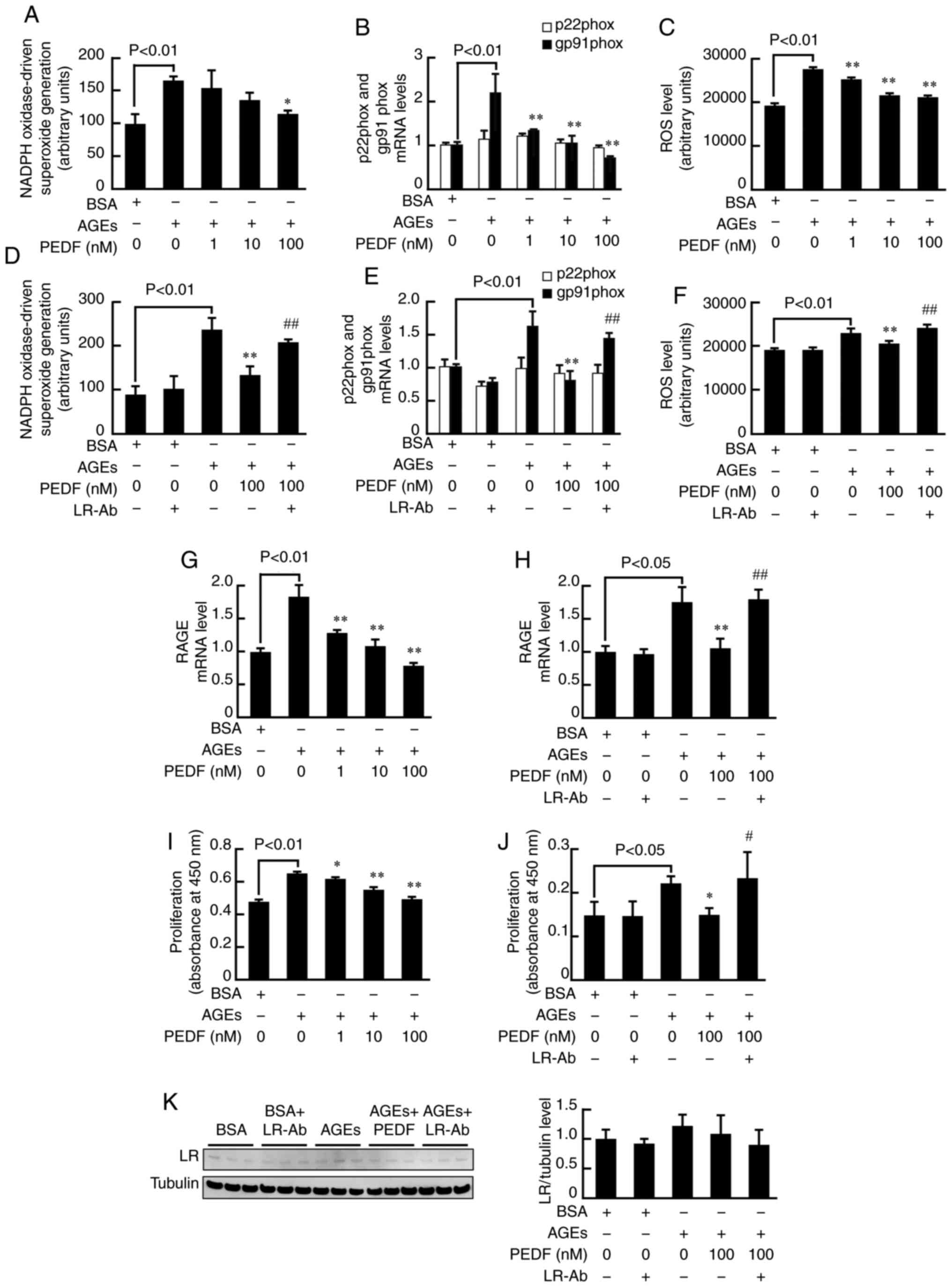
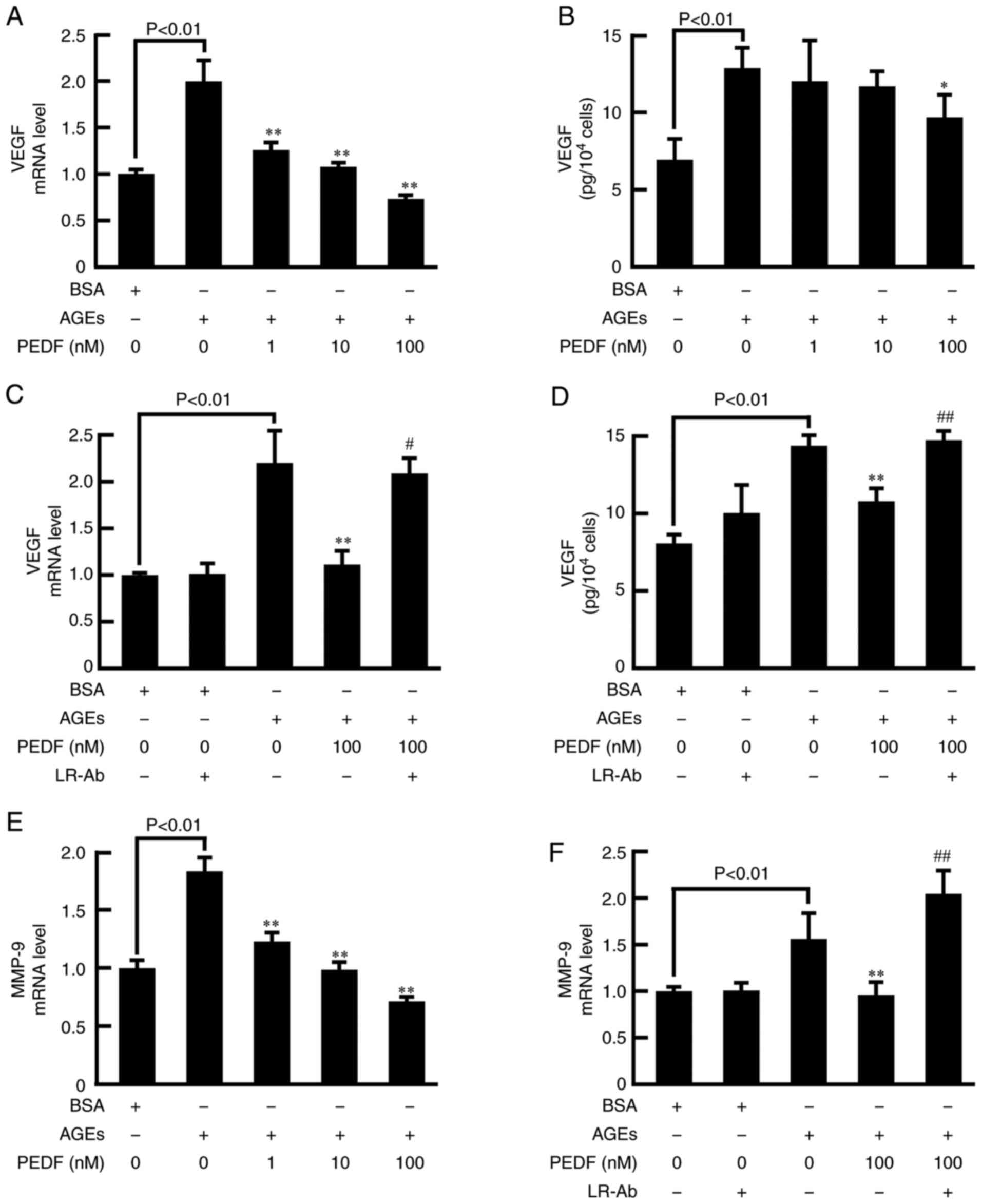
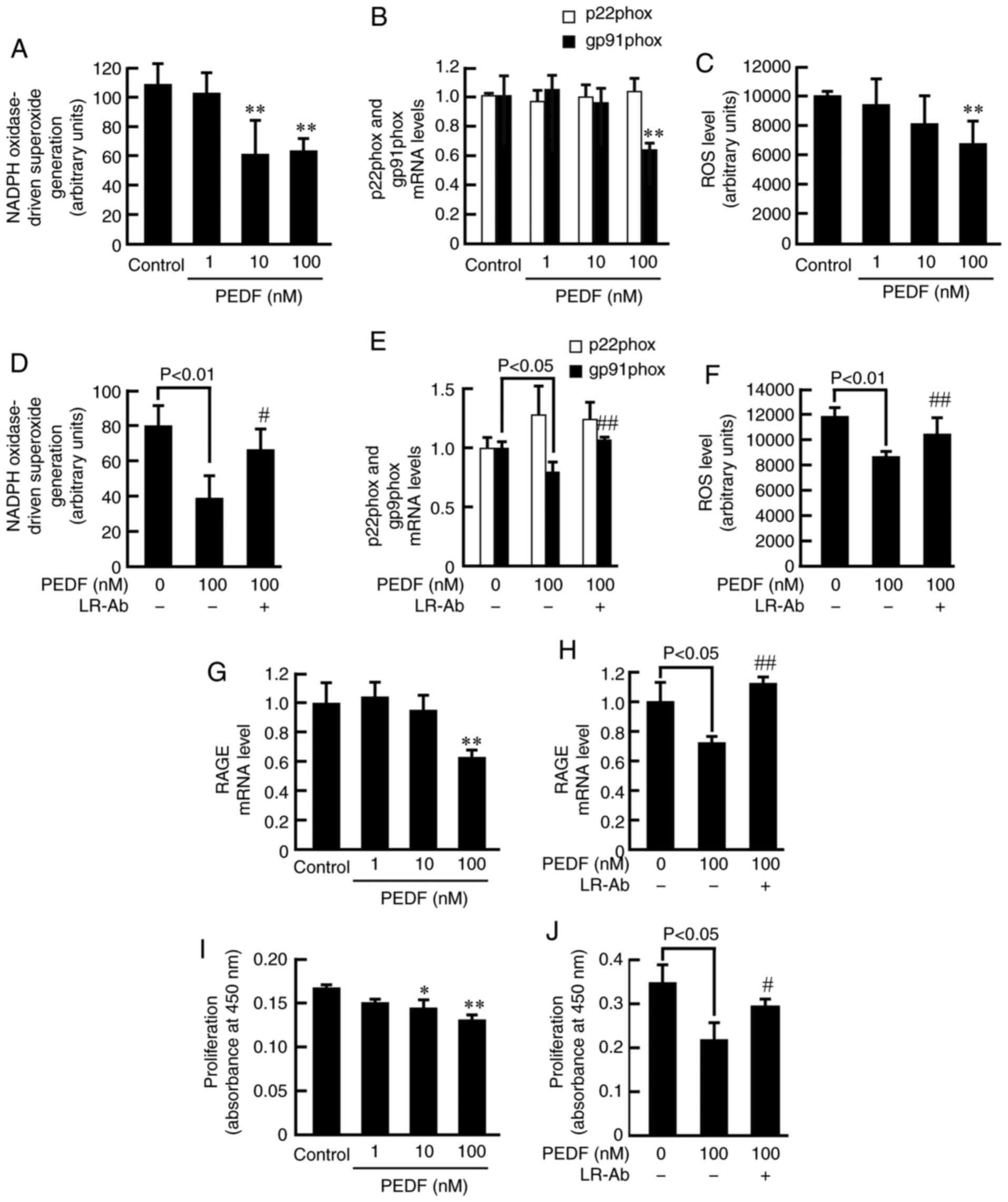
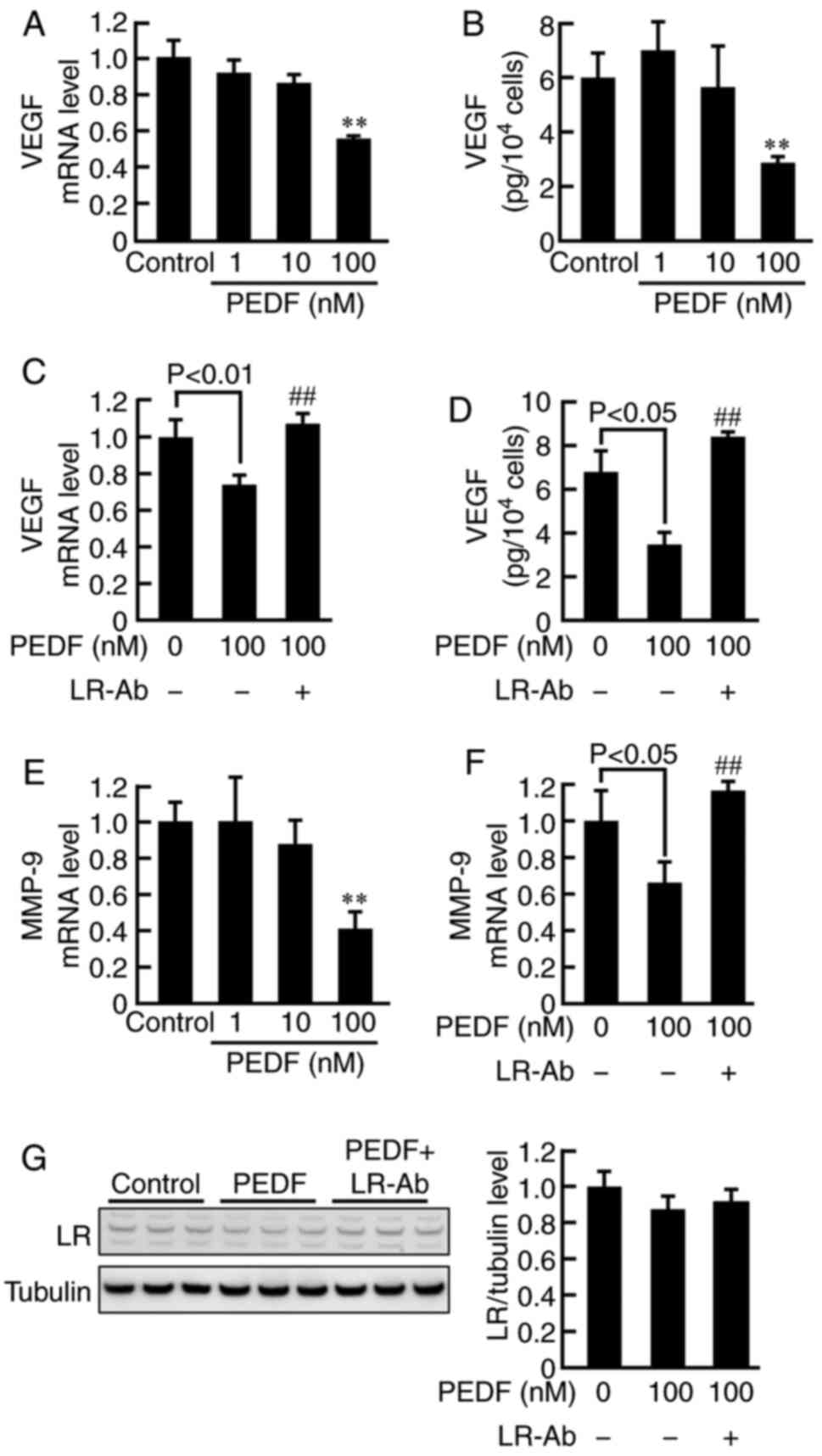
|
1
|
Tombran-Tink J, Chader CG and Johnson LV:
PEDF: A pigment epithelium-derived factor with potent neuronal
differentiative activity. Exp Eye Res. 53:411–414. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dawson DW, Volpert OV, Gillis P, Crawford
SE, Xu H, Benedict W and Bouck NP: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor: A potent inhibitor of angiogenesis. Science. 285:245–248.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Duh EJ, Yang HS, Suzuma I, Miyagi M,
Youngman E, Mori K, Katai M, Yan L, Suzuma K, West K, et al:
Pigment epithelium-derived factor suppresses ischemia-induced
retinal neovascularization and VEGF-induced migration and growth.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 43:821–829. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yamagishi S, Amano S, Inagaki Y, Okamoto
T, Takeuchi M and Inoue H: Pigment epithelium-derived factor
inhibits leptin-induced angiogenesis by suppressing vascular
endothelial growth factor gene expression through anti-oxidative
properties. Microvasc Res. 65:186–190. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Doll JA, Stellmach VM, Bouck NP, Bergh AR,
Lee C, Abramson LP, Cornwell ML, Pins MR, Borensztajn J and
Crawford SE: Pigment epithelium-derived factor regulates the
vasculature and mass of the prostate and pancreas. Nat Med.
