|
1
|
Torre LA, Siegel RL, Ward EM and Jemal A:
Global cancer incidence and mortality rates and trends-an update.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:16–27. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeeshan R and Mutahir Z: Cancer
metastasis-tricks of the trade. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. 17:172–182.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dudjak LA: Cancer metastasis. Semin Oncol
Nurs. 8:40–50. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang J and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: At the crossroads of development
and tumor metastasis. Dev Cell. 14:818–829. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg R: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Linder S and Wiesner C: Tools of the
trade: Podosomes as multipurpose organelles of monocytic cells.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 72:121–135. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Popow-Woźniak A, Mazur AJ, Mannherz HG,
Malicka-Błaszkiewicz M and Nowak D: Cofilin overexpression affects
actin cytoskeleton organization and migration of human colon
adenocarcinoma cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 138:725–736.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leong H, Robertson A, Stoletov K, Leith
SJ, Chin CA, Chien AE, Hague MN, Ablack A, Carmine-Simmen K,
McPherson VA, et al: Invadopodia are required for cancer cell
extravasation and are a therapeutic target for metastasis. Cell
Rep. 8:1558–1570. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parekh A and Weaver AM: Regulation of
invadopodia by mechanical signaling. Exp Cell Res. 343:89–95.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Artym VV, Yamada KM and Mueller SC: ECM
Degradation assays for analyzing local cell invasion. Methods Mol
Biol. 522:211–219. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
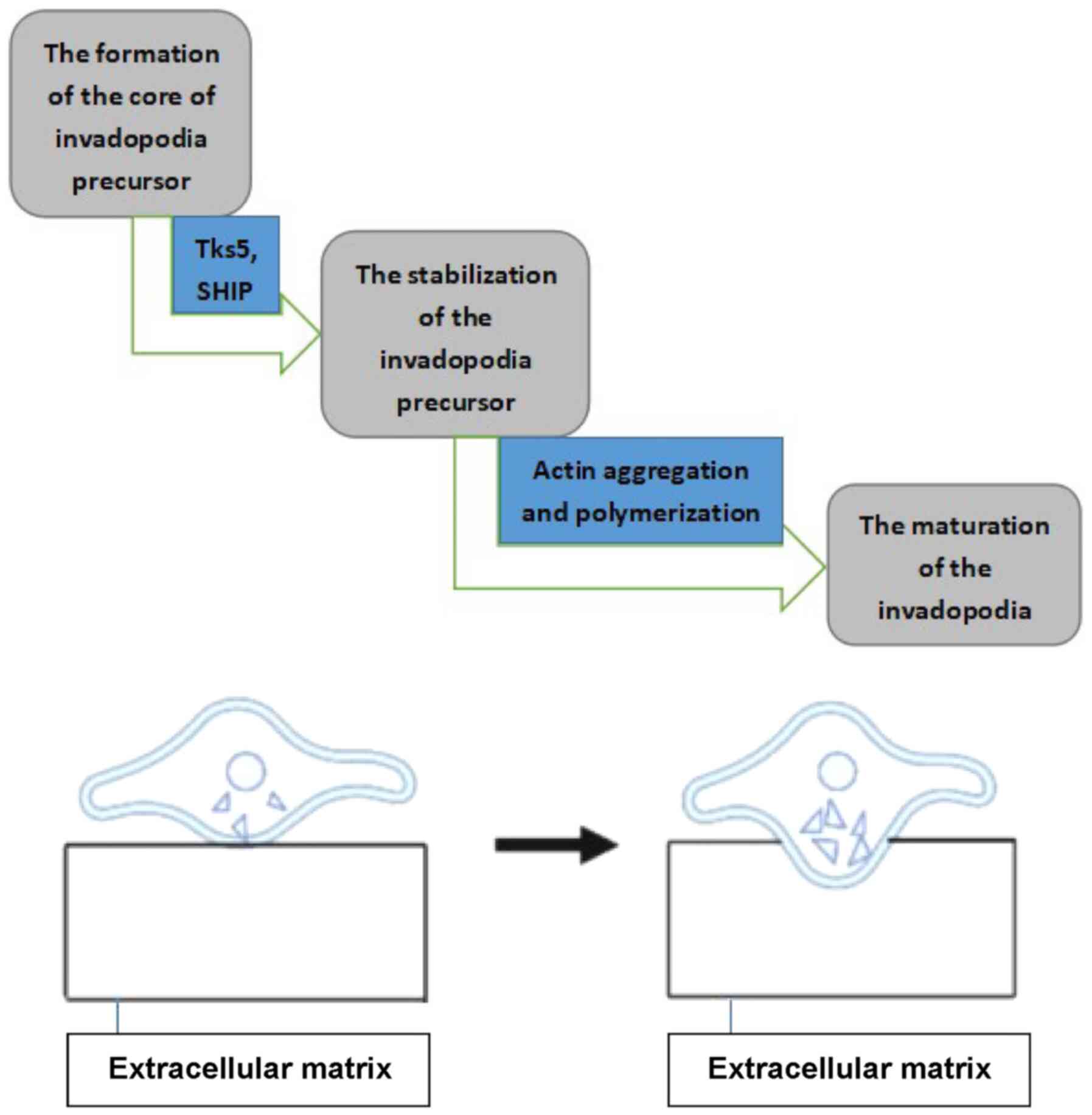
Beaty BT and Condeelis J: Digging a little
deeper: The stages of invadopodium formation and maturation. Eur J
Cell Biol. 93:438–444. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eddy RJ, Weidmann MD, Sharma VP and
Condeelis JS: Tumor cell invadopodia: Invasive protrusions that
orchestrate metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 27:595–607.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sharma V, Eddy R, Entenberg D, Kai M,
Gertler FB and Condeelis J: Tks5 and SHIP2 regulate invadopodium
maturation, but not initiation, in breast carcinoma cells. Curr
Biol. 23:2079–2089. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hughes SK, Oudin MJ, Tadros J, Neil J, Del
Rosario A, Joughin BA, Ritsma L, Wyckoff J, Vasile E, Eddy R, et
al: PTP1B-dependent regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase
signaling by the actin-binding protein Mena. Mol Biol Cell.
