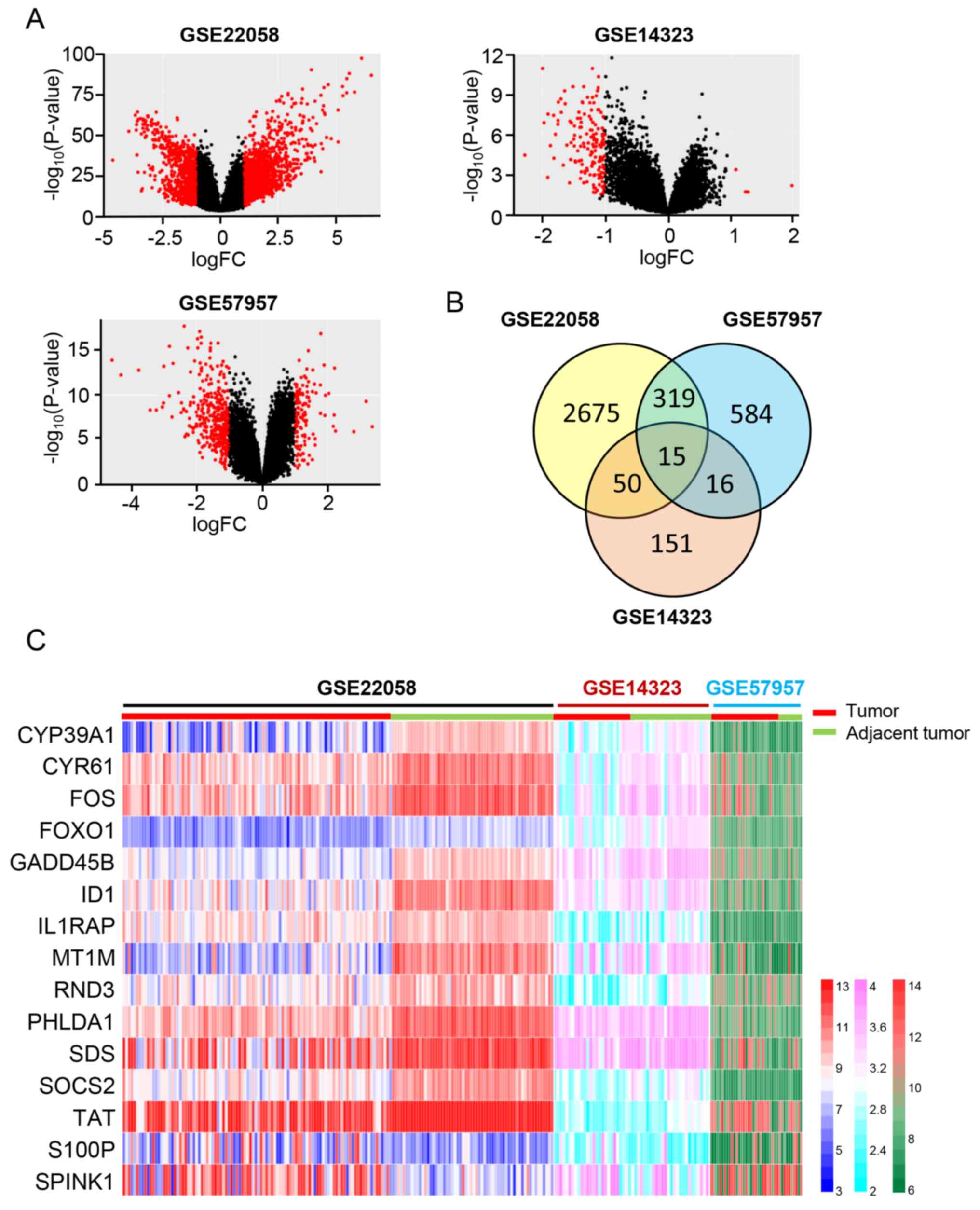
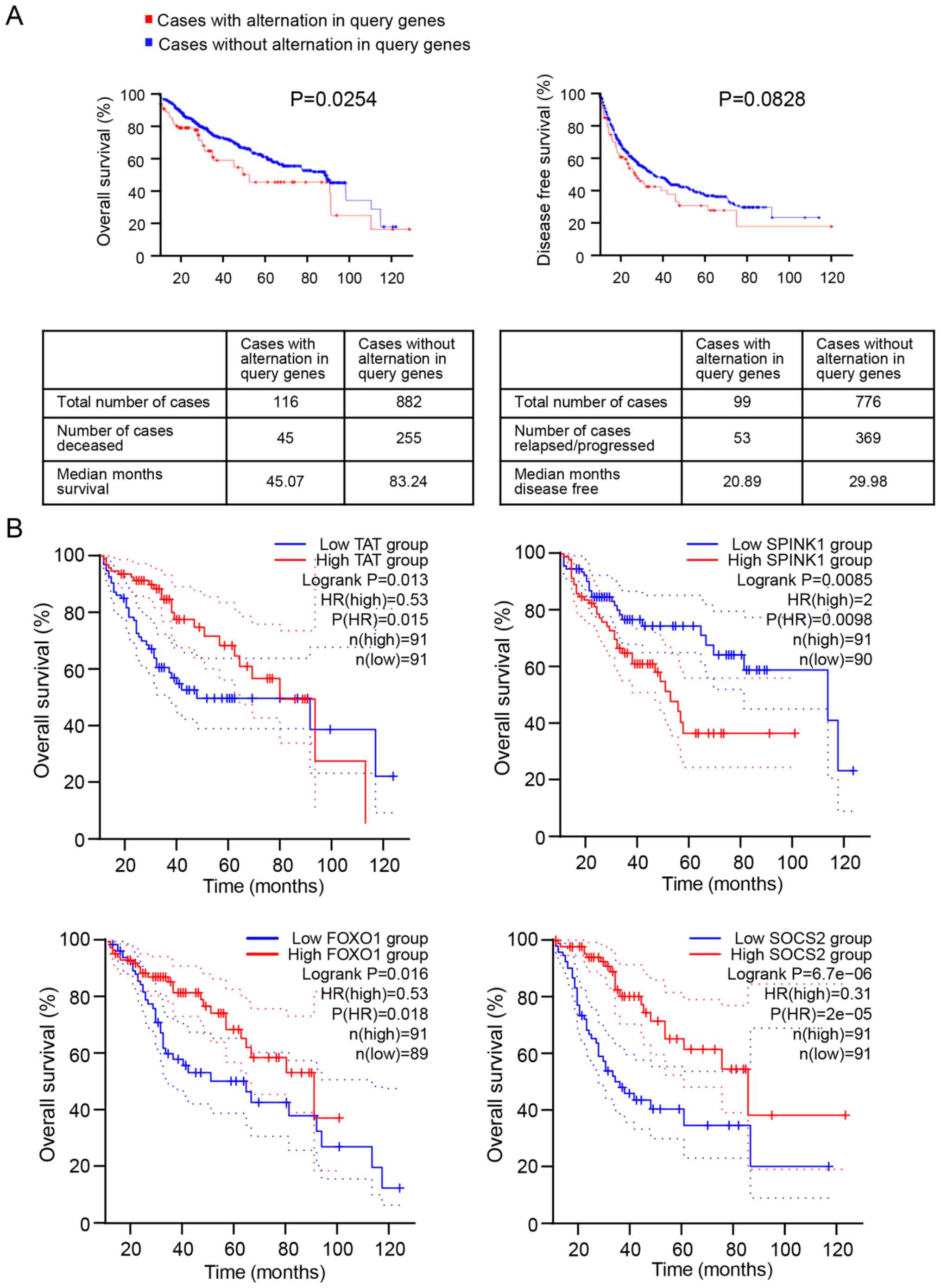
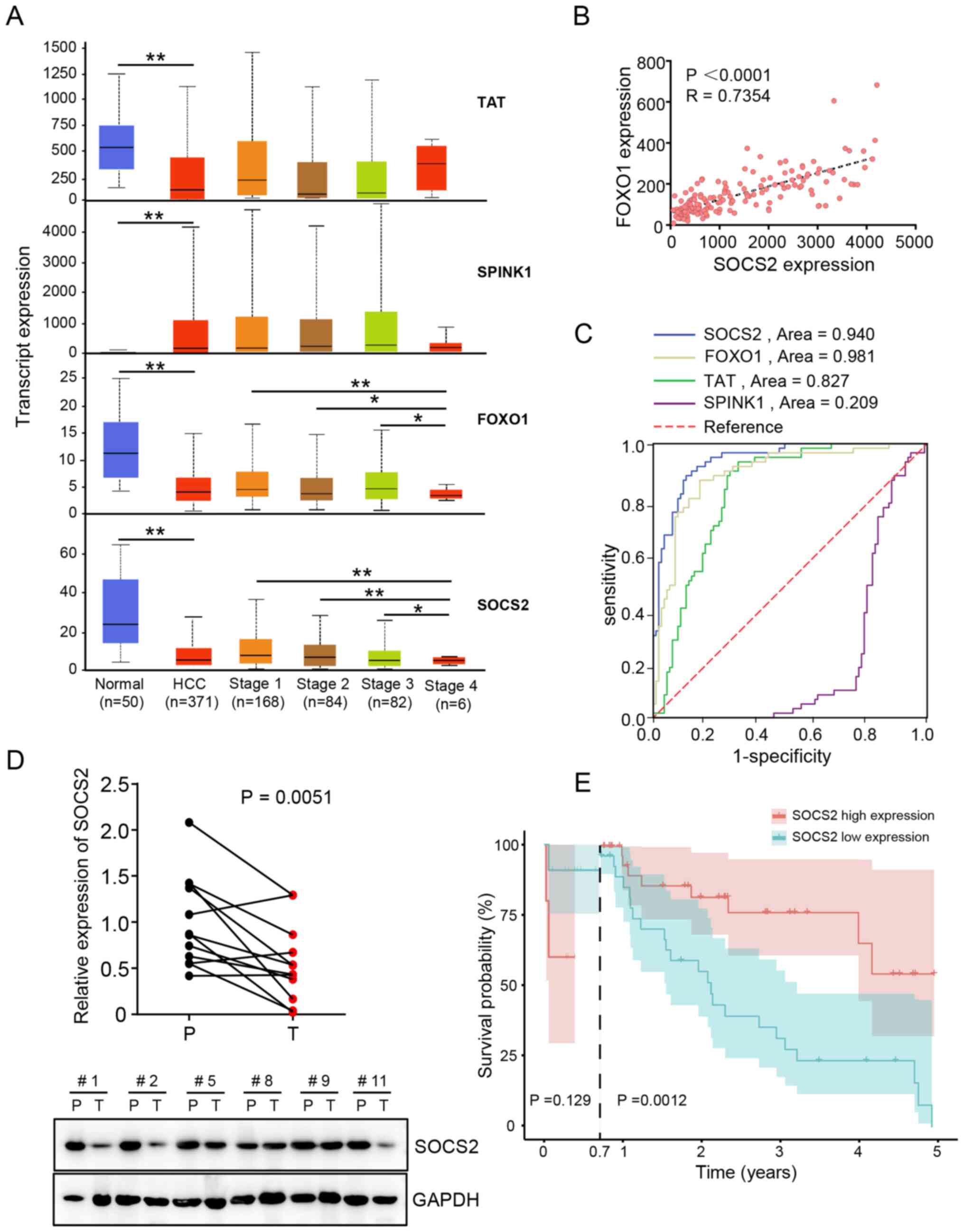
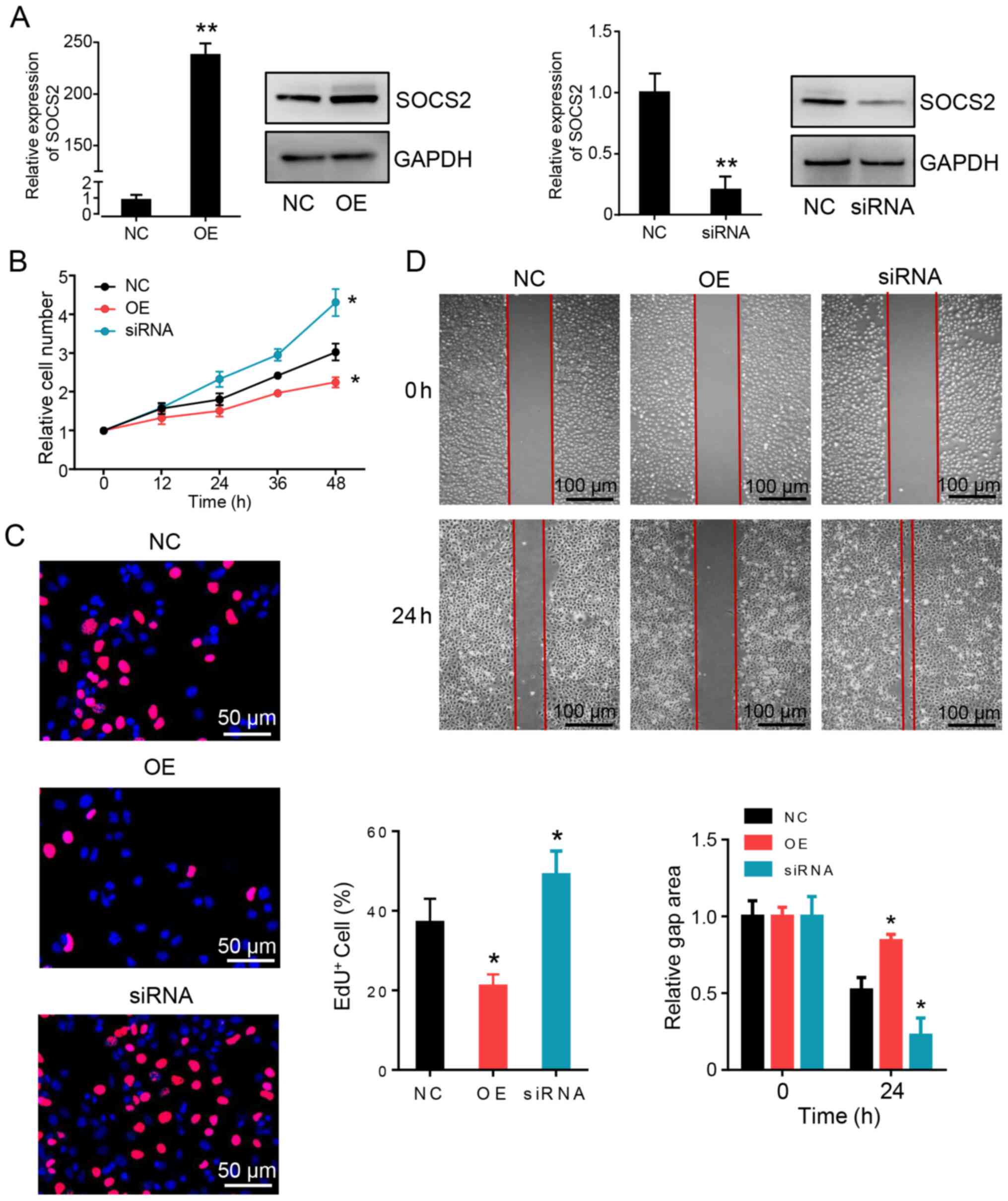
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clini. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kulik L and El-Serag HB: Epidemiology and
management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
156:477–491.e1. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang H, Lu Z and Zhao X: Tumorigenesis,
diagnosis, and therapeutic potential of exosomes in liver cancer. J
Hematol Oncol. 12:1332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dhanasekaran R and Felsher DW: A tale of
