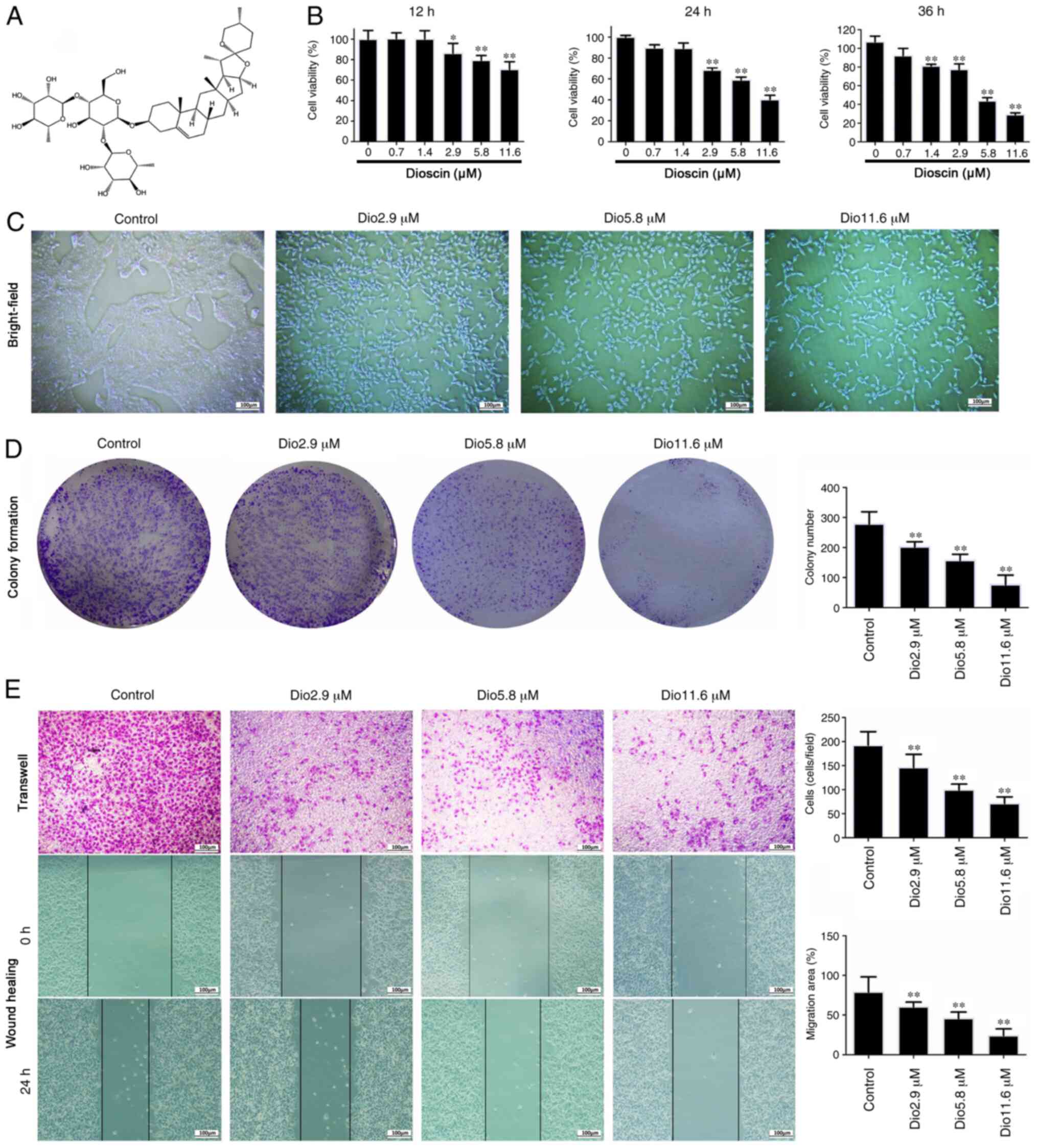
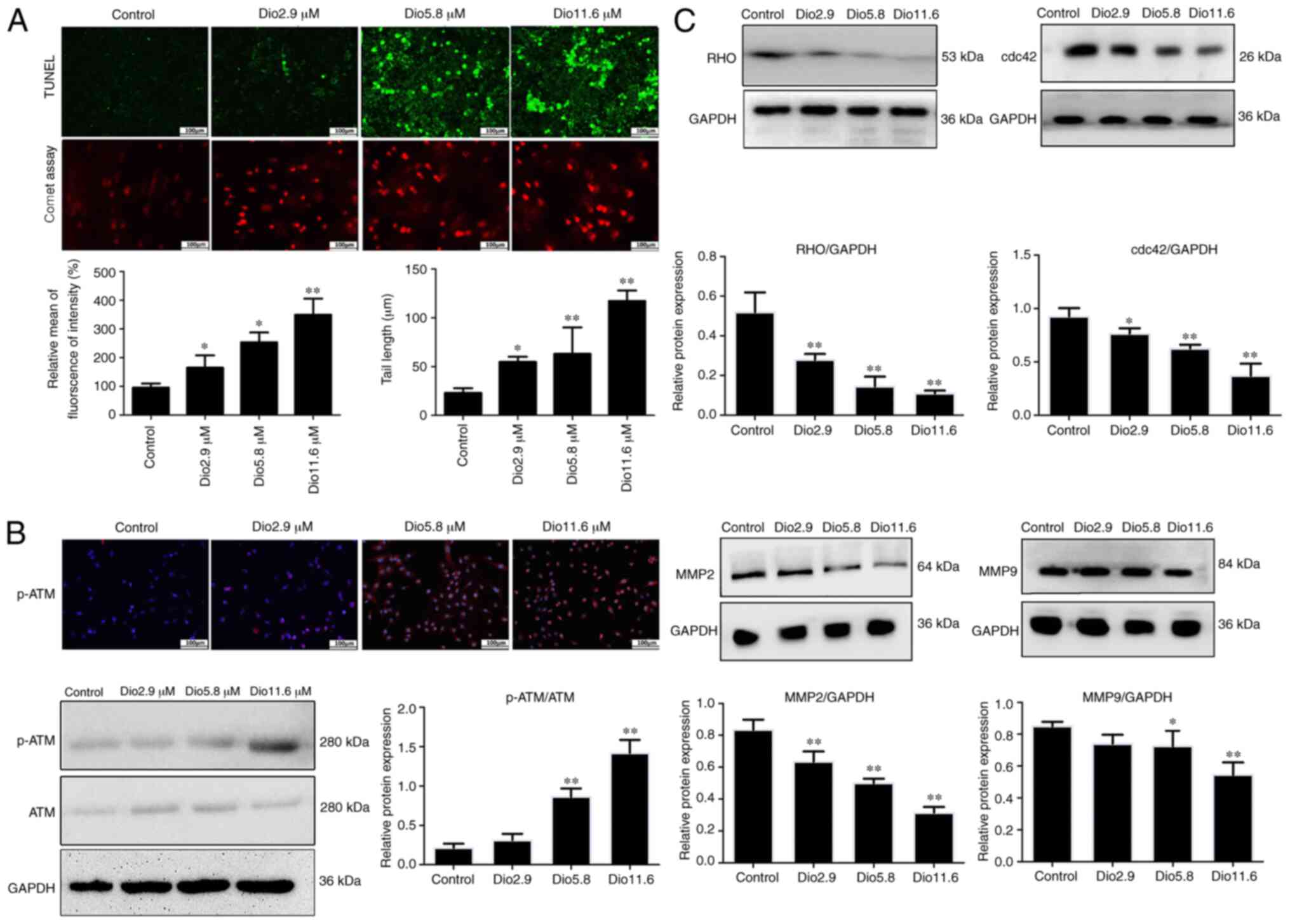
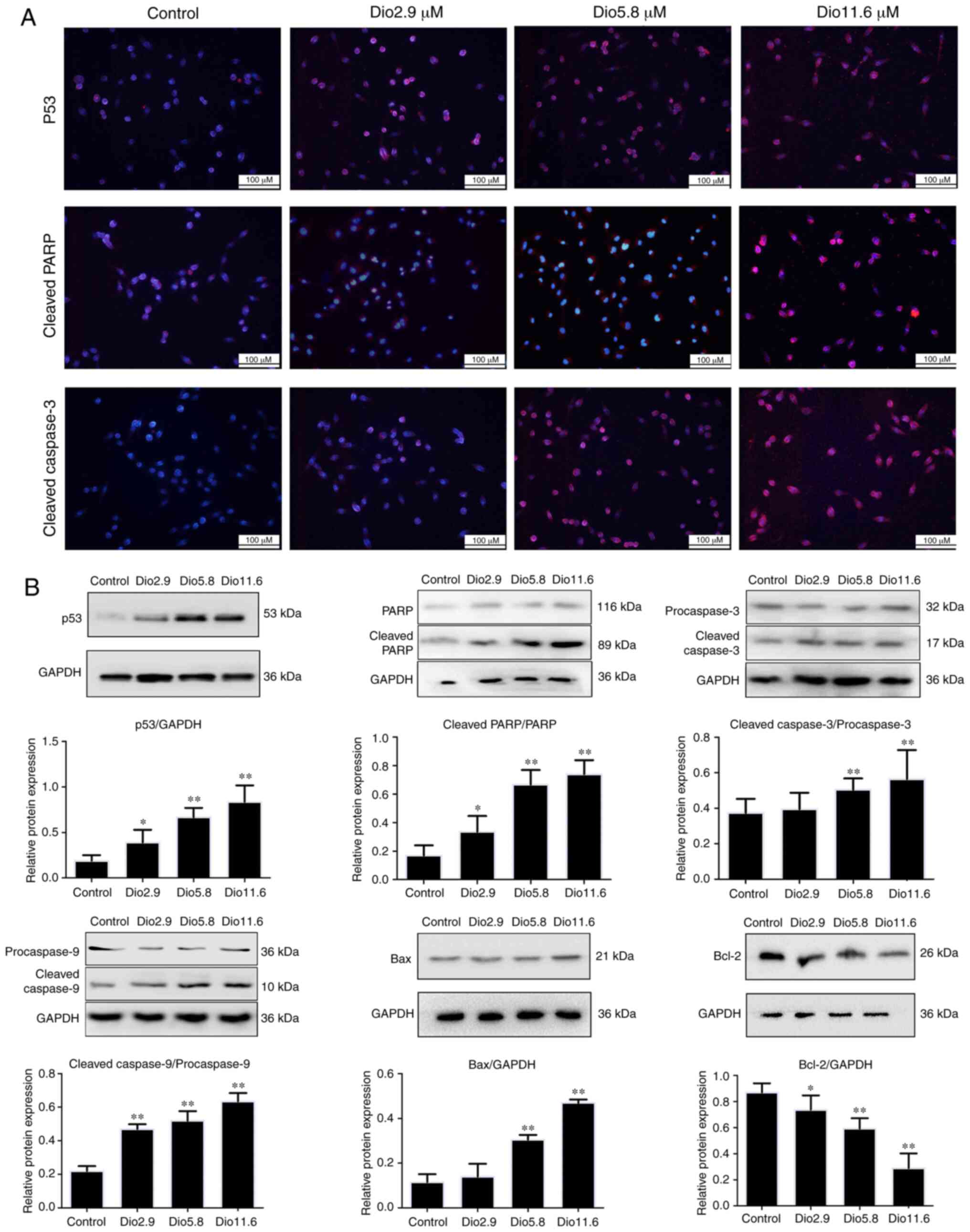
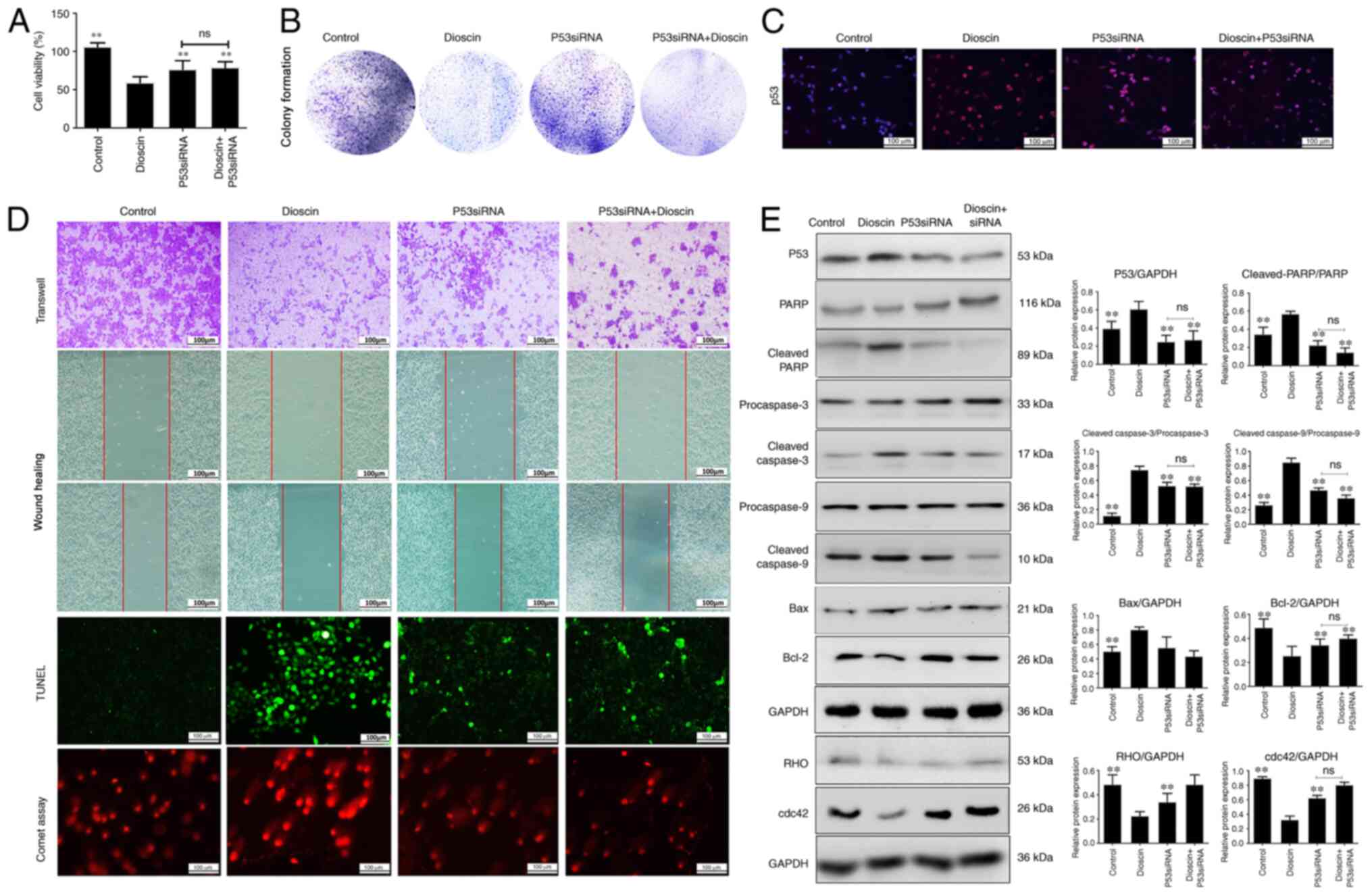
|
1
|
Trakatelli M, Ulrich C, del Marmol V,
Euvrard S, Stockfleth E and Abeni D: Epidemiology of nonmelanoma
skin cancer (NMSC) in Europe: Accurate and comparable data are
needed for effective public health monitoring and interventions. Br
J Dematol. 156 (Suppl 3):S1–S7. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Karia PS, Han J and Schmults CD: Cutaneous
squamous cell carcinoma: Estimated incidence of disease, nodal