26:3867–3878. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zervantonakis I, Sudo R, Rimchala T, Chung
S and Kamm R: Abstract #2269: A physiological relevant 3D in vitro
model of cancer cell migration and interactions with endothelium.
Cancer Res. 69:2269. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang DD, Chen YB, Zhao JJ, Zhang XF, Zhu
GC, Weng DS, Pan K, Lv L, Pan QZ, Jiang SS, et al: TES functions as
a Mena-dependent tumor suppressor in gastric cancer carcinogenesis
and metastasis. Cancer Commun (Lond). 39:32019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Magalhaes MA, Eddy RJ,
Hodgson L and Condeelis J: Functions of cofilin in cell locomotion
and invasion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:405–415. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Murphy DA and Courtneidge SA: The ‘ins’
and ‘outs’ of podosomes and invadopodia: Characteristics, formation
and function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:413–426. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Linder S: The matrix corroded: Podosomes
and invadopodia in extracellular matrix degradation. Trends Cell
Biol. 17:107–117. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Baldassarre M, Pompeo A, Beznoussenko G,
Castaldi C, Cortellino S, McNiven MA, Luini A and Buccione R:
Dynamin participates in focal extracellular matrix degradation by
invasive cells. Mol Biol Cell. 14:1074–1084. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Buccione R, Orth JD and McNiven MA: Foot
and mouth: Podosomes, invadopodia and circular dorsal Ruffles. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 5:647–657. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chuang YY: Role of synaptojanin 2 in
glioma cell migration and invasion. Cancer Res. 64:8271–8275.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tu Y: The discovery of artemisinin
(qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat Med. 17:1217–1220.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
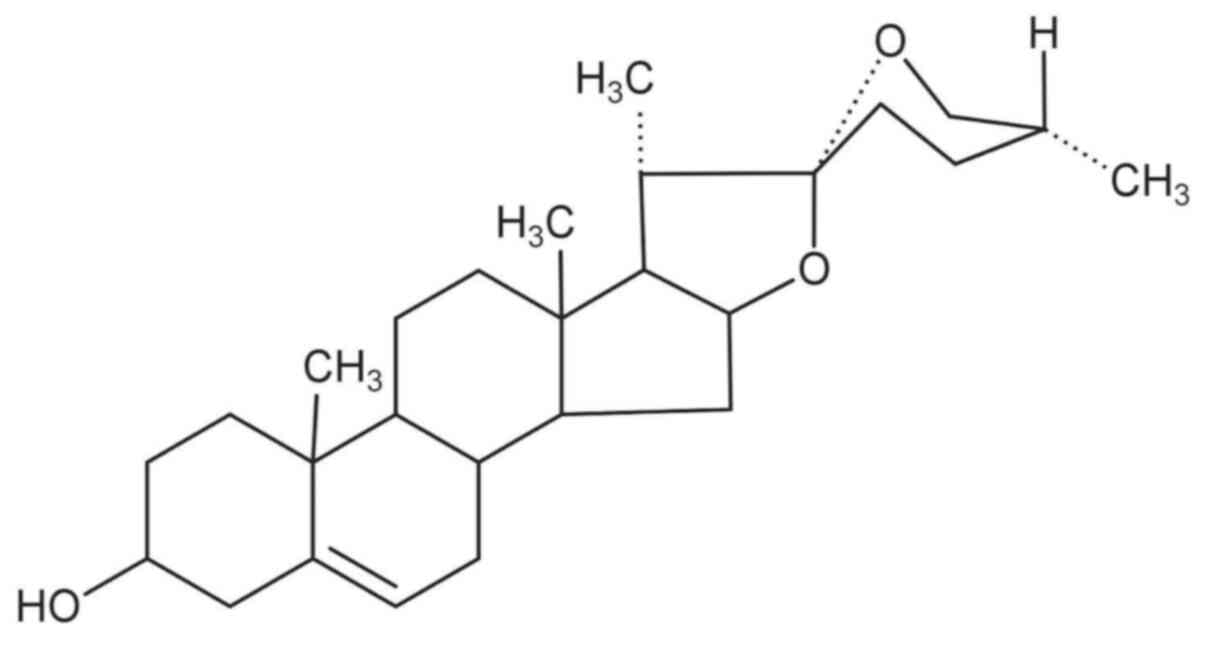
Wang YJ, Pan KL, Hsieh TC, Chang TY, Lin
WH and Hsu JT: Diosgenin, a plant-derived sapogenin, exhibits
antiviral activity in vitro against hepatitis c virus. J Nat Prod.
