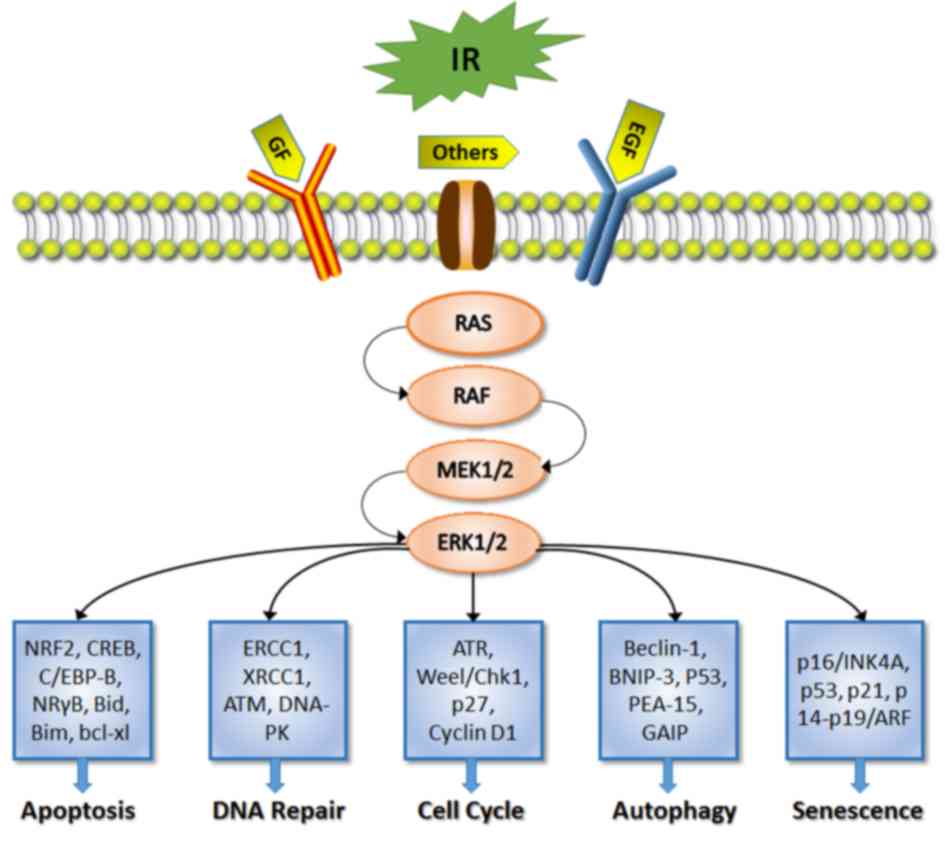
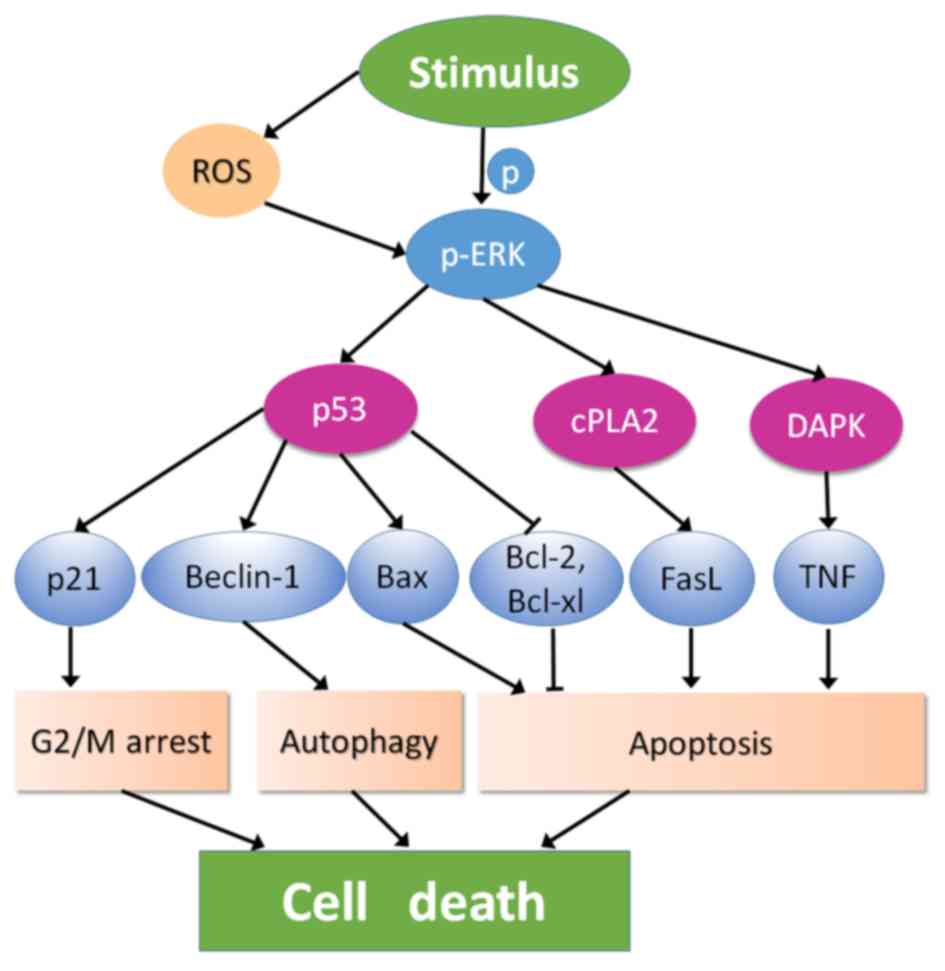
|
1
|
Alicikus ZA, Yamada Y, Zhang Z, Pei X,
Hunt M, Kollmeier M, Cox B and Zelefsky MJ: Ten-year outcomes of
high-dose, intensity-modulated radiotherapy for localized prostate
cancer. Cancer. 117:1429–1437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miller KD, Siegel RL, Lin CC, Mariotto AB,
Kramer JL, Rowland JH, Stein KD, Alteri R and Jemal A: Cancer
treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin.
66:271–289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barker HE, Paget JT, Khan AA and
Harrington KJ: The tumour microenvironment after radiotherapy:
Mechanisms of resistance and recurrence. Nat Rev Cancer.
15:409–425. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hawkins AJ, Golding SE, Khalil A and
Valerie K: DNA double-strand break-induced pro-survival signaling.
Radiother Oncol. 101:13–17. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ding M, Zhang E, He R and Wang X: Newly
developed strategies for improving sensitivity to radiation by
targeting signal pathways in cancer therapy. Cancer Sci.
104:1401–1410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ciccarelli C, Di Rocco A, Gravina GL,
Mauro A, Festuccia C, Del Fattore A, Berardinelli P, De Felice F,
Musio D, Bouché M, et al: Disruption of MEK/ERK/c-Myc signaling
radiosensitizes prostate cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:1685–1699. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morris ZS and Harari PM: Interaction of
radiation therapy with molecular targeted agents. J Clin Oncol.
32:2886–2893. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Roberts PJ and Der CJ: Targeting the
