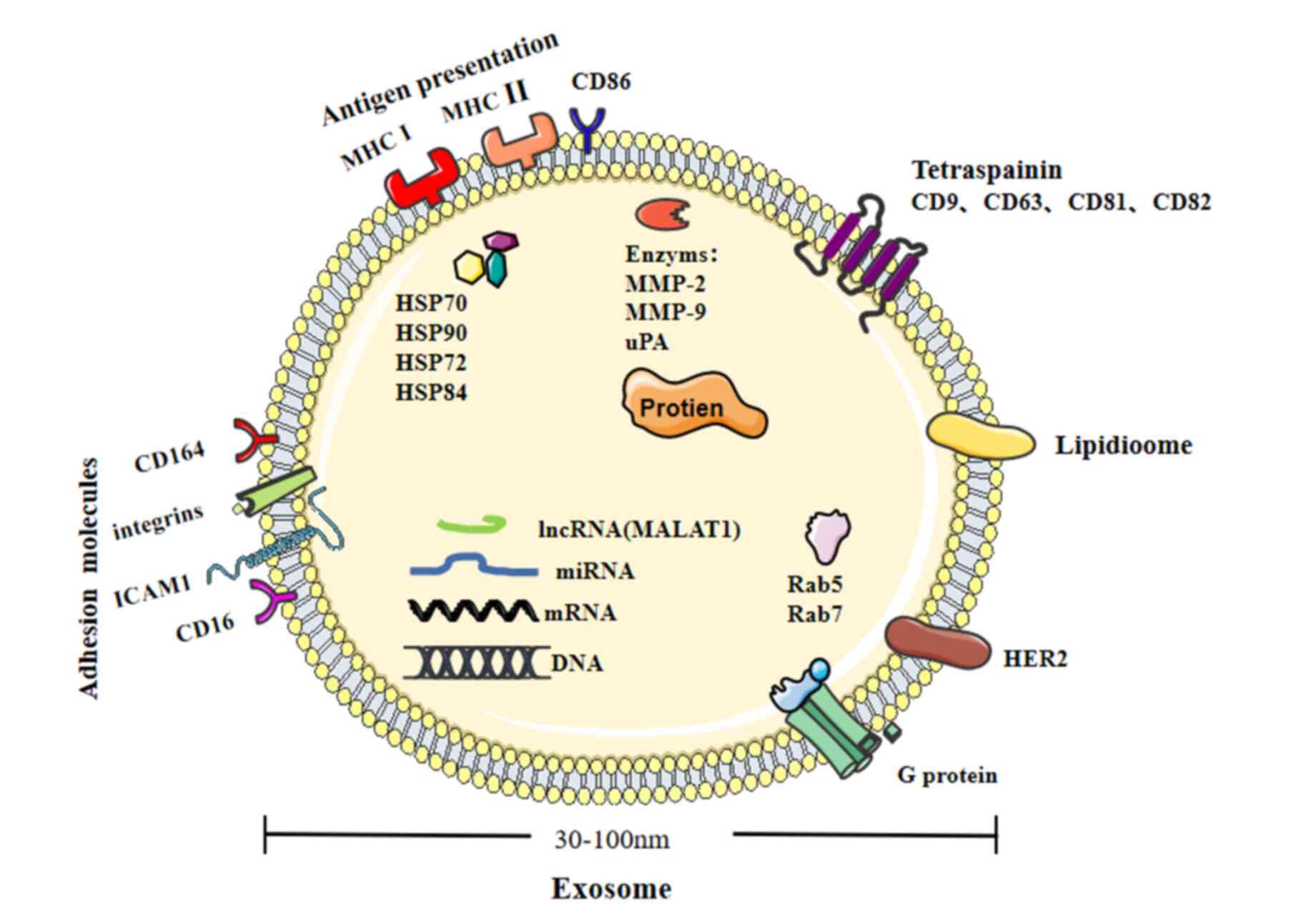
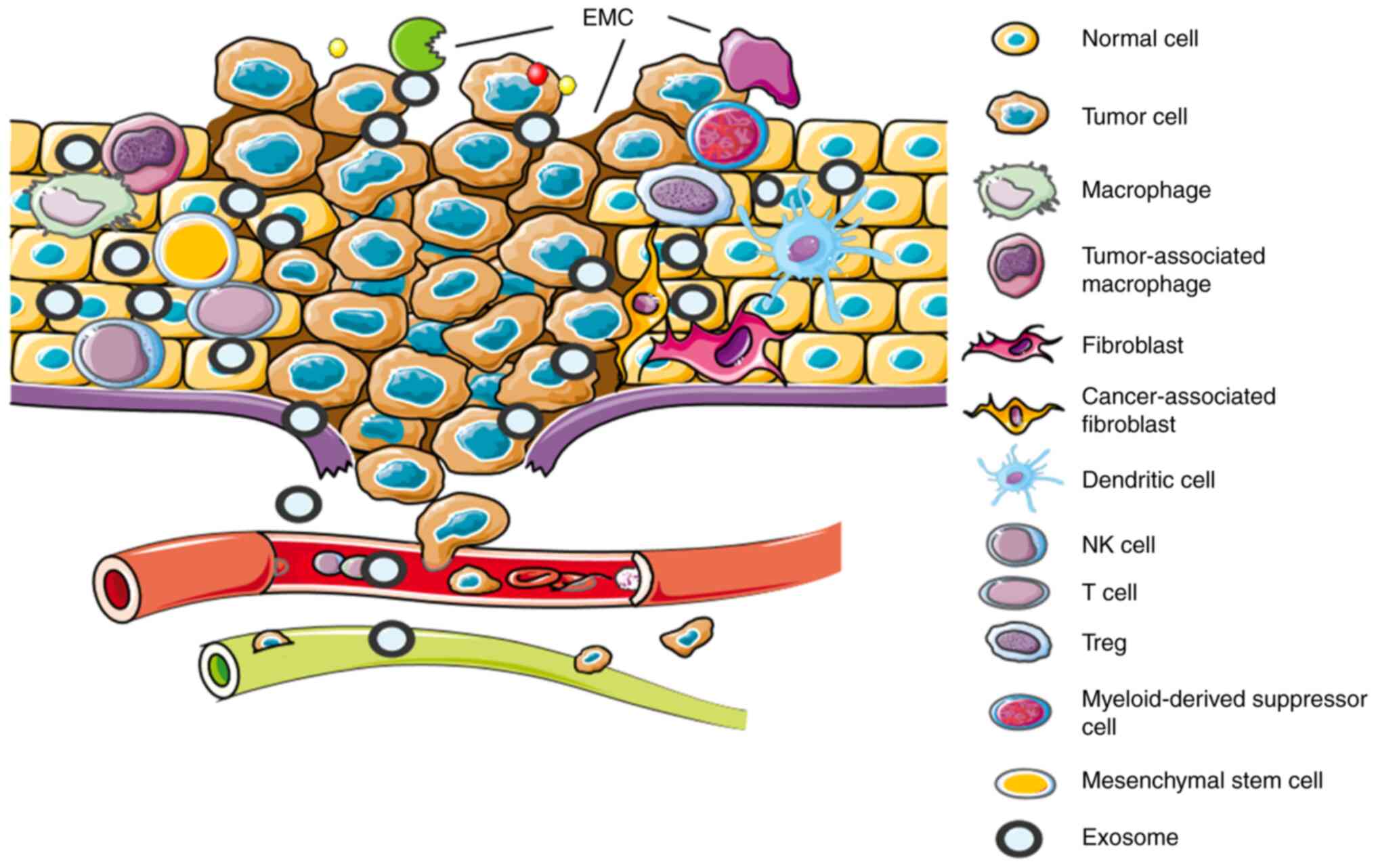
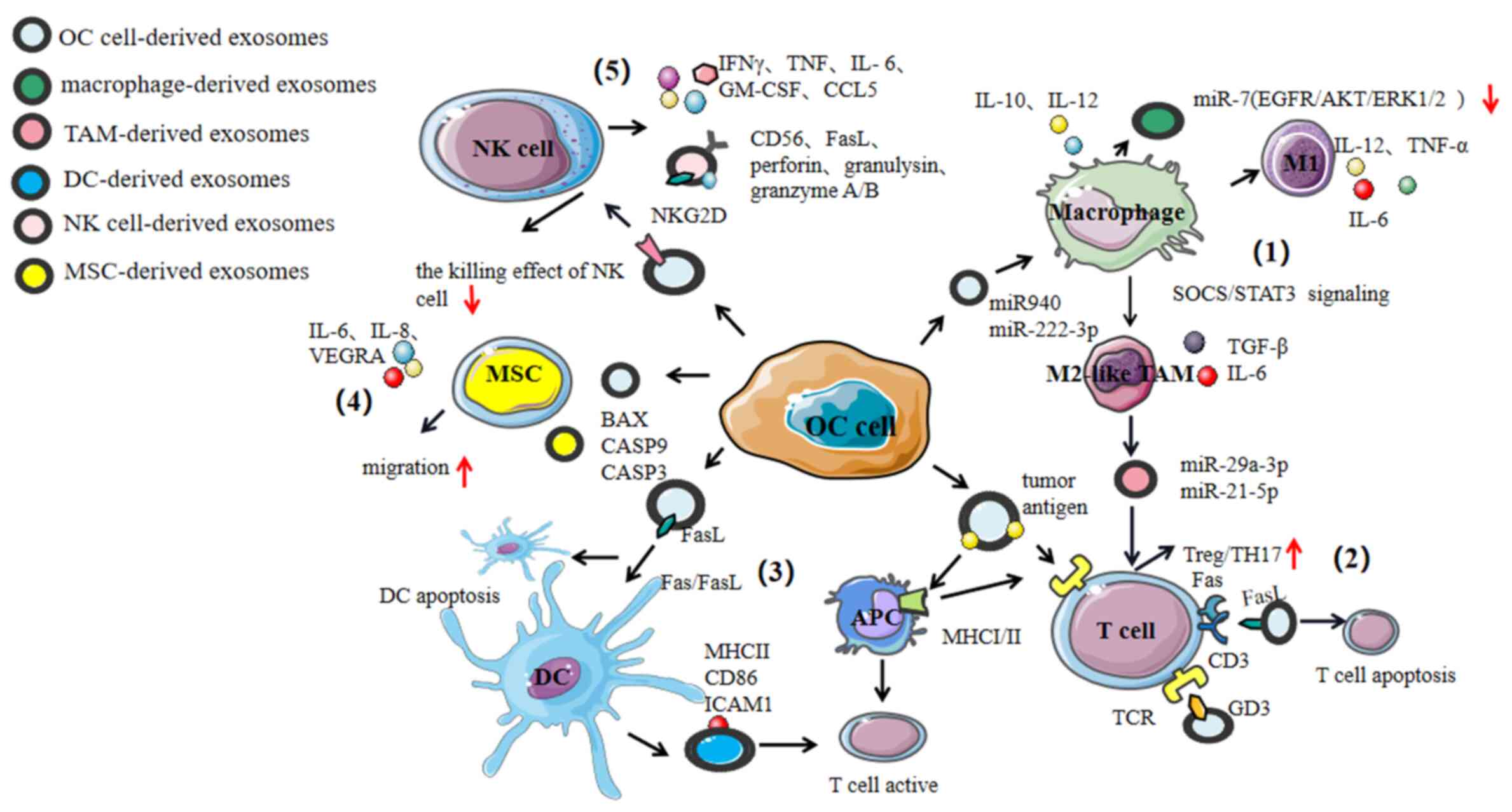
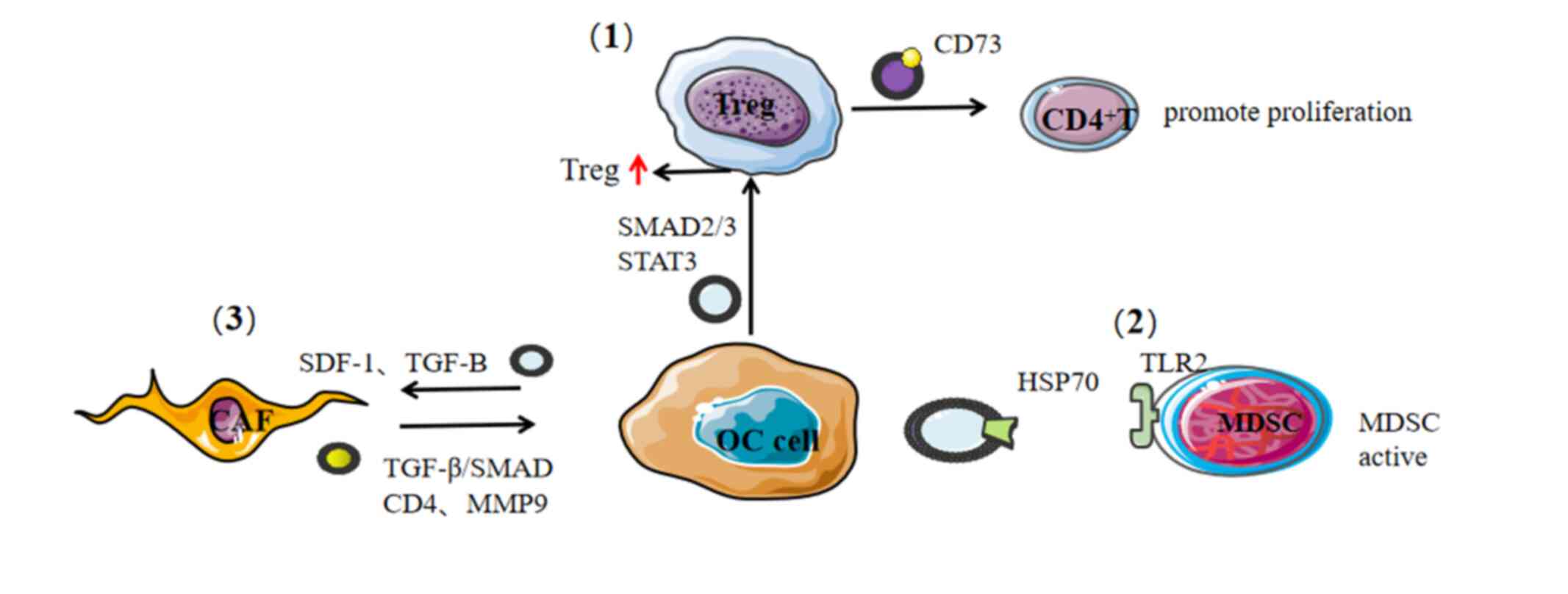
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Drakes ML and Stiff PJ: Regulation of
ovarian cancer prognosis by immune cells in the tumor
microenvironment. Cancers (Basel). 10:3022018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gajewski TF, Schreiber H and Fu YX: Innate
and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat
Immunol. 14:1014–1022. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Albini A, Bruno A, Noonan DM and Mortara
L: Contribution to tumor angiogenesis from innate immune cells
within the tumor microenvironment: Implications for immunotherapy.