74:580–584. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cayen MN and Dvornik D: Effect of
diosgenin on lipid metabolism in rats. J Lipid Res.
20:1621979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen Y, Tang YM, Yu SL, Han YW, Kou JP,
Liu BL and Yu BY: Advances in the pharmacological activities and
mechanisms of diosgenin. Chin J Nat Med. 13:578–587.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li F, Fernandez PP, Rajendran P, Hui KM
and Sethi G: Diosgenin, a steroidal saponin, inhibits STAT3
signaling pathway leading to suppression of proliferation and
chemosensitization of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer
Lett. 292:197–207. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tao X, Yin L, Xu L and Peng J: Dioscin: A
diverse acting natural compound with therapeutic potential in
metabolic diseases, cancer, inflammation and infections. Pharmacol
Res. 137:259–269. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sethi G, Shanmugam MK, Warrier S, Merarchi
M, Arfuso F, Kumar AP and Bishayee A: Pro-Apoptotic and Anti-cancer
properties of diosgenin: A comprehensive and critical review.
Nutrients. 10:6452018.
|
|
31
|
Ma HY, Zhou LL and Wang BX: Antagonistic
effect of DX and diosgenin on hyperlipidemia induced by cholesterol
in vivo and on blood platelet aggregation in vitro. Chin J Hos
Pharmacy. 22:323–325. 2002.
|
|
32
|
Raju J and Mehta R: Cancer chemopreventive
and therapeutic effects of diosgenin, a food saponin. Nutr Cancer.
61:27–35. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen PS, Shih YW, Huang HC and Cheng HW:
Diosgenin, a steroidal saponin, inhibits migration and invasion of
human prostate cancer pc-3 cells by reducing matrix
metalloproteinases expression. PLoS One. 6:e201642011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nie C, Zhou J, Qin X, Shi X, Zeng Q, Liu
J, Yan S and Zhang L: Diosgenin-induced autophagy and apoptosis in
a human prostate cancer cell line. Mol Med Rep. 14:4349–4359.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun GC, Jan CR and Liang WZ: Exploring the
impact of a naturally occurring sapogenin diosgenin on underlying
mechanisms of Ca2+ movement and cytotoxicity in human
prostate cancer cells. Environ Toxicol. 35:395–403. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu M, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y, Li H, Xu Y, Han
X, Peng J and Wan X: Cytotoxicity of dioscin in human gastric
carcinoma cells through death receptor and mitochondrial pathways.
J Appl Toxicol. 33:712–722. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao X, Xu L, Zheng L, Yin L, Qi Y, Han X,
Xu Y and Peng J: Potent effects of dioscin against gastric cancer
in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine. 23:274–282. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rahmati-Yamchi M, Ghareghomi S, Haddadchi
G, Milani M, Aghazadeh M and Daroushnejad H: Fenugreek extract
diosgenin and pure diosgenin inhibit the htert gene expression in
a549 lung cancer cell line. Mol Biol Rep. 41:6247–6252.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xu L, Xu D, Li Z, Gao Y and Chen H:
Synthesis and potent cytotoxic activity of a novel diosgenin
derivative and its phytosomes against lung cancer cells. Beilstein
J Nanotechnol. 10:1933–1942. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Srinivasan S, Koduru S, Kumar R,
Venguswamy G, Kyprianou N and Damodaran C: Diosgenin targets
Akt-mediated prosurvival signaling in human breast cancer cells.
Int J Cancer. 125:961–967. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Swamy MV, Patlolla JM, Jayadev R, Marcus
LA, Choi CI and Rao CV: Chemoprevention of colon cancer by
diosgenin, a steroidal saponin constituent of fenugreek. Cancer
Res. 652005.
|
|
42
|
Shishodia S and Aggarwal BB: Diosgenin
inhibits osteoclastogenesis, invasion, and proliferation through
the downregulation of Akt, I kappa B kinase activation and NF-kappa
B-regulated gene expression. Oncogene. 25:1463–1473.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liagre B, Bertrand J, Leger DY and
Beneytout JL: Diosgenin, a plant steroid, induces apoptosis in
COX-2 deficient K562 cells with activation of the p38 MAP kinase
signalling and inhibition of NF-kappaB binding. Int J Mol Med.