Raf-MEK-ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade for the
treatment of cancer. Oncogene. 26:3291–3310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Neuzillet C, Tijeras-Raballand A, De
Mestier L, Cros J, Faivre S and Raymond E: MEK in cancer and cancer
therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 141:160–171. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kidger AM, Sipthorp J and Cook SJ: ERK1/2
inhibitors: New weapons to inhibit the RAS-regulated
RAF-MEK1/2-ERK1/2 pathway. Pharmacol Ther. 187:45–60. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Samatar AA and Poulikakos PI: Targeting
RAS-ERK signalling in cancer: Promises and challenges. Nat Rev Drug
Discov. 13:928–942. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bonner JA, Vroman BT, Christianson TJ and
Karnitz LM: Ionizing radiation-induced MEK and Erk activation does
not enhance survival of irradiated human squamous carcinoma cells.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 42:921–925. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Teixeiro E and Daniels MA: ERK and cell
death: ERK location and T cell selection. FEBS J. 277:30–38. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cagnol S and Chambard JC: ERK and cell
death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death-apoptosis, autophagy
and senescence. FEBS J. 277:2–21. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Keshet Y and Seger R: The MAP kinase
signaling cascades: A system of hundreds of components regulates a
diverse array of physiological functions. Methods Mol Biol.
661:3–38. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y and
Hu LL: ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med.
