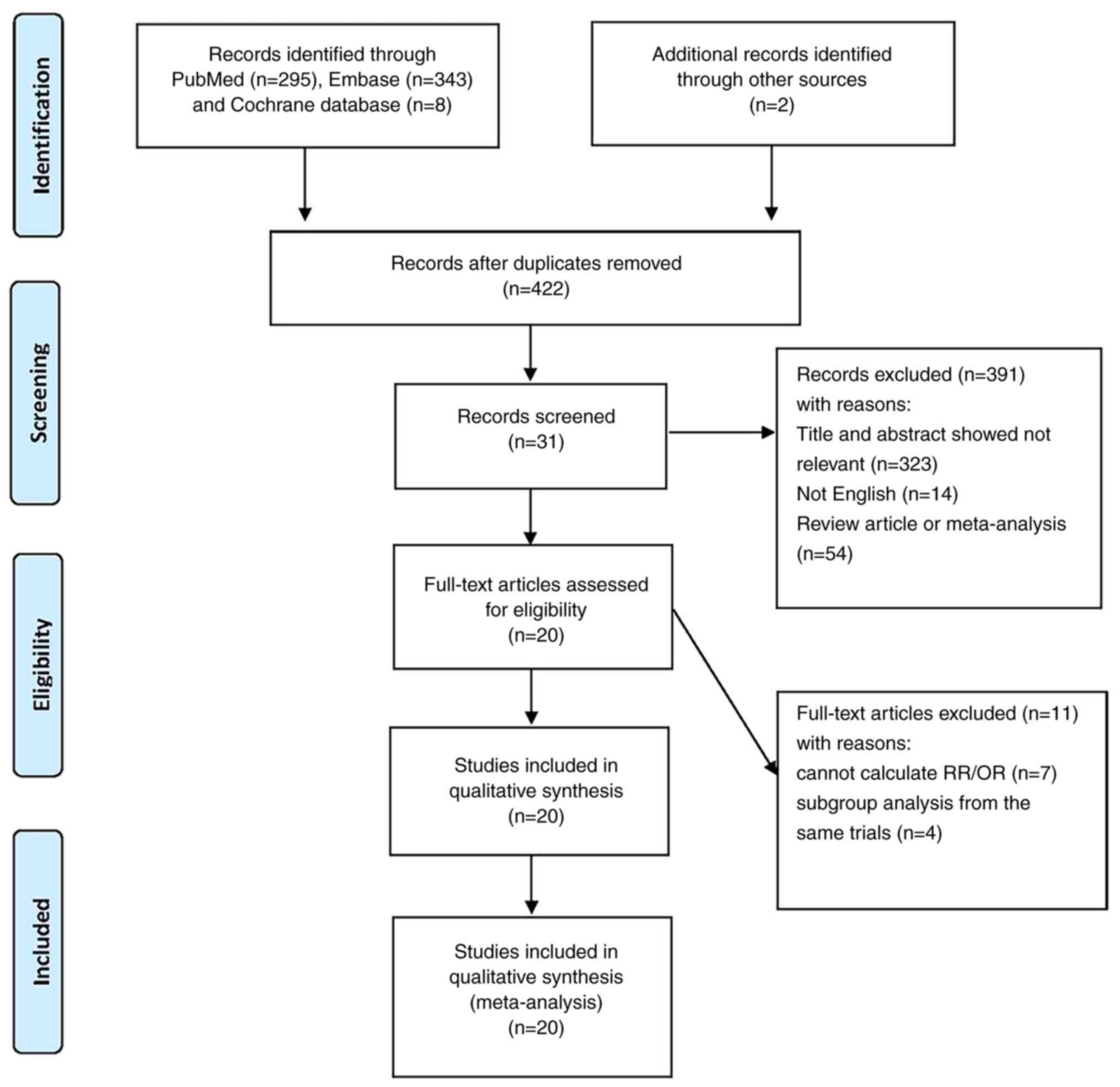
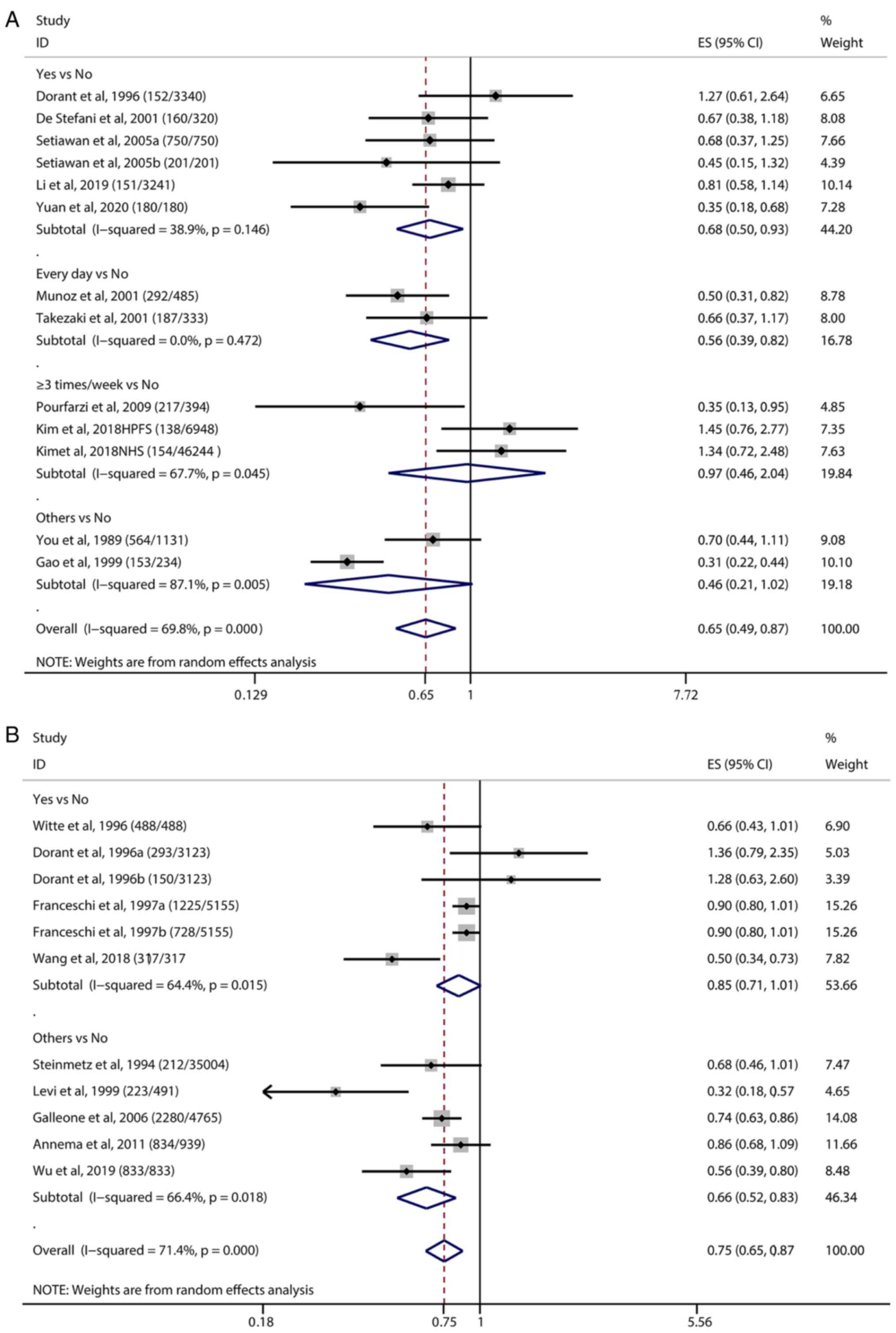
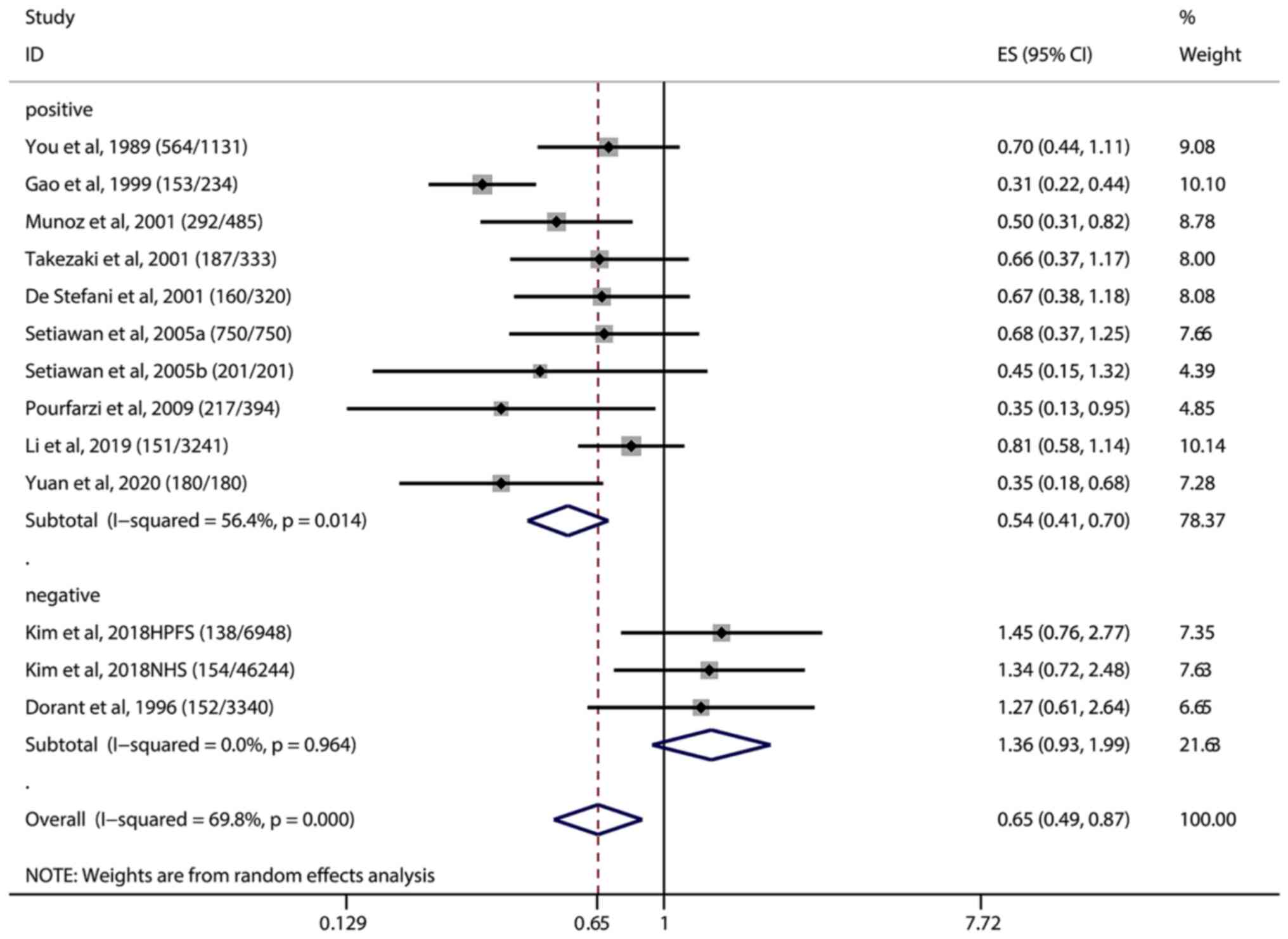
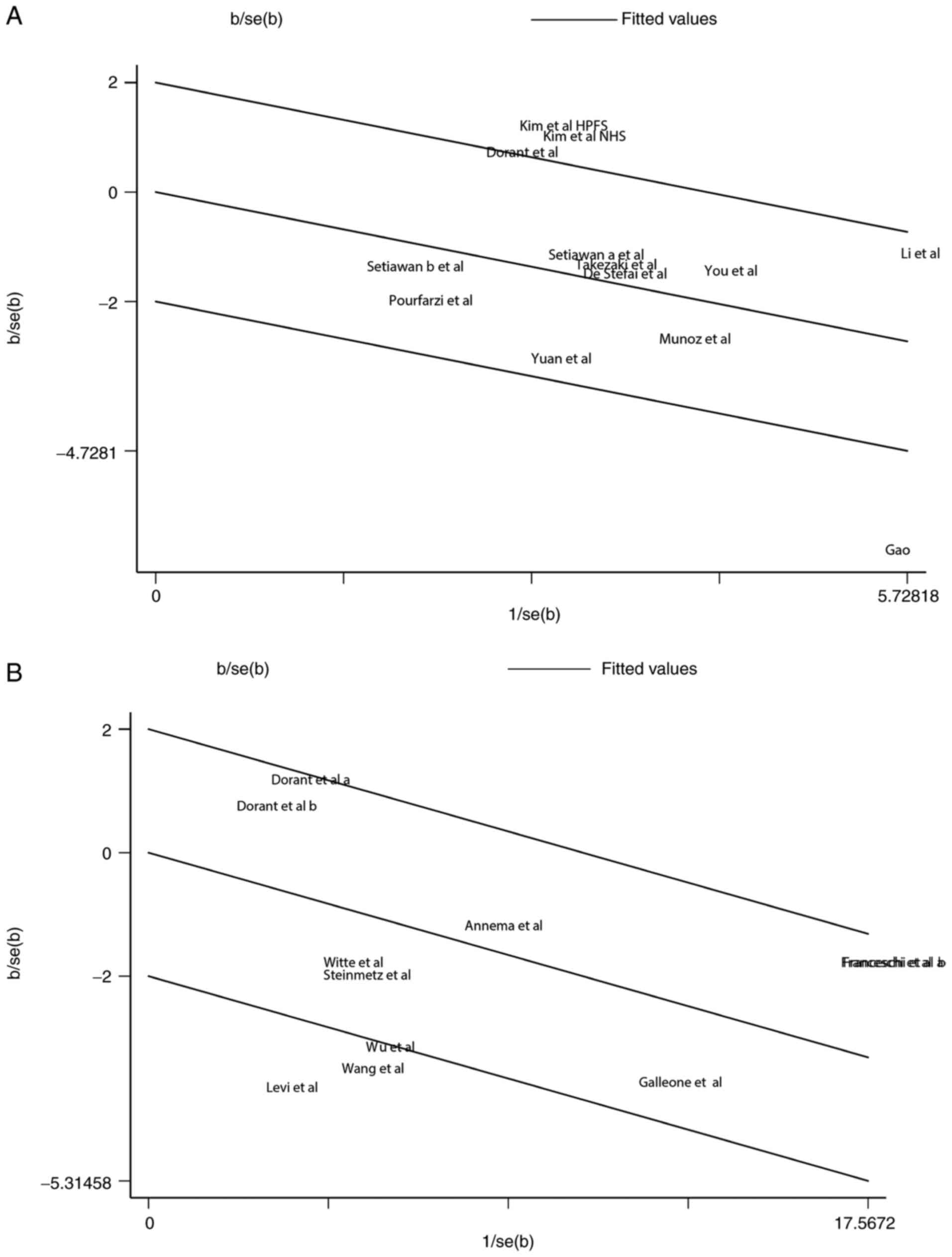
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser
S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D and Bray F: Cancer
incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major
patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 136:E359–E386. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gausman V, Dornblaser D, Anand S, Hayes
RB, O'Connell K, Du M and Liang PS: Risk factors associated with
