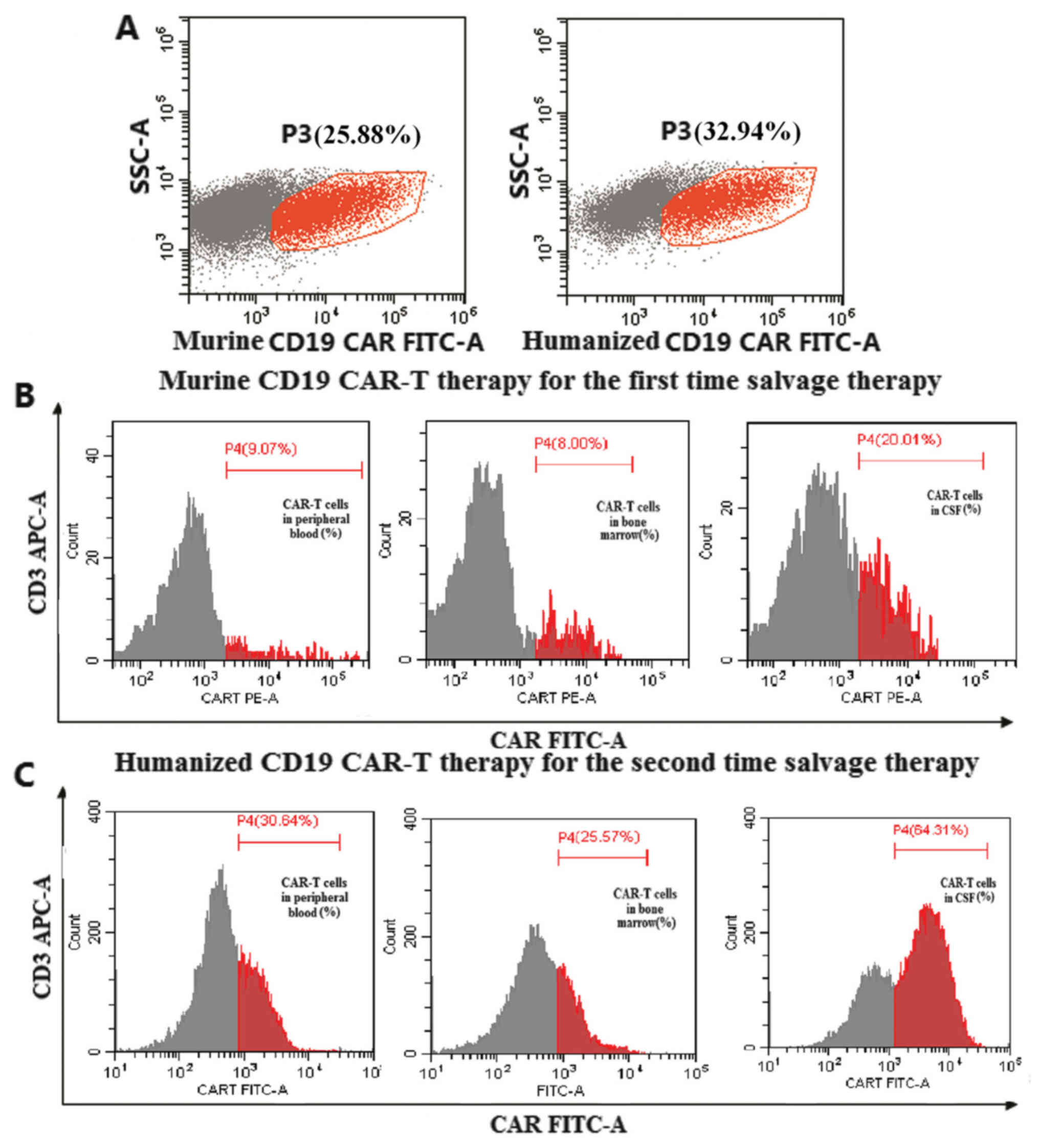
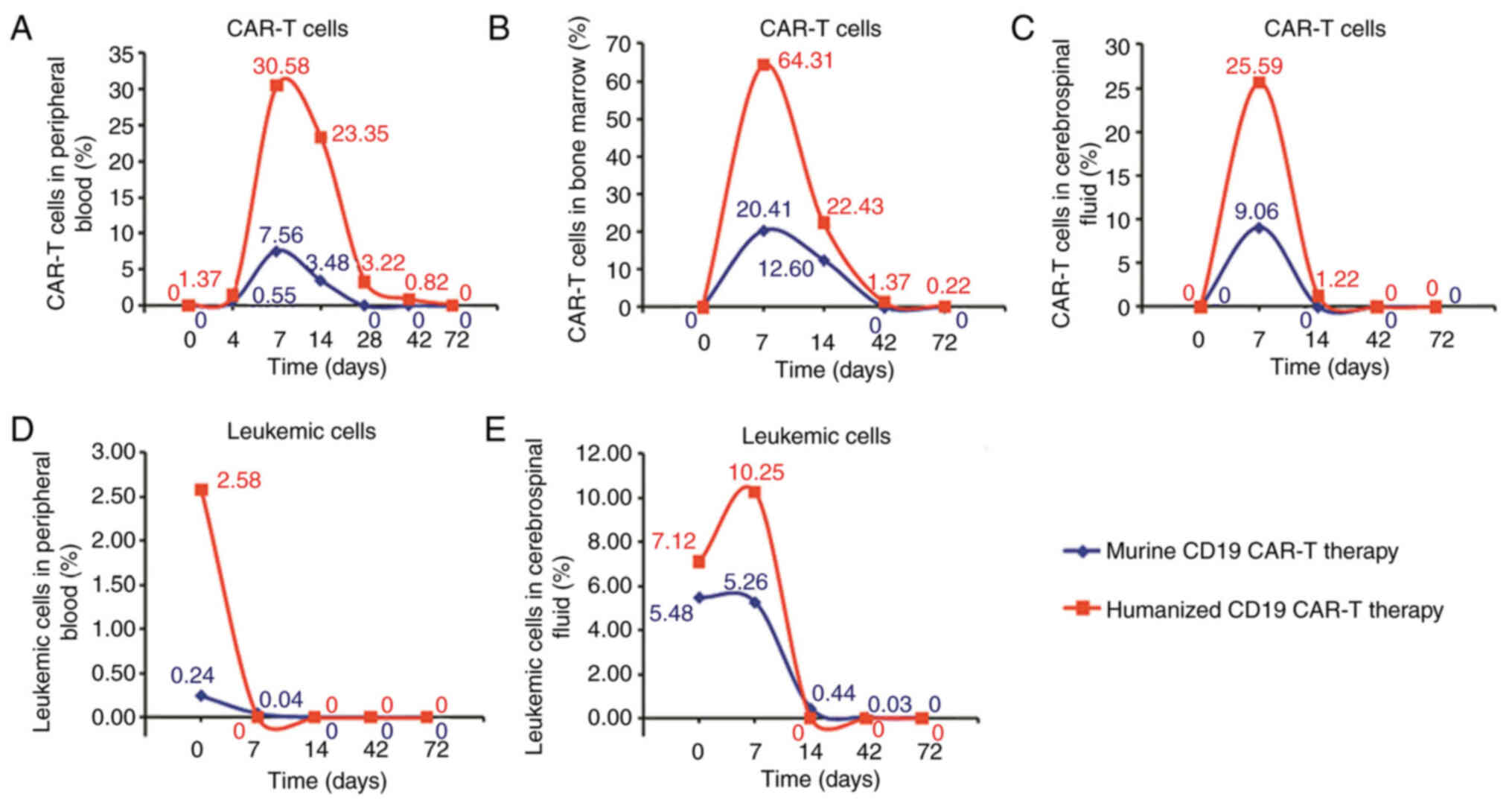
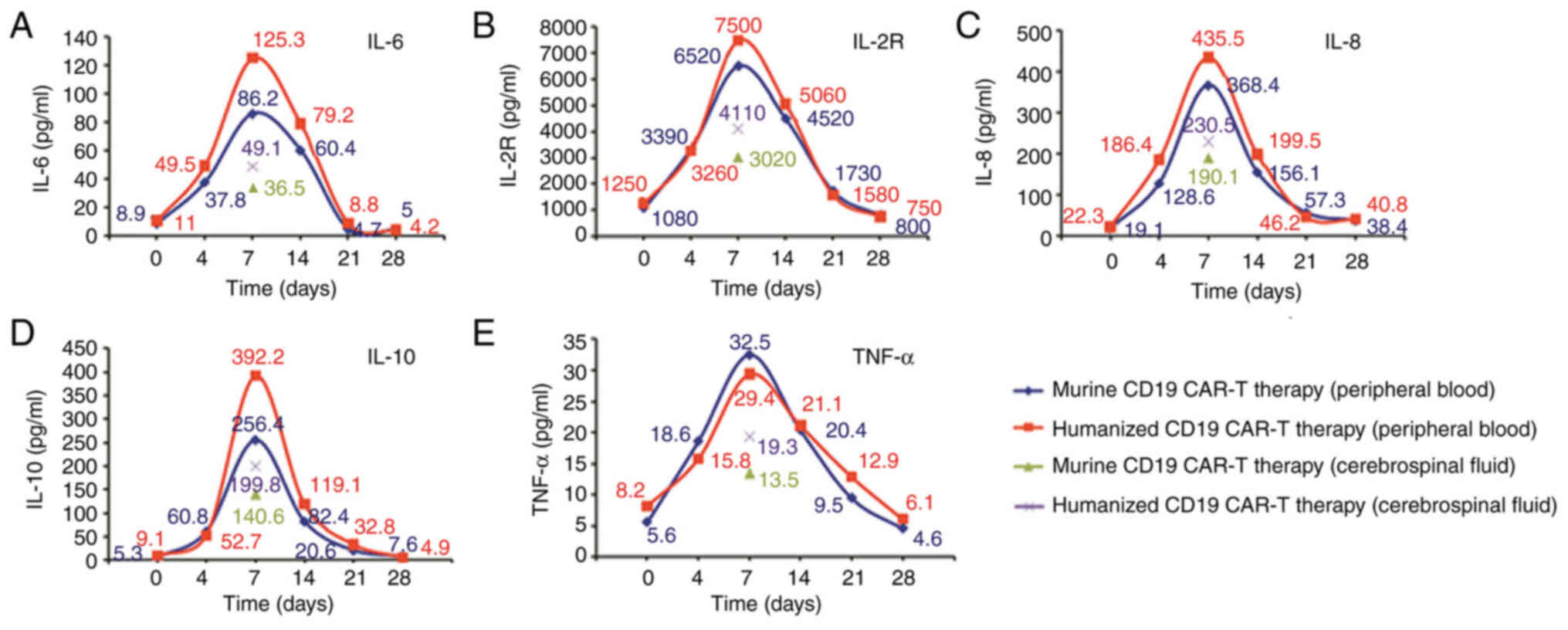
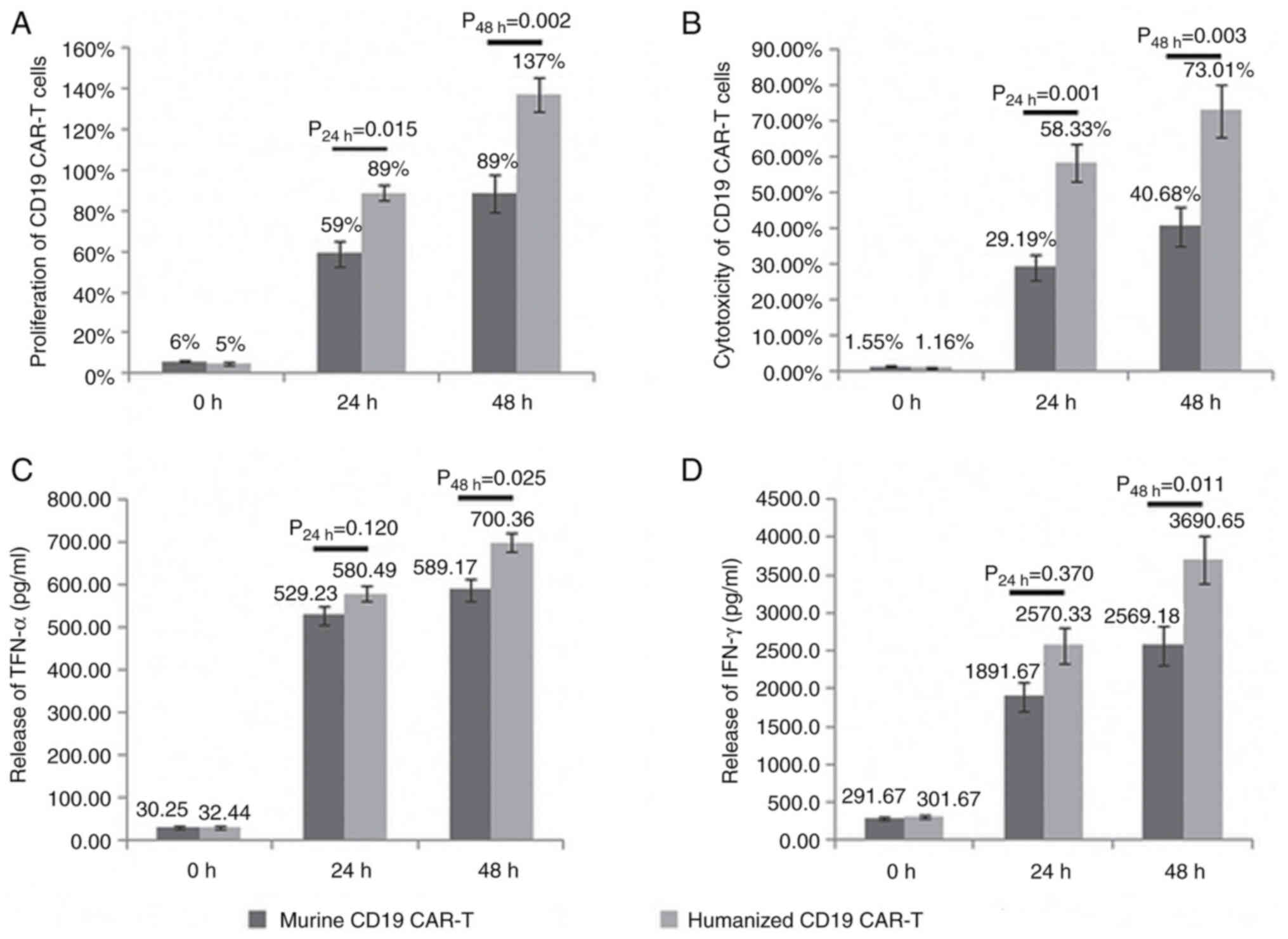
|
1
|
Rozovski U, Ohanian M, Ravandi F,
Garcia-Manero G, Faderl S, Pierce S, Cortes J and Estrov Z:
Incidence of and risk factors for involvement of the central
nervous system in acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma.
56:1392–1397. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Aoki J, Ishiyama K, Taniguchi S, Fukuda T,
Ohashi K, Ogawa H, Kanamori H, Eto T, Iwato K, Sakamaki H, et al:
Outcome of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for
acute myeloid leukemia patients with central nervous system
involvement. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 20:2029–2033. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Krishnan S, Wade R, Moorman AV, Mitchell
C, Kinsey SE, Eden TO, Parker C, Vora A, Richards S and Saha V:
Temporal changes in the incidence and pattern of central nervous
system relapses in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
treated on four consecutive Medical Research Council trials,
1985–2001. Leukemia. 24:450–459. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jin MW, Xu SM and An Q: Central nervous
disease in pediatric patients during acute lymphoblastic leukemia
(ALL): A review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:6015–6019.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Irving BA and Weiss A: The cytoplasmic
domain of the T cell receptor zeta chain is sufficient to couple to
receptor-associated signal transduction pathways. Cell. 64:891–901.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davila ML, Riviere I, Wang X, Bartido S,
Park J, Curran K, Chung SS, Stefanski J, Borquez-Ojeda O, Olszewska
M, et al: Efficacy and toxicity management of 19–28z CAR T cell
therapy in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med.