Front Immunol. 9:5272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cassim S and Pouyssegur J: Tumor
microenvironment: A metabolic player that shapes the immune
response. Int J Mol Sci. 21:1572019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Andre F, Schartz NE, Movassagh M, Flament
C, Pautier P, Morice P, Pomel C, Lhomme C, Escudier B, Le Chevalier
T, et al: Malignant effusions and immunogenic tumour-derived
exosomes. Lancet. 360:295–305. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giordano C, La Camera G, Gelsomino L,
Barone I, Bonofiglio D, Ando S and Catalano S: The biology of
exosomes in breast cancer progression: Dissemination, immune
evasion and metastatic colonization. Cancers (Basel). 12:21792020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kulkarni B, Kirave P, Gondaliya P, Jash K,
Jain A, Tekade RK and Kalia K: Exosomal miRNA in chemoresistance,
immune evasion, metastasis and progression of cancer. Drug Discov
Today. 24:2058–2067. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lundholm M, Schroder M, Nagaeva O, Baranov
V, Widmark A, Mincheva-Nilsson L and Wikström P: Prostate
tumor-derived exosomes down-regulate NKG2D expression on natural
killer cells and CD8+ T cells: Mechanism of immune evasion. PLoS
One. 9:e1089252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng L, Wu S, Zhang K, Qing Y and Xu T: A
comprehensive overview of exosomes in ovarian cancer: Emerging
biomarkers and therapeutic strategies. J Ovarian Res. 10:732017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Beach A, Zhang HG, Ratajczak MZ and Kakar
SS: Exosomes: An overview of biogenesis, composition and role in
ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 7:142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Doyle LM and Wang MZ: Overview of
extracellular vesicles, their origin, composition, purpose, and
methods for exosome isolation and analysis. Cells. 8:7272019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sharma A and Johnson A: Exosome DNA:
Critical regulator of tumor immunity and a diagnostic biomarker. J
Cell Physiol. 235:1921–1932. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Iliev D, Strandskog G, Nepal A, Aspar A,
Olsen R, Jørgensen J, Wolfson D, Ahluwalia BS, Handzhiyski J and
Mironova R: Stimulation of exosome release by extracellular DNA is
conserved across multiple cell types. FEBS J. 285:3114–3133. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang YT, Huang YY, Zheng L, Qin SH, Xu XP,
An TX, Xu Y, Wu YS, Hu XM, Ping BH and Wang Q: Comparison of
isolation methods of exosomes and exosomal RNA from cell culture
medium and serum. Int J Mol Med. 40:834–844. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shyu KG, Wang BW, Pan CM, Fang WJ and Lin
CM: Hyperbaric oxygen boosts long noncoding RNA MALAT1 exosome
secretion to suppress microRNA-92a expression in therapeutic
angiogenesis. Int J Cardiol. 274:271–278. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hannafon BN, Trigoso YD, Calloway CL, Zhao
YD, Lum DH, Welm AL, Zhao ZJ, Blick KE, Dooley WC and Ding WQ:
Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 18:902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kobayashi M, Sawada K, Miyamoto M, Shimizu
A, Yamamoto M, Kinose Y, Nakamura K, Kawano M, Kodama M, Hashimoto
K and Kimura T: Exploring the potential of engineered exosomes as
delivery systems for tumor-suppressor microRNA replacement therapy
in ovarian cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 527:153–161. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mittal S, Gupta P, Chaluvally-Raghavan P
and Pradeep S: Emerging role of extracellular vesicles in immune
regulation and cancer progression. Cancers (Basel). 12:35632020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liang B, Peng P, Chen S, Li L, Zhang M,
Cao D, Yang J, Li H, Gui T, Li X and Shen K: Characterization and
proteomic analysis of ovarian cancer-derived exosomes. J
Proteomics. 80:171–182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Peng P, Yan Y and Keng S: Exosomes in the
ascites of ovarian cancer patients: Origin and effects on
anti-tumor immunity. Oncol Rep. 25:749–762. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luo Z, Wang Q, Lau WB, Lau B, Xu L, Zhao
L, Yang H, Feng M, Xuan Y, Yang Y, et al: Tumor microenvironment:
The culprit for ovarian cancer metastasis? Cancer Lett.
377:174–182. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Da Silva AC, Jammal MP, Crispim PCA, Murta
EFC and Nomelini RS: The role of stroma in ovarian cancer. Immunol
Invest. 49:406–424. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Josephs SF, Ichim TE, Prince SM, Kesari S,
Marincola FM, Escobedo AR and Jafri A: Unleashing endogenous
TNF-alpha as a cancer immunotherapeutic. J Transl Med. 16:2422018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wen Z, Liu H, Li M, Li B, Gao W, Shao Q,
Fan B, Zhao F, Wang Q, Xie Q, et al: Increased metabolites of
5-lipoxygenase from hypoxic ovarian cancer cells promote
tumor-associated macrophage infiltration. Oncogene. 34:1241–1252.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Browning L, Patel MR, Horvath EB, Tawara K
and Jorcyk CL: IL-6 and ovarian cancer: Inflammatory cytokines in
promotion of metastasis. Cancer Manag Res. 10:6685–6693. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sanmarco LM, Ponce NE, Visconti LM,
Eberhardt N, Theumer MG, Minguez AR and Aoki MP: IL-6 promotes M2
macrophage polarization by modulating purinergic signaling and
regulates the lethal release of nitric oxide during Trypanosoma
cruzi infection. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:857–869.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yin Z, Ma T, Lin Y, Lu X, Zhang C, Chen S
and Jian Z: IL-6/STAT3 pathway intermediates M1/M2 macrophage
polarization during the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. J
Cell Biochem. 119:9419–9432. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fu XL, Duan W, Su CY, Mao FY, Lv YP, Teng
YS, Yu PW, Zhuang Y and Zhao YL: Interleukin 6 induces M2
macrophage differentiation by STAT3 activation that correlates with
gastric cancer progression. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
66:1597–1608. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jiang B, Zhu SJ, Xiao SS and Xue M:
miR-217 Inhibits M2-like macrophage polarization by suppressing
secretion of interleukin-6 in ovarian cancer. Inflammation.
42:1517–1529. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
McLean K, Tan L, Bolland DE, Coffman LG,
Peterson LF, Talpaz M, Neamati N and Buckanovich RJ: Leukemia
inhibitory factor functions in parallel with interleukin-6 to
promote ovarian cancer growth. Oncogene. 38:1576–1584. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Y, Zong X, Mitra S, Mitra AK, Matei D
and Nephew KP: IL-6 mediates platinum-induced enrichment of ovarian
cancer stem cells. JCI Insight. 3:e1223602018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bretz NP, Ridinger J, Rupp AK, Rimbach K,
Keller S, Rupp C, Marmé F, Umansky L, Umansky V, Eigenbrod T, et
al: Body fluid exosomes promote secretion of inflammatory cytokines
in monocytic cells via Toll-like receptor signaling. J Biol Chem.
288:36691–3702. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De Marco M, Falco A, Festa M, Raffone A,
Sandullo L, Rosati A, Reppucci F, Cammarota AL, Esposito F, Matassa
DS, et al: Different mechanisms underlie IL-6 release in
chemosensitive and chemoresistant ovarian carcinoma cells. Am J
Cancer Res. 10:2596–2602. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kumari N, Dwarakanath BS, Das A and Bhatt
AN: Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic
resistance. Tumour Biol. 37:11553–11572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Niu XL, Qu Y, Wu J, Zhu YQ, Sun WJ
and Li LZ: Autocrine production of interleukin-6 confers cisplatin
and paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Lett.
295:110–123. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kampan NC, Madondo MT, Reynolds J, Hallo
J, McNally OM, Jobling TW, Stephens AN, Quinn MA and Plebanski M:
Pre-operative sera interleukin-6 in the diagnosis of high-grade
serous ovarian cancer. Sci Rep. 10:22132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Isobe A, Sawada K, Kinose Y, Ohyagi-Hara
C, Nakatsuka E, Makino H, Ogura T, Mizuno T, Suzuki N, Morii E, et
al: Interleukin 6 receptor is an independent prognostic factor and
a potential therapeutic target of ovarian cancer. PLoS One.
10:e01180802015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yuan X, Zhang J, Li D, Mao Y, Mo F, Du W
and Ma X: Prognostic significance of tumor-associated macrophages
in ovarian cancer: A meta-analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 147:181–187.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Maccio A, Gramignano G, Cherchi MC, Tanca
L, Melis L and Madeddu C: Role of M1-polarized tumor-associated
macrophages in the prognosis of advanced ovarian cancer patients.
Sci Rep. 10:60962020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Carroll MJ, Kapur A, Felder M, Patankar MS
and Kreeger PK: M2 macrophages induce ovarian cancer cell
proliferation via a heparin binding epidermal growth factor/matrix
metalloproteinase 9 intercellular feedback loop. Oncotarget.