early-onset colorectal cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
18:2752–2759.e2. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou X, Qian H, Zhang D and Zeng L: Garlic
intake and the risk of colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine
(Baltimore). 99:e185752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Larsson SC, Orsini N and Wolk A: Processed
meat consumption and stomach cancer risk: A meta-analysis. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 98:1078–1087. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sugano K: Effect of Helicobacter pylori
eradication on the incidence of gastric cancer: A systematic review
and meta-analysis. Gastric Cancer. 22:435–445. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Park HK, Lee Y, Kang BW, Kwon KI, Kim JW,
Kwon OS, Cobb LK, Campbell NRC, Blakeman DE and Kim CI: Progress on
sodium reduction in South Korea. BMJ Glob Health. 5:e0020282020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee HS, Duffey KJ and Popkin BM: Sodium
and potassium intake patterns and trends in South Korea. J Hum
Hypertens. 27:298–303. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ford AC, Yuan Y and Moayyedi P:
Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy to prevent gastric cancer:
Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut. 69:2113–2121. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hooi JKY, Lai WY, Ng WK, Suen MMY,
Underwood FE, Tanyingoh D, Malfertheiner P, Graham DY, Wong VWS, Wu
JCY, et al: Global prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection:
Systematic review and meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 153:420–429.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hou N, Huo D and Dignam JJ: Prevention of
colorectal cancer and dietary management. Chin Clin Oncol.
