Introduction
Within the past two decades, the novel protein
Nischarin has been revealed to serve as a tumor suppressor in
ovarian and breast cancers (1–4).
Nischarin expression levels are different in breast cancer cell
lines with different degrees of malignancy (4). A decrease in the mRNA level of
Nischarin is associated with an increase in cell invasiveness
(2,4). In human breast tissues, the expression
level of Nischarin in cancerous tissues is significantly lower
compared with that in non-cancerous tissues (2–4), lower
in cancer tissues with lymph node metastasis compared with those
without (3), lower in increasing
grades 1–3 of invasive cancer tissues (2), and lower in advanced stage breast
cancer tissues compared with those in the early stage (4).
Nischarin is an integrin-binding protein that binds
the cytosolic domain of the integrin α5 subunit (5), and it is present in numerous animals
(6). In humans, its expression has
been identified in several tissues (5,7). The
roles of Nischarin in humans include serving as a neuroprotective
protein that regulates neuronal migration (7), a regulator of brain function (8,9), a
regulator of blood pressure (10)
and a tumor suppressor of ovarian and breast cancer (1,2).
The molecular mechanism underlying the role of
Nischarin is yet to be elucidated; however, it has been reported to
inhibit cell migration and affect the cytoskeleton (5). Certain studies have reported the
mechanisms underlying the effects of Nischarin on cell migration
and invasion. Nischarin induces neuronal apoptosis via the PI3K and
protein kinase B pathways (11),
induces cell apoptosis in human breast cancer, and its expression
is significantly correlated with estrogen receptor status (4). In addition, Nischarin inhibits
Rac-induced migration and invasion in breast cancer cells via
inhibiting p21-activated kinase (PAK1), LIM kinase 1 (LIMK1)
(12–14) and the PAK-independent pathway
(15). Nischarin interacts with
liver kinase B1 (LKB1) to negatively regulate cell migration via
the PAK-LIMK-Cofilin and cyclin D1/CDK4 pathways (16). Furthermore, Nischarin enhances cell
proliferation and invasion by inhibiting the FAK-dependent signal
transduction in human ovarian cancer (1). Nischarin prevents cell migration and
invasion by altering the expression of key focal adhesion proteins
(17). Additionally, Nischarin
regulates cell motility via exosomes; when co-cultured with
exosomes from Nischarin-positive cells, the survival ability,
migration ability and adhesion of breast cancer cells are decreased
(18). In Prkdcscid mice
xenograft tumor models, exosomes secreted by Nischarin-positive
tumor cells inhibit tumor growth (18).
As a member of the integrin family, integrin α5β1 is
associated with the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)
(19–22). Thus, it was hypothesized that
Nischarin, a binding protein of integrin α5β1 (5,23), may
serve a role in cell migration and invasion via regulating the EMT
process. The present study used breast cancer cell lines with
NISCH gene overexpression or knockdown to detect the mRNA
and protein expression levels of EMT transcription regulators via
reverse transcription-quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) and western
blotting. The current study revealed that Nischarin influences the
EMT process via altering EMT-inducing transcription regulators.
Materials and methods
Cell culture
Hormone receptor positive (MCF-7), HER2 positive
(SKBR3) and two triple negative breast cancer (MDA-MB-231 and
Hs578T) cell lines, were purchased from the Cell Bank of the
Chinese Academy of Sciences. The cells were cultured in Dulbecco's
Modified Eagle's Medium (DMEM; Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS) and 100 U/ml
penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) at
37°C and 5% CO2. As the primary goal of the present
study was to study the effects of Nischarin on triple-negative
breast cancer cells, only the two triple negative breast cancer
(MDA-MB-231 and Hs578T) cell lines were used in the next
experiment.
Nischarin overexpression in Hs578T
cells
Complete gene synthesis of the NISCH CDS
(NM_007184) sequence, XhoI and EcoRI restriction
enzyme digestion, and ligation to the pcDNA3.1 vector (Youbao Bio;
Hunan Keai Medical Devices Co., Ltd.) was performed to construct
pcDNA3.1-Nischarin plasmids. Sequencing confirmed that DNA did not
mutate from the sequence. A total of 4 µg plasmid was transfected
into Hs578T cells in 100 µl serum-free DMEM at the logarithmic
growth stage, using Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocol at room
temperature. pcDNA3.1 empty vector plasmid was used as a control
and western blotting was used to validate the expression efficiency
after 24 h transfection.
Inhibition of endogenous Nischarin in
MDA-MB-231 cells via small interfering RNA (siRNA)
A total of 3 NSICH-siRNAs were purchased from
Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd. and their sequences are presented in
Table I. Negative control siRNA
(NC-siRNA) had a universal sequence of: Forward,
5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′ and reverse, 5′-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAA-3′.
