|
1
|
Creasman WT, Odicine F, Maisonneuve P,
Quinn MA, Beller U, Benedet JL, Heintz AP, Ngan HY and Pecorelli S:
Carcinoma of the corpus uteri. FIGO 26th annual report on the
results of treatment in gynecological cancer. Int J Gynaecol
Obstet. 95 (Suppl 1):S105–S143. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Doll A, Abal M, Rigau M, Monge M, Gonzalez
M, Demajo S, Colás E, Llauradó M, Alazzouzi H, Planagumá J, et al:
Novel molecular profiles of endometrial cancer-new light through
old windows. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 108:221–229. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bray F, Dos Santos Silva I, Moller H and
Weiderpass E: Endometrial cancer incidence trends in Europe:
Underlying determinants and prospects for prevention. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:1132–1142. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kourea HP, Nikolaou M, Tzelepi V, Adonakis
G, Kardamakis D, Tsapanos V, Scopa CD, Kalofonos C and Decavalas G:
Expression of phosphorylated Akt, mTOR and MAPK in type I
endometrial carcinoma: Clinical significance. Anticancer Res.
35:2321–2331. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shevra CR, Ghosh A and Kumar M: Cyclin D1
and Ki-67 expression in normal, hyperplastic and neoplastic
endometrium. J Postgrad Med. 61:15–20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morice P, Leary A, Creutzberg C,
Abu-Rustum N and Darai E: Endometrial cancer. Lancet.
387:1094–1108. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takeshita S, Yamashita Y, Shiomi K, Suzuki
N, Yoshida J, Naiki-Ito A, Suzuki S, Akatsuka S, Toyokuni S,
Takahashi T, et al: Expression of P-REX2a is associated with poor
prognosis in endometrial malignancies. Oncotarget. 9:24778–24786.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bokhman JV: Two pathogenetic types of
endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol Oncol. 15:10–17. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
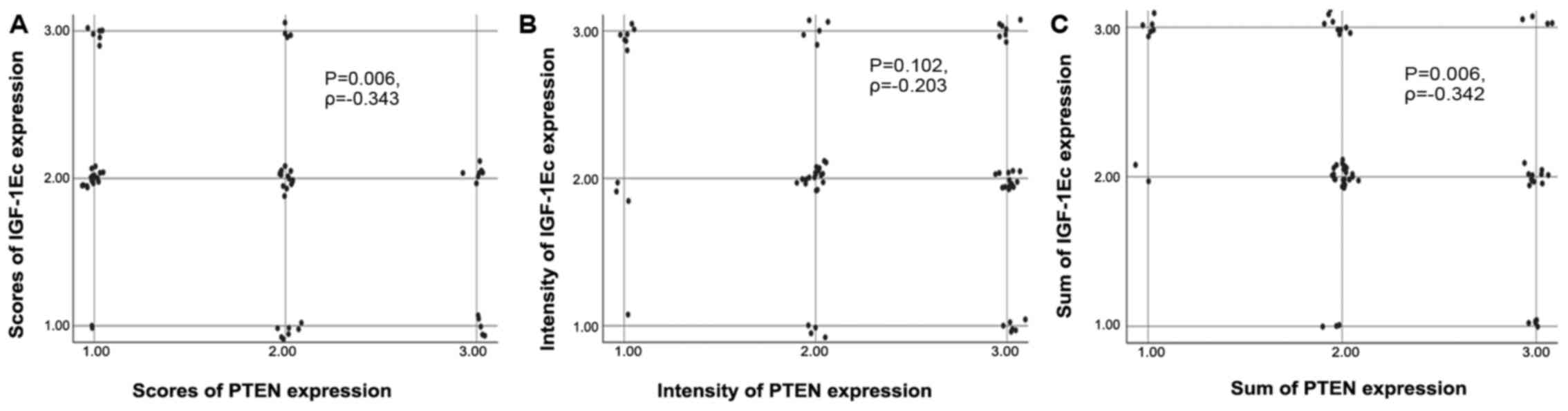