19:1997–2007. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Luca A, Maiello MR, D'alessio A,
Pergameno M and Normanno N: The RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK and the PI3K/AKT
signalling pathways: Role in cancer pathogenesis and implications
for therapeutic approaches. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 16 (Suppl
2):S17–S27. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ramos JW: The regulation of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in mammalian cells. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 40:2707–2719. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yoon S and Seger R: The extracellular
signal-regulated kinase: Multiple substrates regulate diverse
cellular functions. Growth Factors. 24:21–44. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carlson SM, Chouinard CR, Labadorf A, Lam
CJ, Schmelzle K, Fraenkel E and White FM: Large-scale discovery of
ERK2 substrates identifies ERK-mediated transcriptional regulation
by ETV3. Sci Signal. 4:rs112011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sun Y, Liu WZ, Liu T, Feng X, Yang N and
Zhou HF: Signaling pathway of MAPK/ERK in cell proliferation,
differentiation, migration, senescence and apoptosis. J Recept
Signal Transduct Res. 35:600–604. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim EK and Choi EJ: Compromised MAPK
signaling in human diseases: An update. Arch Toxicol. 89:867–882.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Balmanno K and Cook SJ: Tumour cell
survival signalling by the ERK1/2 pathway. Cell Death Differ.
16:368–377. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sakai N, Wada T, Furuichi K, Iwata Y,
Yoshimoto K, Kitagawa K, Kokubo S, Kobayashi M, Hara A, Yamahana J,
et al: Involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and p38
in human diabetic nephropathy. Am J Kidney Dis. 45:54–65. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
DuShane JK, Wilczek MP, Mayberry CL and
Maginnis MS: ERK is a critical regulator of JC polyomavirus
infection. J Virol. 92:e01529–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Muslin AJ: MAPK signalling in
cardiovascular health and disease: Molecular mechanisms and
therapeutic targets. Clin Sci (Lond). 115:203–218. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rai SN, Dilnashin H, Birla H, Singh SS,
Zahra W, Rathore AS, Singh BK and Singh SP: The role of PI3K/Akt
and ERK in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurotox Res. 35:775–795.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hoshino R, Chatani Y, Yamori T, Tsuruo T,
Oka H, Yoshida O, Shimada Y, Ari-I S, Wada H, Fujimoto J and Kohno
M: Constitutive activation of the 41-/43-kDa mitogen-activated
protein kinase signaling pathway in human tumors. Oncogene.
18:813–822. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Park HS, You GE, Yang KH, Kim JY, An S,
Song JY, Lee SJ, Lim YK and Nam SY: Role of AKT and ERK pathways in
controlling sensitivity to ionizing radiation and adaptive response
induced by low-dose radiation in human immune cells. Eur J Cell
Biol. 94:653–660. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Corn BW, Kovner F, Bek S, Wexler I,
Lifschits B and Seger R: ERK signaling in colorectal cancer: A
preliminary report on the expression of phosphorylated ERK and the
effects of radiation therapy. Am J Clin Oncol. 31:255–258. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Panganiban RA, Snow AL and Day RM:
Mechanisms of radiation toxicity in transformed and non-transformed
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 14:15931–15958. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dent P, Yacoub A, Fisher PB, Hagan MP and
Grant S: MAPK pathways in radiation responses. Oncogene.
22:5885–5896. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yan Y, Black CP and Cowan KH:
Irradiation-induced G2/M checkpoint response requires ERK1/2
activation. Oncogene. 26:4689–4698. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Williams TM, Flecha AR, Keller P, Ram A,
Karnak D, Galbán S, Galbán CJ, Ross BD, Lawrence TS, Rehemtulla A
and Sebolt-Leopold J: Cotargeting MAPK and PI3K signaling with
concurrent radiotherapy as a strategy for the treatment of
pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:1193–1202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cuneo KC, Geng L, Fu A, Orton D, Hallahan
DE and Chakravarthy AB: SU11248 (sunitinib) sensitizes pancreatic
cancer to the cytotoxic effects of ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat
Oncol Biol Phys. 71:873–879. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Carter S, Auer KL, Reardon DB, Birrer M,
Fisher PB, Valerie K, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Mikkelsen R and Dent P:
Inhibition of the mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase cascade
potentiates cell killing by low dose ionizing radiation in A431
human squamous carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 16:2787–2796. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hein AL, Ouellette MM and Yan Y:
Radiation-induced signaling pathways that promote cancer cell
survival (review). Int J Oncol. 45:1813–1819. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Carracedo A, Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J,
