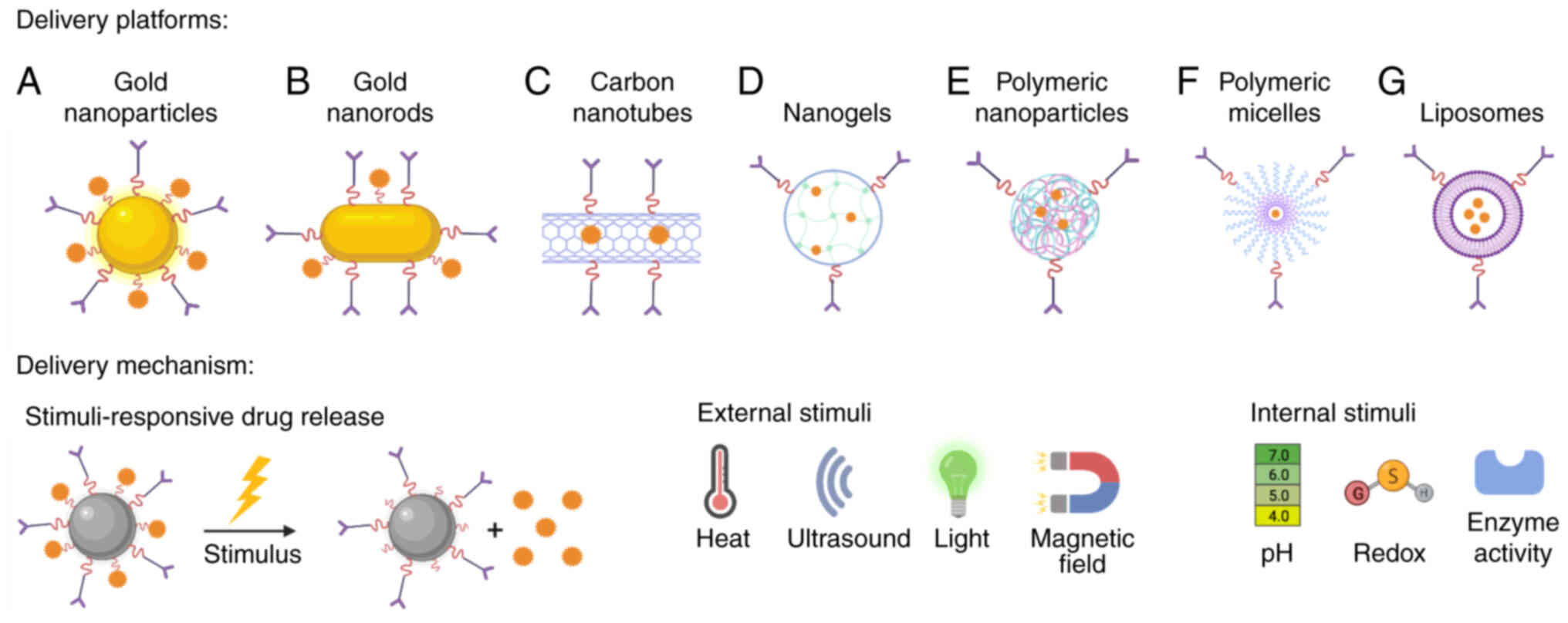
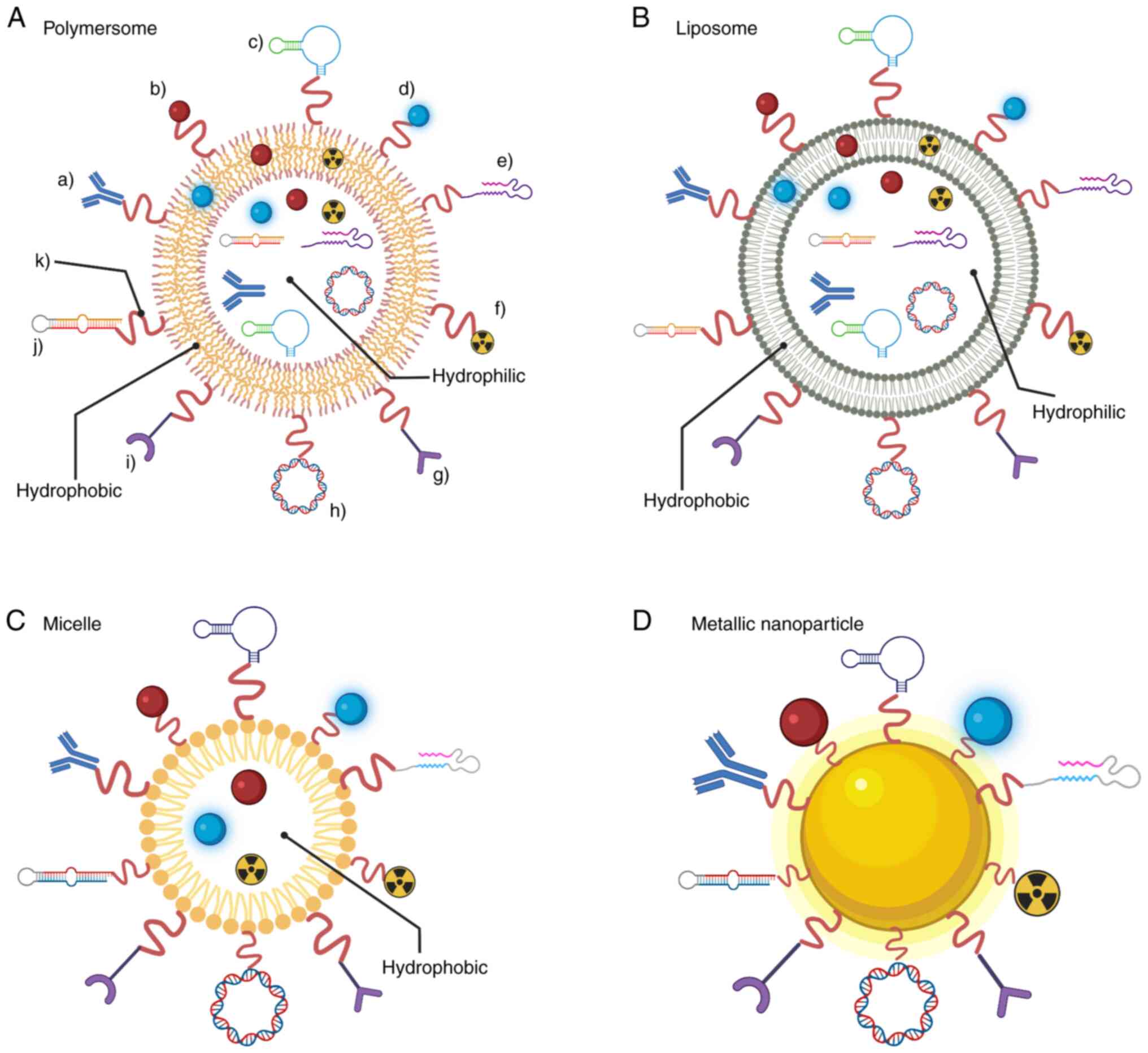
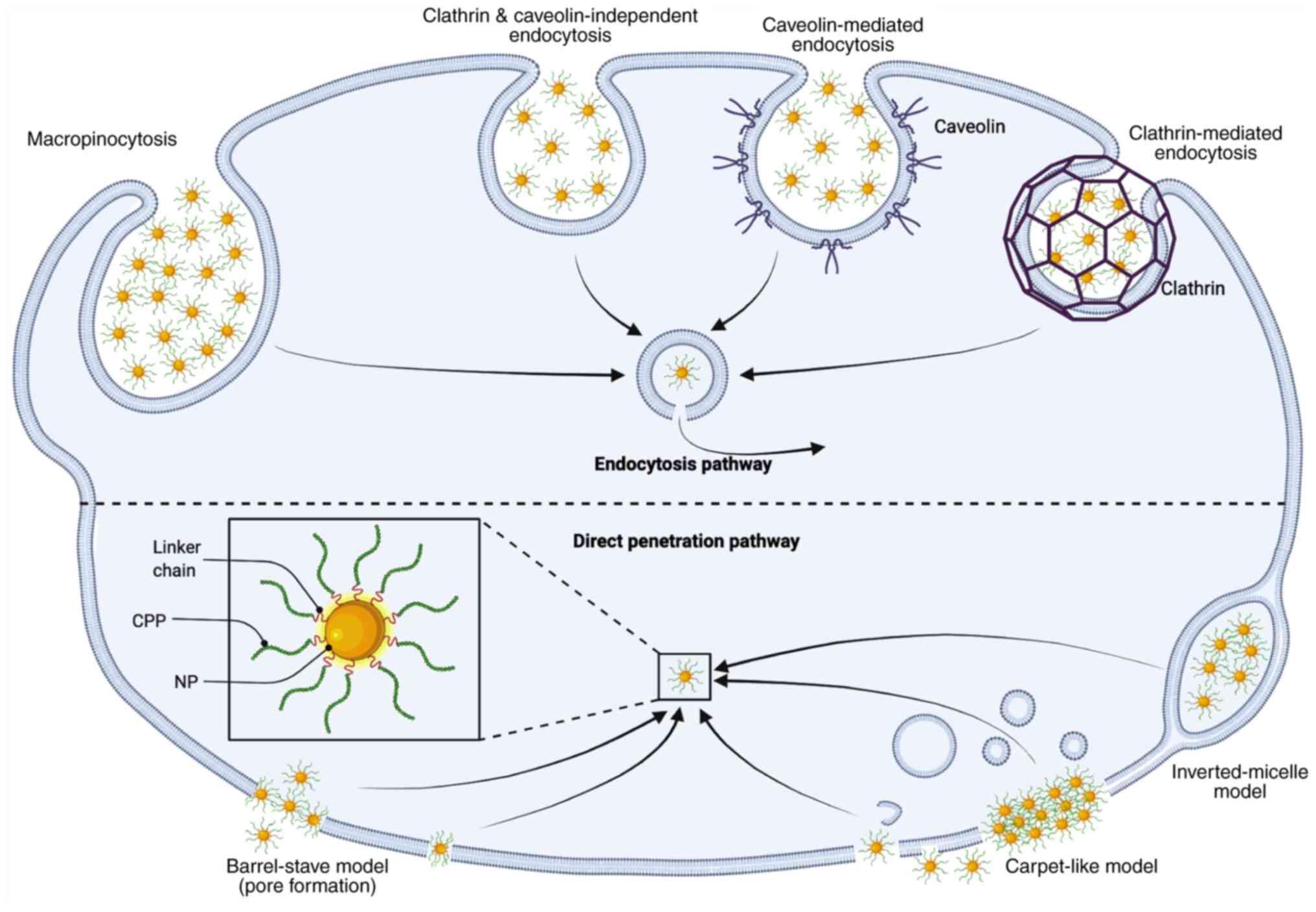
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Parsa Y, Mirmalek SA, Kani FE, Aidun A,
Salimi-Tabatabaee SA, Yadollah-Damavandi S, Jangholi E, Parsa T and
Shahverdi E: A review of the clinical implications of breast cancer
biology. Electron Physician. 8:2416–2424. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wu D, Si M, Xue HY and Wong HL:
Nanomedicine applications in the treatment of breast cancer:
Current state of the art. Int J Nanomedicine. 12:5879–5892. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Logothetis CJ, Gallick GE, Maity SN, Kim
J, Aparicio A, Efstathiou E and Lin SH: Molecular classification of
prostate cancer progression: Foundation for marker-driven treatment
of prostate cancer. Cancer Discov. 3:849–861. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang A, Zhang J, Plymate S and Mostaghel
