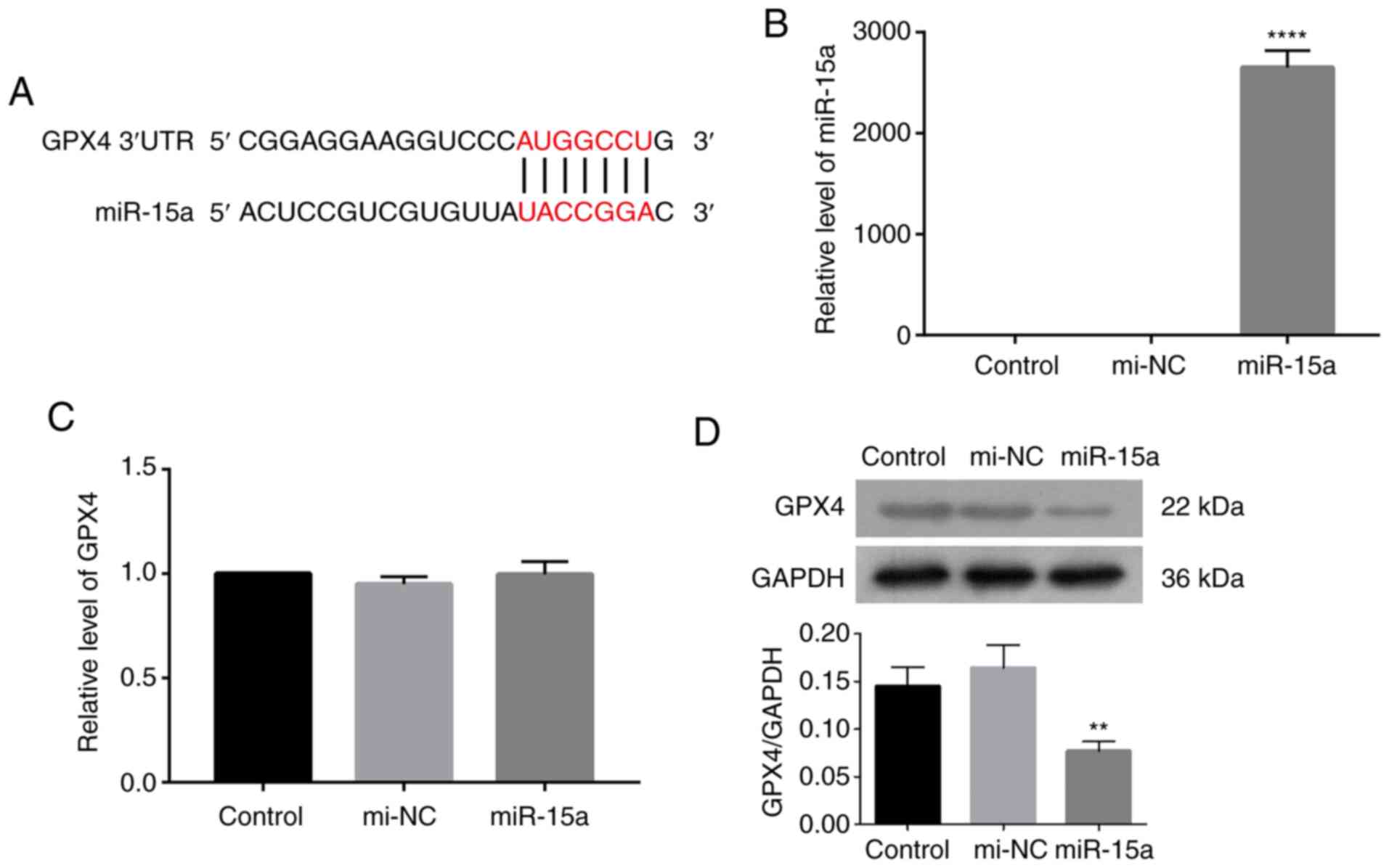
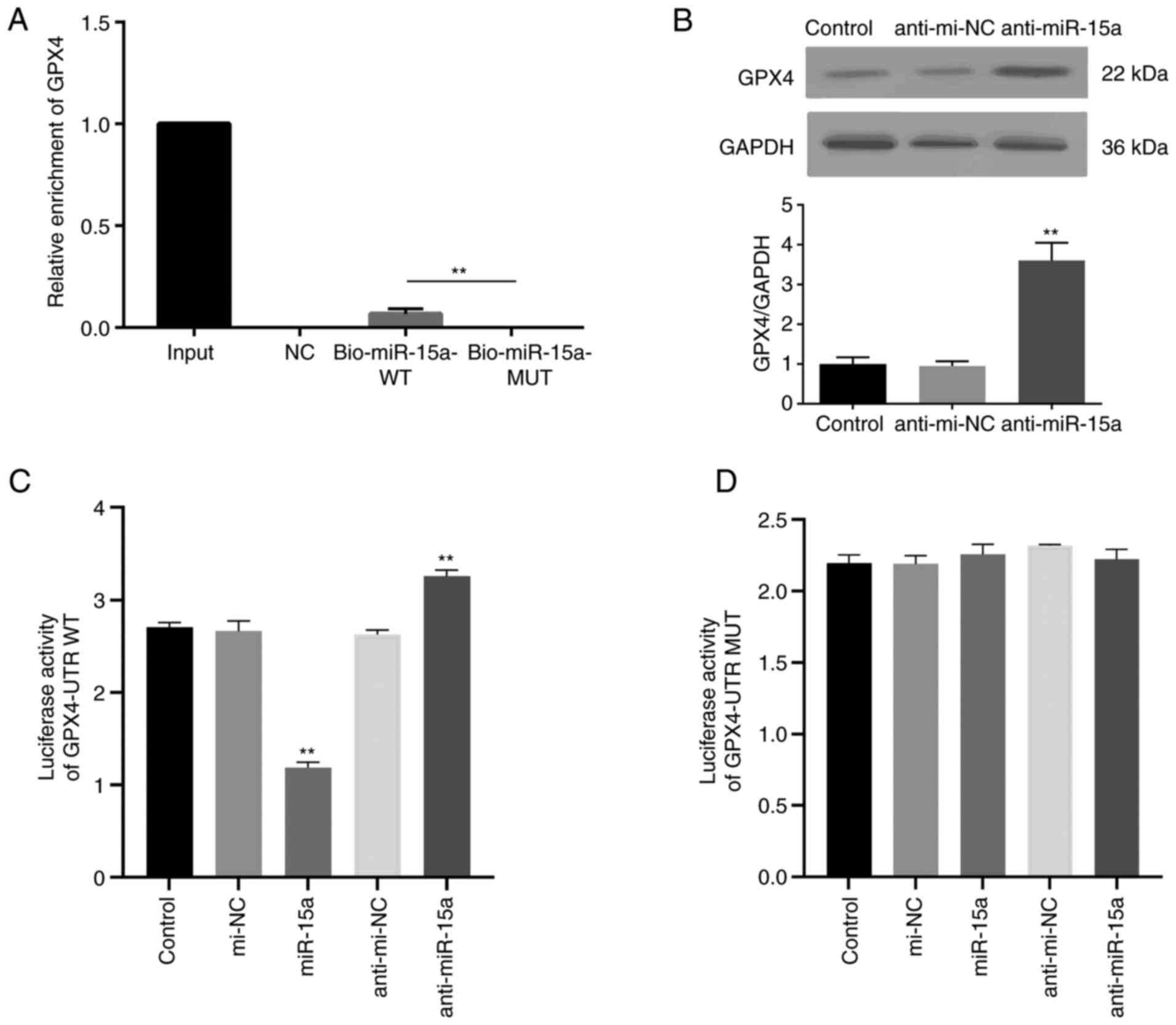
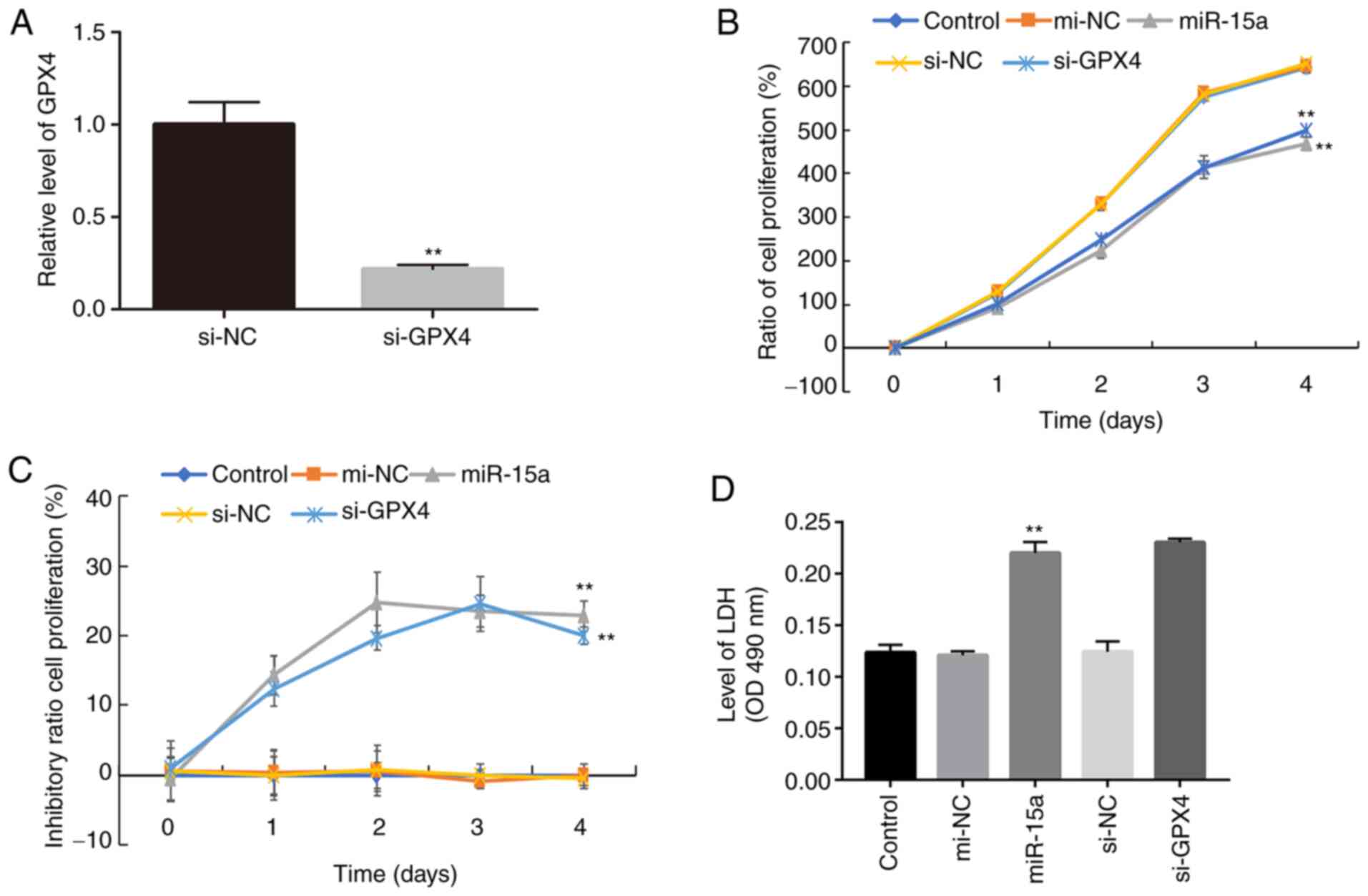
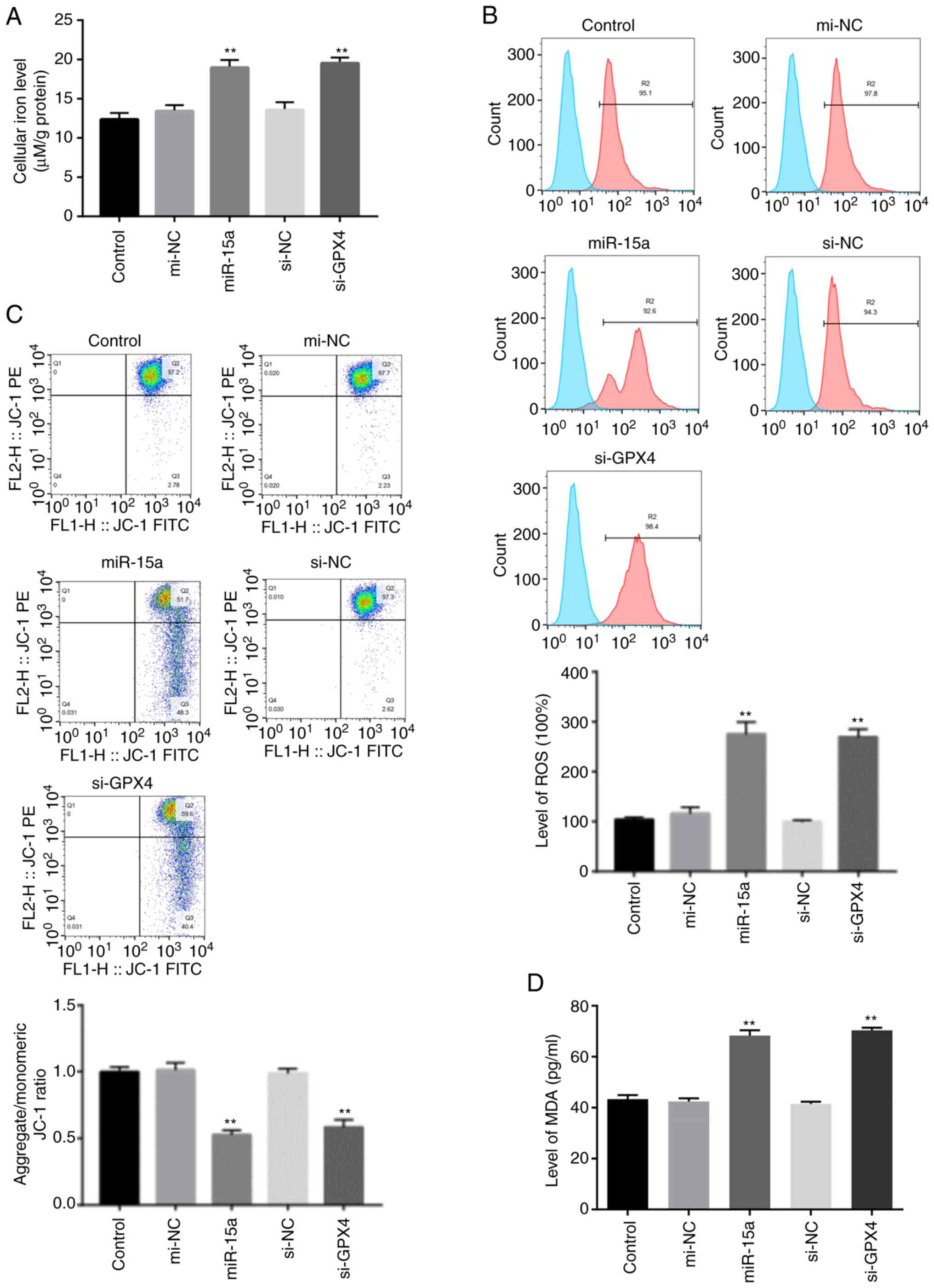
|
1
|
Omar MI, Roobol MJ, Ribal MJ, Abbott T,
Agapow PM, Araujo S, Asiimwe A, Auffray C, Balaur I, Beyer K, et
al: Introducing PIONEER: A project to harness big data in prostate
cancer research. Nat Rev Urol. 17:351–362. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu C, Xia H, Bai S, Zhao J, Edwards H, Li
X, Yang Y, Lyu J, Wang G, Zhan Y, et al: CUDC-907, a novel dual
PI3K and HDAC inhibitor, in prostate cancer: Antitumour activity
and molecular mechanism of action. J Cell Mol Med. 24:7239–7253.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hassannia B, Vandenabeele P and Vanden
Berghe T: Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell.
