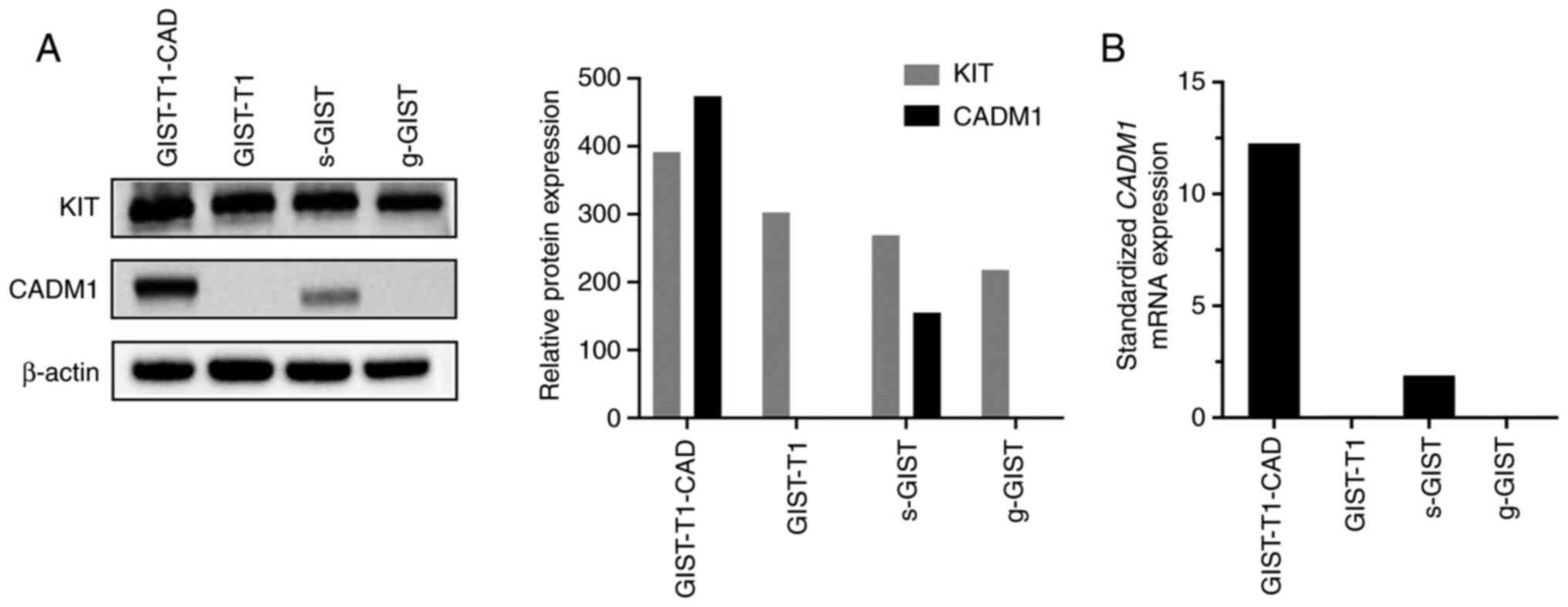
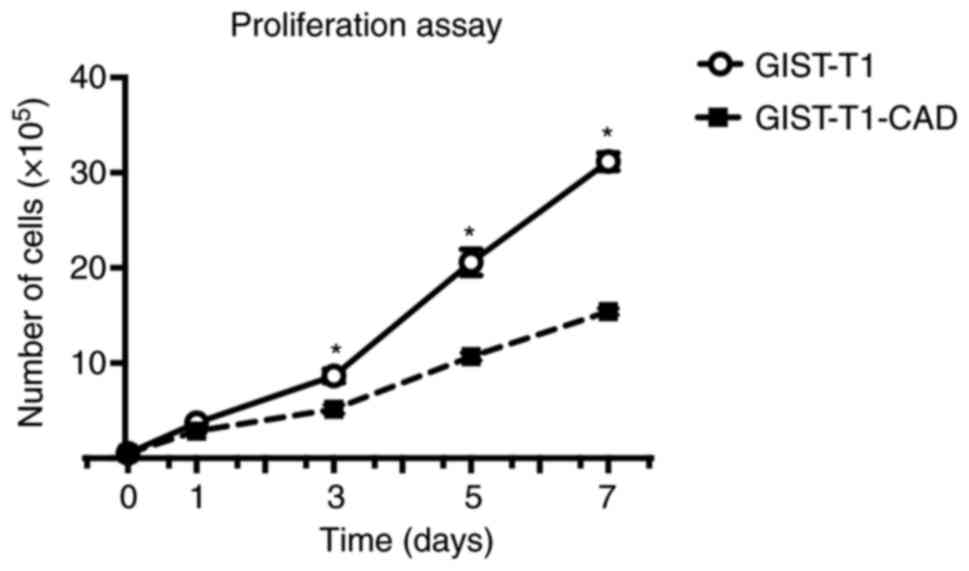
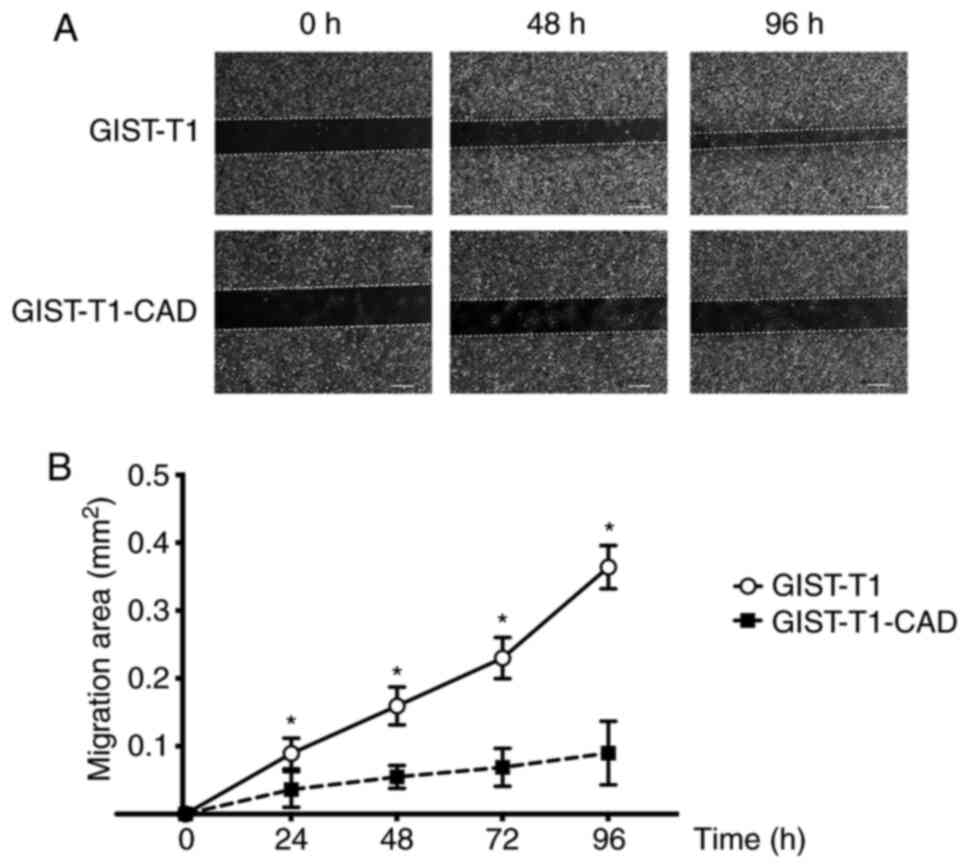
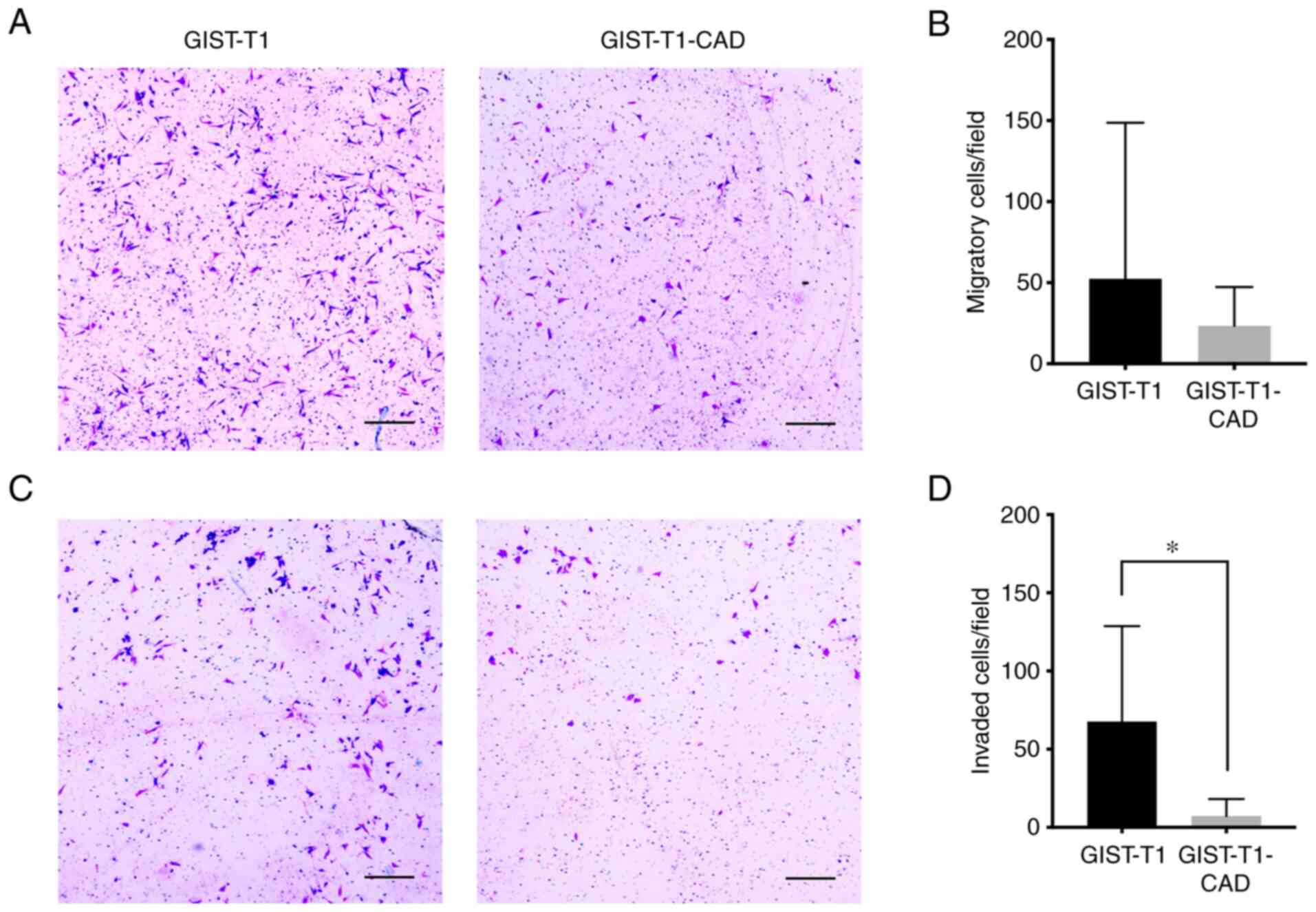
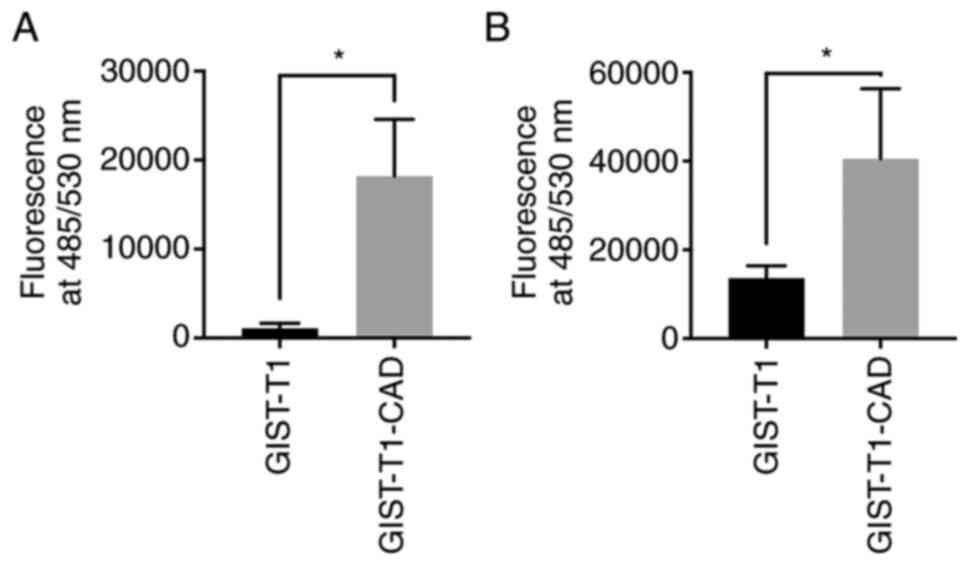
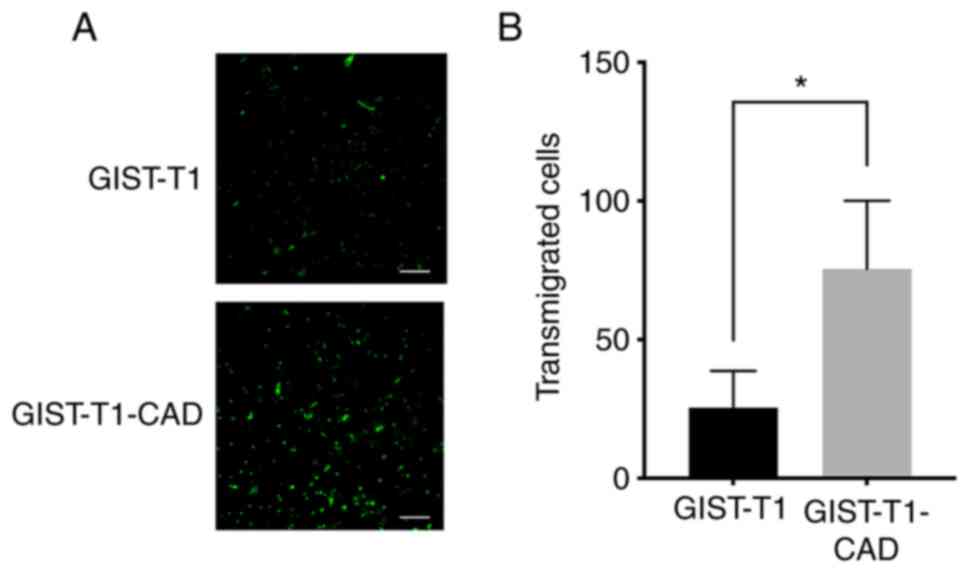
|
1
|
Hirota S, Isozaki K, Moriyama Y, Hashimoto
K, Nishida T, Ishiguro S, Kawano K, Hanada M, Kurata A, Takeda M,
et al: Gain-of-function mutations of c-kit in human
gastrointestinal stromal tumors. Science. 279:577–580. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Miettinen M and Lasota J: Gastrointestinal
stromal tumors-definition, clinical, histological,
immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and