EA: Classical and Non-classical roles for pre-receptor control of
DHT metabolism in prostate cancer progression. Horm Cancer.
7:104–113. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu LL, Xie N, Sun S, Plymate S, Mostaghel
E and Dong X: Mechanisms of the androgen receptor splicing in
prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 33:3140–3150. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Culig Z and Santer FR: Androgen receptor
signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 33:413–427.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rebello RJ, Pearson RB, Hannan RD and
Furic L: Therapeutic approaches targeting MYC-Driven prostate
cancer. Genes (Basel). 8:712017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blee AM, He Y, Yang Y, Ye Z, Yan Y, Pan Y,
Dugdale J, Kuehn E, Kohli M, Jimenez R, et al: TMPRSS2-ERG controls
luminal epithelial lineage and antiandrogen sensitivity in PTEN and
TP53-mutated prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 24:4551–4565. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nadal M, Prekovic S, Gallastegui N, Helsen
C, Abella M, Zielinska K, Gay M, Vilaseca M, Taulès M, Houtsmuller
AB, et al: Structure of the homodimeric androgen receptor
ligand-binding domain. Nat Commun. 8:143882017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Damyanov CA, Maslev IK and Pavlov VS:
Conventional treatment of cancer realities and problems. Ann
Complement Altern Med. 1:1–9. 2018.
|
|
13
|
Schaue D and Mcbride WH: Opportunities and
challenges of radiotherapy for treating cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
12:527–540. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Estanqueiro M, Amaral MH, Conceição J and
Sousa Lobo JM: Nanotechnological carriers for cancer chemotherapy:
The state of the art. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces.