7:86608–86620. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou ZN, Sharma VP, Beaty BT, Roh-Johnson
M, Peterson EA, Van Rooijen N, Kenny PA, Wiley HS, Condeelis JS and
Segall JE: Autocrine HBEGF expression promotes breast cancer
intravasation, metastasis and macrophage-independent invasion in
vivo. Oncogene. 33:3784–3793. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Haque S and Morris JC: Transforming growth
factor-β: A therapeutic target for cancer. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
13:1741–1750. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Steitz AM, Steffes A, Finkernagel F, Unger
A, Sommerfeld L, Jansen JM, Wagner U, Graumann J, Müller R and
Reinartz S: Tumor-associated macrophages promote ovarian cancer
cell migration by secreting transforming growth factor beta induced
(TGFBI) and tenascin C. Cell Death Dis. 11:2492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dasari S, Fang Y and Mitra AK: Cancer
associated fibroblasts: Naughty neighbors that drive ovarian cancer
progression. Cancers (Basel). 10:4062018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Gao Q, Yang Z, Xu S, Li X, Yang X, Jin P,
Liu Y, Zhou X, Zhang T, Gong C, et al: Heterotypic CAF-tumor
spheroids promote early peritoneal metastatis of ovarian cancer. J
Exp Med. 216:688–703. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhuang J, Lu Q, Shen B, Huang X, Shen L,
Zheng X, Huang R, Yan J and Guo H: TGFβ1 secreted by
cancer-associated fibroblasts induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition of bladder cancer cells through lncRNA-ZEB2NAT. Sci Rep.
5:119242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Kan T, Wang W, Ip PP, Zhou S, Wong AS,
Wang X and Yang M: Single-cell EMT-related transcriptional analysis
revealed intra-cluster heterogeneity of tumor cell clusters in
epithelial ovarian cancer ascites. Oncogene. 39:4227–4240. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Han Q, Huang B, Huang Z, Cai J, Gong L,
Zhang Y, Jiang J, Dong W and Wang Z: Tumor cell-fibroblast
heterotypic aggregates in malignant ascites of patients with
ovarian cancer. Int J Mol Med. 44:2245–2255. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liu CL, Pan HW, Torng PL, Fan MH and Mao
TL: SRPX and HMCN1 regulate cancer-associated fibroblasts to
promote the invasiveness of ovarian carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
42:2706–2715. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
De Cicco P, Ercolano G and Ianaro A: The
new era of cancer immunotherapy: Targeting myeloid-derived
suppressor cells to overcome immune evasion. Front Immunol.
11:16802020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sasidharan Nair V and Elkord E: Immune
checkpoint inhibitors in cancer therapy: A focus on T-regulatory
cells. Immunol Cell Biol. 96:21–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li X, Wang J, Wu W, Gao H, Liu N, Zhan G,
Li L, Han L and Guo X: Myeloid-derived suppressor cells promote
epithelial ovarian cancer cell stemness by inducing the
CSF2/p-STAT3 signalling pathway. FEBS J. 287:5218–5235. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Horikawa N, Abiko K, Matsumura N,
Hamanishi J, Baba T, Yamaguchi K, Yoshioka Y, Koshiyama M and
Konishi I: Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in
ovarian cancer inhibits tumor immunity through the accumulation of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Clin Cancer Res. 23:587–599.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Dutsch-Wicherek MM, Szubert S, Dziobek K,
Wisniewski M, Lukaszewska E, Wicherek L, Jozwicki W, Rokita W and
Koper K: Analysis of the treg cell population in the peripheral
blood of ovarian cancer patients in relation to the long-term
outcomes. Ginekol Pol. 90:179–184. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Batlle E and Massague J: Transforming
growth Factor-beta signaling in immunity and cancer. Immunity.
50:924–940. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhou J, Jiang W, Huang W, Ye M and Zhu X:
Prognostic values of transforming growth Factor-Beta subtypes in
ovarian cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2020:21706062020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wen H, Qian M, He J, Li M, Yu Q and Leng
Z: Inhibiting of self-renewal, migration and invasion of ovarian
cancer stem cells by blocking TGF-beta pathway. PLoS One.
15:e02302302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Bai Y, Li LD, Li J, Chen RF, Yu HL, Sun
HF, Wang JY and Lu X: A FXYD5/TGFβ/SMAD positive feedback loop
drives epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor
growth and metastasis in ovarian cancer. Int J Oncol. 56:301–314.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Fukui S, Nagasaka K, Miyagawa Y,
Kikuchi-Koike R, Kawata Y, Kanda R, Ichinose T, Sugihara T, Hiraike
H, Wada-Hiraike O, et al: The proteasome deubiquitinase inhibitor
bAP15 downregulates TGF-β/Smad signaling and induces apoptosis via
UCHL5 inhibition in ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 10:5932–5948. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kulbe H, Chakravarty P, Leinster DA,
Charles KA, Kwong J, Thompson RG, Coward JI, Schioppa T, Robinson
SC, Gallagher WM, et al: A dynamic inflammatory cytokine network in
the human ovarian cancer microenvironment. Cancer Res. 72:66–75.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Carbotti G, Petretto A, Naschberger E,
Sturzl M, Martini S, Mingari MC, Filaci G, Ferrini S and Fabbi M:
Cytokine-Induced Guanylate Binding Protein 1 (GBP1) release from
human ovarian cancer cells. Cancers (Basel). 12:4882020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhao H, Yang L, Baddour J, Achreja A,
Bernard V, Moss T, Marini JC, Tudawe T, Seviour EG, San Lucas FA,
et al: Tumor microenvironment derived exosomes pleiotropically
modulate cancer cell metabolism. Elife. 5:e102502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Whiteside TL: The effect of tumor-derived
exosomes on immune regulation and cancer immunotherapy. Future
Oncol. 13:2583–2592. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gong M, Yu B, Wang J, Wang Y, Liu M, Paul
C, Millard RW, Xiao DS, Ashraf M and Xu M: Mesenchymal stem cells
release exosomes that transfer miRNAs to endothelial cells and
promote angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 8:45200–45212. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wu Q, Zhou L, Lv D, Zhu X and Tang H:
Exosome-mediated communication in the tumor microenvironment
contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma development and
progression. J Hematol Oncol. 12:532019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Dorayappan KDP, Wanner R, Wallbillich JJ,
Saini U, Zingarelli R, Suarez AA, Cohn DE and Selvendiran K:
Hypoxia-induced exosomes contribute to a more aggressive and
chemoresistant ovarian cancer phenotype: A novel mechanism linking
STAT3/Rab proteins. Oncogene. 37:3806–3821. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Matias Ostrowski NBC, Sophie Krumeich,
Isabelle Fanget, Graça Raposo, Ariel Savina, et al: Rab27a and
Rab27b control different steps of the exosome secretion pathway.
Nat Cell Biol. 12:19–30. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Qiu JJ, Lin XJ, Tang XY, Zheng TT, Lin YY
and Hua KQ: Exosomal metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma
Transcript 1 promotes angiogenesis and predicts poor prognosis in
epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Biol Sci. 14:1960–1973. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Tang MKS, Yue PYK, Ip PP, Huang RL, Lai
HC, Cheung ANY, Tse KY, Ngan HYS and Wong AST: Soluble E-cadherin
promotes tumor angiogenesis and localizes to exosome surface. Nat
Commun. 9:22702018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Runz S, Keller S, Rupp C, Stoeck A, Issa
Y, Koensgen D, Mustea A, Sehouli J, Kristiansen G and Altevogt P:
Malignant ascites-derived exosomes of ovarian carcinoma patients
contain CD24 and EpCAM. Gynecol Oncol. 107:563–571. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Lei X, Lei Y, Li JK, Du WX, Li RG, Yang J,
Li J, Li F and Tan HB: Immune cells within the tumor
microenvironment: Biological functions and roles in cancer
immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 470:126–133. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xu SJ, Hu HT, Li HL and Chang S: The role
of miRNAs in immune cell development, immune cell activation, and
tumor immunity: With a focus on macrophages and natural killer
cells. Cells. 8:11402019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Rhee I: Diverse macrophages polarization
in tumor microenvironment. Arch Pharm Res. 39:1588–1596. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Tashiro-Yamaji J, Kubota T and Yoshida R:
Macrophage MHC receptor 2: A novel receptor on allograft
(H-2D(d)K(d))-induced macrophage (H-2D(b)K(b)) recognizing an MHC
class I molecule, H-2K(d), in mice. Gene. 384:1–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Chen X, Zhou J, Li X and Wang X, Lin Y and
Wang X: Exosomes derived from hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer
cells deliver microRNAs to macrophages and elicit a tumor-promoted
phenotype. Cancer Lett. 435:80–91. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ruffell B, Affara NI and Coussens LM:
Differential macrophage programming in the tumor microenvironment.
