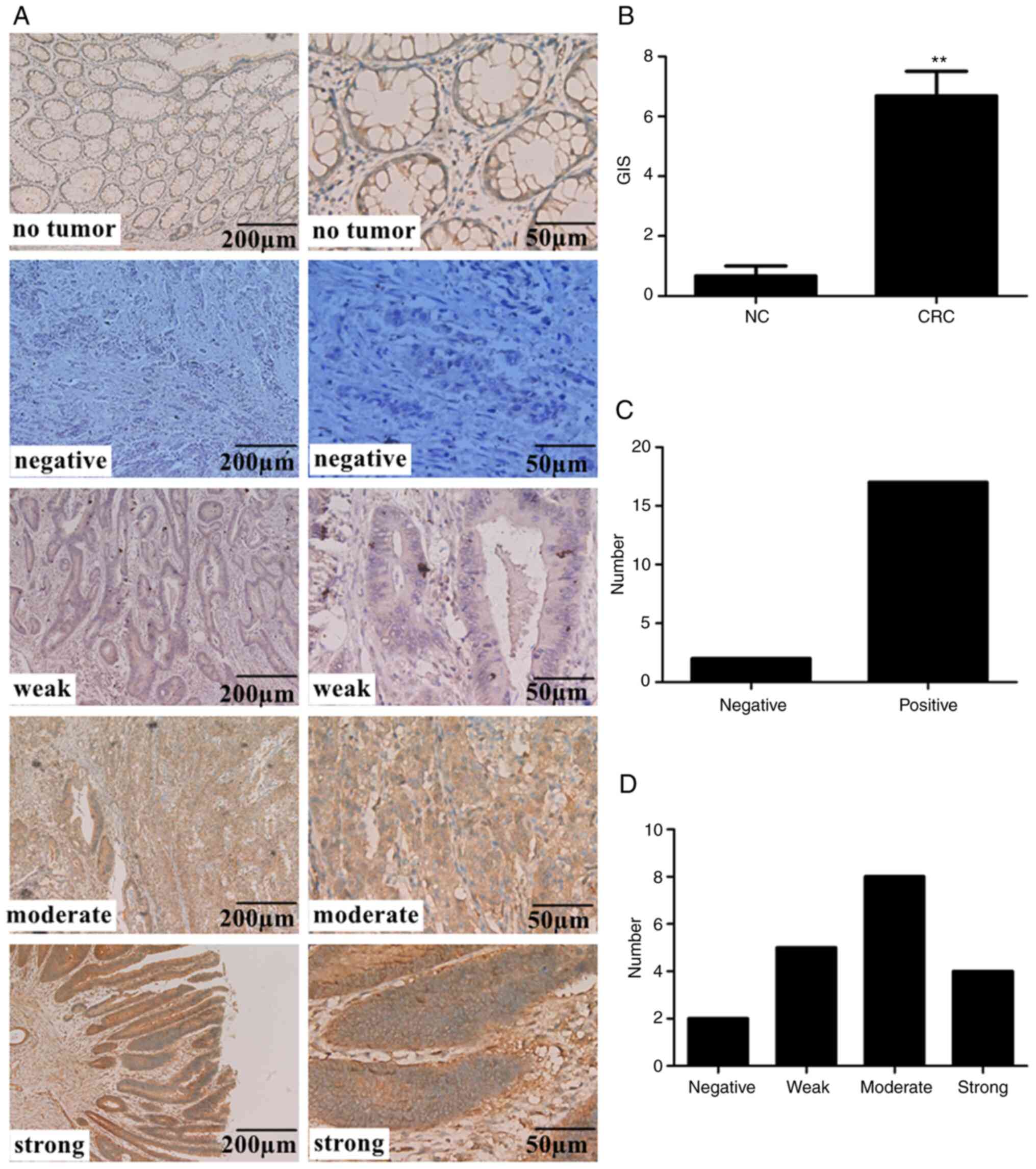
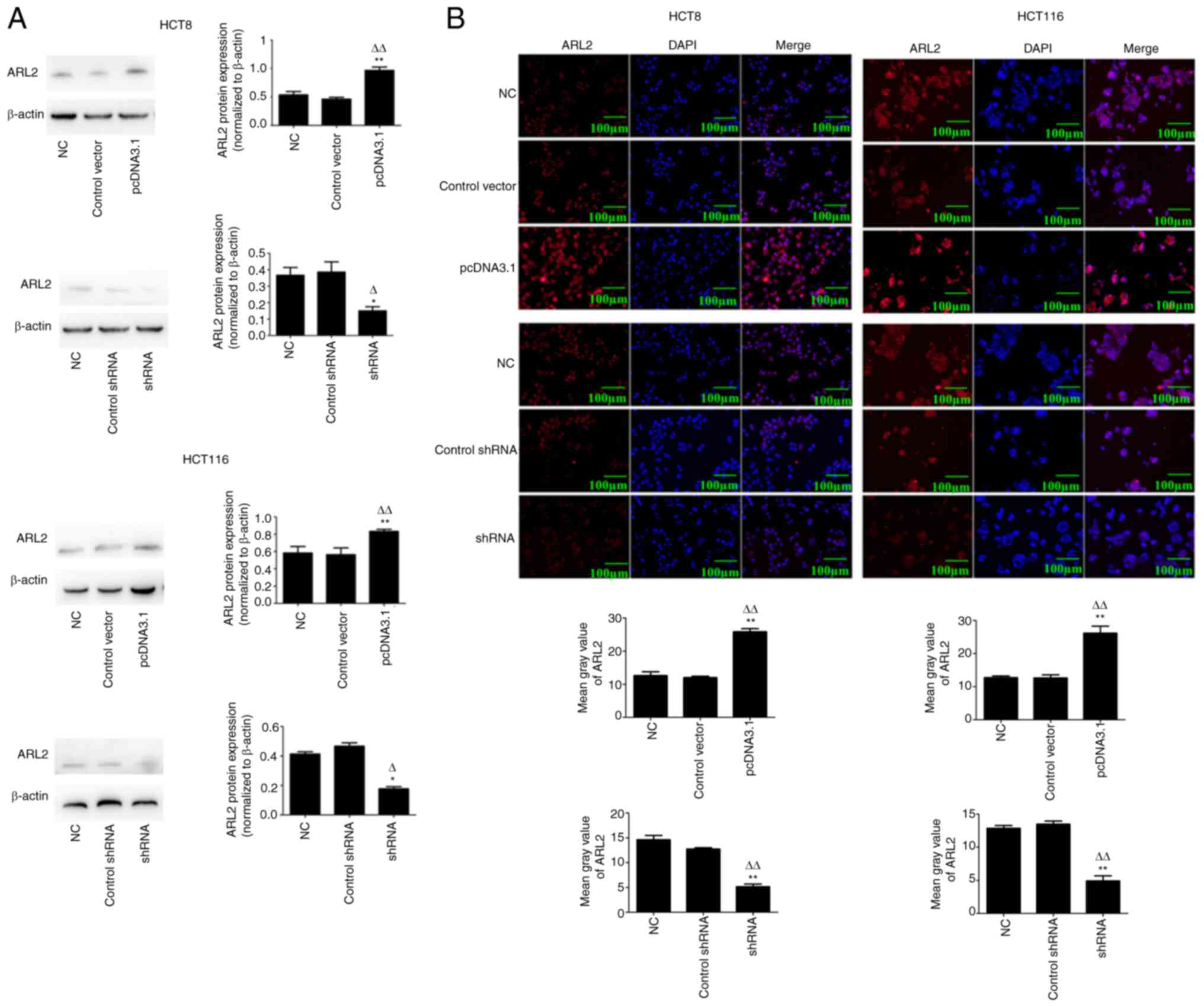
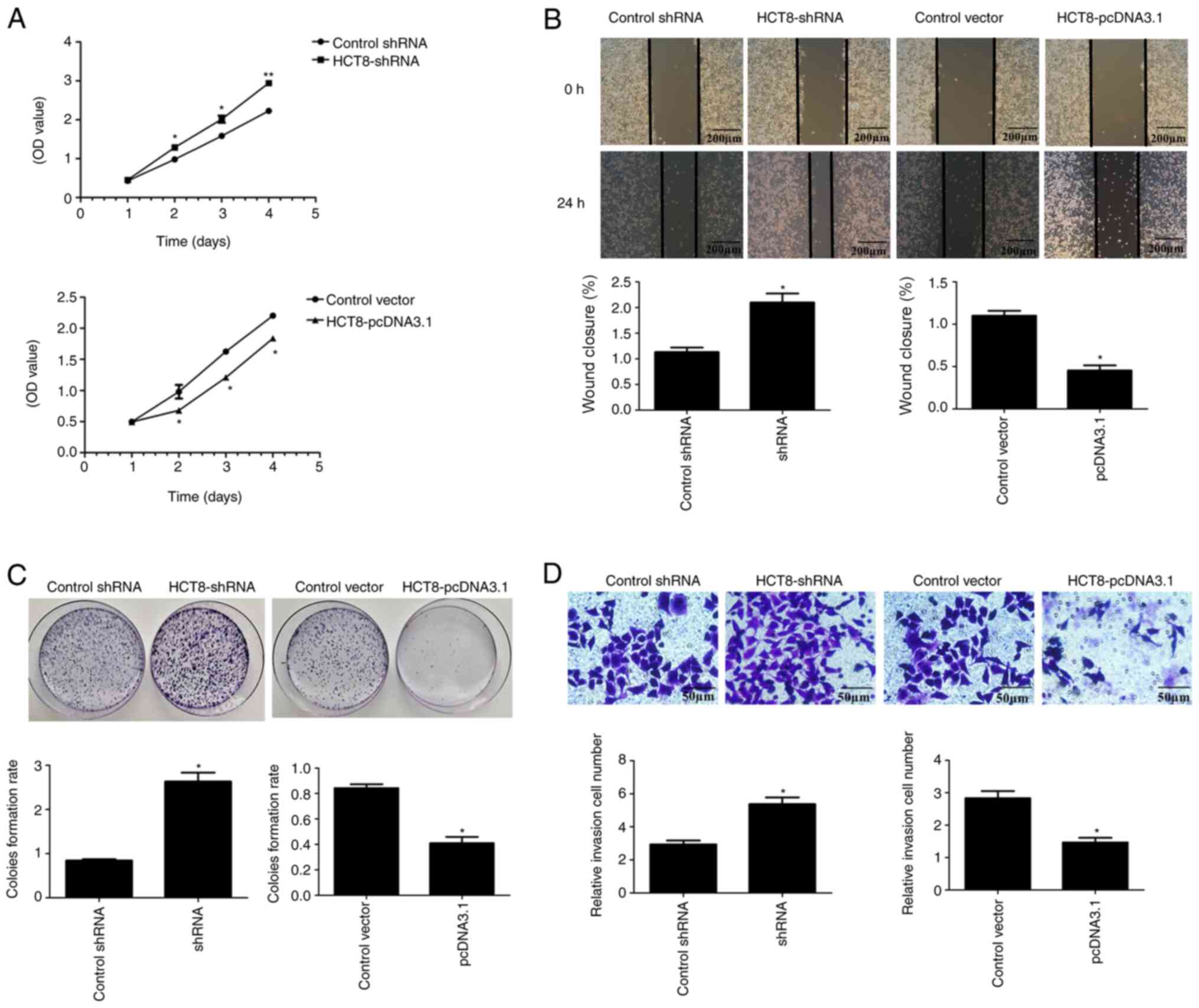
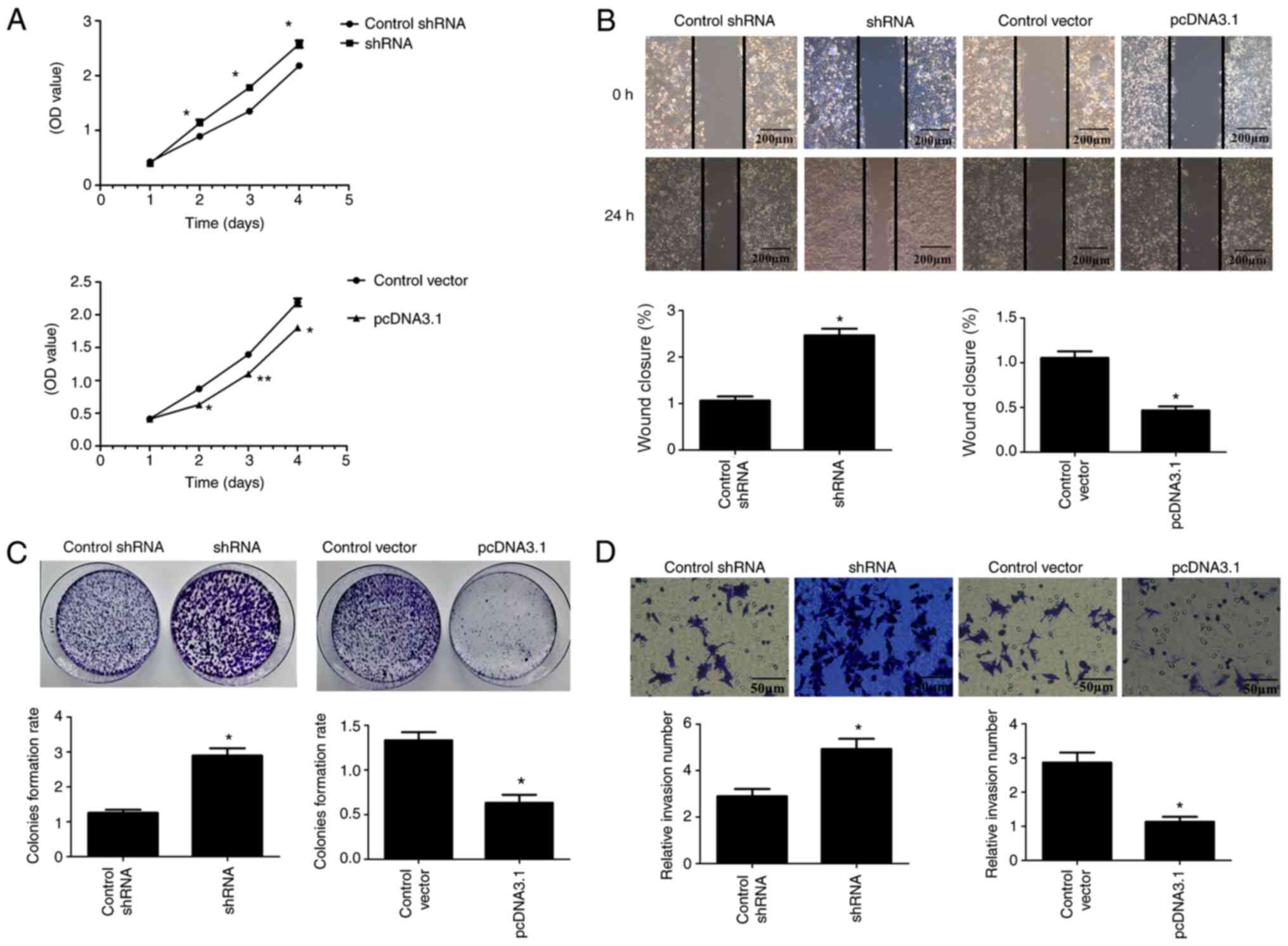
|
1
|
Mattiuzzi C, Sanchis-Gomar F and Lippi G:
Concise update on colorectal cancer epidemiology. Ann Transl Med.
7:609. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gu X, Zheng R, Xia C, Zeng H, Zhang S, Zou
X, Yang Z, Li H and Chen W: Interactions between life expectancy
and the incidence and mortality rates of cancer in China: A
population-based cluster analysis. Cancer Commun (Lond). 38:442018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, Zhang S, Ji JS,
Zou X, Xia C, Sun K, Yang Z, Li H, et al: Changing cancer survival
in China during 2003-15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based