126:631–648. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Vanneman M and Dranoff G: Combining
immunotherapy and targeted therapies in cancer treatment. Nat Rev
Cancer. 12:237–251. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao QX, Zhou GX, Lin SJ, Paus R and Yue
ZC: How chemotherapy and radiotherapy damage the tissue:
Comparative biology lessons from feather and hair models. Exp
Dermatol. 28:413–418. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi J, Kantoff PW, Wooster R and Farokhzad
OC: Cancer nanomedicine: Progress, challenges and opportunities.
Nat Rev Cancer. 17:20–37. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hayashi K, Ono K, Suzuki H, Sawada M,
Moriya M, Sakamoto W and Yogo T: High-frequency,
magnetic-field-responsive drug release from magnetic
nanoparticle/organic hybrid based on hyperthermic effect. ACS Appl
Mater Interfaces. 2:1903–1911. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kong SD, Zhang W, Lee JH, Brammer K, Lal
R, Karin M and Jin S: Magnetically vectored nanocapsules for tumor
penetration and remotely switchable on-demand drug release. Nano
Lett. 10:5088–5092. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang B, Zaro JL, Shen Y, Chen Q, Yu Y, Sun
P, Wang Y, Shen WC, Tu J and Sun C: Acid-sensitive hybrid polymeric
micelles containing a reversibly activatable cell-penetrating
peptide for tumor-specific cytoplasm targeting. J Control Release.
279:147–156. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu Q, Song L, Chen S, Gao J, Zhao P and
Du J: A superparamagnetic polymersome with extremely high T2
relaxivity for MRI and cancer-targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials.
114:23–33. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ke W, Li J, Mohammed F, Wang Y, Tou K, Liu
X, Wen P, Kinoh H, Anraku Y, Chen H, et al: Therapeutic polymersome
nanoreactors with tumor-specific activable cascade reactions for
cooperative cancer therapy. ACS Nano. 13:2357–2369. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao X, Wang S, Wang BL, Deng S, Liu X,
Zhang XN, Luo LL, Fan RR, Xiang ML, You C, et al: Improving the
anti-ovarian cancer activity of docetaxel with biodegradable
self-assembly micelles through various evaluations. Biomaterials.
53:646–658. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mao HL, Qian F, Li S, Shen JW, Ye CK, Hua
L, Zhang LZ, Wu DM, Lu J, Yu RT, et al: Delivery of doxorubicin
from hyaluronic acid-modified glutathione-responsive ferrocene
micelles for combination cancer therapy. Mol Pharm. 16:987–994.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li Z, Tan S, Li S, Shen Q and Wang K:
Cancer drug delivery in the nano era: An overview and perspectives
(Review). Oncol Rep. 38:611–624. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zariwala MG, Bendre H, Markiv A, Farnaud
S, Renshaw D, Taylor KM and Somavarapu S: Hydrophobically modified
chitosan nanoliposomes for intestinal drug delivery. Int J
Nanomedicine. 13:5837–5848. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu Y, Liu X, Cai Z, Zhang H, Gao H, He W,
Wu P, Cai C, Zhu JJ and Yan Z: Enhancing the plasmon resonance
absorption of multibranched gold nanoparticles in the near-infrared
region for photothermal cancer therapy: Theoretical predictions and
experimental verification. Chem Mater. 31:471–482. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bellassai N, D'Agata R, Jungbluth V and
Spoto G: Surface plasmon resonance for biomarker detection:
Advances in Non-invasive cancer diagnosis. Front Chem. 7:5702019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kishimoto TK, Ferrari JD, Lamothe RA,
Kolte PN, Griset AP, O'Neil C, Chan V, Browning E, Chalishazar A,
Kuhlman W, et al: Improving the efficacy and safety of biologic
drugs with tolerogenic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol. 11:890–899.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Böhmová E, Machová D, Pechar M, Pola R,
Venclíková K, Janoušková O and Etrych T: Cell-penetrating peptides:
A useful tool for the delivery of various cargoes into cells.
