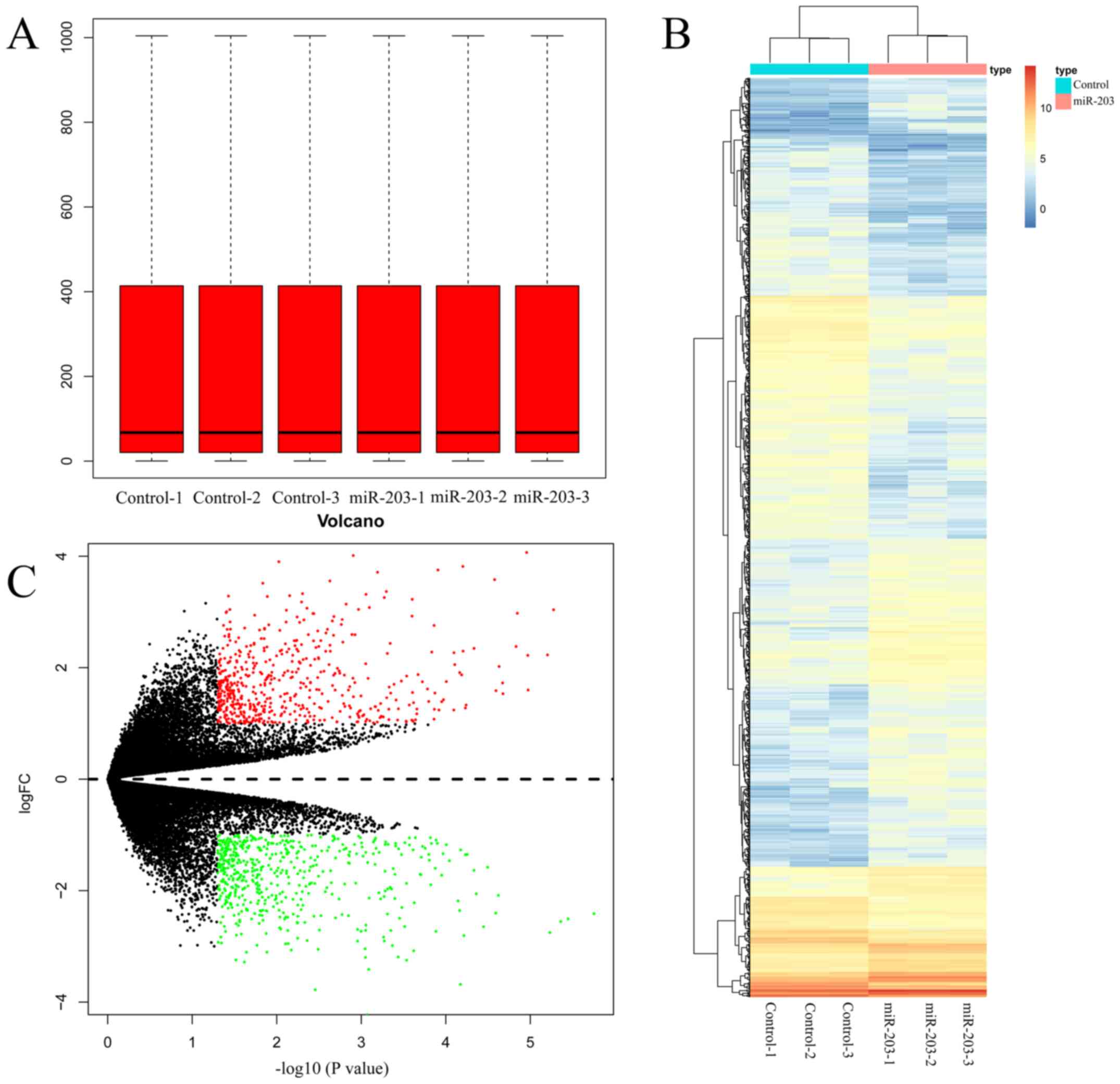
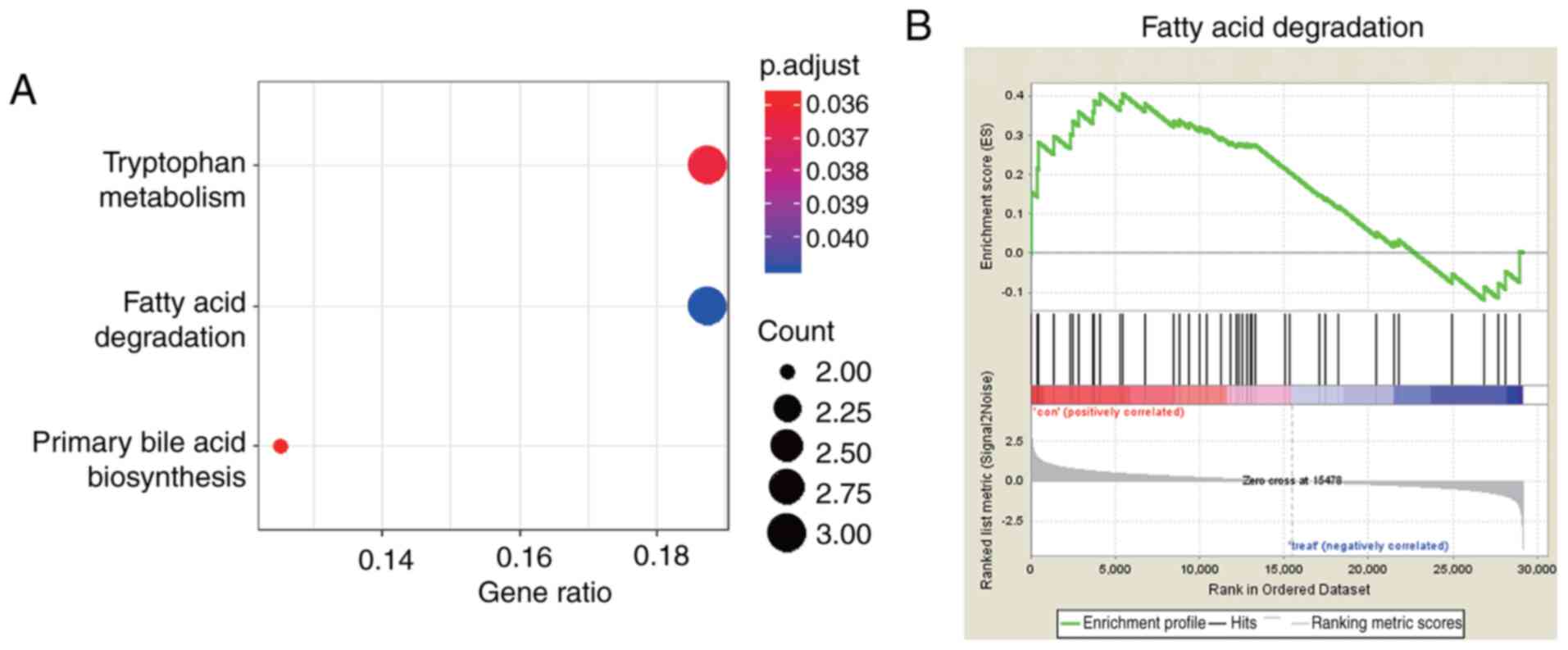
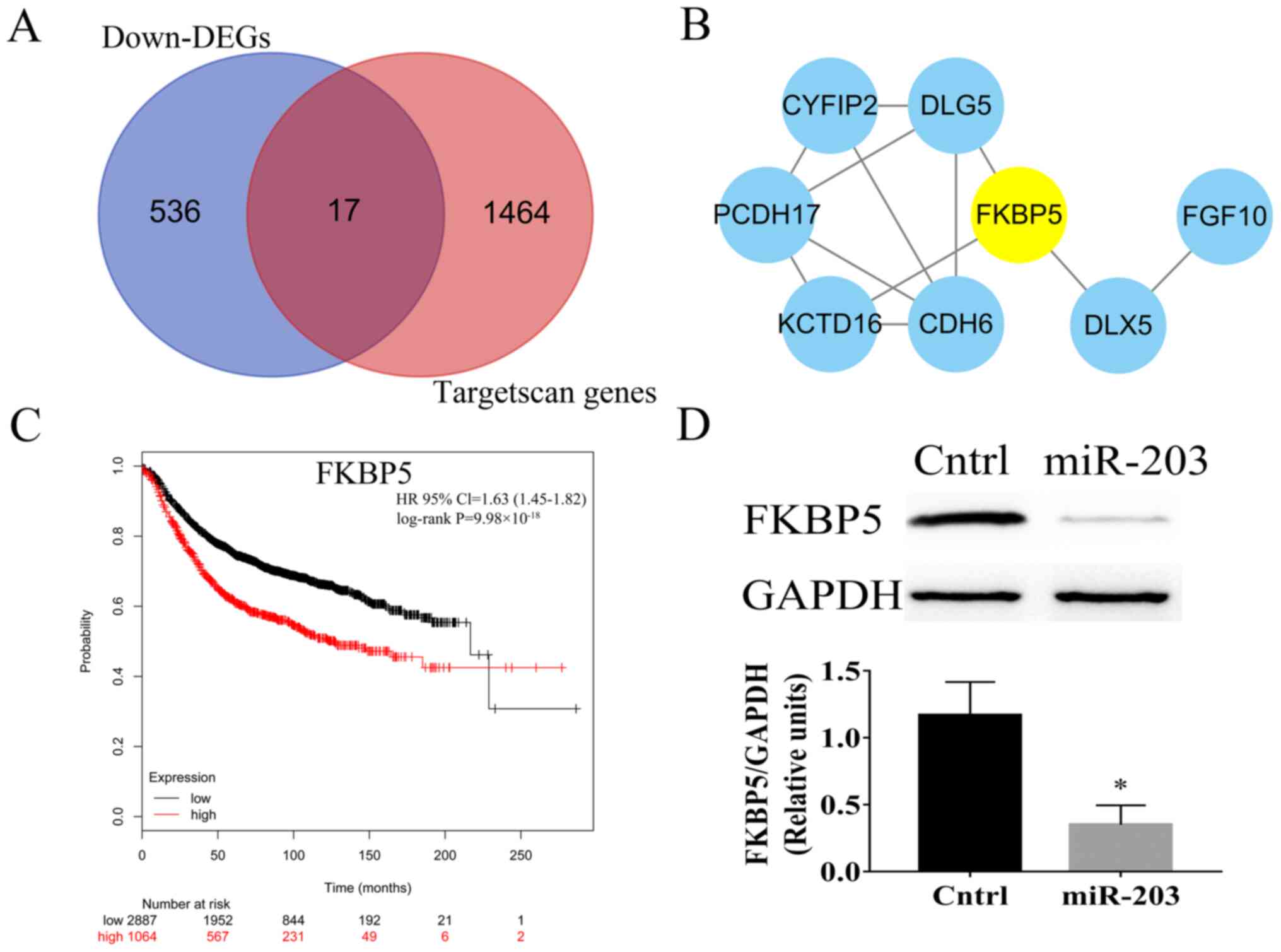
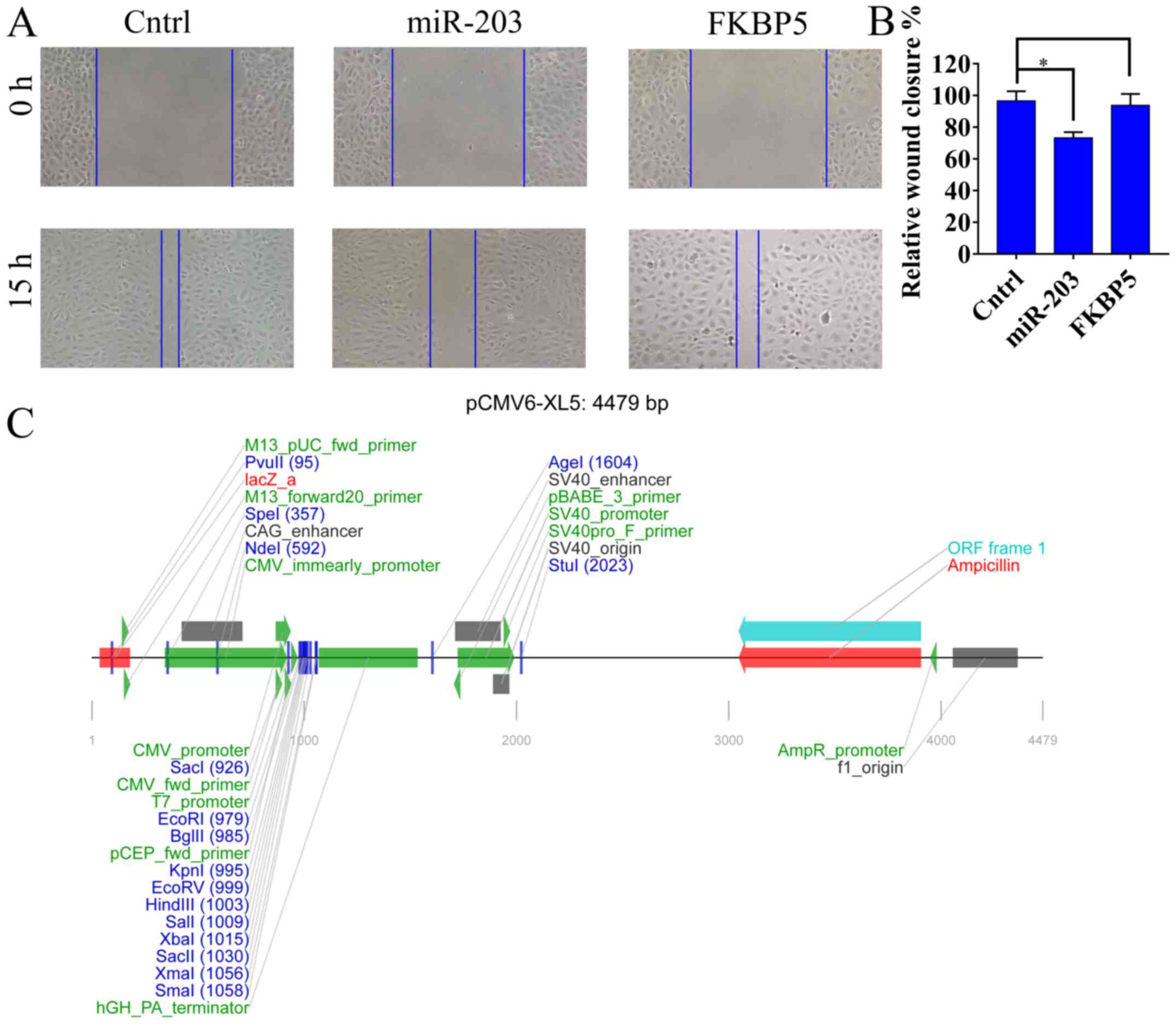
|
1
|
Telli ML, Gradishar WJ and Ward JH: NCCN
Guidelines Updates: Breast Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
17:552–555. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DeSantis CE, Ma J, Gaudet MM, Newman LA,
Miller KD, Goding Sauer A, Jemal A and Siegel RL: Breast cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:438–451. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Madhavan D, Zucknick M, Wallwiener M, Cuk
K, Modugno C, Scharpff M, Schott S, Heil J, Turchinovich A, Yang R,
et al: Circulating miRNAs as surrogate markers for circulating
tumor cells and prognostic markers in metastatic breast cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 18:5972–5982. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wang C, Zheng X, Shen C and Shi Y:
MicroRNA-203 suppresses cell proliferation and migration by