cancer registries. Lancet Glob Health. 6:e555–e567. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dai W, Li Y, Mo S, Feng Y, Zhang L, Xu Y,
Li Q and Cai G: A robust gene signature for the prediction of early
relapse in stage I–III colon cancer. Mol Oncol. 12:463–475. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chen K, Koe CT, Xing ZB, Tian X, Rossi F,
Wang C, Tang Q, Zong W, Hong WJ, Taneja R, et al: Arl2- and
Msps-dependent microtubule growth governs asymmetric division. J
Cell Biol. 212:661–676. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ozdemir ES, Jang H, Gursoy A, Keskin O and
Nussinov R: Arl2-mediated allosteric release of farnesylated KRas4B
from shuttling factor PDEδ. J Phys Chem B. 122:7503–7513. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Stettin D, Waldmann A, Wolters M, Trunz B,
Schauder P and Hahn A: Infection with Helicobacter pylori-outcome
of a cross-sectional investigation. Dtsch Med Wochenschr.
132:2677–2682. 2007.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang F and Cheong JK: The renewed battle
against RAS-mutant cancers. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:1845–1858. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cox AD, Fesik SW, Kimmelman AC, Luo J and
Der CJ: Drugging the undruggable RAS: Mission possible? Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 13:828–851. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Stephen AG, Esposito D, Bagni RK and
McCormick F: Dragging ras back in the ring. Cancer Cell.
25:272–281. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Guan G, Cheng W, Jiang Y, Shan F,
Wu A, Cheng P and Guo Z: ARL2 overexpression inhibits glioma
proliferation and tumorigenicity via down-regulating AXL. BMC
Cancer. 18:5992018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li HJ, Sun XM, Li ZK, Yin QW, Pang H, Pan
JJ, Li X and Chen W: LncRNA UCA1 promotes mitochondrial function of
bladder cancer via the MiR-195/ARL2 signaling pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 43:2548–2561. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Béghin A, Matera E, Brunet-Manquat S and
Dumontet C: Expression of Arl2 is associated with p53 localization
and chemosensitivity in a breast cancer cell line. Cell Cycle.