16:1095–1101. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cai H, Gong L, Liu J, Zhou Q and Zheng Z:
Diosgenin inhibits tumor angiogenesis through regulating
GRP78-mediated HIF-1α and VEGF/VEGFR signaling pathways. Pharmazie.
74:680–684. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lepage C, Léger DY, Bertrand J, Martin F,
Beneytout JL and Liagre B: Diosgenin induces death receptor-5
through activation of p38 pathway and promotes TRAIL-induced
apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 301:193–202.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fang K, Dong H, Jiang S, Li F, Wang D,
Yang D, Gong J, Huang W and Lu F: Diosgenin and 5-Methoxypsoralen
ameliorate insulin resistance through ER-α/PI3K/Akt-signaling
pathways in HepG2 cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2016:74936942016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Corbiere C, Liagre B, Bianchi A, Bordji K,
Dauça M, Netter P and Beneytout JL: Different contribution of
apoptosis to the antiproliferative effects of diosgenin and other
plant steroids, hecogenin and tigogenin, on human 1547 osteosarcoma
cells. Int J Oncol. 22:899–905. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Corbiere C, Liagre B, Terro F and
Beneytout JL: Induction of antiproliferative effect by diosgenin
through activation of p53, release of apoptosis-inducing factor
(AIF) and modulation of caspase-3 activity in different human
cancer cells. Cell Res. 14:188–196. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang WC, Liu SF, Chang WT, Shiue YL, Hsieh
PF, Hung TJ, Hung CY, Hung YJ, Chen MF and Yang YL: The effects of
diosgenin in the Regulation of renal proximal tubular fibrosis. Exp
Cell Res. 323:255–262. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
He Z, Chen H, Li G, Zhu H, Gao Y, Zhang L
and Sun J: Diosgenin inhibits the migration of human breast cancer