siRNA (100 nm) was added to MDA-MB-231 cells at the logarithmic
growth stage for transfection in 100 µl serum-free DMEM and culture
with Lipofectamine 3000 (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.), according to the manufacturer's protocol at room
temperature. Western blotting was used to validate the silence
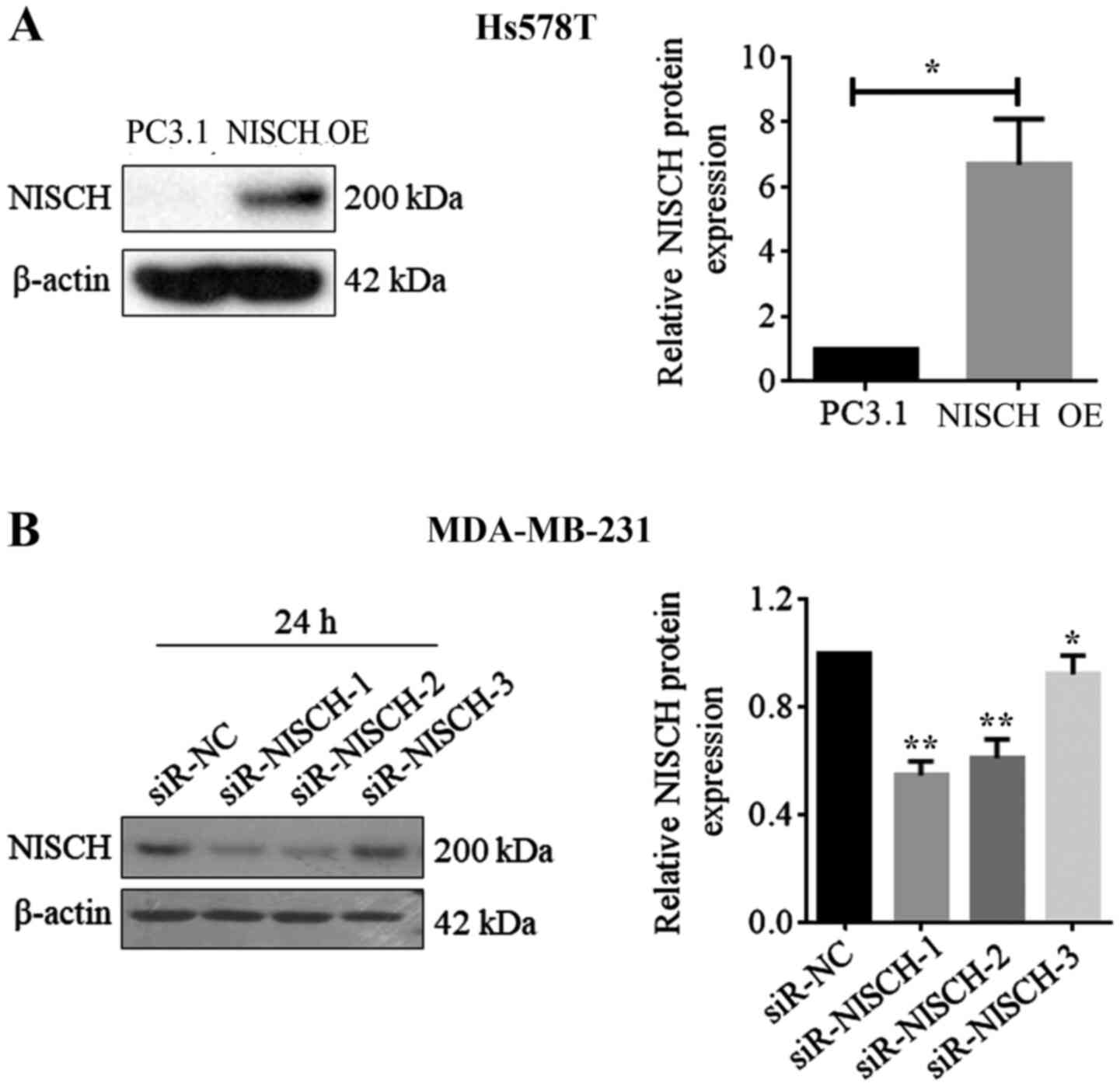
efficiency after 24 h transfection. According to the results, all
three NSICH-siRNAs had the ability to reduce NISCH gene expression,
however, siRNA-1 showed the highest efficiency (Fig. 1B). Therefore, NSICH-siRNA-1 (labeled
as si-NISCH-1) was selected for further NISCH gene silencing
experiments.
 | Table I.NISCH siRNA sequences. |
Table I.
NISCH siRNA sequences.
| NISCH
siRNA | Forward
(5′→3′) | Reverse
(5′→3′) |
|---|
| siRNA-1 |
GCAGAGAGAAAGAUUGAUATT |
UAUCAAUCUUUCUCUCUGCAA |
| siRNA-2 |
CCGUUCGACCUAUCAAUAUTT |
AUAUUGAUAGGUCGAACGGCA |
| siRNA-3 |
GGAAGUCCUUGUUCCUGAATT |
UUCAGGAACAAGGACUUCCTT |
MTT experiment
NISCH-overexpressing Hs578T cells
(transfected with pcDNA3.1-NISCH plasmids) or controls (transfected
with pcDNA3.1 empty vector plasmids), and NISCH-silenced
MDA-MB-231 cells (transfected with NISCH-siRNA1) or controls
(transfected with NC-siRNA.) were seeded into a 96-well plate at a
density of 1×103−1×104 and cultured for 72 h
at 37°C with 5% CO2. The cells were cultured for
different durations (24, 48 and 72 h) to allow for formazan
formation. MTT (50 µl; Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) was added to 1
mg/ml PBS solution in each well and incubated for 1–4 h at 37°C,
and the absorbance at 570 nm was detected using a plate reader
(Molecular Devices) to evaluate cell proliferation (24).
Colony formation assay
Hs578T cells with NISCH overexpression and
the controls, and MDA-MB-231 cells with NISCH-knockdown and
the controls were seeded into 6-well plates at a density of
3000-10,000 cells/well, followed by culture for 2–3 weeks at 37°C.
Colonies were fixed with 100% methanol for 20 min and then stained
with 0.1% crystal violet for 20 min (25), both at room temperature.
Transwell cell migration and invasion
assays
Serum-free DMEM (300 µl) was added to the upper
chamber and 800 µl medium was added to the lower chamber of a
Transwell plate, followed by incubation at 37°C for 2 h or
overnight. Hs578T and MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with
plasmids or siRNA respectively and were serum starved for 24 h.
Subsequently, the culture medium used for the activation was
removed, and 800 µl medium containing 10% FBS was added to the
lower chamber of the Transwell plate. Matrigel was coated on the
upper chamber for the invasion assay in cell culture incubator at
37°C for 30 min, and Matrigel was not used for the migration assay.
A total of 300 µl (1×105) serum-starved cells were added
to the upper chamber. Following incubation for 24 h at 37°C, the
cells in the upper chamber were removed, and the invaded cells that
had passed through the membrane were fixed using 100% methanol for
30 min and stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 20 min, both at
room temperature. Images were captured under a light microscope
(magnification, ×40) and ≥3 fields were randomly selected for
counting (26).
Western blotting
Western blot analysis for the protein was performed
according to a previously published protocol (27). The total protein was extracted from
the indicated cells using lysis buffer (1X PBS, 900 µl; 2.1 mg/ml
Aprotinin, 10 µl; 1 mg/ml Leupeptin, 0.5 µl; 4.9 mg/ml
MgCl2, 1 µl; 100 mM Sodium Ortho-Vabadate, 10 µl; 10%
Triton X-100, 100 µl; and 100 mM PMSF, 10 µl). Protein
concentration was determined using the Pierce®
Bicinchoninic Acid Protein Assay Reagent A kit (Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.). The absorbance value at 570 nm was determined
and the protein concentration of the sample was calculated
according to the standard curve. Equal amounts of protein (20
µg/lane) were separated via 4% SDS-PAGE and transferred to a
polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) membrane (EMD Millipore). The
sealed PVDF membrane was blocked with 5% fat free milk in PBS at
room temperature for 2 h, then it washed using 1X PBST buffer
solution three times while being agitated (10 min each) at room
temperature, and then transferred to a primary diluted solution
with primary antibodies (dilution, 1:1,000) and incubated at 4°C
overnight. The membrane was washed again using 1X PBST buffer
solution three times while being agitated (10 min each) at room
temperature. Followed by transfer to 1X PBST with secondary
antibodies and incubation in a shaker at room temperature for 2 h.