35:830–849. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hao S, Yu J, He W, Huang Q, Zhao Y, Liang
B, Zhang S, Wen Z, Dong S, Rao J, et al: Cysteine dioxygenase 1
mediates erastin-induced ferroptosis in human gastric cancer cells.
Neoplasia. 19:1022–1032. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang Y, Shi J, Liu X, Feng L, Gong Z,
Koppula P, Sirohi K, Li X, Wei Y, Lee H, et al: BAP1 links
metabolic regulation of ferroptosis to tumour suppression. Nat Cell
Biol. 20:1181–1192. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME,
Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, Cheah JH, Clemons PA, Shamji
AF, Clish CB, et al: Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by
GPX4. Cell. 156:317–331. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Seibt TM, Proneth B and Conrad M: Role of
GPX4 in ferroptosis and its pharmacological implication. Free Radic
Biol Med. 133:144–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Louandre C, Marcq I, Bouhlal H, Lachaier
E, Godin C, Saidak Z, François C, Chatelain D, Debuysscher V,
Barbare JC, et al: The retinoblastoma (Rb) protein regulates
ferroptosis induced by sorafenib in human hepatocellular carcinoma
cells. Cancer Lett. 356:971–977. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sui X, Zhang R, Liu S, Duan T, Zhai L,
Zhang M, Han X, Xiang Y, Huang X, Lin H and Xie T: RSL3 drives
ferroptosis through GPX4 Inactivation and ROS production in
colorectal cancer. Front Pharmacol. 9:13712018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zou Y, Palte MJ, Deik AA, Li H, Eaton JK,
Wang W, Tseng YY, Deasy R, Kost-Alimova M, Dančík V, et al: A
GPX4-dependent cancer cell state underlies the clear-cell
morphology and confers sensitivity to ferroptosis. Nat Commun.
10:16172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Baldassarri M, Fallerini C, Cetta F,
Ghisalberti M, Bellan C, Furini S, Spiga O, Crispino S, Gotti G,
Ariani F, et al: Omic approach in non-smoker female with lung
squamous cell carcinoma pinpoints to germline susceptibility and
personalized medicine. Cancer Res Treat. 50:356–365. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karbasforooshan H, Roohbakhsh A and Karimi
G: SIRT1 and microRNAs: The role in breast, lung and prostate
cancers. Exp Cell Res. 367:1–6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun Z, Shi K, Yang S, Liu J, Zhou Q, Wang
G, Song J, Li Z, Zhang Z and Yuan W: Effect of exosomal miRNA on
cancer biology and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 17:1472018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Guelfi G, Cochetti G, Stefanetti V,
Zampini D, Diverio S, Boni A and Mearini E: Next Generation
Sequencing of urine exfoliated cells: An approach of prostate
cancer microRNAs research. Sci Rep. 8:71112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang K, Wu L, Zhang P, Luo M, Du J, Gao
T, O'Connell D, Wang G, Wang H and Yang Y: miR-9 regulates
ferroptosis by targeting glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase GOT1 in
melanoma. Mol Carcinog. 57:1566–1576. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Luo M, Wu L, Zhang K, Wang H, Zhang T,
Gutierrez L, O'Connell D, Zhang P, Li Y, Gao T, et al: miR-137
regulates ferroptosis by targeting glutamine transporter SLC1A5 in
melanoma. Cell Death Differ. 25:1457–1472. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tomita K, Fukumoto M, Itoh K, Kuwahara Y,
Igarashi K, Nagasawa T, Suzuki M, Kurimasa A and Sato T: MiR-7-5p
is a key factor that controls radioresistance via intracellular
Fe2+ content in clinically relevant radioresistant
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 518:712–718. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Deng T, Liu R, Ning T, Yang H,
Liu D, Zhang Q, Lin D, Ge S, Bai M, et al: CAF secreted miR-522
suppresses ferroptosis and promotes acquired chemo-resistance in
gastric cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cui Y, Yang Y, Ren L, Yang J, Wang B, Xing
T, Chen H and Chen M: miR-15a-3p suppresses prostate cancer cell
proliferation and invasion by targeting SLC39A7 via downregulating
Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