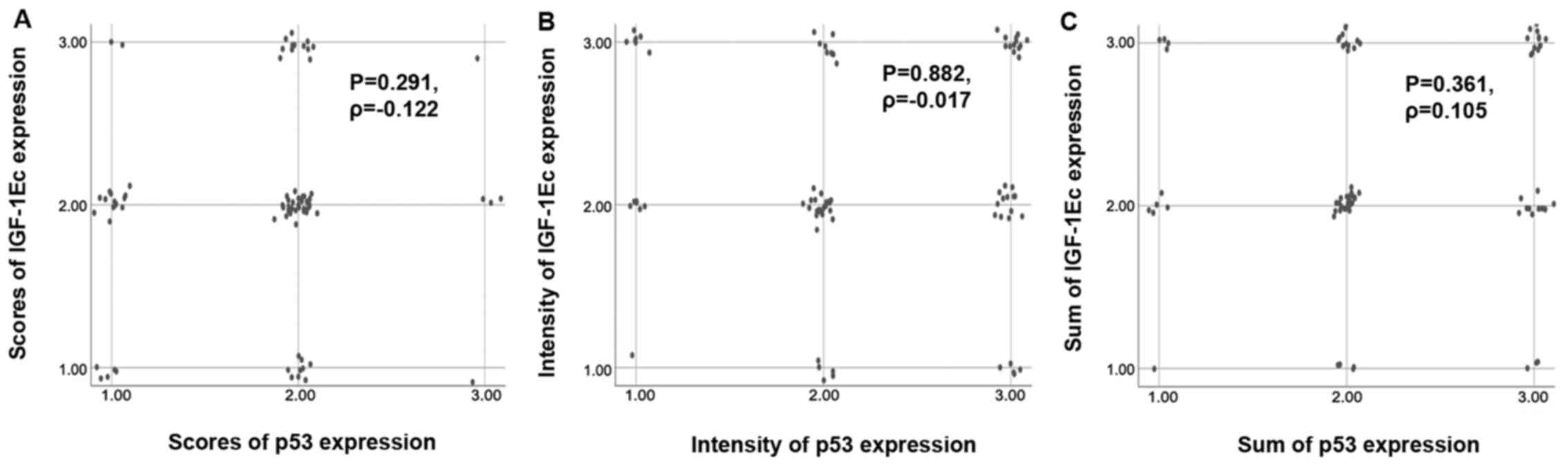
|
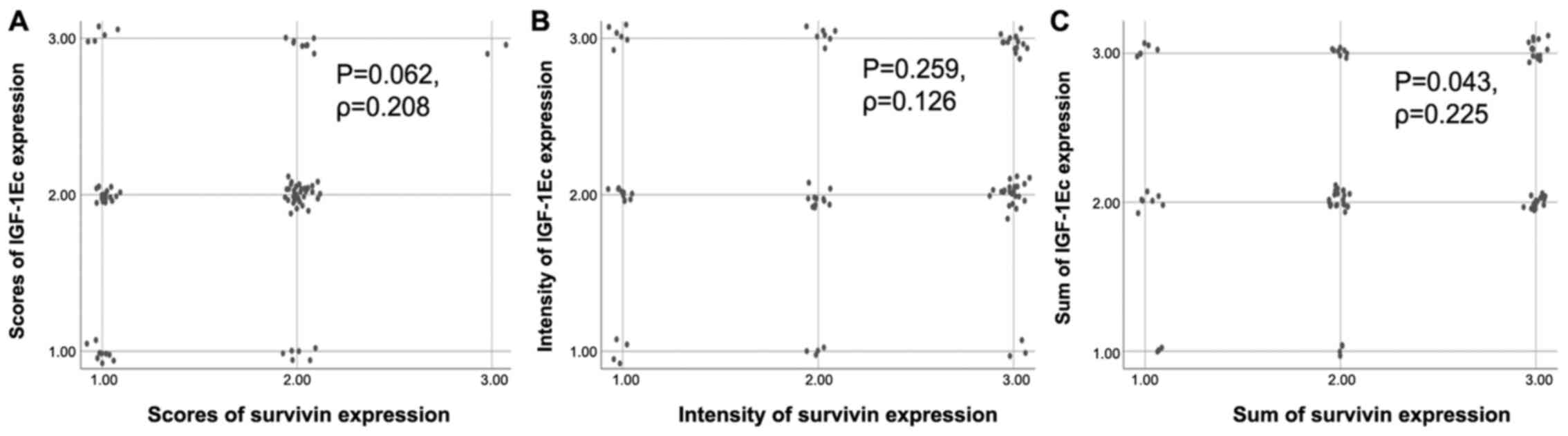
|
10
|
Parazzini F, La Vecchia C, Bocciolone L
and Franceschi S: The epidemiology of endometrial cancer. Gynecol
Oncol. 41:1–16. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Steiner E, Eicher O, Sagemuller J, Schmidt
M, Pitch H, Tanner B, Hengstler JG, Hofmann M and Knapstein PG:
Multivariate independent prognostic factors in endometrial
carcinoma: A clinicopathological study in 181 patients: 10
experience at the department of obstetrics and gynecology of the
mainz university. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 13:197–203. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Prat J: Prognostic parameters of
endometrial carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 35:649–662. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Daughaday WH and Rotwein P: Insulin-like
factors I and II. Peptide, messenger ribonucleic acid and gene
structures, serum and tissue concentrations. Endocr Rev. 10:68–91.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
De Meyts P and Whittaker J: Structural
biology of insulin and IGF1 receptors: Implications for drug
design. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 1:769–783. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Federici M, Porzio O, Zucaro L, Giovannone
B, Borboni P, Marini MA, Lauro D and Sesti G: Increased abundance
of insulin/IGF-I hybrid receptors in adipose tissue from NIDDM
patients. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 135:41–47. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakae J, Kido Y and Accili D: Distinct and
overlapping functions of insulin and IGF-I receptors. Endocr Rev.
22:818–835. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baserga R, Peruzzi F and Reiss K: The
IGF-1 receptor in cancer biology. Int J Cancer. 107:873–877. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taguchi A and White MF: Insulin-like
signaling, nutrient homeostasis, and life span. Annu Rev Physiol.
