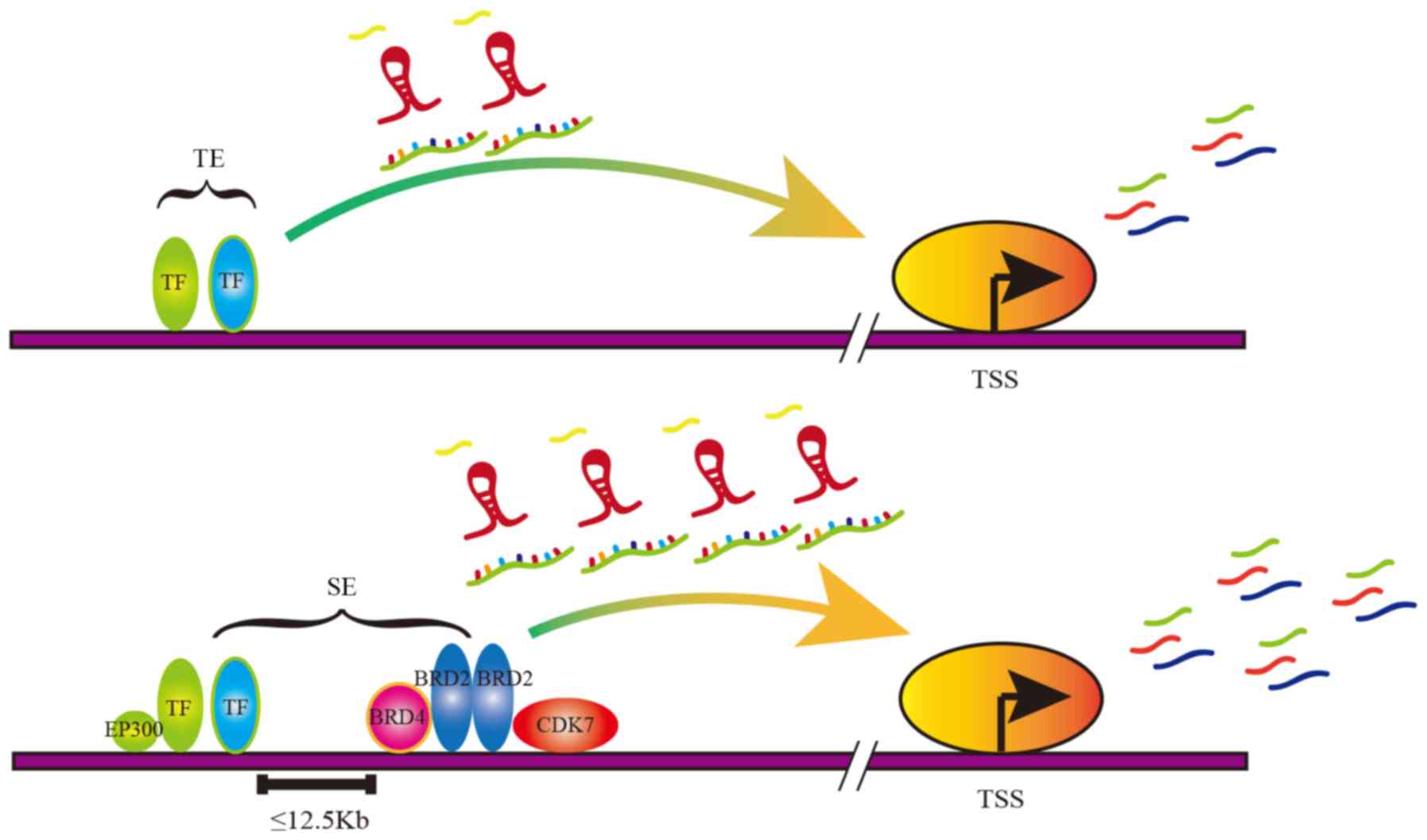
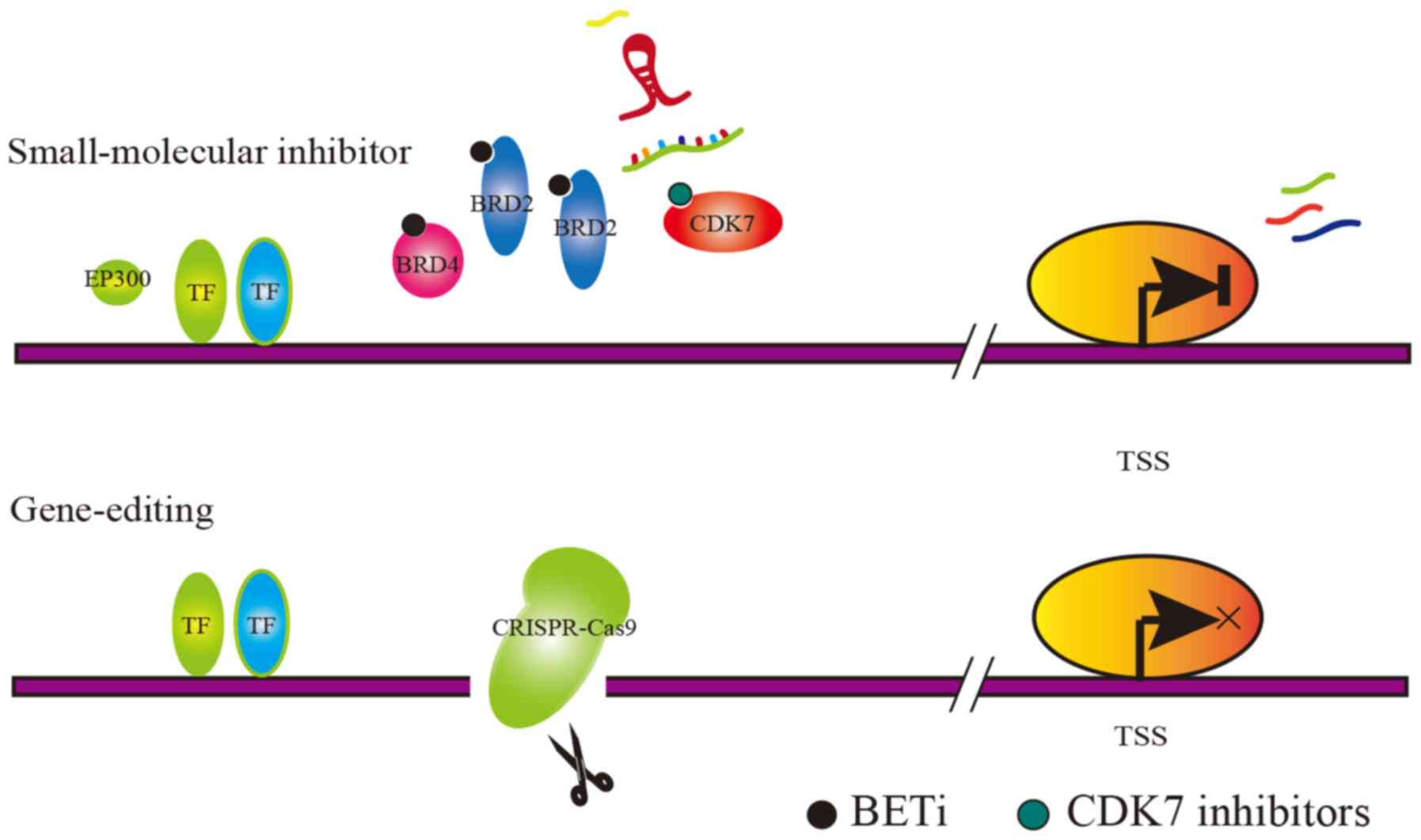
|
1
|
Banerji J, Rusconi S and Schaffner W:
Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA
sequences. Cell. 27:299–308. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sur I and Taipale J: The role of enhancers
in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:483–493. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rickels R and Shilatifard A: Enhancer
Logic and mechanics in development and disease. Trends Cell Biol.
28:608–630. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bulger M and Groudine M: Functional and
mechanistic diversity of distal transcription enhancers. Cell.
144:327–339. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Whyte WA, Orlando DA, Hnisz D, Abraham BJ,
Lin CY, Kagey MH, Rahl PB, Lee TI and Young RA: Master
transcription factors and mediator establish super-enhancers at key
cell identity genes. Cell. 153:307–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pott S and Lieb JD: What are
super-enhancers? Nat Genet. 47:8–12. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hnisz D, Abraham BJ, Lee TI, Lau A,
Saint-Andre V, Sigova AA, Hoke HA and Young RA: Super-enhancers in
the control of cell identity and disease. Cell. 155:934–947. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Christensen CL, Kwiatkowski N, Abraham BJ,
Carretero J, Al-Shahrour F, Zhang T, Chipumuro E, Herter-Sprie GS,
Akbay EA, Altabef A, et al: Targeting transcriptional addictions in
small cell lung cancer with a covalent CDK7 inhibitor. Cancer Cell.
