|
1
|
Global Burden of Disease Cancer
Collaboration, ; Fitzmaurice C, Akinyemiju TF, Al Lami FH, Alam T,
Alizadeh-Navaei R, Allen C, Alsharif U, Alvis-Guzman N, Amini E, et
al: Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality,
years of life lost, years lived with disability, and
disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2016:
A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA
Oncol. 1:1533–1568. 2018.
|
|
2
|
Lepage C, Rachet B, Jooste V, Faivre J and
Coleman MP: Continuing rapid increase in esophageal adenocarcinoma
in England and Wales. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:2694–2649. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Edgren G, Adami HO, Weiderpass E and Nyren
O: A global assessment of the oesophageal adenocarcinoma epidemic.
Gut. 62:1406–1414. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
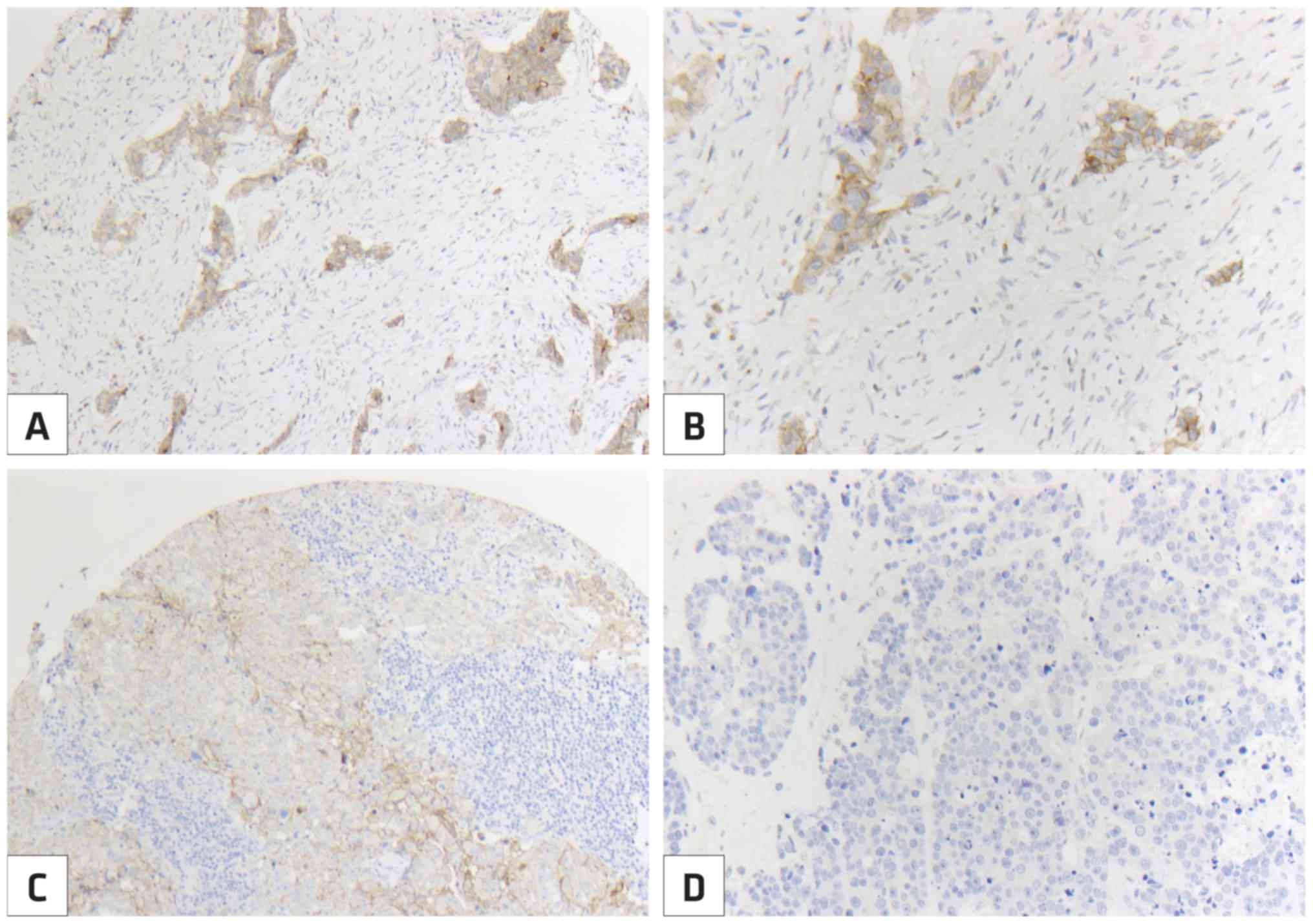
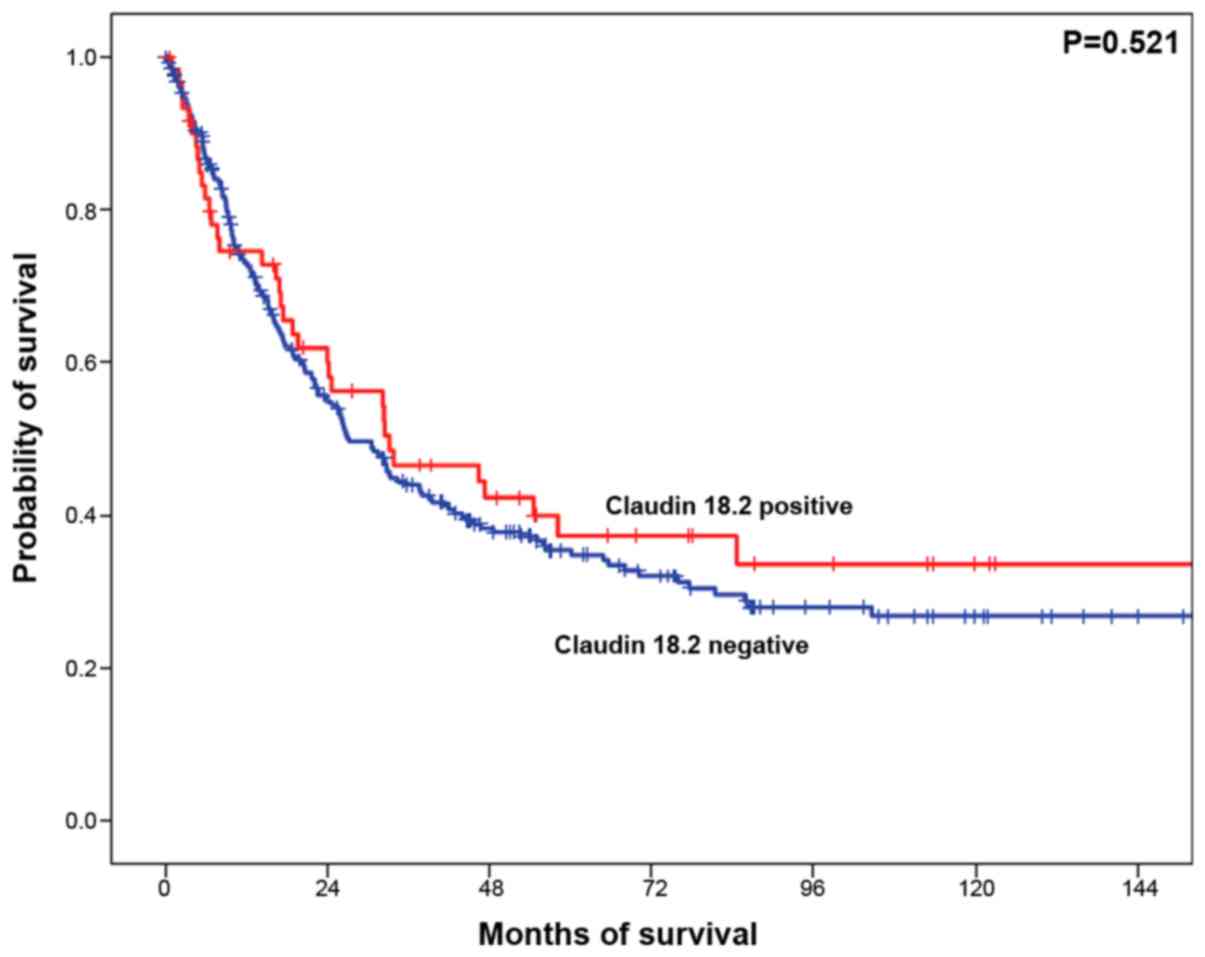
4
|
Al-Batran SE, Goetze TO, Mueller DW, Vogel
A, Winkler M, Lorenzen S, Novotny A, Pauligk C, Homann N, Jungbluth
T, et al: The RENAISSANCE (AIO-FLOT5) trial: Effect of chemotherapy
alone vs. Chemotherapy followed by surgical resection on survival
and quality of life in patients with limited-metastatic
adenocarcinoma of the stomach or esophagogastric junction-a phase
III trial of the German AIO/CAO-V/CAOGI. BMC Cancer. 17:8932017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pohl H, Sirovich B and Welch HG:
Esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence: Are we reaching the peak?