two complications of obesity: NASH and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 70:1056–1058. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kudo M: Systemic therapy for
hepatocellular carcinoma: Recent advances and future perspective.
Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 116:8–17. 2019.(In Japanese).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weng Q, Chen M, Li M, Zheng YF, Shao G,
Fan W, Xu XM and Ji J: Global microarray profiling identified
hsa_circ_ 0064428 as a potential immune-associated prognosis
biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Med Genet. 56:32–38.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lin J, Lin W, Ye Y, Wang L, Chen X, Zang S
and Huang A: Kindlin-2 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion
and metastasis by increasing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 36:1342017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bhatia V, Yadav A, Tiwari R, Nigam S, Goel
S, Carskadon S, Gupta N, Goel A, Palanisamy N and Ateeq B:
Epigenetic silencing of miRNA-338-5p and miRNA-421 drives
SPINK1-positive prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 25:2755–2768.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chandran UR, Ma C, Dhir R, Bisceglia M,
Lyons-Weiler M, Liang W, Michalopoulos G, Becich M and Monzon FA:
Gene expression profiles of prostate cancer reveal involvement of
multiple molecular pathways in the metastatic process. BMC Cancer.
7:642007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Liu L, Lin J and He H: Identification of
potential crucial genes associated with the pathogenesis and
prognosis of endometrial cancer. Front Genet. 10:3732019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu G, Cheng Z, Wu Z and Wang H:
Identification of potential key genes associated with osteosarcoma
based on integrated bioinformatics analyses. J Cell Biochem.