7:3074–3082. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hass HG, Vogel U, Scheurlen M and Jobst J:
Gene-expression analysis identifies specific patterns of
dysregulated molecular pathways and genetic subgroups of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 36:5087–5096. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Peng R, Men J, Ma R, Wang Q, Wang Y, Sun Y
and Ren J: miR-214 down-regulates ARL2 and suppresses growth and
invasion of cervical cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
484:623–630. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Martinelli E, Martini G, Cardone C,
Troiani T, Liguori G, Vitagliano D, Napolitano S, Morgillo F,
Rinaldi B, Melillo RM, et al: AXL is an oncotarget in human
colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 6:23281–23296. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Uribe DJ, Mandell EK, Watson A, Martinez
JD, Leighton JA, Ghosh S and Rothlin CV: The receptor tyrosine
kinase AXL promotes migration and invasion in colorectal cancer.
PLoS One. 12:e01799792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bläker H: Grading of tumors in the tubular
digestive tract: Esophagus, stomach, colon and rectum. Pathologe.
37:293–298. 2016.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hou P, Li L, Chen F, Chen Y, Liu H, Li J,
Bai J and Zheng J: PTBP3-mediated regulation of ZEB1 mRNA stability
promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 78:387–398. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Qiu C, Bu X and Jiang Z: Protocadherin-10
acts as a tumor suppressor gene, and is frequently downregulated by
promoter methylation in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Rep.
36:383–389. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tohidi F, Sadat SM, Bolhassani A and
Yaghobi R: Construction and production of HIV–VLP harboring MPER-V3
for potential vaccine study. Curr HIV Res. 15:434–439.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seetharaman S and Etienne-Manneville S:
Microtubules at focal adhesions-a double-edged sword. J Cell Sci.
132:jcs2328432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
van Vuuren RJ, Botes M, Jurgens T, Joubert
AM and van den Bout I: Novel sulphamoylated 2-methoxy estradiol
derivatives inhibit breast cancer migration by disrupting
microtubule turnover and organization. Cancer Cell Int. 19:12019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Galmarini CM, Martin M, Bouchet BP,
Guillen-Navarro MJ, Martínez-Diez M, Martinez-Leal JF, Akhmanova A
and Aviles P: Plocabulin, a novel tubulin-binding agent, inhibits
angiogenesis by modulation of microtubule dynamics in endothelial
cells. BMC Cancer. 18:1642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Long LM, He BF, Huang GQ, Guo YH, Liu YS
and Huo JR: microRNA-214 functions as a tumor suppressor in human
colon cancer via the suppression of ADP-ribosylation factor-like
protein 2. Oncol Lett. 9:645–650. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou C, Cunningham L, Marcus AI, Li Y and
Kahn RA: Arl2 and Arl3 regulate different microtubule-dependent
processes. Mol Biol Cell. 17:2476–2487. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Newman LE, Schiavon CR, Zhou C and Kahn
RA: The abundance of the ARL2 GTPase and its GAP, ELMOD2, at
mitochondria are modulated by the fusogenic activity of mitofusins
and stressors. PLoS One. 12:e01751642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song X, Akasaka H and Wang H,
Abbasgholizadeh R, Shin JH, Zang F, Chen J, Logsdon CD, Maitra A,
Bean AJ and Wang H: Hematopoietic progenitor kinase 1
down-regulates the oncogenic receptor tyrosine kinase AXL in
pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem. 295:2348–2358. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bae CA, Ham IH, Oh HJ, Lee D, Woo J, Son
SY, Yoon JH, Lorens JB, Brekken RA, Kim TM, et al: Inhibiting the
GAS6/AXL axis suppresses tumor progression by blocking the
interaction between cancer-associated fibroblasts and cancer cells
in gastric carcinoma. Gastric Cancer. 23:824–836. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vajkoczy P, Knyazev P, Kunkel A, Capelle
HH, Behrndt S, von Tengg-Kobligk H, Kiessling F, Eichelsbacher U,
Essig M, Read TA, et al: Dominant-negative inhibition of the Axl
receptor tyrosine kinase suppresses brain tumor cell growth and
invasion and prolongs survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:5799–5804. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cheng P, Phillips E, Kim SH, Taylor D,
Hielscher T, Puccio L, Hjelmeland AB, Lichter P, Nakano I and
Goidts V: Kinome-wide shRNA screen identifies the receptor tyrosine
kinase AXL as a key regulator for mesenchymal glioblastoma
stem-like cells. Stem Cell Reports. 4:899–913. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|