MDA-MB-231 cells by suppressing Vav2 activity. Phytomedicine.
21:871–876. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wani SA and Kumar P. Fenugreek: A review
on its nutraceutical properties and utilization in various food
products. J Saudi Soc Agricultural Sci. 17:97–106. 2018.
|
|
52
|
Wang C, Huo X, Wang L, Meng Q, Liu Z, Liu
Q, Sun H, Sun P, Peng J and Liu K: Dioscin strengthens the
efficiency of Adriamycin in MCF-7 and MCF-7/ADR cells through
autophagy induction: More than just down-regulation of MDR1. Sci
Rep. 6:284032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Belsches AP, Haskell MD and Parsons SJ:
Role of c-Src tyrosine kinase in EGF-induced mitogenesis. Front
Biosci. 2:d501–d518. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
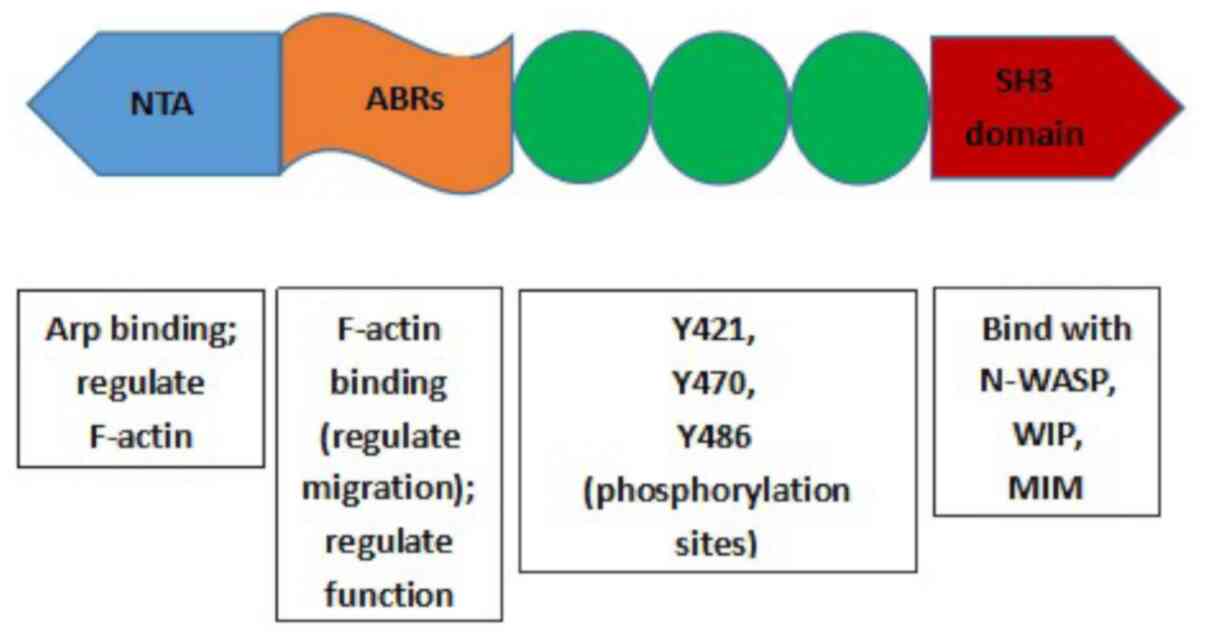
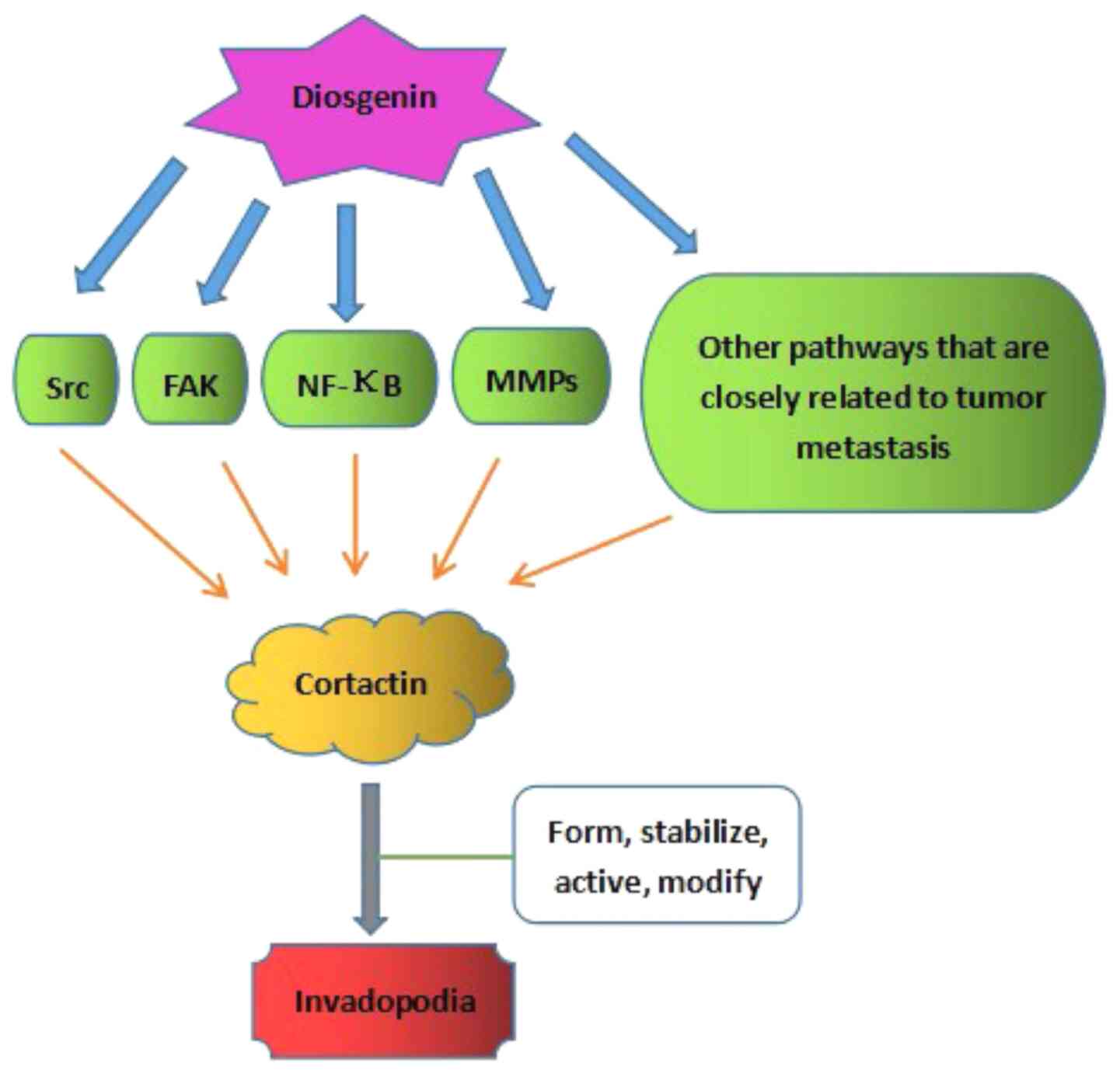
Yin M, Ma W and An L: Cortactin in cancer
cell migration and invasion. Oncotarget. 8:88232–88243. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chien HT, Cheng SD, Chuang WY, Liao CT,
Wang HM and Huang SF: Clinical implications of fadd gene
amplification and protein overexpression in taiwanese oral cavity
squamous cell carcinomas. PLoS One. 11:e01648702016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bryce NS, Clark ES, Leysath JL, Currie JD,
Webb DJ and Weaver AM: Cortactin promotes cell motility by
enhancing lamellipodial persistence. Curr Biol. 15:1276–1285. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Uruno T, Liu J, Li Y, Smith N and Zhan X:
Sequential interaction of actin-related proteins 2 and 3 (Arp2/3)
complex with neural Wiscott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP) and
cortactin during branched actin filament network formation. J Biol
Chem. 278:26086–26093. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cosenbinker LI and Kapus A: Cortactin: The
gray eminence of the cytoskeleton. Physiology (Bethesda).
