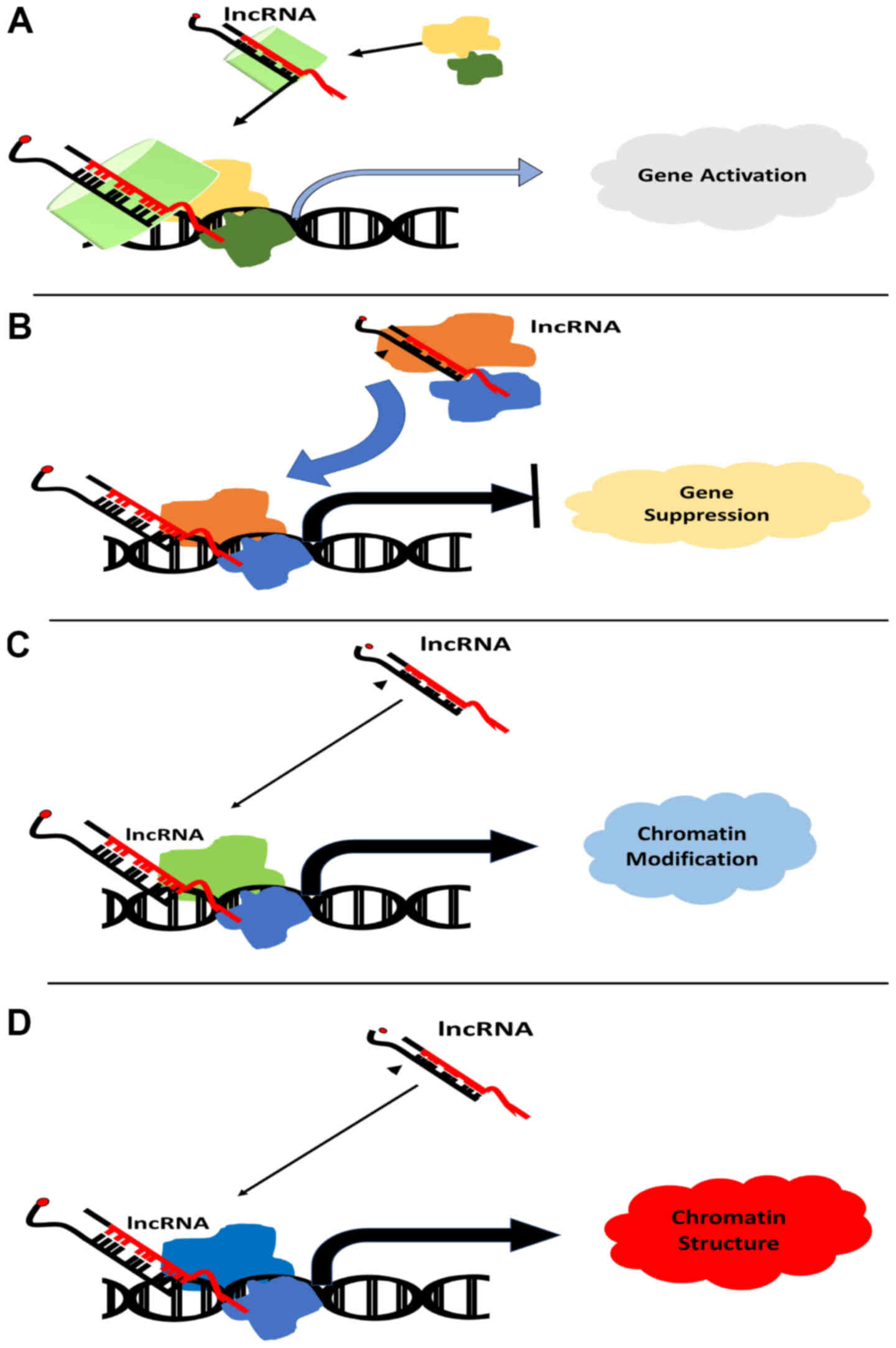
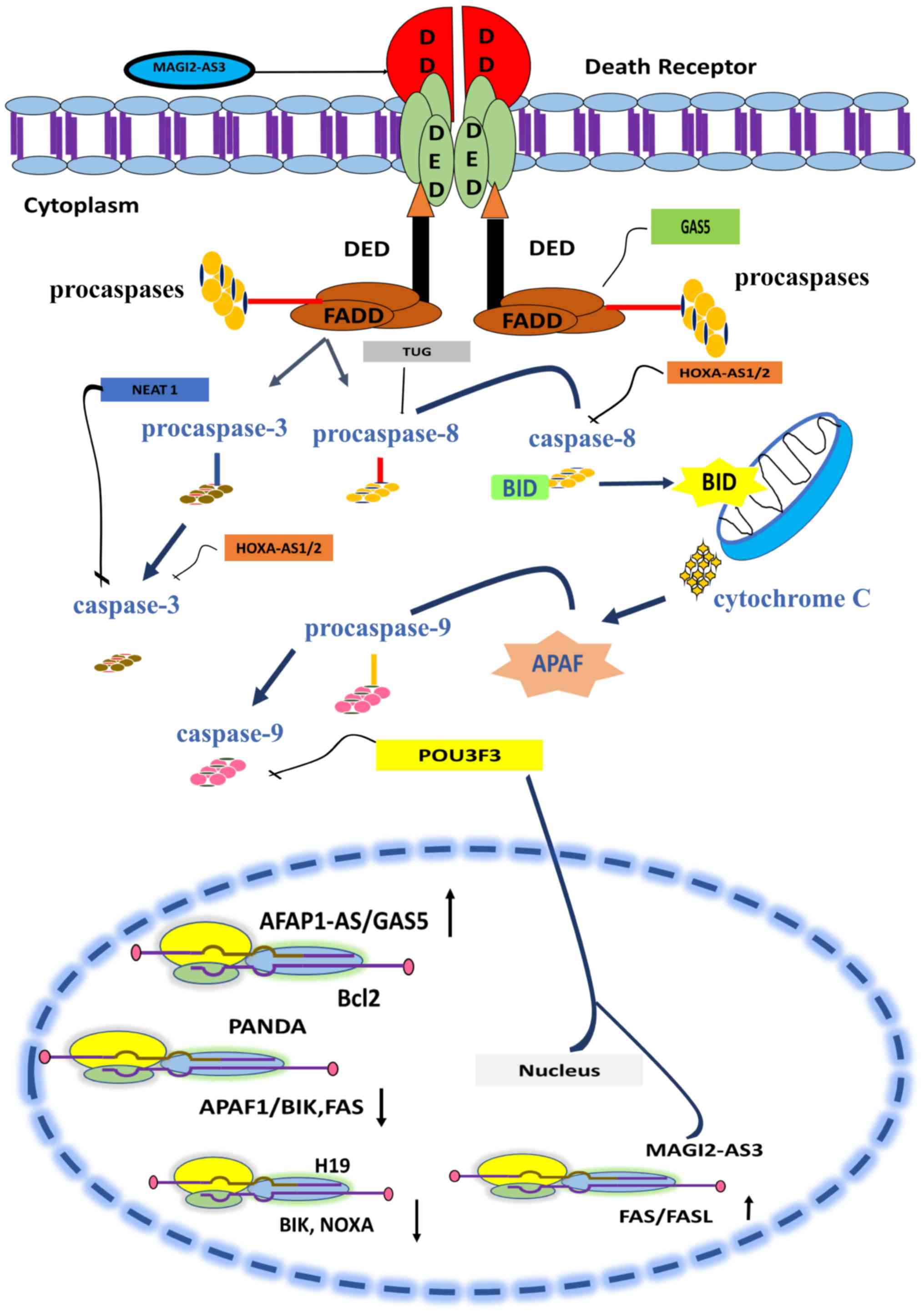
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeSantis CE, Fedewa SA, Goding Sauer A,
Kramer JL, Smith RA and Jemal A: Breast cancer statistics, 2015:
Convergence of incidence rates between black and white women. CA
Cancer J Clin. 66:31–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zur Hausen H, Bund T and de Villiers EM:
Specific nutritional infections early in life as risk factors for
human colon and breast cancers several decades later. Int J Cancer.
144:1574–1583. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Naoum GE, Buchsbaum DJ, Tawadros F,
Farooqi A and Arafat WO: Journey of TRAIL from bench to bedside and
its potential role in immuno-oncology. Oncol Rev.
11:3322017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Johnstone RW, Frew AJ and Smyth MJ: The
TRAIL apoptotic pathway in cancer onset, progression and therapy.
Nat Rev Cancer. 8:782–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shi X, Li Y, Sun Y, Zhao X, Sun X, Gong T,
Liang Z, Ma Y and Zhang X: Genome-wide analysis of lncRNAs, miRNAs,
and mRNAs forming a prognostic scoring system in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. PeerJ. 8:e83682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tirosh I and Suvà ML: Deciphering human
tumor biology by single-cell expression profiling. Ann Rev Cancer
Biol. 3:151–166. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Farooqi AA, Mukhtar S, Riaz AM, Waseem S,
Minhaj S, Dilawar BA, Malik BA, Nawaz A and Bhatti S: Wnt and SHH
in prostate cancer: Trouble mongers occupy the TRAIL towards