26:909–922. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsang FH, Law CT, Tang TC, Cheng CL, Chin
DW, Tam WV, Wei L, Wong CC, Ng IO and Wong CM: Aberrant
super-enhancer landscape in human hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 69:2502–2517. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xie JJ, Jiang YY, Jiang Y, Li CQ, Lim MC,
An O, Mayakonda A, Ding LW, Long L, Sun C, et al:
Super-Enhancer-driven long non-coding RNA LINC01503, regulated by
tp63, is over-expressed and oncogenic in squamous cell carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 154:2137–2151. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Peng L, Jiang B, Yuan X, Qiu Y, Peng J,
Huang Y, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Lin Z, Li J, et al:
Super-Enhancer-associated long noncoding RNA HCCL5 is activated by
zeb1 and promotes the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 79:572–584. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lin L, Huang M, Shi X, Mayakonda A, Hu K,
Jiang YY, Guo X, Chen L, Pang B, Doan N, et al:
Super-enhancer-associated MEIS1 promotes transcriptional
dysregulation in Ewing sarcoma in co-operation with EWS-FLI1.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47:1255–1267. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cao X, Dang L, Zheng X, Lu Y, Lu Y, Ji R,
Zhang T, Ruan X, Zhi J, Hou X, et al: Targeting
super-enhancer-driven oncogenic transcription by cdk7 inhibition in
anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid. 29:809–823. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang L and Hu G: Remodeling
super-enhancers and oncogenic transcription. Cell Cycle.
15:3157–3158. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ma M, Ru Y, Chuang LS, Hsu NY, Shi LS,
Hakenberg J, Cheng WY, Uzilov A, Ding W, Glicksberg BS, et al:
Disease-associated variants in different categories of disease
located in distinct regulatory elements. BMC Genomics. 16 (Suppl
8):S32015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dalla-Favera R, Bregni M, Erikson J,
Patterson D, Gallo RC and Croce CM: Human c-myc onc gene is located
on the region of chromosome 8 that is translocated in Burkitt
lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 79:7824–7827. 1982.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Taub R, Kirsch I, Morton C, Lenoir G, Swan
D, Tronick S, Aaronson S and Leder P: Translocation of the c-myc
gene into the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus in human Burkitt
lymphoma and murine plasmacytoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
79:7837–7841. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ar-Rushdi A, Nishikura K, Erikson J, Watt
R, Rovera G and Croce CM: Differential expression of the
translocated and the untranslocated c-myc oncogene in Burkitt
lymphoma. Science. 222:390–393. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Erikson J, Ar-Rushdi A, Drwinga HL, Nowell
PC and Croce CM: Transcriptional activation of the translocated
c-myc oncogene in burkitt lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
80:820–824. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kubota S, Tokunaga K, Umezu T,
Yokomizo-Nakano T, Sun Y, Oshima M, Tan KT, Yang H, Kanai A,
Iwanaga E, et al: Lineage-specific RUNX2 super-enhancer activates
MYC and promotes the development of blastic plasmacytoid dendritic
cell neoplasm. Nat Commun. 10:16532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chipumuro E, Marco E, Christensen CL,
Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Hatheway CM, Abraham BJ, Sharma B, Yeung C,
Altabef A, et al: CDK7 inhibition suppresses super-enhancer-linked
oncogenic transcription in MYCN-driven cancer. Cell. 159:1126–1139.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sengupta S and George RE:
Super-Enhancer-driven transcriptional dependencies in cancer.
Trends Cancer. 3:269–281. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hnisz D, Shrinivas K, Young RA,
Chakraborty AK and Sharp PA: A Phase separation model for
transcriptional control. Cell. 169:13–23. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoo H, Triandafillou C and Drummond DA:
Cellular sensing by phase separation: Using the process, not just
the products. J Biol Chem. 294:7151–7159. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sabari BR, Dall'Agnese A, Boija A, Klein
IA, Coffey EL, Shrinivas K, Abraham BJ, Hannett NM, Zamudio AV,
Manteiga JC, et al: Coactivator condensation at super-enhancers
links phase separation and gene control. Science. 361:eaar39582018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang JT, Smith J, Chen BC, Schmidt H,
Rasoloson D, Paix A, Lambrus BG, Calidas D, Betzig E and Seydoux G:
Regulation of RNA granule dynamics by phosphorylation of
serine-rich, intrinsically disordered proteins in C.