targeting BIRC5 and LASP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer
cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 31:582012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Taipaleenmäki H, Browne G, Akech J, Zustin
J, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Hesse E, Stein GS and Lian JB:
Targeting of Runx2 by miR-135 and miR-203 Impairs Progression of
Breast Cancer and Metastatic Bone Disease. Cancer Res.
75:1433–1444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Qu Y, Li WC, Hellem MR, Rostad K, Popa M,
McCormack E, Oyan AM, Kalland KH and Ke XS: miR-182 and miR-203
induce mesenchymal to epithelial transition and self-sufficiency of
growth signals via repressing SNAI2 in prostate cells. Int J
Cancer. 133:544–555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu HP, Zhang Y, Liu ZT, Qi H, Zheng XM,
Qi LH and Wang JY: miR-203 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of
ovarian cancer cells by targeting SOCS3. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:9286–9294. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shen J, Zhang J, Xiao M, Yang J and Zhang
N: miR-203 Suppresses Bladder Cancer Cell Growth and Targets
Twist1. Oncol Res. 26:1155–1165. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang F, Qiu W, Li R, Hu J, Luo S, Zhang T,
He X and Zheng C: Genome-wide identification of the interactions
between key genes and pathways provide new insights into the
toxicity of bisphenol F and S during early development in
zebrafish. Chemosphere. 213:559–567. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima
K and Tanabe M: New approach for understanding genome variations in
KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res 47D. D590–D595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy - analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Smyth GK, Michaud J and Scott HS: Use of
within-array replicate spots for assessing differential expression
in microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 21:2067–2075. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Furumichi M
and Tanabe M: KEGG for integration and interpretation of
large-scale molecular data sets. Nucleic Acids Res 40D. D109–D114.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES, et al: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4:e050052015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 47D. D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lánczky A, Nagy Á, Bottai G, Munkácsy G,
Szabó A, Santarpia L and Győrffy B: miRpower: A web-tool to
validate survival-associated miRNAs utilizing expression data from
2178 breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 160:439–446.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rueden CT, Schindelin J, Hiner MC, DeZonia
BE, Walter AE, Arena ET and Eliceiri KW: ImageJ2: ImageJ for the
next generation of scientific image data. BMC Bioinformatics.