2:132013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu X, Shi J, Fang WX, Guo XY, Zhang LY,
Liu YP and Li Z: Allium vegetables are associated with reduced risk
of colorectal cancer: A hospital-based matched case-control study
in China. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 15:e132–e141. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li WQ, Zhang JY, Ma JL, Li ZX, Zhang L,
Zhang Y, Guo Y, Zhou T, Li JY, Shen L, et al: Effects of
Helicobacter pylori treatment and vitamin and garlic
supplementation on gastric cancer incidence and mortality:
Follow-up of a randomized intervention trial. BMJ. 366:l50162019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Z, Ying X, Shan F and Ji J: The
association of garlic with helicobacter pylori infection and
gastric cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Helicobacter. 23:e125322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nicastro HL, Ross SA and Milner JA: Garlic
and onions: Their cancer prevention properties. Cancer Prev Res
(Phila). 8:181–189. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Desai G, Schelske-Santos M, Nazario CM,
Rosario-Rosado RV, Mansilla-Rivera I, Ramírez-Marrero F, Nie J,
Myneni AA, Zhang ZF, Freudenheim JL and Mu L: Onion and garlic
intake and breast cancer, a case-control study in Puerto Rico. Nutr
Cancer. 72:791–800. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chan JM, Wang F and Holly EA: Vegetable
and fruit intake and pancreatic cancer in a population-based
case-control study in the San Francisco bay area. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 14:2093–2097. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takezaki T, Gao CM, Wu JZ, Ding JH, Liu
YT, Zhang Y, Li SP, Su P, Liu TK and Tajima K: Dietary protective
and risk factors for esophageal and stomach cancers in a
low-epidemic area for stomach cancer in Jiangsu Province, China:
Comparison with those in a high-epidemic area. Jpn J Cancer Res.
92:1157–1165. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
You WC, Chang YS, Heinrich J, Ma JL, Liu
WD, Zhang L, Brown LM, Yang CS, Gail MH, Fraumeni JF Jr and Xu GW:
An intervention trial to inhibit the progression of precancerous
gastric lesions: Compliance, serum micronutrients and S-allyl
cysteine levels, and toxicity. Eur J Cancer Prev. 10:257–263. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang HR, Pan YM and Zhang L: Mechanism for
allicin to sensitize gastric cancer cells to chemotherapy. World
Chinese J Digestol. 27:1248–1255. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wu S and Li Z: Effect of allicin on the
proliferation and apoptosis of gastric cancer cells SGC-7901
through inhibiting autophagy of endoplasmic reticulum. Anti-Tumor
Pharmacy. 9:226–230. 2019.
|
|
22
|
Arreola R, Quintero-Fabián S, López-Roa
RI, Flores-Gutiérrez EO, Reyes-Grajeda JP, Carrera-Quintanar L and
Ortuño-Sahagún D: Immunomodulation and anti-inflammatory effects of
garlic compounds. J Immunol Res. 2015:4016302015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu CS, Huang AC, Lai KC, Huang YP, Lin MW,
Yang JS and Chung JG: Diallyl trisulfide induces apoptosis in human
primary colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 28:949–954. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhu B, Zou L, Qi L, Zhong R and Miao X:
Allium vegetables and garlic supplements do not reduce risk of
colorectal cancer, based on meta-analysis of prospective studies.
Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:1991.2001.e1-4; quiz e121.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Turati F, Guercio V, Pelucchi C, La
Vecchia C and Galeone C: Colorectal cancer and adenomatous polyps
in relation to allium vegetables intake: A meta-analysis of
observational studies. Mol Nutr Food Res. 58:1907–1914. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kodali RT and Eslick GD: Meta-analysis:
Does garlic intake reduce risk of gastric cancer? Nutr Cancer.
67:1–11. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu JY, Hu YW, Zhou JJ, Zhang MW, Li D and
Zheng S: Consumption of garlic and risk of colorectal cancer: An
updated meta-analysis of prospective studies. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:15413–15422. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fleischauer AT, Poole C and Arab L: Garlic
consumption and cancer prevention: Meta-analyses of colorectal and
stomach cancers. Am J Clin Nutr. 72:1047–1052. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chiavarini M, Minelli L and Fabiani R:
Garlic consumption and colorectal cancer risk in man: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Public Health Nutr. 19:308–317. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Turati F, Pelucchi C, Guercio V, La
Vecchia C and Galeone C: Allium vegetable intake and gastric
cancer: A case-control study and meta-analysis. Mol Nutr Food Res.