apoptosis. Cell Prolif. 44:508–515. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Walensky LD: Cheating death: New molecules
block BAX. Trends Mol Med. 25:259–261. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mazurek N, Byrd JC, Sun Y, Hafley M,
Ramirez K, Burks J and Bresalier RS: Cell-surface galectin-3
confers resistance to TRAIL by impeding trafficking of death
receptors in metastatic colon adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Death
Differ. 19:523–533. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seyrek K, Richter M and Lavrik IN:
Decoding the sweet regulation of apoptosis: The role of
glycosylation and galectins in apoptotic signaling pathways. Cell
Death Differ. 26:981–993. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ivanova S, Polajnar M, Narbona-Perez AJ,
Hernandez-Alvarez MI, Frager P, Slobodnyuk K, Plana N, Nebreda AR,
Palacin M, Gomis RR, et al: Regulation of death receptor signaling
by the autophagy protein TP53INP2. EMBO J. 38:e993002019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kaufmann T, Strasser A and Jost PJ: Fas
death receptor signalling: Roles of Bid and XIAP. Cell Death
Differ. 19:42–50. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Walczak H, Degli-Esposti MA, Johnson RS,
Smolak PJ, Waugh JY, Boiani N, Timour MS, Gerhart MJ, Schooley KA,
Smith CA, et al: TRAIL-R2: A novel apoptosis-mediating receptor for
TRAIL. EMBO J. 16:5386–5397. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rahman M, Davis SR, Pumphrey JG, Bao J,
Nau MM, Meltzer PS and Lipkowitz S: TRAIL induces apoptosis in
triple-negative breast cancer cells with a mesenchymal phenotype.