6:224ra252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lee DW, Kochenderfer JN, Stetler-Stevenson
M, Cui YK, Delbrook C, Feldman SA, Fry TJ, Orentas R, Sabatino M,
Shah NN, et al: T cells expressing CD19 chimeric antigen receptors
for acute lymphoblastic leukaemia in children and young adults: A
phase 1 dose-escalation trial. Lancet. 385:517–528. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neelapu SS, Tummala S, Kebriaei P, Wierda
W, Gutierrez C, Locke FL, Komanduri KV, Lin Y, Jain N, Daver N, et
al: Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy - assessment and
management of toxicities. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 15:47–62. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee DW, Gardner R, Porter DL, Louis CU,
Ahmed N, Jensen M, Grupp SA and Mackall CL: Current concepts in the
diagnosis and management of cytokine release syndrome. Blood.
124:188–195. 2014.Erratum in: Blood 128: 1533, 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brudno JN and Kochenderfer JN: Toxicities
of chimeric antigen receptor T cells: Recognition and management.
Blood. 127:3321–3330. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Maude SL, Barrett D, Teachey DT and Grupp
SA: Managing cytokine release syndrome associated with novel T
cell-engaging therapies. Cancer J. 20:119–122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu Y, Sun J, Wu Z, Yu J, Cui Q, Pu C,
Liang B, Luo Y, Shi J, Jin A, et al: Predominant cerebral cytokine
release syndrome in CD19-directed chimeric antigen
receptor-modified T cell therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 9:702016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lamers CH, Willemsen R, van Elzakker P,
van Steenbergen-Langeveld S, Broertjes M, Oosterwijk-Wakka J,
Oosterwijk E, Sleijfer S, Debets R and Gratama JW: Immune responses
to transgene and retroviral vector in patients treated with ex
vivo-engineered T cells. Blood. 117:72–82. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Grupp SA, Kalos M, Barrett D, Aplenc R,
Porter DL, Rheingold SR, Teachey DT, Chew A, Hauck B, Wright JF, et
al: Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells for acute lymphoid
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 368:1509–1518. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mulazzani M, Fräßle SP, von Mücke-Heim I,
Langer S, Zhou X, Ishikawa-Ankerhold H, Leube J, Zhang W, Dötsch S,
Svec M, et al: Long-term in vivo microscopy of CAR T cell dynamics
during eradication of CNS lymphoma in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:24275–24284. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Turtle CJ, Hanafi LA, Berger C, Gooley TA,
Cherian S, Hudecek M, Sommermeyer D, Melville K, Pender B, Budiarto
TM, et al: CD19 CAR-T cells of defined
CD4+:CD8+ composition in adult B cell ALL
patients. J Clin Invest. 126:2123–2138. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sommermeyer D, Hill T, Shamah SM, Salter
AI, Chen Y, Mohler KM and Riddell SR: Fully human CD19-specific
chimeric antigen receptors for T-cell therapy. Leukemia.
31:2191–2199. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Song DG, Ye Q, Poussin M, Liu L, Figini M
and Powell DJ Jr: A fully human chimeric antigen receptor with
potent activity against cancer cells but reduced risk for off-tumor
toxicity. Oncotarget. 6:21533–21546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao Y, Liu Z, Wang X, Wu H, Zhang J, Yang
J, Zhang F, Liu L, Long J, Lu P, et al: Treatment with humanized
selective CD19CAR-T cells shows efficacy in highly treated B-ALL
patients who have relapsed after receiving murine-based CD19CAR-T
therapies. Clin Cancer Res. 25:5595–5607. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Demehri S, Corbin A, Loriaux M, Druker BJ
and Deininger MW: Establishment of a murine model of aggressive
systemic mastocytosis/mast cell leukemia. Exp Hematol. 34:284–288.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tsukahara T, Ohmine K, Yamamoto C,
Uchibori R, Ido H, Teruya T, Urabe M, Mizukami H, Kume A, Nakamura
M, et al: CD19 target-engineered T-cells accumulate at tumor
lesions in human B-cell lymphoma xenograft mouse models. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 438:84–89. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liu D and Zhao J: Cytokine release
syndrome: Grading, modeling, and new therapy. J Hematol Oncol.
