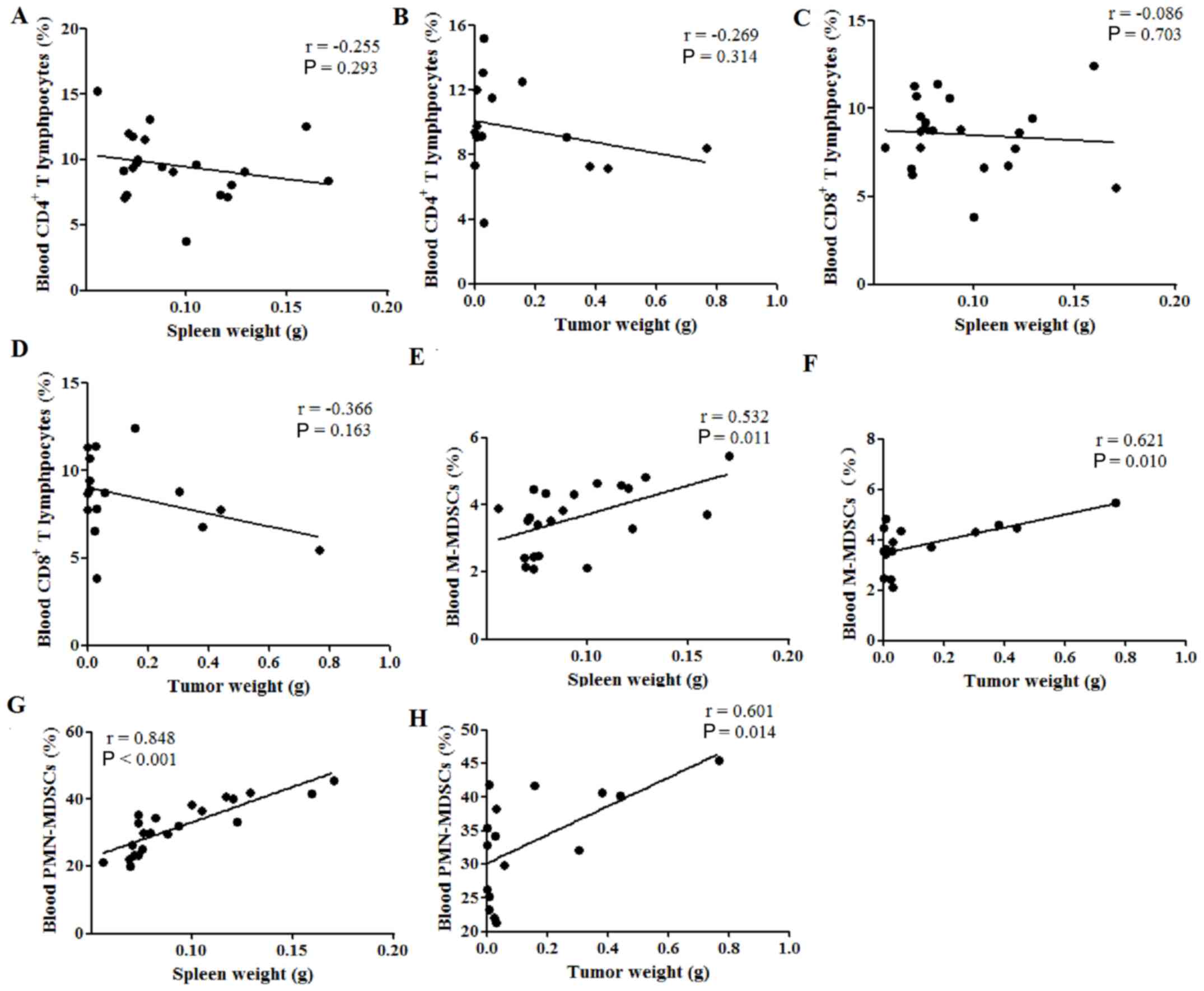
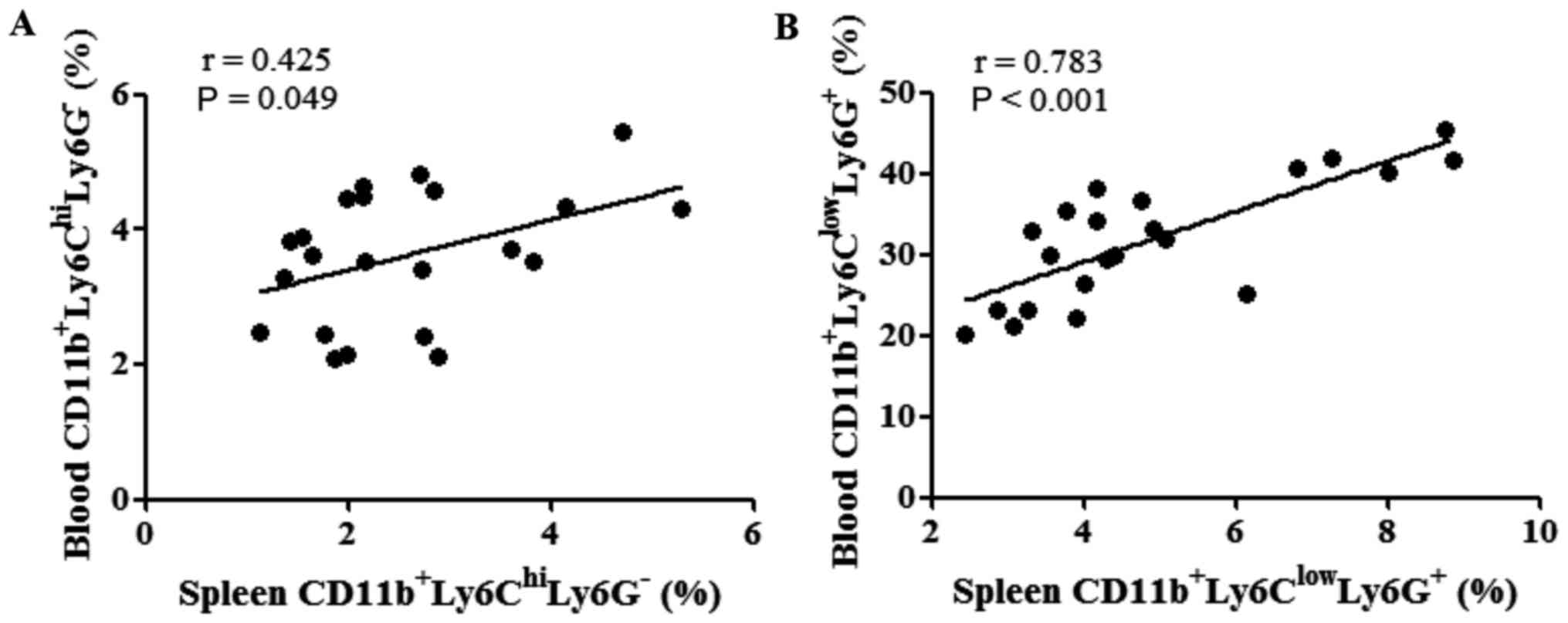
|
1
|
Ugel S, Peranzoni E, Desantis G, Chioda M,
Walter S, Weinschenk T, Ochando JC, Cabrelle A, Mandruzzato S and
Bronte V: Immune tolerance to tumor antigens occurs in a
specialized environment of the spleen. Cell Rep. 2:628–639. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Marvel D and Gabrilovich DI:
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment:
Expect the unexpected. J Clin Invest. 125:3356–3364. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jiang W, Li Y, Wei W, Li JW, Li L, Zhang
C, Zhang SQ, Kong GY and Li ZF: Spleen contributes to restraint
stress induced hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Int
Immunopharmacol. 83:1064202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xia Y, Wei Y, Li Z-Y, Cai XY, Zhang LL,
Dong XR, Zhang S, Zhang RG, Meng R, Zhu F, et al: Catecholamines
contribute to the neovascularization of lung cancer via
tumor-associated macrophages. Brain Behav Immun. 81:111–121. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wu C, Ning H, Liu M, Lin J, Luo S, Zhu W,
Xu J, Wu WC, Liang J, Shao CK, et al: Spleen mediates a distinct
hematopoietic progenitor response supporting tumor-promoting
myelopoiesis. J Clin Invest. 128:3425–3438. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kumar V, Patel S, Tcyganov E and
Gabrilovich DI: The nature of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in
the tumor microenvironment. Trends Immunol. 37:208–220. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cortez-Retamozo V, Etzrodt M, Newton A,
Rauch PJ, Chudnovskiy A, Berger C, Ryan RJ, Iwamoto Y, Marinelli B,
Gorbatov R, et al: Origins of tumor-associated macrophages and
neutrophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2491–2496. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cortez-Retamozo V, Etzrodt M, Newton A,
Ryan R, Pucci F, Sio SW, Kuswanto W, Rauch PJ, Chudnovskiy A,
Iwamoto Y, et al: Angiotensin II drives the production of
tumor-promoting macrophages. Immunity. 38:296–308. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Han Y, Liu Q, Hou J, Gu Y, Zhang Y, Chen
Z, Fan J, Zhou W, Qiu S, Zhang Y, et al: Tumor-Induced Generation
of Splenic Erythroblast-like Ter-Cells Promotes Tumor Progression.
