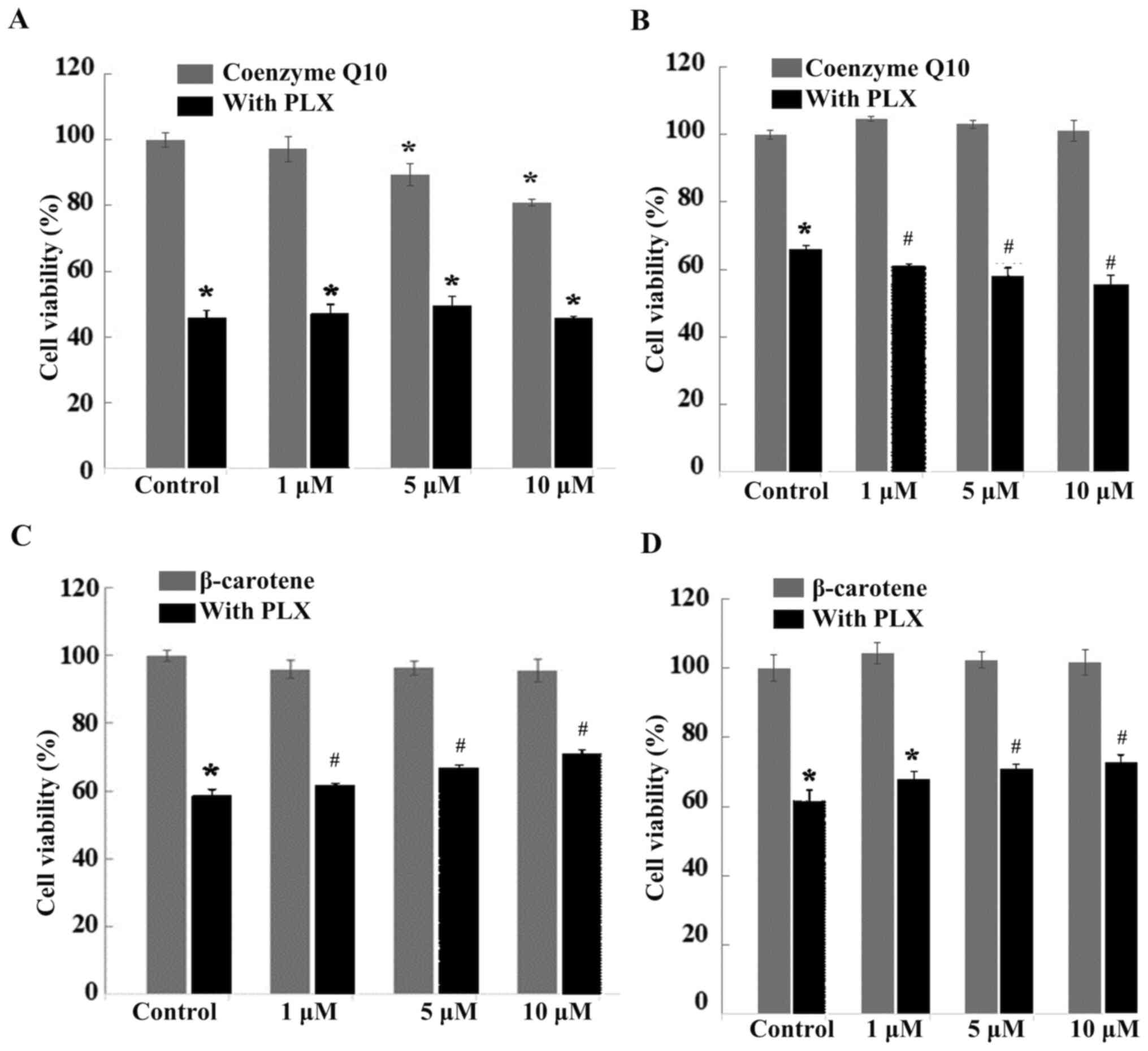
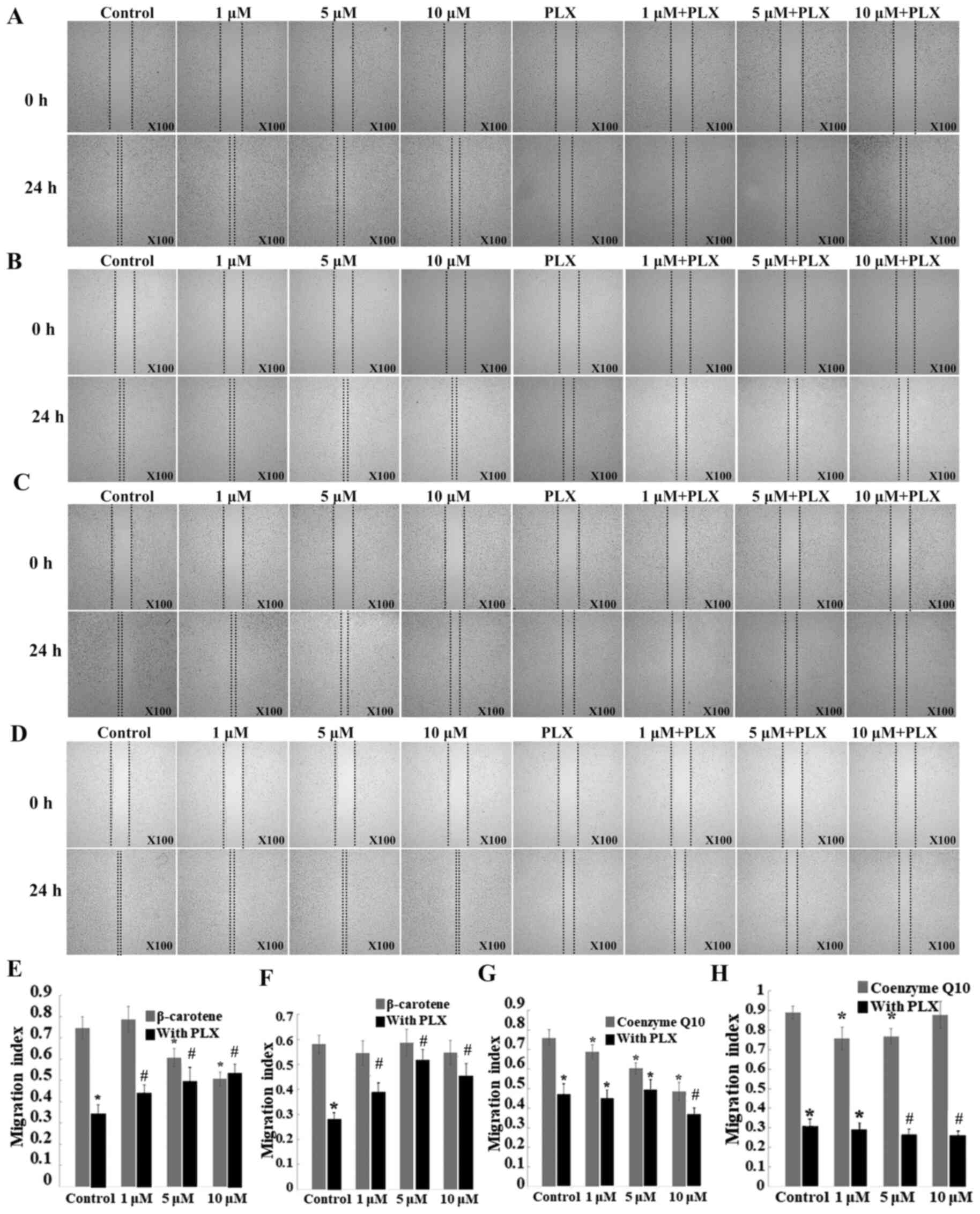
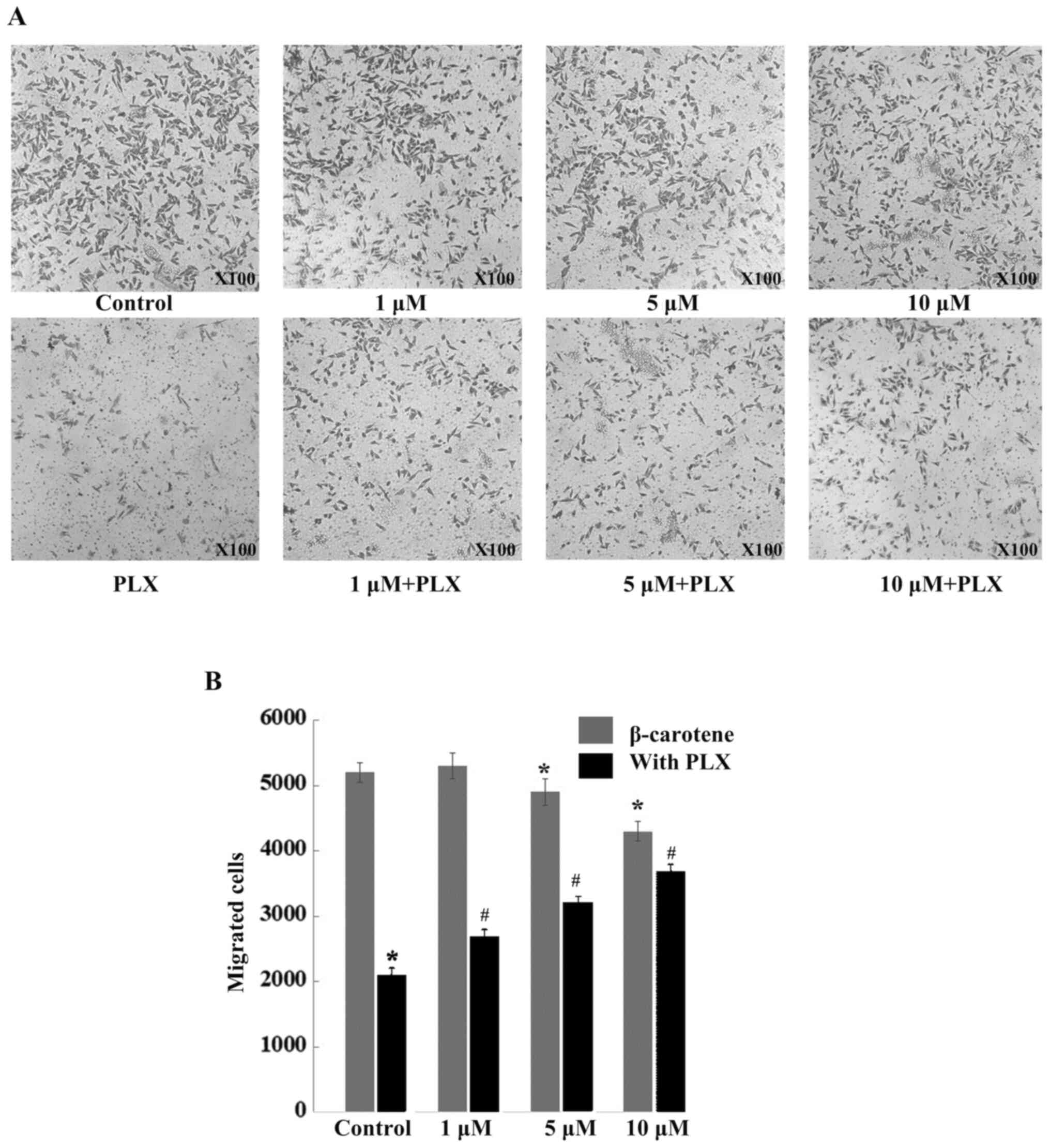
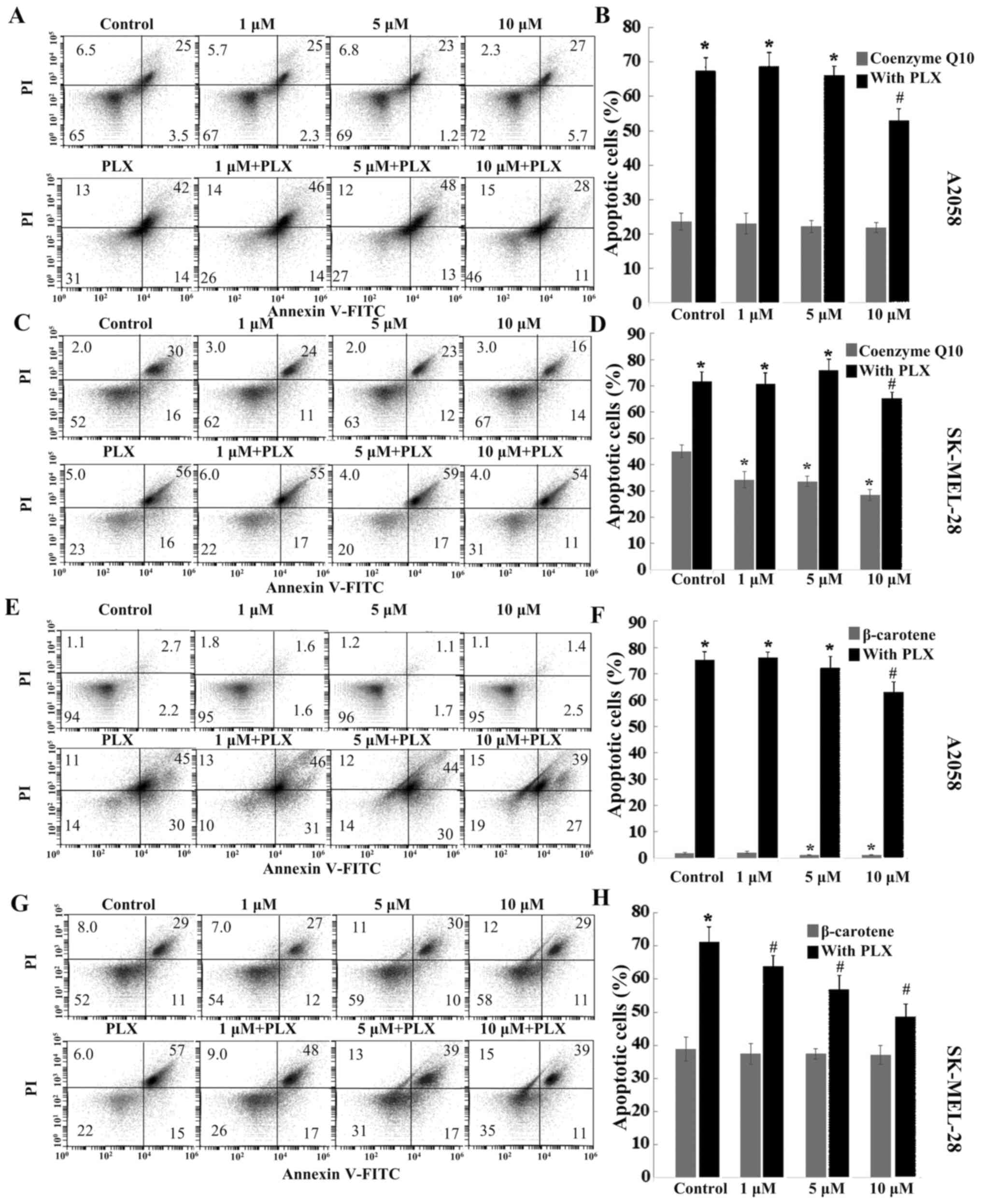
|
1
|
Sandru A, Voinea S, Panaitescu E and
Blidaru A: Survival rates of patients with metastatic malignant
melanoma. J Med Life. 7:572–576. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Karimkhani C, Green AC, Nijsten T,
Weinstock MA, Dellavalle RP, Naghavi M and Fitzmaurice C: The
global burden of melanoma: Results from the global burden of
disease study 2015. Br J Dermatol. 177:134–140. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schadendorf D, van Akkooi ACJ, Berking C,
Griewank KG, Gutzmer R, Hauschild A, Stang A, Roesch A and Ugurel
S: Melanoma. Lancet. 392:971–984. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boniol M, Autier P, Boyle P and Gandini S:
Cutaneous melanoma attributable to sunbed use: Systematic review
and meta-analysis. BMJ. 345:e47572012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu F, Yang X, Geng M and Huang M:
Targeting ERK, an Achilles' Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer
therapy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 8:552–562. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chapman PB, Hauschild A, Robert C, Haanen