Trends Immunol. 33:119–126. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Funes SC, Rios M, Escobar-Vera J and
Kalergis AM: Implications of macrophage polarization in
autoimmunity. Immunology. 154:186–195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Madeddu C, Gramignano G, Kotsonis P, Coghe
F, Atzeni V, Scartozzi M and Macciò A: Microenvironmental M1
tumor-associated macrophage polarization influences cancer-related
anemia in advanced ovarian cancer: Key role of interleukin-6.
Haematologica. 103:e388–e391. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Reinartz S, Schumann T, Finkernagel F,
Wortmann A, Jansen JM, Meissner W, Krause M, Schwörer AM, Wagner U,
Müller-Brüsselbach S and Müller R: Mixed-polarization phenotype of
ascites-associated macrophages in human ovarian carcinoma:
Correlation of CD163 expression, cytokine levels and early relapse.
Int J Cancer. 134:32–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Nowak M and Klink M: The role of
tumor-associated macrophages in the progression and chemoresistance
of ovarian cancer. Cells. 9:12992020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Zhu Q, Wu X, Wu Y and Wang X: Interaction
between Treg cells and tumor-associated macrophages in the tumor
microenvironment of epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep.
36:3472–3478. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhou J, Li X, Wu X, Zhang T, Zhu Q and
Wang X, Wang H, Wang K, Lin Y and Wang X: Exosomes released from
tumor-associated macrophages transfer miRNAs that induce a
Treg/Th17 cell imbalance in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer
Immunol Res. 6:1578–1592. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Huang YJ, Huang TH, Yadav VK, Sumitra MR,
Tzeng DT, Wei PL, Shih JW and Wu AT: Preclinical investigation of
ovatodiolide as a potential inhibitor of colon cancer stem cells
via downregulating sphere-derived exosomal
beta-catenin/STAT3/miR-1246 cargoes. Am J Cancer Res. 10:2337–2354.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xiao L, He Y, Peng F, Yang J and Yuan C:
Endometrial cancer cells promote M2-like macrophage polarization by
delivering exosomal miRNA-21 under hypoxia condition. J Immunol
Res. 2020:97310492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wang X, Luo G, Zhang K, Cao J, Huang C,
Jiang T, Liu B, Su L and Qiu Z: Hypoxic tumor-derived exosomal
miR-301a Mediates M2 macrophage polarization via PTEN/PI3Kgamma to
promote pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 78:4586–4598.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Bardi GT, Smith MA and Hood JL: Melanoma
exosomes promote mixed M1 and M2 macrophage polarization. Cytokine.
105:63–72. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Li X, Lei Y, Wu M and Li N: Regulation of
macrophage activation and polarization by HCC-derived exosomal
lncRNA TUC339. Int J Mol Sci. 19:29582018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Piao YJ, Kim HS, Hwang EH, Woo J, Zhang M
and Moon WK: Breast cancer cell-derived exosomes and macrophage
polarization are associated with lymph node metastasis. Oncotarget.
9:7398–7410. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Pritchard A, Tousif S, Wang Y, Hough K,
Khan S, Strenkowski J, Chacko BK, Darley-Usmar VM and Deshane JS:
Lung tumor cell-derived exosomes promote M2 macrophage
polarization. Cells. 9:13032020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Chen X, Ying X and Wang X, Wu X, Zhu Q and
Wang X: Exosomes derived from hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer
deliver microRNA-940 to induce macrophage M2 polarization. Oncol
Rep. 38:522–528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Li X and Tang M: Exosomes released from M2
macrophages transfer miR-221-3p contributed to EOC progression
through targeting CDKN1B. Cancer Med. 9:5976–5988. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ying X, Wu Q, Wu X, Zhu Q and Wang X,
Jiang L, Chen X and Wang X: Epithelial ovarian cancer-secreted
exosomal miR-222-3p induces polarization of tumor-associated
macrophages. Oncotarget. 7:43076–43087. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Wu Q, Wu X, Ying X, Zhu Q and Wang X,
Jiang L, Chen X, Wu Y and Wang X: Suppression of endothelial cell
migration by tumor associated macrophage-derived exosomes is
reversed by epithelial ovarian cancer exosomal lncRNA. Cancer Cell
Int. 17:622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hu Y, Li D, Wu A, Qiu X, Di W, Huang L and
Qiu L: TWEAK-stimulated macrophages inhibit metastasis of
epithelial ovarian cancer via exosomal shuttling of microRNA.
Cancer Lett. 393:60–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Baj-Krzyworzeka M, Szatanek R, Weglarczyk
K, Baran J and Zembala M: Tumour-derived microvesicles modulate
biological activity of human monocytes. Immunol Lett. 113:76–82.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Baj-Krzyworzeka M, Baran J, Weglarczyk K,
Szatanek R, Szaflarska A, Siedlar M and Zembala M: Tumour-derived
microvesicles (TMV) mimic the effect of tumour cells on monocyte
subpopulations. Anticancer Res. 30:3515–3520. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Baj-Krzyworzeka M, Mytar B, Szatanek R,
Surmiak M, Weglarczyk K, Baran J and Siedlar M: Colorectal
cancer-derived microvesicles modulate differentiation of human
monocytes to macrophages. J Transl Med. 14:362016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Moradi-Chaleshtori M, Bandehpour M, Soudi
S, Mohammadi-Yeganeh S and Hashemi SM: In vitro and in vivo
evaluation of anti-tumoral effect of M1 phenotype induction in
macrophages by miR-130 and miR-33 containing exosomes. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Yue S, Ye X, Zhou T, Gan D, Qian H, Fang
W, Yao M, Zhang D, Shi H and Chen T: PGRN−/−
TAMs-derived exosomes inhibit breast cancer cell invasion and
migration and its mechanism exploration. Life Sci. 264:1186872020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Han JJ, Yu M, Houston N, Steinberg SM and
Kohn EC: Progranulin is a potential prognostic biomarker in
advanced epithelial ovarian cancers. Gynecol Oncol. 120:5–10. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Carlson AM, Maurer MJ, Goergen KM, Kalli
KR, Erskine CL, Behrens MD, Knutson KL and Block MS: Utility of
progranulin and serum leukocyte protease inhibitor as diagnostic
and prognostic biomarkers in ovarian cancer. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 22:1730–1735. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Dong T, Yang D, Li R, Zhang L, Zhao H,
Shen Y, Zhang X, Kong B and Wang L: PGRN promotes migration and
invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through an epithelial
mesenchymal transition program and the activation of cancer
associated fibroblasts. Exp Mol Pathol. 100:17–25. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Dou R, Hong Z, Tan X, Hu F, Ding Y, Wang
W, Liang Z, Zhong R, Wu X and Weng X: Fas/FasL interaction mediates
imbalanced cytokine/cytotoxicity responses of iNKT cells against
Jurkat cells. Mol Immunol. 99:145–153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Wallin RP, Screpanti V, Michaelsson J,
Grandien A and Ljunggren HG: Regulation of perforin-independent NK
cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Eur J Immunol. 33:2727–2735. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Tanaka H, Kai S, Yamaguchi M, Misawa M,
Fujimori Y, Yamamoto M and Hara H: Analysis of natural killer (NK)
cell activity and adhesion molecules on NK cells from umbilical
cord blood. Eur J Haematol. 71:29–38. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Konjevic GM, Vuletic AM, Mirjacic
Martinovic KM, Larsen AK and Jurisic VB: The role of cytokines in
the regulation of NK cells in the tumor environment. Cytokine.