70:191–212. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Samani AA, Yakar S, LeRoith D and Brodt P:
The role of the IGF system in cancer growth and metastasis:
Overview and recent insights. Endocr Rev. 28:20–47. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Milingos DS, Philippou A, Armakolas A,
Papageorgiou E, Sourla A, Protopapas A, Liapi A, Antsaklis A,
Mastrominas M and Koutsilieris M: Insulin-like growth factor-1Ec
(MGF) expression in eutropic and ectopic endometrium:
Characterization of the MGF E-peptide actions in vitro. Mol Med.
17:21–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jones JI and Clemmons DR: Insulin-like
growth factors and their binding proteins: Biological actions.
Endocr Rev. 13:3–34. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Majchrzak-Baczmańska D and Malinowski A:
Does IGF-1 play a role in the biology of endometrial cancer?
Ginekol Pol. 87:598–604. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Flannery CA, Saleh FL, Choe GH, Selen DJ,
Kodaman PH, Kliman HJ, Wood TL and Taylor HS: Differential
expression of IR-A, IR-B and IGF-1R in endometrial physiology and
distinct signature in adenocarcinoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
101:2883–2891. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dai C, Li N, Song G, Yang Y and Ning X:
Insulin-like growth factor 1 regulates growth of endometrial
carcinoma through PI3k signaling pathway in insulin-resistant type
2 diabetes. Am J Transl Res. 8:3329–3336. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Alexandraki KI, Philippou A, Boutzios G,
Theohari I, Koutsilieris M, Delladetsima IK and Kaltsas GA: IGF-IEc
expression is increased in secondary compared to primary foci in
neuroendocrine neoplasms. Oncotarget. 8:79003–79011. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mazerbourg S and Monget P: Insulin-like
growth factor binding proteins and IGFBP proteases: A dynamic
system regulating the ovarian folliculogenesis. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 9:1342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rutanen EM, Nyman T, Lehtovirta P, Ammala
M and Pekonen F: Suppressed expression of insulin-like growth
factor binding protein-1 mRNA in the endometrium: A molecular
mechanism associating endometrial cancer with its risk factors. Int
J Cancer. 59:307–312. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Suvanto-Luukkonen E, Sundostrom H,
Penttinen J, Kauppila A and Rutane EM: Insulin-like growth
factor-binding protein-1: A biochemical marker of endometrial
response to progestin during hormone replacement therapy.
Maturitas. 22:255–262. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Vassilakos G, Philippou A, Tsakiroglou P
and Koutsilieris M: Biological activity of the e domain of the
IGF-1Ec as addressed by synthetic peptides. Hormones (Athens).
13:182–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Philippou A, Maridaki M, Pneumaticos S and
Koutsilieris M: The complexity of the IGF1 gene splicing,
posttranslational modification and bioactivity. Mol Med.
20:202–214. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kornfeld S: Structure and function of the
mannose-6-phosphate/insulinlike growth factor II receptors. Annu
Rev Biochem. 61:307–330. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
LeRoith D and Roberts CT Jr: The
insulin-like growth factor system and cancer. Cancer Lett.
195:127–137. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Baxter RC and Martin JL: Binding proteins
for the insulin-like growth factors: Structure, regulation and
function. Prog Growth Factor Res. 1:49–68. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Murphy LJ and Ghahary A: Uterine
insulin-like growth factor-1: Regulation of expression and its role
in estrogen-induced uterine proliferation. Endocr Rev. 11:443–453.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu H and Rohan T: Role of the insulin-like
growth factor family in cancer development and progression. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 92:1472–1489. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mourmouras N, Philippou A, Christopoulos
P, Kostoglou K, Grivaki C, Konstantinidis C, Serafetinides E,
Delakas D and Koutsilieris M: Different expression of IGF-I
transcripts in bladder cancer. Anticancer Res. 38:3453–3459. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kelley KM, Oh Y, Gargosky SE, Gucev Z,
Matsumoto T, Hwa V, Ng L, Simpson DM and Rosenfeld RG: Insulin-like
growth factor-binding proteins (IBFBPs) and their regulatory
dynamics. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 28:619–637. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Clemmons DR: Insulin-like growth factor
binding proteins and their role in controlling IGF actions.
Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 8:45–62. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Burroughs KD, Donn SE, Barrett JC and
Taylor JA: Insulin-like growth factor-I: A key regulator of human
cancer risk? J Natl Cancer Inst. 91:579–581. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Adamo ML, Ben-Hur H, LeReith D and Roberts
CT Jr: Transcription initiation in the two leader exons of the rat
IGF-1 gene occurs from disperse versus localized sites. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 176:887–893. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Adamo ML, Neuenschwander S, LeRoith D and
Roberts CT Jr: Structure, expression, and regulation of the IGF-I
gene. Adv Exp Med Biol. 343:1–11. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Adamo ML: Regulation of insulin-like
growth factor I gene expression. Implications for normal and
pathological growth. Diabetes Rev. 3:2–27. 1995.