JB, Ascierto P, Larkin J, Dummer R, Garbe C, Testori A, Maio M, et
al: Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E
mutation. N Engl J Med. 364:2507–2516. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Menzies AM, Haydu LE, Visintin L, Carlino
MS, Howle JR, Thompson JF, Kefford RF, Scolyer RA and Long GV:
Distinguishing clinicopathologic features of patients with V600E
and V600K BRAF-mutant metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res.
18:3242–3249. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sanchez JN, Wang T and Cohen MS: BRAF and
MEK Inhibitors: Use and resistance in BRAF-mutated cancers. Drugs.
78:549–566. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Livingstone E, Zimmer L, Piel S and
Schadendorf D: PLX4032: Does it keep its promise for metastatic
melanoma treatment? Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19:1439–1449. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bradish JR, Montironi R, Lopez-Beltran A,
Post KM, MacLennan GT and Cheng L: Towards personalized therapy for
patients with malignant melanoma: Molecular insights into the
biology of BRAF mutations. Future Oncol. 9:245–253. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hamid O, Cowey CL, Offner M, Faries M and
Carvajal RD: Efficacy, Safety, and tolerability of approved
combination BRAF and MEK inhibitor regimens for BRAF-mutant
melanoma. Cancers (Basel). 11:16422019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Barrueto L, Caminero F, Cash L, Makris C,
Lamichhane P and Deshmukh RR: Resistance to checkpoint inhibition
in cancer immunotherapy. Transl Oncol. 13:1007382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Flaherty KT, Infante JR, Daud A, Gonzalez
R, Kefford RF, Sosman J, Hamid O, Schuchter L, Cebon J, Ibrahim N,
et al: Combined BRAF and MEK inhibition in melanoma with BRAF V600
mutations. N Engl J Med. 367:1694–1703. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Flaherty KT, Puzanov I, Kim KB, Ribas A,
McArthur GA, Sosman JA, O'Dwyer PJ, Lee RJ, Grippo JF, Nolop K and
Chapman PB: Inhibition of mutated, activated BRAF in metastatic
melanoma. N Engl J Med. 363:809–819. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang CY, Park H, Malone DC, Wang CY,
Wilson DL, Yeh YM, Van Boemmel-Wegmann S and Lo-Ciganic WH: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors and immune-related adverse events in patients
with advanced melanoma: A systematic review and network
meta-analysis. JAMA Netw Open. 3:e2016112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wolchok JD, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R,
Rutkowski P, Grob JJ, Cowey CL, Lao CD, Wagstaff J, Schadendorf D,
Ferrucci PF, et al: Overall survival with combined nivolumab and
ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 377:1345–1356. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ascierto PA, Del Vecchio M, Robert C,
Mackiewicz A, Chiarion-Sileni V, Arance A, Lebbé C, Bastholt L,
Hamid O, Rutkowski P, et al: Ipilimumab 10 mg/kg versus ipilimumab
3 mg/kg in patients with unresectable or metastatic melanoma: A
randomised, double-blind, multicentre, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:611–622. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hodi FS, Chesney J, Pavlick AC, Robert C,
Grossmann KF, McDermott DF, Linette GP, Meyer N, Giguere JK,
Agarwala SS, et al: Combined nivolumab and ipilimumab versus
ipilimumab alone in patients with advanced melanoma: 2-year overall
survival outcomes in a multicentre, randomised, controlled, phase 2
trial. Lancet Oncol. 17:1558–1568. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Robert C, Schachter J, Long GV, Arance A,
Grob JJ, Mortier L, Daud A, Carlino MS, McNeil C, Lotem M, et al:
Pembrolizumab versus ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med.