Cell. 173:634–648.e12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kristinsson SY, Gridley G, Hoover RN,
Check D and Landgren O: Long-term risks after splenectomy among
8,149 cancer-free American veterans: A cohort study with up to 27
years follow-up. Haematologica. 99:392–398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lv X, Yang F, Guo X, Yang T, Zhou T, Dong
X, Long Y, Xiao D and Chen Y: Hypersplenism is correlated with
increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with
post-hepatitis cirrhosis. Tumour Biol. 37:8889–8900. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dubeykovskaya Z, Si Y, Chen X, Worthley
DL, Renz BW, Urbanska AM, Hayakawa Y, Xu T, Westphalen CB,
Dubeykovskiy A, et al: Neural innervation stimulates splenic TFF2
to arrest myeloid cell expansion and cancer. Nat Commun.
7:105172016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li B, Zhang S, Huang N, Chen H, Wang P,
Yang J and Li Z: CCL9/CCR1 induces myeloid derived suppressor cell
recruitment to the spleen in a murine H22 orthotopic hepatoma
model. Oncol Rep. 41:608–618. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li B, Zhang S, Huang N, Chen H, Wang P, Li
J, Pu Y, Yang J and Li Z: Dynamics of the spleen and its
significance in a murine H22 orthotopic hepatoma model. Exp Biol
Med (Maywood). 241:863–872. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miller MR, Mandell JB, Beatty KM, Harvey
SA, Rizzo MJ, Previte DM, Thorne SH and McKenna KC: Splenectomy
promotes indirect elimination of intraocular tumors by
CD8+ T cells that is associated with IFNγ- and
Fas/FasL-dependent activation of intratumoral macrophages. Cancer
Immunol Res. 2:1175–1185. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bronte V and Pittet MJ: The spleen in
local and systemic regulation of immunity. Immunity. 39:806–818.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wen SW, Everitt SJ, Bedő J, Chabrot M,
Ball DL, Solomon B, MacManus M, Hicks RJ, Möller A and Leimgruber
A: Spleen volume variation in patients with locally advanced
non-small cell lung cancer receiving platinum-based
chemo-radiotherapy. PLoS One. 10:e01426082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang W, Li Y, Li ZZ, Sun J, Li JW, Wei W,
Li L, Zhang C, Huang C, Yang SY, et al: Chronic restraint stress
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by mobilizing splenic
myeloid cells through activating β-adrenergic signaling. Brain
Behav Immun. 80:825–838. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang W, Li Y, Sun J, Li L, Li JW, Zhang
C, Huang C, Yang J, Kong GY and Li ZF: Spleen contributes to
restraint stress induced changes in blood leukocytes distribution.
Sci Rep. 7:65012017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li Y, Jiang W, Li ZZ, Zhang C, Huang C,
Yang J, Kong GY and Li ZF: Repetitive restraint stress changes
spleen immune cell subsets through glucocorticoid receptor or
β-adrenergic receptor in a stage dependent manner. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 495:1108–1114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gabrilovich DI: Myeloid-derived suppressor
sells. Cancer Immunol Res. 5:3–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li L, Duan M, Chen W, Jiang A, Li X, Yang
J and Li Z: The spleen in liver cirrhosis: Revisiting an old enemy
with novel targets. J Transl Med. 15:1112017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
McKim DB, Patterson JM, Wohleb ES, Jarrett
BL, Reader BF, Godbout JP and Sheridan JF: Sympathetic release of
splenic monocytes promotes recurring anxiety following repeated
social defeat. Biol Psychiatry. 79:803–813. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Swirski FK, Nahrendorf M, Etzrodt M,
Wildgruber M, Cortez-Retamozo V, Panizzi P, Figueiredo JL, Kohler
RH, Chudnovskiy A, Waterman P, et al: Identification of splenic
reservoir monocytes and their deployment to inflammatory sites.