|
|
43
|
Simmons JG, Van Wyk JJ, Hoyt EC and Lund
PK: Multiple transcription start sites in the rat insulin-like
growth factor-I gene give rise to IGF-I mRNAs that encode different
IGF-I precursors and are processed differently in vitro. Growth
Factors. 9:205–221. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Bell GI, Stempien MM, Fong NM and Rall LB:
Sequences of liver cDNAs encoding two different mouse insulin-like
growth factor 1 precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 14:7873–7882. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Temmerman L, Slonimsky E and Rosenthal N:
Class 2 IGF-1 isoforms are dispensabile for viability, growth and
maintenance of IGF-1 serum levels. Growth Horm IGF Res. 20:255–263.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Matheny RW Jr, Nindl BC and Adamo ML:
Minireview: Mechano-growth factor: A putative product of IGF-I gene
expression involved in tissue repair and regeneration.
Endocrinology. 151:865–875. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kasprzak A, Szaflarski W, Szmeja J,
Andrzejewska M, Przybyszewska W, Kaczmarek E, Koczorowska M,
Kościński T, Zabel M and Drews M: Differential expression of IGF-1
mRNA isoforms in colorectal carcinoma and normal colon tissue. Int
J Oncol. 42:305–316. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Philippou A, Armakolas A and Koutsilieris
M: Evidence for the possible biological significance of the igf-1
gene alternative splicing in prostate cancer. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 4:312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jansen M, van Schaik FM, Richer AT,
Bullock B, Woods DE, Gabbay KH, Nauubaum AL, Sussenbach JS and Van
den Brande JL: Sequence of cDNA encoding human insulin-like growth
factor I precursor. Nature. 306:609–611. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Brisson BK, Spinazzola J, Park S and
Barton ER: Viral expression of insulin-like growth factor I
E-peptide increases skeletal muscle mass but at the expense of
strength. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 306:E965–E974. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Rotwein P, Pollock KM, Didier DK and Krivi
GG: Organization and sequence of the human insulin-like growth
factor I gene. Alternative RNA processing produces two insulin-like
growth factor I precursor peptides. J Biol Chem. 261:4828–4832.
1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Duguay SJ: Post-translational processing
of insulin-like growth factors. Horm Metab Res. 31:43–49. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Barton ER: The ABCs of IGF-I isoforms:
Impact on muscle hypertrophy and implications for repair. Appl
Physiol Nutr Metab. 31:791–797. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wallis M: New insulin-like growth factor
(IGF)-precursor sequences from mammalian genomes: The molecular
evolution of IGFs and associated peptides in primates. Growth Horm
IGF Res. 19:12–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Siegfriend JM, Kasprzyk PG, Treston AM,
Mulshine JL, Quinn KA and Cuttitta F: A mitogenic peptide amide
encoded within the E peptide domain of the insulin-like growth
factor IB prohormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:8107–8111. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kuo YH and Chen TT: Novel activities of
pro-IGF-I E peptides: Regulation of morphological differentiation
and anchorage-independent growth in human neuroblastoma cells. Exp
Cell Res. 280:75–89. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Chew SL, Lavender P, Clark AJ and Ross RJ:
An alternatively spliced human insulin-like growth factor-1
transcript with hepatic tissue expression that diverts away from
mitogenic IBE1 peptide. Endocrinology. 136:1939–1944. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Tian XC, Chen MJ, Pantschenko AG, Yang TJ
and Chen TT: Recombinant E-peptides of pro-IGF-I have mitogenic
activity. Endocrinology. 140:3387–3390. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen MJ, Chiou PP, Lin P, Lin CM, Siri S,
Peck K and Chen TT: Suppression of growth and cancer-induced
angiogenesis of aggressive human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231)
on the chorionallantoic membrane of developing chicken embryos by
E-peptide of pro-IGF-I. J Cell Biochem. 101:1316–1327. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Armakolas A, Dimakakos A, Loucogiannaki C,
Armakolas N, Antonopoulos A, Florou C, Tsioli P, Papageorgiou E,
Alexandrou TP, Stathaki M, et al: IL-6 is associated to IGF-1Ec
upregulation and Ec peptide secretion, from prostate tumors. Mol
Med. 24:62018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Garrouste F, Remacle-Bonnet M, Fauriat C,
Marvaldi J, Luis J and Pommier G: Prevention of cytokine-induced
apoptosis by insulin-like growth factor-I is independent of cell
adhesion molecules ijn HT29-D4 colon carcinoma cells-evidence for a
NF-kappaB-dependent survival mechanism. Cell Death Differ.