120:13554–13561. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ni M, Liu X, Wu J, Zhang D, Tian J, Wang
T, Liu S, Meng Z, Wang K, Duan X, et al: Identification of
candidate biomarkers correlated with the pathogenesis and prognosis
of non-small cell lung cancer via integrated bioinformatics
analysis. Front Genet. 9:4692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Wu J, Zhang D, Bing Z, Tian J, Ni
M, Zhang X, Meng Z and Liu S: Identification of potential key genes
associated with the pathogenesis and prognosis of gastric cancer
based on integrated bioinformatics analysis. Front Genet.
9:2652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Burchard J, Zhang C, Liu AM, Poon RT, Lee
NP, Wong KF, Sham PC, Lam BY, Ferguson MD, Tokiwa G, et al:
microRNA-122 as a regulator of mitochondrial metabolic gene network
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Syst Biol. 6:4022010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu AM, Yao TJ, Wang W, Wong KF, Lee NP,
Fan ST, Poon RT, Gao C and Luk JM: Circulating miR-15b and miR-130b
in serum as potential markers for detecting hepatocellular
carcinoma: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open. 2:e0008252012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mah WC, Thurnherr T, Chow PK, Chung AY,
Ooi LL, Toh HC, Teh BT, Saunthararajah Y and Lee CG: Methylation
profiles reveal distinct subgroup of hepatocellular carcinoma
patients with poor prognosis. PLoS One. 9:e1041582014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mas VR, Maluf DG, Archer KJ, Yanek K, Kong
X, Kulik L, Freise CE, Olthoff KM, Ghobrial RM, McIver P and Fisher
R: Genes involved in viral carcinogenesis and tumor initiation in
hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Med.
15:85–94. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Edgar R and Barrett T: NCBI GEO standards
and services for microarray data. Nat Biotechnol. 24:1471–1472.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harding JJ, Nandakumar S, Armenia J,
Khalil DN, Albano M, Ly M, Shia J, Hechtman JF, Kundra R, El Dika
I, et al: Prospective genotyping of hepatocellular carcinoma:
Clinical implications of next-generation sequencing for matching
patients to targeted and immune therapies. Clin Cancer Res.
25:2116–2126. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schulze K, Imbeaud S, Letouze E,
Alexandrov LB, Calderaro J, Rebouissou S, Couchy G, Meiller C,
Shinde J, Soysouvanh F, et al: Exome sequencing of hepatocellular
carcinomas identifies new mutational signatures and potential
therapeutic targets. Nat Genet. 47:505–511. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ahn SM, Jang SJ, Shim JH, Kim D, Hong SM,
Sung CO, Baek D, Haq F, Ansari AA, Lee SY, et al: Genomic portrait
of resectable hepatocellular carcinomas: Implications of RB1 and
FGF19 aberrations for patient stratification. Hepatology.
60:1972–1982. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Fujimoto A, Totoki Y, Abe T, Boroevich KA,
Hosoda F, Nguyen HH, Aoki M, Hosono N, Kubo M, Miya F, et al:
Whole-genome sequencing of liver cancers identifies etiological
influences on mutation patterns and recurrent mutations in
chromatin regulators. Nat Genet. 44:760–764. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sanchez-Vega F, Mina M, Armenia J, Chatila
WK, Luna A, La KC, Dimitriadoy S, Liu DL, Kantheti HS, Saghafinia
S, et al: Oncogenic signaling pathways in the cancer genome atlas.
Cell. 173:321–337.e10. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen DG, Zhu B, Lv SQ, Zhu H, Tang J,
Huang C, Li Q, Zhou P, Wang DL and Li GH: Inhibition of EGR1
inhibits glioma proliferation by targeting CCND1 promoter. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 36:1862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xu Z, Xu M, Liu P, Zhang S, Shang R, Qiao
Y, Che L, Ribback S, Cigliano A, Evert K, et al: The mTORC2-Akt1
cascade is crucial for c-Myc to promote hepatocarcinogenesis in
mice and humans. Hepatology. 70:1600–1613. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoon H, Kim M, Jang K, Shin M, Besser A,
Xiao X, Zhao D, Wander SA, Briegel K, Morey L, et al: p27
transcriptionally coregulates cJun to drive programs of tumor
progression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:7005–7014. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu P, Zhang G, Hou S and Sha LG: MAPK8
mediates resistance to temozolomide and apoptosis of glioblastoma
cells through MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
106:1419–1427. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lacey A, Hedrick E, Cheng Y, Mohankumar K,
Warren M and Safe S: Interleukin-24 (IL24) is suppressed by
PAX3-FOXO1 and is a novel therapy for rhabdomyosarcoma. Mol Cancer
Ther. 17:2756–2766. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim JH, Lee MJ, Yu GR, Kim SW, Jang KY, Yu
HC, Cho BH and Kim DG: Alterations in the p53-SOCS2 axis contribute
to tumor growth in colon cancer. Exp Mol Med. 50:1–10. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Senapati P, Dey S, Sudarshan D, Das S,
Kumar M, Kaypee S, Mohiyuddin A, Kodaganur GS and Kundu TK:
Oncogene c-fos and mutant R175H p53 regulate expression of
Nucleophosmin implicating cancer manifestation. FEBS J.