Rojo F, Salmena L, Alimonti A, Egia A, Sasaki AT, Thomas G, Kozma
SC, et al: Inhibition of mTORC1 leads to MAPK pathway activation
through a PI3K-dependent feedback loop in human cancer. J Clin
Invest. 118:3065–3074. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cho JH, Hong WG, Jung YJ, Lee J, Lee E,
Hwang SG, Um HD and Park JK: Γ-Ionizing radiation-induced
activation of the EGFR-p38/ERK-STAT3/CREB-1-EMT pathway promotes
the migration/invasion of non-small cell lung cancer cells and is
inhibited by podophyllotoxin acetate. Tumour Biol. 37:7315–7325.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Lee HC, An S, Lee H, Woo SH, Jin HO, Seo
SK, Choe TB, Yoo DH, Lee SJ, Hong YJ, et al: Activation of
epidermal growth factor receptor and its downstream signaling
pathway by nitric oxide in response to ionizing radiation. Mol
Cancer Res. 6:996–1002. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sambade MJ, Camp JT, Kimple RJ, Sartor CI
and Shields JM: Mechanism of lapatinib-mediated radiosensitization
of breast cancer cells is primarily by inhibition of the
Raf>MEK>ERK mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade and
radiosensitization of lapatinib-resistant cells restored by direct
inhibition of MEK. Radiother Oncol. 93:639–644. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park JS, Qiao L, Su ZZ, Hinman D,
Willoughby K, McKinstry R, Yacoub A, Duigou GJ, Young CS, Grant S,
et al: Ionizing radiation modulates vascular endothelial growth
factor (VEGF) expression through multiple mitogen activated protein
kinase dependent pathways. Oncogene. 20:3266–3280. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang X, Ma N, Yao W, Li S and Ren Z:
RAD51 is a potential marker for prognosis and regulates cell
proliferation in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 19:3562019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
King HO, Brend T, Payne HL, Wright A, Ward
TA, Patel K, Egnuni T, Stead LF, Patel A, Wurdak H and Short SC:
RAD51 is a selective DNA repair target to radiosensitize glioma
stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 8:125–139. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chowdhury P, Dey P, De D and Ghosh U:
Gamma ray-induced in vitro cell migration via EGFR/ERK/Akt/p38
activation is prevented by olaparib pretreatment. Int J Radiat
Biol. 96:651–660. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lee YJ, Soh JW, Dean NM, Cho CK, Kim TH,
Lee SJ and Lee YS: Protein kinase Cdelta overexpression enhances
radiation sensitivity via extracellular regulated protein kinase
1/2 activation, abolishing the radiation-induced G(2)-M arrest.
Cell Growth Differ. 13:237–246. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Singh S, Upadhyay AK, Ajay AK and Bhat MK:
p53 regulates ERK activation in carboplatin induced apoptosis in
cervical carcinoma: A novel target of p53 in apoptosis. FEBS Lett.
581:289–295. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cheng G, Kong D, Hou X, Liang B, He M,
Liang N, Ma S and Liu X: The tumor suppressor, p53, contributes to
radiosensitivity of lung cancer cells by regulating autophagy and
apoptosis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 28:153–159. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Premkumar K and Shankar BS: Involvement of
MAPK signalling in radioadaptive response in BALB/c mice exposed to
low dose ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol. 92:249–262. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lee SY, Jeong EK, Ju MK, Jeon HM, Kim MY,
Kim CH, Park HG, Han SI and Kang HS: Induction of metastasis,
cancer stem cell phenotype, and oncogenic metabolism in cancer
cells by ionizing radiation. Mol Cancer. 16:102017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kaczanowski S: Apoptosis: Its origin,
history, maintenance and the medical implications for cancer and
aging. Phys Biol. 13:0310012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gerl R and Vaux DL: Apoptosis in the
development and treatment of cancer. Carcinogenesis. 26:263–270.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:872011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Pistritto G, Trisciuoglio D, Ceci C,
Garufi A and D'Orazi G: Apoptosis as anticancer mechanism: Function
and dysfunction of its modulators and targeted therapeutic
strategies. Aging (Albany NY). 8:603–619. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chen N, Zhang R, Konishi T and Wang J:
Upregulation of NRF2 through autophagy/ERK 1/2 ameliorates ionizing
radiation induced cell death of human osteosarcoma U-2 OS. Mutat
Res. 813:10–17. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Boucher MJ, Morisset J, Vachon PH, Reed
JC, Lainé J and Rivard N: MEK/ERK signaling pathway regulates the
expression of Bcl-2, Bcl-X(L), and Mcl-1 and promotes survival of
human pancreatic cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 79:355–369. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kurland JF, Voehringer DW and Meyn RE: The
MEK/ERK pathway acts upstream of NF kappa B1 (p50) homodimer
activity and Bcl-2 expression in a murine B-cell lymphoma cell
line. MEK inhibition restores radiation-induced apoptosis. J Biol
Chem. 278:32465–32470. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chatterjee N and Walker GC: Mechanisms of
DNA damage, repair, and mutagenesis. Environ Mol Mutagen.