The PVDF membrane was immersed in 1X PBST buffer and washed on a
shaker three times (15 min each), and the specific protein bands
were observed by utilizing a Precision Plus Protein™ Dual Color
Standards (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). Primary antibodies against
the following were used: NISCH (cat. no. D6T4X), ZEB1 (cat.
no. E2G6Y), Slug Twist1 (cat. no. E7E2G), E-cadherin (cat. no.
4A2), Snail (cat. no. C15D3), N-cadherin (cat. no. D4R1H) and
vimentin (cat. no. D21H3) (all from Cell Signaling Technology,
Inc.). Goat anti-rabbit IgG secondary antibody conjugated with
horseradish peroxidase (cat. no. BL003A; Biosharp Life Sciences;
dilution, 1:5,000) was also used. Protein bands were detected with
an ECL chemiluminescence reaction kit (Thermo Scientific) and
densitometry analysis was performed using ImageJ (version 1.38,
National Institutes of Health).
RT-qPCR analysis
RT-qPCR analysis was performed as described
previously (28). In brief, Hs578T
cells with NISCH overexpression, MDA-MB-231 cells with
NISCH-knockdown and their respective controls were lysed using
TRIzol reagent (Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) and total RNA was
extracted. Total RNA was precipitated using isopropanol and then
dissolved with DEPC-H2 (Generay Biotech). The first
strand of cDNA was synthesized by M-MLV-inverse transferase using a
RT-PCR kit (Promega Corporation) according to the manufacturer's
protocol. An ABI 7300 real-time PCR system was used for qPCR
amplification according to the manufacturer's protocols, with the
2X Power SYBR-Green PCR Master mix (Applied Biosystems). The
thermocycling conditions were: Initial denaturation of 95°C for 10
min, followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 15 sec for denaturation,
60°C for 1 min for annealing and elongation, followed by 95°C for
15 sec and 60°C for 15 sec. The specificity of the amplification
was determined by the DNA dissociation curve. The relative mRNA
expression was determined by relative standard curve method
(2−ΔΔCq) (29) using
β-actin as reference. The sequences of the primers are listed in
Table II.
 | Table II.Primer sequences. |
Table II.
Primer sequences.
| Primer | Forward
(5′→3′) | Reverse
(5′→3′) |
|---|
| β-actin |
AGCAGTTGTAGCTACCCGCCCA |
GGCGGGCACGTTGAAGGTCT |
| NISCH |
AGGGTGAACAGGGCGAGGAG |
AGGCGGCGAACTGGCGGATA |
| ZEB1 |
ACACGACCACAGATACGGCA |
ATGGGAGACACCAAACCAAC |
| Slug |
CCTCCATCTGACACCTCC |
CCCAGGCTCACATATTCC |
| Twist1 |
CGACGACAGCCTGAGCAACA |
CCACAGCCCGCAGACTTCTT |
| Snail |
CCCAGCCCCAGCTACCACCT |
GCCCCCTCTCCTCTTCCTTCTC |
| Vimentin |
TGCGTGAAATGGAAGAGAACTT |
TGGGTATCAACCAGAGGGAGTG |
| E-cadherin |
AGAGGCTTCTGGTGAAATCG |
GGAAAGCTTCTCACGGCATA |
| N-cadherin |
AAGAGAGTGGAAGTGTCCGA |
GATCAGCAGAAGTGTCCCTG |
Statistical analysis
SPSS version 18 (SPSS, Inc.) was used for
statistical analysis. A two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test was
used for comparisons in group. One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's
post hoc test was used for comparisons between groups. P<0.05
was considered to indicate a statistically significant
difference.
Results
Expression of Nischarin protein in
different breast cancer cell lines
Western blotting was performed to detect Nischarin
basal expression in different breast cancer cell lines, including
hormone receptor positive cells (MCF-7), HER2 positive cells
(SKBR3) and two triple-negative cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and Hs578T).
The expression levels of Nischarin were different in each cell line
(Fig. S1) and the experiments were
repeated three times. The present study, aimed at investigating the
effect of changes in Nischarin protein levels on cell
proliferation, colony formation, migration, invasion and
EMT-related regulators in triple-negative breast cancer cell lines.
Therefore, the two triple-negative cell lines (MDA-MB-231 and
Hs578T) were selected for further analysis. In addition, results
for the expression levels of Nischarin showed that its expression
in MDA-MB-231 cells was higher than that of Hs578T cells.
Subsequently, MDA-MB-231 cells were selected for NISCH gene
silencing and Hs578T cells were selected for NISCH gene
overexpression.
Nischarin inhibits the proliferation
and colony formation of breast cancer cells
Hs578T cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1-NISCH
plasmids for overexpression of NISCH and with pcDNA3.1 empty
vector as a control. Western blot analysis demonstrated that the
protein expression of Nischarin increased after 24 and 48 h. As
NISCH-siRNA1 showed the most significant inhibition of the
protein expression of Nischarin, NISCH-siRNA1 was selected
for silencing NISCH in MDA-MB-231 cells and it was confirmed
that Nischarin protein expression was decreased when NISCH
was silenced (Fig. 1). These results
suggest that successful NISCH overexpression and knockdown
were performed. In the MTT and colony formation assays, it was
identified that when NISCH was overexpressed in Hs578T
cells, the cell proliferation did not significantly change at 24,
48 and 72 h (Fig. 2A); however, the
colony formation decreased after 2 weeks (Fig. 2B). By contrast, the proliferation and
colony formation of MDA-MB-231 cells increased following
NISCH silencing (Fig. 2).