Br Cancer Res Treat. 113:217–230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ahmad M and Shi Y: TRAIL-induced apoptosis
of thyroid cancer cells: Potential for therapeutic intervention.
Oncogene. 19:3363–3371. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao L, Dong A, Gu J, Liu Z, Zhang Y,
Zhang W, Wang Y, He L, Qian C, Qian Q and Liu X: The antitumor
activity of TRAIL and IL-24 with replicating oncolytic adenovirus
in colorectal cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 13:1011–1022. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brooks AD and Sayers TJ: Reduction of the
antiapoptotic protein cFLIP enhances the susceptibility of human
renal cancer cells to TRAIL apoptosis. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
54:499–505. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Voelkel-Johnson C: TRAIL-mediated
signaling in prostate, bladder and renal cancer. Nat Rev Urol.
8:417–427. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cuello M, Ettenberg SA, Nau MM and
Lipkowitz S: Synergistic induction of apoptosis by the combination
of trail and chemotherapy in chemoresistant ovarian cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 81:380–390. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Finnberg NK and El-Deiry WS: TRAIL death
receptors as tumor suppressors and drug targets. Cell Cycle.
7:1525–1528. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Y and Zhang B: TRAIL resistance of
breast cancer cells is associated with constitutive endocytosis of
death receptors 4 and 5. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1861–1871. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tollefson AE, Toth K, Doronin K,
Kuppuswamy M, Doronina OA, Lichtenstein DL, Hermiston TW, Smith CA
and Wold WS: Inhibition of TRAIL-induced apoptosis and forced
internalization of TRAIL receptor 1 by adenovirus proteins. J
Virol. 75:8875–8887. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Suliman A, Lam A, Datta R and Srivastava
RK: Intracellular mechanisms of TRAIL: Apoptosis through
mitochondrial-dependent and-independent pathways. Oncogene.
20:2122–2133. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Screaton RA, Kiessling S, Sansom OJ,
Millar CB, Maddison K, Bird A, Clarke AR and Frisch SM:
Fas-associated death domain protein interacts with methyl-CpG
binding domain protein 4: A potential link between genome
surveillance and apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:5211–5216.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aggarwal BB, Bhardwaj U and Takada Y:
Regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis by ectopic expression of
antiapoptotic factors. Vitamins & Hormones Elsevier. 453–483.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jang CW, Chen CH, Chen CC, Chen JY, Su YH
and Chen RH: TGF-Beta induces apoptosis through Smad-mediated
expression of DAP-kinase. Nat Cell Biol. 4:51–58. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kruidering M and Evan GI: Caspase-8 in
apoptosis: The beginning of ‘the end’? IUBMB Life. 50:85–90. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Farooqi AA and De Rosa G: TRAIL and
microRNAs in the treatment of prostate cancer: Therapeutic
potential and role of nanotechnology. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
97:8849–8857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Falschlehner C, Emmerich CH, Gerlach B and
Walczak H: TRAIL signalling: Decisions between life and death. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 39:1462–1475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Han Li C and Chen Y: Small and long
non-coding RNAs: Novel targets in perspective cancer therapy. Curr
Genomics. 16:319–326. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Müller V, Oliveira-Ferrer L, Steinbach B,
Pantel K and Schwarzenbach H: Interplay of lncRNA H19/miR-675 and
lncRNA NEAT1/miR-204 in breast cancer. Mol Oncol. 13:1137–1149.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Javed Z, Ahmed Shah F, Rajabi S, Raza Q,
Iqbal Z, Ullah M, Ahmad T, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad M, Pezzani R, et
al: LncRNAs as potential therapeutic targets in thyroid cancer.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 21:281–287. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang A, Bao Y, Wu Z, Zhao T, Wang D, Shi
J, Liu B, Sun S, Yang F, Wang L and Qu L: Long noncoding RNA
EGFR-AS1 promotes cell growth and metastasis via affecting HuR
mediated mRNA stability of EGFR in renal cancer. Cell Death Dis.