21:352–361. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mizutani K, Miki H, He H, Maruta H and
Takenawa T: Essential role of neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
protein in podosome formation and degradation of extracellular
matrix in src-transformed fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 62:669–674.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Kinley AW, Weed SA, Weaver AM, Karginov
AV, Bissonette E, Cooper JA and Parsons JT: Cortactin Interacts
with WIP in regulating Arp2/3 activation and membrane protrusion.
Curr Biol. 13:384–393. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lin J, Liu J, Wang Y, Zhu J, Zhou K, Smith
N and Zhan X: Differential regulation of cortactin and
N-WASP-mediated actin polymerization by missing in metastasis (MIM)
protein. Oncogene. 24:2059–2066. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Buday L and Downward J: Roles of cortactin
in tumor pathogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1775:263–273.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
He Y, Ren Y, Wu B, Decourt B, Lee AC,
Taylor A and Suter DM: Src and cortactin promote lamellipodia
protrusion and filopodia formation and stability in growth cones.
Mol Biol Cell. 26:3229–3244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Krueger EW, Orth JD, Cao H and McNiven MA:
A Dynamin-Cortactin-Arp2/3 complex mediates actin reorganization in
growth factor-stimulated cells. Mol Biol Cell. 14:1085–1096. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Oser M, Yamaguchi H, Mader CC,
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Arias M, Chen X, Desmarais V, van Rheenen J,
Koleske AJ and Condeelis J: Cortactin regulates cofilin and N-WASp
activities to control the stages of invadopodium assembly and
maturation. J Cell Biol. 186:571–587. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ayala I, Baldassarre M, Giacchetti G,
Caldieri G, Tetè S, Luini A and Buccione R: Multiple regulatory
inputs converge on cortactin to control invadopodia biogenesis and
extracellular matrix degradation. J Cell Sci. 121:369–378. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ren XL, Qiao YD, Li JY, Li XM, Zhang D,
Zhang XJ, Zhu XH, Zhou WJ, Shi J, Wang W, et al: Cortactin recruits
FMNL2 to promote actin polymerization and endosome motility in
invadopodia formation. Cancer Lett. 419:245–256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Desmarais V, Yamaguchi H, Oser M, Soon L,
Mouneimne G, Sarmiento C, Eddy R and Condeelis J: N-WASP and
cortactin are involved in invadopodium-dependent chemotaxis to EGF
In breast tumor cells. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 66:303–316. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Uruno T, Liu J, Zhang P, Fan YX, Egile C,
Li R, Mueller SC and Zhan X: Activation of Arp2/3 complex-mediated
actin polymerization by cortactin. Nat Cell Biol. 3:259–266. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Weaver AM, Karginov AV, Kinley AW, Weed
SA, Li Y, Parsons JT and Cooper JA: Cortactin promotes and
stabilizes Arp2/3-induced actin filament network formation. Curr
Biol. 11:370–374. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Artym VV, Zhang Y, Seillier-Moiseiwitsch
F, Yamada KM and Mueller SC: dynamic interactions of cortactin and
membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase at invadopodia: Defining
the stages of invadopodia formation and function. Cancer Res.
66:3034–3043. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Khaitlina SY: Intracellular transport
based on actin polymerization. Biochemistry (Mosc). 79:917–927.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ren G, Crampton MS and Yap AS: Cortactin:
Coordinating adhesion and the actin cytoskeleton at cellular
protrusions. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 66:865–873. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tehrani S, Faccio R, Chandrasekar I, Ross
FP and Cooper JA: Cortactin has an essential and specific role in
osteoclast actin assembly. Mol Biol Cell. 17:2882–2895. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
van Rossum AG, Moolenaar WH and Schuuring
E: Cortactin affects cell migration by regulating intercellular
adhesion and cell spreading. Exp Cell Res. 312:1658–1670. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Steven M: Markwell; Amanda Gatesman Ammer,
Interval ET, Schafer DA Hames RA and Weed SA: Abstract 5067: Casein
kinase 2 alpha phosphorylation of cortactin governs actin
cytoskeletal regulation of invadopodia function. Cancer Res. 76 (14
Suppl):S5067. 2016.
|
|
77
|
Jeannot P and Besson A: Cortactin function
in invadopodia. Small GTPases. 11:256–270. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Meng DF, Xie P, Peng LX, Sun R, Luo DH,
Chen QY, Lv X, Wang L, Chen MY, Mai HQ, et al: CDC42-interacting
protein 4 promotes metastasis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by
mediating invadopodia formation and activating EGFR signaling. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 36:212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Genna A, Lapetina S, Lukic N, Twafra S,
Meirson T, Sharma VP, Condeelis JS and Gil-Henn H: Pyk2 and FAK
differentially regulate invadopodia formation and function in
breast cancer cells. J Cell Biol. 217:375–395. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kempiak SJ, Yamaguchi H, Sarmiento C,
Sidani M, Ghosh M, Eddy RJ, Desmarais V, Way M, Condeelis J and
Segall JE: A Neural Wiskott-aldrich syndrome protein-mediated
pathway for localized activation of actin polymerization that is
regulated by cortactin. J Biol Chem. 280:5836–5842. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Wang W, Liu Y and Liao K: Tyrosine
phosphorylation of cortactin by the FAK-Src complex at focal
adhesions regulates cell motility. BMC Cell Biol. 12:492011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Huang C, Ni Y, Wang T, Gao Y, Haudenschild
CC and Zhan X: Down-regulation of the filamentous actin
cross-linking activity of cortactin by Src-mediated tyrosine
phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 272:13911–13915. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Leger DY, Liagre B and Beneytout JL: Role
of MAPKs and NF-kappaB in diosgenin-induced megakaryocytic
differentiation and subsequent apoptosis in HEL cells. Int J Oncol.