Physiol Res. 67 (Suppl 2):S267–S279. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kauffman WB, Fuselier T, He J and Wimley
WC: Mechanism matters: A taxonomy of cell penetrating peptides.
Trends Biochem Sci. 40:749–764. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Frankel AD and Pabo CO: Cellular uptake of
the tat protein from human immunodeficiency virus. Cell.
55:1189–1193. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Green M and Loewenstein PM: Autonomous
functional domains of chemically synthesized human immunodeficiency
virus tat trans-activator protein. Cell. 55:1179–1188. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bechara C and Sagan S: Cell-penetrating
peptides: 20 years later, where do we stand? FEBS Lett.
587:1693–1702. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Guidotti G, Brambilla L and Rossi D:
Cell-penetrating peptides: From basic research to clinics. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 38:406–424. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Huang K and García AE: Free energy of
translocating an arginine-rich cell-penetrating peptide across a
lipid bilayer suggests pore formation. Biophys J. 104:412–420.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Herce HD, Garcia AE, Litt J, Kane RS,
Martin P, Enrique N, Rebolledo A and Milesi V: Arginine-rich
peptides destabilize the plasma membrane, consistent with a pore
formation translocation mechanism of cell-penetrating peptides.
Biophys J. 97:1917–1925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Islam MZ, Ariyama H, Alam JM and Yamazaki
M: Entry of cell-penetrating peptide transportan 10 into a single
vesicle by translocating across lipid membrane and its induced
pores. Biochemistry. 53:386–396. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sharmin S, Islam MZ, Karal MAS, Alam
Shibly SU, Dohra H and Yamazaki M: Effects of lipid composition on
the entry of cell-penetrating peptide oligoarginine into single
vesicles. Biochemistry. 55:4154–4165. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lindgren M and Langel U: Classes and
prediction of cell-penetrating peptides. Methods in molec8ular
biology (Clifton N.J.). 683:3–19. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cai D, Gao W, He B, Dai W, Zhang H, Wang
X, Wang J, Zhang X and Zhang Q: Hydrophobic penetrating peptide
PFVYLI-modified stealth liposomes for doxorubicin delivery in
breast cancer therapy. Biomaterials. 35:2283–2294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang Y, Yang Y, Xie X, Cai X, Zhang H,
Gong W, Wang Z and Mei X: PEGylated liposomes with NGR ligand and
heat-activable cell-penetrating peptide-doxorubicin conjugate for
tumor-specific therapy. Biomaterials. 35:4368–4381. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Morshed RA, Muroski ME, Dai Q, Wegscheid
ML, Auffinger B, Yu D, Han Y, Zhang L, Wu M, Cheng Y and Lesniak
MS: Cell-penetrating peptide-modified gold nanoparticles for the
delivery of doxorubicin to brain metastatic breast cancer. Mol
Pharm. 13:1843–1854. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu X, Xu Y, Solis LM, Tao W, Wang L,
Behrens C, Xu X, Zhao L, Liu D, Wu J, et al: Long-circulating siRNA
nanoparticles for validating Prohibitin1-targeted non-small cell
lung cancer treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 112:7779–7784. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Parvani JG, Gujrati MD, Mack MA, Schiemann
WP and Lu ZR: Silencing β3 integrin by targeted ECO/siRNA
nanoparticles inhibits EMT and metastasis of triple-negative breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 75:2316–2325. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Vaidya AM, Sun Z, Ayat N, Schilb A, Liu X,
Jiang H, Sun D, Scheidt J, Qian V, He S, et al: Systemic delivery
of tumor-targeting siRNA Nanoparticles against an oncogenic LncRNA
facilitates effective triple-negative breast cancer therapy.