10:1542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Luo H, Xu C, Le W, Ge B and Wang T: lncRNA
CASC11 promotes cancer cell proliferation in bladder cancer through
miRNA-150. J Cell Biochem. 120:13487–13493. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Luo J, Wang K, Yeh S, Sun Y, Liang L, Xiao
Y, Xu W, Niu Y, Cheng L, Maity SN, et al: LncRNA-p21 alters the
antiandrogen enzalutamide-induced prostate cancer neuroendocrine
differentiation via modulating the EZH2/STAT3 signaling. Nat
Commun. 10:25712019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang Y and Ruan F: LncRNA LEF1-AS1
promotes ovarian cancer development through interacting with
miR-1285-3p. Cancer Manag Res. 12:687–694. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
He RZ, Luo DX and Mo YY: Emerging roles of
lncRNAs in the post-transcriptional regulation in cancer. Genes
Dis. 6:62019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lau E: Non-coding RNA: Zooming in on
lncRNA functions. Nat Rev Genet. 15:574–575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
van Leeuwen S and Mikkers H: Long
non-coding RNAs: Guardians of development. Differentiation.
80:175–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ye N, Wang B, Quan ZF, Cao SJ, Wen XT,
Huang Y, Huang XB, Wu R, Ma XP, Yan QG, et al: Functional roles of
long non-coding RNA in human breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 15:5993–5997. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R, Singhal U,
Sahu A, Hosono Y, Barrette TR, Prensner JR, Evans JR, Zhao S, et
al: The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human
transcriptome. Nat Genet. 47:199–208. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cheetham S, Gruhl F, Mattick J and Dinger
M: Long noncoding RNAs and the genetics of cancer. Br J Cancer.
108:2419–2425. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lee JT and Bartolomei MS: X-inactivation,
imprinting, and long noncoding RNAs in health and disease. Cell.
152:1308–1323. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Zhang TH, Liang LZ, Liu XL, Wu JN, Su K,
Chen JY and Zheng QY: LncRNA UCA1/miR-124 axis modulates
TGFβ1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of
tongue cancer cells through JAG1/Notch signaling. J Cell Biochem.
120:10495–10504. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kawakami T, Zhang C, Taniguchi T, Kim CJ,
Okada Y, Sugihara H, Hattori T, Reeve AE, Ogawa O and Okamoto K:
Characterization of loss-of-inactive X in Klinefelter syndrome and
female-derived cancer cells. Oncogene. 23:6163–6169. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Postlmayr A and Wutz A: Insights into the
establishment of chromatin states in pluripotent cells from studies
of X inactivation. J Mol Biol. 429:1521–1531. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li X, Hou L, Yin L and Zhao S: LncRNA XIST
interacts with miR-454 to inhibit cells proliferation, epithelial
mesenchymal transition and induces apoptosis in triple-negative
breast cancer. J Biosci. 45:452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zheng R, Lin S, Guan L, Yuan H, Liu K, Liu
C, Ye W, Liao Y, Jia J and Zhang R: Long non-coding RNA XIST
inhibited breast cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion via
miR-155/CDX1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 498:1002–1008. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhao L, Zhao Y, He Y, Li Q and Mao Y: The
functional pathway analysis and clinical significance of miR-20a
and its related lncRNAs in breast cancer. Cell Signal. 51:152–165.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen Y and Li CH: Novel therapeutic
targets for hepatocellular carcinoma treatment. Hepatocellular
Carcinoma Basic Res. 352012.doi: 10.5772/28894.
|
|
54
|
Battistelli C, Sabarese G, Santangelo L,
Montaldo C, Gonzalez FJ, Tripodi M and Cicchini C: The lncRNA
HOTAIR transcription is controlled by HNF4α-induced chromatin
topology modulation. Cell Death Differ. 26:890–901. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Qu X, Alsager S, Zhuo Y and Shan B: HOX
transcript antisense RNA (HOTAIR) in cancer. Cancer Lett.
454:90–97. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bhan A and Mandal SS: LncRNA HOTAIR: A
master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1856:151–164. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Cai B, Song X, Cai J and Zhang S: HOTAIR:
A cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Neoplasma. 61:379–391. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yang Z, Zhou L, Wu LM, Lai MC, Xie HY,
Zhang F and Zheng SS: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
predicts tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
following liver transplantation. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:1243–1250.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hajjari M and Salavaty A: HOTAIR: An
oncogenic long non-coding RNA in different cancers. Cancer Bio Med.