elegans. Elife. 3:e45912014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wippich F, Bodenmiller B, Trajkovska MG,
Wanka S, Aebersold R and Pelkmans L: Dual specificity kinase DYRK3
couples stress granule condensation/dissolution to mTORC1
signaling. Cell. 152:791–805. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Milin AN and Deniz AA: Reentrant phase
transitions and non-equilibrium dynamics in membraneless
organelles. Biochemistry. 57:2470–2477. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakamura Y, Hattori N, Iida N, Yamashita
S, Mori A, Kimura K, Yoshino T and Ushijima T: Targeting of
super-enhancers and mutant BRAF can suppress growth of BRAF-mutant
colon cancer cells via repression of MAPK signaling pathway. Cancer
Lett. 402:100–109. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gunnell A, Webb HM, Wood CD, McClellan MJ,
Wichaidit B, Kempkes B, Jenner RG, Osborne C, Farrell PJ and West
MJ: RUNX super-enhancer control through the Notch pathway by
Epstein-Barr virus transcription factors regulates B cell growth.
Nucleic Acids Res. 44:4636–4650. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ke L, Zhou H, Wang C, Xiong G, Xiang Y,
Ling Y, Khabir A, Tsao GS, Zeng Y, Zeng M, et al: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma super-enhancer-driven ETV6 correlates with prognosis.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:9683–9688. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dave K, Sur I, Yan J, Zhang J, Kaasinen E,
Zhong F, Blaas L, Li X, Kharazi S, Gustafsson C, et al: Mice
deficient of Myc super-enhancer region reveal differential control
mechanism between normal and pathological growth. Elife.
6:e233822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lai B, Lee JE, Jang Y, Wang L, Peng W and
Ge K: MLL3/MLL4 are required for CBP/p300 binding on enhancers and
super-enhancer formation in brown adipogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res.
45:6388–6403. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen K, Chen Z, Wu D, Zhang L, Lin X, Su
J, Rodriguez B, Xi Y, Xia Z, Chen X, et al: Broad H3K4me3 is
associated with increased transcription elongation and enhancer
activity at tumor-suppressor genes. Nat Genet. 47:1149–1157. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Suzuki HI, Young RA and Sharp PA:
Super-enhancer-mediated RNA processing revealed by integrative
microrna network analysis. Cell. 168:1000–1014.e15. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liang J, Zhou H, Gerdt C, Tan M, Colson T,
Kaye KM, Kieff E and Zhao B: Epstein-Barr virus super-enhancer
eRNAs are essential for MYC oncogene expression and lymphoblast
proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:14121–14126. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ounzain S and Pedrazzini T: Super-enhancer
lncs to cardiovascular development and disease. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1863:1953–1960. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peng L, Jiang B, Yuan X, Qiu Y, Peng J,
Huang Y, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Lin Z, Li J, et al:
Super-Enhancer-associated long noncoding RNA HCCL5 Is activated by
zeb1 and promotes the malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 79:572–584. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fontanals-Cirera B, Hasson D, Vardabasso
C, Di Micco R, Agrawal P, Chowdhury A, Gantz M, de
Pablos-Aragoneses A, Morgenstern A, Wu P, et al: Harnessing BET
inhibitor sensitivity reveals AMIGO2 as a melanoma survival gene.
Mol Cell. 68:731–744.e9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Pelish HE, Liau BB, Nitulescu II,
Tangpeerachaikul A, Poss ZC, Da SD, Caruso BT, Arefolov A, Fadeyi
O, Christie AL, et al: Mediator kinase inhibition further activates
super-enhancer- associated genes in AML. Nature. 526:273–276. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
See YX, Wang BZ and Fullwood MJ: Chromatin
interactions and regulatory elements in cancer: From bench to
bedside. Trends Genet. 35:145–158. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu X, Enomoto K, Zhao L, Zhu YJ,
Willingham MC, Meltzer P, Qi J and Cheng SY: Bromodomain and
extraterminal protein inhibitor JQ1 suppresses thyroid tumor growth
in a mouse model. Clin Cancer Res. 23:430–440. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Augert A and MacPherson D: Treating
transcriptional addiction in small cell lung cancer. Cancer Cell.