372:2521–2532. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Larkin J, Chiarion-Sileni V, Gonzalez R,
Grob JJ, Rutkowski P, Lao CD, Cowey CL, Schadendorf D, Wagstaff J,
Dummer R, et al: Five-year survival with combined nivolumab and
ipilimumab in advanced melanoma. N Engl J Med. 381:1535–1546. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dummer R, Ascierto PA, Nathan P, Robert C
and Schadendorf D: Rationale for immune checkpoint inhibitors plus
targeted therapy in metastatic melanoma: A review. JAMA Oncol. Sep
24–2020.doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2020.4401 (Epub ahead of print).
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Godic A, Poljsak B, Adamic M and Dahmane
R: The role of antioxidants in skin cancer prevention and
treatment. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014:8604792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ahmad R, Wani A and Ahsan H: Role of
antioxidants in pathophysiology. J Med Erudite. 2:9–15. 2013.
|
|
25
|
Bairati I, Meyer F, Gélinas M, Fortin A,
Nabid A, Brochet F, Mercier JP, Têtu B, Harel F, Mâsse B, et al: A
randomized trial of antioxidant vitamins to prevent second primary
cancers in head and neck cancer patients. J Natl Cancer Inst.
97:481–488. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Devasagayam TP, Tilak JC, Boloor KK, Sane
KS, Ghaskadbi SS and Lele RD: Free radicals and antioxidants in
human health: Current status and future prospects. J Assoc
Physicians India. 52:794–804. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ma J, Zhang Q, Chen S, Fang B, Yang Q,
Chen C, Miele L, Sarkar FH, Xia J and Wang Z: Mitochondrial
dysfunction promotes breast cancer cell migration and invasion
through HIF1alpha accumulation via increased production of reactive
oxygen species. PLoS One. 8:e694852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kvam E and Tyrrell RM: The role of melanin
in the induction of oxidative DNA base damage by ultraviolet A
irradiation of DNA or melanoma cells. J Invest Dermatol.
113:209–213. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun L, Guo Y, Zhang Y and Zhuang Y:
Antioxidant and Anti-tyrosinase activities of phenolic extracts
from rape bee pollen and inhibitory melanogenesis by cAMP/MITF/TYR
pathway in B16 mouse melanoma cells. Front Pharmacol. 8:1042017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Umemura T, Naoi M, Takahashi T, Fukui Y,
Yasue T, Ohashi M and Nagatsu T: Cytotoxic effect of
1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium ion on human melanoma cell lines,
HMV–II and SK-MEL-44, is dependent on the melanin contents and
caused by inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport. Biochem
Med Metab Biol. 44:51–58. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Oliveira S, Coelho P, Prudêncio C, Vieira
M, Soares R, Guerreiro SG and Fernandes R: Melanoma and obesity:
Should antioxidant vitamins be addressed? Life Sci. 165:83–90.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sarangarajan R, Meera S, Rukkumani R,
Sankar P and Anuradha G: Antioxidants: Friend or foe? Asian Pac J
Trop Med. 10:1111–1116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang G, Yan Y, Ma Y and Yang Y: Vitamin C
at high concentrations induces cytotoxicity in malignant melanoma
but promotes tumor growth at low concentrations. Mol Carcinog.
56:1965–1976. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Le Gal K, Ibrahim MX, Wiel C, Sayin VI,
Akula MK, Karlsson C, Dalin MG, Akyürek LM, Lindahl P, Nilsson J
and Bergo MO: Antioxidants can increase melanoma metastasis in
mice. Sci Transl Med. 7:308re3082015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Piskounova E, Agathocleous M, Murphy MM,
Hu Z, Huddlestun SE, Zhao Z, Leitch AM, Johnson TM, DeBerardinis RJ
and Morrison SJ: Oxidative stress inhibits distant metastasis by
human melanoma cells. Nature. 527:186–191. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Poljsak B and Milisav I: The role of
antioxidants in cancer, friends or foes? Curr Pharm Des.
