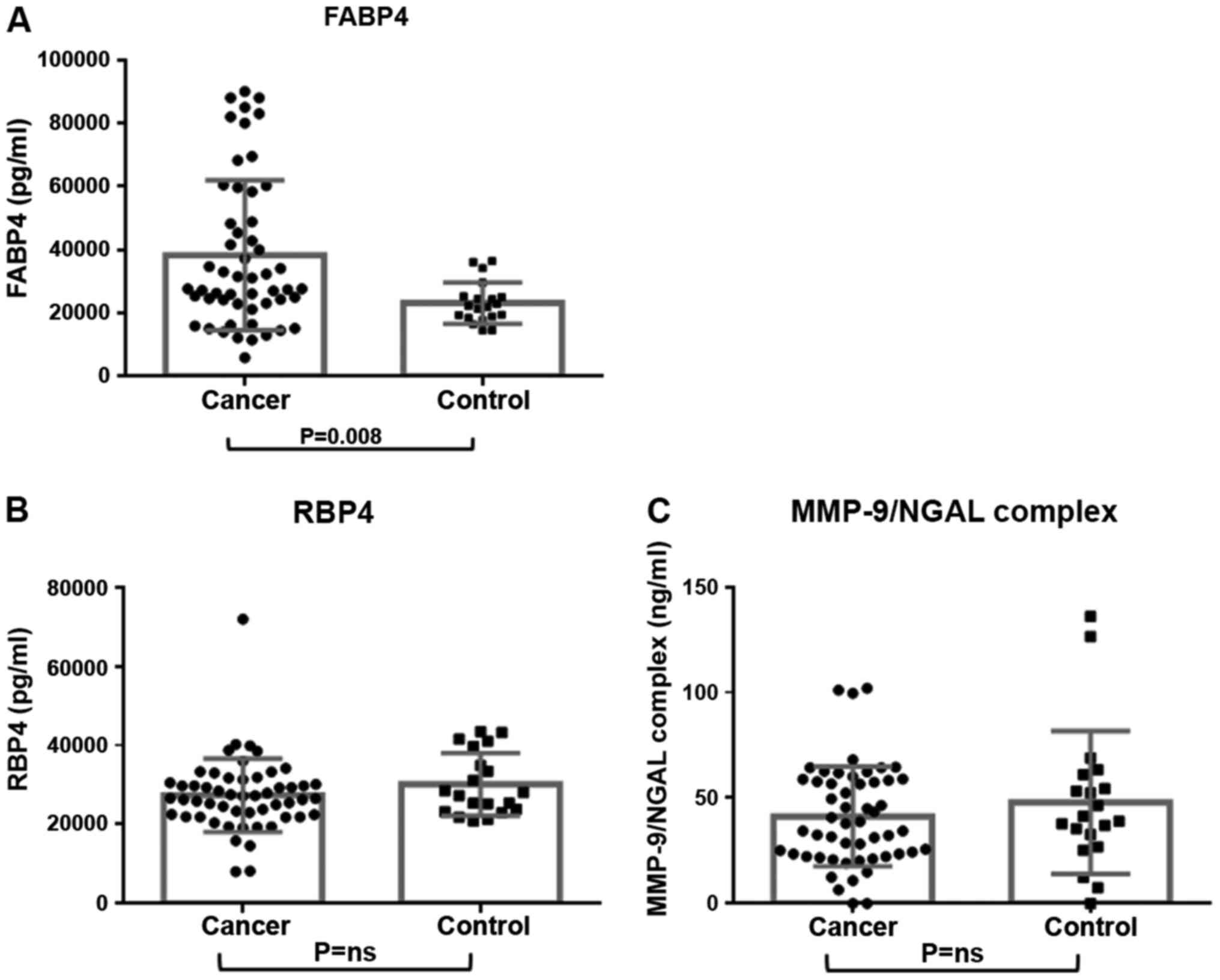
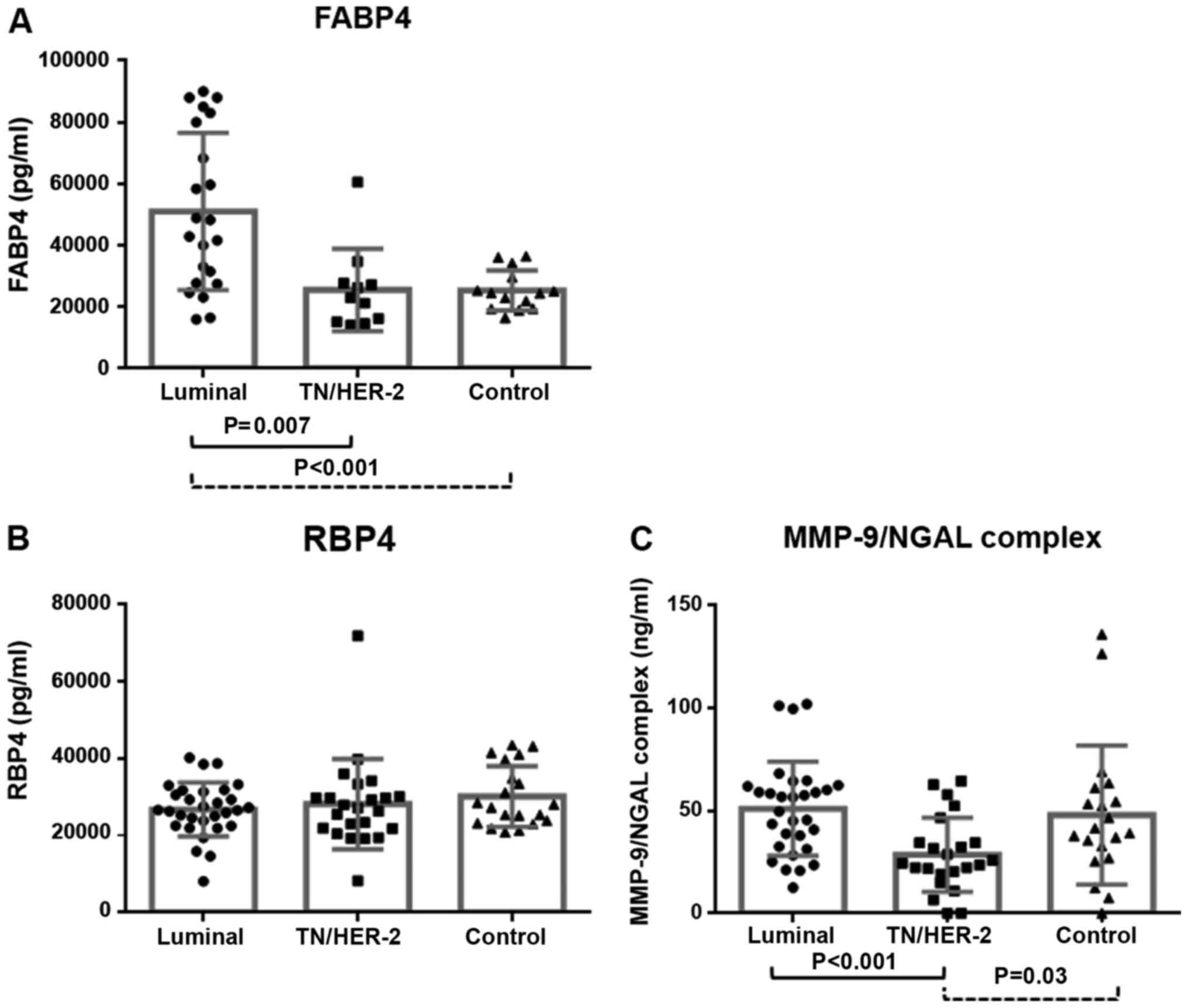
|
1
|
Bertucci F and Birnbaum D: Reasons for
breast cancer heterogeneity. J Biol. 7:62008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Laversanne M, Brewster
DH, Gombe Mbalawa C, Kohler B, Piñeros M, Steliarova-Foucher E,
Swaminathan R, Antoni S, et al: Cancer incidence in five
continents: Inclusion criteria, highlights from Volume X and the
global status of cancer registration. Int J Cancer. 137:2060–2071.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harbeck N, Penault-Llorca F, Cortes J,
Gnant M, Houssami N, Poortmans P, Ruddy K, Tsang J and Cardoso F:
Breast cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5:662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
DeSantis C, Ma J, Bryan L and Jemal A:
Breast cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 64:52–62. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Early Breast Cancer Trialists'
Collaborative Group (EBCTCG), : Effects of chemotherapy and
hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year
survival: An overview of the randomised trials. Lancet.
