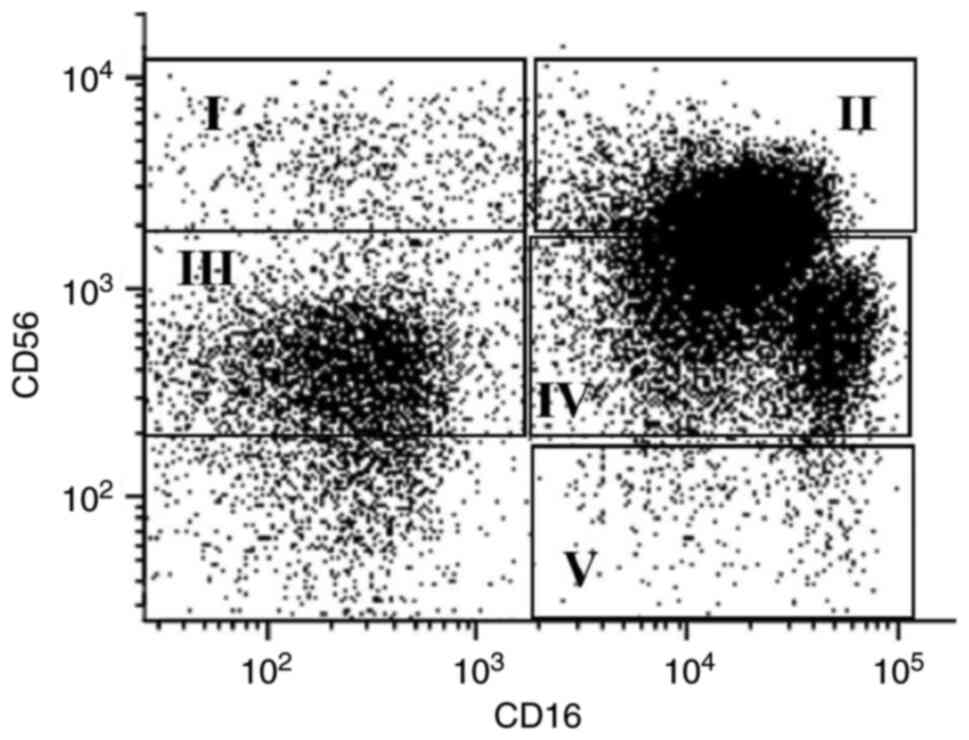
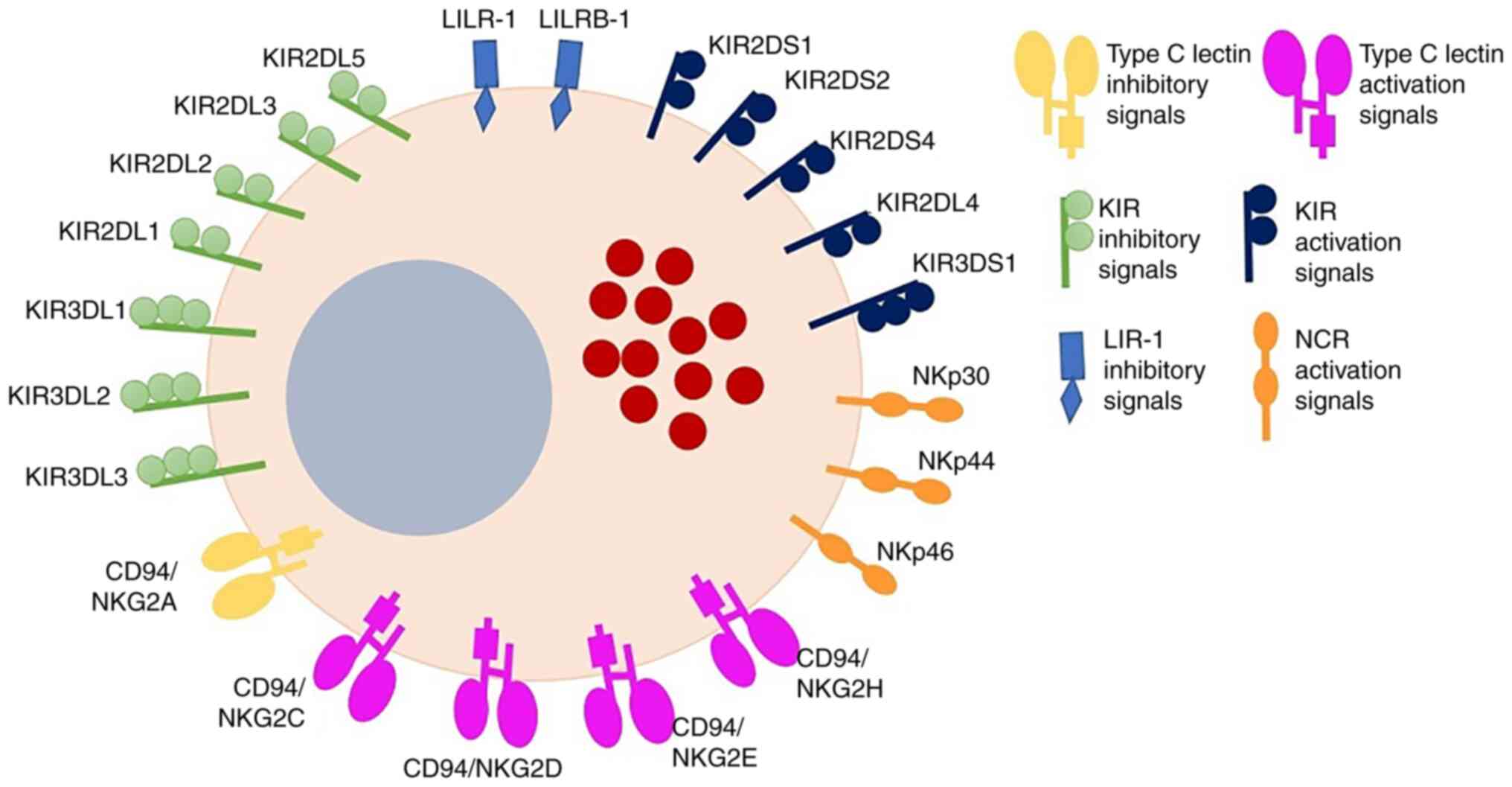
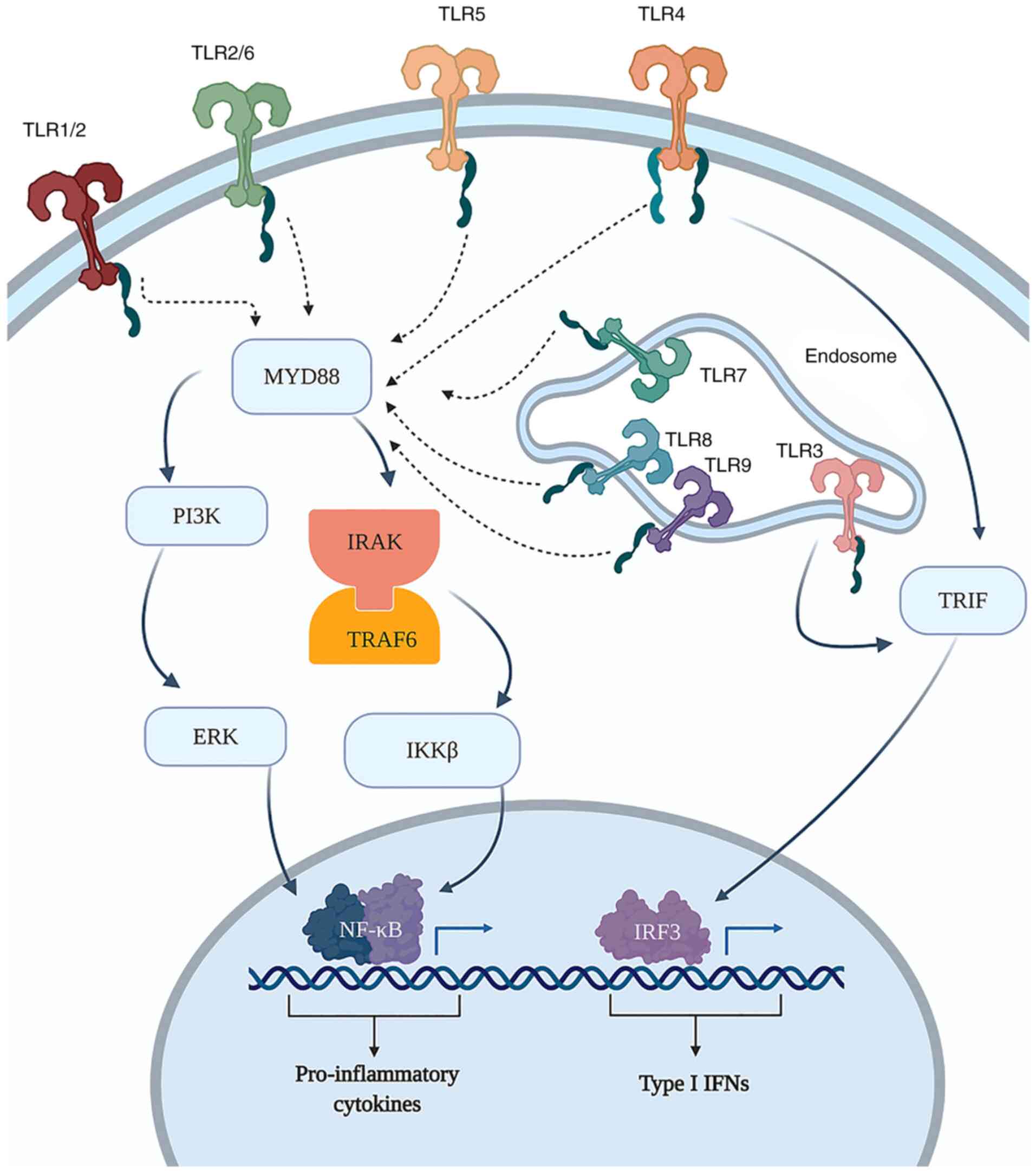
|
1
|
Timonen BYT, Ortaldo JR and Herberman RB:
Characteristics of human large granular lymphocytes and
relationship to natural killer and K cells. J Exp Med. 153:569–582.
1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Galy A, Travis M, Cen D and Chen B: Human
T, B, natural killer, and dendritic cells arise from a common bone
marrow progenitor cell subset. Immunity. 3:459–473. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Scoville SD, Freud AG and Caligiuri MA:
Modeling human natural killer cell development in the era of innate
lymphoid cells. Front Immunol. 8:3602017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nitta T, Yagita H, Sato K and Okumura K:
Involvement of CD56 (NKH-1/Leu-19 antigen) as an adhesion molecule
in natural killer-target cell interaction. J Exp Med.
170:1757–1761. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lanier LL, Le AM, Civin CI, Loken MR and
Phillips JH: The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1)
antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic
T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 136:4480–4486. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vivier E, Artis D, Colonna M, Diefenbach
A, Di Santo JP, Eberl G, Koyasu S, Locksley RM, McKenzie ANJ,
Mebius RE, et al: Innate lymphoid cells: 10 years on. Cell.
174:1054–1066. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chiorean EG and Miller JS: The biology of
natural killer cells and implications for therapy of human disease.
J Hematotherapy Stem Cell Res. 10:451–463. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fauriat C, Long EO, Ljunggren HG and
Bryceson YT: Regulation of human NK-cell cytokine and chemokine
production by target cell recognition. Blood. 115:2167–2176. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lotze MT and Thomson AW: Natural killer
cells: Basic science and clinical application. Academic Press;
2009
|
|
10
|
Reeves RK, Li H, Jost S, Blass E, Li H,
Schafer JL, Varner V, Manickam C, Eslamizar L, Altfeld M, et al:
Antigen-specific NK cell memory in rhesus macaques. Nat Immunol.