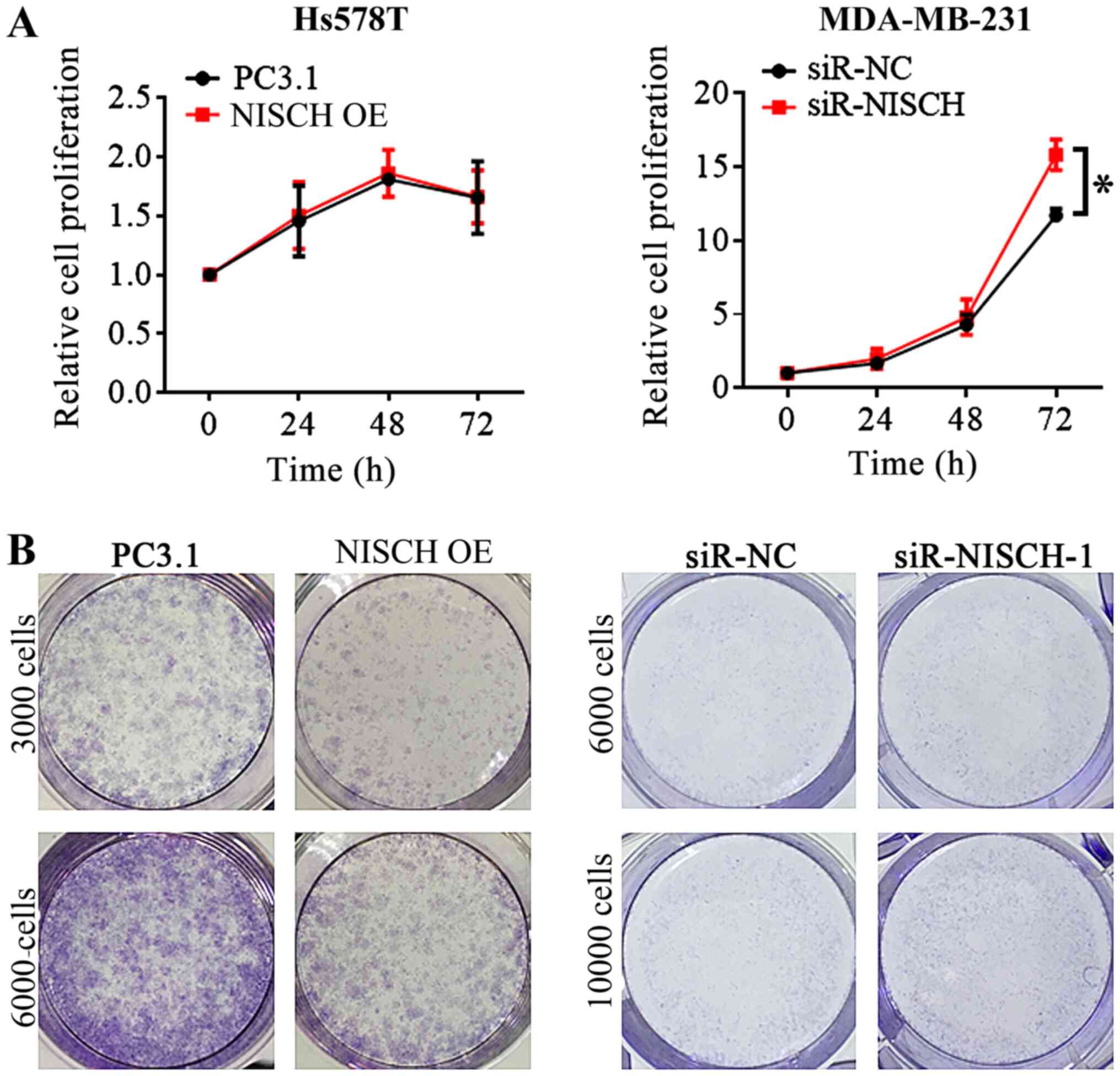 | Figure 2.MTT experiment and colony formation
assay for Hs578T cells with NISCH overexpressed and MDA-MB-231
cells with knocked down NISCH. (A) In MTT experiments, cells
were seeded into a 96-well plate, each well contains
1×103−1×104 cells. The relative cell
proliferation was not significantly different between the Hs578T
overexpressing NISCH and control cells, but it is increased
in NISCH knockdown MDA-MB-231 cells than that in control
cells at 72 h. (B) In the colony formation assay, cells were seeded
into 6-well plates at a density of 3000–10,000 cells/well, followed
by culture for 2 weeks. The ability of colony formation decreased
in NISCH overexpressed Hs578T cells and increased in
NISCH knockdown MDA-MB-231 cells. *P<0.05 vs. siR-NC.
NISCH, Nischarin; siR, small interfering RNA; PC3.1,
pcDNA3.1 empty vector; NC, negative control; OE,
overexpression. |
Nischarin inhibits the migration and
invasion capacities of breast cancer cells
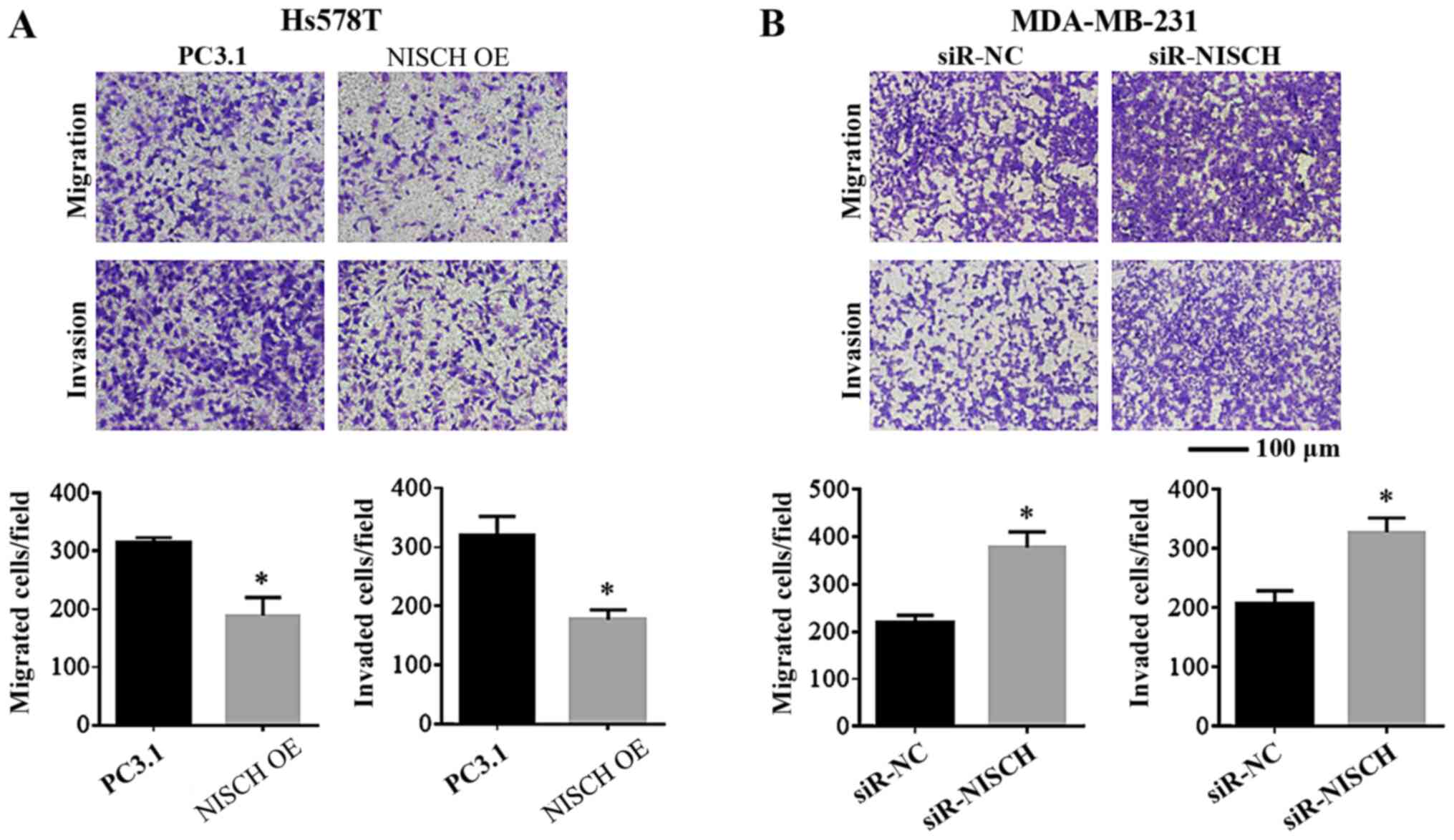
To understand the effects of Nischarin on the
migration and invasion of breast cancer cells, these were
investigated in breast cancer cells with NISCH
overexpression and knockdown. Hs578T cells transfected with
pcDNA3.1-Nischarin plasmids were used for NISCH gene
overexpression analysis and pcDNA3.1 empty vector was used as a
control (pcDNA3.1-control). MDA-MB-231 cells transfected with