59:171–179. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Meng S, Zhang X, Giovannucci EL, Ma J,
Fuchs CS and Cho E: No association between garlic intake and risk
of colorectal cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 37:152–155. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Higgins JP, Altman DG, Gøtzsche PC, Jüni
P, Moher D, Oxman AD, Savovic J, Schulz KF, Weeks L, Sterne JAC, et
al: The cochrane collaboration's tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomised trials. BMJ. 343:d59282011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De Stefani E, Correa P, Boffetta P, Ronco
A, Brennan P, Deneo-Pellegrini H and Mendilaharsu M: Plant foods
and risk of gastric cancer: A case-control study in Uruguay. Eur J
Cancer Prev. 10:357–364. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Setiawan VW, Yu GP, Lu QY, Lu ML, Yu SZ,
Mu L, Zhang JG, Kurtz RC, Cai L, Hsieh CC and Zhang ZF: Allium
vegetables and stomach cancer risk in China. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 6:387–395. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dorant E, van den Brandt PA, Goldbohm RA
and Sturmans F: Consumption of onions and a reduced risk of stomach
carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 110:12–20. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Muñoz N, Plummer M, Vivas J, Moreno V, De
Sanjosé S, Lopez G and Oliver W: A case-control study of gastric
cancer in Venezuela. Int J Cancer. 93:417–423. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
You WC, Blot WJ, Chang YS, Ershow A, Yang
ZT, An A, Henderson BE, Fraumeni JF Jr and Wang TG: Allium
vegetables and reduced risk of stomach cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
81:162–164. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim H, Keum N, Giovannucci EL, Fuchs CS
and Bao Y: Garlic intake and gastric cancer risk: Results from two
large prospective US cohort studies. Int J Cancer. 143:1047–1053.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gao CM, Takezaki T, Ding JH, Li MS and
Tajima K: Protective effect of allium vegetables against both
esophageal and stomach cancer: A simultaneous case-referent study
of a high-epidemic area in Jiangsu Province, China. Jpn J Cancer
Res. 90:614–621. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pourfarzi F, Whelan A, Kaldor J and
Malekzadeh R: The role of diet and other environmental factors in
the causation of gastric cancer in Iran-A population based study.
Int J Cancer. 125:1953–1960. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Dorant E, van den Brandt PA and Goldbohm
RA: A prospective cohort study on the relationship between onion
and leek consumption, garlic supplement use and the risk of
colorectal carcinoma in The Netherlands. Carcinogenesis.
17:477–484. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang W, Dong Z, Zhang X, Li W, Li P and
Chen X: Dietary and the risk of sporadic colorectal cancer in
China: A case-control study. Iran J Public Health. 47:1327–1335.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Levi F, Pasche C, La Vecchia C, Lucchini F
and Franceschi S: Food groups and colorectal cancer risk. Br J
Cancer. 79:1283–1287. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Steinmetz KA, Kushi LH, Bostick RM, Folsom
AR and Potter JD: Vegetables, fruit, and colon cancer in the Iowa
women's health study. Am J Epidemiol. 139:1–15. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Franceschi S, Parpinel M, La Vecchia C,
Favero A, Talamini R and Negri E: Role of different types of
vegetables and fruit in the prevention of cancer of the colon,
rectum, and breast. Epidemiology. 9:338–341. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yuan P, Lin L, Zheng K, Wang W, Wu S,
Huang L, Wu B, Chen T, Li X and Cai L: Risk factors for gastric
cancer and related serological levels in Fujian, China:
hospital-based case-control study. BMJ Open. 10:e0423412020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Galeone C, Pelucchi C, Levi F, Negri E,
Franceschi S, Talamini R, Giacosa A and La Vecchia C: Onion and
garlic use and human cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 84:1027–1032. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Witte JS, Longnecker MP, Bird CL, Lee ER,
Frankl HD and Haile RW: Relation of vegetable, fruit, and grain
consumption to colorectal adenomatous polyps. Am J Epidemiol.
144:1015–1025. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Annema N, Heyworth JS, McNaughton SA,
Iacopetta B and Fritschi L: Fruit and vegetable consumption and the
risk of proximal colon, distal colon, and rectal cancers in a
case-control study in Western Australia. J Am Diet Assoc.
