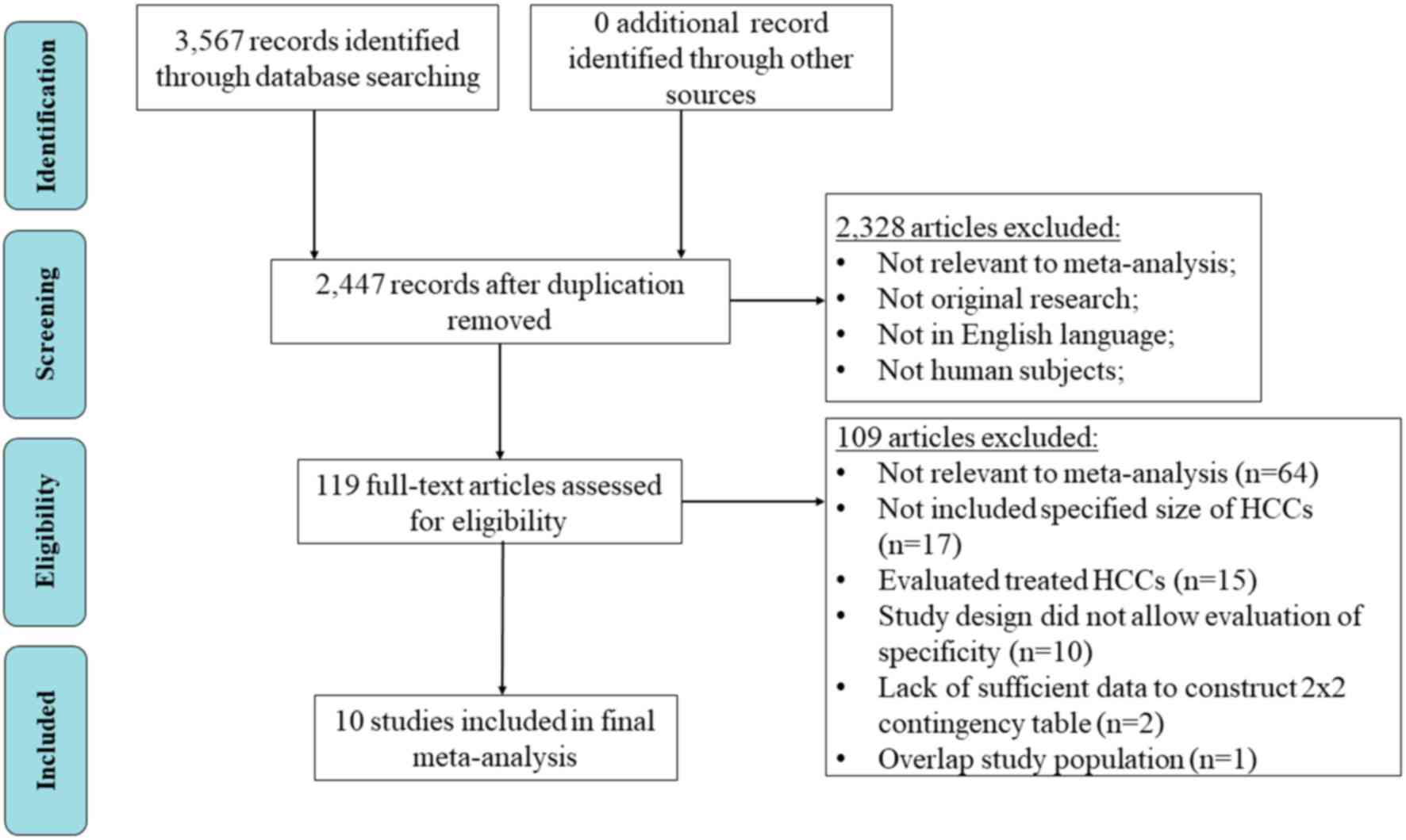
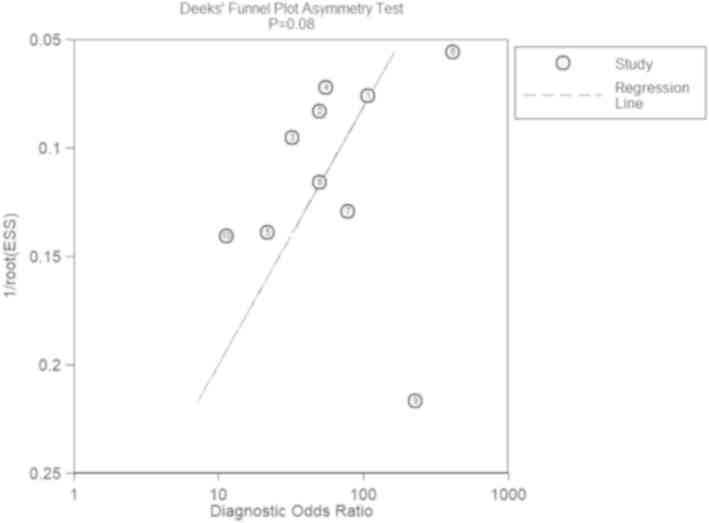
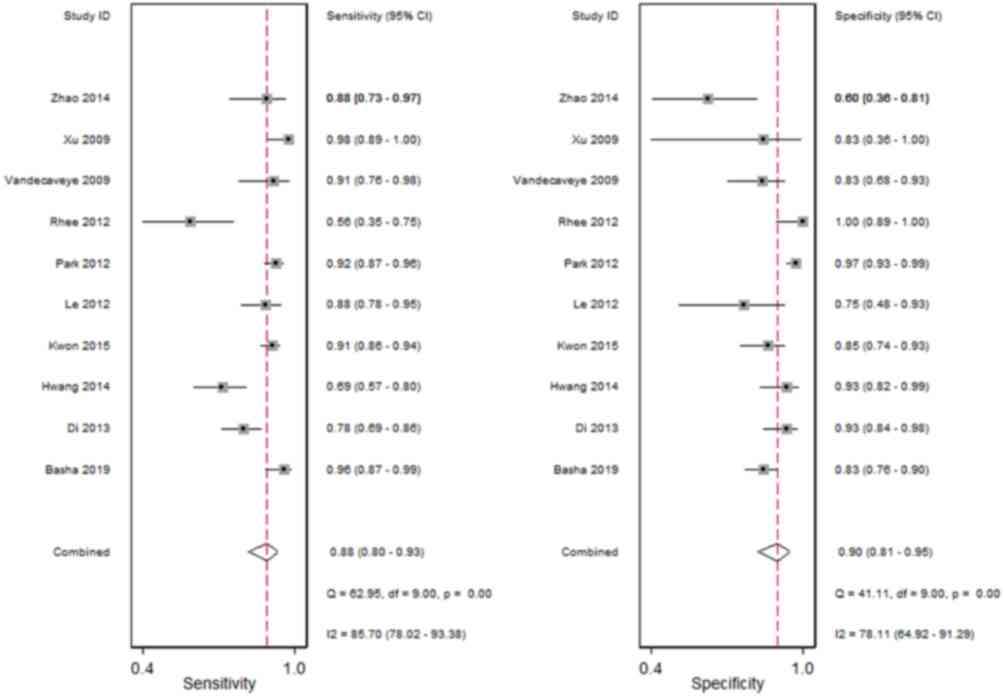
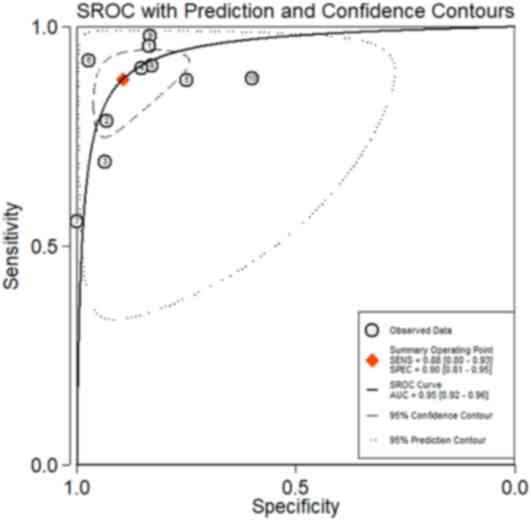
|
1
|
Wallace MC, Preen D, Jeffrey GP and Adams
LA: The evolving epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: A global
perspective. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 9:765–779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hackl C, Schlitt HJ, Kirchner GI, Knoppke
B and Loss M: Liver transplantation for malignancy: Current
treatment strategies and future perspectives. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:5331–5344. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wald C, Russo MW, Heimbach JK, Hussain HK,
Pomfret EA and Bruix J: New OPTN/UNOS policy for liver transplant
allocation: Standardization of liver imaging, diagnosis,
classification, and reporting of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Radiology. 266:376–382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zamora-Valdes D, Taner T and Nagorney DM:
Surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Control.
24:10732748177292582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Balogh J, Victor D III, Asham EH,
Burroughs SG, Boktour M, Saharia A, Li X, Ghobrial RM and Monsour
HP Jr: Hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. J Hepatocell Carcinoma.
