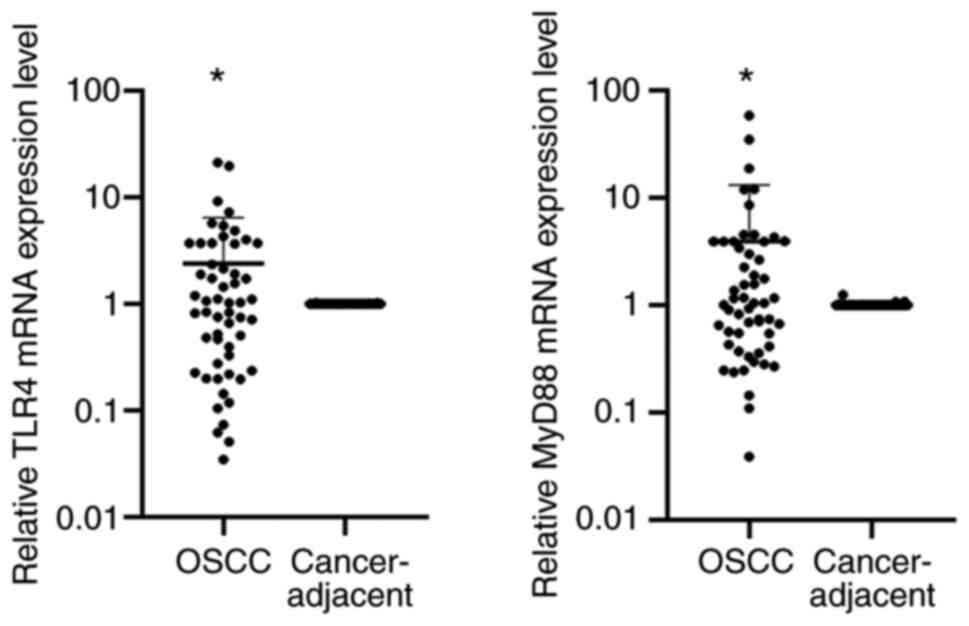
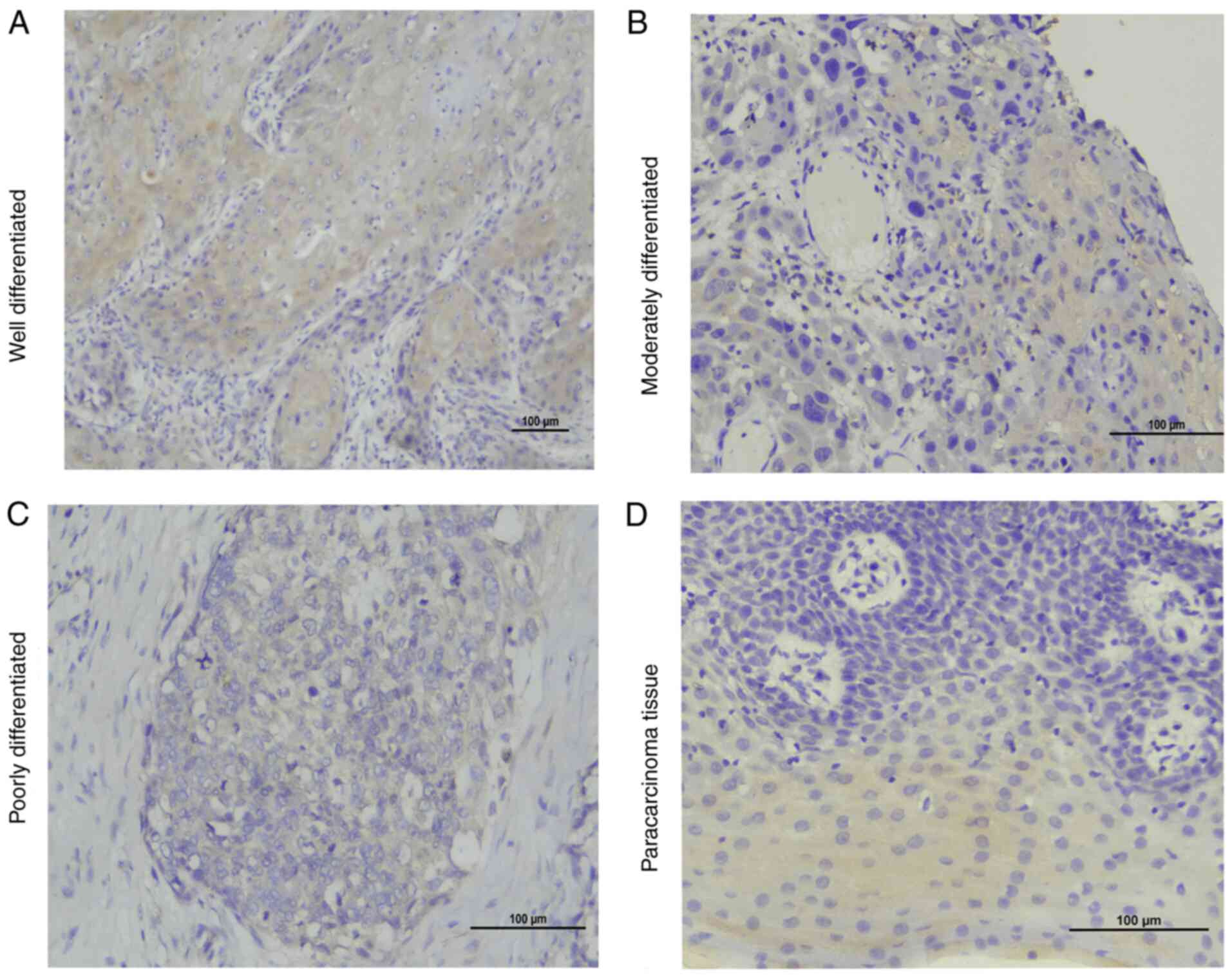
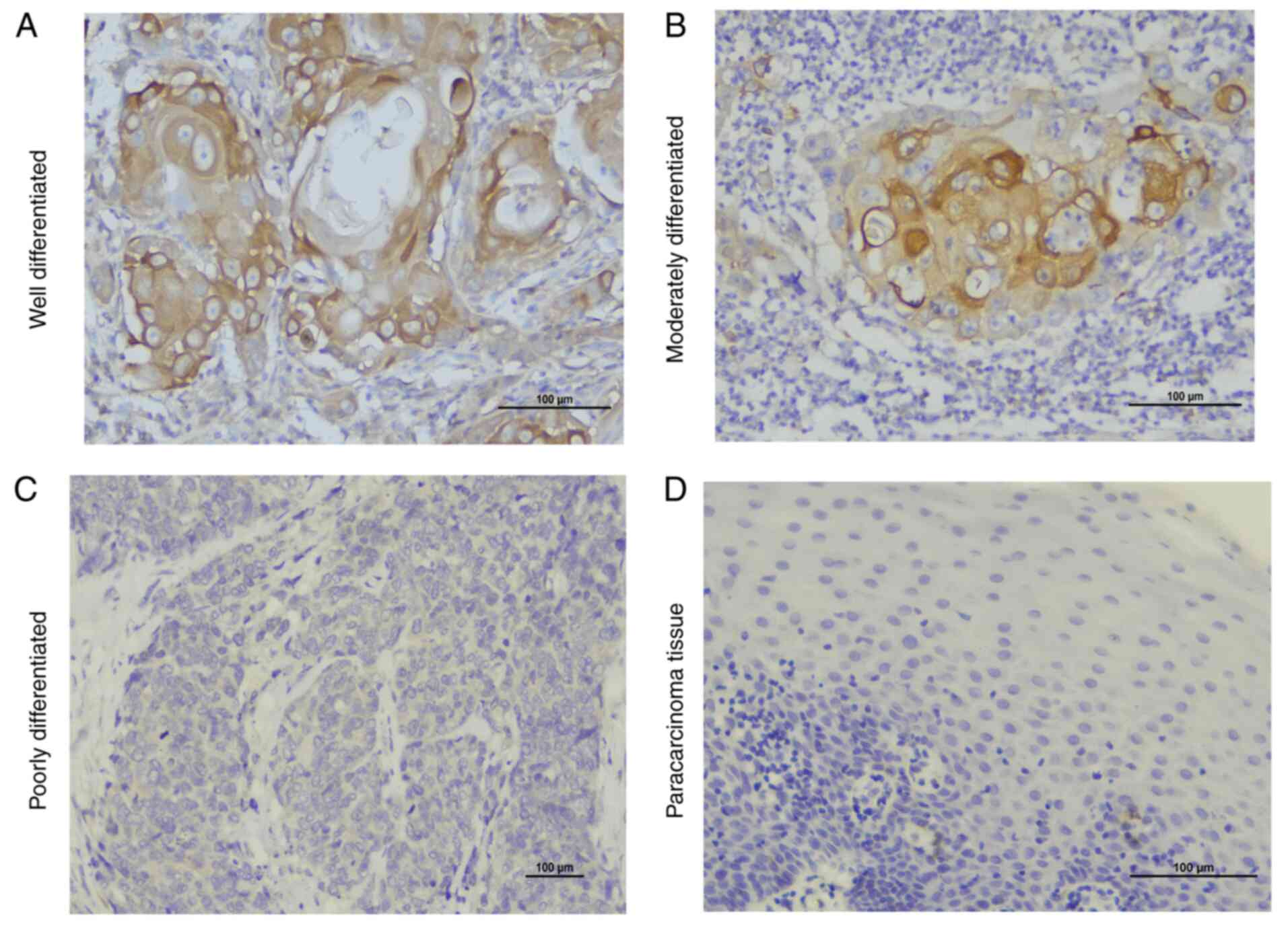
|
1
|
de Groen RAL, Schrader AMR, Kersten MJ,
Pals ST and Vermaat JSP: MYD88 in the driver's seat of B-cell
lymphomagenesis: From molecular mechanisms to clinical
implications. Haematologica. 104:23372019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ali J, Sabiha B, Jan HU, Haider SA, Khan
AA and Ali SS: Genetic etiology of oral cancer. Oral Oncol.