16:927–932. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nikzad R, Angelo LS, Aviles-Padilla K, Le
DT, Singh VK, Bimler L, Vukmanovic-Stejic M, Vendrame E, Ranganath
T, Simpson L, et al: Human natural killer cells mediate adaptive
immunity to viral antigens. Sci Immunol. 4:eaat81162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Freud AG, Yokohama A, Becknell B, Lee MT,
Mao HC, Ferketich AK and Caligiuri MA: Evidence for discrete stages
of human natural killer cell differentiation in vivo. J Exp Med.
203:1033–1043. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rosmaraki EE, Douagi I, Roth C, Colucci F,
Cumano A and Di Santo JP: Identification of committed NK cell
progenitors in adult murine bone marrow. Eur J Immunol.
31:1900–1909. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huntington ND, Vosshenrich CAJ and Di
Santo JP: Developmental pathways that generate natural-killer-cell
diversity in mice and humans. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:703–714. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA and Caligiuri MA:
The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol.
22:633–640. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Poli A, Michel T, Thérésine M, Andrès E,
Hentges F and Zimmer J: CD56bright natural killer (NK) cells: An
important NK cell subset. Immunology. 126:458–465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cooper MA, Fehniger TA, Turner SC, Chen
KS, Ghaheri BA, Carson WE and Caligiuri MA: Human natural killer
cells: A unique innate immunoregulatory role for the CD56bright
subset. Blood. 96:3146–3151. 2000.
|
|
18
|
Nagler A, Lanier LL, Cwirla S and Phillips
JH: Comparative studies of human FcRIII-positive and negative
natural killer cells. J Immunol. 143:3183–3191. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Caligiuri MA, Murray C, Robertson MJ, Wang
E, Cochran K, Cameron C, Schow P, Ross ME, Klumpp TR, Soiffer RJ,
et al: Selective modulation of human natural killer cells in vivo
after prolonged infusion of low dose recombinant interleukin 2. J
Clin Invest. 91:123–132. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mrózek E, Anderson P and Caligiuri MA:
Role of interleukin-15 in the development of human CD56+ natural
killer cells from CD34+ hematopoietic progenitor cells. Blood.
87:2632–2640. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Frey M, Packianathan NB, Fehniger TA, Ross
ME, Wang WC, Stewart CC, Caligiuri MA and Evans SS: Differential
expression and function of L-selectin on CD56bright and CD56dim
natural killer cell subsets. J Immunol. 161:400–408.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Berahovich RD, Lai NL, Wei Z, Lanier LL
and Schall TJ: Evidence for NK cell subsets based on chemokine
receptor expression. J Immunol. 177:7833–7840. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chan A, Hong DL, Atzberger A, Kollnberger
S, Filer AD, Buckley CD, McMichael A, Enver T and Bowness P:
CD56bright human NK cells differentiate into CD56dim cells: Role of
contact with peripheral fibroblasts. J Immunol. 179:89–94. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Béziat V, Duffy D, Quoc SN, Le
Garff-Tavernier M, Decocq J, Combadière B, Debré P and Vieillard V:
CD56brightCD16+ NK cells: A functional intermediate stage of NK
cell differentiation. J Immunol. 186:6753–6761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T
and Ugolini S: Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol.
9:503–510. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Kelly JM, Westwood
JA, Street SE, Yagita H, Takeda K, van Dommelen SL, Degli-Esposti
MA and Hayakawa Y: Activation of NK cell cytotoxicity. Mol Immunol.