28:201–207. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Siar CH, Rahman ZA, Tsujigiwa H, Mohamed
OM, Alblazi K, Nagatsuka H and Ng KH: Invadopodia proteins,
cortactin, N-WASP and WIP differentially promote local invasiveness
in ameloblastoma. J Oral Pathol Med. 45:591–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Tong Q, Qing Y, Wu Y, Hu X, Jiang L and Wu
X: Dioscin inhibits colon tumor growth and tumor angiogenesis
through regulating VEGFR2 and AKT/MAPK signaling pathways. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 281:166–173. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Farhan MA, Azad AK, Touret N and Murray
AG: FGD5 Regulates VEGF Receptor-2 Coupling to PI3 kinase and
receptor recycling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 37:2301–2310.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Choi KW, Park HJ, Jung DH, Kim TW, Park
YM, Kim BO, Sohn EH, Moon EY, Um SH, Rhee DK and Pyo S: Inhibition
of TNF-α-induced adhesion molecule expression by diosgenin in mouse
vascular smooth muscle cells via downregulation of the MAPK, Akt
and NF-κB signaling pathways. Vascul Pharmacol. 53:273–280.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li S, Cheng B, Hou L, Huang L, Cui Y, Xu
D, Shen X and Li S: Dioscin inhibits colon cancer cells' growth by
reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial dysfunction and p38
and JNK pathways. Anticancer Drugs. 29:234–242. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Lin SC, Gou GH, Hsia CW, Ho CW, Huang KL,
Wu YF, Lee SY and Chen YH: Simulated microgravity disrupts
cytoskeleton organization and increases apoptosis of rat neural
crest stem cells via upregulating CXCR4 expression and
RhoA-ROCK1-p38 MAPK-p53 signaling. Stem Cells Dev. 25:1172–1193.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Chiang CT, Way TD, Tsai SJ and Lin JK:
Diosgenin, a naturally occurring steroid, suppresses fatty acid
synthase expression in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells
through modulating Akt, mTOR and JNK phosphorylation. FEBS Lett.
581:5735–5742. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wang YC, Wu DW, Wu TC, Wang L, Chen CY and
Lee H: Dioscin overcome TKI resistance in EGFR-mutated lung
adenocarcinoma cells via Down-regulation of tyrosine phosphatase
SHP2 expression. Int J Biol Sci. 14:47–56. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Gao M, Chen L, Yu H, Sun Q, Kou J and Yu
B: Diosgenin down-regulates NF-κB p65/p50 and p38MAPK pathways and
attenuates acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice.
Int Immunopharmacol. 15:240–245. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Song JS, Ma L, Kou J and Yu BY: Diosgenin
reduces leukocytes adhesion and migration linked with inhibition of
intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression and NF-kB p65
activation in endothelial cells. Chin J Nat Med. 10:142–149.
2012.
|
|
94
|
Tavora B, Reynolds LE, Batista S,
Demircioglu F, Fernandez I, Lechertier T, Lees DM, Wong PP,
Alexopoulou A, Elia G, et al: Endothelial-cell FAK targeting
sensitizes tumours to DNA-damaging therapy. Nature. 514:112–116.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Liu Z, Zhang HM, Yuan J, Lim T, Sall A,
Taylor GA and Yang D: Focal adhesion kinase mediates the
interferon-gamma-inducible GTPase-induced phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase/Akt survival pathway and further initiates a positive
feedback loop of NF-kappaB activation. Cell Microbiol.
10:1787–1800. 2010.
|
|
96
|
Chen J, Zhang W, Wang Y, Zhao D, Wu M, Fan
J, Li J, Gong Y, Dan N, Yang D, et al: The diacylglycerol kinase α
(DGKα)/Akt/NF-κB feedforward loop promotes esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma (ESCC) progression via FAK-dependent and FAK-independent
manner. Oncogene. 38:2533–2550. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Irby RB and Yeatman TJ: Role of Src
expression and activation in human cancer. Oncogene. 19:5636–5642.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Zhou X, Yang F, Zhang Q, Miao Y, Hu X, Li
A, Hou G, Wang Q and Kang J: FAM129B promoted tumor invasion and
proliferation via facilitating the phosphorylation of FAK signaling
and associated with adverse clinical outcome of non-small cell lung
cancer patients. Onco Targets Ther. 11:7493–7501. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Avizienyte E and Frame MC: Src and FAK
signalling controls adhesion fate and the epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:542–547. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Mitra SK and Schlaepfer DD:
Integrin-regulated FAK-Src signaling in normal and cancer cells.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 18:516–523. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Liang Y, Yi L, Liu P, Jiang L, Wang H, Hu
A, Sun C and Dong J: CX3CL1 involves in breast cancer metastasizing
to the spine via the Src/FAK signaling pathway. J Cancer.