NISCH-siRNA-1 were used for NISCH-silencing analysis
and cells transfected with NC-siRNA were used as a control. Using a
Transwell assay, it was identified that the migration and invasion
capacities were reduced in Hs578T cells with NISCH
overexpression (Fig. 3A). By
contrast, migration and invasion were enhanced in
NISCH-silenced MDA-MB-231 cells (Fig. 3B).
Influence of Nischarin on EMT
regulators in breast cancer cells
The epithelial-related molecule E-cadherin,
mesenchymal markers (N-cadherin and vimentin) and several EMT
regulating transcription factors, including Twist, Snail, Slug and
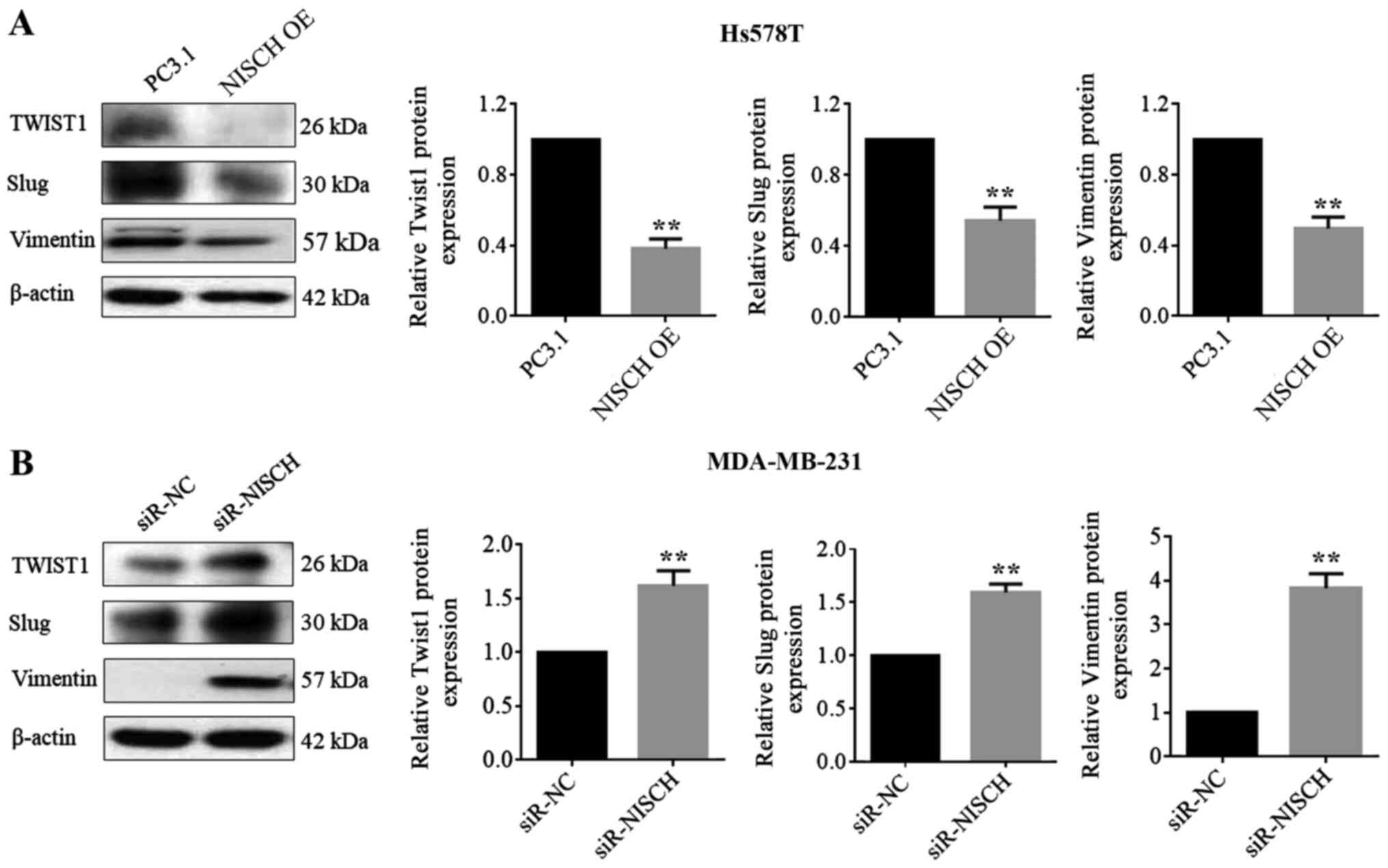
ZEB, are involved in the EMT process (30). RT-qPCR were performed to detect the
mRNA expression levels of these factors in HS578T cells with
NISCH overexpression and MDA-MB-231 cells with
NISCH-knockdown. It was demonstrated that when NISCH
was overexpressed, the mRNA expression level of E-cadherin
increased, while the mRNA expression levels of Snail, ZEB1,
N-cadherin, Slug, Twist1 and vimentin decreased (Fig. 4A). When NISCH was silenced, the mRNA
expression level of E-cadherin was decreased, while that of Snail,
N-cadherin, Slug, Twist1, ZEB1 and vimentin were increased
(Fig. 4B). In a western blotting
experiment for the proteins, Twist1, Slug and vimentin exhibited
corresponding changes in expression levels (Fig. 5), but the remaining four proteins
(E-cadherin, N-cadherin, ZEB, Snail) couldn't be successfully
detected.