9:774–780. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamagishi S, Nakamura K, Matsui T, Inagaki
Y, Takenaka K, Jinnouchi Y, Yoshida Y, Matsuura T, Narama I,
Motomiya Y, et al: Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits
advanced glycation end product-induced retinal vascular
hyperpermeability by blocking reactive oxygen species-mediated
vascular endothelial growth factor expression. J Biol Chem.
281:20213–20220. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fujimura T, Yamagishi S, Ueda S, Fukami K,
Shibata R, Matsumoto Y, Kaida Y, Hayashida A, Koike K, Matsui T, et
al: Administration of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF)
reduces proteinuria by suppressing decreased nephrin and increased
VEGF expression in the glomeruli of adriamycin-injected rats.
Nephrol Dial Transplant. 24:1397–1406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Matsui T, Higashimoto Y, Taira J and
Yamagishi S: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) binds to
caveolin-1 and inhibits the pro-inflammatory effects of caveolin-1
in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 441:405–410.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matsui T, Nishino Y, Ojima A, Maeda S,
Tahara N and Yamagishi S: Pigment epithelium-derived factor
improves metabolic derangements and ameliorates dysregulation of
adipocytokines in obese type 2 diabetic rats. Am J Pathol.
184:1094–1103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Takenaka K, Yamagishi S, Matsui T,
Nakamura K, Jinnouchi Y, Yoshida Y, Ueda S, Katsuki Y, Katsuda Y
and Imaizumi T: Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF)
administration inhibits occlusive thrombus formation in rats: A
possible participation of reduced intraplatelet PEDF in thrombosis
of acute coronary syndromes. Atherosclerosis. 197:25–33. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamagishi SI and Matsui T: Pigment
epithelium-derived factor: A novel therapeutic target for
cardiometabolic diseases and related complications. Curr Med Chem.
25:1480–1500. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Abe R, Shimizu T, Yamagishi S, Shibaki A,
Amano S, Inagaki Y, Watanabe H, Sugawara H, Nakamura H, Takeuchi M,
et al: Overexpression of pigment epithelium-derived factor
decreases angiogenesis and inhibits the growth of human malignant
melanoma cells in vivo. Am J Pathol. 164:1225–1232. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Takenaka K, Yamagishi S, Jinnouchi Y,
Nakamura K, Matsui T and Imaizumi T: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor (PEDF)-induced apoptosis and inhibition of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression in MG63 human
osteosarcoma cells. Life Sci. 77:3231–3241. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mirochnik Y, Aurora A, Schulze-Hoepfner
FT, Deabes A, Shifrin V, Beckmann R, Polsky C and Volpert OV: Short
pigment epithelial-derived factor-derived peptide inhibits
angiogenesis and tumor growth. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1655–1663. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou D, Cheng SQ, Ji HF, Wang JS, Xu HT,
Zhang GQ and Pang D: Evaluation of protein pigment
epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) and microvessel density (MVD) as
prognostic indicators in breast cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
136:1719–1727. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seki R, Yamagishi S, Matsui T, Yoshida T,
Torimura T, Ueno T, Sata M and Okamura T: Pigment
epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) inhibits survival and
proliferation of VEGF-exposed multiple myeloma cells through its
anti-oxidative properties. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 431:693–697.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Becerra SP and Notario V: The effects of
PEDF on cancer biology: Mechanisms of action and therapeutic
potential. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:258–271. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gong Q, Qiu S, Li S, Ma Y, Chen M, Yao Y,
Che D, Feng J, Cai W, Ma J, et al: Proapoptotic PEDF functional
peptides inhibit prostate tumor growth-a mechanistic study. Biochem
Pharmacol. 92:425–437. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou D, Zhang M, Xu P, Yu Y, Ye G, Zhang L
and Wu A: Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor is
associated with a good prognosis and is correlated with
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related genes in infiltrating
ductal breast carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 11:116–124. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yamagishi SI, Koga Y, Sotokawauchi A,
Hashizume N, Fukahori S, Matsui T and Yagi M: Therapeutic potential
