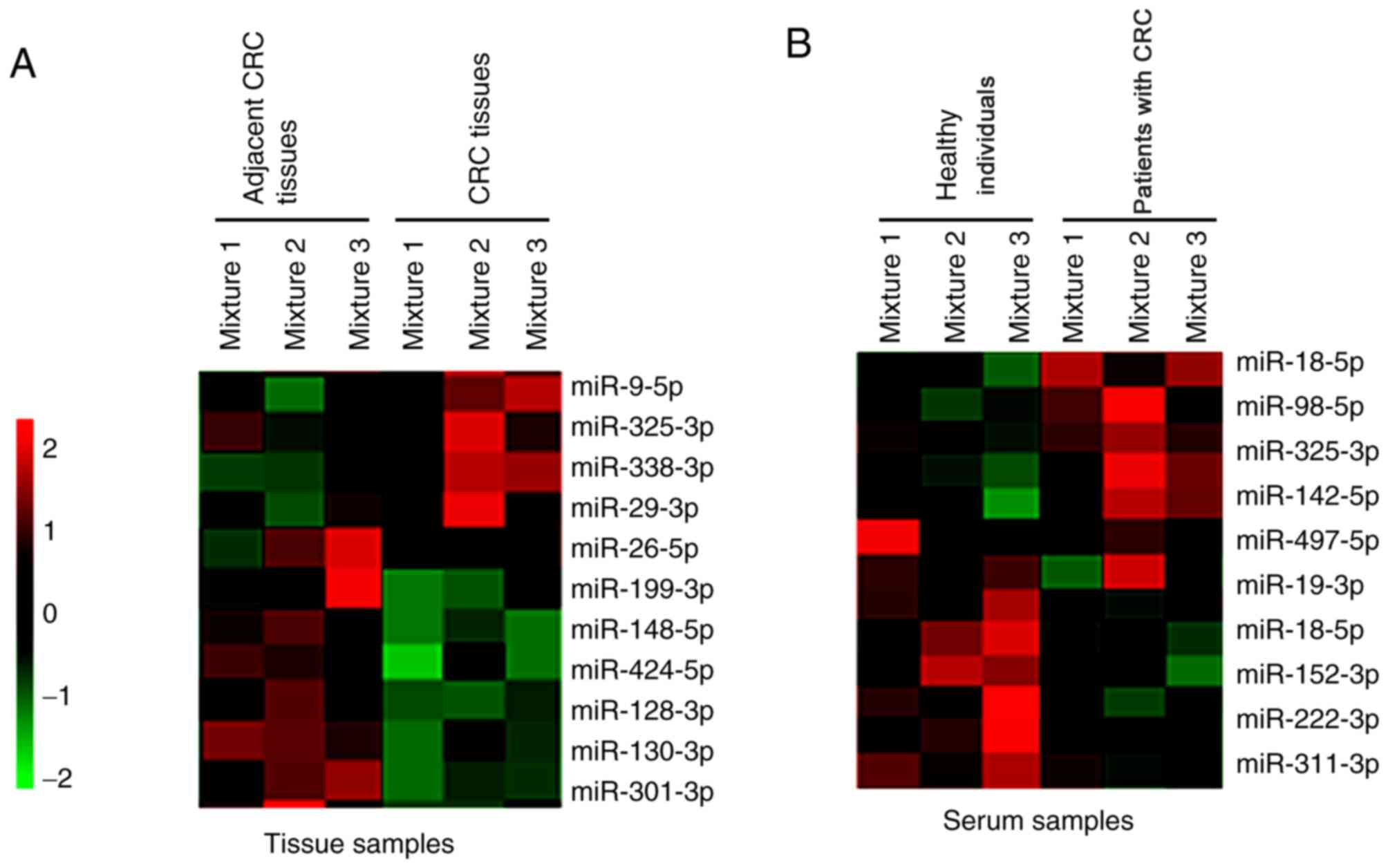
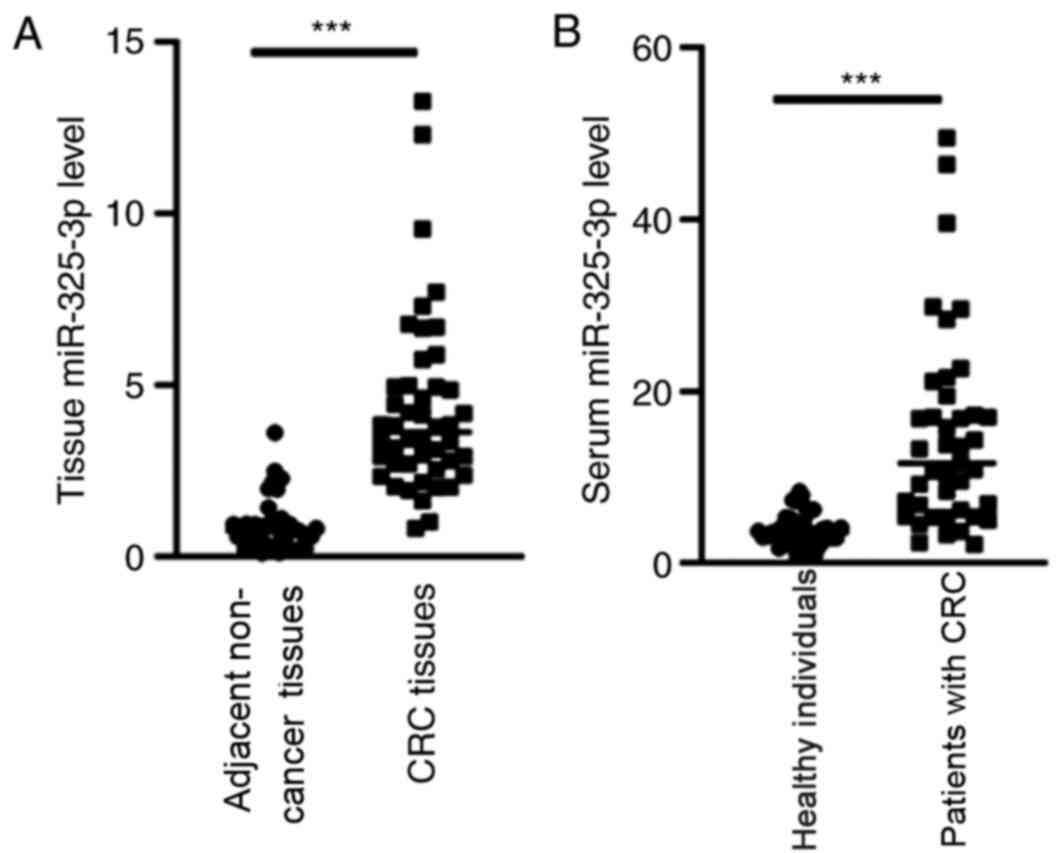
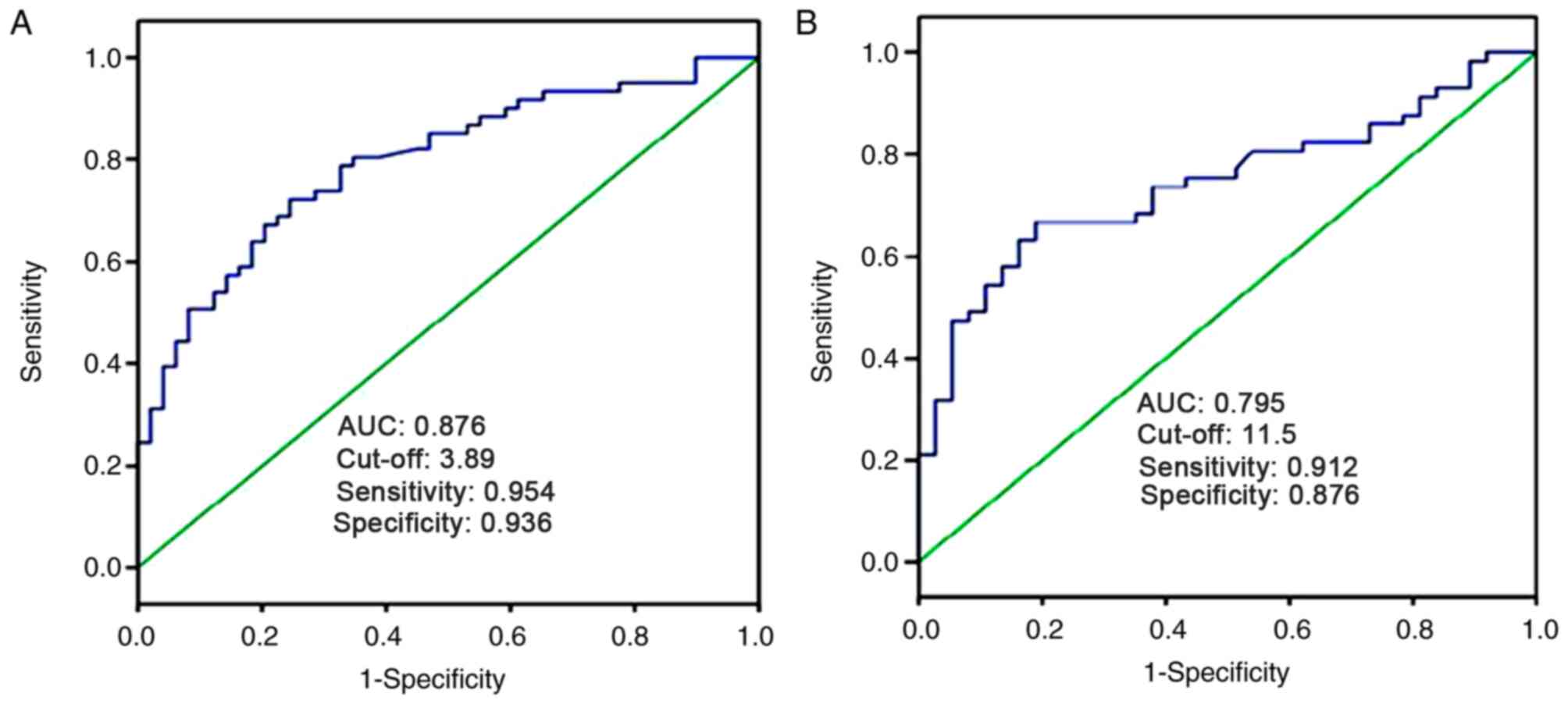
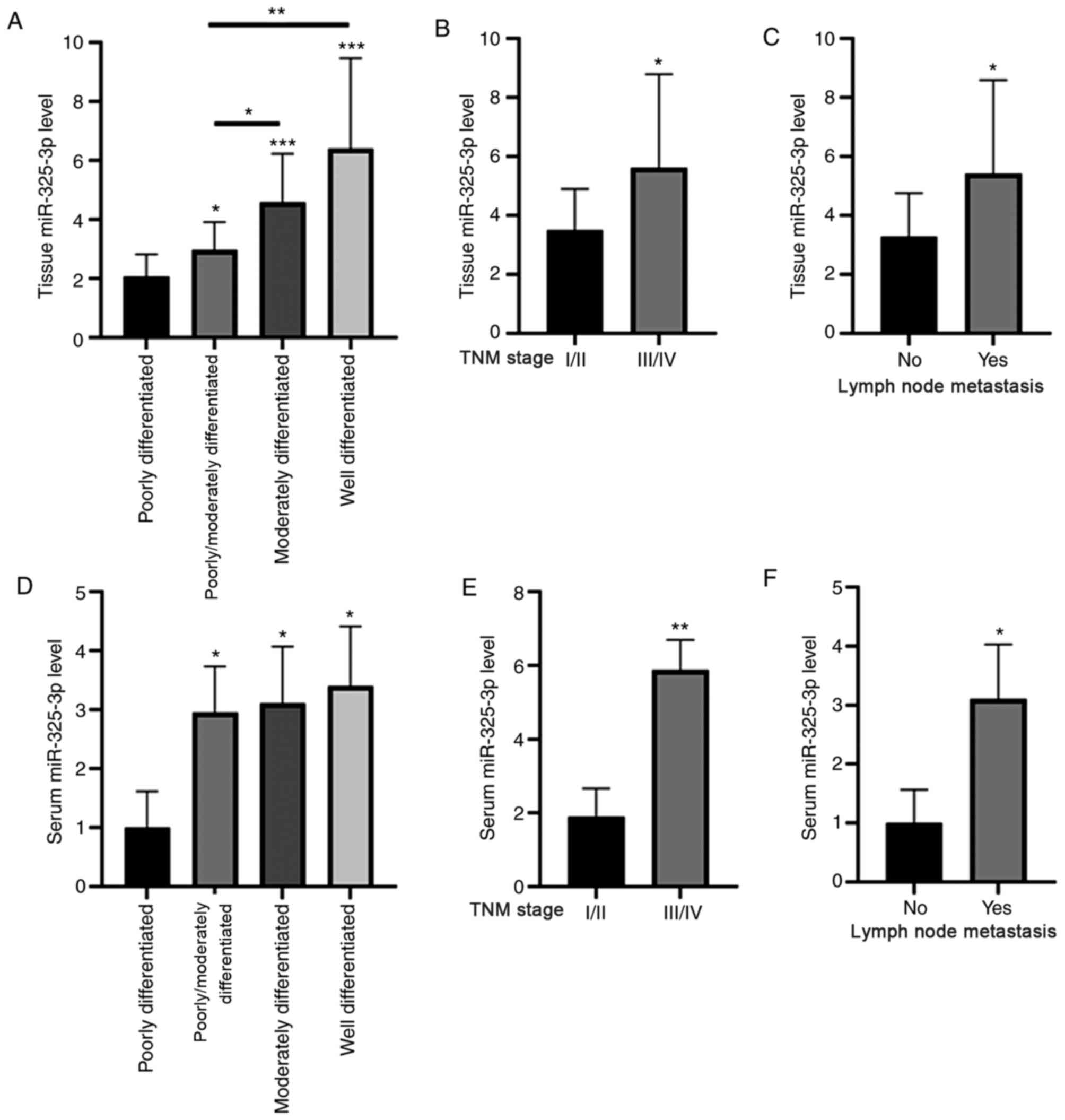
|
1
|
Xu L, Zhang Y, Wang H, Zhang G, Ding Y and
Zhao L: Tumor suppressor miR-1 restrains epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma via the MAPK and
PI3K/AKT pathway. J Transl Med. 12:2442014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang Y, Chen Z and Li J: The current
status of treatment for colorectal cancer in China: A systematic
review. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e82422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu Y, Han S, Lei K, Chang X, Wang K, Li Z
and Liu J: Anti-Warburg effect of rosmarinic acid via miR-155 in
colorectal carcinoma cells. Eur J Cancer Prev. 25:481–489. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang H, Wang R and Wang M: miR-331-3p
suppresses cell invasion and migration in colorectal carcinoma by
directly targeting NRP2. Oncol Lett. 18:6501–6508. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao DW, Li MM, Han JP, Wang Y, Jiang LX
and Chang HL: miR-30c exerts tumor suppressive functions in
colorectal carcinoma by directly targeting BCL9. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 23:3335–3343. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ding T, Cui P, Zhou Y, Chen C, Zhao J,
Wang H, Guo M, He Z and Xu L: Antisense oligonucleotides against
miR-21 inhibit the growth and metastasis of colorectal carcinoma
via the DUSP8 pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 13:244–255. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fasihi A, M Soltani B, Atashi A and Nasiri
S: Introduction of hsa-miR-103a and hsa-miR-1827 and hsa-miR-137 as
new regulators of Wnt signaling pathway and their relation to
colorectal carcinoma. J Cell Biochem. 119:5104–5117. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ghanbari R, Mosakhani N, Asadi J, Nouraee
N, Mowla SJ, Yazdani Y, Mohamadkhani A, Poustchi H, Knuutila S and
Malekzadeh R: Downregulation of plasma MiR-142-3p and MiR-26a-5p in
patients with colorectal carcinoma. Iran J Cancer Prev.