58:235–263. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Golding SE, Morgan RN, Adams BR, Hawkins
AJ, Povirk LF and Valerie K: Pro-survival AKT and ERK signaling
from EGFR and mutant EGFRvIII enhances DNA double-strand break
repair in human glioma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:730–738. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Valerie K and Povirk LF: Regulation and
mechanisms of mammalian double-strand break repair. Oncogene.
22:5792–5812. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Meyn RE, Munshi A, Haymach JV, Milas L and
Ang KK: Receptor signaling as a regulatory mechanism of DNA repair.
Radiother Oncol. 92:316–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yacoub A, McKinstry R, Hinman D, Chung T,
Dent P and Hagan MP: Epidermal growth factor and ionizing radiation
up-regulate the DNA repair genes XRCC1 and ERCC1 in DU145 and LNCaP
prostate carcinoma through MAPK signaling. Radiat Res. 159:439–452.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yacoub A, Park JS, Qiao L, Dent P and
Hagan MP: MAPK dependence of DNA damage repair: Ionizing radiation
and the induction of expression of the DNA repair genes XRCC1 and
ERCC1 in DU145 human prostate carcinoma cells in a MEK1/2 dependent
fashion. Int J Radiat Biol. 77:1067–1078. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Engeland K: Cell cycle arrest through
indirect transcriptional repression by p53: I have a DREAM. Cell
Death Differ. 25:114–132. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhao H and Piwnica-Worms H: ATR-mediated
checkpoint pathways regulate phosphorylation and activation of
human Chk1. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4129–4139. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Abbott DW and Holt JT: Mitogen-activated
protein kinase kinase 2 activation is essential for progression
through the G2/M checkpoint arrest in cells exposed to ionizing
radiation. J Biol Chem. 274:2732–2742. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yan Y, Black CP, Cao PT, Haferbier JL,
Kolb RH, Spieker RS, Ristow AM and Cowan KH:
Gamma-irradiation-induced DNA damage checkpoint activation involves
feedback regulation between extracellular signal-regulated kinase
1/2 and BRCA1. Cancer Res. 68:5113–5121. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Dossett LA, Kudchadkar RR and Zager JS:
BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma. Expert Opin Drug Saf.
14:559–570. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Caunt CJ, Sale MJ, Smith PD and Cook SJ:
MEK1 and MEK2 inhibitors and cancer therapy: The long and winding
road. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:577–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Affolter A, Muller MF, Sommer K,
Stenzinger A, Zaoui K, Lorenz K, Wolf T, Sharma S, Wolf J, Perner
S, et al: Targeting irradiation-induced mitogen-activated protein
kinase activation in vitro and in an ex vivo model for human head
and neck cancer. Head Neck. 38 (Suppl 1):E2049–E2061. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Frémin C and Meloche S: From basic
research to clinical development of MEK1/2 inhibitors for cancer
therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 3:82010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Estrada-Bernal A, Chatterjee M, Haque SJ,
Yang L, Morgan MA, Kotian S, Morrell D, Chakravarti A and Williams
TM: MEK inhibitor GSK1120212-mediated radiosensitization of
pancreatic cancer cells involves inhibition of DNA double-strand
break repair pathways. Cell Cycle. 14:3713–3724. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Marampon F, Gravina GL, Di Rocco A,
Bonfili P, Di Staso M, Fardella C, Polidoro L, Ciccarelli C,
Festuccia C, Popov VM, et al: MEK/ERK inhibitor U0126 increases the
radiosensitivity of rhabdomyosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo by
downregulating growth and DNA repair signals. Mol Cancer Ther.