18:5292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salam NK, Nuti R and Sherman W: Novel
method for generating structure-based pharmacophores using
energetic analysis. J Chem Inf Model. 49:2356–2368. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Irwin JJ, Sterling T, Mysinger MM, Bolstad
ES and Coleman RG: ZINC: A free tool to discover chemistry for
biology. J Chem Inf Model. 52:1757–1768. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang Y, Wang X, Xiong Y, Li CD, Xu Q, Shen
L, Chandra Kaushik A and Wei DQ: An Integrated Pan-Cancer Analysis
and Structure-Based Virtual Screening of GPR15. Int J Mol Sci.
20:62262019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yu Y, Luo W, Yang ZJ, Chi JR, Li YR, Ding
Y, Ge J, Wang X and Cao XC: miR-190 suppresses breast cancer
metastasis by regulation of TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition. Mol Cancer. 17:702018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang H, Tan Z, Hu H, Liu H, Wu T, Zheng C,
Wang X, Luo Z, Wang J, Liu S, et al: microRNA-21 promotes breast
cancer proliferation and metastasis by targeting LZTFL1. BMC
Cancer. 19:7382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia Y, Wang Y, Wang Q, Ghaffar M, Wang Y,
Sheng W and Zhang F: Increased miR-203-3p and reduced miR-21-5p
synergistically inhibit proliferation, migration, and invasion in
esophageal cancer cells. Anticancer Drugs. 30:38–45. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang W, Wu Y, Cheng D and He Z: Mechanism
of epithelial mesenchymal transition inhibited by miR 203 in non
small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 43:437–446. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Currie E, Schulze A, Zechner R, Walther TC
and Farese RV Jr: Cellular fatty acid metabolism and cancer. Cell
Metab. 18:153–161. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chen TT and Li H: Fatty acid metabolism
and prospects for targeted therapy of cancer. Eur J Lipid Sci
Technol. 119:16003662017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen JC and Wu X: [miR-203 inhibits lung
cancer cell metastasis by targeting fatty acid binding protein 4].
Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 38:578–583. 2018.(In Chinese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mikalayeva V, Ceslevičienė I, Sarapinienė
I, Žvikas V, Skeberdis VA, Jakštas V and Bordel S: Fatty Acid
Synthesis and Degradation Interplay to Regulate the Oxidative
Stress in Cancer Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20:13482019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Moore NL, Edwards DP and Weigel NL: Cyclin
A2 and its associated kinase activity are required for optimal
induction of progesterone receptor target genes in breast cancer
cells. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 144B. 471–482. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sun NK, Huang SL, Chang PY, Lu HP and Chao
CC: Transcriptomic profiling of taxol-resistant ovarian cancer
cells identifies FKBP5 and the androgen receptor as critical
markers of chemotherapeutic response. Oncotarget. 5:11939–11956.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hou J and Wang L: FKBP5 as a selection
biomarker for gemcitabine and Akt inhibitors in treatment of
pancreatic cancer. PLoS One. 7:e362522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sato A and Asano T, Ito K and Asano T:
17-Allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin and ritonavir inhibit renal
cancer growth by inhibiting the expression of heat shock factor-1.
Int J Oncol. 41:46–52. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sato A and Asano T, Okubo K, Isono M and
Asano T: Nelfinavir and Ritonavir Kill Bladder Cancer Cells
Synergistically by Inducing Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Oncol
Res. 26:323–332. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|