of pigment epithelium-derived factor in cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
25:313–324. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamagishi S: Potential clinical utility of
advanced glycation end product cross-link breakers in age- and
diabetes-associated disorders. Rejuvenation Res. 15:564–572. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sadowska-Bartosz I and Bartosz G: Effect
of glycation inhibitors on aging and age-related diseases. Mech
Ageing Dev. 160:1–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rowan S, Bejarano E and Taylor A:
Mechanistic targeting of advanced glycation end-products in
age-related diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1864:3631–3643. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamagishi SI and Matsui T: Therapeutic
potential of DNA-aptamers raised against AGE-RAGE axis in
diabetes-related complications. Curr Pharm Des. 24:2802–2809. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rungratanawanich W, Qu Y, Wang X, Essa MM
and Song BJ: Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and other
adducts in aging-related diseases and alcohol-mediated tissue
injury. Exp Mol Med. 53:168–188. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ishibashi Y, Matsui T, Takeuchi M and
Yamagishi S: Metformin inhibits advanced glycation end products
(AGEs)-induced growth and VEGF expression in MCF-7 breast cancer
cells by suppressing AGEs receptor expression via AMP-activated
protein kinase. Horm Metab Res. 45:387–390. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matsui T, Higashimoto Y and Yamagishi S:
Laminin receptor mediates anti-inflammatory and anti-thrombogenic
effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor in myeloma cells.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 443:847–851. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Matsui T, Higashimoto Y, Nishino Y,
Nakamura N, Fukami K and Yamagishi SI: RAGE-aptamer blocks the
development and progression of experimental diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetes. 66:1683–1695. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nakamura N, Matsui T, Ishibashi Y,
Sotokawauchi A, Fukami K, Higashimoto Y and Yamagishi SI:
RAGE-aptamer attenuates the growth and liver metastasis of
malignant melanoma in nude mice. Mol Med. 23:295–306. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Saika K and Sobue T: Epidemiology of
breast cancer in Japan and the US. JMAJ. 52:39–44. 2009.
|
|
31
|
Akram M, Iqbal M, Daniyal M and Khan AU:
Awareness and current knowledge of breast cancer. Biol Res.
50:332017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Peairs KS, Barone BB, Snyder CF, Yeh HC,
Stein KB, Derr RL, Brancati FL and Wolff AC: Diabetes mellitus and
breast cancer outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Clin Oncol. 29:40–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang M, Yang Y and Liao Z: Diabetes and
cancer: Epidemiological and biological links. World J Diabetes.
11:227–238. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yamagishi S, Matsui T and Fukami K: Role
of receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and its
ligands in cancer risk. Rejuvenation Res. 18:48–56. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Matou-Nasri S, Sharaf H, Wang Q, Almobadel
N, Rabhan Z, Al-Eidi H, Yahya WB, Trivilegio T, Ali R, Al-Shanti N
and Ahmed N: Biological impact of advanced glycation endproducts on
estrogen receptor-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1863:2808–2820. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee KJ, Yoo JW, Kim YK, Choi JH, Ha TY and
Gil M: Advanced glycation end products promote triple negative
breast cancer cells via ERK and NF-κB pathway. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 495:2195–2201. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Walter KR, Ford ME, Gregoski MJ, Kramer
RM, Knight KD, Spruill L, Nogueira LM, Krisanits BA, Phan V, La Rue
AC, et al: Advanced glycation end products are elevated in estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer patients, alter response to
therapy, and can be targeted by lifestyle intervention. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 173:559–571. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Omofuma OO, Turner DP, Peterson LL,
Merchant AT, Zhang J and Steck SE: Dietary advanced glycation
end-products (AGE) and risk of breast cancer in the prostate, lung,
colorectal and ovarian cancer screening trial (PLCO). Cancer Prev
Res (Phila). 13:601–610. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Peterson LL, Park S, Park Y, Colditz GA,
Anbardar N and Turner DP: Dietary advanced glycation end products
and the risk of postmenopausal breast cancer in the national
institutes of health-AARP diet and health study. Cancer.