70:23–28. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Oh HN, Seo JH, Lee MH, Kim C, Kim E, Yoon
G, Cho SS, Cho YS, Choi HW, Shim JH and Chae JI: Licochalcone C
induced apoptosis in human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by
regulation of the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
119:10118–10130. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Rivera C: Essentials of oral cancer. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:11884–11894. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Edwards BK, Brown ML, Wingo PA, Howe HL,
Ward E, Ries LA, Schrag D, Jamison PM, Jemal A, Wu XC, et al:
Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2002,
featuring population-based trends in cancer treatment. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 97:1407–1427. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lindemann A, Takahashi H, Patel AA, Osman
AA and Myers JN: Targeting the DNA damage response in OSCC with TP
53 mutations. J Dent Res. 97:635–644. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roi A, Roi CI, Negruțiu ML, Riviș M,
Sinescu C and Rusu LC: The challenges of OSCC diagnosis: Salivary
cytokines as potential biomarkers. J Clin Med. 9:28662020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen R, Alvero AB, Silasi DA and Mor G:
Inflammation, cancer and chemoresistance: Taking advantage of the
toll-like receptor signaling pathway. Am J Reprod Immunol.
57:93–107. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mehmeti M, Allaoui R, Bergenfelz C, Saal
LH, Ethier SP, Johansson ME, Jirström K and Leandersson K:
Expression of functional toll like receptor 4 in estrogen
receptor/progesterone receptor-negative breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 17:1302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Semlali A, Reddy Parine N, Arafah M,
Mansour L, Azzi A, Al Shahrani O, Al Amri A, Shaik JP, Aljebreen
AM, Alharbi O, et al: Expression and polymorphism of toll-like
receptor 4 and effect on NF-κB mediated inflammation in colon
cancer patients. PLoS One. 11:e01463332016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Takazawa Y, Kiniwa Y, Ogawa E, Uchiyama A,
Ashida A, Uhara H, Goto Y and Okuyama R: Toll-like receptor 4
signaling promotes the migration of human melanoma cells. Tohoku J
Exp Med. 234:57–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Luo XZ, He QZ and Wang K: Expression of
toll-like receptor 4 in ovarian serous adenocarcinoma and
correlation with clinical stage and pathological grade. Int J Clin
Exp Med. 8:14323–14327. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang JQ, Jeelall YS, Ferguson LL and
Horikawa K: Toll-like receptors and cancer: MYD88 mutation and
inflammation. Front Immunol. 5:3672014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deguine J and Barton GM: MyD88: A central
player in innate immune signaling. F1000Prime Rep. 6:972014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang EL, Qian ZR, Nakasono M, Tanahashi T,
Yoshimoto K, Bando Y, Kudo E, Shimada M and Sano T: High expression
of toll-like receptor 4/myeloid differentiation factor 88 signals
correlates with poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer.