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:1468–1470. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Barrett JC: Mechanisms of multistep
carcinogenesis and carcinogen risk assessment. Environ Health
Perspect. 100:9–20. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nones K, Waddell N, Wayte N, Patch AM,
Bailey P, Newell F, Holmes O, Fink JL, Quinn MCJ, Tang YH, et al:
Genomic catastrophes frequently arise in esophageal adenocarcinoma
and drive tumorigenesis. Nat Commun. 5:52242014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Galipeau PC, Paulson TG, Sanchez CA,
Arnaudo J, Liu K, Sather CL, Kostadinov RL, Odze RD, Kuhner MK, et
al: Temporal and spatial evolution of somatic chromosomal
alterations: A case-cohort study of barrett's esophagus. Cancer
Prev Res (Phila). 7:114–127. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Robert Koch-Institut (Hrsg) und die
Gesellschaft der epidemiologischen Krebsregister in Deutschland
e.V. (Hrsg). Berlin: Krebs in Deutschland für. 2013/2014. 2017
|
|
10
|
Tustumi F, Kimura CM, Takeda FR, Uema RH,
Salum RA, Ribeiro-Junior U and Cecconello I: Prognostic factors and
survival analysis in esophageal carcinoma. Arq Bras Cir Dig.
29:138–141. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsukita S, Furuse M and Itoh M:
Multifunctional strands in tight junctions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
2:285–293. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsukita S, Yamazaki Y, Katsuno T, Tamura A
and Tsukita S: Tight junction-based epithelial microenvironment and
cell proliferation. Oncogene. 27:6930–6938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Van Itallie CM and Anderson JM: Claudins
and epithelial paracellular transport. Annu Rev Physiol.
68:403–429. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mineta K, Yamamoto Y, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka
H, Tada Y, Saito K, Tamura A, Igarashi M, Endo T, Takeuchi K and
Tsukita S: Predicted expansion of the claudin multigene family.
FEBS Lett. 585:606–612. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sahin U, Koslowski M, Dhaene K, Usener D,
Brandenburg G, Seitz G, Huber C and Türeci O: Claudin-18 splice
variant 2 is a pan-cancer target suitable for therapeutic antibody
development. Clin Cancer Res. 14:7624–7634. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Singh P, Toom S and Huang Y: Anti-Claudin
18.2 antibody as new targeted therapy for advanced gastric cancer.
J Hematol Oncol. 10:1052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Woll S, Schlitter AM, Dhaene K, Roller M,
Esposito I, Sahin U and Türeci Ö: Claudin 18.2 is a target for
IMAB362 antibody in pancreatic neoplasms. Int J Cancer.
