–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nyström L, Rutqvist LE, Wall S, Lindgren
A, Lindqvist M, Rydén S, Andersson I, Bjurstam N, Fagerberg G,
Frisell J, et al: Breast cancer screening with mammography:
Overview of Swedish randomised trials. Lancet. 341:973–978. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pilewskie M, Hirsch A, Eaton A, Stempel M
and Gemignani ML: Breast cancer in the elderly: Is MRI helpful?
Breast J. 21:651–657. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hatada I, Hayashizaki Y, Hirotsune S,
Komatsubara H and Mukai T: A genomic scanning method for higher
organisms using restriction sites as landmarks. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 88:9523–9527. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Boetes C, Veltman J, van Die L, Bult P,
Wobbes T and Barentsz JO: The role of MRI in invasive lobular
carcinoma. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 86:31–37. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lo GG, Ai V, Chan JKF, Li KW, Cheung PSY,
Wong TT, Ma M, Lee R and Chien D: Diffusion-weighted magnetic
resonance imaging of breast lesions: First experiences at 3 T. J
Comput Assist Tomogr. 33:63–69. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kuhl CK, Schrading S, Leutner CC,
Morakkabati-Spitz N, Wardelmann E, Fimmers R, Kuhn W and Schild HH:
Mammography, breast ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging for
surveillance of women at high familial risk for breast cancer. J
Clin Oncol. 23:8469–8476. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Burkett BJ and Hanemann CW: A review of
supplemental screening ultrasound for breast cancer: Certain
populations of women with dense breast tissue may benefit. Acad
Radiol. 23:1604–1609. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Paydary K, Seraj SM, Zadeh MZ,
Emamzadehfard S, Shamchi SP, Gholami S, Werner TJ and Alavi A: The
evolving role of FDG-PET/CT in the diagnosis, staging, and
treatment of breast cancer. Mol Imaging Biol. 21:1–10. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Uematsu T, Kasami M and Yuen S: Comparison
of FDG PET and MRI for evaluating the tumor extent of breast cancer
and the impact of FDG PET on the systemic staging and prognosis of
patients who are candidates for breast-conserving therapy. Breast
Cancer. 16:97–104. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nogami Y, Iida M, Banno K, Kisu I, Adachi
M, Nakamura K, Umene K, Masuda K, Tominaga E, Tanaka K, et al:
Application of FDG-PET in cervical cancer and endometrial cancer:
Utility and future prospects. Anticancer Res. 34:585–592.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Park SH, Seo M, Choi HJ, Bae K, Bang M and
Jun S: More accurate than MRI measurement of tumor size in breast
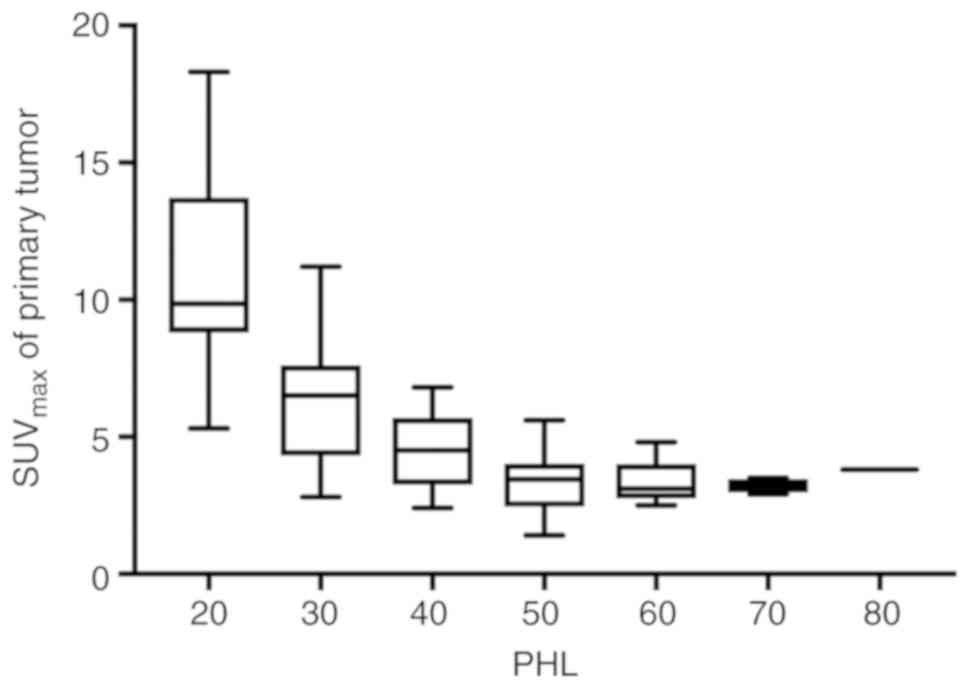
cancer by using the peri-tumoral halo uptake layer method of the
18F-FDG PET/CT scan. Hell J Nucl Med. 21:108–114. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jun S, Kim H and Nam HY: A new method for
segmentation of FDG PET metabolic tumour volume using the
peritumoural halo layer and a 10-step colour scale. A study in
patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma. Nucl Med (Stuttg).