metastasis, and deaths from disease in the United States, 2012. J
Am Acad Dermatol. 68:957–966. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li Q, Peng YS, Chen PJ, Wang ML, Cao C,
Xiong H, Zhang J, Chen MH, Peng XB and Zeng K: Peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist-mediated inhibition of
cell growth is independent of apoptosis in human epidermoid
carcinoma A431 cells. Oncol Lett. 15:6578–6584. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhai XX, Ding JC, Tang ZM, Li JG, Li YC,
Yan YH, Sun JC and Zhang CX: Effects of resveratrol on the
proliferation, apoptosis and telomerase ability of human A431
epidermoid carcinoma cells. Oncol Lett. 11:3015–3018. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li H, Tang Z, Chu P, Song Y, Yang Y, Sun
B, Niu M, Qaed E, Shopit A, Han G, et al: Neuroprotective effect of
phosphocreatine on oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
induced apoptosis in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of dual
PI3K/Akt and Nrf2/HO-1 pathways. Free Radic Biol Med. 120:228–238.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Afaq F and Katiyar SK: Polyphenols: Skin
photoprotection and inhibition of photocarcinogenesis. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 11:1200–1215. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sajadimajd S, Bahramsoltani R, Iranpanah
A, Kumar Patra J, Das G, Gouda S, Rahimi R, Rezaeiamiri E, Cao H,
Giampieri F, et al: Advances on natural polyphenols as anticancer
agents for skin cancer. Pharmacol Res. 151:1045842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang Y, Xu Y, Qi Y, Xu L, Song S, Yin L,
Tao X, Zhen Y, Han X, Ma X, et al: Protective effects of dioscin
against doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity via adjusting
FXR-mediated oxidative stress and inflammation. Toxicology.