10:159–168. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chung EJ, Urick ME, Kurshan N, Shield W
III, Asano H, Smith PD, Scroggins BS, Burkeen J and Citrin DE:
MEK1/2 inhibition enhances the radiosensitivity of cancer cells by
downregulating survival and growth signals mediated by EGFR
ligands. Int J Oncol. 42:2028–2036. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Hayes TK, Neel NF, Hu C, Gautam P, Chenard
M, Long B, Aziz M, Kassner M, Bryant KL, Pierobon M, et al:
Long-Term ERK inhibition in KRAS-mutant pancreatic cancer is
associated with MYC degradation and senescence-like growth
suppression. Cancer Cell. 29:75–89. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kroeze SG, Fritz C, Hoyer M, Lo SS,
Ricardi U, Sahgal A, Stahel R, Stupp R and Guckenberger M: Toxicity
of concurrent stereotactic radiotherapy and targeted therapy or
immunotherapy: A systematic review. Cancer Treat Rev. 53:25–37.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Luebker SA and Koepsell SA: Diverse
mechanisms of BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma identified in
clinical and preclinical studies. Front Oncol. 9:2682019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lito P, Rosen N and Solit DB: Tumor
adaptation and resistance to RAF inhibitors. Nat Med. 19:1401–1409.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Jaiswal BS, Durinck S, Stawiski EW, Yin J,
Wang W, Lin E, Moffat J, Martin SE, Modrusan Z and Seshagiri S: ERK
mutations and amplification confer resistance to ERK-Inhibitor
therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 24:4044–4055. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Hollmann CA, Owens T, Nalbantoglu J,
Hudson TJ and Sladek R: Constitutive activation of extracellular
signal-regulated kinase predisposes diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
cell lines to CD40-mediated cell death. Cancer Res. 66:3550–3557.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Bacus SS, Gudkov AV, Lowe M, Lyass L, Yung
Y, Komarov AP, Keyomarsi K, Yarden Y and Seger R: Taxol-induced
apoptosis depends on MAP kinase pathways (ERK and p38) and is
independent of p53. Oncogene. 20:147–155. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Tang D, Wu D, Hirao A, Lahti JM, Liu L,
Mazza B, Kidd VJ, Mak TW and Ingram AJ: ERK activation mediates
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA damage independently of
p53. J Biol Chem. 277:12710–12717. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Mukherjee S, Dash S, Lohitesh K and
Chowdhury R: The dynamic role of autophagy and MAPK signaling in
determining cell fate under cisplatin stress in osteosarcoma cells.
PLoS One. 12:e01792032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Martin P, Poggi MC, Chambard JC, Boulukos
KE and Pognonec P: Low dose cadmium poisoning results in sustained
ERK phosphorylation and caspase activation. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 350:803–807. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Martin P and Pognonec P: ERK and cell
death: Cadmium toxicity, sustained ERK activation and cell death.
FEBS J. 277:39–46. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Lin T, Mak NK and Yang MS: MAPK regulate
p53-dependent cell death induced by benzo[a]pyrene: Involvement of
p53 phosphorylation and acetylation. Toxicology. 247:145–153. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Lee YJ, Soh JW, Jeoung DI, Cho CK, Jhon
GJ, Lee SJ and Lee YS: PKC epsilon-mediated ERK1/2 activation
involved in radiation-induced cell death in NIH3T3 cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1593:219–229. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Watanabe H, Kurabayashi T and Miura M:
Inhibition of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)
pathway and the induction of radioresistance in rat 3Y1 cells. Int
J Radiat Biol. 80:451–457. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Yang R, Piperdi S and Gorlick R:
Activation of the RAF/mitogen-activated protein/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase kinase/extracellular signal-regulated
kinase pathway mediates apoptosis induced by chelerythrine in
osteosarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 14:6396–6404. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Randhawa H, Kibble K, Zeng H, Moyer MP and
Reindl KM: Activation of ERK signaling and induction of colon
cancer cell death by piperlongumine. Toxicol In Vitro.
27:1626–1633. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhao L, Li J, Hao YH, Gao YB, Wang SM,
Zhang J, Dong J, Zhou HM, Liu SC and Peng RY: Microwave-induced
apoptosis and cytotoxicity of NK cells through ERK1/2 signaling.
Biomed Environ Sci. 30:323–332. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Han HY, Kim H, Jeong SH, Lim DS and Ryu
MH: Sulfasalazine induces autophagic cell death in oral cancer
cells via Akt and ERK pathways. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:6939–6944. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Bastola T, An RB, Kim YC, Kim J and Seo J:
Cearoin induces autophagy, ERK activation and apoptosis via ROS
generation in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells. Molecules. 22(pii):
E2422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Tian X, Geng J, Zheng Q, Wang L, Huang P,
Tong J and Zheng S: Single high dose irradiation induces cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
through the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathways. Int J Radiat Biol. 1–8.