126:2648–2657. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hao L, Zhang C, Qiu Y, Wang L, Luo Y, Jin
M and Zhang Y, Guo TB, Matsushima K and Zhang Y: Recombination of
CXCR4, VEGF, and MMP-9 predicting lymph node metastasis in human
breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 253:34–42. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Schneider BP and Sledge GW Jr: Drug
insight: VEGF as a therapeutic target for breast cancer. Nat Clin
Pract Oncol. 4:181–189. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dofara SG, Chang SL and Diorio C: Gene
polymorphisms and circulating levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9: A review
of their role in breast cancer risk. Anticancer Res. 40:3619–3631.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nakamura N, Matsui T, Nishino Y,
Sotokawauchi A, Higashimoto Y and Yamagishi SI: Long-term local
injection of RAGE-aptamer suppresses the growth of malignant
melanoma in nude mice. J Oncol. 2019:73876012019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yamagishi S, Abe R, Inagaki Y, Nakamura K,
Sugawara H, Inokuma D, Nakamura H, Shimizu T, Takeuchi M, Yoshimura
A, et al: Minodronate, a newly developed nitrogen-containing
bisphosphonate, suppresses melanoma growth and improves survival in
nude mice by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor signaling.
Am J Pathol. 165:1865–1874. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yamagishi S and Imaizumi T: Diabetic
vascular complications: Pathophysiology, biochemical basis and
potential therapeutic strategy. Curr Pharm Des. 11:2279–2299. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gutsche K, Randi EB, Blank V, Fink D,
Wenger RH, Leo C and Scholz CC: Intermittent hypoxia confers
pro-metastatic gene expression selectively through NF-κB in
inflammatory breast cancer cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 101:129–142.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lewis K, Kiepas A, Hudson J, Senecal J, Ha
JR, Voorand E, Annis MG, Sabourin V, Ahn R, La Selva R, et al:
p66ShcA functions as a contextual promoter of breast cancer
metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. 22:72020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jia L, Huang S, Yin X, Zan Y, Guo Y and
Han L: Quercetin suppresses the mobility of breast cancer by
suppressing glycolysis through Akt-mTOR pathway mediated autophagy
induction. Life Sci. 208:123–130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yamagishi S, Inagaki Y, Nakamura K, Abe R,
Shimizu T, Yoshimura A and Imaizumi T: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor inhibits TNF-alpha-induced interleukin-6 expression in
endothelial cells by suppressing NADPH oxidase-mediated reactive
oxygen species generation. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 37:497–506. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Hou J, Ge C, Cui M, Liu T, Liu X, Tian H,
Zhao F, Chen T, Cui Y, Yao M, et al: Pigment epithelium-derived
factor promotes tumor metastasis through an interaction with
laminin receptor in hepatocellular carcinomas. Cell Death Dis.
8:e29692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yamagishi S, Matsui T and Inoue H:
Inhibition by advanced glycation end products (AGEs) of pigment
epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) gene expression in microvascular
endothelial cells. Drugs Exp Clin Res. 31:227–232. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ide Y, Matsui T, Ishibashi Y, Takeuchi M
and Yamagishi S: Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits
advanced glycation end product-elicited mesangial cell damage by
blocking NF-kappaB activation. Microvasc Res. 80:227–232. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ishibashi Y, Matsui T, Ohta K, Tanoue R,
Takeuchi M, Asanuma K, Fukami K, Okuda S, Nakamura K and Yamagishi
S: PEDF inhibits AGE-induced podocyte apoptosis via PPAR-gamma
activation. Microvasc Res. 85:54–58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|