12:1–9. 2015.
|
|
60
|
Bhan A, Hussain I, Ansari KI, Kasiri S,
Bashyal A and Mandal SS: Antisense transcript long noncoding RNA
(lncRNA) HOTAIR is transcriptionally induced by estradiol. J Mol
Biol. 425:3707–3722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Amândio AR, Necsulea A, Joye E, Mascrez B
and Duboule D: Hotair is dispensible for mouse development. PLoS
Genet. 12:e10062322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Sørensen KP, Thomassen M, Tan Q, Bak M,
Cold S, Burton M, Larsen MJ and Kruse TA: Long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR is an independent prognostic marker of metastasis in
estrogen receptor-positive primary breast cancer. Breast cancer Res
Treat. 142:529–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tao S, He H and Chen Q: Estradiol induces
HOTAIR levels via GPER-mediated miR-148a inhibition in breast
cancer. J Transl Med. 13:1312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lv R, Zhang J, Zhang W, Huang Y, Wang N,
Zhang Q and Qu S: Circulating HOTAIR expression predicts the
clinical response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with
breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 22:249–256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang M, Wu WB, Wang ZW and Wang XH:
lncRNA NEAT1 is closely related with progression of breast cancer
via promoting proliferation and EMT. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
21:1020–1026. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li W, Zhang Z, Liu X, Cheng X, Zhang Y,
Han X, Zhang Y, Liu S, Yang J, Xu B, et al: The FOXN3-NEAT1-SIN3A
repressor complex promotes progression of hormonally responsive
breast cancer. J Clin Invest. 127:3421–3440. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shin VY, Chen J, Cheuk IW, Siu MT, Ho CW,
Wang X, Jin H and Kwong A: Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 confers
oncogenic role in triple-negative breast cancer through modulating
chemoresistance and cancer stemness. Cell Death Dis. 10:2702019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Qian K, Liu G, Tang Z, Hu Y, Fang Y, Chen
Z and Xu X: The long non-coding RNA NEAT1 interacted with miR-101
modulates breast cancer growth by targeting EZH2. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 615:1–9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li X, Wang S, Li Z, Long X, Guo Z, Zhang
G, Zu J, Chen Y and Wen L: The lncRNA NEAT1 facilitates cell growth
and invasion via the miR-211/HMGA2 axis in breast cancer. Int J
Biol Macromol. 105:346–353. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Ke H, Zhao L, Feng X, Xu H, Zou L, Yang Q,
Su X, Peng L and Jiao B: NEAT1 is required for survival of breast
cancer cells through FUS and miR-548. Gene Regul Syst Bio. 10
(Suppl 1):S11–S17. 2016.
|
|
71
|
Godinho M, Meijer D, Setyono-Han B,
Dorssers LC and van Agthoven T: Characterization of BCAR4, a novel
oncogene causing endocrine resistance in human breast cancer cells.
J Cell Physiol. 226:1741–1749. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Godinho MF, Wulfkuhle JD, Look MP,
Sieuwerts AM, Sleijfer S, Foekens JA, Petricoin EF III, Dorssers LC
and van Agthoven T: BCAR4 induces antioestrogen resistance but
sensitises breast cancer to lapatinib. Br J Cancer. 107:947–955.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xing Z, Park PK, Lin C and Yang L: LncRNA
BCAR4 wires up signaling transduction in breast cancer. RNA Biol.
12:681–689. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sun Q, Hao Q and Prasanth KV: Nuclear long
noncoding RNAs: Key regulators of gene expression. Trends Genet.
34:142–157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Godinho MF, Sieuwerts AM, Look MP, Meijer
D, Foekens JA, Dorssers LC and van Agthoven T: Relevance of BCAR4
in tamoxifen resistance and tumour aggressiveness of human breast
cancer. Br J Cancer. 103:1284–1291. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Niknafs YS, Han S, Ma T, Speers C, Zhang
C, Wilder-Romans K, Iyer MK, Pitchiaya S, Malik R, Hosono Y, et al:
The lncRNA landscape of breast cancer reveals a role for DSCAM-AS1
in breast cancer progression. Nat Commun. 7:127912016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang Z and Zöller M: Exosomes, metastases,
and the miracle of cancer stem cell markers. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
38:259–295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Ouyang D, Su J, Huang P, Li M, Li Q, Zhao
P, Chen Q, Zou Q, Feng X, Qian K, et al: Identification of lncRNAs
via microarray analysis for predicting HER2-negative breast cancer
response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
11:2621–2628. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chen YK and Yen Y: The ambivalent role of
lncRNA Xist in carcinogenesis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 15:314–323. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Mazor G, Levin L, Picard D, Ahmadov U,
Carén H, Borkhardt A, Reifenberger G, Leprivier G, Remke M and
Rotblat B: The lncRNA TP73-AS1 is linked to aggressiveness in
glioblastoma and promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma
cancer stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 10:2462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang Y, Yang L, Chen T, Liu X, Guo Y, Zhu
Q, Tong X, Yang W, Xu Q, Huang D and Tu K: A novel lncRNA
MCM3AP-AS1 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by
targeting miR-194-5p/FOXA1 axis. Mol Cancer. 18:282019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kang CL, Qi B, Cai QQ, Fu LS, Yang Y, Tang
C, Zhu P, Chen QW, Pan J, Chen MH and Wu XZ: LncRNA AY promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by stimulating ITGAV
transcription. Theranostics. 9:4421–4436. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhang H, Zhu M, Du Y, Zhang H, Zhang Q,
Liu Q, Huang Z, Zhang L, Li H, Xu L, et al: A panel of 12-lncRNA
signature predicts survival of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Cancer.
