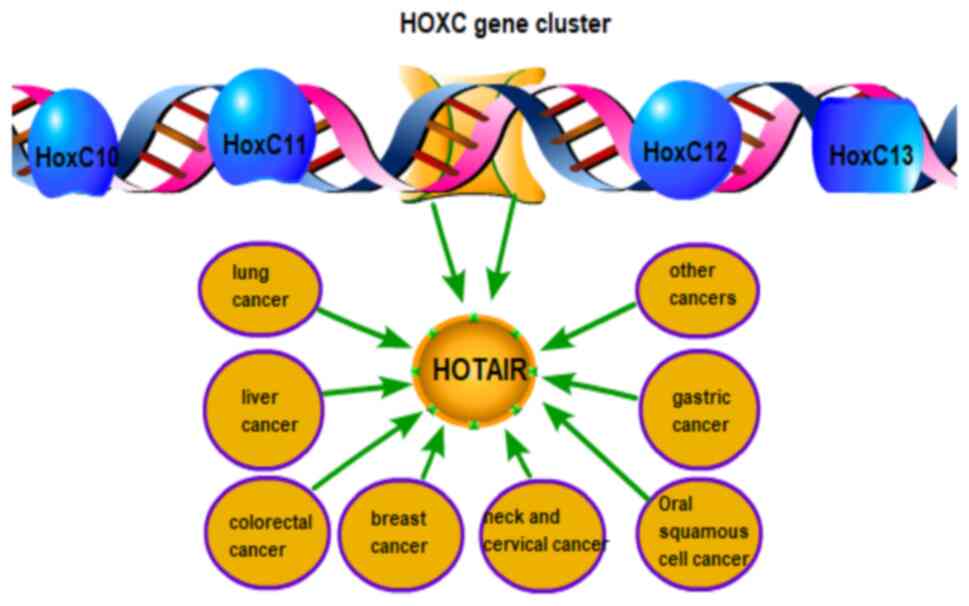
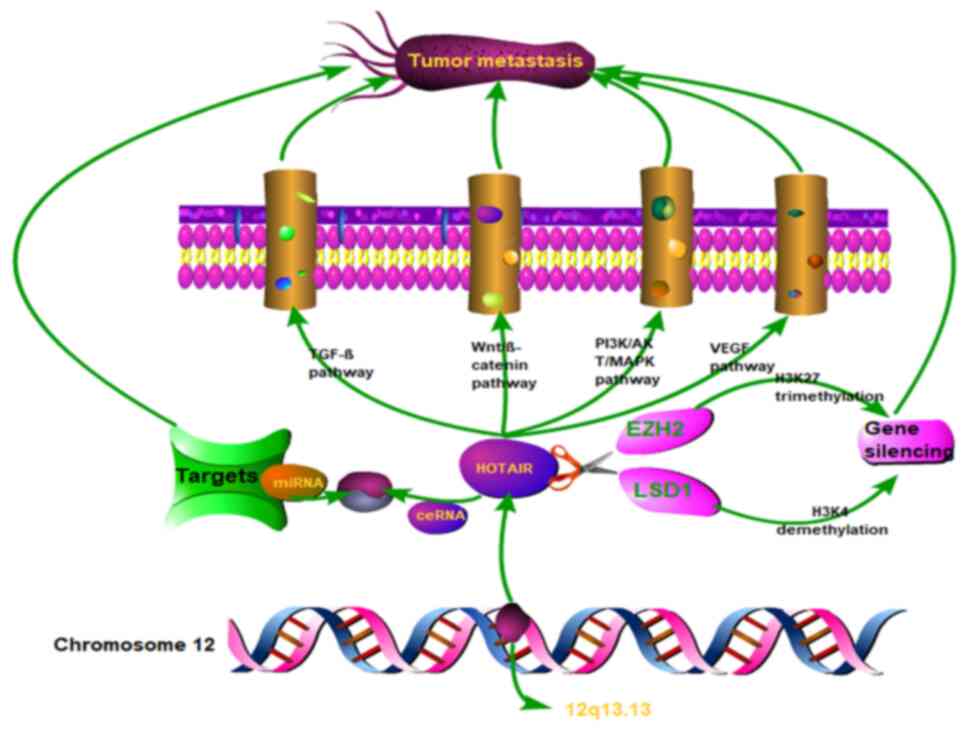
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dušek L, Mužík J, Malúšková D, Májek O,
Pavlík T, Koptíková J, Gregor J, Brabec P and Abrahámová J:
Epidemiology of screening-targeted cancers according to new data of
the Czech national cancer registry. Klin Onkol. 27 (Suppl
2):S19–S39. 2014.(In Czech). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rosenberg AR, Kroon L, Chen L, Li CI and
Jones B: Insurance status and risk of cancer mortality among
adolescents and young adults. Cancer. 121:1279–1286. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Van der Weyden L, Arends MJ, Rust AG,
Poulogiannis G, McIntyre RE and Adams DJ: Increased tumorigenesis
associated with loss of the tumor suppressor gene Cadm1. Mol
Cancer. 11:292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chan XH, Nama S, Gopal F, Rizk P, Ramasamy
S, Sundaram G, Ow GS, Ivshina AV, Tanavde V, Haybaeck J, et al:
Targeting glioma stem cells by functional inhibition of a
prosurvival oncomiR-138 in malignant gliomas. Cell Rep. 2:591–602.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shroff EH, Eberlin LS, Dang VM, Gouw AM,
Gabay M, Adam SJ, Bellovin DI, Tran PT, Philbrick WM, Garcia-Ocana
A, et al: MYC oncogene overexpression drives renal cell carcinoma
in a mouse model through glutamine metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 112:6539–6544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang J, Zhang P, Wang L, Piao HL and Ma
L: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in carcinogenesis and metastasis.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 46:1–5. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baek D, Villén J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi
SP and Bartel DP: The impact of microRNAs on protein output.