3:41–53. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Forner A, Vilana R, Ayuso C, Bianchi L,
Solé M, Ayuso JR, Boix L, Sala M, Varela M, Llovet JM, et al:
Diagnosis of hepatic nodules 20 mm or smaller in cirrhosis:
Prospective validation of the noninvasive diagnostic criteria for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 47:97–104. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Le Moigne F, Durieux M, Bancel B, Boublay
N, Boussel L, Ducerf C, Berthezène Y and Rode A: Impact of
diffusion-weighted MR imaging on the characterization of small
hepatocellular carcinoma in the cirrhotic liver. Magn Reson
Imaging. 30:656–665. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu PJ, Yan FH, Wang JH, Lin J and Ji Y:
Added value of breathhold diffusion-weighted MRI in detection of
small hepatocellular carcinoma lesions compared with dynamic
contrast-enhanced MRI alone using receiver operating characteristic
curve analysis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 29:341–349. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SS, Kim SH, Song KD, Choi SY and Heo
NH: Value of gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI and diffusion-weighted
imaging in the differentiation of hypervascular hyperplastic nodule
from small (<3 cm) hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma in
patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis: A retrospective
case-control study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 51:70–80. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhong X, Tang H, Lu B, You J, Piao J, Yang
P and Li J: Differentiation of small hepatocellular carcinoma from
dysplastic nodules in cirrhotic liver: Texture analysis based on
MRI improved performance in comparison over gadoxetic acid-enhanced
MR and diffusion-weighted imaging. Front Oncol. 9:13822020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME,
Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA and Bossuyt
PM; QUADAS-2 Group, : QUADAS-2: A revised tool for the quality
assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med.
155:529–536. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Reitsma JB, Glas AS, Rutjes AW, Scholten
RJ, Bossuyt PM and Zwinderman AH: Bivariate analysis of sensitivity
and specificity produces informative summary measures in diagnostic
reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:982–990. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Choo SP, Tan WL, Goh BKP, Tai WM and Zhu
AX: Comparison of hepatocellular carcinoma in Eastern versus
Western populations. Cancer. 122:3430–3446. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Basha MAA, Refaat R, Mohammad FF, Khamis
MEM, El-Maghraby AM, El Sammak AA, Al-Molla RM, Mohamed HAE,
Alnaggar AA, Hassan HA, et al: The utility of diffusion-weighted
imaging in improving the sensitivity of LI-RADS classification of
small hepatic observations suspected of malignancy. Abdom Radiol
(NY). 44:1773–1784. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Di Martino M, Di Miscio R, De Filippis G,
Lombardo CV, Saba L, Geiger D and Catalano C: Detection of small
(≤2 cm) HCC in cirrhotic patients: Added value of diffusion
MR-imaging. Abdom Imaging. 38:1254–1262. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang J, Kim YK, Kim JM, Lee WJ, Choi D
and Hong SS: Pretransplant diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma by
gadoxetic acid-enhanced and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance
imaging. Liver Transpl. 20:1436–1446. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kwon HJ, Byun JH, Kim JY, Hong GS, Won HJ,
Shin YM and Kim PN: Differentiation of small (≤2 cm) hepatocellular
carcinomas from small benign nodules in cirrhotic liver on
gadoxetic acid-enhanced and diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance
images. Abdom Imaging. 40:64–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park MJ, Kim YK, Lee MW, Lee WJ, Kim YS,
Kim SH, Choi D and Rhim H: Small hepatocellular carcinomas:
Improved sensitivity by combining gadoxetic acid-enhanced and
diffusion-weighted MR imaging patterns. Radiology. 264:761–770.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao XT, Li WX, Chai WM and Chen KM:
Detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma using gadoxetic
acid-enhanced MRI: Is the addition of diffusion-weighted MRI at
3.0T beneficial? J Dig Dis. 15:137–145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, Verslype C, Op
de Beeck K, Komuta M, Topal B, Roebben I, Bielen D, Roskams T,
Nevens F and Dymarkowski S: Diffusion-weighted MRI provides
additional value to conventional dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI for
detection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur Radiol. 19:2456–2466.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rhee H, Kim MJ, Park MS and Kim KA:
Differentiation of early hepatocellular carcinoma from benign
hepatocellular nodules on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI. Br J Radiol.