378:53–64. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xia Y, Jia C, Xue Q, Jiang J, Xie Y, Wang
R, Ran Z, Xu F, Zhang Y and Ye T: Antipsychotic drug
trifluoperazine suppresses colorectal cancer by inducing G0/G1
arrest and apoptosis. Front Pharmacol. 10:10292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao H, Sun Y, Song S, Qi Y, Tao X, Xu L,
Yin L, Han X, Xu Y, Li H, et al: Protective effects of dioscin
against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through
inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Front Pharmacol.
8:1202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li XJ, Li ZF, Wang JJ, Han Z, Liu Z and
Liu BG: Effects of microRNA-374 on proliferation, migration,
invasion, and apoptosis of human SCC cells by targeting Gadd45a
through P53 signaling pathway. Biosci Rep. 37:BSR201707102017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mao Z, Han X, Chen D, Xu Y, Xu L, Yin L,
Sun H, Qi Y, Fang L, Liu K and Peng J: Potent effects of dioscin
against hepatocellular carcinoma through regulating TP53-induced
glycolysis and apoptosis regulator (TIGAR)-mediated apoptosis,
autophagy and DNA damage. Br J Pharmacol. 176:919–937. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Si L, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y, Han X, Xu Y, Zhao
Y, Liu K and Peng J: Potent effects of dioscin against pancreatic
cancer via miR-149-3P-mediated inhibition of the Akt1 signaling
pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 174:553–568. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun D, Yu M, Li Y, Xing H, Gao Y, Huang Z,
Hao W, Lu K, Kong C, Shimozato O, et al: Histone deacetylase 2 is
involved in DNA damage-mediated cell death of human osteosarcoma
cells through stimulation of the ATM/p53 pathway. FEBS Open Bio.
9:478–489. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lavin MF and Kozlov S: ATM activation and
DNA damage response. Cell Cycle. 6:931–942. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsu YL, Chia CC, Chen PJ, Huang SE, Huang
SC and Kuo PL: Shallot and licorice constituent isoliquiritigenin
arrests cell cycle progression and induces apoptosis through the
induction of ATM/p53 and initiation of the mitochondrial system in
human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells. Mol Nutr food Res. 53:826–835.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tao X, Sun X, Yin L, Han X, Xu L, Qi Y, Xu
Y, Li H, Lin Y, Liu K and Peng J: Dioscin ameliorates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury through the downregulation of TLR4
signaling via HMGB-1 inhibition. Free Radical Bio Med. 84:103–115.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun M, Ren J, Du H, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Wang
S and He L: A combined A431 cell membrane chromatography and online
high performance liquid chromatography /mass spectrometry method
for screening compounds from total alkaloid of Radix Caulophylli
acting on the human EGFR. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life
Sci. 878:2712–2718. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Pliskova M, Vondracek J, Kren V, Gazak R,
Sedmera P, Walterova D, Psotova J, Simanek V and Machala M: Effects
of silymarin flavonolignans and synthetic silybin derivatives on
estrogen and aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation. Toxicology.