42:501–510. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Krzewski K and Strominger JL: The killer's
kiss: The many functions of NK cell immunological synapses. Curr
Opin Cell Biol. 20:597–605. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guicciardi ME and Gores GJ: Life and death
by death receptors. FASEB J. 23:1625–1637. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Abel AM, Yang C, Thakar MS and Malarkannan
S: Natural killer cells: Development, maturation, and clinical
utilization. Front Immunol. 9:1–23. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Barry M, Heibein JA, Pinkoski MJ, Lee SF,
Moyer RW, Green DR and Bleackley RC: Granzyme B short-circuits the
need for caspase 8 activity during granule-mediated cytotoxic
T-lymphocyte killing by directly cleaving Bid. Mol Cell Biol.
20:3781–3794. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pinkoski MJ, Waterhouse NJ, Heibein JA,
Wolf BB, Kuwana T, Goldstein JC, Newmeyer DD, Bleackley RC and
Green DR: Granzyme B-mediated apoptosis proceeds predominantly
through a Bcl-2-inhibitable mitochondrial pathway. J Biol Chem.
276:12060–12067. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Amand M, Iserentant G, Poli A, Sleiman M,
Fievez V, Sanchez IP, Sauvageot N, Michel T, Aouali N, Janji B, et
al: Human CD56dimCD16dim cells as an
individualized natural killer cell subset. Front Immunol.
8:6992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Iannello A and Ahmad A: Role of
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in the efficacy of
therapeutic anti-cancer monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 24:487–499. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zambello R, Falco M, Della Chiesa M,
Trentin L, Carollo D, Castriconi R, Cannas G, Carlomagno S,
Cabrelle A, Lamy T, et al: Expression and function of KIR and
natural cytotoxicity receptors in NK-type lymphoproliferative
diseases of granular lymphocytes. Blood. 102:1797–1805. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bryceson YT, March ME, Ljunggren HG and
Long EO: Activation, coactivation, and costimulation of resting
human natural killer cells. Immunol Rev. 214:73–91. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li NL, Davidson CL, Humar A and Burshtyn
DN: Modulation of the inhibitory receptor leukocyte Ig-like
receptor 1 on human natural killer cells. Front Immunol.
2:462011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ljunggren HG and Kärre K: In search of the
‘missing self’: MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol
Today. 11:237–244. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tomasello E, Blery M, Vely E and Vivier E:
Signaling pathways engaged by NK cell receptors: Double concerto
for activating receptors, inhibitory receptors and NK cells. Semin
Immunol. 12:139–147. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lanier LL: Up on the tightrope: Natural
killer cell activation and inhibition. Nat Immunol. 9:495–502.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Blanca IR, Bere EW, Young HA and Ortaldo
JR: Human B cell activation by autologous NK cells is regulated by
CD40-CD40 ligand interaction: Role of memory B cells and CD5+ B
cells. J Immunol. 167:6132–6139. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zingoni A, Sornasse T, Cocks BG, Tanaka Y,
Santoni A and Lanier LL: Cross-talk between activated human NK
cells and CD4+ T cells via OX40-OX40 ligand interactions. J
Immunol. 173:3716–3724. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Orange JS and Ballas ZK: Natural killer
cells in human health and disease. Clin Immunol. 118:1–10. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chalifour A, Jeannin P, Gauchat JF,
Blaecke A, Malissard M, N'Guyen T, Thieblemont N and Delneste Y:
Direct bacterial protein PAMP recognition by human NK cells
involves TLRs and triggers α-defensin production. Blood.
104:1778–1783. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Perrot I, Deauvieau F, Massacrier C,
Hughes N, Garrone P, Durand I, Demaria O, Viaud N, Gauthier L,
Blery M, et al: TLR3 and Rig-like receptor on myeloid dendritic
cells and Rig-like receptor on human NK cells are both mandatory
for production of IFN-gamma in response to double-stranded RNA. J
Immunol. 185:2080–2088. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qiu F, Maniar A, Quevedo Diaz M, Chapoval
AI and Medvedev AE: Activation of cytokine-producing and antitumor
activities of natural killer cells and macrophages by engagement of
Toll-like and NOD-like receptors. Innate Immun. 17:375–387. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sivori S, Carlomagno S, Moretta L and
Moretta A: Comparison of different CpG oligodeoxynucleotide classes
for their capability to stimulate human NK cells. Eur J Immunol.