10:1550–1559. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Yang G, Lu X and Yuan L: LncRNA: A link
between RNA and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1839:1097–1109. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Farooqi AA, Attar R, Qureshi MZ, Fayyaz S,
Sohail MI, Sabitaliyevich UY, Nurmurzayevich SB, Yelekenova A,
Yaylim I and Alaaeddine N: Interplay of long non-coding RNAs and
TGF/SMAD signaling in different cancers. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-Grand). 64:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Jiang Y, Lin L, Zhong S, Cai Y, Zhang F,
Wang X, Miao R, Zhang B, Gao S and Hu X: Overexpression of novel
lncRNA NLIPMT inhibits metastasis by reducing phosphorylated
glycogen synthase kinase 3β in breast cancer. J Cell Physiol.
234:10698–10708. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Liu Y, Sharma S and Watabe K: Roles of
lncRNA in breast cancer. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 7:94–108. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Guan Y, Bhandari A, Xia E, Yang F, Xiang J
and Wang O: lncRNA FOXD3-AS1 is associated with clinical
progression and regulates cell migration and invasion in breast
cancer. Cell Biochem Funct. 37:239–244. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Liu AN, Qu HJ, Gong WJ, Xiang JY, Yang MM
and Zhang W: LncRNA AWPPH and miRNA-21 regulates cancer cell
proliferation and chemosensitivity in triple-negative breast cancer
by interacting with each other. J Cell Biochem. 120:14860–14866.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shi SJ, Wang LJ, Yu B, Li YH, Jin Y and
Bai XZ: LncRNA-ATB promotes trastuzumab resistance and
invasion-metastasis cascade in breast cancer. Oncotarget.
6:11652–11663. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Augoff K, McCue B, Plow EF and
Sossey-Alaoui K: miR-31 and its host gene lncRNA LOC554202 are
regulated by promoter hypermethylation in triple-negative breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 11:52012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Li Z, Hou P, Fan D, Dong M, Ma M, Li H,
Yao R, Li Y, Wang G, Geng P, et al: The degradation of EZH2
mediated by lncRNA ANCR attenuated the invasion and metastasis of
breast cancer. Cell Death Differ. 24:59–71. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Guo R, Su Y, Xue J, Si J, Chi Y and Wu J:
Abstract P6-05-01: A novel cleaved cytoplasmic lncRNA LacRNA
interacts with PHB2 and suppresses breast cancer metastasis via
repressing MYC targets. Cancer Res. 792019.doi: 10.1158/1538-7445.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Li W, Jia G, Qu Y, Du Q and Liu B and Liu
B: Long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) HOXA11-AS promotes breast cancer
invasion and metastasis by regulating epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Med Sci Monit. 23:3393–3403. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Li Z, Dong M, Fan D, Hou P, Li H, Liu L,
Lin C, Liu J, Su L, Wu L, et al: LncRNA ANCR down-regulation
promotes TGF-β-induced EMT and metastasis in breast cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:67329–67343. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Naval J, de Miguel D, Gallego-Lleyda A,
Anel A and Martinez-Lostao L: Importance of TRAIL molecular anatomy
in receptor oligomerization and signaling. Implications for Cancer
Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 11:4442019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Mert U and Sanlioglu AD: Intracellular
localization of DR5 and related regulatory pathways as a mechanism
of resistance to TRAIL in cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 74:245–255.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Li T, Liu Y, Xiao H and Xu G: Long
non-coding RNA TUG1 promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in
human breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 24:535–543. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yang J, Meng X, Yu Y, Pan L, Zheng Q and
Lin W: LncRNA POU3F3 promotes proliferation and inhibits apoptosis
of cancer cells in triple-negative breast cancer by inactivating
caspase 9. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 83:1117–1123. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Shan TD, Xu JH, Yu T, Li JY, Zhao LN,
Ouyang H, Luo S, Lu XJ, Huang CZ, Lan QS, et al: Knockdown of
linc-POU3F3 suppresses the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration
resistance of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 7:961–975. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Rossi MN and Antonangeli F: LncRNAs: New
players in apoptosis control. Int J Cell Biol. 2014:4738572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Qu Y, Wang Y, Wang P, Lin N, Yan X and Li
Y: Overexpression of long noncoding RNA HOXA-AS2 predicts an
adverse prognosis and promotes tumorigenesis via SOX4/PI3K/AKT
pathway in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Biol Int. May 5–2020.doi:
10.1002/cbin.11370 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Awasthee N, Rai V, Verma SS, Francis KS,
Nair MS and Gupta SC: Anti-cancer activities of Bharangin against
breast cancer: Evidence for the role of NF-κB and lncRNAs. Biochim
Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1862:2738–2749. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Dianatpour A, Faramarzi S, Geranpayeh L,
Mirfakhraie R, Motevaseli E and Ghafouri-Fard S: Expression
analysis of AFAP1-AS1 and AFAP1 in breast cancer. Cancer Biomark.
