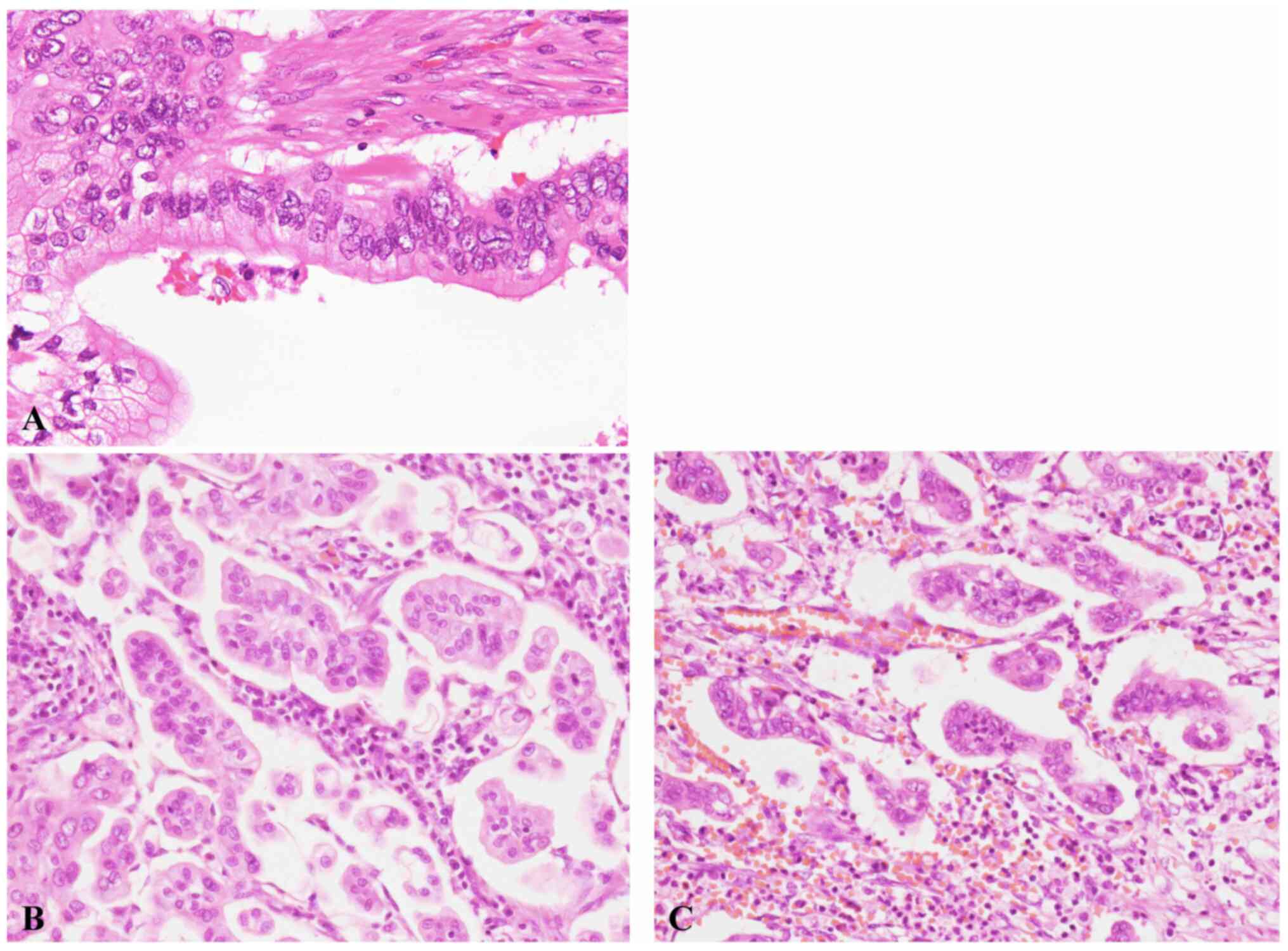
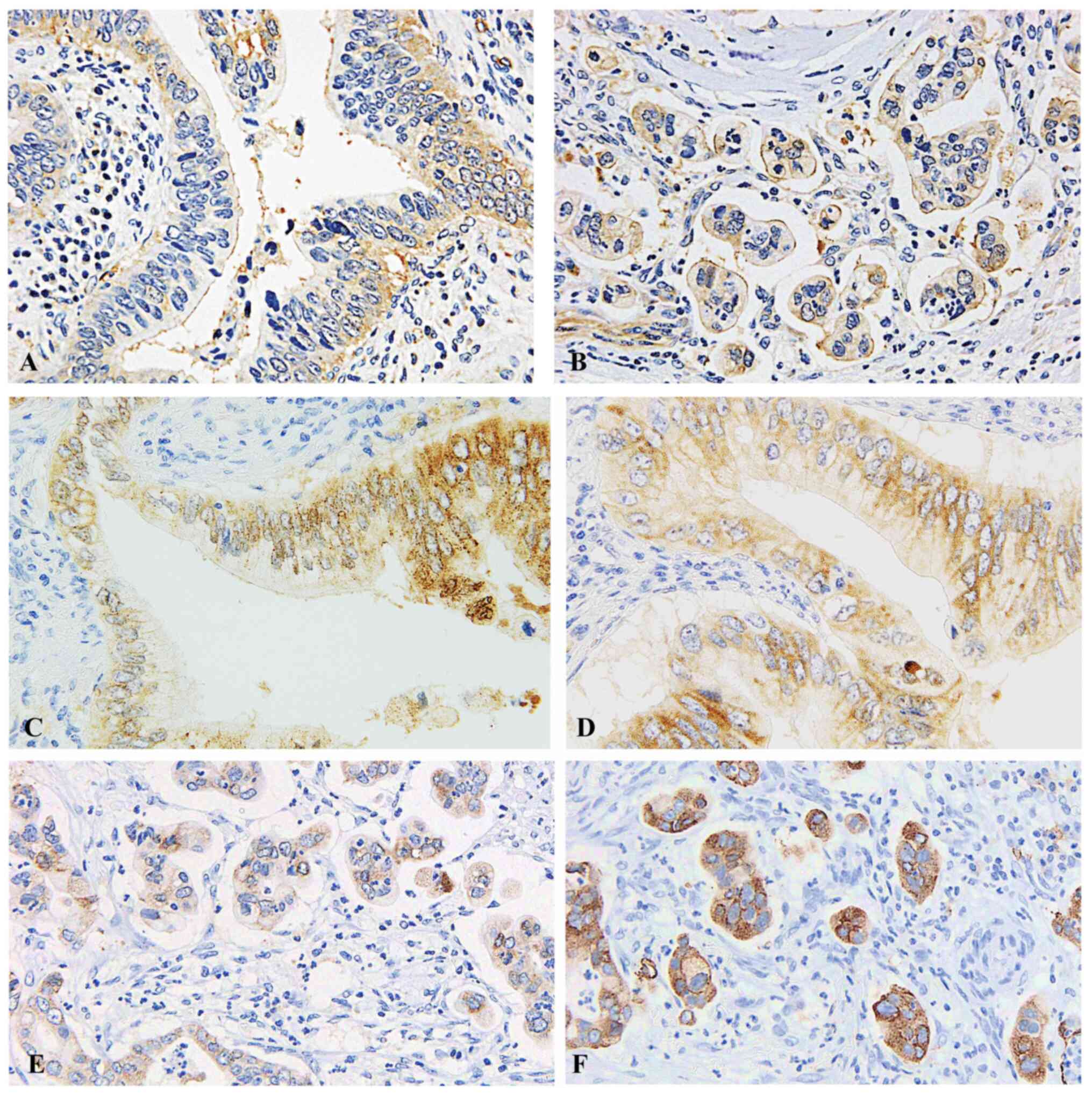
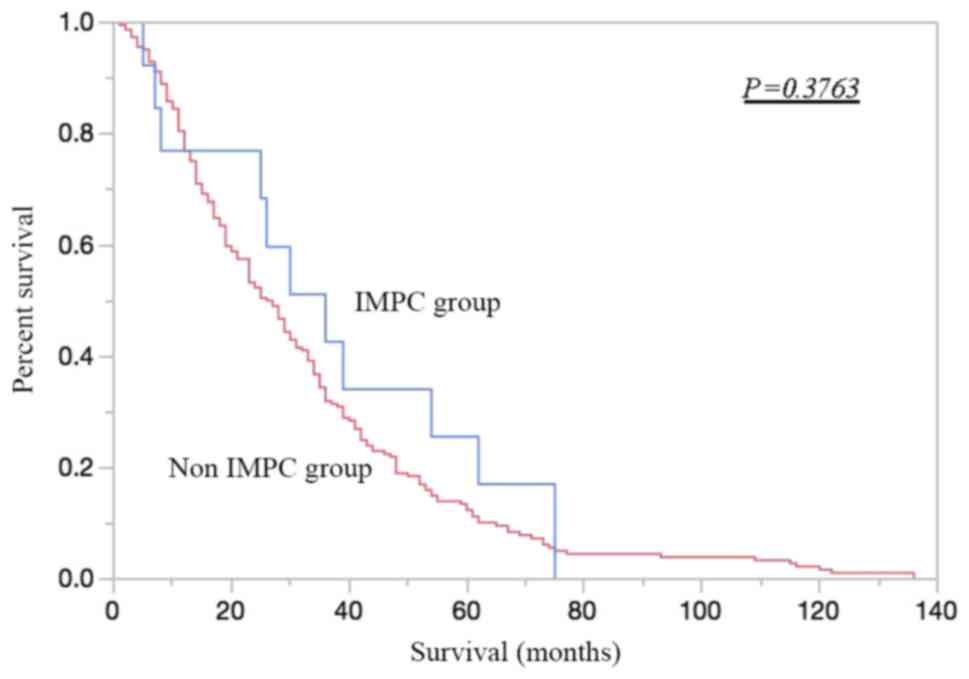
Spandidos Publications style
Ryota H, Ishida M, Ebisu Y, Yanagimoto H, Yamamoto T, Kosaka H, Hirooka S, Yamaki S, Kotsuka M, Matsui Y, Matsui Y, et al: Clinicopathological characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with invasive micropapillary carcinoma component with emphasis on the usefulness of PKCζ immunostaining for detection of reverse polarity. Oncol Lett 22: 525, 2021.
APA