differential diagnosis. Virchows Arch. 438:1–12. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Heinrich MC, Corless CL, Duensing A,
McGreevey L, Chen CJ, Joseph N, Singer S, Griffith DJ, Haley A,
Town A, et al: PDGFRA activating mutations in gastrointestinal
stromal tumors. Science. 299:708–710. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kinoshita K, Hirota S, Isozaki K, Ohashi
A, Nishida T, Kitamura Y, Shinomura Y and Matsuzawa Y: Absence of
c-kit gene mutations in gastrointestinal stromal tumours from
neurofibromatosis type 1 patients. J Pathol. 202:80–85. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agaram NP, Wong GC, Guo T, Maki RG, Singer
S, Dematteo RP, Besmer P and Antonescu CR: Novel V600E BRAF
mutations in imatinib-naive and imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal
stromal tumors. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 47:853–859. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pantaleo MA, Astolfi A, Urbini M, Nannini
M, Paterini P, Indio V, Saponara M, Formica S, Ceccarelli C,
Casadio R, et al: Analysis of all subunits, SDHA, SDHB, SDHC, SDHD,
of the succinate dehydrogenase complex in KIT/PDGFRA wild-type
GIST. Eur J Hum Genet. 22:32–39. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Emory TS, Sobin LH, Lukes L, Lee DH and
O'Leary TJ: Prognosis of gastrointestinal smooth-muscle (stromal)
tumors: Dependence on anatomic site. Am J Surg Pathol. 23:82–87.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang Z, Wang F, Liu S and Guan W:
Comparative clinical features and short-term outcomes of gastric
and small intestinal gastrointestinal stromal tumours: A
retrospective study. Sci Rep. 9:100332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Antonescu CR, Viale A, Sarran L,
Tschernyavsky SJ, Gonen M, Segal NH, Maki RG, Socci ND, DeMatteo RP
and Besmer P: Gene expression in gastrointestinal stromal tumors is
distinguished by KIT genotype and anatomic site. Clin Cancer Res.