26:783–784. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gerlach D, Tontsch-Grunt U, Baum A, Popow
J, Scharn D, Hofmann MH, Engelhardt H, Kaya O, Beck J, Schweifer N,
et al: The novel BET bromodomain inhibitor BI 894999 represses
super-enhancer-associated transcription and synergizes with CDK9
inhibition in AML. Oncogene. 37:2687–2701. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen D, Zhao Z, Huang Z, Chen DC, Zhu XX,
Wang YZ, Yan YW, Tang S, Madhavan S, Ni W, et al: Super enhancer
inhibitors suppress MYC driven transcriptional amplification and
tumor progression in osteosarcoma. Bone Res. 6:112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Kitazono M, Chuman Y, Aikou T and Fojo T:
Construction of gene therapy vectors targeting thyroid cells:
Enhancement of activity and specificity with histone deacetylase
inhibitors and agents modulating the cyclic adenosine
3′,5′-monophosphate pathway and demonstration of activity in
follicular and anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cells. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 86:834–840. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wong R, Ngoc P, Leong WZ, Yam A, Zhang T,
Asamitsu K, Iida S, Okamoto T, Ueda R, Gray NS, et al: Enhancer
profiling identifies critical cancer genes and characterizes cell
identity in adult T-cell leukemia. Blood. 130:2326–2338. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Eliades P, Abraham BJ, Ji Z, Miller DM,
Christensen CL, Kwiatkowski N, Kumar R, Njauw CN, Taylor M, Miao B,
et al: High MITF expression is associated with super-enhancers and
suppressed by CDK7 inhibition in melanoma. J Invest Dermatol.
138:1582–1590. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kwiatkowski N, Zhang T, Rahl PB, Abraham
BJ, Reddy J, Ficarro SB, Dastur A, Amzallag A, Ramaswamy S, Tesar
B, et al: Targeting transcription regulation in cancer with a
covalent CDK7 inhibitor. Nature. 511:616–620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sharifnia T, Wawer MJ, Chen T, Huang QY,
Weir BA, Sizemore A, Lawlor MA, Goodale A, Cowley GS, Vazquez F, et
al: Small-molecule targeting of brachyury transcription factor
addiction in chordoma. Nat Med. 25:292–300. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hu S, Marineau JJ, Rajagopal N, Hamman KB,
Choi YJ, Schmidt DR, Ke N, Johannessen L, Bradley MJ, Orlando DA,
et al: Discovery and characterization of SY-1365, a selective,
covalent inhibitor of CDK7. Cancer Res. 79:3479–3491. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Dooley KE, Warburton A and McBride AA:
Tandemly Integrated HPV16 Can Form a Brd4-dependent
super-enhancer-like element that drives transcription of viral
oncogenes. Mbio. 7:e01446–e01416. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sengupta D, Kannan A, Kern M, Moreno MA,
Vural E, Stack BJ, Suen JY, Tackett AJ and Gao L: Disruption of
BRD4 at H3K27Ac-enriched enhancer region correlates with decreased
c-Myc expression in Merkel cell carcinoma. Epigenetics. 10:460–466.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Loven J, Hoke HA, Lin CY, Lau A, Orlando
DA, Vakoc CR, Bradner JE, Lee TI and Young RA: Selective inhibition
of tumor oncogenes by disruption of super-enhancers. Cell.
153:320–334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zuber V, Bettella F, Witoelar A,
Andreassen OA, Mills IG and Urbanucci A: Bromodomain protein 4
discriminates tissue-specific super-enhancers containing
disease-specific susceptibility loci in prostate and breast cancer.
BMC Genomics. 18:2702017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chapuy B, McKeown MR, Lin CY, Monti S,
Roemer MG, Qi J, Rahl PB, Sun HH, Yeda KT, Doench JG, et al:
Discovery and characterization of super-enhancer-associated
dependencies in diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Cancer Cell.