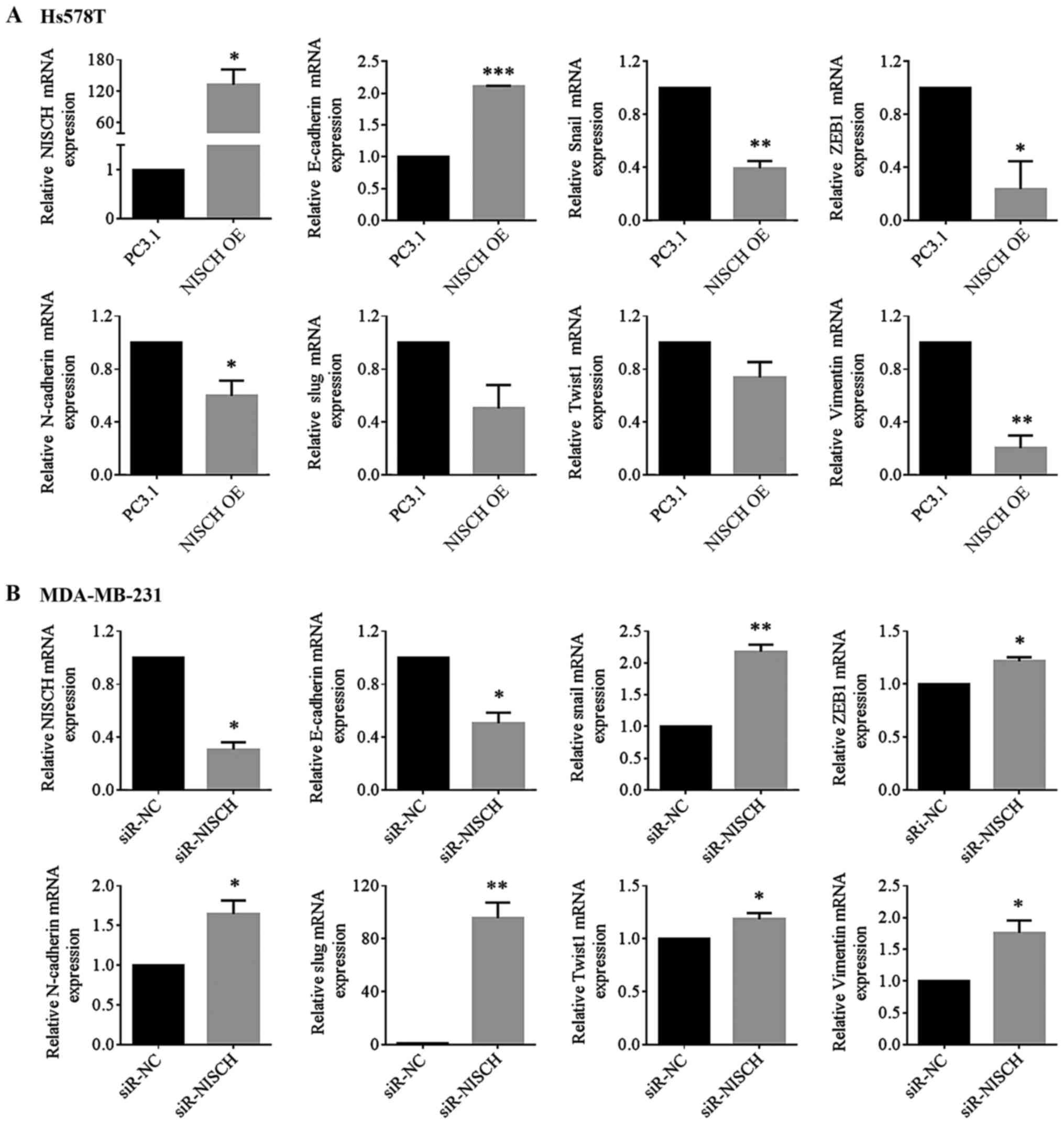 | Figure 4.NISCH influences the
expression of epithelial-mesenchymal transition-associated genes.
The relative mRNAs level of E-cadherin, Snail, ZEB1, N-cadherin,
Slug, Twist1 and vimentin were detected in (A) HS578T cells
overexpressed with NISCH (*P<0.05; **P<0.01 and
***P<0.001 vs. PC3.1) and in (B) MDA-MB-231 cells with knocked
down NISCH (*P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. siR-NC). A
two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test was used for statistical
analysis in three independent samples. NISCH, Nischarin;
siR, small interfering RNA; PC3.1, pcDNA3.1 empty vector; NC,
negative control; OE, overexpression. |
Discussion
It has been demonstrated in a number of studies that
Nischarin suppresses tumor growth and metastasis of breast cancer
(2,4,6).