9:768–779. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Alexia C, Fallot G, Lasfer M,
Schweizer-Groyer G and Groyer A: An evaluation of the role of
insulin-like growth factors (IGF) and of type-I IGF receptor
signaling in hepatocarcinogenesis and in the resistance of
hepatocarcinoma cells against drug-induced apoptosis. Biochem
Pharmacol. 86:1003–1015. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Wang HS and Chard T: IGFs and IGF-binding
proteins in the regulation of human ovarian and endometrial
function. J Endocrinol. 161:1–13. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Bogdanos J, Karamanolakis D, Tenta R,
Tsintavis A, Milathianakis C, Mitsiades C and Koutsilieris M:
Endocrine/paracrine/autocrine survival factor activity of bone
microenviroment participates in the development of androgen
ablation and chemotherpay refractoriness of prostate cancer
metastasis in skeleton. Endocr Relat Cancer. 10:279–289. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Koutsilieris M: Pathophysiology of uterine
leiomyomas. Biochem Cell Biol. 70:273–278. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Koutsilieris M, Mitsiades C and Sourla A:
Insulin-like growth factor I and urokinase-type plasminogen
activator bioregulation system as a survival mechanism of prostate
cancer cells in osteoblastic metastases: Development of
anti-survival factor therapy for hormone-reflactory prostate
cancer. Mol Med. 6:251–267. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Hernandez AV, Pasupuleti V, Benites-Zapata
VA, Thota P, Deshpande A and Perez-Lopez FR: Insulin resistance and
endometrial cancer risk: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Eur J
Cancer. 51:2747–2758. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pavelic J, Radakovic B and Pavelic K:
Insulin-like growth factor 2 and its receptors (IGF 1R and IGF
2R/mannose 6-phospate) in endometrial adenocarcinoma. Gynecol
Oncol. 105:727–735. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Stavropoulos A, Varras M, Vasilakaki T,
Varra VK, Tsavari A, Varra FN, Nonni A, Kavantzas N and Lazaris AC:
Expression of p53 and PTEN in human primary endometrial carcinomas:
Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical analysis and study of
their concomitant expression. Oncol Lett. 17:4575–4589.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Stavropoulos A, Varras M, Vasilakaki T,
Varra VK, Varra FN, Tsavari A, Nonni A, Kavantzas N and Lazaris AC:
Expression of anti-apoptotic protein survivin in human endometrial
carcinoma: Clinical and pathological correlations as a separate
factor and in combination with concomitant PTEN and p53 expression.
Oncol Lett. 20:1033–1054. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Galimi F, Torti D, Sassi F, Isella C, Corà
D, Gastaldi S, Ribero D, Muratore A, Massucco P, Siatis D, et al:
Genetic and expression analysis of MET, MACC1, and HGF in
metastatic colorectal cancer: Response to met inhibition in patient
xenografts and pathologic correlations. Clin Cancer Res.
17:3146–3156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li M, Xin X, Wu T, Hua T and Wang H and
Wang H: Stromal cells of endometrial carcinoma promotes
proliferation of epithelial cells through the HGF/c-Met/Akt
signaling pathway. Tumour Biol. 36:6239–6248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Harpaz N, Taboada S, Ko HM, Yu J, Yang Q,
Xu H and Cao W: Expression of MACC1 and MET in inflammatory bowel
disease-associated colonic neoplasia. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
20:703–711. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhang Q, Xu P, Lu Y and Dou H: Correlation
of MACC1/c-Myc expression in endometrial carcinoma with
clinical/pathlogical features or prognosis. Med Sci Monit.
24:4738–4744. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Yang E and Yan H: Expression of ELF5 in
endometrial carcinoma tissues and its clinical significance. Oncol
Lett. 16:3473–3480. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Singh N, Hirschowitz L, Zaino R,
Alvarado-Cabrero I, Duggan MA, Ali-Fehmi R, Euscher E, Hecht JL,
Horn LC, Ioffe O, et al: Pathologic prognostic factors in
endometrial carcinoma (other than tumor type and grade). Int J
Gynecol Pathol. 38 (Suppl 1):S93–S113. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Sadlecki P, Bodnar M, Grabiec M, Marszalek
A, Walentowicz P, Sokup A, Zegarska J and Walentowicz-Sadlecka M:
The role of Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α, Glucose thransporter-1,
(GLUT-1) and carbon anhydrase IX in endometrial cancer patients.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:6168502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Liu F, Sun Y, Liu B, Lu J, Li H, Zhu H,
Gao H, Zhou X and Chang H: Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces
epithelial-mesenchymanl transition in hepatocellular carcinoma by
activating survivin. Oncol Rep. 40:952–958. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bansal N, Yendluri V and Wenham RM: The
molecular biology of endometrial cancers and the implications for
pathogenesis, classification, and targeted therapies. Cancer
Control. 16:8–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Llauradó M, Ruiz A, Majem B, Ertekin T,
Colás E, Pedrola N, Devis L, Rigau M, Sequeiros T, Montes M, et al:
Molecular bases of endometrial cancer: New roles for new actors in
the diagnosis and the therapy of the disease. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
358:244–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Meng X, Dizon DS, Yang S, Wang X, Zhu D,
Thiel KW and Leslie KK: Strategies for molecularly enhanced
chemotherpay to achieve synthetic lethality in endometrial tumors
with mutant p53. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2013:8281652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sugihara T: Loss of adherens junction
protein E-cadherin is a biomarker of high grade histology and poor
prognosis in endometrial cancer. Ann Clin Lab Res. 4:12016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Gómez-Macías GS, Garza-Rodríguez ML,
Garza-Guajardo R, Monsiváis-Ovalle D, Ancer-Rodríguez J,
Barrera-Saldaña HA and Barboza-Quintana O: Overexpression of the
matrix metalloproteinase 11 gene is a potential biomarker for type
1 endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett. 16:1073–1078. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Buchynska LG, Brieiva OV and Iurchenko NP:
Assessment of HER-2/neu, c-MYC and CCNE1 gene copy number
variations and protein expression in endometrial carcinomas. Exp
Oncol. 41:138–143. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Reaven GM: Banting lecture 1988. Role of
insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 37:1595–1607. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lee DY and Lee TS: Associations between
metabolic syndrome and gynecologic cancer. Obstet Gynecol Sci.
