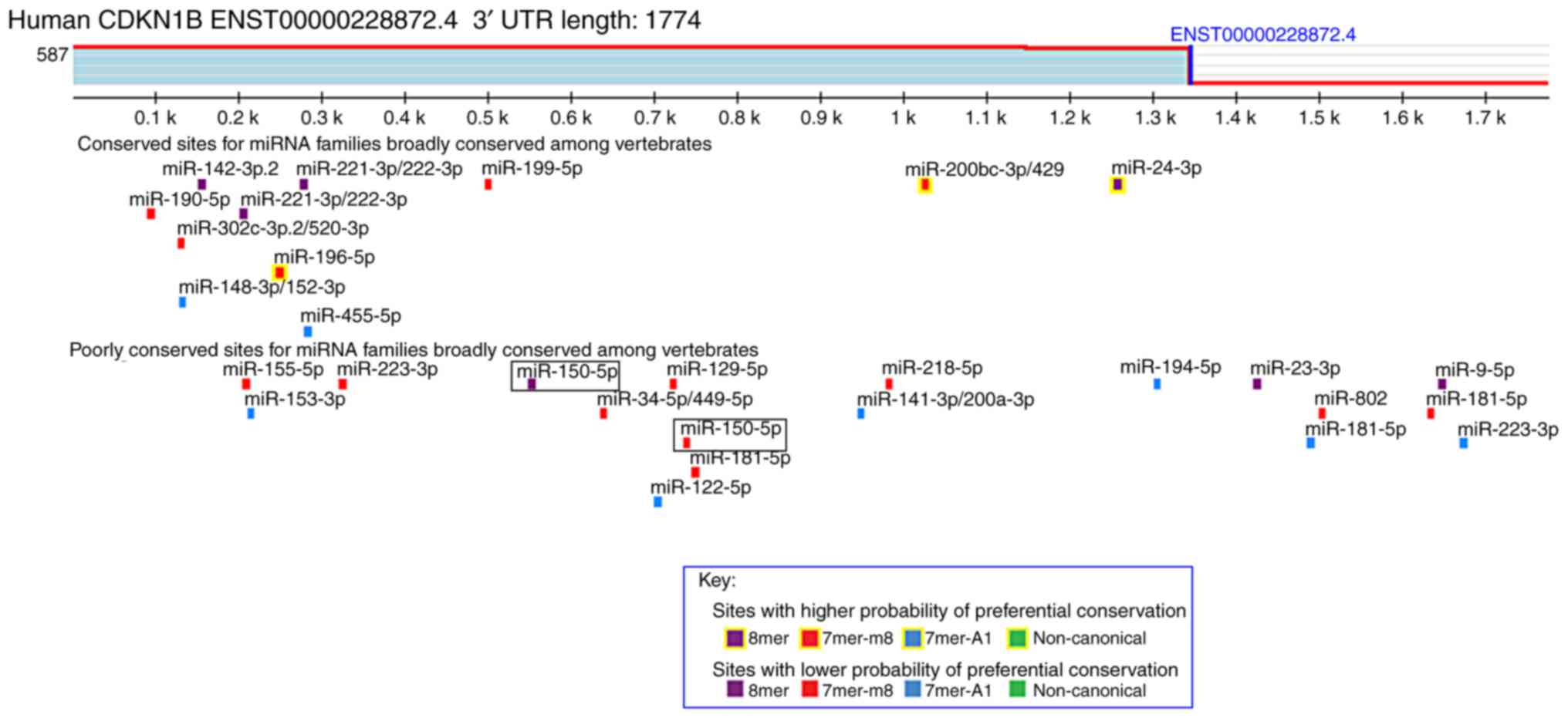
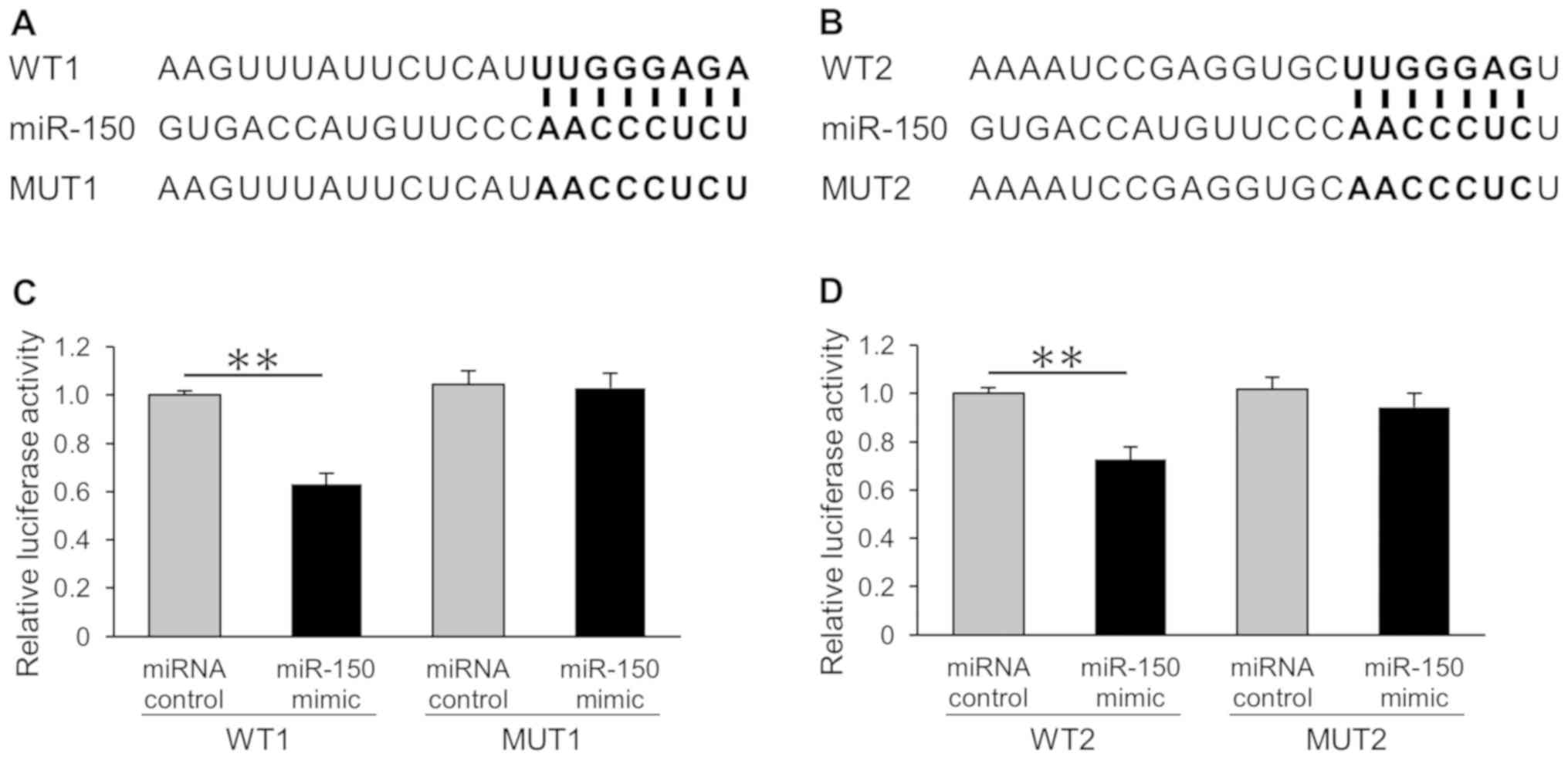
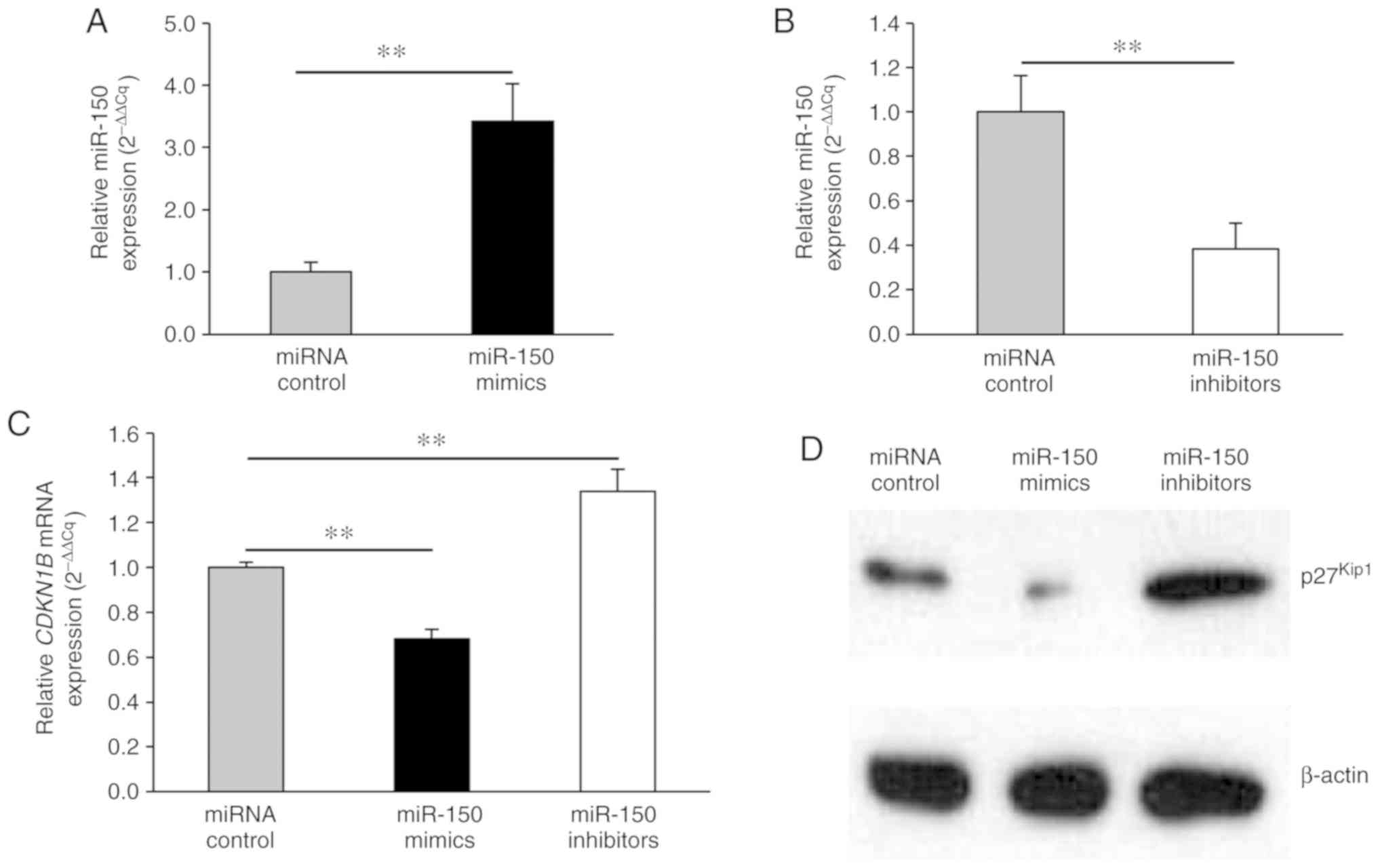
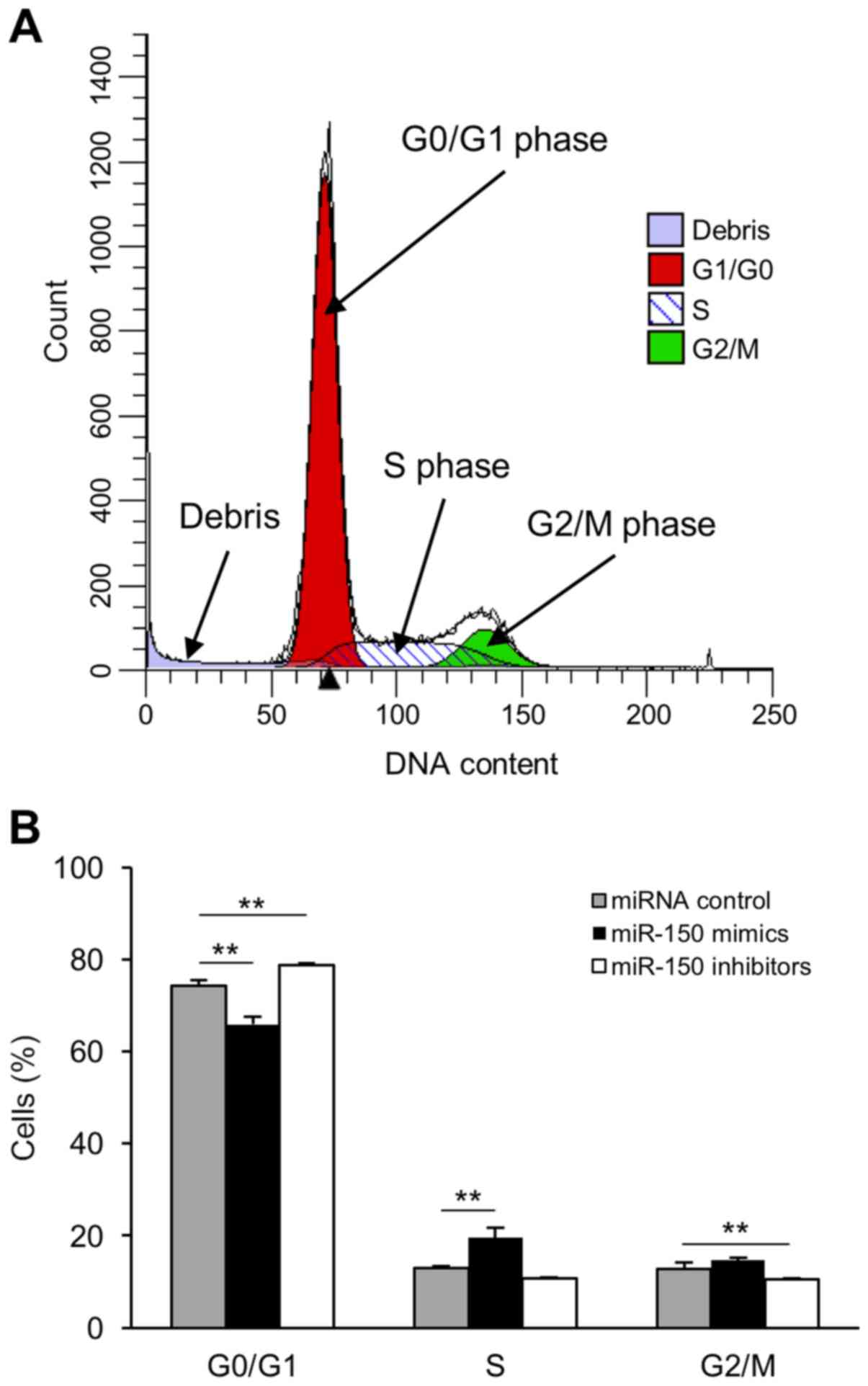
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 66:7–30. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hagemann T, Bozanovic T, Hooper S, Ljubic
A, Slettenaar VI, Wilson JL, Singh N, Gayther SA, Shepherd JH and
Van Trappen PO: Molecular profiling of cervical cancer progression.
Br J Cancer. 96:321–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lai EC: miRNAs: Whys and wherefores of
