|
1
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Xu J, Kromer C,
Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS: CBTRUS statistical
report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro Oncol. 18
(Suppl_5):v1–v75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ostrom QT, Cote DJ, Ascha M, Kruchko C and
Barnholtz-Sloan JS: Adult glioma incidence and survival by race or
ethnicity in the United States from 2000 to 2014. JAMA Oncol.
4:1254–1262. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang T, Nam DH, Ram Z, Poon WS, Wang J,
Boldbaatar D, Mao Y, Ma W, Mao Q, You Y, et al: CGCG clinical
practice guidelines for the management of adult diffuse gliomas.
Cancer Lett. 375:263–273. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P,
Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss
R, et al: Circular RNAs in the mammalian brain are highly abundant,
conserved, and dynamically expressed. Mol Cell. 58:870–885. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M and Glavač D:
Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, function, and a role as possible cancer
biomarkers. Int J Genomics. 2017:62183532017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Conn SJ, Pillman KA, Toubia J, Conn VM,
Salmanidis M, Phillips CA, Roslan S, Schreiber AW, Gregory PA and
Goodall GJ: The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of
circRNAs. Cell. 160:1125–1134. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xu Y, Yao Y, Zhong X, Leng K, Qin W, Qu L,
Cui Y and Jiang X: Downregulated circular RNA hsa_circ_0001649
regulates proliferation, migration and invasion in
cholangiocarcinoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 49:455–461.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang SJ, Chen X, Li CP, Li XM, Liu C, Liu
BH, Shan K, Jiang Q, Zhao C and Yan B: Identification and
characterization of circular RNAs as a new class of putative
biomarkers in diabetes retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
58:6500–6509. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang W, Wang Y, Piao H, Li B, Huang M, Zhu
Z, Li D, Wang T, Xu R and Liu K: Circular RNAs as potential
biomarkers and therapeutics for cardiovascular disease. PeerJ.
7:e68312019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin P, Huang Y, Zhu P, Zou Y, Shao T and
Wang O: CircRNA circHIPK3 serves as a prognostic marker to promote
glioma progression by regulating miR-654/IGF2BP3 signaling. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 503:1570–1574. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen J, Chen T, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang
Y, Li X, Xie X, Wang J, Huang M, et al: circPTN sponges
miR-145-5p/miR-330-5p to promote proliferation and stemness in
glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
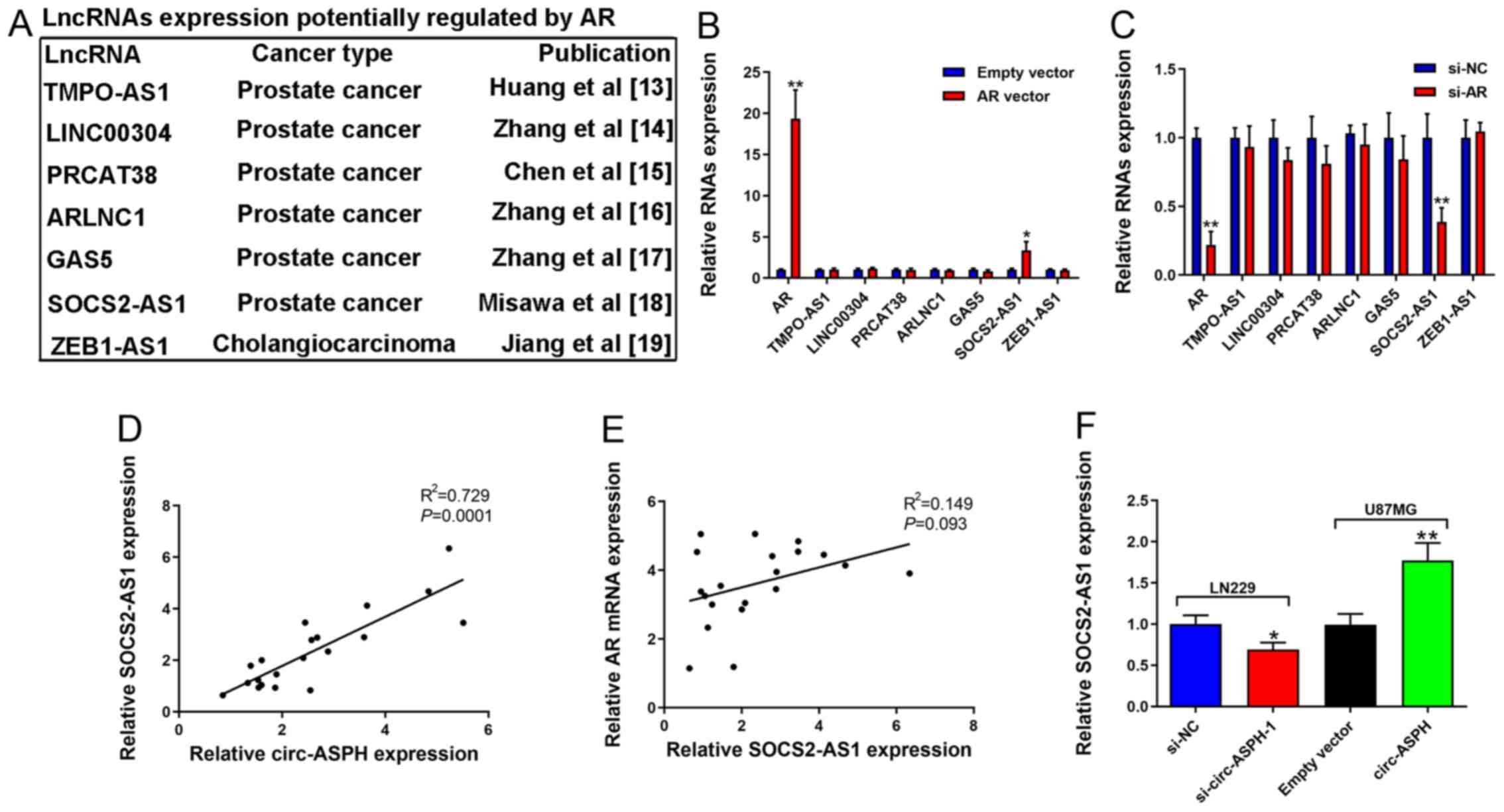
Rahim B and O'Regan R: AR Signaling in
breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 9:212017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Misawa A, Takayama K, Urano T and Inoue S:
Androgen-induced long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) SOCS2-AS1 promotes
cell growth and inhibits apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Biol
Chem. 291:17861–17880. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Su H, Lin F, Deng X, Shen L, Fang Y, Fei
Z, Zhao L, Zhang X, Pan H, Xie D, et al: Profiling and
bioinformatics analyses reveal differential circular RNA expression
in radioresistant esophageal cancer cells. J Transl Med.