63:215–224. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Esposito K, Capuano A and Giugliano D:
Metabolic syndrome and cancer: Holistic or reductionist? Endocrine.
45:362–364. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Esposito K, Chiodini P, Colao A, Lenzi A
and Giugliano D: Metabolic syndrome and risk of cancer: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care. 35:2402–2411.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Trabert B, Wentzensen N, Felix AS, Yang
HP, Sherman ME and Brinton LA: Metabolic syndrome and risk of
endometrial cancer in the united states: A study in the
SEER-medicare linked database. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev.
24:261–267. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Jee SH, Kim HJ and Lee J: Obesity, insulin
resistance and cancer risk. Yonsei Med J. 46:449–455. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
van Kruijsdijk RC, van der Wall E and
Visseren FL: Obesity and cancer: The role of dysfunctional adipose
tissue. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:2569–2578. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Iyengar NM, Hudis CA and Dannenberg AJ:
Obesity and cancer: Local and systemic mechanisms. Annu Rev Med.
66:297–309. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Yagen JD and Davidson NE: Estrogen
carcinogenesis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 354:270–282. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
André F, Rigot V, Remacle-Bonnet M, Luis
J, Pommier G and Marvaldi J: Protein kinases C-gamma and -delta are
involved in insulin-like growth factor I-induced migration of
colonic epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 116:64–77. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
André F, Rigot V, Thimonier J, Montixi C,
Parat F, Pommier G, Marvaldi J and Luis J: Integrins and E-cadherin
cooperate with IGF-I to induce migration of epithelial colonic
cells. Int J Cancer. 83:497–505. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Akagi Y, Liu W, Zebrowski B, Xie K and
Ellis LM: Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor
expression in human colon cancer by insulin-like growth factor-I.
Cancer Res. 58:4008–4014. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wu Y, Yakar S, Zhao L, Hemminghausen L and
LeRoith D: Circulating insulin-like growth factor-I levels regulate
colon cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 62:1030–1035.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Fader AN, Arriba LN, Frasure HE and von
Gruenigen VE: Endometrial cancer and obesity: Epidiomiology,
biomarkers, prevention and survivorship. Gynecol Oncol.
114:121–127. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Koczorowska MM, Kwasniewska A and
Gozdzicka-Jozefiak A: IGF1 mRNA isoform expression in the cervix of
HPV-positive woman with pre-cancerous and cancerous lesions. Exp
Ther Med. 2:149–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Philippou A, Armakolas A, Pantleakou Z,
Pissimissis N, Nezos A, Theos A, Kaparelou M, Armakolas N,
Pneumaticos SG and Koutsilieris M: IGFF1Ec expression in MG-63
human osteoblast-like osteosarcoma cells. Anticancer Res.
31:4259–4265. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
McKoy G, Ashley W, Mander J, Yang SY,
Williams N, Russell B and Goldspink G: Expression of insulin-like
growth factor-1 splice variants and structural genes in rabbit
skeletal muscle induced by stretch and stimulation. J Physiol.
516:583–592. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Hameed M, Orrell RW, Cobbold M, Goldspink
G and Harridge SD: Expression of IGF-I splice variants in young and
old human skeletal muscle after high resistance exercise. J
Physiol. 547:247–254. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hameed M, Lange KH, Andersen JL,
Schjerling P, Kjaer M, Harrigde SD and Goldspink G: The effect of
recombinant human growth hormone and resistance training of IGF-I
mRNA expression in the muscles of elderly men. J Physiol.
555:231–240. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Bickel CS, Slade J, Mahoney E, Haddad F,
Dudley GA and Adams GR: Time course of molecular responses of human
skeletal muscle to acute bouts or resistance exercise. J Appl
Physiol (1985). 98:482–488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Kim JS, Cross JM and Bamman MM: Impact of
resistance loading on myostatin expression and cell cycle
regulation in young and older men and women. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 288:E1110–E1119. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Philippou A, Papageorgiou E, Bogdanis G,
Halapas A, Sourla A, Maridaki M, Pissimissis N and Koutsilieris M:
Expression of IGF-1 isoforms after exercise-induced muscle damage
in humans: Characterization of the MGF E peptide actions in vitro.