Ryota, H., Ishida, M., Ebisu, Y., Yanagimoto, H., Yamamoto, T., Kosaka, H. ... Satoi, S. (2021). Clinicopathological characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with invasive micropapillary carcinoma component with emphasis on the usefulness of PKCζ immunostaining for detection of reverse polarity. Oncology Letters, 22, 525. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2021.12786
MLA
Ryota, H., Ishida, M., Ebisu, Y., Yanagimoto, H., Yamamoto, T., Kosaka, H., Hirooka, S., Yamaki, S., Kotsuka, M., Matsui, Y., Tsuta, K., Satoi, S."Clinicopathological characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with invasive micropapillary carcinoma component with emphasis on the usefulness of PKCζ immunostaining for detection of reverse polarity". Oncology Letters 22.1 (2021): 525.
Chicago
Ryota, H., Ishida, M., Ebisu, Y., Yanagimoto, H., Yamamoto, T., Kosaka, H., Hirooka, S., Yamaki, S., Kotsuka, M., Matsui, Y., Tsuta, K., Satoi, S."Clinicopathological characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma with invasive micropapillary carcinoma component with emphasis on the usefulness of PKCζ immunostaining for detection of reverse polarity". Oncology Letters 22, no. 1 (2021): 525. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2021.12786