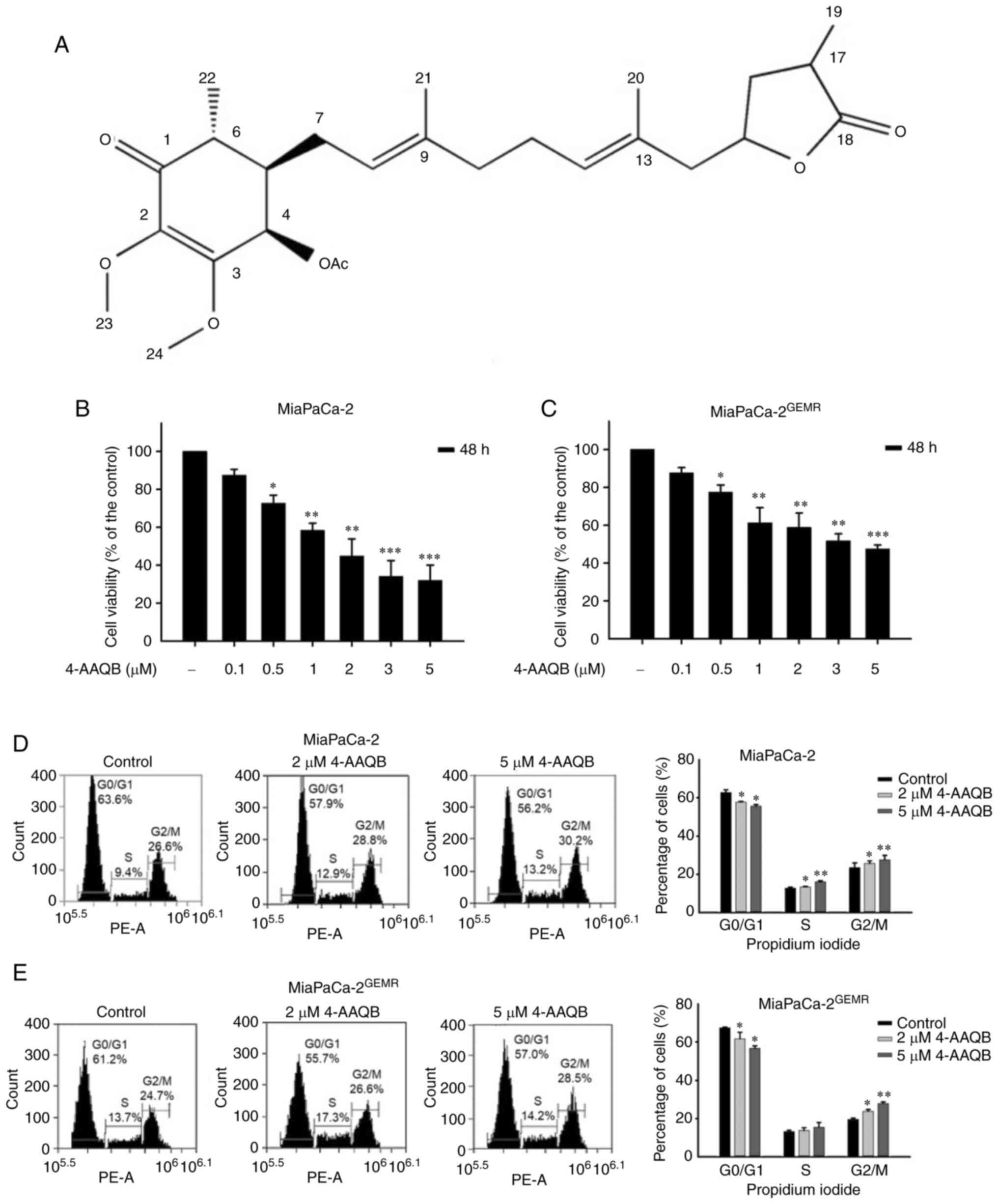
