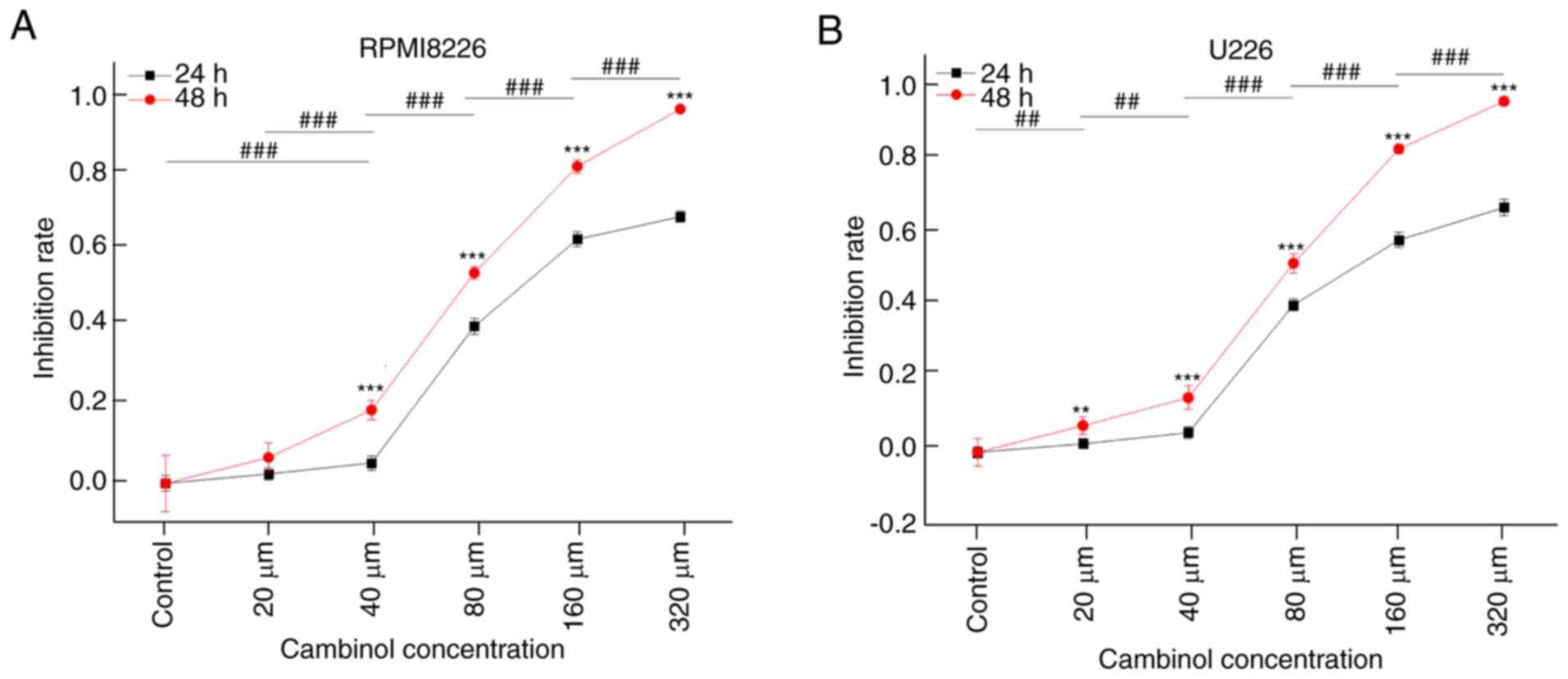
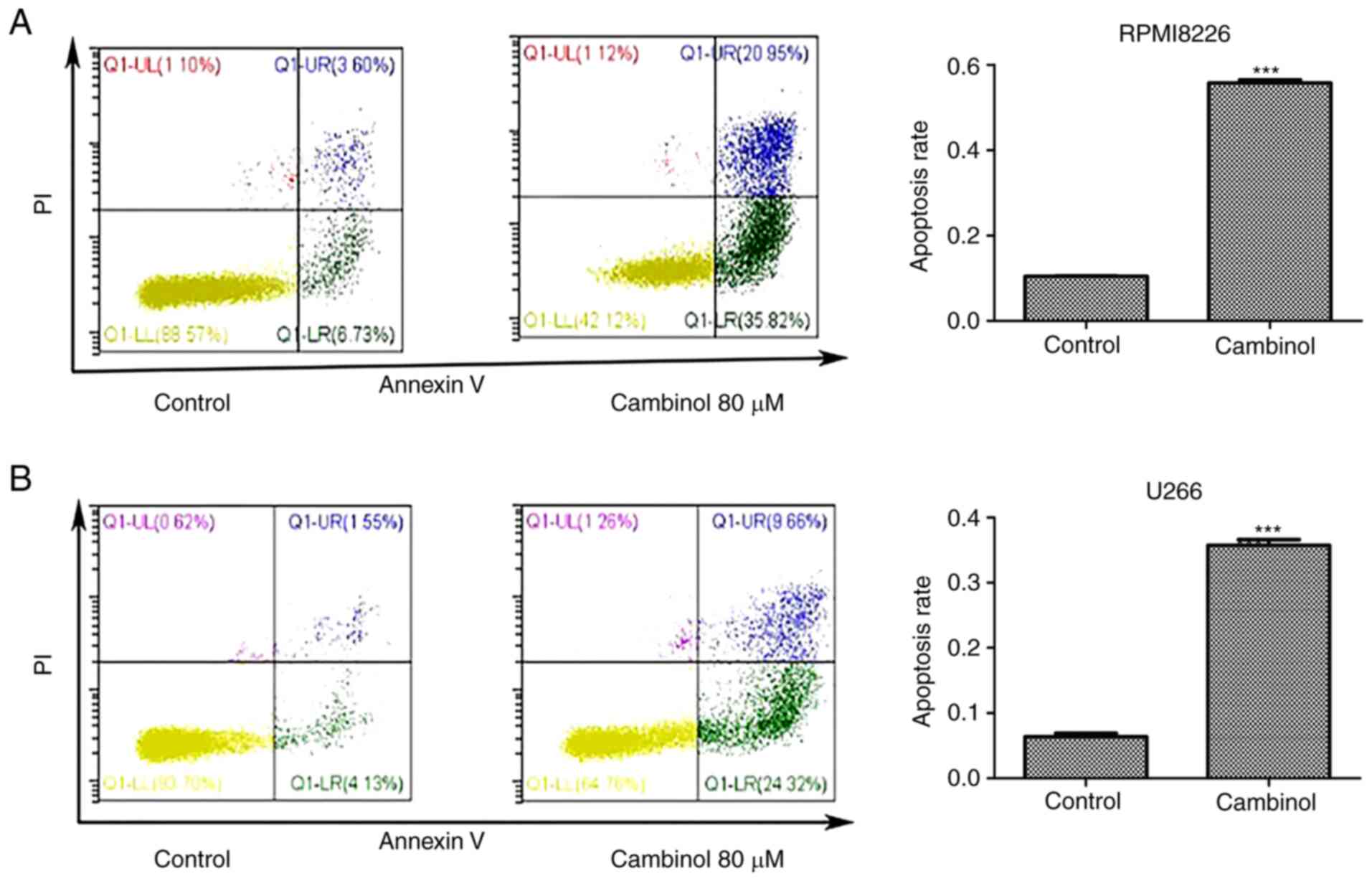
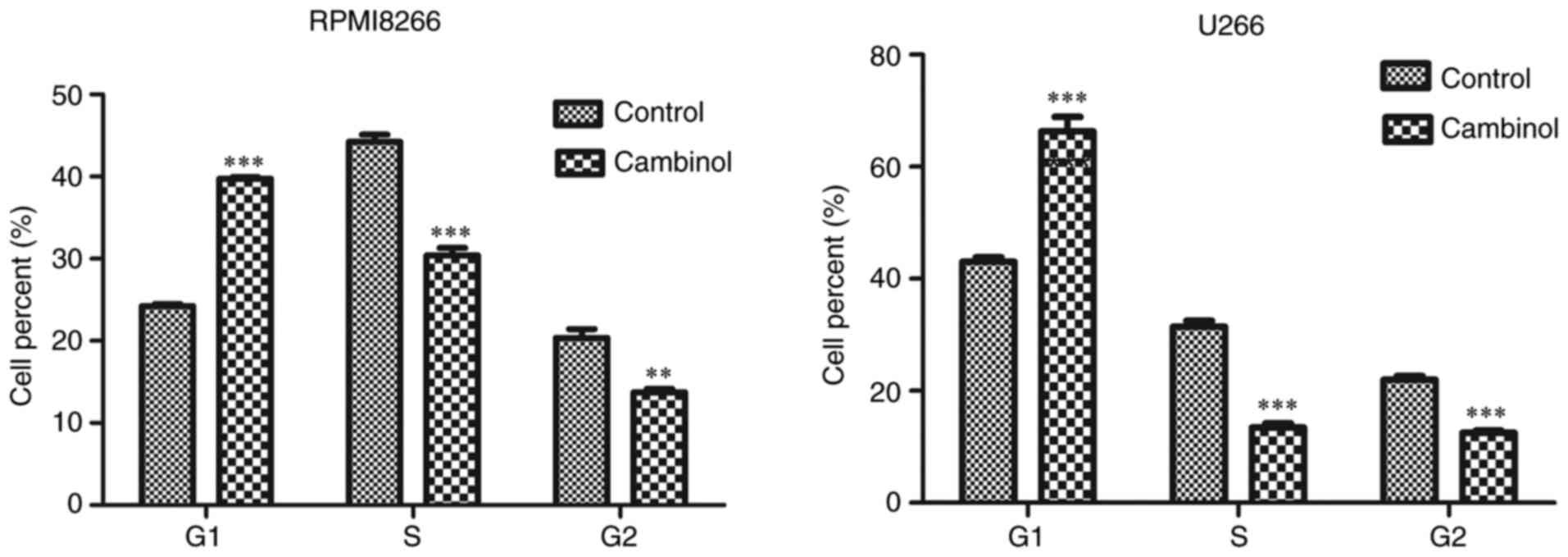
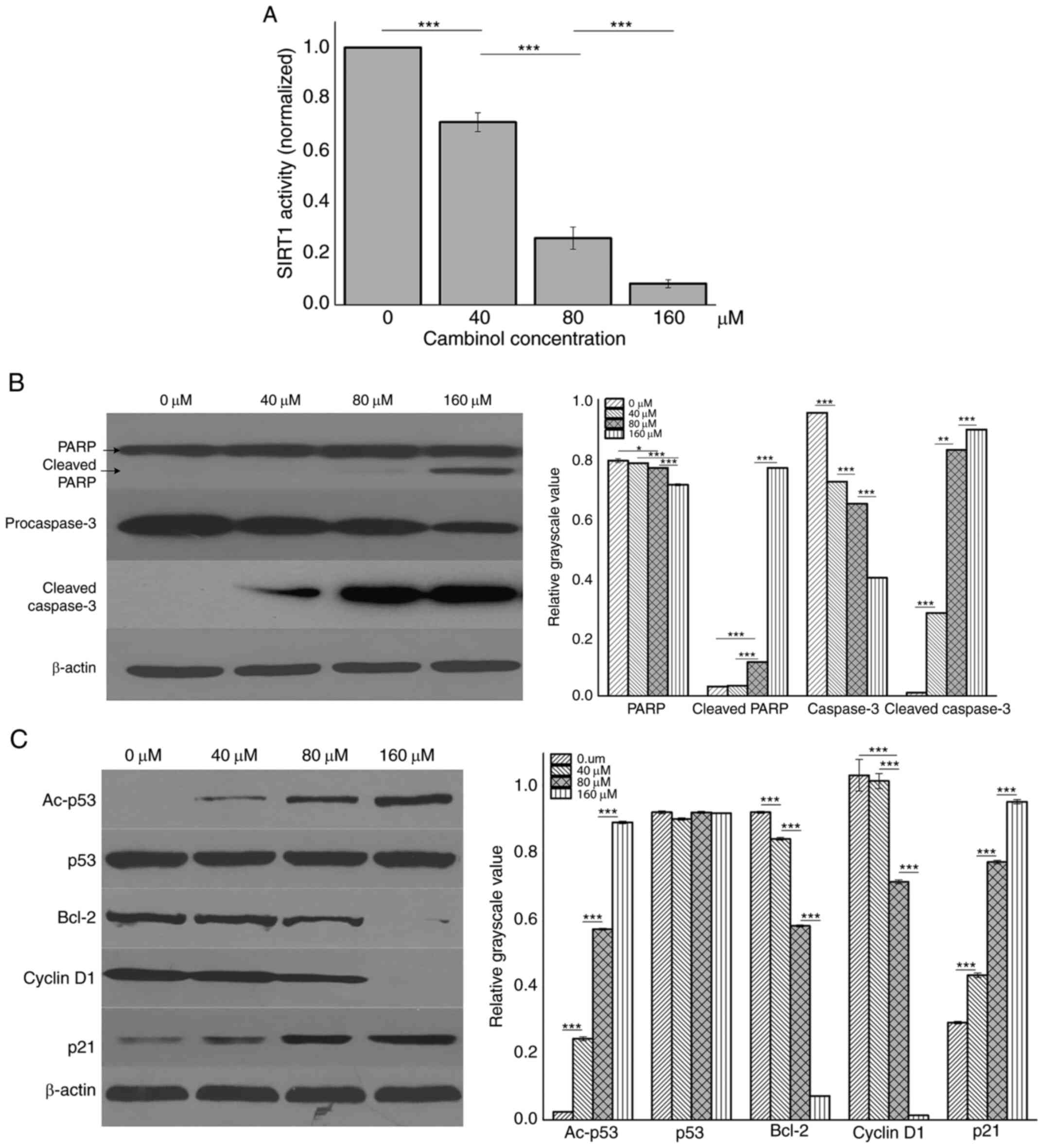
|
1
|
Lynch HT, Watson P, Tarantolo S, Wiernik
PH, Quinn-Laquer B, Isgur Bergsagel K, Huiart L, Olopade OI, Sobol
H, Sanger W, et al: Phenotypic heterogeneity in multiple myeloma
families. J Clin Oncol. 23:685–693. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Terpos E; International Myeloma Society, :
Multiple myeloma: Clinical updates from the American Society of
hematology annual meeting, 2017. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk.