Bioconjug Chem. 30:907–919. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pasut G, Paolino D, Celia C, Mero A,
Joseph AS, Wolfram J, Cosco D, Schiavon O, Shen H and Fresta M:
Polyethylene glycol (PEG)-dendron phospholipids as innovative
constructs for the preparation of super stealth liposomes for
anticancer therapy. J Control Release. 199:106–113. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Nag M, Gajbhiye V, Kesharwani P and Jain
NK: Transferrin functionalized chitosan-PEG nanoparticles for
targeted delivery of paclitaxel to cancer cells. Colloids Surfaces
B Biointerfaces. 148:363–370. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ebbesen MF, Olesen MTJ, Gjelstrup MC,
Pakula MM, Larsen EKU, Hansen IM, Hansen PL, Mollenhauer J, Malle
BM and Howard KA: Tunable CD44-specific cellular retargeting with
hyaluronic acid nanoshells. Pharm Res. 32:1462–1474. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhong L, Xu L, Liu Y, Li Q, Zhao D, Li Z,
Zhang H, Zhang H, Kan Q, Wang Y, et al: Transformative hyaluronic
acid-based active targeting supramolecular nanoplatform improves
long circulation and enhances cellular uptake in cancer therapy.
Acta Pharm Sin B. 9:397–409. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ben Djemaa S, David S, Hervé-Aubert K,
Falanga A, Galdiero S, Allard-Vannier E, Chourpa I and Munnier E:
Formulation and in vitro evaluation of a siRNA delivery nanosystem
decorated with gH625 peptide for triple negative breast cancer
theranosis. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 131:99–108. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mäe M, Myrberg H, El-Andaloussi S and
Langel Ü: Design of a tumor homing cell-penetrating peptide for
drug delivery. Int J Pept Res Ther. 15:11–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lim KJ, Sung BH, Shin JR, Lee YW, Kim DJ,
Yang KS and Kim SC: A cancer specific cell-penetrating peptide,
BR2, for the efficient delivery of an scFv into cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e660842013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fang SL, Fan TC, Fu HW, Chen CJ, Hwang CS,
Hung TJ, Lin LY and Chang MD: A novel cell-penetrating peptide
derived from human eosinophil cationic protein. PLoS One.
8:e573182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kalyanaraman B: Teaching the basics of the
mechanism of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity: Have we been
barking up the wrong tree? Redox Biol. 29:1013942020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fales AM, Yuan H and Vo-Dinh T:
Cell-penetrating peptide enhanced intracellular Raman imaging and
photodynamic therapy. Mol Pharm. 10:2291–2298. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hossain MK, Cho HY, Kim KJ and Choi JW: In
situ monitoring of doxorubicin release from biohybrid nanoparticles
modified with antibody and cell-penetrating peptides in breast
cancer cells using surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Biosens
Bioelectron. 71:300–305. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wan Y, Dai W, Nevagi RJ, Toth I and Moyle
PM: Multifunctional peptide-lipid nanocomplexes for efficient
targeted delivery of DNA and siRNA into breast cancer cells. Acta
Biomater. 59:257–268. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hu G, Chun X, Wang Y, He Q and Gao H:
Peptide mediated active targeting and intelligent particle size
reduction-mediated enhanced penetrating of fabricated nanoparticles
for triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Oncotarget.
6:41258–41274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Sardan M, Kilinc M, Genc R, Tekinay AB and
Guler MO: Cell penetrating peptide amphiphile integrated liposomal
systems for enhanced delivery of anticancer drugs to tumor cells.
Faraday Discuss. 166:269–283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang X, Chen X, Yang X, Gao W, He B, Dai
W, Zhang H, Wang X, Wang J, Zhang X, et al: A nanomedicine based
combination therapy based on QLPVM peptide functionalized liposomal
tamoxifen and doxorubicin against Luminal A breast cancer.
Nanomedicine. 12:387–397. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang H, Wang H, Liang J, Jiang Y, Guo Q,
Peng H, Xu Q and Huang Y: Cell-penetrating apoptotic peptide/p53
DNA nanocomplex as adjuvant therapy for drug-resistant breast
cancer. Mol Pharm. 11:3352–3360. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Chen J, Li S and Shen Q: Folic acid and
cell-penetrating peptide conjugated PLGA-PEG bifunctional
nanoparticles for vincristine sulfate delivery. Eur J Pharm Sci.