24:5234–5244. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yamamoto Y and Yamashita S: Plasma ratio
of ubiquinol and ubiquinone as a marker of oxidative stress. Mol
Aspects Med. 18 (Suppl):S79–S84. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Saha SP and Whayne TF Jr: Coenzyme Q-10 in
human health: Supporting evidence? South Med J. 109:17–21. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Overvad K, Diamant B, Holm L, Holmer G,
Mortensen SA and Stender S: Coenzyme Q10 in health and disease. Eur
J Clin Nutr. 53:764–770. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Folkers K, Osterborg A, Nylander M, Morita
M and Mellstedt H: Activities of vitamin Q10 in animal models and a
serious deficiency in patients with cancer. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 234:296–299. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Folkers K: The potential of coenzyme Q10
(NSC-140865) in cancer treatment. Cancer Chemother Rep. 2(4):
19–22. 1974.
|
|
42
|
Rusciani L, Proietti I, Rusciani A,
Paradisi A, Sbordoni G, Alfano C, Panunzi S, De Gaetano A and Lippa
S: Low plasma coenzyme Q10 levels as an independent prognostic
factor for melanoma progression. J Am Acad Dermatol. 54:234–241.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jolliet P, Simon N, Barré J, Pons JY,
Boukef M, Paniel BJ and Tillement JP: Plasma coenzyme Q10
concentrations in breast cancer: Prognosis and therapeutic
consequences. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. 36:506–509.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
El-Attar E, Kamel A, Karmouty A, Wehida N,
Nassra R, El Nemr M and Kandil NS: Assessment of serum CoQ10 levels
and other antioxidant markers in breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 21:465–471. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lund EL, Quistorff B, Spang-Thomsen M and
Kristjansen PE: Effect of radiation therapy on small-cell lung
cancer is reduced by ubiquinone intake. Folia Microbiol (Praha).
43:505–506. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lockwood K, Moesgaard S and Folkers K:
Partial and complete regression of breast cancer in patients in
relation to dosage of coenzyme Q10. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
199:1504–1508. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Roffe L, Schmidt K and Ernst E: Efficacy
of coenzyme Q10 for improved tolerability of cancer treatments: A
systematic review. J Clin Oncol. 22:4418–4424. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Coenzyme Q10 (PDQ(R)): Health Professional
Version. PDQ Cancer Information Summaries Bethesda, MD: 2002
|
|
49
|
Hong SK, Starenki D, Wu PK and Park JI:
Suppression of B-RafV600E melanoma cell survival by targeting
mitochondria using triphenyl-phosphonium-conjugated nitroxide or
ubiquinone. Cancer Biol Ther. 18:106–114. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Diplock AT: Safety of antioxidant vitamins
and beta-carotene. Am J Clin Nutr. 62 (Suppl 6):1510S–1516S. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fiedor J and Burda K: Potential role of
carotenoids as antioxidants in human health and disease. Nutrients.
6:466–488. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Guruvayoorappan C and Kuttan G:
Beta-carotene inhibits tumor-specific angiogenesis by altering the
cytokine profile and inhibits the nuclear translocation of
transcription factors in B16F-10 melanoma cells. Integr Cancer
Ther. 6:258–270. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pradeep CR and Kuttan G: Effect of
beta-carotene on the inhibition of lung metastasis in mice.
Phytomedicine. 10:159–164. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
IARC Working Group on the Evaluation of
Cancer-Preventive Agents, . IARC Handbooks of Cancer Prevention.
Carotenoids; Lyon; 1998
|
|
55
|
Mayne ST, Handelman GJ and Beecher G:
Beta-carotene and lung cancer promotion in heavy smokers-a
plausible relationship? J Natl Cancer Inst. 88:1513–1515. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Stryker WS, Stampfer MJ, Stein EA, Kaplan
L, Louis TA, Sober A and Willett WC: Diet, plasma levels of
beta-carotene and alpha-tocopherol, and risk of malignant melanoma.
Am J Epidemiol. 131:597–611. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Epstein JH: Effects of beta-carotene on
ultraviolet induced cancer formation in the hairless mouse skin.
Photochem Photobiol. 25:211–213. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Black HS: Radical interception by
carotenoids and effects on UV carcinogenesis. Nutr Cancer.
31:212–217. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Alpha-Tocopherol, Beta Carotene Cancer
Prevention Study Group: The effect of vitamin E and beta carotene
on the incidence of lung cancer and other cancers in male smokers.
N Engl J Med. 330:1029–1035. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Middha P, Weinstein SJ, Mannisto S,
Albanes D and Mondul AM: β-carotene supplementation and lung cancer
incidence in the alpha-tocopherol, beta-carotene cancer prevention
study: The role of tar and nicotine. Nicotine Tob Res.
21:1045–1050. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhang YP, Chu RX and Liu H: Vitamin A
intake and risk of melanoma: A meta-analysis. PLoS One.
9:e1025272014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Chen HY, Huang SM, Yang CM and Hu ML:
Diverse effects of β-carotene on secretion and expression of VEGF
in human hepatocarcinoma and prostate tumor cells. Molecules.
17:3981–3988. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jang M, Kim SS and Lee J: Cancer cell
metabolism: Implications for therapeutic targets. Exp Mol Med.