285:3503–3524. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huang H, Wang Q, Du T, Lin C, Lai Y, Zhu
D, Wu W, Ma X, Bai S, Li Z, et al: Matrine inhibits the progression
of prostate cancer by promoting expression of GADD45B. Prostate.
78:327–335. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Habel N, Stefanovska B, Carene D,
Patino-Garcia A, Lecanda F and Fromigue O: CYR61 triggers
osteosarcoma metastatic spreading via an IGF1Rβ-dependent EMT-like
process. BMC Cancer. 19:622019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Z, Li W, Pang Y, Zhou Z and Liu S,
Cheng K, Qin Q, Jia Y and Liu S: SF3B4 is regulated by
microRNA-133b and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 38:57–68. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Toh TB, Lim JJ and Chow EK: Epigenetics in
cancer stem cells. Mol Cancer. 16:292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cantini L, Bertoli G, Cava C, Dubois T,
Zinovyev A, Caselle M, Castiglioni I, Barillot E and Martignetti L:
Identification of microRNA clusters cooperatively acting on
epithelial to mesenchymal transition in triple negative breast
cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:2205–2215. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liang Y, Zhang C and Dai DQ:
Identification of differentially expressed genes regulated by
methylation in colon cancer based on bioinformatics analysis. World
J Gastroenterol. 25:3392–3407. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Al-Zoughbi W, Schauer S, Pichler M and
Hoefler G: Early loss of forkhead transcription factor, O subgroup,
member 1 protein in the development of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Pathobiology. 85:342–347. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Quentmeier H, Geffers R, Jost E, Macleod
RA, Nagel S, Röhrs S, Romani J, Scherr M, Zaborski M and Drexler
HG: SOCS2: Inhibitor of JAK2V617F-mediated signal transduction.
Leukemia. 22:2169–2175. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Monti-Rocha R, Cramer A, Gaio Leite P,
Antunes MM, Pereira RVS, Barroso A, Queiroz-Junior CM, David BA,
Teixeira MM, Menezes GB and Machado FS: SOCS2 is critical for the
balancing of immune response and oxidate stress protecting against
acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury. Front Immunol.
9:31342018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Das R, Gregory PA, Fernandes RC, Denis I,
Wang Q, Townley SL, Zhao SG, Hanson AR, Pickering MA, Armstrong HK,
et al: MicroRNA-194 promotes prostate cancer metastasis by
inhibiting SOCS2. Cancer Res. 77:1021–1034. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Gokay S, Kendirci M, Ustkoyuncu PS, Kardas
F, Bayram AK, Per H and Poyrazoğlu HG: Tyrosinemia type II: Novel
mutations in TAT in a boy with unusual presentation. Pediatr Int.
58:1069–1072. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fu L, Dong SS, Xie YW, Tai LS, Chen L,
Kong KL, Man K, Xie D, Li Y, Cheng Y, et al: Down-regulation of
tyrosine aminotransferase at a frequently deleted region 16q22
contributes to the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatology. 51:1624–1634. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Huang K, Xie W, Wang S, Li Q, Wei X, Chen
B, Hua Y, Li S, Peng B and Shen S: High SPINK1 expression predicts
poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Invest Surg. 33:1–10. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Xu L, Lu C, Huang Y, Zhou J, Wang X, Liu
C, Chen J and Le H: SPINK1 promotes cell growth and metastasis of
lung adenocarcinoma and acts as a novel prognostic biomarker. BMB
Rep. 51:648–653. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|