47:430–443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hu H, Wang J, Wang H, Tan T, Li J, Wang Z,
Sun K, Li Y and Zhang Z: Cell-penetrating peptide-based
nanovehicles potentiate lymph metastasis targeting and deep
penetration for anti-metastasis therapy. Theranostics. 8:3597–3610.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Cabral H, Makino J, Matsumoto Y, Mi P, Wu
H, Nomoto T, Toh K, Yamada N, Higuchi Y, Konishi S, et al: Systemic
targeting of lymph node metastasis through the blood vascular
system by using size-controlled nanocarriers. ACS Nano.
9:4957–4967. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Kang S, Ahn S, Lee J, Kim JY, Choi M,
Gujrati V, Kim H, Kim J, Shin EC and Jon S: Effects of gold
nanoparticle-based vaccine size on lymph node delivery and
cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses. J Control Release. 256:56–67.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Su J, Sun H, Meng Q, Yin Q, Tang S, Zhang
P, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Yu H and Li Y: Long circulation
red-blood-cell-mimetic nanoparticles with peptide-enhanced tumor
penetration for simultaneously inhibiting growth and lung
metastasis of breast cancer. Adv Funct Mater. 26:1243–1252. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Hamilton AM, Aidoudi-Ahmed S, Sharma S,
Kotamraju VR, Foster PJ, Sugahara KN, Ruoslahti E and Rutt BK:
Nanoparticles coated with the tumor-penetrating peptide iRGD reduce
experimental breast cancer metastasis in the brain. J Mol Med.
93:991–1001. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Jabir MS, Taha AA, Sahib UI, Taqi ZJ,
Al-Shammari AM and Salman AS: Novel of nano delivery system for
Linalool loaded on gold nanoparticles conjugated with CALNN peptide
for application in drug uptake and induction of cell death on
breast cancer cell line. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
94:949–964. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wan X, Liu C, Lin Y, Fu J, Lu G and Lu Z:
pH sensitive peptide functionalized nanoparticles for co-delivery
of erlotinib and DAPT to restrict the progress of triple negative
breast cancer. Drug Deliv. 26:470–480. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Liang DS, Su HT, Liu YJ, Wang AT and Qi
XR: Tumor-specific penetrating peptides-functionalized hyaluronic
acid-d-α-tocopheryl succinate based nanoparticles for multi-task
delivery to invasive cancers. Biomaterials. 71:11–23. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ding J, Yao J, Xue J, Li R, Bao B, Jiang
L, Zhu JJ and He Z: Tumor-homing Cell-penetrating peptide linked to
colloidal mesoporous silica Encapsulated
(-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate as drug delivery system for breast
cancer therapy in vivo. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 7:18145–18155.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Ding J, Liang T, Zhou Y, He Z, Min Q,
Jiang L and Zhu J: Hyaluronidase-triggered anticancer drug and
siRNA delivery from cascaded targeting nanoparticles for
drug-resistant breast cancer therapy. Nano Res. 10:690–703. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Ding J, Liang T, Min Q, Jiang L and Zhu
JJ: ‘Stealth and Fully-Laden’ Drug carriers: Self-assembled
nanogels encapsulated with epigallocatechin gallate and siRNA for
drug-resistant breast cancer therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces.
10:9938–9948. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Huang R, Li J, Kebebe D, Wu Y, Zhang B and
Liu Z: Cell penetrating peptides functionalized gambogic
acid-nanostructured lipid carrier for cancer treatment. Drug Deliv.