117:30–40. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Pahl JHW, Cerwenka A and Ni J: Memory-Like
NK Cells: Remembering a previous activation by cytokines and NK
cell receptors. Front Immunol. 9:27962018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Gianchecchi E, Delfino DV and Fierabracci
A: NK cells in autoimmune diseases: Linking innate and adaptive
immune responses. Autoimmun Rev. 17:142–154. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Zitti B and Bryceson YT: Natural killer
cells in inflammation and autoimmunity. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
42:37–46. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Rodriguez GM, Galpin KJC, McCloskey CW and
Vanderhyden BC: The tumor microenvironment of epithelial ovarian
cancer and its influence on response to immunotherapy. Cancers
(Basel). 10:2422018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Zhu L, Kalimuthu S, Oh JM, Gangadaran P,
Baek SH, Jeong SY, Lee SW, Lee J and Ahn BC: Enhancement of
antitumor potency of extracellular vesicles derived from natural
killer cells by IL-15 priming. Biomaterials. 190-191:38–50. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Jong AY, Wu CH, Li J, Sun J, Fabbri M,
Wayne AS and Seeger RC: Large-scale isolation and cytotoxicity of
extracellular vesicles derived from activated human natural killer
cells. J Extracell Vesicles. 6:12943682017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Lugini L, Cecchetti S, Huber V, Luciani F,
Macchia G, Spadaro F, Paris L, Abalsamo L, Colone M, Molinari A, et
al: Immune surveillance properties of human NK cell-derived
exosomes. J Immunol. 189:2833–2842. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Di Pace A, Tumino N, Besi F, Alicata C,
Conti LA, Munari E, Maggi E, Vacca P and Moretta L:
Characterization of human NK cell-derived exosomes: Role of DNAM1
receptor in exosome-mediated cytotoxicity against tumor. Cancers
(Basel). 12:6612020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Zhu L, Kalimuthu S, Gangadaran P, Oh JM,
Lee HW, Baek SH, Jeong SY, Lee SW, Lee J and Ahn BC: Exosomes
derived from natural killer cells exert therapeutic effect in
melanoma. Theranostics. 7:2732–2745. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Neviani P, Wise PM, Murtadha M, Liu CW, Wu
CH, Jong AY, Seeger RC and Fabbri M: Natural killer-derived
exosomal miR-186 inhibits neuroblastoma growth and immune escape
mechanisms. Cancer Res. 79:1151–1164. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Terrén I, Orrantia A, Vitallé J,
Zenarruzabeitia O and Borrego F: NK cell metabolism and tumor
microenvironment. Front Immunol. 10:22782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Labani-Motlagh A, Israelsson P, Ottander
U, Lundin E, Nagaev I, Nagaeva O, Dehlin E, Baranov V and
Mincheva-Nilsson L: Differential expression of ligands for NKG2D
and DNAM-1 receptors by epithelial ovarian cancer-derived exosomes
and its influence on NK cell cytotoxicity. Tumour Biol.
37:5455–5466. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Ishii S and Koziel MJ: Immune responses
during acute and chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. Clin
Immunol. 128:133–147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Kaech SM and Cui W: Transcriptional
control of effector and memory CD8+ T cell differentiation. Nat Rev
Immunol. 12:749–761. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Thommen DS and Schumacher TN: T cell
dysfunction in cancer. Cancer Cell. 33:547–562. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Hiltbrunner S, Larssen P, Eldh M,
Martinez-Bravo MJ, Wagner AK, Karlsson MC and Gabrielsson S:
Exosomal cancer immunotherapy is independent of MHC molecules on
exosomes. Oncotarget. 7:38707–38717. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Torralba D, Baixauli F, Villarroya-Beltri
C, Fernández-Delgado I, Latorre-Pellicer A, Acín-Pérez R,
Martín-Cófreces NB, Jaso-Tamame ÁL, Iborra S, Jorge I, et al:
Priming of dendritic cells by DNA-containing extracellular vesicles
from activated T cells through antigen-driven contacts. Nat Commun.
9:26582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Raposo G, Nijman HW, Stoorvogel W,
Liejendekker R, Harding CV, Melief CJ and Geuze HJ: B lymphocytes
secrete antigen-presenting vesicles. J Exp Med. 183:1161–1172.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Yang J, Bi L, He X, Wang Z, Qian Y, Xiao L
and Shi B: Follicular helper T cell derived exosomes promote B cell
proliferation and differentiation in antibody-mediated rejection
after renal transplantation. Biomed Res Int.
2019:63879242019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Fernandez-Messina L, Rodriguez-Galan A, de
Yebenes VG, Gutierrez-Vazquez C, Tenreiro S, Seabra MC, Ramiro AR
and Sánchez-Madrid F: Transfer of extracellular vesicle-microRNA
controls germinal center reaction and antibody production. EMBO
Rep. 21:e489252020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Li Y, Yang Y, Xiong A, Wu X, Xie J, Han S
and Zhao S: Comparative gene expression analysis of lymphocytes
treated with exosomes derived from ovarian cancer and ovarian
cysts. Front Immunol. 8:6072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Xu HY, Li N, Yao N, Xu XF, Wang HX, Liu XY
and Zhang Y: CD8+ T cells stimulated by exosomes derived from RenCa
cells mediate specific immune responses through the FasL/Fas
signaling pathway and, combined with GM-CSF and IL-12, enhance the
anti-renal cortical adenocarcinoma effect. Oncol Rep. 42:866–879.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Taylor DD, Gerçel-Taylor C, Lyons KS,
Stanson J and Whiteside TL: T-Cell apoptosis and suppression of
T-Cell Receptor/CD3-zeta by Fas Ligand-Containing membrane vesicles
shed from ovarian tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 9:5113–5119.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Abusamra AJ, Zhong Z, Zheng X, Li M, Ichim
TE, Chin JL and Min WP: Tumor exosomes expressing Fas ligand
mediate CD8+ T-cell apoptosis. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 35:169–173.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Filipazzi P, Burdek M, Villa A, Rivoltini
L and Huber V: Recent advances on the role of tumor exosomes in
immunosuppression and disease progression. Semin Cancer Biol.
22:342–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Wang X, Yao Y and Jin M: Circ-0001068 is a
novel biomarker for ovarian cancer and inducer of PD1 expression in
T cells. Aging (Albany NY). 12:19095–19106. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Asare-Werehene M, Communal L, Carmona E,
Han Y, Song YS, Burger D, Mes-Masson AM and Tsang BK: Plasma
gelsolin inhibits CD8+ T-cell function and regulates
glutathione production to confer chemoresistance in ovarian cancer.
Cancer Res. 80:3959–3971. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Taylor DD and Gercel-Taylor C:
Tumour-derived exosomes and their role in cancer-associated T-cell
signalling defects. Br J Cancer. 92:305–311. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Shenoy GN, Loyall J, Berenson CS, Kelleher
RJ Jr, Iyer V, Balu-Iyer SV, Odunsi K and Bankert RB: Sialic
Acid-Dependent inhibition of T Cells by Exosomal Ganglioside GD3 in
ovarian tumor microenvironments. J Immunol. 201:3750–3758. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Webb TJ, Li X, Giuntoli RL II, Lopez PH,
Heuser C, Schnaar RL, Tsuji M, Kurts C, Oelke M and Schneck JP:
Molecular identification of GD3 as a suppressor of the innate
immune response in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 72:3744–3752. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Shenoy GN, Loyall J, Maguire O, Iyer V,
Kelleher RJ Jr, Minderman H, Wallace PK, Odunsi K, Balu-Iyer SV and
Bankert RB: Exosomes Associated with human ovarian tumors harbor a
reversible checkpoint of T-cell Responses. Cancer Immunol Res.