215:80–89. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao L, Tao X, Qi Y, Xu L, Yin L and Peng
J: Protective effect of dioscin against doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity via adjusting microRNA-140-5p-mediated myocardial
oxidative stress. Redox Bio. 16:189–198. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yao H, Tao X, Xu L, Qi Y, Yin L, Han X, Xu
Y, Zheng L and Peng J: Dioscin alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease through adjusting lipid metabolism via SIRT1/AMPK signaling
pathway. Pharmacol Res. 131:51–60. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu Y, Mao Z, Xu L, Yin L, Tao X, Tang Z,
Qi Y, Sun P and Peng J: Protective effect of dioscin against
intestinal ischemia/reperfusion injury via adjusting
miR-351-5p-mediated oxidative stress. Pharmacol Res. 137:56–63.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng L, Han X, Hu Y, Zhao X, Yin L, Xu L,
Qi Y, Xu Y, Han X, Liu K and Peng J: Dioscin ameliorates intestinal
ischemia/ reperfusion injury via adjusting
miR-351-5p/MAPK13-mediated inflammation and apoptosis. Pharmacol
Res. 139:431–439. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qiao Y, Xu L, Tao X, Yin L, Qi Y, Xu Y,
Han X, Tang Z, Ma X, Liu K and Peng J: Protective effects of
dioscin against fructose-induced renal damage via adjusting
Sirt3-mediated oxidative stress, fibrosis, lipid metabolism and
inflammation. Toxicol Lett. 284:37–45. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng L, Yin L, Xu L, Qi Y, Li H, Xu Y,
Han X, Liu K and Peng J: Potective effect of dioscin against
thioacetamide-induced acute liver injury via FXR/AMPK signaling
pathway in vivo. Biomed Pharmacother. 97:481–488. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yin L, Qi Y, Xu Y, Xu L, Han X, Tao X,
Song S and Peng J: Dioscin inhibits HSC-T6 cell migration via
adjusting SDC-4: Insights from iTRAQ-based quantitative proteomics.
Front Pharmacol. 8:6652017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Tao X, Yin L, Xu L, Xu Y, Qi Y,
Han X, Song S, Zhao Y, Lin Y, et al: Protective effects of dioscin
against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity via regulating
miR-34a/Sirt1 signal pathway. Br J Pharmacol. 174:2512–2527. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yao H, Xu Y, Yin L, Tao X, Xu L, Qi Y, Han
X, Sun P, Liu K and Peng J: Dioscin protects ANIT-induced
intrahepatic cholestasis through regulating transporters, apoptosis
and oxidative stress. Front Pharmacol. 8:1162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu Y, Tao X, Han X, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y,
Zhao Y, Xu Y, Wang C and Peng J: Dioscin attenuates gastric
ischemia/reperfusion injury through the down-regulation of
PKC/ERK1/2 signaling via PKCα and PKCβ2 inhibition. Chem Bio
Interact. 258:234–244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Qi M, Yin L, Xu L, Tao X, Qi Y, Han X,
Wang C, Xu Y, Sun H, Liu K and Peng J: Dioscin alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory kidney injury via the
microRNA let-7i/TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway. Pharmacol Res.
111:509–522. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tao X, Yin L, Xu L and Peng J: Dioscin: A
diverse acting natural compound with therapeutic potential in
metabolic diseases, cancer, inflammation and infections. Pharmacol
Res. 137:259–269. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhao X, Yin L, Fang L, Xu L, Sun P, Xu M,
Liu K and Peng J: Protective effects of dioscin against systemic
inflammatory response syndromevia adjusting TLR2/MyD88/NF-κb signal
pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 65:458–469. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lv L, Zheng L, Dong D, Xu L, Yin L, Xu Y,
Qi Y, Han X and Peng J: Dioscin, a natural steroid saponin, induces
apoptosis and DNA damage through reactive oxygen species: A
potential new drug for treatment of glioblastoma multiforme. Food
Chem Toxicol. 59:657–669. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Si L, Zheng L, Xu L, Yin L, Han X, Qi Y,
Xu Y, Wang C and Peng J: Dioscin suppresses human laryngeal cancer
cells growth via induction of cell-cycle arrest and MAPK-mediated
mitochondrial-derived apoptosis and inhibition of tumor invasion.
Eur J Pharmacol. 774:105–117. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tao X, Xu L, Yin L, Han X, Qi Y, Xu Y,
Song S, Zhao Y and Peng J: Dioscin induces prostate cancer cell
apoptosis through activation of estrogen receptor-β. Cell Death
Dis. 8:e29892017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wei Y, Xu Y, Han X, Qi Y, Xu L, Xu Y, Yin
L, Sun H, Liu K and Peng J: Anti-cancer effects of dioscin on three
kinds of human lung cancer cell lines through inducing DNA damage
and activating mitochondrial signal pathway. Food Chem Toxicol.