2020.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
97
|
Wang Z, Ma L, Su M, Zhou Y, Mao K, Li C,
Peng G, Zhou C, Shen B and Dou J: Baicalin induces cellular
senescence in human colon cancer cells via upregulation of DEPP and
the activation of Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis.
9:2172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Brown L and Benchimol S: The involvement
of MAPK signaling pathways in determining the cellular response to
p53 activation: Cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
281:3832–3840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Xu J, Patel NH, Saleh T, Cudjoe EK Jr,
Alotaibi M, Wu Y, Lima S, Hawkridge AM and Gewirtz DA: Differential
radiation sensitivity in p53 Wild-Type and p53-Deficient tumor
cells associated with senescence but not apoptosis or
(Nonprotective) Autophagy. Radiat Res. 190:538–557. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Wang Y, Xu H, Lu Z, Yu X, Lv C, Tian Y and
Sui D: Pseudo-Ginsenoside Rh2 induces A549 cells apoptosis via the
Ras/Raf/ERK/p53 pathway. Exp Ther Med. 15:4916–4924.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lv C, Hong Y, Miao L, Li C, Xu G, Wei S,
Wang B, Huang C and Jiao B: Wentilactone A as a novel potential
antitumor agent induces apoptosis and G2/M arrest of human lung
carcinoma cells, and is mediated by HRas-GTP accumulation to
excessively activate the Ras/Raf/ERK/p53-p21 pathway. Cell Death
Dis. 4:e9522013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Liu Y, Yang Y, Ye YC, Shi QF, Chai K,
Tashiro S, Onodera S and Ikejima T: Activation of ERK-p53 and
ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2 are involved in autophagic
cell death induced by the c-Met inhibitor SU11274 in human lung
cancer A549 cells. J Pharmacol Sci. 118:423–432. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Woessmann W, Chen X and Borkhardt A:
Ras-mediated activation of ERK by cisplatin induces cell death
independently of p53 in osteosarcoma and neuroblastoma cell lines.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 50:397–404. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Pognonec P: ERK and cell death: Overview.
FEBS J. 277:12010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Wainstein E and Seger R: The dynamic
subcellular localization of ERK: Mechanisms of translocation and
role in various organelles. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 39:15–20. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Cook SJ, Stuart K, Gilley R and Sale MJ:
Control of cell death and mitochondrial fission by ERK1/2 MAP
kinase signalling. FEBS J. 284:4177–4195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Denoyelle C, Abou-Rjaily G, Bezrookove V,
Verhaegen M, Johnson TM, Fullen DR, Pointer JN, Gruber SB, Su LD,
Nikiforov MA, et al: Anti-oncogenic role of the endoplasmic
reticulum differentially activated by mutations in the MAPK
pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 8:1053–1063. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Fehrenbacher N, Bar-Sagi D and Philips M:
Ras/MAPK signaling from endomembranes. Mol Oncol. 3:297–307. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Shaul YD and Seger R: The MEK/ERK cascade:
From signaling specificity to diverse functions. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1773:1213–1226. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Klemke RL, Cai S, Giannini AL, Gallagher
PJ, de Lanerolle P and Cheresh DA: Regulation of cell motility by
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Cell Biol. 137:481–492. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Ajenjo N, Canon E, Sanchez-Perez I,
Matallanas D, León J, Perona R and Crespo P: Subcellular
localization determines the protective effects of activated ERK2
against distinct apoptogenic stimuli in myeloid leukemia cells. J
Biol Chem. 279:32813–32823. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Maik-Rachline G, Hacohen-Lev-Ran A and
Seger R: Nuclear ERK: Mechanism of translocation, substrates, and
role in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20(pii): E11942019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Huang K, Chen Y, Zhang R, Wu Y, Ma Y, Fang
X and Shen S: Honokiol induces apoptosis and autophagy via the
ROS/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro
and in vivo. Cell Death Dis. 9:1572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Yeh PS, Wang W, Chang YA, Lin CJ, Wang JJ
and Chen RM: Honokiol induces autophagy of neuroblastoma cells
through activating the PI3K/Akt/mTOR and endoplasmic reticular
stress/ERK1/2 signaling pathways and suppressing cell migration.
Cancer Lett. 370:66–77. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|