134:731–739. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sahin U, Schuler M, Richly H, Bauer S,
Krilova A, Dechow T, Jerling M, Utsch M, Rohde C, Dhaene K, et al:
A phase I dose-escalation study of IMAB362 (Zolbetuximab) in
patients with advanced gastric and gastro-oesophageal junction
cancer. Eur J Cancer. 100:17–26. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Al-Batran S, Al-Batran SE, Schuler MH, et
al: FAST: An international, multicenter, randomized, phase II trial
of epirubicin, oxaliplatin, and capecitabine (EOX) with or without
IMAB362, a first-in-class anti-CLDN18.2 antibody, as first-line
therapy in patients with advanced CLDN18.2+ gastric and
gastroesophageal junction (GEJ) adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 34
(no. 18-Suppl):2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Trarbach T, Schuler M, Zvirbule Z, Lordick
F, Krilova A, Helbig U, Schulze-Bergkamen H, Thuss-Patience PC,
Wichert G, Schmiegel W, et al: 636P-Efficacy and safety of multiple
doses of IMAB362 in patients with advanced gastro-esophageal
cancer: Results of a phase II study. Ann Oncol. 25 (Suppl
4):iv210–iv253. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sahin U, Al-Batran SE, Hozaeel W, et al:
IMAB362 plus zoledronic acid (ZA) and interleukin-2 (IL-2) in
patients (pts) with advanced gastroesophageal cancer (GEC):
Clinical activity and safety data from the PILOT phase I trial. J
Clin Oncol. 33 (no. 15_Suppl):2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Holscher AH, Schneider PM, Gutschow C and
Schroder W: Laparoscopic ischemic conditioning of the stomach for
esophageal replacement. Ann Surg. 245:241–246. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Shapiro J, van Lanschot JJB, Hulshof MCCM,
van Hagen P, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BPL, van Laarhoven
HWM, Nieuwenhuijzen GAP, Hospers GAP, Bonenkamp JJ, et al:
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for
oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): Long-term results of a
randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 16:1090–1098. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hoeppner J, Lordick F, Brunner T, Glatz T,
Bronsert P, Rothling N, Schmoor C, Lorenz D, Ell C, Hopt UT and
Siewert JR: ESOPEC: Prospective randomized controlled multicenter
phase III trial comparing perioperative chemotherapy (FLOT
protocol) to neoadjuvant chemoradiation (CROSS protocol) in
patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus (NCT02509286). BMC
Cancer. 16:5032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wittekind C and Oberschmid B: Pathology
and new UICC classification of esophageal carcinoma. Onkologe.
16:453–461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
UICC, . TNM: Klassifikation maligner
Tumoren. 8th. Wiley; 2017
|
|
27
|
Schneider PM, Metzger R, Schaefer H,
Baumgarten F, Vallbohmer D, Brabender J, Wolfgarten E,
Bollschweiler E, Baldus SE, Dienes HP and Hoelscher AH: Response
evaluation by endoscopy, rebiopsy, and endoscopic ultrasound does
not accurately predict histopathologic regression after neoadjuvant
chemoradiation for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 248:902–908. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Simon R, Mirlacher M and Sauter G: Tissue
microarrays. Method Mol Med. 114:257–268. 2005.
|
|
29
|
Helbig D, Ihle MA, Putz K, Tantcheva-Poor
I, Mauch C, Buttner R and Quaas A: Oncogene and therapeutic target
analyses in atypical fibroxanthomas and pleomorphic dermal
sarcomas. Oncotarget. 7:21763–21774. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tureci O, Sahin U, Schulze-Bergkamen H,
Zvirbule Z, Lordick F, Koeberle D, Thuss-Patience P, Ettrich T,
Arnold D, Bassermann F, et al: A multicentre, phase IIa study of
zolbetuximab as a single agent in patients with recurrent or
refractory advanced adenocarcinoma of the stomach or lower
oesophagus: The MONO study. Ann Oncol. 30:1487–1495. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fukayama M and Ushiku T: Epstein-Barr
virus-associated gastric carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract. 207:529–537.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network, .
Comprehensive molecular characterization of gastric adenocarcinoma.
Nature. 513:202–209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hewitt LC, Inam IZ, Saito Y, Yoshikawa T,
Quaas A, Hoelscher A, Bollschweiler E, Fazzi GE, Melotte V, Langley
RE, et al: Epstein-Barr virus and mismatch repair deficiency status
differ between oesophageal and gastric cancer: A large multi-centre
study. Eur J Cancer. 94:104–114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|