9:3603–3612. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Saijo K, Schmedt C, Su IH, Karasuyama H,
Lowell CA, Reth M, Adachi T, Patke A, Santana A and Tarakhovsky A:
Essential role of Src-family protein tyrosine kinases in NF-kappaB
activation during B cell development. Nat Immunol. 4:274–279.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Chen L, Chen H and Liu F: RACK1 to
modulate expression of MMP10 via Src/NF-κB pathway in gastric
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 35 (15_suppl):e155292017.
|
|
104
|
Lai SW, Bamodu OA, Tsai WC, Chang YM, Lee
WH, Yeh CT and Chao TY: The therapeutic targeting of the
FGFR1/Src/NF-κB signaling axis inhibits pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma stemness and oncogenicity. Clin Exp Metastasis.
35:663–677. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Peng X, Zhang Q, Zeng Y, Li J, Wang L and
Ai P: Evodiamine inhibits the migration and invasion of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro via repressing MMP-2
expression. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 76:1173–1184.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Lian S, Xia Y, Khoi PN, Ung TT, Yoon HJ,
Kim NH, Kim KK and Jung YD: Cadmium induces matrix
metalloproteinase-9 expression via ROS-dependent EGFR, NF-кB, and
AP-1 pathways in human endothelial cells. Toxicology. 338:104–116.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Hung CY, Lee CH, Chiou HL, Lin CL, Chen
PN, Lin MT, Hsieh YH and Chou MC: Praeruptorin-B Inhibits
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-Acetate-induced cell invasion by
targeting AKT/NF-κB via matrix metalloproteinase-2/-9 expression in
human cervical cancer cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 52:1255–1266.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Sabir N, Hussain T, Mangi MH, Zhao D and
Zhou X: Matrix metalloproteinases: Expression, regulation and role
in the immunopathology of tuberculosis. Cell Prolif.
52:e126492019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Liu LP, Liang HF, Chen XP, Zhang WG, Yang
SL, Xu T and Ren L: The role of NF-kappaB in Hepatitis B virus X
protein-mediated upregulation of VEGF and MMPs. Cancer Invest.
28:443–451. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Zhang X, Jin M, Tadesse N, Dang J, Zhou T,
Zhang H, Wang S, Guo Z and Ito Y: Dioscorea zingiberensis C.
H. Wright: An overview on its traditional use, phytochemistry,
pharmacology, clinical applications, quality control, and toxicity.
J Ethnopharmacol. 220:283–293. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wu FC and Jiang JG: Effects of diosgenin
and its derivatives on atherosclerosis. Food Funct. 10:7022–7036..
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Tao W, Luo X, Cui B, Liang D, Wang C, Duan
Y, Li X, Zhou S, Zhao M, Li Y, et al: Practice of traditional
Chinese medicine for psycho-behavioral intervention improves
quality of life in cancer patients: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Oncotarget. 6:39725–39739. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Wang J, Wong YK and Liao F: What has
traditional Chinese medicine delivered for modern medicine? Expert
Rev Mol Med. 20:e42018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
White NJ: Qinghaosu (Artemisinin): The
price of success. Science. 320:330–334. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhou L, Zuo Z and Chow MS: Danshen: An
overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and
clinical use. J Clin Pharmacol. 45:1345–1349. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Yi-Lan LI, Shan-Shan Q and Guo-Xing LI:
Effect of glossy ganoderma on antitumor and immune function in
mice. Chin J Prevention Control Chronic Non-Communicable Dis.
2004.
|
|
117
|
Liu P, Zhao H and Luo Y: Anti-aging
implications of astragalus membranaceus (Huangqi): A Well-known
Chinese tonic. Aging Dis. 8:868–886. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wang K, Wu J, Duan X, Wu J, Zhang D, Zhang
X and Zhang B: Huangqi injection in the treatment of chronic heart
failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 96:e81672017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
de Martel C, Forman D and Plummer M:
Gastric cancer: Epidemiology and risk factors. Gastroenterol Clin
North Am. 42:219–240. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Camargo MC, Anderson WF, King JB, Correa
P, Thomas CC, Rosenberg PS, Eheman CR and Rabkin CS: Divergent
trends for gastric cancer incidence by anatomical subsite in US
adults. Gut. 60:1644–169. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Steevens J, Botterweck AAM, Dirx MJ, van
den Brandt PA and Schouten LJ: Trends in incidence of oesophageal
and stomach cancer subtypes in Europe. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
22:669–678. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|