24:777–790. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xiong L, Wu F, Wu Q, Xu L, Cheung OK, Kang
W, Mok MT, Szeto L, Lun CY, Lung RW, et al: Aberrant enhancer
hypomethylation contributes to hepatic carcinogenesis through
global transcriptional reprogramming. Nat Commun. 10:3352019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Andricovich J, Perkail S, Kai Y, Casasanta
N, Peng W and Tzatsos A: Loss of KDM6A activates super-enhancers to
induce gender-specific squamous-like pancreatic cancer and confers
sensitivity to bet inhibitors. Cancer Cell. 33:512–526.e8e0. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Gelato KA, Schöckel L, Klingbeil O,
Rückert T, Lesche R, Toedling J, Kalfon E, Heroult M, Lejeune P,
Mönning U, et al: Super-enhancers define a proliferative
PGC-1alpha-expressing melanoma subgroup sensitive to BET
inhibition. Oncogene. 37:512–521. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Tasdemir N, Banito A, Roe JS,
Alonso-Curbelo D, Camiolo M, Tschaharganeh DF, Huang CH, Aksoy O,
Bolden JE, Chen CC, et al: BRD4 Connects enhancer remodeling to
senescence immune surveillance. Cancer Discov. 6:612–629. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Togel L, Nightingale R, Chueh AC,
Jayachandran A, Tran H, Phesse T, Wu R, Sieber OM, Arango D,
Dhillon AS, et al: Dual targeting of bromodomain and extraterminal
domain proteins and WNT or MAPK signaling, inhibits c-MYC
expression and proliferation of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cancer
Ther. 15:1217–1226. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Drier Y, Cotton MJ, Williamson KE,
Gillespie SM, Ryan RJ, Kluk MJ, Carey CD, Rodig SJ, Sholl LM,
Afrogheh AH, et al: An oncogenic MYB feedback loop drives alternate
cell fates in adenoid cystic carcinoma. Nat Genet. 48:265–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ceribelli M, Hou ZE, Kelly PN, Huang DW,
Wright G, Ganapathi K, Evbuomwan MO, Pittaluga S, Shaffer AL,
Marcucci G, et al: A Druggable TCF4- and BRD4-Dependent
transcriptional network sustains malignancy in blastic plasmacytoid
dendritic cell neoplasm. Cancer Cell. 30:764–778. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Liu J, Duan Z, Guo W, Zeng L, Wu Y, Chen
Y, Tai F, Wang Y, Lin Y, Zhang Q, et al: Targeting the
BRD4/FOXO3a/CDK6 axis sensitizes AKT inhibition in luminal breast
cancer. Nat Commun. 9:52002018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang Z, Ma P, Jing Y, Yan Y, Cai MC,
Zhang M, Zhang S, Peng H, Ji ZL, Di W, et al: BET Bromodomain
Inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in ovarian cancer by
downregulating FoxM1. Theranostics. 6:219–230. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Mottok A and Gascoyne RD: Bromodomain
inhibition in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma-giving MYC a brake.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:4–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tolani B, Gopalakrishnan R, Punj V, Matta
H and Chaudhary PM: Targeting Myc in KSHV-associated primary
effusion lymphoma with BET bromodomain inhibitors. Oncogene.
33:2928–2937. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Shen C, Ipsaro JJ, Shi J, Milazzo JP, Wang
E, Roe JS, Suzuki Y, Pappin DJ, Joshua-Tor L and Vakoc CR:
NSD3-short is an adaptor protein that couples BRD4 to the CHD8
chromatin remodeler. Mol Cell. 60:847–859. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chan KH, Zengerle M, Testa A and Ciulli A:
Impact of target warhead and linkage vector on inducing protein
degradation: Comparison of bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET)
degraders derived from triazolodiazepine (JQ1) and
tetrahydroquinoline (I-BET726) BET inhibitor scaffolds. J Med Chem.
61:504–513. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Amorim S, Stathis A, Gleeson M, Iyengar S,
Magarotto V, Leleu X, Morschhauser F, Karlin L, Broussais F, Rezai
K, et al: Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with lymphoma or
multiple myeloma: A dose-escalation, open-label, pharmacokinetic,
phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol. 3:e196–e204. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Albrecht BK, Gehling VS, Hewitt MC,
Vaswani RG, Cote A, Leblanc Y, Nasveschuk CG, Bellon S, Bergeron L,
Campbell R, et al: Identification of a Benzoisoxazoloazepine
inhibitor (CPI-0610) of the bromodomain and extra-terminal (BET)
family as a candidate for human clinical trials. J Med Chem.
59:1330–1339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Siu KT, Ramachandran J, Yee AJ, Eda H,
Santo L, Panaroni C, Mertz JA, Sims IR, Cooper MR and Raje N:
Preclinical activity of CPI-0610, a novel small-molecule
bromodomain and extra-terminal protein inhibitor in the therapy of
multiple myeloma. Leukemia. 31:1760–1769. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhao L, Okhovat JP, Hong EK, Kim YH and
Wood GS: Preclinical studies support combined inhibition of bet
family proteins and histone deacetylases as epigenetic therapy for
cutaneous t-cell lymphoma. Neoplasia. 21:82–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tripathy D, Bardia A and Sellers WR:
Ribociclib (LEE011): Mechanism of action and clinical impact of
this selective cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 Inhibitor in various
solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 23:3251–3262. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Geoerger B, Bourdeaut F, DuBois SG,
Fischer M, Geller JI, Gottardo NG, Marabelle A, Pearson A, Modak S,
Cash T, et al: A phase I study of the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib
(LEE011) in pediatric patients with malignant rhabdoid tumors,
neuroblastoma and other solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
23:2433–2441. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ribociclib extends survival in HR+ breast
cancer. Cancer Discov. 8:OF52018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Ribociclib approved for advanced breast
cancer. Cancer Discov. 7:OF32017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Cheng W, Yang Z, Wang S, Li Y, Wei H, Tian
X and Kan Q: Recent development of CDK inhibitors: An overview of
CDK/inhibitor co-crystal structures. Eur J Med Chem. 164:615–639.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Nagaraja S, Vitanza NA, Woo PJ, Taylor KR,
Liu F, Zhang L, Li M, Meng W, Ponnuswami A, Sun W, et al:
Transcriptional dependencies in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma.