6:236–247. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Clayton A, Al-Taei S, Webber J, Mason MD
and Tabi Z: Cancer exosomes express CD39 and CD73, which suppress T
cells through adenosine production. J Immunol. 187:676–683. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Kelleher RJ Jr, Balu-Iyer S, Loyall J,
Sacca AJ, Shenoy GN, Peng P, Iyer V, Fathallah AM, Berenson CS,
Wallace PK, et al: Extracellular vesicles present in human ovarian
tumor microenvironments induce a Phosphatidylserine-Dependent
arrest in the T-cell signaling cascade. Cancer Immunol Res.
3:1269–1278. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Li X and Wang X: The emerging roles and
therapeutic potential of exosomes in epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol
Cancer. 16:922017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Wang Y, Xiang Y, Xin VW, Wang XW, Peng XC,
Liu XQ, Wang D, Li N, Cheng JT, Lyv YN, et al: Dendritic cell
biology and its role in tumor immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol.
13:1072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Skokos D, Botros HG, Demeure C, Morin J,
Peronet R, Birkenmeier G, Boudaly S and Mécheri S: Mast
cell-derived exosomes induce phenotypic and functional maturation
of dendritic cells and elicit specific immune responses in vivo. J
Immunol. 170:3037–3045. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Robbins PD and Morelli AE: Regulation of
immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Immunol.
14:195–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Lindenbergh MFS, Koerhuis DGJ, Borg EGF,
van't Veld EM, Driedonks TAP, Wubbolts R, Stoorvogel W and Boes M:
Bystander T-Cells Support Clonal T-Cell activation by controlling
the release of dendritic Cell-Derived Immune-Stimulatory
extracellular vesicles. Front Immunol. 10:4482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Zheng L, Li Z, Ling W, Zhu D, Feng Z and
Kong L: Exosomes derived from dendritic cells attenuate liver
injury by modulating the balance of Treg and Th17 Cells after
ischemia reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 46:740–756. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Li QL, Bu N, Yu YC, Hua W and Xin XY:
Exvivo experiments of human ovarian cancer ascites-derived exosomes
presented by dendritic cells derived from umbilical cord blood for
immunotherapy treatment. Clin Med Oncol. 2:461–467. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Pitt JM, André F, Amigorena S, Soria JC,
Eggermont A, Kroemer G and Zitvogel L: Dendritic cell-derived
exosomes for cancer therapy. J Clin Invest. 126:1224–1232. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Ridge SM, Sullivan FJ and Glynn SA:
Mesenchymal stem cells: Key players in cancer progression. Mol
Cancer. 16:312017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
De Miguel MP, Fuentes-Julián S,
Blázquez-Martínez A, Pascual CY, Aller MA, Arias J and
Arnalich-Montiel F: Immunosuppressive properties of mesenchymal
stem cells: Advances and applications. Curr Mol Med. 12:574–591.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Lis R, Touboul C, Raynaud CM, Malek JA,
Suhre K, Mirshahi M and Rafii A: Mesenchymal cell interaction with
ovarian cancer cells triggers pro-metastatic properties. PLoS One.
7:e383402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Zhang B, Tian X, Hao J, Xu G and Zhang W:
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived extracellular vesicles in tissue
regeneration. Cell Transplant. 29:9636897209085002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Khare D, Or R, Resnick I, Barkatz C,
Almogi-Hazan O and Avni B: Mesenchymal stromal Cell-Derived
exosomes affect mRNA expression and function of B-Lymphocytes.
Front Immunol. 9:30532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Yang Y, Bucan V, Baehre H, von der Ohe J,
Otte A and Hass R: Acquisition of new tumor cell properties by
MSC-derived exosomes. Int J Oncol. 47:244–252. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Sharma S, Alharbi M, Kobayashi M, Lai A,
Guanzon D, Zuniga F, Ormazabal V, Palma C, Scholz-Romero K, Rice
GE, et al: Proteomic analysis of exosomes reveals an association
between cell invasiveness and exosomal bioactivity on endothelial
and mesenchymal cell migration in vitro. Clin Sci (Lond).
132:2029–2044. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Dean M, Fojo T and Bates S: Tumour stem
cells and drug resistance. Nat Rev Cancer. 5:275–284. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Vera N, Acuna-Gallardo S, Grunenwald F,
Caceres-Verschae A, Realini O, Acuna R, Lladser A, Illanes SE and
Varas-Godoy M: Small extracellular vesicles released from ovarian
cancer spheroids in response to Cisplatin Promote the
Pro-Tumorigenic activity of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci.
20:49722019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Qiu L, Wang J, Chen M, Chen F and Tu W:
Exosomal microRNA-146a derived from mesenchymal stem cells
increases the sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells to docetaxel and
taxane via a LAMC2-mediated PI3K/Akt axis. Int J Mol Med.
46:609–620. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Reza AMMT, Choi YJ, Yasuda H and Kim JH:
Human adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal-miRNAs are
critical factors for inducing anti-proliferation signalling to
A2780 and SKOV-3 ovarian cancer cells. Sci Rep. 6:384982016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Melzer C, Rehn V, Yang Y, Bahre H, von der
Ohe J and Hass R: Taxol-Loaded MSC-Derived exosomes provide a
therapeutic vehicle to target metastatic breast cancer and other
carcinoma cells. Cancers (Basel). 11:7982019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Tanaka A and Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T
cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 27:109–118. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X,
Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L,
Burow M, et al: Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in
ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced
survival. Nat Med. 10:942–949. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Szajnik M, Czystowska M, Szczepanski MJ,
Mandapathil M and Whiteside TL: Tumor-derived microvesicles induce,
expand and up-regulate biological activities of human regulatory T
cells (Treg). PLoS One. 5:e114692010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Gabrilovich DI: Myeloid-Derived suppressor
cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 5:3–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Chalmin F, Ladoire S, Mignot G, Vincent J,
Bruchard M, Remy-Martin JP, Boireau W, Rouleau A, Simon B, Lanneau
D, et al: Membrane-associated Hsp72 from tumor-derived exosomes
mediates STAT3-dependent immunosuppressive function of mouse and
human myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 120:457–471.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Balaburski GM, Leu JI, Beeharry N, Hayik
S, Andrake MD, Zhang G, Herlyn M, Villanueva J, Dunbrack RL Jr, Yen
T, et al: A modified HSP70 inhibitor shows broad activity as an
anticancer agent. Mol Cancer Res. 11:219–229. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Gobbo J, Marcion G, Cordonnier M, Dias
AMM, Pernet N, Hammann A, Richaud S, Mjahed H, Isambert N, Clausse
V, et al: Restoring anticancer immune response by targeting
Tumor-Derived exosomes with a HSP70 Peptide Aptamer. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 108:2015.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Liu T, Han C, Wang S, Fang P, Ma Z, Xu L
and Yin R: Cancer-associated fibroblasts: An emerging target of
anti-cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. 12:862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Cho JA, Park H, Lim EH, Kim KH, Choi JS,
Lee JH, Shin JW and Lee KW: Exosomes from ovarian cancer cells
induce adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells to acquire the
physical and functional characteristics of tumor-supporting
myofibroblasts. Gynecol Oncol. 123:379–386. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Yeung TL, Leung CS, Wong KK, Samimi G,
Thompson MS, Liu J, Zaid TM, Ghosh S, Birrer MJ and Mok SC: TGF-β
modulates ovarian cancer invasion by upregulating CAF-derived
versican in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 73:5016–5028.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Li W, Zhang X, Wang J, Li M, Cao C, Tan J,
Ma D and Gao Q: TGFβ1 in fibroblasts-derived exosomes promotes
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of ovarian cancer cells.
Oncotarget. 8:96035–96047. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Zhang J, Li S, Li L, Li M, Guo C, Yao J
and Mi S: Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and
function. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 13:17–24. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Au Yeung CL, Co NN, Tsuruga T, Yeung TL,
Kwan SY, Leung CS, Li Y, Lu ES, Kwan K, Wong KK, et al: Exosomal
transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in
ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat Commun.