111:1479–1490. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Myneni AA, Chang SC, Niu R, Liu L, Swanson
MK, Li J, Su J, Giovino GA, Yu S, Zhang ZF and Mu L: Raw garlic
consumption and lung cancer in a Chinese population. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 25:624–633. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shi X, Lv Y, Mao C, Yuan J, Yin Z, Gao X
and Zhang Z: Garlic consumption and all-cause mortality among
Chinese oldest-old individuals: A population-based cohort study.
Nutrients. 11:15042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Powell JT and Sweeting MJ: Retrospective
studies. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 50:6752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Yin X, Zhang R, Feng C, Zhang J, Liu D, Xu
K, Wang X, Zhang S, Li Z, Liu X and Ma H: Diallyl disulfide induces
G2/M arrest and promotes apoptosis through the p53/p21 and MEK-ERK
pathways in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
32:1748–1756. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Choi YH: Diallyl trisulfide induces
apoptosis and mitotic arrest in AGS human gastric carcinoma cells
through reactive oxygen species-mediated activation of
AMP-activated protein kinase. Biomed Pharmacother. 94:63–71. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xiao D, Pinto JT, Gundersen GG and
Weinstein IB: Effects of a series of organosulfur compounds on
mitotic arrest and induction of apoptosis in colon cancer cells.
Mol Cancer Ther. 4:1388–1398. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shang A, Cao SY, Xu XY, Gan RY, Tang GY,
Corke H, Mavumengwana V and Li HB: Bioactive compounds and
biological functions of garlic (Allium sativum L.). Foods.
8:2462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yin X, Zhang J, Li X, Liu D, Feng C, Liang
R, Zhuang K, Cai C, Xue X, Jing F, et al: DADS suppresses human
esophageal xenograft tumors through RAF/MEK/ERK and
mitochondria-dependent pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 15:12422–12441.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang W, Ha M, Gong Y, Xu Y, Dong N and
Yuan Y: Allicin induces apoptosis in gastric cancer cells through
activation of both extrinsic and intrinsic pathways. Oncol Rep.
24:1585–1592. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang X, Zhu Y, Duan W, Feng C and He X:
Allicin induces apoptosis of the MGC-803 human gastric carcinoma
cell line through the p38 mitogen-activated protein
kinase/caspase-3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 11:2755–2760.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Park SY, Cho SJ, Kwon HC, Lee KR, Rhee DK
and Pyo S: Caspase-independent cell death by allicin in human
epithelial carcinoma cells: Involvement of PKA. Cancer Lett.
224:123–132. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Xiao D, Pinto JT, Soh JW, Deguchi A,
Gundersen GG, Palazzo AF, Yoon JT, Shirin H and Weinstein IB:
Induction of apoptosis by the garlic-derived compound
S-allylmercaptocysteine (SAMC) is associated with microtubule
depolymerization and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase 1 activation.
Cancer Res. 63:6825–6837. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jiang X, Zhu X, Huang W, Xu H, Zhao Z, Li
S, Li S, Cai J and Cao J: Garlic-derived organosulfur compound
exerts antitumor efficacy via activation of MAPK pathway and
modulation of cytokines in SGC-7901 tumor-bearing mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 48:135–145. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhu X, Jiang X, Li A, Sun Y, Liu Y, Sun X,
Feng X, Li S and Zhao Z: S-allylmercaptocysteine suppresses the
growth of human gastric cancer xenografts through induction of
apoptosis and regulation of MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 491:821–826. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yan JY, Tian FM, Hu WN, Zhang JH, Cai HF
and Li N: Apoptosis of human gastric cancer cells line SGC 7901
induced by garlic-derived compound S-allylmercaptocysteine (SAMC).
Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 17:745–751. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Li X, Ni J, Tang Y, Wang X, Tang H, Li H,
Zhang S and Shen X: Allicin inhibits mouse colorectal tumorigenesis
through suppressing the activation of STAT3 signaling pathway. Nat
Prod Res. 33:2722–2725. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bat-Chen W, Golan T, Peri I, Ludmer Z and
Schwartz B: Allicin purified from fresh garlic cloves induces
apoptosis in colon cancer cells via Nrf2. Nutr Cancer. 62:947–957.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yin X, Feng C, Han L, Ma Y, Jiao Y, Wang
J, Jia L, Jing F, Gao X, Zhang Y and Zhang J: Diallyl disulfide
inhibits the metastasis of type II esophageal-gastric junction
adenocarcinoma cells via NF-κB and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways
in vitro. Oncol Rep. 39:784–794. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|