Nature. 455:64–71. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Selbach M, Schwanhäusser B, Thierfelder N,
Fang Z, Khanin R and Rajewsky N: Widespread changes in protein
synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature. 455:58–63. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bushati N and Cohen SM: microRNA
functions. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 23:175–205. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wan Y and Chang HY: HOTAIR: Flight of
noncoding RNAs in cancer metastasis. Cell Cycle. 9:3391–3392. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hao Y, Baker D and Ten Dijke P:
TGF-β-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer
metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 20:27672019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Qin W, Kang P, Xu Y, Leng K, Li Z, Huang
L, Gao J, Cui Y and Zhong X: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes
tumorigenesis and forecasts a poor prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma.
Sci Rep. 8:121762018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Tian H, Yang J and Gong Z: Long
noncoding RNAs regulate cell growth, proliferation, and apoptosis.
DNA Cell Biol. 35:459–470. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rossi MN and Antonangeli F: LncRNAs: New
players in apoptosis control. Int J Cell Biol. 2014:4738572014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou S, He Y, Yang S, Hu J, Zhang Q, Chen
W, Xu H, Zhang H, Zhong S, Zhao J and Tang J: The regulatory roles
of lncRNAs in the process of breast cancer invasion and metastasis.
Biosci Rep. 38:BSR201807722018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou T, Ding JW, Wang XA and Zheng XX:
Long noncoding RNAs and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis.
248:51–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bhan A and Mandal SS: LncRNA HOTAIR: A
master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1856:151–164. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nieto MA: The ins and outs of the
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in health and disease. Annu
Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:347–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Skrypek N, Goossens S, De Smedt E,
Vandamme N and Berx G: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition:
Epigenetic reprogramming driving cellular plasticity. Trends Genet.
33:943–959. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Syed V: TGF-β signaling in cancer. J Cell
Biochem. 117:1279–1287. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mani SA, Yang J, Brooks M, Schwaninger G,
Zhou A, Miura N, Kutok JL, Hartwell K, Richardson AL and Weinberg
RA: Mesenchyme forkhead 1 (FOXC2) plays a key role in metastasis
and is associated with aggressive basal-like breast cancers. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:10069–10074. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
David CJ, Huang YH, Chen M, Su J, Zou Y,
Bardeesy N, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA and Massagué J: TGF-β tumor
suppression through a lethal EMT. Cell. 164:1015–1030. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wong SHM, Fang CM, Chuah LH, Leong CO and
Ngai SC: E-cadherin: Its dysregulation in carcinogenesis and
clinical implications. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 121:11–22. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gupta RA, Shah N, Wang KC, Kim J, Horlings
HM, Wong DJ, Tsai MC, Hung T, Argani P, Rinn JL, et al: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer
metastasis. Nature. 464:1071–1076. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu XL, Lu RY, Wang LK, Wang YY, Dai YJ,
Wang CY, Yang YJ, Guo F, Xue J and Yang DD: Long noncoding RNA
HOTAIR silencing inhibits invasion and proliferation of human colon
cancer LoVo cells via regulating IGF2BP2. J Cell Biochem. Oct
18–2018.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dasgupta P, Kulkarni P, Majid S, Shahryari
V, Hashimoto Y, Bhat NS, Shiina M, Deng G, Saini S, Tabatabai ZL,
et al: MicroRNA-203 inhibits long noncoding RNA HOTAIR and
regulates tumorigenesis through epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition pathway in renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cancer Ther.