54:272–285. 2015.
|
|
23
|
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, Bassett
LW, Berry D, Bland KI, Borgen PI, Clark GM, Edge SB, Hayes DF, et
al: Staging system for breast cancer: revisions for the 6th edition
of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. Surg Clin North Am. 83:803–819.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mendelson E, Baum J, Berg W, Merritt C and
Rubin E: Breast imaging reporting and data system. BI-RADS.
2003.
|
|
25
|
Zhengfeng L: Diagnostic ultrasound system
quality control testing methods. Chin Med Dev. 07:27–32. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Hengdi W: Image quality control standards
and procedures of MRI devices. POSTRUM. 28:19–23. 2013.(In
Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Jun Y, Jianwei W, Shuyue A and Wei H:
Quality control and administration of PET/CT. Chin Med Euipment J.
27:71–73. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Grimsby GM, Gray R, Dueck A, Carpenter S,
Stucky CC, Aspey H, Giurescu ME and Pockaj B: Is there concordance
of invasive breast cancer pathologic tumor size with magnetic
resonance imaging? Am J Surg. 198:500–504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Luparia A, Mariscotti G, Durando M, Ciatto
S, Bosco D, Campanino PP, Castellano I, Sapino A and Gandini G:
Accuracy of tumour size assessment in the preoperative staging of
breast cancer: Comparison of digital mammography, tomosynthesis,
ultrasound and MRI. Radiol Med (Torino). 118:1119–1136. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lai HW, Chen DR, Wu YC, Chen CJ, Lee CW,
Kuo SJ, Chen ST and Wu HK: Comparison of the diagnostic accuracy of
magnetic resonance imaging with sonography in the prediction of
breast cancer tumor size: A concordance analysis with
histopathologically determined tumor size. Ann Surg Oncol.
22:3816–3823. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gruber I, Rueckert M, Kagan K, Staebler A,
Siegmann KC, Hartkopf A, Wallwiener D and Hahn M: Measurement of
tumour size with mammography, sonography and magnetic resonance
imaging as compared to histological tumour size in primary breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 13:3282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hieken TJ, Harrison J, Herreros J and
Velasco JM: Correlating sonography, mammography, and pathology in
the assessment of breast cancer size. Am J Surg. 182:351–354. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jethava A, Ali S, Wakefield D, Crowell R,
Sporn J and Vrendenburgh J: Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in
predicting breast tumor size: Comparative analysis of MRI vs
histopathological assessed breast tumor size. Conn Med. 79:261–267.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Caresia Aroztegui AP, García Vicente AM,
Alvarez Ruiz S, Delgado Bolton RC, Orcajo Rincon J, Garcia Garzon
JR, de Arcocha Torres M and Garcia-Velloso MJ: 18F-FDG PET/CT in
breast cancer: Evidence-based recommendations in initial staging.
Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177282852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pritchard KI, Julian JA, Holloway CM,
McCready D, Gulenchyn KY, George R, Hodgson N, Lovrics P, Perera F,
Elavathil L, et al: Prospective study of
2-[18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography
in the assessment of regional nodal spread of disease in patients
with breast cancer: An Ontario clinical oncology group study. J
Clin Oncol. 30:1274–1279. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Riegger C, Herrmann J, Nagarajah J,
Hecktor J, Kuemmel S, Otterbach F, Hahn S, Bockisch A, Lauenstein
T, Antoch G, et al: Whole-body FDG PET/CT is more accurate than
conventional imaging for staging primary breast cancer patients.
Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 39:852–863. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Avril N, Rosé CA, Schelling M, Dose J,
Kuhn W, Bense S, Weber W, Ziegler S, Graeff H and Schwaiger M:
Breast imaging with positron emission tomography and fluorine-18
fluorodeoxyglucose: Use and limitations. J Clin Oncol.
18:3495–3502. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hyun SH, Ahn HK, Park YH, Im YH, Kil WH,
Lee JE, Nam SJ, Cho EY and Choi JY: Volume-based metabolic tumor
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy is associated with an
increased risk of recurrence in breast cancer. Radiology.
275:235–244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim J, Yoo SW, Kang SR, Cho SG, Oh JR,
Chong A, Min JJ, Bom HS, Yoon JH and Song HC: Prognostic
significance of metabolic tumor volume measured by (18)F-FDG PET/CT
in operable primary breast cancer. Nucl Med Mol Imaging.
46:278–285. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Oh JR, Seo JH, Chong A, Min JJ, Song HC,
Kim YC and Bom HS: Whole-body metabolic tumour volume of 18F-FDG
PET/CT improves the prediction of prognosis in small cell lung
cancer. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 39:925–935. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jun S, Park JG and Seo Y: Accurate FDG PET
tumor segmentation using the peritumoral halo layer method: A study
in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer
Imaging. 18:352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|