365:1687–1717. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Colomer R, Aranda-Lopez I, Albanell J,
García-Caballero T, Ciruelos E, López-García MÁ, Cortés J, Rojo F,
Martín M and Palacios-Calvo J: Biomarkers in breast cancer: A
consensus statement by the Spanish Society of Medical Oncology and
the Spanish Society of Pathology. Clin Transl Oncol. 20:815–826.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kashyap D and Kaur H: Cell-free miRNAs as
non-invasive biomarkers in breast cancer: Significance in early
diagnosis and metastasis prediction. Life Sci. 246:1174172020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bourgain C, Pourtau L, Mazouni C, Bungener
M and Bonastre EJ: Imperfect biomarkers for adjuvant chemotherapy
in early stage breast cancer with good prognosis. Soc Sci Med.
246:1127352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guaita-Esteruelas S, Bosquet A, Saavedra
P, Gumà J, Girona J, Lam EW, Amillano K, Borràs J and Masana L:
Exogenous FABP4 increases breast cancer cell proliferation and
activates the expression of fatty acid transport proteins. Mol
Carcinog. 56:208–217. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guaita-Esteruelas S, Saavedra-Garcia P,
Bosquet A, Borràs J, Girona J, Amiliano K, Rodríguez-Balada M,
Heras M, Masana L and Gumà J: Adipose-derived fatty acid-binding
proteins plasma concentrations are increased in breast cancer
patients. Oncologist. 22:1309–1315. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guaita-Esteruelas S, Guma J, Masana L and
Borras J: The peritumoural adipose tissue microenvironment and
cancer. The roles of fatty acid binding protein 4 and fatty acid
binding protein 5. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 462:107–118. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zimmerman AW and Veerkamp JH: New insights
into the structure and function of fatty acid-binding proteins.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 59:1096–1116. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zeng J, Sauter ER and Li B: FABP4: A new
player in obesity-associated breast cancer. Trends Mol Med.
26:437–440. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Prentice KJ, Saksi J and Hotamisligil GS:
Adipokine FABP4 integrates energy stores and counterregulatory
metabolic responses. J Lipid Res. 60:734–740. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cao H, Sekiya M, Ertunc ME, Burak MF,
Mayers JR, White A, Inouye K, Rickey LM, Ercal BC, Furuhashi M, et
al: Adipocyte lipid chaperone AP2 is a secreted adipokine
regulating hepatic glucose production. Cell Metab. 17:768–778.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hao J, Zhang Y, Yan X, Yan F, Sun Y, Zeng
J, Waigel S, Yin Y, Fraig MM, Egilmez NK, et al: Circulating
adipose fatty acid binding protein is a new link underlying
obesity-associated breast/mammary tumor development. Cell Metab.