36:961–967. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Girart MV, Fuertes MB, Domaica CI, Rossi
LE and Zwirner NW: Engagement of TLR3, TLR7, and NKG2D regulate
IFN-gamma secretion but not NKG2D-mediated cytotoxicity by human NK
cells stimulated with suboptimal doses of IL-12. J Immunol.
179:3472–3479. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sivori S, Carlomagno S, Pesce S, Moretta
A, Vitale M and Marcenaro E: TLR/NCR/KIR: Which one to use and
when? Front Immunol. 5:1052014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Saikh KU, Lee JS, Kissner TL, Dyas B and
Ulrich RG: Toll-like receptor and cytokine expression patterns of
CD56+ T cells are similar to natural killer cells in response to
infection with Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus replicons. J
Infect Dis. 188:1562–1570. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lauzon NM, Mian F, MacKenzie R and Ashkar
AA: The direct effects of Toll-like receptor ligands on human NK
cell cytokine production and cytotoxicity. Cell Immunol.
241:102–112. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Becker I, Salaiza N, Aguirre M, Delgado J,
Carrillo-Carrasco N, Kobeh LG, Ruiz A, Cervantes R, Torres AP,
Cabrera N, et al: Leishmania lipophosphoglycan (LPG) activates NK
cells through toll-like receptor-2. Mol Biochem Parasitol.
130:65–74. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Schmidt KN, Leung B, Kwong M, Zarember KA,
Satyal S, Navas TA, Wang F and Godowski PJ: APC-independent
activation of NK cells by the toll-like receptor 3 agonist
double-stranded RNA. J Immunol. 172:138–143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sivori S, Falco M, Della Chiesa M,
Carlomagno S, Vitale M, Moretta L and Moretta A: CpG and
double-stranded RNA trigger human NK cells by toll-like receptors:
Induction of cytokine release and cytotoxicity against tumors
dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:10116–10121. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Gorski KS, Waller EL, Bjornton-Severson J,
Hanten JA, Riter CL, Kieper WC, Gorden KB, Miller JS, Vasilakos JP,
Tomai MA and Alkan SS: Distinct indirect pathways govern human
NK-cell activation by TLR-7 and TLR-8 agonists. Int Immunol.
18:1115–1126. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Alter G, Suscovich TJ, Teigen N, Meier A,
Streeck H, Brander C and Altfeld M: Single-stranded RNA derived
from HIV-1 serves as a potent activator of NK cells. J Immunol.
178:7658–7666. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mian MF, Lauzon NM, Andrews DW, Lichty BD
and Ashkar AA: FimH can directly activate human and murine natural
killer cells via TLR4. Mol Ther. 18:1379–1388. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
He S, Chu J, Wu LC, Mao H, Peng Y,
Alvarez-Breckenridge CA, Hughes T, Wei M, Zhang J, Yuan S, et al:
MicroRNAs activate natural killer cells through Toll-like receptor
signaling. Blood. 121:4663–4671. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Guo Q and Zhang C: Critical role of
Toll-like receptor signaling in NK cell activation. Chinese Sci
Bull. 57:3192–3202. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Adib-Conquy M, Scott-Algara D, Cavaillon
JM and Souza-Fonseca-Guimaraes F: TLR-mediated activation of NK
cells and their role in bacterial/viral immune responses in
mammals. Immunol Cell Biol. 92:256–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ljunggren HG and Malmberg KJ: Prospects
for the use of NK cells in immunotherapy of human cancer. Nat Rev
Immunol. 7:329–339. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Algarra I, García-Lora A, Cabrera T,
Ruiz-Cabello F and Garrido F: The selection of tumor variants with
altered expression of classical and nonclassical MHC class I
molecules: Implications for tumor immune escape. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 53:904–910. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Samarakoon A, Chu H and Malarkannan S:
Murine NKG2D ligands:‘Double, double toil and trouble.’. Mol
Immunol. 46:1011–1019. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Imai K, Matsuyama S, Miyake S, Suga K and
Nakachi K: Natural cytotoxic activity of peripheral-blood
lymphocytes and cancer incidence: An 11-year follow-up study of a
general population. Lancet. 356:1795–1799. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Coca S, Perez-Piqueras J, Martinez D,
Colmenarejo A, Saez MA, Vallejo C, Martos JA and Moreno M: The
prognostic significance of intratumoral natural killer cells in
patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer. 79:2320–2328. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Ishigami S, Natsugoe S, Tokuda K, Nakajo
A, Che X, Iwashige H, Aridome K, Hokita S and Aikou T: Prognostic
value of intratumoral natural killer cells in gastric carcinoma.