45:e452013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang HM, Yang HL, Thiyagarajan V, Huang
TH, Huang PJ, Chen SC, Liu JY, Hsu LS, Chang HW and Hseu YC:
Coenzyme Q0 enhances ultraviolet b-induced apoptosis in human
estrogen receptor-positive breast (MCF-7) cancer cells. Integr
Cancer Ther. 16:385–396. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen HY, Yang CM, Chen JY, Yueh TC and Hu
ML: Multicarotenoids at physiological levels inhibit metastasis in
human hepatocarcinoma SK-Hep-1 cells. Nutr Cancer. 67:676–686.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lobo V, Patil A, Phatak A and Chandra N:
Free radicals, antioxidants and functional foods: Impact on human
health. Pharmacogn Rev. 4:118–126. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Bowman BA and Russell RM: Present
Knowledge in Nutrition. ILSI Press; Washington D.C.: 2006
|
|
69
|
Hajhashemi V, Vaseghi G, Pourfarzam M and
Abdollahi A: Are antioxidants helpful for disease prevention? Res
Pharm Sci. 5:1–8. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Salganik RI: The benefits and hazards of
antioxidants: Controlling apoptosis and other protective mechanisms
in cancer patients and the human population. J Am Coll Nutr. 20
(Suppl 5):464S–475S. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Prasad KN, Kumar A, Kochupillai V and Cole
WC: High doses of multiple antioxidant vitamins: Essential
ingredients in improving the efficacy of standard cancer therapy. J
Am Coll Nutr. 18:13–25. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Prasad KN, Cole WC, Kumar B and Prasad KC:
Scientific rationale for using high-dose multiple micronutrients as
an adjunct to standard and experimental cancer therapies. J Am Coll
Nutr. 20 (5 Suppl):450S–463S; discussion 473S-475S. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nechuta S, Lu W, Chen Z, Zheng Y, Gu K,
Cai H, Zheng W and Shu XO: Vitamin supplement use during breast
cancer treatment and survival: A prospective cohort study. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 20:262–271. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Lecumberri E, Dupertuis YM, Miralbell R
and Pichard C: Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate
(EGCG) as adjuvant in cancer therapy. Clin Nutr. 32:894–903. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Seely D, Wu P, Fritz H, Kennedy DA, Tsui
T, Seely AJ and Mills E: Melatonin as adjuvant cancer care with and
without chemotherapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized trials. Integr Cancer Ther. 11:293–303. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Prasad KN and Kumar R: Effect of
individual and multiple antioxidant vitamins on growth and
morphology of human nontumorigenic and tumorigenic parotid acinar
cells in culture. Nutr Cancer. 26:11–19. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Jaber S and Polster BM: Idebenone and
neuroprotection: Antioxidant, pro-oxidant, or electron carrier? J
Bioenerg Biomembr. 47:111–118. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Picardo M, Grammatico P, Roccella F,
Roccella M, Grandinetti M, Del Porto G and Passi S: Imbalance in
the antioxidant pool in melanoma cells and normal melanocytes from
patients with melanoma. J Invest Dermatol. 107:322–326. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rusciani L, Proietti I, Paradisi A,
Rusciani A, Guerriero G, Mammone A, De Gaetano A and Lippa S:
Recombinant interferon alpha-2b and coenzyme Q10 as a postsurgical
adjuvant therapy for melanoma: A 3-year trial with recombinant
interferon-alpha and 5-year follow-up. Melanoma Res. 17:177–183.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Martucci A, Reurean-Pintilei D and Manole
A: Bioavailability and sustained plasma concentrations of CoQ10 in
healthy volunteers by a novel oral timed-release preparation.
Nutrients. 11:5272019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Lee BJ, Tseng YF, Yen CH and Lin PT:
Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation (300 mg/day) on
antioxidation and anti-inflammation in coronary artery disease
patients during statins therapy: A randomized, placebo-controlled
trial. Nutr J. 12:1422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Frontinan-Rubio J, Santiago-Mora RM,
Nieva-Velasco CM, Ferrín G, Martínez-González A, Gómez MV, Moreno
M, Ariza J, Lozano E, Arjona-Gutiérrez J, et al: Regulation of the
oxidative balance with coenzyme Q10 sensitizes human glioblastoma
cells to radiation and temozolomide. Radiother Oncol. 128:236–244.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Abdulhasan MK, Li Q, Dai J, Abu-Soud HM,
Puscheck EE and Rappolee DA: CoQ10 increases mitochondrial mass and
polarization, ATP and Oct4 potency levels, and bovine oocyte MII
during IVM while decreasing AMPK activity and oocyte death. J
Assist Reprod Genet. 34:1595–1607. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Awa H, Futamura A, Higashiguchi T, Ito A,
Mori N, Murai M, Ohara H, Chihara T and Kaneko T: Effects of
combined treatment with branched-chain amino acids, citric acid,
L-carnitine, coenzyme Q10, zinc, and various vitamins in
tumor-bearing mice. Biol Pharm Bull. 40:266–271. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Bahar M, Khaghani S, Pasalar P, Paknejad
M, Khorramizadeh MR, Mirmiranpour H and Nejad SG: Exogenous
coenzyme Q10 modulates MMP-2 activity in MCF-7 cell line as a
breast cancer cellular model. Nutr J. 9:622010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Qi XF, Kim DH, Yoon YS, Kim SK, Cai DQ,
Teng YC, Shim KY and Lee KJ: Involvement of oxidative stress in
simvastatin-induced apoptosis of murine CT26 colon carcinoma cells.