28:689–705 e5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ginestier C, Hur MH, Charafe-Jauffret E,
Monville F, Dutcher J, Brown M, Jacquemier J, Viens P, Kleer CG,
Liu S, et al: ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human
mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell
Stem Cell. 1:555–567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peek ME, Bhatnagar A, McCarty NA and
Zughaier SM: Pyoverdine, the major siderophore in pseudomonas
aeruginosa, evades NGAL recognition. Interdiscip Perspect Infect
Dis. 2012:8435092012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Flowe DR: The lipocalin protein family:
Structure and function. Biochem J. 318:1–14. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kawaguchi R, Yu J, Honda J, Hu J,
Whitelegge J, Ping P, Wiita P, Bok D and Sun H: A membrane receptor
for retinol binding protein mediates cellular uptake of vitamin A.
Science. 315:820–825. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Berry DC, Jin H, Majumdar A and Noy N:
Signaling by vitamin A and retinol-binding protein regulates gene
expression to inhibit insulin responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:4340–4345. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Norseen J, Hosooka T, Hammarstedt A, Yore
MM, Kant S, Aryal P, Kiernan UA, Phillips DA, Maruyama H, Kraus BJ,
et al: Retinol-binding protein 4 inhibits insulin signaling in
adipocytes by inducing proinflammatory cytokines in macrophages
through a c-Jun N-terminal kinase- and toll-like receptor
4-dependent and retinol-independent mechanism. Mol Cell Biol.
32:2010–2019. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abola MV, Thompson CL, Chen Z, Chak A,
Berger NA, Kirwan JP and Li L: Serum levels of retinol-binding
protein 4 and risk of colon adenoma. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:L1–L4.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng Y, Liu C, Zhang N, Wang S and Zhang
Z: Proteomics analysis for finding serum markers of ovarian cancer.
Biomed Res Int. 2014:1790402014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen Y, Azman SN, Kerishnan JP, Zain RB,
Chen YN, Wong YL and Gopinath SC: Identification of host-immune
response protein candidates in the sera of human oral squamous cell
carcinoma patients. PLoS One. 9:e1090122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Formelli F, Meneghini E, Cavadini E,
Camerini T, Di Mauro MG, De Palo G, Veronesi U, Berrino F and
Micheli A: Plasma retinol and prognosis of postmenopausal breast
cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:42–48. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiao C, Cui L, Ma A, Li N and Si H:
Elevated Serum Levels of Retinol-Binding Protein 4 Are Associated
with Breast Cancer Risk: A Case-Control Study. PLoS One.
11:e01674982016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Provatopoulou X, Gounaris A, Kalogera E,
Zagouri F, Flessas I, Goussetis E, Nonni A, Papassotiriou I and
Zografos G: Circulating levels of matrix metalloproteinase-9
(MMP-9), neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) and
their complex MMP-9/NGAL in breast cancer disease. BMC Cancer.
9:3902009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Barasch J, Hollmen M, Deng R, Hod EA,
Rupert PB, Abergel RJ, Allred BE, Xu K, Darrah SF, Tekabe Y, et al:
Disposal of iron by a mutant form of lipocalin 2. Nat Commun.
7:129732016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chakraborty S, Kaur S, Guha S and Batra
SK: The multifaceted roles of neutrophil gelatinase associated
lipocalin (NGAL) in inflammation and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1826:129–169. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Candido S, Abrams SL, Steelman LS,
Lertpiriyapong K, Fitzgerald TL, Martelli AM, Cocco L, Montalto G,
Cervello M, Polesel J, et al: Roles of NGAL and MMP-9 in the tumor
microenvironment and sensitivity to targeted therapy. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1863:438–448. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Torti SV and Torti FM: Iron and cancer:
More ore to be mined. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:342–355. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roli L, Pecoraro V and Trenti T: Can NGAL
be employed as prognostic and diagnostic biomarker in human
cancers? A systematic review of current evidence. Int J Biol
Markers. 32:e53–e61. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen YC, Chang SC, Huang YH, Lee YJ, Chang
CC, Liao JW and Hsu WL: Expression and the molecular forms of
neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and matrix
metalloproteinase 9 in canine mammary tumours. Vet Comp Oncol.