59:118–128. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao X, Tao X, Xu L, Yin L, Qi Y, Xu Y,
Han X and Peng J: Dioscin induces apoptosis in human cervical
carcinoma HeLa and SiHa cells through ROS-mediated DNA damage and
the mitochondrial signaling pathway. Molecules. 21:7302016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhao X, Xu L, Zheng L, Yin L, Qi Y, Han X,
Xu Y and Peng J: Potent effects of dioscin against gastric cancer
in vitro and in vivo. Phytomedicine. 23:274–282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kou Y, Ji L, Wang H, Wang W, Zheng H, Zhou
J, Liu L, Qi X, Liu Z, Du B and Lu L: Connexin 43 upregulation by
dioscin inhibits melanoma progression via suppressing malignancy
and inducing M1 polarization. Int J Cancer. 141:1690–1703. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang Y, Fu M, Liu J, Yang Y, Yu Y, Li J,
Pan W, Fan L, Li G, Li X and Wang X: Inhibition of tumor metastasis
by targeted daunorubicin and dioscin codelivery liposomes modified
with PFV for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer. Int J
Nanomedicine. 14:4071–4090. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zeng N, Hongbo T, Xu Y, Wu M and Wu Y:
Anticancer activity of caffeic acid nbutyl ester against A431 skin
carcinoma cell line occurs via induction of apoptosis and
inhibition of the mTOR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
17:5652–5657. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhao J, Xu Y, Wang C, Ding Y, Chen M, Wang
Y, Peng J, Li L and Lv L: Soluplus/TPGS mixed micelles for dioscin
delivery in cancer therapy. Drug Dev Ind Pharm. 43:1197–1204. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Z, Wang CZ, Du GJ, Qi LW, Calway T,
He TC, Du W and Yuan CS: Genistein induces G2/M cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis via ATM/p53-dependent pathway in human colon cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 43:289–296. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ling G, Ahmadian A, Persson A, Unden AB,
Afink G, Williams C, Uhlén M, Toftgård R, Lundeberg J and Pontén F:
PATCHED and p53 gene alterations in sporadic and hereditary basal
cell cancer. Oncogene. 53:7770–7778. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chang IY, Kim JH, Park KH and Yoon SP:
Experimental varicocele induces p53-dependent germ cell apoptosis
through activation of γ-H2AX. Urol Int. 85:216–220. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lee CF, Yang JS, Tsai FJ, Chiang NN, Lu
CC, Huang YS, Chen C and Chen FA: Kaempferol induces
ATM/p53-mediated death receptor and mitochondrial apoptosis in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Oncol. 48:2007–2014.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Maira F, Catania A, Candido S, Russo AE,
McCubrey JA, Libra M, Malaponte G and Fenga C: Molecular targeted
therapy in melanoma: A way to reverse resistance to conventional
drugs. Curr Drug Deliv. 9:17–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu J, Yin S, Reddy N, Spencer C and Sheng
S: Bax mediates the apoptosis-sensitizing effect of maspin. Cancer
Res. 64:1703–1711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Nikolaou V, Stratigos A, Bafaloukos D and
Katsambas A: Antiangiogenic and antiapoptotic treatment in advanced
melanoma. Clin Dermatol. 31:257–263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sarig-Nadir O and Seliktar D: The role of
matrix metalloproteinases in regulating neuronal and nonneuronal
cell invasion into PEGylated fibrinogen hydrogels. Biomaterials.
31:6411–6416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhu Y, Zhou J, Xia H, Chen X, Qiu M, Huang
J, Liu S, Tang Q, Lang N, Liu Z, et al: The Rho GTPase RhoE is a
p53-regulated candidate tumor suppressor in cancer cells. Int J
Oncol. 44:896–904. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Takeba Y, Matsumoto N, Watanabe M,
Takenoshita-Nakaya S, Ohta Y, Kumai T, Takagi M, Koizumi S, Asakura
T and Otsubo T: The Rho kinase inhibitor fasudil is involved in
p53-mediated apoptosis in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69:1545–1555. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Dornan D, Shimizu H, Mah A, Dudhela T, Eby
M, O'rourke K, Seshagiri S and Dixit VM: ATM engages
autodegradation of the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP1 after DNA damage.
Science. 313:1122–1126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|