17:1061–1069. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hong Q, Li O, Zheng W, Xiao WZ, Zhang L,
Wu D, Cai GY, He JC and Chen XM: LncRNA HOTAIR regulates HIF-1α/AXL
signaling through inhibition of miR-217 in renal cell carcinoma.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e27722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang H, Cai K, Wang J, Wang X, Cheng K,
Shi F, Jiang L, Zhang Y and Dou J: MiR-7, inhibited indirectly by
lincRNA HOTAIR, directly inhibits SETDB1 and reverses the EMT of
breast cancer stem cells by downregulating the STAT3 pathway. Stem
Cells. 32:2858–2868. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gong X and Zhu Z: Long noncoding RNA
HOTAIR contributes to progression in hepatocellular carcinoma by
sponging miR-217-5p. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 35:387–396. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang AH, Tan P, Zhuang Y, Zhang XT, Yu ZB
and Li LN: Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits
invasion and migration of oesophageal cancer cells via
up-regulation of microRNA-204. J Cell Mol Med. 23:6595–6610. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wu Y, Zhang L, Zhang L, Wang Y, Li H, Ren
X, Wei F, Yu W, Liu T, Wang X, et al: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
promotes tumor cell invasion and metastasis by recruiting EZH2 and
repressing E-cadherin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol.
46:2586–2594. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ren Y, Jia HH, Xu YQ, Zhou X, Zhao XH,
Wang YF, Song X, Zhu ZY, Sun T, Dou Y, et al: Paracrine and
epigenetic control of CAF-induced metastasis: The role of HOTAIR
stimulated by TGF-ß1 secretion. Mol Cancer. 17:52018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Song Y, Wang R, Li LW, Liu X, Wang YF,
Wang QX and Zhang Q: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR mediates the
switching of histone H3 lysine 27 acetylation to methylation to
promote epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Int
J Oncol. 54:77–86. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu M, Zhang H, Li Y, Wang R, Li Y, Zhang
H, Ren D, Liu H, Kang C and Chen J: HOTAIR, a long noncoding RNA,
is a marker of abnormal cell cycle regulation in lung cancer.
Cancer Sci. 109:2717–2733. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu YW, Sun M, Xia R, Zhang EB, Liu XH,
Zhang ZH, Xu TP, De W, Liu BR and Wang ZX: LincHOTAIR
epigenetically silences miR34a by binding to PRC2 to promote the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in human gastric cancer. Cell
Death Dis. 6:e18022015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim HJ, Yim GW, Baek SM, Kim JW and Kim
YT: Long noncoding RNA HOTAIR is associated with human cervical
cancer progression. Gynecol Oncol. 133 (Suppl 1):S52014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Berrondo C, Flax J, Kucherov V, Siebert A,
Osinski T, Rosenberg A, Fucile C, Richheimer S and Beckham CJ:
Expression of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR correlates with
disease progression in bladder cancer and is contained in bladder
cancer patient urinary exosomes. PLoS One. 11:e01472362016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Heldin CH, Vanlandewijck M and Moustakas
A: Regulation of EMT by TGFβ in cancer. FEBS Lett. 586:1959–1970.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ochoa-Hernández AB, Juárez-Vázquez CI,
Rosales-Reynoso MA and Barros-Núñez P: WNT-β-catenin signaling
pathway and its relationship with cancer. Cir Cir. 80:389–398.
2012.(In Spanish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Gao JZ, Li J, Du JL and Li XL: Long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR is a marker for hepatocellular carcinoma
progression and tumor recurrence. Oncol Lett. 11:1791–1798. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Salmerón-Bárcenas EG, Illades-Aguiar B,
Del Moral-Hernández O, Ortega-Soto A and Hernández-Sotelo D: HOTAIR
knockdown decreased the activity Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
and increased the mRNA levels of its negative regulators in Hela
cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 53:948–960. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cheng C, Qin Y, Zhi Q, Wang J and Qin C:
Knockdown of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits cisplatin
resistance of gastric cancer cells through inhibiting the PI3K/Akt
and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways by up-regulating miR-34a. Int
J Biol Macromol. 107:2620–2629. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xiao Z, Qu Z, Chen Z, Fang Z, Zhou K,
Huang Z, Guo X and Zhang Y: LncRNA HOTAIR is a prognostic biomarker
for the proliferation and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer via
MiR-203a-3p-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 46:1275–1285. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Li GJ, Ding H and Miao D: Long-noncoding
RNA HOTAIR inhibits immunologic rejection of mouse leukemia cells
through activating the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in a mouse
model of leukemia. J Cell Physiol. 234:10386–10396. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li J, Yang S, Su N, Wang Y, Yu J, Qiu H
and He X: Overexpression of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR leads to
chemoresistance by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in human
ovarian cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:2057–2065. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ge XS, Ma HJ, Zheng XH, Ruan HL, Liao XY,
Xue WQ, Chen YB, Zhang Y and Jia WH: HOTAIR, a prognostic factor in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, inhibits WIF-1 expression and
activates Wnt pathway. Cancer Sci. 104:1675–1682. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ying Y and Tao Q: Epigenetic disruption of
the WNT/beta-catenin signaling pathway in human cancers.