18:321–334. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Robak P, Drozdz I, Szemraj J and Robak T:
Drug resistance in multiple myeloma. Cancer Treat Rev. 70:199–208.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu XH, Liu J, Shen CY, Ding LL, Zhong F,
Ouyang Y, Wang YC and He S: The role of ubiquitin-specific protease
14 (USP14) in cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) of
multiple myeloma cells. Eur J Haematol. 98:4–12. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu M, Jiang L and Guan XY: The genetic
and epigenetic alterations in human hepatocellular carcinoma: A
recent update. Protein Cell. 5:673–691. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Khochbin S, Verdel A, Lemercier C and
Seigneurin-Berny D: Functional significance of histone deacetylase
diversity. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 11:162–166. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tang Y, Zhao W, Chen Y, Zhao Y and Gu W:
Acetylation is indispensable for p53 activation. Cell. 133:612–626.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Conte M, De Palma R and Altucci L: HDAC
inhibitors as epigenetic regulators for cancer immunotherapy. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 98:65–74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin X, Wei Y, Xu F, Zhao M, Dai K, Shen R,
Yang S and Zhang N: SIRT1 promotes formation of breast cancer
through modulating Akt activity. J Cancer. 9:2012–2023. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kumar A and Chauhan S: How much successful
are the medicinal chemists in modulation of SIRT1: A critical
review. Eur J Med Chem. 119:45–69. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roth M, Wang Z and Chen WY: Sirtuins in
hematological aging and malignancy. Crit Rev Oncog. 18:531–547.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hwang ES and Song SB: Nicotinamide is an
inhibitor of SIRT1 in vitro, but can be a stimulator in cells. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 74:3347–3362. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li L and Bhatia R: Role of SIRT1 in the
growth and regulation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia stem
cells. Curr Opin Hematol. 22:324–329. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tae IH, Park EY, Dey P, Son JY, Lee SY,
Jung JH, Saloni S, Kim MH and Kim HS: Novel SIRT1 inhibitor
15-deoxy-Δ12,14-prostaglandin J2 and its derivatives exhibit
anticancer activity through apoptotic or autophagic cell death
pathways in SKOV3 cells. Int J Oncol. 53:2518–2530. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mellini P, Valente S and Mai A: Sirtuin
modulators: An updated patent review (2012–2014). Expert Opin Ther
Pat. 25:5–15. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirsch BM and Zheng W: Sirtuin mechanism
and inhibition: Explored with N(ε)-acetyl-lysine analogs. Mol
Biosyst. 7:16–28. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Panathur N, Gokhale N, Dalimba U, Koushik
PV, Yogeeswari P and Sriram D: New indole-isoxazolone derivatives:
Synthesis, characterisation and in vitro SIRT1 inhibition studies.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 25:2768–2772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oon CE, Strell C, Yeong KY, Ostman A and
Prakash J: SIRT1 inhibition in pancreatic cancer models:
Contrasting effects in vitro and in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol.