10:3282–3290. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuan J, Kihara T, Kimura N, Hashikura Y,
Ohkouchi M, Isozaki K, Takahashi T, Nishida T, Ito A and Hirota S:
Differential expression of CADM1 in gastrointestinal stromal tumors
of different sites and with different gene abnormalities. Pathol
Oncol Res. 27:6020082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Biederer T, Sara Y, Mozhayeva M, Atasoy D,
Liu X, Kavalali ET and Sudhof TC: SynCAM, a synaptic adhesion
molecule that drives synapse assembly. Science. 297:1525–1531.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kuramochi M, Fukuhara H, Nobukuni T, Kanbe
T, Maruyama T, Ghosh HP, Pletcher M, Isomura M, Onizuka M, Kitamura
T, et al: TSLC1 is a tumor-suppressor gene in human non-small-cell
lung cancer. Nat Genet. 27:427–430. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Allinen M, Peri L, Kujala S,
Lahti-Domenici J, Outila K, Karppinen SM, Launonen V and Winqvist
R: Analysis of 11q21-24 loss of heterozygosity candidate target
genes in breast cancer: Indications of TSLC1 promoter
hypermethylation. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 34:384–389. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Honda T, Tamura G, Waki T, Jin Z, Sato K,
Motoyama T, Kawata S, Kimura W, Nishizuka S and Murakami Y:
Hypermethylation of the TSLC1 gene promoter in primary gastric
cancers and gastric cancer cell lines. Jpn J Cancer Res.
93:857–860. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zeng D, Wu X, Zheng J, Zhuang Y, Chen J,
Hong C, Zhang F, Wu M and Lin D: Loss of CADM1/TSLC1 expression is
associated with poor clinical outcome in patients with esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2016:69476232016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sasaki H, Nishikata I, Shiraga T, Akamatsu
E, Fukami T, Hidaka T, Kubuki Y, Okayama A, Hamada K, Okabe H, et
al: Overexpression of a cell adhesion molecule, TSLC1, as a
possible molecular marker for acute-type adult T-cell leukemia.
Blood. 105:1204–1213. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fisser MC, Rommer A, Steinleitner K,
Heller G, Herbst F, Wiese M, Glimm H, Sill H and Wieser R:
Induction of the proapoptotic tumor suppressor gene cell adhesion
molecule 1 by chemotherapeutic agents is repressed in therapy
resistant acute myeloid leukemia. Mol Carcinog. 54:1815–1819. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dewan MZ, Takamatsu N, Hidaka T,
Hatakeyama K, Nakahata S, Fujisawa J, Katano H, Yamamoto N and
Morishita K: Critical role for TSLC1 expression in the growth and
organ infiltration of adult T-cell leukemia cells in vivo. J Virol.
82:11958–11963. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kikuchi S, Iwai M, Sakurai-Yageta M,
Tsuboi Y, Ito T, Maruyama T, Tsuda H, Kanai Y, Onizuka M, Sato Y
and Murakami Y: Expression of a splicing variant of the CADM1
specific to small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 103:1051–1057.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Funaki T, Ito T, Tanei ZI, Goto A, Niki T,
Matsubara D and Murakami Y: CADM1 promotes malignant features of
small-cell lung cancer by recruiting 4.1R to the plasma membrane.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 534:172–178. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masuda M, Maruyama T, Ohta T, Ito A,
Hayashi T, Tsukasaki K, Kamihira S, Yamaoka S, Hoshino H, Yoshida
T, et al: CADM1 interacts with Tiam1 and promotes invasive
phenotype of human T-cell leukemia virus type I-transformed cells
and adult T-cell leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 285:15511–15522.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baines AJ, Lu HC and Bennett PM: The
Protein 4.1 family: Hub proteins in animals for organizing membrane
proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1838:605–619. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Murakami S, Sakurai-Yageta M, Maruyama T
and Murakami Y: Trans-homophilic interaction of CADM1 activates
PI3K by forming a complex with MAGuK-family proteins MPP3 and Dlg.
PLoS One. 9:e828942014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tatsumi K, Taatjes DJ, Wadsworth MP,
Bouchard BA and Bovill EG: Cell adhesion molecule 1 (CADM1) is
ubiquitously present in the endothelium and smooth muscle cells of
the human macro- and micro-vasculature. Histochem Cell Biol.
138:815–820. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ross EA, Douglas MR, Wong SH, Ross EJ,
Curnow SJ, Nash GB, Rainger E, Scheel-Toellner D, Lord JM, Salmon M
and Buckley CD: Interaction between integrin alpha9beta1 and
vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) inhibits neutrophil
apoptosis. Blood. 107:1178–1183. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sana TR, Janatpour MJ, Sathe M, McEvoy LM
and McClanahan TK: Microarray analysis of primary endothelial cells
challenged with different inflammatory and immune cytokines.
Cytokine. 29:256–269. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chilmi S, Nakahata S, Fauzi YR, Ichikawa
T, Tani C, Suwanruengsri M, Yamaguchi R, Matsuura T, Kurosawa G and
Morishita K: Development of anti-human CADM1 monoclonal antibodies
as a potential therapy for adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma. Int J
Hematol. 112:496–503. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|