Cancer. 88:577–583. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Villegas FR, Coca S, Villarrubia VG,
Jiménez R, Chillón MJ, Jareño J, Zuil M and Callol L: Prognostic
significance of tumor infiltrating natural killer cells subset CD57
in patients with squamous cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 35:23–28.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Habif G, Crinier A, André P, Vivier E and
Narni-Mancinelli E: Targeting natural killer cells in solid tumors.
Cell Mol Immunol. 16:415–422. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Guillerey C, Huntington ND and Smyth MJ:
Targeting natural killer cells in cancer immunotherapy. Nat
Immunol. 17:1025–1036. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Vitale M, Cantoni C, Pietra G, Mingari MC
and Moretta L: Effect of tumor cells and tumor microenvironment on
NK-cell function. Eur J Immunol. 44:1582–1592. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Mushtaq MU, Papadas A, Pagenkopf A,
Flietner E, Morrow Z, Chaudhary SG and Asimakopoulos F: Tumor
matrix remodeling and novel immunotherapies: The promise of
matrix-derived immune biomarkers. J Immunother Cancer. 6:652018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Diermayr S, Himmelreich H, Durovic B,
Mathys-Schneeberger A, Siegler U, Langenkamp U, Hofsteenge J,
Gratwohl A, Tichelli A, Paluszewska M, et al: NKG2D ligand
expression in AML increases in response to HDAC inhibitor valproic
acid and contributes to allorecognition by NK-cell lines with
single KIR-HLA class I specificities. Blood. 111:1428–1436. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chang MC, Cheng HI, Hsu K, Hsu YN, Kao CW,
Chang YF, Lim KH and Chen CG: NKG2A down-regulation by dasatinib
enhances natural killer cytotoxicity and accelerates effective
treatment responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia.
Front Immunol. 9:31522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sanchez-Correa B, Morgado S, Gayoso I,
Bergua JM, Casado JG, Arcos MJ, Bengochea ML, Duran E, Solana R and
Tarazona R: Human NK cells in acute myeloid leukaemia patients:
Analysis of NK cell-activating receptors and their ligands. Cancer
Immunol Immunother. 60:1195–1205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Rouce RH, Shaim H, Sekine T, Weber G,
Ballard B, Ku S, Barese C, Murali V, Wu MF, Liu H, et al: The
TGF-β/SMAD pathway is an important mechanism for NK cell immune
evasion in childhood B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia.
30:800–811. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Valenzuela-Vazquez L, Núñez-Enríquez JC,
Sánchez-Herrera J, Jiménez-Hernández E, Martín-Trejo JA,
Espinoza-Hernández LE, Medina-Sanson A, Flores-Villegas LV,
Peñaloza-González JG, Refugio Torres-Nava J, et al: Functional
characterization of NK cells in Mexican pediatric patients with
acute lymphoblastic leukemia: Report from the Mexican
Interinstitutional Group for the Identification of the Causes of
Childhood Leukemia. PLoS One. 15:e02273142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Jarosz M, Hak Ł, Więckiewicz J, Balcerska
A and Myśliwska J: Clinical immunology NK cells in children with
acute lymphoblastic leukemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma after
cessation of intensive chemotherapy. Cent Eur J Immunol. 34:94–99.