In Vivo. 23:567–575. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Carpenter V, Matthews K, Devlin G, Stuart
S, Jensen J, Conaglen J, Jeanplong F, Goldspink P, Yang SY,
Goldspink G, et al: Mechano-growth factor reduces loss of cardiac
function in acute myocardial infarction. Heart Lung Circ. 17:33–39.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Stavropoulou A, Halapas A, Sourla A,
Philippou A, Papageorgiou E, Papalois A and Koutsilieris M: IGF-1
expression in infarcted myocardium and MGF E peptide actions in rat
cardiomyocytes in vitro. Mol Med. 15:127–135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Armakolas A, Philippou A, Panteleakou Z,
Nezos A, Sourla A, Petraki C and Koutsilieris M: Preferential
expression of IGF-IEc (MGF) transcript in cancerous tissues of
human prostate: Evidence for a novel and autonomous growth factor
activity of MGF E peptide in human prostate cancer cells. Prostate.
70:1233–1242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Liu JP, Baker J, Perkins AS, Robertson EJ
and Efstratiadis A: Mice carrying null mutations of the genes
encoding insulin-like growth factor I (Igf-1) and type 1 IGF
receptor (Igf1r). Cell. 75:59–72. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Siddle K, Ursø B, Niesler CA, Cope DL,
Molina L, Surinya KH and Soos MA: Specificity in ligand binding and
intracellular signaling by insulin and insulin-like growth factor
receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 29:513–525. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Laviola L, Natalicchio A and Giorgiono F:
The IGF-I signaling pathway. Curr Pharm Des. 13:663–669. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Barton ER, Park S, James JK, Makarewich
CA, Philippou A, Eletto D, Lei H, Brisson B, Ostrovsky O, Li Z and
Argon Y: Deletion of muscle GRP94 impairs both muscle and body
growth by inhibiting local IGF production. FASEB J. 26:3691–3702.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Wu JW, Boudreau DM, Park Y, Simonds NI and
Freedman AN: Commonly used diabetes and cardiovascular medications
and cancer recurrence and cancer-specific mortality: A review of
the literature. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 13:1071–1099. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhang ZJ and Li S: The prognostic value of
metformin for cancer patients with concurrent diabetes: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab.
16:707–710. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Bredholt G, Mannelqvist M, Stefansson IM,
Birkeland E, Bø TH, Øyan AM, Trovik J, Kalland KH, Jonassen I,
Salvesen HB, et al: Tumor necrosis is an important hallmark of
aggressive endometrial cancer and associates with hypoxia,
angiogenesis and inflammation responses. Oncotarget. 6:39676–39691.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Armakolas A, Kararelou M, Dimakakos A,
Papageorgiou E, Armakolas N, Antonopoulos A, Petraki C, Lekarakou
M, Lelovas P, Stathaki M, et al: Oncogenic role of the Ec peptide
of the IGF-1Ec isoform in prostate cancer. Mol Med. 21:167–179.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Papageorgiou E, Philippou A, Armakolas A,
Christopoulos PF, Dimakakos A and Koutsilieris M: The human Ec
peptide: The active core of a progression growth factor with
species-specific mode of action. Hormones (Athens). 15:423–434.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Karagiannis AK, Philippou A,
Tseleni-Balafouta S, Zevolis E, Nakouti T, Tsopanomichalou-Gklotsou
M, Psarras V and Koutsilieris M: IGF-IEc expression is associeted
with advanced differentied thyroid cancer. Anticancer Res.
39:2811–2819. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Irwin JC, de las Fuentes L, Dsupin BA and
Giudice LC: Insulin-like growth factor regulation of human
endometrial stromal cell function: Coordinate effects on
insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, cell proliferation
and prolactin secretion. Regul Pept. 48:165–177. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Tang XM, Rossi MJ, Mastrerson BJ and
Chegini N: Insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-I receptors,
and IGF binding proteins 1–4 in human uterine tissue: Tissue
localization and IGF-I action in endometrial stromal and myometrial
smooth muscle cells in vitro. Biol Reprod. 50:1113–1125. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Giudice LC, Dsupin BA, Jin IH, Vu TH and
Hoffman AF: Differential expression of messenger ribonucleic acids
encoding insulin-like growth factors and their receptors in human
uterine endometrium and decidua. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
76:1115–1122. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Zhou J, Dsupin BA, Giudice LC and Bondy
CA: Insulin-like growth factor system gene expression in human
endometrium during menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
79:1723–1734. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Laatikainen TJ, Toma EI and Voutilainen
RJ: The expression of insulin-like growth factor and its binding
protein RNA in the endometrium of postmenopausal patients with
breast cancer receiving tamoxifen. Cancer. 76:1406–1410. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Elkas J, Gray K, Howard L, Petit N, Pohl J
and Armstrong A: The effects of tamoxifen on endometrial
insulin-like growth factor-1 expression. Obstet Gynecol. 91:45–50.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Mairano E, Loverro G, Viale G, Giannini T,
Napoli A and Perlino E: Insulin-like growth factor-I expression in
normal and diseased endometrium. Int J Cancer. 80:188–193. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
O'Toole SA, Dunn E, Sheppard BL, Sheils O,
O'Leary JJ, Wuttke W and Seidlova-Wuttke D: Oestrogen regulated
gene expression in normal and malignant endometrial tissue.