7:111502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Dickman CT, Lawson J, Jabalee J, MacLellan
SA, LePard NE, Bennewith KL and Garnis C: Selective extracellular
vesicle exclusion of miR-142-3p by oral cancer cells promotes both
internal and extracellular malignant phenotypes. Oncotarget.
8:15252–15266. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Kanlikilicer P, Rashed MH, Bayraktar R,
Mitra R, Ivan C, Aslan B, Zhang X, Filant J, Silva AM,
Rodriguez-Aguayo C, et al: Ubiquitous release of exosomal tumor
suppressor miR-6126 from ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Res.
76:7194–7207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Rashed MH, Kanlikilicer P,
Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Pichler M, Bayraktar R, Bayraktar E, Ivan C,
Filant J, Silva A, Aslan B, et al: Exosomal miR-940 maintains
SRC-mediated oncogenic activity in cancer cells: A possible role
for exosomal disposal of tumor suppressor miRNAs. Oncotarget.
8:20145–20164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Masoumi-Dehghi S, Babashah S and
Sadeghizadeh M: MicroRNA-141-3p-containing small extracellular
vesicles derived from epithelial ovarian cancer cells promote
endothelial cell angiogenesis through activating the JAK/STAT3 and
NF-κB signaling pathways. J Cell Commun Signal. 14:233–244. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Yoshimura A, Sawada K, Nakamura K, Kinose
Y, Nakatsuka E, Kobayashi M, Miyamoto M, Ishida K, Matsumoto Y,
Kodama M, et al: Exosomal miR-99a-5p is elevated in sera of ovarian
cancer patients and promotes cancer cell invasion by increasing
fibronectin and vitronectin expression in neighboring peritoneal
mesothelial cells. BMC Cancer. 18:10652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Kobayashi M, Salomon C, Tapia J, Illanes
SE, Mitchell MD and Rice GE: Ovarian cancer cell invasiveness is
associated with discordant exosomal sequestration of Let-7 miRNA
and miR-200. J Transl Med. 12:42014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Pan C, Stevic I, Muller V, Ni Q,
Oliveira-Ferrer L, Pantel K and Schwarzenbach H: Exosomal microRNAs
as tumor markers in epithelial ovarian cancer. Mol Oncol.
12:1935–1948. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Kobayashi M, Sawada K, Nakamura K,
Yoshimura A, Miyamoto M, Shimizu A, Ishida K, Nakatsuka E, Kodama
M, Hashimoto K, et al: Exosomal miR-1290 is a potential biomarker
of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma and can discriminate
patients from those with malignancies of other histological types.
J Ovarian Res. 11:812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Cheng L, Zhang K, Qing Y, Li D, Cui M, Jin
P and Xu T: Proteomic and lipidomic analysis of exosomes derived
from ovarian cancer cells and ovarian surface epithelial cells. J
Ovarian Res. 13:92020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Nakamura K, Sawada K, Kinose Y, Yoshimura
A, Toda A, Nakatsuka E, Hashimoto K, Mabuchi S, Morishige KI,
Kurachi H, et al: Exosomes promote ovarian cancer cell invasion
through transfer of CD44 to peritoneal mesothelial cells. Mol
Cancer Res. 15:78–92. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Dorayappan KDP, Wallbillich JJ, Cohn DE
and Selvendiran K: The biological significance and clinical
applications of exosomes in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
142:199–205. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Enriquez VA, Cleys ER, Da Silveira JC,
Spillman MA, Winger QA and Bouma GJ: High LIN28A expressing ovarian
cancer cells secrete exosomes that induce invasion and migration in
HEK293 cells. Biomed Res Int. 2015:7013902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Stope MB, Klinkmann G, Diesing K, Koensgen
D, Burchardt M and Mustea A: Heat Shock Protein HSP27 secretion by
ovarian cancer cells is linked to intracellular expression levels,
occurs independently of the endoplasmic reticulum pathway and
HSP27's phosphorylation status, and is mediated by exosome
liberation. Dis Markers. 2017:15753742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Nam GH, Choi Y, Kim GB, Kim S, Kim SA and
Kim IS: Emerging prospects of exosomes for cancer treatment: From
conventional therapy to immunotherapy. Adv Mater. 32:e20024402020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Koyama Y, Ito T, Hasegawa A, Eriguchi M,
Inaba T, Ushigusa T and Sugiura K: Exosomes derived from tumor
cells genetically modified to express Mycobacterium tuberculosis
antigen: A novel vaccine for cancer therapy. Biotechnol Lett.
38:1857–1866. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Kalimuthu S, Gangadaran P, Rajendran RL,
Zhu L, Oh JM, Lee HW, Gopal A, Baek SH, Jeong SY, Lee SW, et al: A
new approach for loading anticancer drugs into mesenchymal stem
Cell-Derived exosome mimetics for cancer therapy. Front Pharmacol.
9:11162018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Feng Y, Hang W, Sang Z, Li S, Xu W, Miao
Y, Xi X and Huang Q: Identification of exosomal and non-exosomal
microRNAs associated with the drug resistance of ovarian cancer.
Mol Med Rep. 19:3376–3392. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Zhu X, Shen H, Yin X, Yang M, Wei H, Chen
Q, Feng F, Liu Y, Xu W and Li Y: Macrophages derived exosomes
deliver miR-223 to epithelial ovarian cancer cells to elicit a
chemoresistant phenotype. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:812019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Kanlikilicer P, Bayraktar R, Denizli M,
Rashed MH, Ivan C, Aslan B, Mitra R, Karagoz K, Bayraktar E, Zhang
X, et al: Exosomal miRNA confers chemo resistance via targeting
Cav1/p-gp/M2-type macrophage axis in ovarian cancer. EBioMedicine.
38:100–112. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Guo H, Ha C, Dong H, Yang Z, Ma Y and Ding
Y: Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived exosomal microRNA-98-5p
promotes cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer by targeting
CDKN1A. Cancer Cell Int. 19:3472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Cao YL, Zhuang T, Xing BH, Li N and Li Q:
Exosomal DNMT1 mediates cisplatin resistance in ovarian cancer.
Cell Biochem Funct. 35:296–303. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Kim SM, Yang Y, Oh SJ, Hong Y, Seo M and
Jang M: Cancer-derived exosomes as a delivery platform of
CRISPR/Cas9 confer cancer cell tropism-dependent targeting. J
Control Release. 266:8–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Tsou P, Katayama H, Ostrin EJ and Hanash
SM: The emerging role of B Cells in tumor immunity. Cancer Res.
76:5597–5601. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Im EJ, Lee CH, Moon PG, Rangaswamy GG, Lee
B, Lee JM, Lee JC, Jee JG, Bae JS, Kwon TK, et al: Sulfisoxazole
inhibits the secretion of small extracellular vesicles by targeting
the endothelin receptor A. Nat Commun. 10:13872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Walker S, Busatto S, Pham A, Tian M, Suh
A, Carson K, Quintero A, Lafrence M, Malik H, Santana MX and
Wolfram J: Extracellular vesicle-based drug delivery systems for
cancer treatment. Theranostics. 9:8001–8017. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Pisano S, Pierini I, Gu J, Gazze A,
Francis LW, Gonzalez D, Conlan RS and Corradetti B: Immune (Cell)
Derived Exosome Mimetics (IDEM) as a treatment for ovarian cancer.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:5535762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Ge L, Zhang N, Li D, Wu Y, Wang H and Wang
J: Circulating exosomal small RNAs are promising non-invasive
diagnostic biomarkers for gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med.
24:14502–14513. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Chen Z, Liang Q, Zeng H, Zhao Q, Guo Z,
Zhong R, Xie M, Cai X, Su J, He Z, et al: Exosomal CA125 as a
promising biomarker for ovarian cancer diagnosis. J Cancer.
11:6445–6453. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Wang Y, Li Q, Shi H, Tang K, Qiao L, Yu G,
Ding C and Yu S: Microfluidic Raman biochip detection of exosomes:
A promising tool for prostate cancer diagnosis. Lab Chip.
20:4632–4637. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|