22:49–54. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Zhang H and Lu B: microRNAs as biomarkers
of ovarian cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 20:373–385. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Huang YS, Chang CC, Lee SS, Jou YS and
Shih HM: Xist reduction in breast cancer upregulates AKT
phosphorylation via HDAC3-mediated repression of PHLPP1 expression.
Oncotarget. 7:432562016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Gooding AJ, Zhang B, Jahanbani FK, Gilmore
HL, Chang JC, Valadkhan S and Schiemann WP: The lncRNA BORG drives
breast cancer metastasis and disease recurrence. Sci Rep.
7:126982017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gooding AJ, Zhang B, Gunawardane L, Beard
A, Valadkhan S and Schiemann WP: The lncRNA BORG facilitates the
survival and chemoresistance of triple-negative breast cancers.
Oncogene. 38:20202019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Deng R, Liu B, Wang Y, Yan F, Hu S, Wang
H, Wang T, Li B, Deng X, Xiang S, Yang Y and Zhang J: High
expression of the newly found long noncoding RNA Z38 promotes cell
proliferation and oncogenic activity in breast cancer. J Cancer.
7:576–578. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Wang Y, Zheng C, Li T, Zhang R, Wang Y,
Zhang J, He Q, Sun Z and Wang X: Long noncoding RNA Z38 promotes
cell proliferation and metastasis and inhibits cell apoptosis in
human gastric cancer. Oncolo Lett. 16:6051–6058. 2018.
|
|
111
|
Nie ZL, Wang YS, Mei YP, Lin X, Zhang GX,
Sun HL, Wang YL, Xia YX and Wang SK: Prognostic significance of
long noncoding RNA Z38 as a candidate biomarker in breast cancer. J
Clin Lab Anal. 32:e221932018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Zhang F, Li J, Xiao H, Zou Y, Liu Y and
Huang W: AFAP1-AS1: A novel oncogenic long non-coding RNA in human
cancers. Cell Proliferation. 51:e123972018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Ma D, Chen C, Wu J, Wang H and Wu D:
Up-regulated lncRNA AFAP1-AS1 indicates a poor prognosis and
promotes carcinogenesis of breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 26:74–83.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Fan S, Yang Z, Ke Z, Huang K, Liu N, Fang
X and Wang K: Downregulation of the long non-coding RNA TUG1 is
associated with cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in
breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 95:1636–1643. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Tang T, Cheng Y, She Q, Jiang Y, Chen Y,
Yang W and Li Y: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 sponges miR-197 to
enhance cisplatin sensitivity in triple negative breast cancer.
Biomed Pharmacother. 107:338–346. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Ghavami S, Hashemi M, Ande SR, Yeganeh B,
Xiao W, Eshraghi M, Bus CJ, Kadkhoda K, Wiechec E, Halayko AJ and
Los M: Apoptosis and cancer: Mutations within caspase genes. J Med
Genet. 46:497–510. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Rossin A, Miloro G and Hueber AO: TRAIL
and FasL functions in cancer and autoimmune diseases: Towards an
increasing complexity. Cancers. 11:6392019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Eberle J: Countering TRAIL resistance in
melanoma. Cancers. 11:6562019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Kolben T, Jeschke U, Reimer T, Karsten N,
Schmoeckel E, Semmlinger A, Mahner S, Harbeck N and Kolben TM:
Induction of apoptosis in breast cancer cells in vitro by Fas
ligand reverse signaling. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 144:249–256.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Yang Y, Yang H, Xu M, Zhang H, Sun M, Mu
P, Dong T, Du S and Liu K: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) MAGI2-AS3
inhibits breast cancer cell growth by targeting the Fas/FasL
signalling pathway. Hum Cell. 31:232–241. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Si X, Zang R, Zhang E, Liu Y, Shi X, Zhang
E, Shao L, Li A, Yang N, Han X, et al: LncRNA H19 confers
chemoresistance in ERα-positive breast cancer through epigenetic
silencing of the pro-apoptotic gene BIK. Oncotarget. 7:81452–81462.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Sun H, Wang G, Peng Y, Zeng Y, Zhu QN, Li
TL, Cai JQ, Zhou HH and Zhu YS: H19 lncRNA mediates
17β-estradiol-induced cell proliferation in MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 33:3045–3052. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhang K, Luo Z, Zhang Y, Zhang L, Wu L,
Liu L, Yang J, Song X and Liu J: Circulating lncRNA H19 in plasma
as a novel biomarker for breast cancer. Cancer Biomark. 17:187–194.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Lin Y and Tao H: Diagnostic value of
plasma exosomal lncRNA H19 for breast cancer. Chin J Clin
Laboratory Sci. 36:99–101. 2018.
|
|
125
|
Han J, Han B, Wu X, Hao J, Dong X, Shen Q
and Pang H: Knockdown of lncRNA H19 restores chemo-sensitivity in
paclitaxel-resistant triple-negative breast cancer through
triggering apoptosis and regulating Akt signaling pathway. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 359:55–61. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Li J, Tian H, Yang J and Gong Z: Long
noncoding RNAs regulate cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis.