Toxicol Lett. 199:277–287. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ashkani-Esfahani S, Bagheri F, Emami Y,
Esmaeilzadeh E, Azarpira N, Hassanabadi N, Keshtkar M, Farjam M,
Koohi-Hosseinabadi O and Noorafshan A: Protective effects of
Co-Enzyme Q10 on thioacetamide-induced acute liver damage and its
correlation with behavioral, biochemical, and pathological factors.
Iran Red Crescent Med J. 18:e291662016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Omenn GS, Goodman GE, Thornquist MD,
Balmes J, Cullen MR, Glass A, Keogh JP, Meyskens FL Jr, Valanis B,
Williams JH Jr, et al: Risk factors for lung cancer and for
intervention effects in CARET, the beta-carotene and retinol
efficacy trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 88:1550–1559. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Druesne-Pecollo N, Latino-Martel P, Norat
T, Barrandon E, Bertrais S, Galan P and Hercberg S: Beta-carotene
supplementation and cancer risk: A systematic review and
metaanalysis of randomized controlled trials. Int J Cancer.
127:172–184. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sowmya Shree G, Yogendra Prasad K, Arpitha
HS, Deepika UR, Nawneet Kumar K, Mondal P and Ganesan P: β-carotene
at physiologically attainable concentration induces apoptosis and
down-regulates cell survival and antioxidant markers in human
breast cancer (MCF-7) cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 436:1–12. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Shultz TD, Chew BP, Seaman WR and Luedecke
LO: Inhibitory effect of conjugated dienoic derivatives of linoleic
acid and beta-carotene on the in vitro growth of human cancer
cells. Cancer Lett. 63:125–133. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Mebratu Y and Tesfaigzi Y: How ERK1/2
activation controls cell proliferation and cell death: Is
subcellular localization the answer? Cell Cycle. 8:1168–1175. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Choi JS, Park SY, Yi EY, Kim YJ and Jeong
JW: Coenzyme Q10 decreases basic fibroblast growth factor
(bFGF)-induced angiogenesis by blocking ERK activation. Oncol Res.
19:455–461. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhao Q, Ma YM, Jing L, Zheng TX, Jiang HF,
Li PA and Zhang JZ: Coenzyme Q10 protects astrocytes from
ultraviolet B-induced damage through inhibition of ERK 1/2 pathway
overexpression. Neurochem Res. 44:1755–1763. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Shin JY, Choi JW, Kim DG, Zhou ZQ, Shin
YK, Seo JH, Song HJ, Choi BM, Bae GS and Park SJ: Protective
effects of Coenzyme Q10 against acute pancreatitis. Int
Immunopharmacol. 88:1069002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Atay C, Kwak T, Lavilla-Alonso S,
Donthireddy L, Richards A, Moberg V, Pilon-Thomas S, Schell M,
Messina JL, Rebecca VW, et al: BRAF targeting sensitizes resistant
melanoma to cytotoxic T cells. Clin Cancer Res. 25:2783–2794. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Pieper N, Zaremba A, Leonardelli S,
Harbers FN, Schwamborn M, Lübcke S, Schrörs B, Baingo J, Schramm A,
Haferkamp S, et al: Evolution of melanoma cross-resistance to
CD8+ T cells and MAPK inhibition in the course of BRAFi
treatment. Oncoimmunology. 7:e14501272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Tan BL, Norhaizan ME, Liew WP and Sulaiman
Rahman H: Antioxidant and oxidative stress: A mutual interplay in
age-related diseases. Front Pharmacol. 9:11622018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Jhun J, Lee SH, Byun JK, Jeong JH, Kim EK,
Lee J, Jung YO, Shin D, Park SH and Cho ML: Coenzyme Q10 suppresses
Th17 cells and osteoclast differentiation and ameliorates
experimental autoimmune arthritis mice. Immunol Lett. 166:92–102.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Pilipow K, Scamardella E, Puccio S, Gautam
S, De Paoli F, Mazza EM, De Simone G, Polletti S, Buccilli M, Zanon
V, et al: Antioxidant metabolism regulates CD8+ T memory
stem cell formation and antitumor immunity. JCI Insight.
3:e1222992018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Molyneux SL, Young JM, Florkowski CM,
Lever M and George PM: Coenzyme Q10: Is there a clinical role and a
case for measurement? Clin Biochem Rev. 29:71–82. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Toti E, Chen CO, Palmery M, Villaño
Valencia D and Peluso I: Non-provitamin A and provitamin A
carotenoids as immunomodulators: Recommended dietary allowance,
therapeutic index, or personalized nutrition? Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018:46378612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bronte E, Bronte G, Novo G, Rinaldi G,
Bronte F, Passiglia F and Russo A: Cardiotoxicity mechanisms of the
combination of BRAF-inhibitors and MEK-inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther.
192:65–73. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|