miRNA-mediated regulation. Curr Biol. 15:R458–R460. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB and Bartel
DP: Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome
Res. 19:92–105. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ebert MS and Sharp PA: Roles for microRNAs
in conferring robustness to biological processes. Cell.
149:515–524. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Farazi TA, Spitzer JI, Morozov P and
Tuschl T: miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 223:102–115. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang F, Ren X and Zhang X: Role of
microRNA-150 in solid tumors. Oncol Lett. 10:11–16. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Feng J, Yang Y, Zhang P, Wang F, Ma Y, Qin
H and Wang Y: miR-150 functions as a tumour suppressor in human
colorectal cancer by targeting c-Myb. J Cell Mol Med. 18:2125–2134.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Srivastava SK, Bhardwaj A, Singh S, Arora
S, Wang B, Grizzle WE and Singh AP: MicroRNA-150 directly targets
MUC4 and suppresses growth and malignant behavior of pancreatic
cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 32:1832–1839. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang S, Chen Y, Wu W, Ouyang N, Chen J,
Li H, Liu X, Su F, Lin L and Yao Y: miR-150 promotes human breast
cancer growth and malignant behavior by targeting the pro-apoptotic
purinergic P2X7 receptor. PLoS One. 8:e807072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin M, Yang Z, Ye W, Xu H and Hua X:
MicroRNA-150 predicts a favorable prognosis in patients with
epithelial ovarian cancer, and inhibits cell invasion and
metastasis by suppressing transcriptional repressor ZEB1. PLoS One.