85:e837–e844. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang A, Bashir MR, Corwin MT, Cruite I,
Dietrich CF, Do RKG, Ehman EC, Fowler KJ, Hussain HK, Jha RC, et
al: Evidence supporting LI-RADS major features for CT- and MR
imaging-based diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic
review. Radiology. 286:29–48. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ronot M, Purcell Y and Vilgrain V:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: Current imaging modalities for diagnosis
and prognosis. Dig Dis Sci. 64:934–950. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hanna RF, Miloushev VZ, Tang A,
Finklestone LA, Brejt SZ, Sandhu RS, Santillan CS, Wolfson T, Gamst
A and Sirlin CB: Comparative 13-year meta-analysis of the
sensitivity and positive predictive value of ultrasound, CT, and
MRI for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma. Abdom Radiol (NY).
41:71–90. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hsiao CY, Chen PD and Huang KW: A
prospective assessment of the diagnostic value of contrast-enhanced
ultrasound, dynamic computed tomography and magnetic resonance
imaging for patients with small liver tumors. J Clin Med.
8:13532019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Jiang H, Chen J, Zhou Y, Huang Z
and Song B: Gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced magnetic resonance
imaging outperformed multidetector computed tomography in
diagnosing small hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Liver
Transpl. 23:1505–1518. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li J, Li X, Weng J, Lei L, Gong J, Wang J,
Li Z, Zhang L and He S: Gd-EOB-DTPA dynamic contrast-enhanced
magnetic resonance imaging is more effective than enhanced 64-slice
CT for the detection of small lesions in patients with
hepatocellular carcinoma. Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e139642018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kierans AS, Kang SK and Rosenkrantz AB:
The diagnostic performance of dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging
for detection of small hepatocellular carcinoma measuring up to 2
cm: A meta-analysis. Radiology. 278:82–94. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu LM, Hu J, Gu HY, Hua J and Xu JR: Can
diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) alone be
used as a reliable sequence for the preoperative detection and
characterisation of hepatic metastases? A meta-analysis. Eur J
Cancer. 49:572–584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mannelli L, Bhargava P, Osman SF, Raz E,
Moshiri M, Laffi G, Wilson GJ and Maki JH: Diffusion-weighted
imaging of the liver: A comprehensive review. Curr Probl Diagn
Radiol. 42:77–83. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, Li C, Wang R, Ren J, Yang J and
Zhang Y: Combined application of gadoxetic acid disodium-enhanced
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and diffusion-weighted imaging
(DWI) in the diagnosis of chronic liver disease-induced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS One.
10:e01442472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
van den Bos IC, Hussain SM, Dwarkasing RS,
Hop WC, Zondervan PE, de Man RA, IJzermans JN, Walker CW and
Krestin GP: MR imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma: Relationship
between lesion size and imaging findings, including signal
intensity and dynamic enhancement patterns. J Magn Reson Imaging.
26:1548–1555. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Parikh T, Drew SJ, Lee VS, Wong S, Hecht
EM, Babb JS and Taouli B: Focal liver lesion detection and
characterization with diffusion-weighted MR imaging: Comparison
with standard breath-hold T2-weighted imaging. Radiology.
246:812–822. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pankaj Jain T, Kan WT, Edward S, Fernon H
and Kansan Naider R: Evaluation of ADCratio on liver MRI
diffusion to discriminate benign versus malignant solid liver
lesions. Eur J Radiol Open. 5:209–214. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Goshima S, Kanematsu M, Kondo H, Yokoyama
R, Kajita K, Tsuge Y, Watanabe H, Shiratori Y, Onozuka M and
Moriyama N: Diffusion-weighted imaging of the liver: Optimizing b
value for the detection and characterization of benign and
malignant hepatic lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging. 28:691–697. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Miller FH, Hammond N, Siddiqi AJ, Shroff
S, Khatri G, Wang Y, Merrick LB and Nikolaidis P: Utility of
diffusion-weighted MRI in distinguishing benign and malignant
hepatic lesions. J Magn Reson Imaging. 32:138–147. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Le Moigne F, Boussel L, Haquin A, Bancel
B, Ducerf C, Berthezène Y and Rode A: Grading of small
hepatocellular carcinomas (≤2 cm): Correlation between histology,
T2 and diffusion-weighted imaging. Br J Radiol. 87:201307632014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Okamura S, Sumie S, Tonan T, Nakano M,
Satani M, Shimose S, Shirono T, Iwamoto H, Aino H, Niizeki T, et
al: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging predicts
malignant potential in small hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver
Dis. 48:945–952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mori Y, Tamai H, Shingaki N, Moribata K,
Deguchi H, Ueda K, Inoue I, Maekita T, Iguchi M, Kato J, et al:
Signal intensity of small hepatocellular carcinoma on apparent
diffusion coefficient mapping and outcome after radiofrequency
ablation. Hepatol Res. 45:75–87. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|