Maturitas. 51:187–198. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Bruchim I, Sarfstein R and Werner H: The
IGF hormonal network in endometrial cancer: Functions, regulation,
and targeting approaches. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 5:762014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Soufla G, Sifakis S and Spandidos DA: FGF2
transcript levels are positively correlated with EGF and IGF-1 in
the malignant endometrium. Cancer Lett. 259:146–155. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Pengchong H and Tao H: Expression of
IGF-1R, VEGF-C and D2-40 and their correlation with lymph node
metastasis in endometrial adenocarcinoma. Eur J Gynecol Oncol.
32:660–664. 2011.
|
|
131
|
Yi HK, Kim SY, Hwang PH, Kim CY, Yang DH,
Oh Y and Lee DY: Impact of PTEN on the expression of insulin-like
growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding proteins in human gastric
adenocarcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 330:760–767.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
McCamplell AS, Broaddus RR, Loose DS and
Davies PJ: Overexpression of the insulin-like growth factor I
receptor and activation of the AKT pathway in hyperplastic
endometrium. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6373–6378. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Dong L, Du M and Lv Q: Picropodophyllin
inhibits type I endometrial cancer cell proliferation via
disruption of the PI3K/Akt pathway. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 51:753–760. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Leung PS, Aronson WJ, Ngo TH, Golding LA
and Barnard RJ: Exercise alters the IGF axis in vivo and increases
p53 protein in prostate tumor cells in vitro. J Appl Physiol
(1985). 96:450–454. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Tucci P: Caloric restriciton: Is mammalian
life exptension linked to p53? Aging (Albany NY). 4:525–534. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Luo X, Jiang X, Li J, Bai Y, Li Z, Wei P,
Sun S, Liang Y, Han S, Li X and Zhang B: Insulin-like growth
factor-1 attenuates oxidative stress-induced hepatocyte premature
senescence in liver fibrogenesis via regulating nuclear
p53-progerin interaction. Cell Death Dis. 10:4512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Tran D, Bergholz J, Zhang H, He H, Wang Y,
Zhang Y, Li Q, Kirkland JL and Xiao ZX: Insulin-like growth
factor-1 regulates the SIRT1-p53 pathway in cellular senescence.
Aging Cell. 13:669–678. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Attias-Geva Z, Bentov I, Kidrom D, Amichay
K, Sarfstein R, Fishman A, Bruchim I and Werner H: p53 regulates
insulin-like growth factor-I receptor gene expression in uterine
serous carcinoma and predicts responsiveness to an insulin-like
growth factor-I receptor-directed targeted therapy. Eur J Cancer.
48:1570–1580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Altieri DC: Survivin, cancer networks and
pathway-directed drug discovery. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:61–70. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Takai N, Miyazaki T, Nishida M, Nasu K and
Miyakawa I: Survivin expression correlates with clinical stage,
histological grade, invasive behavior and survival rate in
endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 184:105–116. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Tran J, Master Z, Yu JL, Rak J, Dumont DJ
and Kerbel RS: A role for survivin in chemoresistance of
endothelial cells mediated by VEGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
99:4349–4354. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Altieri DC: Survivin, versatile modulation
of cell division and apoptosis in cancer. Oncogene. 22:8581–8589.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Altieri DC: Survivin and apoptosis
control. Adv Cancer Res. 88:31–35. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Mita AC, Mita MM, Nawrocki ST and Giles
FJ: Survivin: Key regular of mitosis and apoptosis and novel target
for cancer therapeutics. Clin Cancer Res. 14:5000–5005. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Liu X, Chen H, Hou Y, Ma X, Ye M, Huang R,
Hu B, Cao H, Xu L, Liu M, et al: Adaptive EGF expression sensitizes
pancreatic cancer cells to ionizing radiation through activation of
the cyclin D1/P53/PARP pathway. Int J Oncol. 54:1466–1480.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Vaira V, Lee CW, Goel HL, Bosari S,
Languino LR and Altieri DC: Regulation of surivivn expression by
IGF-I/mTOR signaling. Oncogene. 26:2678–2684. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Song K, Shankar E, Yang J, Bane KL,
Wahdan-Alaswad R and Danielpour D: Critical role of a
survivin/TGF-β/mTORC1 axis in IGF-I-mediated growth of prostate
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 8:e618962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Sato A, Oya M, Ito K, Mizuno R, Horiguchi
Y, Umezawa K, Hayakawa M and Murai M: Survivin associates with cell
proliferation in renal cancer cells: Regulation of survivin
expression by insulin-like growth factor-1, interferon-gamma and a
novel NK-kappaB inhibitor. Int J Oncol. 28:841–846. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Oh SH, Jin Q, Kim ES, Khuri FR and Lee HY:
Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling pathway induces
resistance to the apoptotic activitis of SCH66336 (lonafarnib)
through Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated increases in
survivin expression. Clin Cancer Res. 14:1581–1589. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Morgillo F, Woo JK, Kim ES, Hong WK and
Lee HY: Heterodimerization of insulin-like growth factor
receptor/epidermal growth factor receptor and induction of survivin
expression counteract the antitumor action of erlotinid. Cancer
Res. 66:10100–10111. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|