DNA Cell Biol. 35:459–470. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Hung T, Wang Y, Lin MF, Koegel AK, Kotake
Y, Grant GD, Horlings HM, Shah N, Umbricht C, Wang P, et al:
Extensive and coordinated transcription of noncoding RNAs within
cell-cycle promoters. Nat Genet. 43:621–629. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Zhang A, Xu M and Mo YY: Role of the
lncRNA-p53 regulatory network in cancer. J Mol Cell Biol.
6:181–191. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Pickard MR and Williams GT: The hormone
response element mimic sequence of GAS5 lncRNA is sufficient to
induce apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Oncotarget. 7:101042016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Zong Y, Zhang Y, Sun X, Xu T, Cheng X and
Qin Y: miR-221/222 promote tumor growth and suppress apoptosis by
targeting lncRNA GAS5 in breast cancer. Biosci Rep.
39:BSR201818592019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Zhang Z, Zhu Z, Watabe K, Zhang X, Bai C,
Xu M, Wu F and Mo YY: Negative regulation of lncRNA GAS5 by miR-21.
Cell Death Differ. 20:1558–1568. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Wickramasinghe NS, Manavalan TT, Dougherty
SM, Riggs KA, Li Y and Klinge CM: Estradiol downregulates miR-21
expression and increases miR-21 target gene expression in MCF-7
breast cancer cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 37:2584–2595. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
He X, Chen X, Zhang X, Duan X, Pan T, Hu
Q, Zhang Y, Zhong F, Liu J, Zhang H, et al: An Lnc RNA
(GAS5)/SnoRNA-derived piRNA induces activation of TRAIL gene by
site-specifically recruiting MLL/COMPASS-like complexes. Nucleic
Acids Res. 43:3712–3725. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Wang Y, Chu J, Yi P, Dong W, Saultz J,
Wang Y, Wang H, Scoville S, Zhang J, Wu LC, et al: SMAD4 promotes
TGF-β-independent NK cell homeostasis and maturation and antitumor
immunity. J Clin Invest. 128:5123–5136. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Cano-González A and López-Rivas A:
Opposing roles of TGF-β and EGF in the regulation of TRAIL-induced
apoptosis in human breast epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2104–2114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Hou L, Tu J, Cheng F, Yang H, Yu F, Wang
M, Liu J, Fan J and Zhou G: Long noncoding RNA ROR promotes breast
cancer by regulating the TGF-β pathway. Cancer Cell Int.
18:1422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Zhang Y, Zhu M, Sun Y, Li W, Wang Y and Yu
W: Upregulation of lncRNA CASC2 suppresses cell proliferation and
metastasis of breast cancer via inactivation of the TGF-β signaling
pathway. Oncol Res. 27:379–387. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Batlle E and Massagué J: Transforming
growth factor-β signaling in immunity and cancer. Immunity.
50:924–940. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Arase M, Horiguchi K, Ehata S, Morikawa M,
Tsutsumi S, Aburatani H, Miyazono K and Koinuma D: Transforming
growth factor-β-induced lnc RNA-Smad7 inhibits apoptosis of mouse
breast cancer JygMC(A) cells. Cancer Sci. 105:974–982. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Hoshino Y, Katsuno Y, Ehata S and Miyazono
K: Autocrine TGF-β protects breast cancer cells from apoptosis
through reduction of BH3-only protein, Bim. J Biochem. 149:55–65.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Xu ST, Xu JH, Zheng ZR, Zhao QQ, Zeng XS,
Cheng SX, Liang YH and Hu QF: Long non-coding RNA ANRIL promotes
carcinogenesis via sponging miR-199a in triple-negative breast
cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:14–21. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Zhao JJ, Hao S, Wang LL, Hu CY, Zhang S,
Guo LJ, Zhang G, Gao B, Jiang Y, Tian WG and Luo DL: Long
non-coding RNA ANRIL promotes the invasion and metastasis of
thyroid cancer cells through TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:57903–57918. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Chen J, Shin VY, Siu MT, Ho JC, Cheuk I
and Kwong A: miR-199a-5p confers tumor-suppressive role in
triple-negative breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 16:8872016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Zhang Y, Fan KJ, Sun Q, Chen AZ, Shen WL,
Zhao ZH, Zheng XF and Yang X: Functional screening for miRNAs
targeting Smad4 identified miR-199a as a negative regulator of
TGF-β signalling pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:9286–9297. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Wang J, Su Z, Lu S, Fu W, Liu Z, Jiang X
and Tai S: LncRNA HOXA-AS2 and its molecular mechanisms in human
cancer. Clin Chim Acta. 485:229–233. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Fang Y, Wang J, Wu F, Song Y, Zhao S and
Zhang Q: Long non-coding RNA HOXA-AS2 promotes proliferation and
invasion of breast cancer by acting as a miR-520c-3p sponge.
Oncotarget. 8:460902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|