102:908–915. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Huang HY, Zhang ZJ, Cao CB, Wang N, Liu
FF, Peng JQ, Ren XJ and Qian J: The TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
mediates the growth of colon cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
18:3834–3843. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Zhao F, Zhang H, Zhu Y, Wu K and
Tan G: Significance of TLR4/MyD88 expression in breast cancer. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7034–7039. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mills SE, Carter D, Greenson JK, Reuter VE
and Stoler MH: Sternberg's diagnostic surgical pathology, 5th
edition. 2-2. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philidelphia, PA,
USA: pp. 2348. 2012
|
|
19
|
The Union for International Cancer Control
(UICC), . TNM History, Evolution and Milestones. https://www.uicc.org/sites/main/files/atoms/files/TNM-History-2021.pdfSeptember
11–2021
|
|
20
|
Lin SC, Lo YC and Wu H: Helical assembly
in the MyD88-IRAK4-IRAK2 complex in TLR/IL-1R signalling. Nature.
465:885–890. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song Y, Zhou M, Cao Y, Qi J, Geng J and
Liu X: Expression of GLP-1 receptor and CD26 in human thyroid
C-cells: The association of thyroid C-cell tumorigenesis with
incretin-based medicine. Oncol Lett. 13:2684–2690. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
González-Moles MÁ, Warnakulasuriya S,
González-Ruiz I, González-Ruiz L, Ayén Á, Lenouvel D, Ruiz-Ávila I
and Ramos-García P: Clinicopathological and prognostic
characteristics of oral squamous cell carcinomas arising in
patients with oral lichen planus: A systematic review and a
comprehensive meta-analysis. Oral Oncol. 106:1046882020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Warnakulasuriya S, Johnson NW and Van der
Waal I: Nomenclature and classification of potentially malignant
disorders of the oral mucosa. J Oral Pathol Med. 36:575–580. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Güneri P and Epstein JB: Late stage
diagnosis of oral cancer: Components and possible solutions. Oral
Oncol. 50:1131–1136. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cheng YS, Rees T and Wright J: A review of
research on salivary biomarkers for oral cancer detection. Clin
Transl Med. 3:32014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rivera C: The challenge of the state of
susceptibility to oral cancer. J Oral Res. 4:8–9. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sakurai T, Kashida H, Watanabe T, Hagiwara
S, Mizushima T, Iijima H, Nishida N, Higashitsuji H, Fujita J and
Kudo M: Stress response protein cirp links inflammation and
tumorigenesis in colitis-associated cancer. Cancer Res.
74:6119–6128. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Oshima H and Oshima M: The inflammatory
network in the gastrointestinal tumor microenvironment: Lessons
from mouse models. J Gastroenterol. 47:97–106. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang L, Zhu R, Huang Z, Li H and Zhu H:
Lipopolysaccharide-induced toll-like receptor 4 signaling in cancer
cells promotes cell survival and proliferation in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 58:2223–2236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Coussens LM and Werb Z: Inflammation and
cancer. Nature. 420:860–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fukata M, Chen A, Klepper A, Krishnareddy
S, Vamadevan AS, Thomas LS, Xu R, Inoue H, Arditi M, Dannenberg AJ
and Abreu MT: Cox-2 is regulated by toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4)
signaling: Role in proliferation and apoptosis in the intestine.
Gastroenterology. 131:862–877. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sahu U, Choudhury A, Parvez S, Biswas S
and Kar S: Induction of intestinal stemness and tumorigenicity by
aberrant internalization of commensal non-pathogenic E. coli. Cell
Death Dis. 8:e26672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Paarnio K, Väyrynen S, Klintrup K, Ohtonen
P, Mäkinen MJ, Mäkelä J and Karttunen TJ: Divergent expression of
bacterial wall sensing toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in colorectal
cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 23:4831–4838. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu L, Wang L and Chen S: Dual character of
toll-like receptor signaling: Pro-tumorigenic effects and
anti-tumor functions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1835:144–154.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mikulandra M, Pavelic J and Glavan TM:
Recent findings on the application of toll-like receptors agonists
in cancer therapy. Curr Med Chem. 24:2011–2032. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kubo T, Hatton RD, Oliver J, Liu X, Elson
CO and Weaver CT: Regulatory T cell suppression and anergy are
differentially regulated by proinflammatory cytokines produced by
TLR-activated dendritic cells. J Immunol. 173:7249–7258. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Sharma Y and Bala K: Role of toll like
receptor in progression and suppression of oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rev. 14:4562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Su Q, Li L, Sun Y, Yang H, Ye Z and Zhao
J: Effects of the TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB signaling pathway on NLRP3
inflammasome in coronary microembolization-induced myocardial
injury. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:1497–1508. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lawrence T: The nuclear factor NF-kappaB
pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
1:a0016512009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Qin DP, Sun PN, Zhou YJ, Chen FM, Zhang
CL, Han JX and Yang XJ: Effect of tripterygium wilfordii polycoride
upon inflammation and TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway in ulcerative
colitis rats model. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 96:1444–1449. 2016.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
He Z, Deng R, Huang X, Ni Y, Yang X, Wang
Z and Hu Q: Lipopolysaccharide enhances OSCC migration by promoting
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Oral Pathol Med. 44:685–692.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Todosi AM, Gavrilescu MM, Aniţei GM, Filip
B and Scripcariu V: Colon cancer at the molecular level-usefulness
of epithelial-mesenchymal transition analysis. Rev Med Chir Soc Med
Nat Iasi. 116:1106–1111. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu X, Burfeind KG, Michaelis KA, Braun
TP, Olson B, Pelz KR, Morgan TK and Marks DL: MyD88 signalling is
critical in the development of pancreatic cancer cachexia. J
Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 10:378–390. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang Y and Zeng Y: Curcumin reduces
inflammation in knee osteoarthritis rats through blocking
TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signal pathway. Drug Dev Res. 80:353–359. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ju M, Liu B, He H, Gu Z, Liu Y, Su Y, Zhu
D, Cang J and Luo Z: MicroRNA-27a alleviates LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice via inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis through
modulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway. Cell Cycle. 17:2001–2018.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Singh MV, Cicha MZ, Nunez S, Meyerholz DK,
Chapleau MW and Abboud FM: Angiotensin II-induced hypertension and
cardiac hypertrophy are differentially mediated by TLR3- and
TLR4-dependent pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
316:H1027–H1038. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jain A and Pasare C: Innate control of
adaptive immunity: Beyond the three-signal paradigm. J Immunol.
198:3791–3800. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dange RB, Agarwal D, Teruyama R and
Francis J: Toll-like receptor 4 inhibition within the
paraventricular nucleus attenuates blood pressure and inflammatory
response in a genetic model of hypertension. J Neuroinflammation.
12:312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kang YM, Zhang DM, Yu XJ, Yang Q, Qi J, Su
Q, Suo YP, Yue LY, Zhu GQ and Qin DN: Chronic infusion of
enalaprilat into hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates
angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by
restoring neurotransmitters and cytokines. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
274:436–444. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zhu HT, Bian C, Yuan JC, Chu WH, Xiang X,
Chen F, Wang CS, Feng H and Lin JK: Curcumin attenuates acute
inflammatory injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling
pathway in experimental traumatic brain injury. J
Neuroinflammation. 11:592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Agarwal D, Welsch MA, Keller JN and
Francis J: Chronic exercise modulates RAS components and improves
balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines in the brain
of SHR. Basic Res Cardiol. 106:1069–1085. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Gress TW, Nieto FJ, Shahar E, Wofford MR
and Brancati FL: Hypertension and antihypertensive therapy as risk
factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis risk in
communities study. N Engl J Med. 342:905–912. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Bensimhon HF and Cavender MA: Hypertension
treatment in diabetes: Focus on heart failure prevention. Heart
Fail Clin. 15:551–563. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Stamler J, Vaccaro O, Neaton JD and
Wentworth D: Diabetes, other risk factors, and 12-yr cardiovascular
mortality for men screened in the multiple risk factor intervention
trial. Diabetes Care. 16:434–444. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chervonsky A: Innate receptors and
microbes in induction of autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol.
21:641–647. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Duparc T, Plovier H, Marrachelli VG, Van
Hul M, Essaghir A, Ståhlman M, Matamoros S, Geurts L, Pardo-Tendero
MM, Druart C, et al: Hepatocyte MyD88 affects bile acids, gut
microbiota and metabolome contributing to regulate glucose and
lipid metabolism. Gut. 66:620–632. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Androulidaki A, Wachsmuth L, Polykratis A
and Pasparakis M: Differential role of MyD88 and TRIF signaling in
myeloid cells in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes. PLoS One.
13:e01940482018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Marwick TH: Diabetic heart disease.
Postgrad Med J. 84:188–192. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Marwick TH, Ritchie R, Shaw JE and Kaye D:
Implications of underlying mechanisms for the recognition and
management of diabetic cardiomyopathy. J Am Coll Cardiol.
71:339–351. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mitchell JB, Bubolz T, Paul JE, Pashos CL,
Escarce JJ, Muhlbaier LH, Wiesman JM, Young WW, Epstein RS and
Javitt JC: Using medicare claims for outcomes research. Med Care.