25:757–765. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Perillo E, Hervé-Aubert K, Allard-Vannier
E, Falanga A, Galdiero S and Chourpa I: Synthesis and in vitro
evaluation of fluorescent and magnetic nanoparticles functionalized
with a cell penetrating peptide for cancer theranosis. J Colloid
Interface Sci. 499:209–217. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Cao H, Zou L, He B, Zeng L, Huang Y, Yu H,
Zhang P, Yin Q, Zhang Z and Li Y: Albumin biomimetic nanocorona
improves tumor targeting and penetration for synergistic therapy of
metastatic breast cancer. Adv Funct Mater. 27:16056792017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Jing H, Cheng W, Li S, Wu B, Leng X, Xu S
and Tian J: Novel cell-penetrating peptide-loaded nanobubbles
synergized with ultrasound irradiation enhance EGFR siRNA delivery
for triple negative Breast cancer therapy. Colloids Surfaces B
Biointerfaces. 146:387–395. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Govindarajan S, Sivakumar J, Garimidi P,
Rangaraj N, Kumar JM, Rao NM and Gopal V: Targeting human epidermal
growth factor receptor 2 by a cell-penetrating peptide-affibody
bioconjugate. Biomaterials. 33:2570–2582. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sharma S, Kotamraju VR, Mölder T, Tobi A,
Teesalu T and Ruoslahti E: Tumor-penetrating nanosystem strongly
suppresses breast tumor growth. Nano Lett. 17:1356–1364. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Li G, Gao Y, Gong C, Han Z, Qiang L, Tai
Z, Tian J and Gao S: Dual-blockade immune checkpoint for breast
cancer treatment based on a tumor-penetrating peptide assembling
nanoparticle. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 11:39513–39524. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Xie X, Yang Y, Lin W, Liu H, Liu H, Yang
Y, Chen Y, Fu X and Deng J: Cell-penetrating peptide-siRNA
conjugate loaded YSA-modified nanobubbles for ultrasound triggered
siRNA delivery. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces. 136:641–650.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Braun GB, Sugahara KN, Yu OM, Kotamraju
VR, Mölder T, Lowy AM, Ruoslahti E and Teesalu T:
Urokinase-controlled tumor penetrating peptide. J Control Release.
232:188–195. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Fei L, Yap LP, Conti PS, Shen WC and Zaro
JL: Tumor targeting of a cell penetrating peptide by fusing with a
pH-sensitive histidine-glutamate co-oligopeptide. Biomaterials.
35:4082–4087. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Lang J, Zhao X, Qi Y, Zhang Y, Han X, Ding
Y, Guan J, Ji T, Zhao Y and Nie G: Reshaping prostate tumor
microenvironment to suppress metastasis via cancer-associated
fibroblast inactivation with peptide-assembly-based nanosystem. ACS
Nano. 13:12357–12371. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xiang B, Dong DW, Shi NQ, Gao W, Yang ZZ,
Cui Y, Cao DY and Qi XR: PSA-responsive and PSMA-mediated
multifunctional liposomes for targeted therapy of prostate cancer.
Biomaterials. 34:6976–6991. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zhou J, Fan J and Hsieh JT: Inhibition of
mitogen-elicited signal transduction and growth in prostate cancer
with a small peptide derived from the functional domain of
DOC-2/DAB2 delivered by a unique vehicle. Cancer Res. 66:8954–8958.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhang T, Xue X, He D and Hsieh JT: A
prostate cancer-targeted polyarginine-disulfide linked PEI
nanocarrier for delivery of microRNA. Cancer Lett. 365:156–165.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Kumar A, Huo S, Zhang X, Liu J, Tan A, Li
S, Jin S, Xue X, Zhao Y, Ji T, et al: Neuropilin-1-targeted gold
nanoparticles enhance therapeutic efficacy of Platinum(IV) drug for
prostate cancer treatment. ACS Nano. 8:4205–4220. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Menon JU, Tumati V, Hsieh JT, Nguyen KT
and Saha D: Polymeric nanoparticles for targeted radiosensitization
of prostate cancer cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 103:1632–1639.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wadajkar AS, Menon JU, Tsai YS, Gore C,
Dobin T, Gandee L, Kangasniemi K, Takahashi M, Manandhar B, Ahn JM,
et al: Prostate cancer-specific thermo-responsive polymer-coated
iron oxide nanoparticles. Biomaterials. 34:3618–3625. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yuan L, Liu CY, Chen Y, Zhang ZH, Zhou L
and Qu D: Antitumor activity of tripterine via cell-penetrating
peptide-coated nanostructured lipid carriers in a prostate cancer
model. Int J Nanomedicine. 8:4339–4350. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Jiménez-Mancilla N, Ferro-Flores G,
Santos-Cuevas C, Ocampo-García B, Luna-Gutiérrez M, Azorín-Vega E,
Isaac-Olivé K, Camacho-López M and Torres-García E: Multifunctional
targeted therapy system based on (99m) Tc/(177) Lu-labeled gold
nanoparticles-Tat(49–57)-Lys(3)-bombesin internalized in nuclei of
prostate cancer cells. J Label Compd Radiopharm. 56:663–671. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
DePorter SM and McNaughton BR: Engineered
M13 bacteriophage nanocarriers for intracellular delivery of
exogenous proteins to human prostate cancer cells. Bioconjug Chem.
25:1620–1625. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|