14:2252016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dudekula DB, Panda AC, Grammatikakis I, De
S, Abdelmohsen K and Gorospe M: CircInteractome: A web tool for
exploring circular RNAs and their interacting proteins and
microRNAs. RNA Biol. 13:34–42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42:D92–D97. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qu Y, Zhu J, Liu J and Qi L: Circular RNA
circ_0079593 indicates a poor prognosis and facilitates cell growth
and invasion by sponging miR-182 and miR-433 in glioma. J Cell
Biochem. 120:18005–18013. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gucalp A and Traina TA: The Androgen
Receptor: Is it a promising target? Ann Surg Oncol. 24:2876–2880.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Schweizer MT and Yu EY: AR-signaling in
human malignancies: Prostate cancer and beyond. Cancers (Basel).
9:72017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Huang W, Su X, Yan W, Kong Z, Wang D,
Huang Y, Zhai Q, Zhang X, Wu H, Li Y, et al: Overexpression of
AR-regulated lncRNA TMPO-AS1 correlates with tumor progression and
poor prognosis in prostate cancer. Prostate. 78:1248–1261. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang P, Lu Y, Kong Z, Zhang Y, Fu F, Su
X, Huang Y, Wan X and Li Y: Androgen-responsive lncRNA LINC00304
ppromotes cell cycle and proliferation via regulating CCNA1.
Prostate. 79:994–1006. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Z, Song X, Li Q, Xie L, Guo T, Su T,
Tang C, Chang X, Liang B and Huang D: Androgen receptor-activated
enhancers simultaneously regulate oncogene TMPRSS2 and lncRNA
PRCAT38 in prostate cancer. Cells. 8:8642019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Pitchiaya S, Cieślik M, Niknafs
YS, Tien JC, Hosono Y, Iyer MK, Yazdani S, Subramaniam S, Shukla
SK, et al: Analysis of the androgen receptor-regulated lncRNA
landscape identifies a role for ARLNC1 in prostate cancer
progression. Nat Genet. 50:814–824. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang Y, Su X, Kong Z, Fu F, Zhang P, Wang
D, Wu H, Wan X and Li Y: An androgen reduced transcript of lncRNA
GAS5 promoted prostate cancer proliferation. PLoS One.
12:e01823052017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang X, Li J, Wang W, Hu Z, Guan C, Zhao
Y, Li W and Cui Y: AR-induced ZEB1-AS1 represents poor prognosis in
cholangiocarcinoma and facilitates tumor stemness, proliferation
and invasion through mediating miR-133b/HOXB8. Aging (Albany NY).
12:1237–1255. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Hou JC and Ji
ZL: CircRNA: A novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer.
25:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao ZG, Yang P, Huang J and Ding YQ:
CircFBXW7 alleviates glioma progression through regulating
miR-23a-3p/PTEN axis. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 304:279–290. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huo LW, Wang YF, Bai XB, Zheng HL and Wang
MD: circKIF4A promotes tumorogenesis of glioma by targeting
miR-139-3p to activate Wnt5a signaling. Mol Med. 26:292020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang HY, Zhang BW, Zhang ZB and Deng QJ:
Circular RNA TTBK2 regulates cell proliferation, invasion and
ferroptosis via miR-761/ITGB8 axis in glioma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 24:2585–2600. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Glažar P, Papavasileiou P and Rajewsky N:
circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA. 20:1666–1670. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang Q, Li F, He AT and Yang BB: Circular
RNAs: Expression, localization, and therapeutic potentials. Mol
Ther. Jan 21–2021.(Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.01.018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mumtaz PT, Taban Q, Dar MA, Mir S, Haq ZU,
Zargar SM, Shah RA and Ahmad SM: Deep insights in circular RNAs:
From biogenesis to therapeutics. Biol Proced. 22:102020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li C, Tian Y, Liang Y and Li Q:
Circ_0008035 contributes to cell proliferation and inhibits
apoptosis and ferroptosis in gastric cancer via miR-599/EIF4A1
axis. Cancer Cell Int. 20:842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ba Y, Liu Y, Li C, Zhu Y and Xing W: HIPK3
promotes growth and metastasis of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma via regulation of miR-599/c-MYC axis. Onco Targets Ther.
13:1967–1978. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiang Y, Wang X, Zhang J and Lai R:
MicroRNA-599 suppresses glioma progression by targeting RAB27B.
Oncol Lett. 16:1243–1252. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang T, Ma G, Zhang Y, Huo H and Zhao Y:
miR-599 inhibits proliferation and invasion of glioma by targeting
periostin. Biotechnol Lett. 39:1325–1333. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|