32 (Suppl 7):JS38–JS51. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Dong B, Qi D, Yang L, Huang Y, Xiao X, Tai
N, Wen L and Wong FS: TLR4 regulates cardiac lipid accumulation and
diabetic heart disease in the nonobese diabetic mouse model of type
1 diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 303:H732–H742. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jiang DS, Zhang XF, Gao L, Zong J, Zhou H,
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Bian ZY, Zhu LH, Fan GC, et al: Signal regulatory
protein-α protects against cardiac hypertrophy via the disruption
of toll-like receptor 4 signaling. Hypertension. 63:96–104. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Park BS, Song DH, Kim HM, Choi BS, Lee H
and Lee JO: The structural basis of lipopolysaccharide recognition
by the TLR4-MD-2 complex. Nature. 458:1191–1195. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
O'Neill LA and Bowie AG: The family of
five: TIR-domain-containing adaptors in toll-like receptor
signalling. Nat Rev Immunol. 7:353–364. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Blauvelt A, Lebwohl MG and Bissonnette R:
IL-23/IL-17A dysfunction phenotypes inform possible clinical
effects from anti-IL-17A therapies. J Invest Dermatol.
135:1946–1953. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Shirey KA, Lai W, Scott AJ, Lipsky M,
Mistry P, Pletneva LM, Karp CL, McAlees J, Gioannini TL, Weiss J,
et al: The TLR4 antagonist Eritoran protects mice from lethal
influenza infection. Nature. 497:498–502. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Xu Z, Ren T, Xiao C, Li H and Wu T: Nickel
promotes the invasive potential of human lung cancer cells via
TLR4/MyD88 signaling. Toxicology. 285:25–30. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Feng X, Tan W, Cheng S, Wang H, Ye S, Yu
C, He Y, Zeng J, Cen J, Hu J, et al: Upregulation of microRNA-126
in hepatic stellate cells may affect pathogenesis of liver fibrosis
through the NF-κB pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 34:470–480. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Sanoh S, Horiguchi A, Sugihara K, Kotake
Y, Tayama Y, Uramaru N, Ohshita H, Tateno C, Horie T, Kitamura S
and Ohta S: Predictability of metabolism of ibuprofen and naproxen
using chimeric mice with human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos.
40:2267–2272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Inoue T, Nitta K, Sugihara K, Horie T,
Kitamura S and Ohta S: CYP2C9-catalyzed metabolism of S-warfarin to
7-hydroxywarfarin in vivo and in vitro in chimeric mice with
humanized liver. Drug Metab Dispos. 36:2429–2433. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Sherman MH, Yu RT, Tseng TW, Sousa CM, Liu
S, Truitt ML, He N, Ding N, Liddle C, Atkins AR, et al: Stromal
cues regulate the pancreatic cancer epigenome and metabolome. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:1129–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Sun W, Luo Z, Lee J, Kim HJ, Lee K, Tebon
P, Feng Y, Dokmeci MR, Sengupta S and Khademhosseini A:
Organ-on-a-chip for cancer and immune organs modeling. Adv Healthc
Mater. 8:18013632019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Musah S, Mammoto A, Ferrante TC, Jeanty
SSF, Hirano-Kobayashi M, Mammoto T, Roberts K, Chung S, Novak R,
Ingram M, et al: Mature induced-pluripotent-stem-cell-derived human
podocytes reconstitute kidney glomerular-capillary-wall function on
a chip. Nat Biomed Eng. 1:00692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Huh D, Matthews BD, Mammoto A,
Montoya-Zavala M, Hsin HY and Ingber DE: Reconstituting organ-level
lung functions on a chip. Science. 328:1662–1668. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Kim J, Koo BK and Knoblich JA: Human
organoids: Model systems for human biology and medicine. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 21:571–584. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Dotti I, Mora-Buch R, Ferrer-Picón E,
Planell N, Jung P, Masamunt MC, Leal RF, Martín de Carpi J, Llach
J, Ordás I, et al: Alterations in the epithelial stem cell
compartment could contribute to permanent changes in the mucosa of
patients with ulcerative colitis. Gut. 66:2069–2079. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gonneaud A, Asselin C, Boudreau F and
Boisvert FM: Phenotypic analysis of organoids by proteomics.
Proteomics. 17:2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Akhtar AA, Sances S, Barrett R and Breunig
JJ: Organoid and organ-on-a-chip systems: New paradigms for
modeling neurological and gastrointestinal disease. Curr Stem Cell
Rep. 3:98–111. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|