Baranwal et al (2) examined
Nischarin expression in 300 human breast cancer and normal tissue
samples using RT-qPCR and immunohistochemistry. It was identified
that the Nischarin mRNA expression level was higher in normal
breast tissues compared with in cancer tissues. In mice xenograft
models, compared with parental MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer
cells, tumor growth was significantly reduced in MDA-MB-231 cells
that overexpressed Nischarin. In addition, lung metastases of these
cells following tail vein injection were reduced for
Nischarin-overexpressed MDA-MB-231 cells. In tumor xenografts,
MCF-7 human breast cancer cells in which Nischarin expression was
silenced grew significantly faster compared with the parental
cells. Chang et al (4)
demonstrated that overexpression of Nischarin may induce apoptosis
and inhibit cell migration and invasion in breast cancer cell
lines. Jain et al (16)
reported that absence of both Nischarin and LKB1 enhances migration
of MDA-MB-231 cells and tumor growth. The current study evaluated
cell proliferation, migration and invasion of TNBC cell lines via
MTT, colony formation and Transwell assays. It was identified that,
following NISCH-overexpression, cell proliferation was not
significantly altered; however, the colony formation, cell
migration and invasion decreased in HS578T cells overexpressed with
NISCH. Following NISCH knockdown in MBA-MD-231 cells,
the cell proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion
were enhanced. Consistent with previous studies, the present
results suggested that Nischarin serves an inhibitory role in the
migration and invasion of breast cancer cells.
EMT is associated with the migration and invasion of
cells, and it is a significant marker of cancer progression.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the effect of EMT on breast
cancer progression (30–33). EMT is a complex process characterized
by loss of epithelial features and an increase in mesenchymal
features. Studies have demonstrated E-cadherin is downregulated,
vimentin and N-cadherin are upregulated, and cytoskeletal
recombination occurs in the EMT process (34–36). In
addition, changes in the expression of integrins and other
molecules associated with the extracellular matrix have also been
observed (37). Numerous
transcription factors are involved in the regulation of the EMT
process, such as Snail, Slug, ZEB, Twist and β-catenin (34,38,39). In
the current study, when NISCH was overexpressed in Hs578T
cells, the relative mRNA level of E-cadherin increased, while the
mRNA levels of mesenchymal markers, including N-cadherin and
vimentin, decreased. In addition, the mRNA levels of EMT-promoting
factors, such as Snail, ZEB, Twist1 and Slug decreased following
NISCH overexpression. When NISCH was silenced in
MDA-MB-231 cells, opposite results were observed. These results
demonstrated that Nischarin inhibits the EMT process via inhibiting
EMT transcription factors in breast cancer cells.
Major pathways involved in the EMT process in breast
cancer have been found to involve the transforming growth factor-β
pathway, MAPK (FAS/RAF/MEK/ERK) pathway, E-cadherin loss, the
Wnt/β-Catenin pathway, Notch signaling, TNF-α, hypoxia, certain
miRNAs (30) and certain
EMT-associated transcription factors (40). However, the specific EMT signaling
pathway associated with Nischarin remains unclear. A number of
studies have demonstrated that Nischarin-associated signaling
pathway proteins mainly include Rac1, PAK1, LIMK1 and LKB1
(12–16); however, the complete signaling
cascade is yet to be elucidated. Baranwal et al (2) demonstrated that Nischarin regulates the
expression of the a5 integrin, thereby influencing rac-mediated
signaling pathways to regulate tumor development. This previous
study also identified that Nischarin regulates ERK phosphorylation
via inhibiting PAK1. Nischarin can reduce ERK phosphorylation,
which stimulates FAK and further ERK phosphorylation (2). The ERK family is a subfamily of
proteins that is part of the MAPK family (41). It is widely known that the MAPK
pathway is an important pathway in the EMT process (41). Therefore, Nischarin may impact the
EMT process via the MAPK pathway; however, this was not determined
in the present study as factors involved in this pathway, such as
ERK, were not examined.
In conclusion, the current study revealed that
Nischarin inhibits cell migration and invasion by inhibiting the
EMT process via regulating the expression of EMT-associate
transcription factors. The associations between Nischarin and
EMT-associated transcription factors were demonstrated at the mRNA
level. However, there were a number of limitations of this study.
Firstly, corresponding changes at the protein level were not
observed for all markers. Secondarily, numerous signaling pathways
associated EMT can result in changes of these transcription
factors, but the specific pathways underlying these changes could
not be determined. Thirdly, mycoplasma was not tested in the
current experiment. Although it was observed that the cells were a
good length and normal shape, this may still have a potential
influence on the experimental results. Mycoplasma pollution will
lead to slower cell growth and worse state. Therefore, further
experimental studies such as animal experiments are required to
elucidate the underlying mechanism for how Nischarin impacts the
breast cancer cells.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Medical
Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (grant no. LY18H040010)
and the Zhejiang Medical and Health Science Project Fund (grant no.
2018KY189).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are
included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
SNX, YJC and BM conceived and designed the
experiments. YJC, BM, SNX, MLW, YW and YBH performed the
experiments. YJC, BM, SNX, JL, MLW, JC, FGZ, JDZ, XG, LZ and CJX
analyzed the data. YJC, SNX, MLW, JC, FGZ, JDZ, XG, LZ, CJX, YW and
YBH wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Li J, He X, Dong R, Wang Y, Yu J and Qiu
H: Frequent loss of NISCH promotes tumor proliferation and invasion
in ovarian cancer via inhibiting the FAK signal pathway. Mol Cancer
Ther. 14:1202–1212. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Baranwal S, Wang Y, Rathinam R, Lee J, Jin
L, McGoey R, Pylayeva Y, Giancotti F, Blobe GC and Alahari SK:
Molecular characterization of the tumor-suppressive function of
nischarin in breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:1513–1528.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen J, Feng WL, Mo WJ, Ding XW and Xie
SN: Expression of integrin-binding protein nischarin in metastatic
breast cancer. Mol Med Rep. 12:77–82. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chang C, Wei W, Han D, Meng J, Zhu F, Xiao
Y, Wu G1, Shi X and Zhang L: Expression of nischarin negatively
correlates with estrogen receptor and alters apoptosis, migration
and invasion in human breast cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
484:536–542. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Alahari SK, Lee JW and Juliano RL:
Nischarin, a novel protein that interacts with the integrin α5
subunit and inhibits cell migration. J Cell Bio. 151:1141–1154.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Maziveyi M and Alahari SK: Breast cancer
tumor suppressors: A special emphasis on novel protein nischarin.
Cancer Res. 75:4252–4259. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ding Y, Zhang R, Zhang K, Lv X, Chen Y, Li
A, Wang L, Zhang X and Xia Q: Nischarin is differentially expressed
in rat brain and regulates neuronal migration. PLoS One.