Cancer Cell. 31:635–652, 2017.e6. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Cayrol F, Praditsuktavorn P, Fernando TM,
Kwiatkowski N, Marullo R, Calvo-Vidal MN, Phillip J, Pera B, Yang
SN, Takpradit K, et al: THZ1 targeting CDK7 suppresses STAT
transcriptional activity and sensitizes T-cell lymphomas to BCL2
inhibitors. Nat Commun. 8:142902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Ma X, Kuang X, Xia Q, Huang Z, Fan Y, Ning
J, Wen J, Zhang H, Yan J, Zhang Q, et al: Covalent CDK7 inhibitor
THZ1 inhibits myogenic differentiation. J Cancer. 9:3149–3155.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ali I, Choi G and Lee K: BET inhibitors as
anticancer agents: A patent review. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug
Discov. 12:340–364. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Henssen A, Althoff K, Odersky A, Beckers
A, Koche R, Speleman F, Schafers S, Bell E, Nortmeyer M, Westermann
F, et al: Targeting MYCN-Driven Transcription By BET-Bromodomain
inhibition. Clin Cancer Res. 22:2470–2481. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Donati B, Lorenzini E and Ciarrocchi A:
BRD4 and cancer: Going beyond transcriptional regulation. Mol
Cancer. 17:1642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Berthon C, Raffoux E, Thomas X, Vey N,
Gomez-Roca C, Yee K, Taussig DC, Rezai K, Roumier C, Herait P, et
al: Bromodomain inhibitor OTX015 in patients with acute leukaemia:
A dose-escalation, phase 1 study. Lancet Haematol. 3:e186–e195.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Stathis A, Zucca E, Bekradda M, Gomez-Roca
C, Delord JP, de La Motte RT, Uro-Coste E, de Braud F, Pelosi G and
French CA: Clinical response of carcinomas harboring the BRD4-NUT
oncoprotein to the targeted bromodomain inhibitor OTX015/MK-8628.
Cancer Discov. 6:492–500. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Piquereau J, Boet A, Pechoux C, Antigny F,
Lambert M, Gressette M, Ranchoux B, Gambaryan N, Domergue V, Mumby
S, et al: The BET Bromodomain Inhibitor I-BET-151 induces
structural and functional alterations of the heart mitochondria in
healthy male mice and rats. Int J Mol Sci. 20:15272019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Mustafi S, Camarena V, Qureshi R, Yoon H,
Volmar CH, Huff TC, Sant DW, Zheng L, Brothers SP, Wahlestedt C, et
al: Vitamin C supplementation expands the therapeutic window of
BETi for triple negative breast cancer. Ebiomedicine. 43:201–210.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Shen H, Xu W, Guo R, Rong B, Gu L, Wang Z,
He C, Zheng L, Hu X, Hu Z, et al: Suppression of enhancer
overactivation by a RACK7-histone demethylase complex. Cell.
165:331–342. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Katerndahl C, Heltemes-Harris LM, Willette
M, Henzler CM, Frietze S, Yang R, Schjerven H, Silverstein K,
Ramsey LB, Hubbard G, et al: Antagonism of B cell enhancer networks
by STAT5 drives leukemia and poor patient survival. Nat Immunol.