757:59–67. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yao Y, Liu T, Wang X and Zhang D: The
contrary effects of Sirt1 on MCF7 cells depend on CD36 expression
level. J Surg Res. 238:248–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karbasforooshan H, Roohbakhsh A and Karimi
G: SIRT1 and microRNAs: The role in breast, lung and prostate
cancers. Exp Cell Res. 367:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ghosh A, Sengupta A, Seerapu GPK, Nakhi A,
Shivaji Ramarao EVV, Bung N, Bulusu G, Pal M and Haldar D: A novel
SIRT1 inhibitor, 4bb induces apoptosis in HCT116 human colon
carcinoma cells partially by activating p53. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 488:562–569. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou L, Wang Q, Chen X, Fu L, Zhang X,
Wang L, Deng A, Li D, Liu J, Lv N, et al: AML1-ETO promotes SIRT1
expression to enhance leukemogenesis of t(8;21) acute myeloid
leukemia. Exp Hematol. 46:62–69. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sharma VK, Raimondi V, Ruggero K,
Pise-Masison CA, Cavallari I, Silic-Benussi M, Ciminale V and
D'Agostino DM: Expression of miR-34a in T-cells infected by human
T-Lymphotropic Virus 1. Front Microbiol. 9:8322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
He M, Tan B, Vasan K, Yuan H, Cheng F,
Ramos da Silva S, Lu C and Gao SJ: SIRT1 and AMPK pathways are
essential for the proliferation and survival of primary effusion
lymphoma cells. J Pathol. 242:309–321. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bhalla S and Gordon LI: Functional
characterization of NAD dependent de-acetylases SIRT1 and SIRT2 in
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). Cancer Biol Ther.
17:300–309. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim HB, Lee SH, Um JH, Oh WK, Kim DW, Kang
CD and Kim SH: Sensitization of multidrug-resistant human cancer
cells to Hsp90 inhibitors by down-regulation of SIRT1. Oncotarget.
6:36202–36218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Portmann S, Fahrner R, Lechleiter A, Keogh
A, Overney S, Laemmle A, Mikami K, Montani M, Tschan MP, Candinas D
and Stroka D: Antitumor effect of SIRT1 inhibition in human HCC
tumor models in vitro and in vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 12:499–508.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Heltweg B, Gatbonton T, Schuler AD,
Posakony J, Li H, Goehle S, Kollipara R, Depinho RA, Gu Y, Simon JA
and Bedalov A: Antitumor activity of a small-molecule inhibitor of
human silent information regulator 2 enzymes. Cancer Res.
66:4368–4377. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang J: Current developments of targeting
the p53 signaling pathway for cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther. Oct
29–2020.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107720. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Brooks CL and Gu W: New insights into p53
activation. Cell Res. 20:614–621. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li L, Wang L, Li L, Wang Z, Ho Y, McDonald
T, Holyoake TL, Chen W and Bhatia R: Activation of p53 by SIRT1
inhibition enhances elimination of CML leukemia stem cells in
combination with imatinib. Cancer Cell. 21:266–281. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peck B, Chen CY, Ho KK, Di Fruscia P,
Myatt SS, Coombes RC, Fuchter MJ, Hsiao CD and Lam EW: SIRT
inhibitors induce cell death and p53 acetylation through targeting
both SIRT1 and SIRT2. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:844–855. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ceballos MP, Decandido G, Quiroga AD,
Comanzo CG, Livore VI, Lorenzetti F, Lambertucci F,
Chazarreta-Cifre L, Banchio C, Alvarez ML, et al: Inhibition of
sirtuins 1 and 2 impairs cell survival and migration and modulates
the expression of P-glycoprotein and MRP3 in hepatocellular
carcinoma cell lines. Toxicol Lett. 289:63–74. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dykes SS, Friday E, Pruitt K and Cardelli
JA: The histone deacetylase inhibitor cambinol prevents acidic
pHe-induced anterograde lysosome trafficking independently of
sirtuin activity. Biochem Biophys Rep. 3:83–93. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Simmons GE Jr, Pandey S,
Nedeljkovic-Kurepa A, Saxena M, Wang A and Pruitt K: Frizzled 7
expression is positively regulated by SIRT1 and β-catenin in breast
cancer cells. PLoS One. 9:e988612014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Holloway KR, Barbieri A, Malyarchuk S,
Saxena M, Nedeljkovic-Kurepa A, Cameron Mehl M, Wang A, Gu X and
Pruitt K: SIRT1 positively regulates breast cancer associated human
aromatase (CYP19A1) expression. Mol Endocrinol. 27:480–490. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Botta L, Filippi S, Bizzarri BM, Meschinia
R, Caputoa M, Proietti-De-Santisa L, Isideb C, Nebbiosob A,
Gualandia G and Saladinoa R: Oxidative nucleophilic substitution
selectively produces cambinol derivatives with antiproliferative
activity on bladder cancer cell lines. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
29:78–82. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mahajan SS, Scian M, Sripathy S, Posakony
J, Lao U, Loe TK, Leko V, Thalhofer A, Schuler AD, Bedalov A and
Simon JA: Development of pyrazolone and isoxazol-5-one cambinol
analogues as sirtuin inhibitors. J Med Chem. 57:3283–3294. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|