34:472–479. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jia X, Liu H, Xu C, Han S, Shen Y, Miao X,
Hu X, Lin Z, Qian L, Wang Z and Gong W: MiR-15a/16-1 deficiency
induces IL-10-producing CD19+ TIM-1+ cells in
tumor microenvironment. J Cell Mol Med. 23:1343–1353. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Al-Kafaji G, Said HM, Alam MA and Al Naieb
ZT: Blood-based microRNAs as diagnostic biomarkers to discriminate
localized prostate cancer from benign prostatic hyperplasia and
allow cancer-risk stratification. Oncol Lett. 16:1357–1365.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jin W, Chen F, Wang K, Song Y, Fei X and
Wu B: miR-15a/miR-16 cluster inhibits invasion of prostate cancer
cells by suppressing TGF-β signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
104:637–644. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bonci D, Coppola V, Musumeci M, Addario A,
Giuffrida R, Memeo L, D'Urso L, Pagliuca A, Biffoni M, Labbaye C,
et al: The miR-15a-miR-16-1 cluster controls prostate cancer by
targeting multiple oncogenic activities. Nat Med. 14:1271–1277.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shimomura A, Shiino S, Kawauchi J,
Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, Matsuzaki J, Ono M, Takeshita F, Niida S,
Shimizu C, et al: Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting
breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 107:326–334. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Qadir MI and Faheem A: miRNA: A diagnostic
and therapeutic tool for pancreatic cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene
Expr. 27:197–204. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yokoi A, Matsuzaki J, Yamamoto Y, Yoneoka
Y, Takahashi K, Shimizu H, Uehara T, Ishikawa M, Ikeda SI, Sonoda
T, et al: Integrated extracellular microRNA profiling for ovarian
cancer screening. Nat Commun. 9:43192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Omidkhoda N, Wallace Hayes A, Reiter RJ
and Karimi G: The role of MicroRNAs on endoplasmic reticulum stress
in myocardial ischemia and cardiac hypertrophy. Pharmacol Res.
150:1045162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang J, Jia P, Zhao Z and Shen B: Key
regulators in prostate cancer identified by co-expression module
analysis. BMC Genomics. 15:10152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hart M, Nolte E, Wach S, Szczyrba J,
Taubert H, Rau TT, Hartmann A, Grässer FA and Wullich B:
Comparative microRNA profiling of prostate carcinomas with
increasing tumor stage by deep sequencing. Mol Cancer Res.
12:250–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Leite KR, Tomiyama A, Reis ST,
Sousa-Canavez JM, Sañudo A, Camara-Lopes LH and Srougi M: MicroRNA
expression profiles in the progression of prostate cancer-from
high-grade prostate intraepithelial neoplasia to metastasis. Urol
Oncol. 31:796–801. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zidan HE, Abdul-Maksoud RS, Elsayed WSH
and Desoky EAM: Diagnostic and prognostic value of serum miR-15a
and miR-16-1 expression among egyptian patients with prostate
cancer. IUBMB Life. 70:437–444. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aqeilan RI, Calin GA and Croce CM: miR-15a
and miR-16-1 in cancer: Discovery, function and future
perspectives. Cell Death Differ. 17:215–220. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Antognelli C, Mezzasoma L, Fettucciari K,
Mearini E and Talesa VN: Role of glyoxalase I in the proliferation
and apoptosis control of human LNCaP and PC3 prostate cancer cells.
Prostate. 73:121–132. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu M, Gai C, Li Z, Ding D, Zheng J, Zhang
W, Lv S and Li W: Targeted exosome-encapsulated erastin induced
ferroptosis in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci.
110:3173–3182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shin D, Kim EH, Lee J and Roh JL: Nrf2
inhibition reverses resistance to GPX4 inhibitor-induced
ferroptosis in head and neck cancer. Free Radic Biol Med.
129:454–462. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bebber CM, Müller F, Prieto Clemente L,
Weber J and von Karstedt S: Ferroptosis in cancer cell biology.
Cancers (Basel). 12:1642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|