8:e545632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kõks S, Luuk H, Nelovkov A, Areda T and
Vasar E: A screen for genes induced in the amygdaloid area during
cat odor exposure. Genes Brain Behav. 3:80–89. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Keller B, Mestre-Pinto JI,
Álvaro-Bartolomé M, Martinez- Sanvisens D, Farre M, García-Fuster
MJ, García-Sevilla JA and Torrens M; NEURODEP Group, : A biomarker
to differentiate between primary and cocaine-induced major
depression in cocaine use disorder: The role of platelet
IRAS/nischarin (I1-Imidazoline Receptor). Front Psychiatry.
8:2582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang J and Abdel-Rahman AA: Inhibition of
nischarin expression attenuates rilmenidine-evoked hypotension and
phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 production
in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
324:72–78. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wu X, Xu W, Cui G, Yan Y, Wu X, Li L, Tan
X, Wu Q and Gu X: The expression pattern of Nischarin after
lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-induced neuroinflammation in rats brain
cortex. Inflamm Res. 62:929–940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Alahari SK: Nischarin inhibits Rac induced
migration and invasion of epithelial cells by affecting signaling
cascades involving PAK. Exp Cell Res. 288:415–424. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alahari SK, Reddig PJ and Juliano RL: The
integrin-binding protein nischarin regulates cell migration by
inhibiting PAK. EMBO J. 23:2777–2788. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ding Y, Milosavljevic T and Alahari SK:
Nischarin inhibits LIM kinase to regulate cofilin phosphorylation
and cell invasion. Mol Cell Biol. 28:3742–3756. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Reddig PJ, Xu D and Juliano RL: Regulation
of p21-activated kinase-independent Rac1 signal transduction by
nischarin. J Biol Chem. 280:30994–31002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jain P, Baranwal S, Dong S, Struckhoff AP,
Worthylake RA and Alahari SK: Integrin-Binding protein nischarin
interacts with tumor suppressor liver kinase B1 (LKB1) to regulate
cell migration of breast epithelial cells. J Biol Chem.
288:15495–15509. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Maziveyi M, Dong S, Baranwal S and Alahari
SK: Nischarin regulates focal adhesion and Invadopodia formation in
breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 17:212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maziveyi M, Dong S, Baranwal S, Mehrnezhad
A, Rathinam R, Huckaba TM, Mercante DE, Park K and Alahari SK:
Exosomes from nischarin-expressing cells reduce breast cancer cell
motility and tumor growth. Cancer Res. 79:2152–2166. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Altevogt P, Doberstein K and Fogel M:
L1CAM in human cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:1565–1576. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sökeland G and Schumacher U: The
functional role of integrins during intra- and extravasation within
the metastatic cascade. Mol Cancer. 18:122019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Montgomery AM, Becker JC, Siu CH, Lemmon
VP, Cheresh DA, Pancook JD, Zhao X and Reisfeld RA: Human neural
cell adhesion molecule L1 and rat homologue NILE are ligands for
integrin alpha v beta 3. J Cell Biol. 132:475–485. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ruppert M, Aigner S, Hubbe M, Yagita H and
Altevogt P: The L1 adhesion molecule is a cellular ligand for
VLA-5. J Cell Biol. 131:1881–1891. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alahari SK and Nasrallah H: A membrane
proximal region of the integrin alpha5 subunit is important for its
interaction with nischarin. Biochem J. 377:449–457. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grela E, Kozłowska J and Grabowiecka A:
Current methodology of MTT assay in bacteria-A review. Acta
Histochem. 120:303–311. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guzmán C, Bagga M, Kaur A, Westermarck J
and Abankwa D: ColonyArea: An imageJ plugin to automatically
quantify colony formation in clonogenic assays. PLoS One.
9:e924442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Justus CR, Leffler N, Ruiz-Echevarria M
and Yang LV: In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J Vis
Exp. 88:e510462014.
|
|
27
|
Liu Q, Li X, Bao YS, Lu J, Li H, Huang Z
and Liu F: Chemical synthesis and functional characterization of a
new class of ceramide analogues as anti-cancer agents. Bioorg Med
Chem. 27:1489–1496. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sun JG, Ruan F, Zeng XL, Xiang J, Li X, Wu
P, Fung KP and Liu FY: Clitocine potentiates TRAIL-mediated
apoptosis in human colon cancer cells by promoting mcl-1
degradation. Apoptosis. 21:1144–1157. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Method. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lima JF, Nofech-Mozes S, Bayani J and
Bartlett JM: EMT in breast carcinoma-a review. J Clin Med.
5:652016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Bouris P, Skandalis SS, Piperigkou Z,
Afratis N, Karamanou K, Aletras AJ, Moustakas A, Theocharis AD and
Karamanos NK: Estrogen receptor alpha mediates epithelial to
mesenchymal transition, expression of specific matrix effectors and
functional properties of breast cancer cells. Matrix Biol.
43:42–60. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Radisky ES and Radisky DC: Matrix
metalloproteinase-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
breast cancer. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 15:201–212. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cichon MA, Nelson CM and Radisky DC:
Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer
cells by cell contact and adhesion. Cancer Inform. 14:1–13.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gregoire JM, Fleury L, Salazar-Cardozo C,
Alby F, Masson V, Arimondo PB and Ausseil F: Identification of
epigenetic factors regulating the mesenchyme to epithelium
transition by RNA interference screening in breast cancer cells.
BMC Cancer. 16:7002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zañudo JM, Guinn MT, Farquhar K, Szenk M,
Steinway SN, Balázsi G and Albert R: Towards control of cellular
decision-making networks in the epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition. Phys Biol. 16:0310022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Shi J, Chai K, Ying X and Zhou BP:
The role of snail in EMT and tumorigenesis. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 13:963–972. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mrozik KM, Blaschuk OW, Cheong CM,
Zannettino AC and Vandyke K: N-Cadherin in cancer metastasis, its
emerging role in haematological malignancies and potential as a
therapeutic target in cancer. BMC Cancer. 18:9392018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Olea-Flores M, Juárez-Cruz JC,
Mendoza-Catalán MA, Padilla-Benavides T and Navarro-Tito N:
Signaling pathways induced by leptin during epithelial–mesenchymal
transition in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 19:34932018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Olea-Flores M, Zuñiga-Eulogio MD,
Mendoza-Catalán MA, Rodríguez-Ruiz HA, Castañeda-Saucedo E,
Ortuño-Pineda C, Padilla-Benavides T and Navarro-Tito N:
Extracellular-Signal regulated kinase: A central molecule driving
epithelial- mesenchymal transition in cancer. Int J Mol Sci.
20:28852019. View Article : Google Scholar
|