8:e23292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gong L, Ren M, Lv Z, Yang Y and Wang Z:
MiR-92b-3p promotes colorectal carcinoma cell proliferation,
invasion, and migration by inhibiting FBXW7 in vitro and in vivo.
DNA Cell Biol. 37:501–511. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Guo H, Chen Y, Hu X, Qian G, Ge S and
Zhang J: The regulation of Toll-like receptor 2 by miR-143
suppresses the invasion and migration of a subset of human
colorectal carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer. 12:772013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iacona JR and Lutz CS: MiR-146a-5p:
Expression, regulation, and functions in cancer. Wiley Interdiscip
Rev RNA. 10:e15332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang G, Xiong G, Cao Z, Zheng S, You L,
Zhang T and Zhao Y: MiR-497 expression, function and clinical
application in cancer. Oncotarget. 7:55900–55911. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kulda V, Pesta M, Topolcan O, Liska V,
Treska V, Sutnar A, Rupert K, Ludvikova M, Babuska V, Holubec L Jr
and Cerny R: Relevance of miR-21 and miR-143 expression in tissue
samples of colorectal carcinoma and its liver metastases. Cancer
Genet Cytogenet. 200:154–160. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kontos CK, Tsiakanikas P, Avgeris M,
Papadopoulos IN and Scorilas A: MiR-15a-5p, a novel prognostic
biomarker, predicting recurrent colorectal adenocarcinoma. Mol
Diagn Ther. 21:453–464. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Guo J, Fang W, Sun L, Lu Y, Dou L, Huang
X, Tang W, Yu L and Li J: Ultraconserved element uc.372 drives
hepatic lipid accumulation by suppressing miR-195/miR4668
maturation. Nat Commun. 9:6122018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang F, Wang H, Jiang Z, Hu A, Chu L, Sun
Y and Han J: MicroRNA19a mediates gastric carcinoma cell
proliferation through the activation of nuclear factor-κB. Mol Med
Rep. 12:5780–5786. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen S, Dai Y, Zhang X, Jin D, Li X and
Zhang Y: Increased miR-449a expression in colorectal carcinoma
tissues is inversely correlated with serum carcinoembryonic
antigen. Oncol Lett. 7:568–572. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brenner H, Werner S and Chen H:
Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N
Engl J Med. 371:184–185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Igder S, Mohammadiasl J and Mokarram P:
Altered miR-21, miRNA-148a expression in relation to KRAS mutation
status as indicator of adenoma-carcinoma transitional pattern in
colorectal adenoma and carcinoma lesions. Biochem Genet.
57:767–780. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pal I, Rajesh Y, Banik P, Dey G, Dey KK,
Bharti R, Naskar D, Chakraborty S, Ghosh SK, Das SK, et al:
Prevention of epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal
carcinoma by regulation of the E-cadherin-beta-catenin-vinculin
axis. Cancer Lett. 452:254–263. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mylavarapu S, Kumar H, Kumari S, Sravanthi
LS, Jain M, Basu A, Biswas M, Mylavarapu SVS, Das A and Roy M:
Activation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and altered
β-catenin signaling in a novel Indian colorectal carcinoma cell
line. Front Oncol. 9:542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niknami Z, Muhammadnejad A, Ebrahimi A,
Harsani Z and Shirkoohi R: Significance of E-cadherin and Vimentin
as epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in colorectal
carcinoma prognosis. EXCLI J. 19:917–926. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang JJ, Chong QY, Sun XB, You ML, Pandey
V, Chen YJ, Zhuang QS, Liu DX, Ma L, Wu ZS, et al: Autocrine hGH
stimulates oncogenicity, epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
cancer stem cell-like behavior in human colorectal carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:103900–103918. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang P, Gao XY, Yang SQ, Sun ZX, Dian LL,
Qasim M, Phyo AT, Liang ZS and Sun YF: Jatrorrhizine inhibits
colorectal carcinoma proliferation and metastasis through
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:2235–2247. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
You S, Guan Y and Li W:
Epithelialmesenchymal transition in colorectal carcinoma cells is
mediated by DEK/IMP3. Mol Med Rep. 17:1065–1070. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|