17:427–438. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yan L, Borregaard N, Kjeldsen L and Moses
MA: The high molecular weight urinary matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP) activity is a complex of gelatinase B/MMP-9 and neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL). Modulation of MMP-9
activity by NGAL. J Biol Chem. 276:37258–37265. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sung H, Choi JY, Lee SA, Lee KM, Han S,
Jeon S, Song M, Lee Y, Park SK, Yoo KY, et al: The association
between the preoperative serum levels of lipocalin-2 and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and prognosis of breast cancer. BMC
Cancer. 12:1932012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang H: Matrix Metalloproteinase-9
(MMP-9) as a cancer biomarker and MMP-9 biosensors: Recent
advances. Sensors (Basel). 27:32492018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Goldhirsch A, Winer EP, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Piccart-Gebhart M, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ; Panel members, :
Personalizing the treatment of women with early breast cancer:
Highlights of the St gallen international expert consensus on the
primary therapy of early breast cancer 2013. Ann Oncol.
24:2206–2223. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Goldhirsch A, Wood WC, Coates AS, Gelber
RD, Thürlimann B and Senn HJ; Panel members, : Strategies for
subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of
the St. Gallen international expert consensus on the primary
therapy of early breast cancer 2011. Ann Oncol. 22:1736–1747. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Waks AG and Winer EP: Breast cancer
treatment: A Review. JAMA. 321:288–300. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fragomeni SM, Sciallis A and Jeruss JS:
Molecular Subtypes and Local-Regional Control of Breast Cancer.
Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 27:95–120. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kim S, Lee Y and Koo JS: Differential
expression of lipid metabolism-related proteins in different breast
cancer subtypes. PLoS One. 10:e01194732015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu Q, Li B, Li Z, Li J and Sun S and Sun
S: Cancer-associated adipocytes: key players in breast cancer
progression. J Hematol Oncol. 12:952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Koundouros N and Poulogiannis G:
Reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer.
122:4–22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Moreno-Sanchez R, Rodriguez-Enriquez S,
Marin-Hernandez A and Saavedra E: Energy metabolism in tumor cells.
FEBS J. 274:1393–1418. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Merdad A, Karim S, Schulten HJ, Jayapal M,
Dallol A, Buhmeida A, Al-Thubaity F, GariI MA, Chaudhary AG,
Abuzenadah AM and Al-Qahtani MH: Transcriptomics profiling study of
breast cancer from Kingdom of Saudi Arabia revealed altered
expression of Adiponectin and Fatty Acid Binding Protein4: Is lipid
metabolism associated with breast cancer? BMC Genomics. 16 (Suppl
1):S112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lanning NJ, Castle JP, Singh SJ, Leon AN,
Tovar EA, Sanghera A, MacKeigan JP, Filipp FV and Graveel CR:
Metabolic profiling of triple-negative breast cancer cells reveals
metabolic vulnerabilities. Cancer Metab. 5:62017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tayyari F, Gowda GAN, Olopade OF, Berg R,
Yang HH, Lee MP, Ngwa WF, Mittal SK, Raftery D and Mohammed SI:
Metabolic profiles of triple-negative and luminal A breast cancer
subtypes in African-American identify key metabolic differences.
Oncotarget. 9:11677–11690. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hancke K, Grubeck D, Hauser N, Kreienberg
R and Weiss JM: Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein as a novel
prognostic factor in obese breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer
Res Treat. 119:367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li B, Hao J, Yan X, Kong M and Sauter ER:
A-FABP and oestrogens are independently involved in the development
of breast cancer. Adipocyte. 8:379–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Choi J, Cha YJ and Koo JS: Adipocyte
biology in breast cancer: From silent bystander to active
facilitator. Prog Lipid Res. 69:11–20. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|