Epigenetics. 4:307–312. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Noorolyai S, Shajari N, Baghbani E,
Sadreddini S and Baradaran B: The relation between PI3K/AKT
signalling pathway and cancer. Gene. 698:120–128. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Petrulea MS, Plantinga TS, Smit JW,
Georgescu CE and Netea-Maier RT: PI3K/Akt/mTOR: A promising
therapeutic target for non-medullary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer
Treat Rev. 41:707–713. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen J, Lin C, Yong W, Ye Y and Huang Z:
Calycosin and genistein induce apoptosis by inactivation of
HOTAIR/p-Akt signaling pathway in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:722–728. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Hales EC, Taub JW and Matherly LH: New
insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling
axis: Targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell
acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cell Signal. 26:149–161. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Salmena L, Carracedo A and Pandolfi PP:
Tenets of PTEN tumor suppression. Cell. 133:403–414. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sun H, Lesche R, Li DM, Liliental J, Zhang
H, Gao J, Gavrilova N, Mueller B, Liu X and Wu H: PTEN modulates
cell cycle progression and cell survival by regulating
phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5,-trisphosphate and Akt/protein kinase B
signaling pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:6199–6204. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yu Y, Lv F, Liang D, Yang Q, Zhang B, Lin
H, Wang X, Qian G, Xu J and You W: HOTAIR may regulate
proliferation, apoptosis, migration and invasion of MCF-7 cells
through regulating the P53/Akt/JNK signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 90:555–561. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Li E, Zhao Z, Ma B and Zhang J: Long
noncoding RNA HOTAIR promotes the proliferation and metastasis of
osteosarcoma cells through the AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Exp Ther
Med. 14:5321–5328. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li Z, Qian J, Li J and Zhu C: Knockdown of
lncRNA-HOTAIR downregulates the drug-resistance of breast cancer
cells to doxorubicin via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway. Exp
Ther Med. 18:435–442. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Pan S, Liu Y, Liu Q, Xiao Y, Liu B, Ren X,
Qi X, Zhou H, Zeng C and Jia L: HOTAIR/miR-326/FUT6 axis
facilitates colorectal cancer progression through regulating
fucosylation of CD44 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochim Biophys
Acta Mol Cell Res. 1866:750–760. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li Z and Luo J: Epigenetic regulation of
HOTAIR in advanced chronic myeloid leukemia. Cancer Manag Res.
10:5349–5362. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Luan W, Li R, Liu L, Ni X, Shi Y, Xia Y,
Wang J, Lu F and Xu B: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR acts as a
competing endogenous RNA to promote malignant melanoma progression
by sponging miR-152-3p. Oncotarget. 8:85401–85414. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Li T, Qin Y, Zhen Z, Shen H, Cong T,
Schiferle E and Xiao S: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR/microRNA-206
sponge regulates STC2 and further influences cell biological
functions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell Prolif.
52:e126512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Itoh N and Ornitz DM: Fibroblast growth
factors: From molecular evolution to roles in development,
metabolism and disease. J Biochem. 149:121–130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ke J, Yao YL, Zheng J, Wang P, Liu YH, Ma
J, Li Z, Liu XB, Li ZQ, Wang ZH and Xue YX: Knockdown of long
non-coding RNA HOTAIR inhibits malignant biological behaviors of
human glioma cells via modulation of miR-326. Oncotarget.
6:21934–21949. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Olsson AK, Dimberg A, Kreuger J and
Claesson-Welsh L: VEGF receptor signalling-in control of vascular
function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:359–371. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Fu WM, Lu YF, Hu BG, Liang WC, Zhu X, Yang
HD, Li G and Zhang JF: Long noncoding RNA Hotair mediated
angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by direct and indirect
signaling pathways. Oncotarget. 7:4712–4723. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Burger RA: Role of vascular endothelial
growth factor inhibitors in the treatment of gynecologic
malignancies. J Gynecol Oncol. 21:3–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li Z and Li Z: Glucose regulated protein
78: A critical link between tumor microenvironment and cancer
hallmarks. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1826:13–22. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Geng YJ, Xie SL, Li Q, Ma J and Wang GY:
Large intervening non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. J Int Med Res. 39:2119–2128.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu XH, Liu ZL, Sun M, Liu J, Wang ZX and
De W: The long non-coding RNA HOTAIR indicates a poor prognosis and
promotes metastasis in non-small cell lung cancer. BMC Cancer.