18:694–704. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Gryder BE, Yohe ME, Chou HC, Zhang X,
Marques J, Wachtel M, Schaefer B, Sen N, Song Y, Gualtieri A, et
al: PAX3-FOXO1 establishes myogenic super enhancers and confers BET
bromodomain vulnerability. Cancer Discov. 7:884–899. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ott CJ, Federation AJ, Schwartz LS, Kasar
S, Klitgaard JL, Lenci R, Li Q, Lawlor M, Fernandes SM, Souza A, et
al: Enhancer architecture and essential core regulatory circuitry
of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 34:982–995.e7e0.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Schmidt SF, Larsen BD, Loft A, Nielsen R,
Madsen JG and Mandrup S: Acute TNF-induced repression of cell
identity genes is mediated by NF κB-directed redistribution of
cofactors from super-enhancers. Genome Res. 25:1281–1294. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Biswas S and Rao CM: Epigenetics in
cancer: Fundamentals and beyond. Pharmacol Ther. 173:118–134. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Dzobo K, Senthebane DA, Thomford NE, Rowe
A, Dandara C and Parker MI: Not everyone fits the mold: Intratumor
and intertumor heterogeneity and innovative cancer drug design and
development. Omics. 22:17–34. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Kelly AD and Issa JJ: The promise of
epigenetic therapy: Reprogramming the cancer epigenome. Curr Opin
Genet Dev. 42:68–77. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Mill CP, Fiskus W, DiNardo CD, Qian Y,
Raina K, Rajapakshe K, Perera D, Coarfa C, Kadia TM, Khoury JD, et
al: RUNX1 targeted therapy for AML expressing somatic or germline
mutation in RUNX1. Blood. 134:59–73. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Mansour MR, Abraham BJ, Anders L,
Berezovskaya A, Gutierrez A, Durbin AD, Etchin J, Lawton L, Sallan
SE, Silverman LB, et al: Oncogene regulation. An oncogenic
super-enhancer formed through somatic mutation of a noncoding
intergenic element. Science. 346:1373–1377. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Gröschel S, Sanders MA, Hoogenboezem R, de
Wit E, Bouwman B, Erpelinck C, van der Velden V, Havermans M,
Avellino R, van Lom K, et al: A single oncogenic enhancer
rearrangement causes concomitant EVI1 and GATA2 deregulation in
leukemia. Cell. 157:369–381. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Marsman J, Gimenez G, Day RC, Horsfield JA
and Jones GT: A non-coding genetic variant associated with
abdominal aortic aneurysm alters ERG gene regulation. Hum Mol
Genet. 29:554–565. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Kleinstern G, Yan H, Hildebrandt M, Vijai
J, Berndt SI, Ghesquieres H, McKay J, Wang SS, Nieters A, Ye Y, et
al: Inherited variants at 3q13.33 and 3p24.1 are associated with
risk of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and implicate immune
pathways. Hum Mol Genet. 29:70–79. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
He Y, Timofeeva M, Li X, Din F, Blackmur
JP, Vaughan-Shaw P, Svinti V, Farrington SM, Campbell H, Dunlop MG,
et al: A comprehensive study of the effect on colorectal cancer
survival of common germline genetic variation previously linked
with cancer prognosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
28:1944–1946. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Cong Z, Li Q, Yang Y, Guo X, Cui L and You
T: The SNP of rs6854845 suppresses transcription via the DNA
looping structure alteration of super-enhancer in colon cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 514:734–741. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Zhu DL, Chen XF, Hu WX, Dong SS, Lu BJ,
Rong Y, Chen YX, Chen H, Thynn HN, Wang NN, et al: Multiple
functional variants at 13q14 risk locus for osteoporosis regulate
RANKL expression through long-range super-enhancer. J Bone Miner
Res. 33:1335–1346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Eid A, Alshareef S and Mahfouz MM: CRISPR
base editors: Genome editing without double-stranded breaks.
Biochem J. 475:1955–1964. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Leenay RT, Maksimchuk KR, Slotkowski RA,
Agrawal RN, Gomaa AA, Briner AE, Barrangou R and Beisel CL:
Identifying and visualizing functional PAM diversity across
CRISPR-Cas systems. Mol Cell. 62:137–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Jiang F and Doudna JA: CRISPR-Cas9
structures and mechanisms. Annu Rev Biophys. 46:505–529. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kosicki M, Tomberg K and Bradley A: Repair
of double-strand breaks induced by CRISPR-Cas9 leads to large
deletions and complex rearrangements. Nat Biotechnol. 36:765–771.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Anzalone AV, Randolph PB, Davis JR, Sousa
AA, Koblan LW, Levy JM, Chen PJ, Wilson C, Newby GA, Raguram A and
Liu DR: Search-and-replace genome editing without double-strand
breaks or donor DNA. Nature. 576:149–157. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Fernandes Q: Therapeutic strategies in
Sickle Cell Anemia: The past present and future. Life Sci.
178:100–108. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Vu M, Li R, Baskfield A, Lu B, Farkhondeh
A, Gorshkov K, Motabar O, Beers J, Chen G, Zou J, et al: Neural
stem cells for disease modeling and evaluation of therapeutics for
Tay-Sachs disease. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 13:1522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Liu X, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Li M, Zhou F, Li
K, Cao H, Ni M, Liu Y, Gu Z, et al: In situ capture of chromatin
interactions by biotinylated dCas9. Cell. 170:1028–1043.e19e0.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|