9:e1039652014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dezhong L, Xiaoyi Z, Xianlian L, Hongyan
Z, Guohua Z, Bo S, Shenglei Z and Lian Z: miR-150 is a factor of
survival in prostate cancer patients. J BUON. 20:173–179.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang J, Luo N, Luo Y, Peng Z, Zhang T and
Li S: MicroRNA-150 inhibits human CD133-positive liver cancer stem
cells through negative regulation of the transcription factor
c-Myb. Int J Oncol. 40:747–756. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Katada T, Ishiguro H, Kuwabara Y, Kimura
M, Mitui A, Mori Y, Ogawa R, Harata K and Fujii Y: MicroRNA
expression profile in undifferentiated gastric cancer. Int J Oncol.
34:537–542. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li J, Hu L, Tian C, Lu F, Wu J and Liu L:
MicroRNA-150 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and survival by
targeting FOXO4. BMC Mol Biol. 16:242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou L, Qi X, Potashkin JA, Abdul-Karim FW
and Gorodeski GI: MicroRNAs miR-186 and miR-150 down-regulate
expression of the pro-apoptotic purinergic P2X7 receptor by
activation of instability sites at the 3′-untranslated region of
the gene that decrease steady-state levels of the transcript. J
Biol Chem. 283:28274–2886. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu J and Han S: miR-150-5p promotes the
proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cervical
carcinoma cells via targeting SRCIN1. Pathol Res Pract.
215:738–747. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boura E, Silhan J, Herman P, Vecer J, Sulc
M, Teisinger J, Obsilova V and Obsil T: Both the N-terminal loop
and wing W2 of the forkhead domain of transcription factor Foxo4
are important for DNA binding. J Biol Chem. 282:8265–8275. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang Q, Li X, Wang L, Feng YH, Zeng R and
Gorodeski G: Antiapoptotic effects of estrogen in normal and cancer
human cervical epithelial cells. Endocrinology. 145:5568–5579.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cabodi S, del Pilar Camacho-Leal M, Di
Stefano P and Defilippi P: Integrin signalling adaptors: Not only
figurants in the cancer story. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:858–870. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Z, Wang J, Li J, Wang X and Song W:
MicroRNA-150 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and invasion
of cervical cancer through targeting PDCD4. Biomed Pharmacother.
97:511–517. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Polyak K, Lee MH, Erdjument-Bromage H,
Koff A, Roberts JM, Tempst P and Massagué J: Cloning of p27Kip1, a
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of
extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 78:59–66. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Toyoshima H and Hunter T: p27, a novel
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to
p21. Cell. 78:67–74. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pizzini S, Bisognin A, Mandruzzato S,
Biasiolo M, Facciolli A, Perilli L, Rossi E, Esposito G, Rugge M,
Pilati P, et al: Impact of microRNAs on regulatory networks and
pathways in human colorectal carcinogenesis and development of
metastasis. BMC Genomics. 14:5892013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma Y, Zhang P, Wang F, Zhang H, Yang J,
Peng J, Liu W and Qin H: miR-150 as a potential biomarker
associated with prognosis and therapeutic outcome in colorectal
cancer. Gut. 61:1447–1453. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun W, Zhang Z, Wang J, Shang R, Zhou L,
Wang X, Duan J, Ruan B, Gao Y, Dai B, et al: MicroRNA-150
suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis in hepatocellular
carcinoma by inhibiting the GAB1-ERK axis. Oncotarget.
7:11595–11608. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yokobori T, Suzuki S, Tanaka N, Inose T,
Sohda M, Sano A, Sakai M, Nakajima M, Miyazaki T, Kato H and Kuwano
H: miR-150 is associated with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma via targeting the EMT inducer ZEB1. Cancer Sci.
104:48–54. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li H, Ouyang R, Wang Z, Zhou W, Chen H,
Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Li H, Liao M, Wang W, et al: miR-150 promotes
cellular metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer by targeting
FOXO4. Sci Rep. 6:390012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yin QW, Sun XF, Yang GT, Li XB, Wu MS and
Zhao J: Increased expression of microRNA-150 is associated with
poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 8:842–846. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang N, Wei X and Xu L: miR-150 promotes
the proliferation of lung cancer cells by targeting P53. FEBS Lett.
587:2346–2351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu Q, Jin H, Yang Z, Luo G, Lu Y, Li K,
Ren G, Su T, Pan Y, Feng B, et al: miR-150 promotes gastric cancer
proliferation by negatively regulating the pro-apoptotic gene EGR2.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 392:340–345. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|