11:1212018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maude SL, Frey N, Shaw PA, Aplenc R,
Barrett DM, Bunin NJ, Chew A, Gonzalez VE, Zheng Z, Lacey SF, et
al: Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 371:1507–1517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kochenderfer JN, Dudley ME, Carpenter RO,
Kassim SH, Rose JJ, Telford WG, Hakim FT, Halverson DC, Fowler DH,
Hardy NM, et al: Donor-derived CD19-targeted T cells cause
regression of malignancy persisting after allogeneic hematopoietic
stem cell transplantation. Blood. 122:4129–4139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Turtle CJ, Hay KA, Hanafi LA, Li D,
Cherian S, Chen X, Wood B, Lozanski A, Byrd JC, Heimfeld S, et al:
Durable molecular remissions in chronic lymphocytic leukemia
treated with CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptor modified T
cells after failure of ibrutinib. J Clin Oncol. 35:3010–3020. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Johnson LA and June CH: Driving
gene-engineered T cell immunotherapy of cancer. Cell Res. 27:38–58.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lowe KL, Mackall CL, Norry E, Amado R,
Jakobsen BK and Binder G: Fludarabine and neurotoxicity in
engineered T-cell therapy. Gene Ther. 25:176–191. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jain MD, Bachmeier CA, Phuoc VH and Chavez
JC: Axicabtagene ciloleucel (KTE-C19), an anti CD19 CAR T therapy
for the treatment of relapsed/refractory aggressive B cell non
Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 14:1007–1017. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gust J, Hay KA, Hanafi LA, Li D, Myerson
D, Gonzalez-Cuyar LF, Yeung C, Liles WC, Wurfel M, Lopez JA, et al:
Endothelial activation and bloodbrain barrier disruption in
neurotoxicity after adoptive immunotherapy with CD19 CAR T cells.
Cancer Discov. 7:1404–1419. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gardner RA, Finney O, Annesley C, Brakke
H, Summers C, Leger K, Bleakley M, Brown C, Mgebroff S,
Kelly-Spratt KS, et al: Intent-to-treat leukemia remission by CD19
CAR T cells of defined formulation and dose in children and young
adults. Blood. 129:3322–3331. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brentjens RJ, Rivière I, Park JH, Davila
ML, Wang X, Stefanski J, Taylor C, Yeh R, Bartido S, Borquez-Ojeda
O, et al: Safety and persistence of adoptively transferred
autologous CD19-targeted T cells in patients with relapsed or
chemotherapy refractory B-cell leukemias. Blood. 118:4817–4828.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mirzaei HR, Pourghadamyari H, Rahmati M,
Mohammadi A, Nahand JS, Rezaei A, Mirzaei H and Hadjati J:
Gene-knocked out chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells: Tuning up
for the next generation cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett.
423:95–104. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Johnson LA, Scholler J, Ohkuri T, Kosaka
A, Patel PR, McGettigan SE, Nace AK, Dentchev T, Thekkat P, Loew A,
et al: Rational development and characterization of humanized
anti-EGFR variant III chimeric antigen receptor T cells for
glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med. 7:275ra222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alonso-Camino V, Sánchez-Martín D, Compte
M, Nuñez-Prado N, Diaz RM, Vile R and Alvarez-Vallina L: CARbodies:
Human antibodies against cell surface tumor antigens selected from
repertoires displayed on T cell chimeric antigen receptors. Mol
Ther Nucleic Acids. 2:e932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao Y, Wang QJ, Yang S, Kochenderfer JN,
Zheng Z, Zhong X, Sadelain M, Eshhar Z, Rosenberg SA and Morgan RA:
A herceptin-based chimeric antigen receptor with modified signaling
domains leads to enhanced survival of transduced T lymphocytes and
antitumor activity. J Immunol. 183:5563–5574. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|