13:4642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhao WH, Yuan HY, Ren XY, Huang K and Guo
ZY: Association between expression of HOTAIR and invasiveness of
gliomas, and its predictive value. Adv Clin Exp Med. 28:1179–1183.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Kim HJ, Lee DW, Yim GW, Nam EJ, Kim S, Kim
SW and Kim YT: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR is associated with human
cervical cancer progression. Int J Oncol. 46:521–530. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Flavahan WA, Gaskell E and Bernstein BE:
Epigenetic plasticity and the hallmarks of cancer. Science.
357:eaal23802017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Ponting CP, Oliver PL and Reik W:
Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell. 136:629–641.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL,
Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E and
Chang HY: Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin
domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell. 129:1311–1323.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Khalil AM, Guttman M, Huarte M, Garber M,
Raj A, Rivea Morales D, Thomas K, Presser A, Bernstein BE, van
Oudenaarden A, et al: Many human large intergenic noncoding RNAs
associate with chromatin-modifying complexes and affect gene
expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:11667–11672. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ding C, Cheng S, Yang Z, Lv Z, Xiao H, Du
C, Peng C, Xie H, Zhou L, Wu J and Zheng S: Long non-coding RNA
HOTAIR promotes cell migration and invasion via down-regulation of
RNA binding motif protein 38 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int
J Mol Sci. 15:4060–4076. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Godlewski J, Krichevsky AM, Johnson MD,
Chiocca EA and Bronisz A: Belonging to a network-microRNAs,
extracellular vesicles, and the glioblastoma microenvironment.
Neuro Oncol. 17:652–662. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Fan Q, Yang L, Zhang X, Peng X, Wei S, Su
D, Zhai Z, Hua X and Li H: The emerging role of exosome-derived
non-coding RNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Lett. 414:107–115. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gezer U, Özgür E, Cetinkaya M, Isin M and
Dalay N: Long non-coding RNAs with low expression levels in cells
are enriched in secreted exosomes. Cell Biol Int. 38:1076–1079.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ma X, Li Z, Li T, Zhu L, Li Z and Tian NJ:
Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR enhances angiogenesis by induction of
VEGFA expression in glioma cells and transmission to endothelial
cells via glioma cell derived-extracellular vesicles. Am J Transl
Res. 9:5012–5021. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: Molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Gupta GP and Massagué J: Cancer
metastasis: Building a framework. Cell. 127:679–695. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zhang C, Ji Q, Yang Y, Li Q and Wang Z:
Exosome: Function and Role in cancer metastasis and drug
resistance. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 17:15330338187634502018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Yang H, Fu H, Xu W and Zhang X: Exosomal
non-coding RNAs: A promising cancer biomarker. Clin Chem Lab Med.
54:1871–1879. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Tang S, Zheng K, Tang Y, Li Z, Zou T and
Liu D: Overexpression of serum exosomal HOTAIR is correlated with
poor survival and poor response to chemotherapy in breast cancer
patients. J Biosci. 44:372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wang J, Zhou Y, Lu J, Sun Y, Xiao H, Liu M
and Tian L: Combined detection of serum exosomal miR-21 and HOTAIR
as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:1482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhang C, Xu L, Deng G, Ding Y, Bi K, Jin
H, Shu J, Yang J, Deng H, Wang Z and Wang Y: Exosomal HOTAIR
promotes proliferation, migration and invasion of lung cancer by
sponging miR-203. Sci China Life Sci. 63:1265–1268. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Poulet C, Njock MS, Moermans C, Louis E,
Louis R, Malaise M and Guiot J: Exosomal long non-coding RNAs in
lung diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 21:35802020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Yao Z, Jia C, Tai Y, Liang H, Zhong Z,
Xiong Z, Deng M and Zhang Q: Serum exosomal long noncoding RNAs
lnc-FAM72D-3 and lnc-EPC1-4 as diagnostic biomarkers for
hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 12:11843–11863. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang J, Qiu WQ, Zhu H, Liu H, Sun JH,
Chen Y, Shen H, Qian CL and Shen ZY: HOTAIR contributes to the
carcinogenesis of gastric cancer via modulating cellular and
exosomal miRNAs level. Cell Death Dis. 11:7802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|