Science. 325:612–616. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jordan KR, Kapoor P, Spongberg E, Tobin
RP, Gao D, Borges VF and McCarter MD: Immunosuppressive
myeloid-derived suppressor cells are increased in splenocytes from
cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 66:503–513. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang S, Li ZF, Pan D, Huang C, Zhou R and
Liu ZW: Changes of splenic macrophage during the process of liver
cancer induced by diethylnitrosamine in rats. Chin Med J (Engl).
122:3043–3047. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mundy-Bosse BL, Thornton LM, Yang HC,
Andersen BL and Carson WE: Psychological stress is associated with
altered levels of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in breast cancer
patients. Cell Immunol. 270:80–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang H, Zou C, Zhao W, Yu Y, Cui Y, Zhang
H, e F, Qiu Z, Zou C and Gao X: Juglone eliminates MDSCs
accumulation and enhances antitumor immunity. Int Immunopharmacol.
73:118–127. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng R and Chen S and Chen S: Correlation
between myeloid-derived suppressor cells and S100A8/A9 in tumor and
autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 29:919–925. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mohammadpour H, MacDonald CR, Qiao G, Chen
M, Dong B, Hylander BL, McCarthy PL, Abrams SI and Repasky EA: β2
adrenergic receptor-mediated signaling regulates the
immunosuppressive potential of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J
Clin Invest. 129:5537–5552. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Geng J, Yuan Y, Jiao X, Wang R, Liu N,
Chen H, Griffin N and Shan F: Novel modulation on myeloid-derived
suppressor cells (MDSCs) by methionine encephalin (MENK). Int
Immunopharmacol. 68:193–203. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ostrand-Rosenberg S: Myeloid
derived-suppressor cells: Their role in cancer and obesity. Curr
Opin Immunol. 51:68–75. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma M, Huang W and Kong D: IL-17 inhibits
the accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in breast
cancer via activating STAT3. Int Immunopharmacol. 59:148–156. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang K, Li J, Zhang J, Wang L, Zhang Q,
Ge J, Guo Y, Wang B, Huang Y, Yang T, et al: SDF-1/CXCR4 axis
facilitates myeloid-derived suppressor cells accumulation in
osteosarcoma microenvironment and blunts the response to anti-PD-1
therapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 75:1058182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song MK, Chung JS, Lim SN, Lee GW, Lee SM,
Lee NK, Choi JC and Oh SY: Usefulness of spleen volume measured by
computed tomography for predicting clinical outcome in primary
myelofibrosis. Int J Hematol. 104:476–484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nous A, Peeters I, Nieboer K, Vanbinst AM,
De Keyser J and De Raedt S: Post-stroke infections associated with
spleen volume reduction: A pilot study. PLoS One. 15:e02324972020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yoo J, Kim SW, Lee DH, Bae JS and Cho EJ:
Prognostic role of spleen volume measurement using computed
tomography in patients with compensated chronic liver disease from
hepatitis B viral infection. Eur Radiol. 31:1432–1442. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bae JS, Lee DH, Yoo J, Yi NJ, Lee KW, Suh
KS, Kim H and Lee KB: Association between spleen volume and the
post-hepatectomy liver failure and overall survival of patients
with hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. Eur Radiol.
31:2461–2471. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fernández-Placencia R, Golse N, Cano L,
Allard MA, Pittau G, Ciacio O, Cunha AS, Castaing D, Salloum C,
Azoulay D, et al: Spleen volumetry and liver transient
elastography: Predictors of persistent posthepatectomy
decompensation in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery.
168:17–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Marasco G, Colecchia A, Colli A, Ravaioli
F, Casazza G, Reggiani ML, Cucchetti A, Cescon M and Festi D: Role
of liver and spleen stiffness in predicting the recurrence of
hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Hepatol. 70:440–448.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cao ZX, Chen XP and Wu ZD: Effects of
splenectomy in patients with cirrhosis undergoing hepatic resection
for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 9:2460–2463.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|