2009.
|
|
77
|
Hsu KC, Keever-Taylor CA, Wilton A, Pinto
C, Heller G, Arkun K, O'Reilly RJ, Horowitz MM and Dupont B:
Improved outcome in HLA-identical sibling hematopoietic stem-cell
transplantation for acute myelogenous leukemia predicted by KIR and
HLA genotypes. Blood. 105:4878–4884. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Fei F, Lim M, George AA, Kirzner J, Lee D,
Seeger R, Groffen J, Abdel-Azim H and Heisterkamp N: Cytotoxicity
of CD56-positive lymphocytes against autologous B-cell precursor
acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Leukemia. 29:788–797. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Maude SL, Laetsch TW, Buechner J, Rives S,
Boyer M, Bittencourt H, Bader P, Verneris MR, Stefanski HE, Myers
GD, et al: Tisagenlecleucel in children and young adults with
B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 378:439–448. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Park JH, Rivière I, Gonen M, Wang X,
Sénéchal B, Curran KJ, Sauter C, Wang Y, Santomasso B, Mead E, et
al: Long-term follow-up of CD19 CAR therapy in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 378:449–459. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li L, Liu LN, Feller S, Allen C,
Shivakumar R, Fratantoni J, Wolfraim LA, Fujisaki H, Campana D,
Chopas N, et al: Expression of chimeric antigen receptors in
natural killer cells with a regulatory-compliant non-viral method.
Cancer Gene Ther. 17:147–154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Shimasaki N, Fujisaki H, Cho D, Masselli
M, Lockey T, Eldridge P, Leung W and Campana D: A clinically
adaptable method to enhance the cytotoxicity of natural killer
cells against B-cell malignancies. Cytotherapy. 14:830–840. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xie G, Dong H, Liang Y, Ham JD, Rizwan R
and Chen J: CAR-NK cells: A promising cellular immunotherapy for
cancer. EBioMedicine. 59:1029752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liu E, Marin D, Banerjee P, Macapinlac HA,
Thompson P, Basar R, Nassif Kerbauy L, Overman B, Thall P, Kaplan
M, et al: Use of CAR-transduced natural killer cells in
CD19-positive lymphoid tumors. N Engl J Med. 382:545–553. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Sánchez-Cuaxospa M, Contreras-Ramos A,
Pérez-Figueroa E, Medina-Sansón A, Jiménez-Hernández E, Torres-Nava
JR, Rojas-Castillo E and Maldonado-Bernal C: Low expression of
Toll-like receptors in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of
pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int J Oncol.
49:675–681. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Samudio I, Rezvani K, Shaim H, Hofs E,
Ngom M, Bu L, Liu G, Lee JT, Imren S, Lam V, et al: UV-inactivated
HSV-1 potently activates NK cell killing of leukemic cells. Blood.
127:2575–2586. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Flavell DJ, Holmes SE, Warnes SL and
Flavell SU: The TLR3 agonist poly inosinic: Cytidylic acid
significantly augments the therapeutic activity of an anti-CD7
immunotoxin for human T-cell leukaemia. Biomedicines. 7:132019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cheadle EJ, Lipowska-Bhalla G, Dovedi SJ,
Fagnano E, Klein C, Honeychurch J and Illidge TM: A TLR7 agonist
enhances the antitumor efficacy of obinutuzumab in murine lymphoma
models via NK cells and CD4 T cells. Leukemia. 31:1611–1621. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kim H, Khanna V, Kucaba TA, Zhang W,
Sehgal D, Ferguson DM, Griffith TS and Panyam J: TLR7/8 agonist
loaded nanoparticles augment NK Cell-mediated Antibody-based cancer
immunotherapy. Mol Pharm. 17:2109–2124. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Ronsley R, Kariminia A, Ng B, Mostafavi S,
Reid G, Subrt P, Hijiya N and Schultz KR: The TLR9 agonist
(GNKG168) induces a unique immune activation pattern in vivo in
children with minimal residual disease positive acute leukemia:
Results of the TACL T2009-008 phase I study. Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
36:468–481. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|