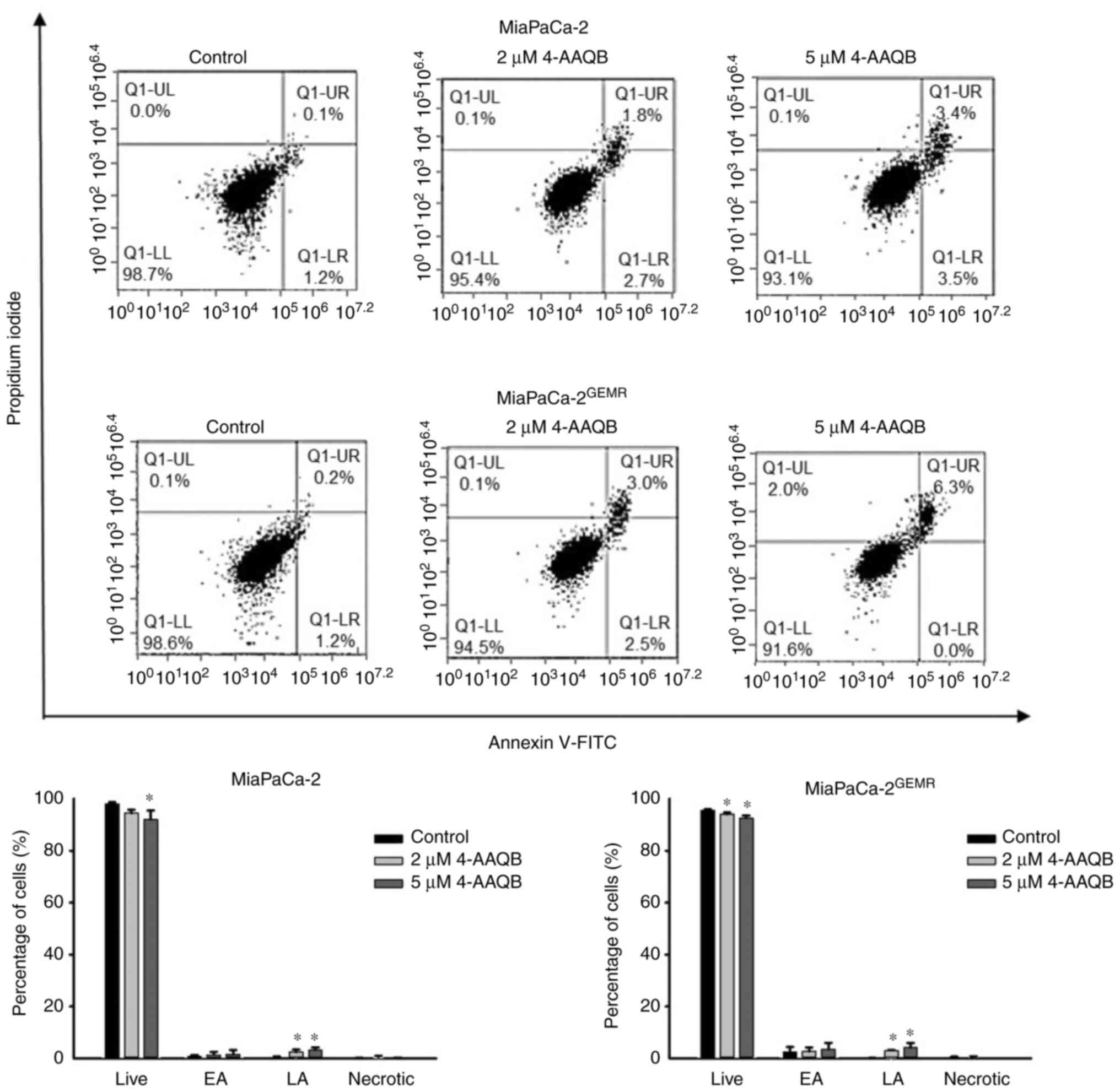
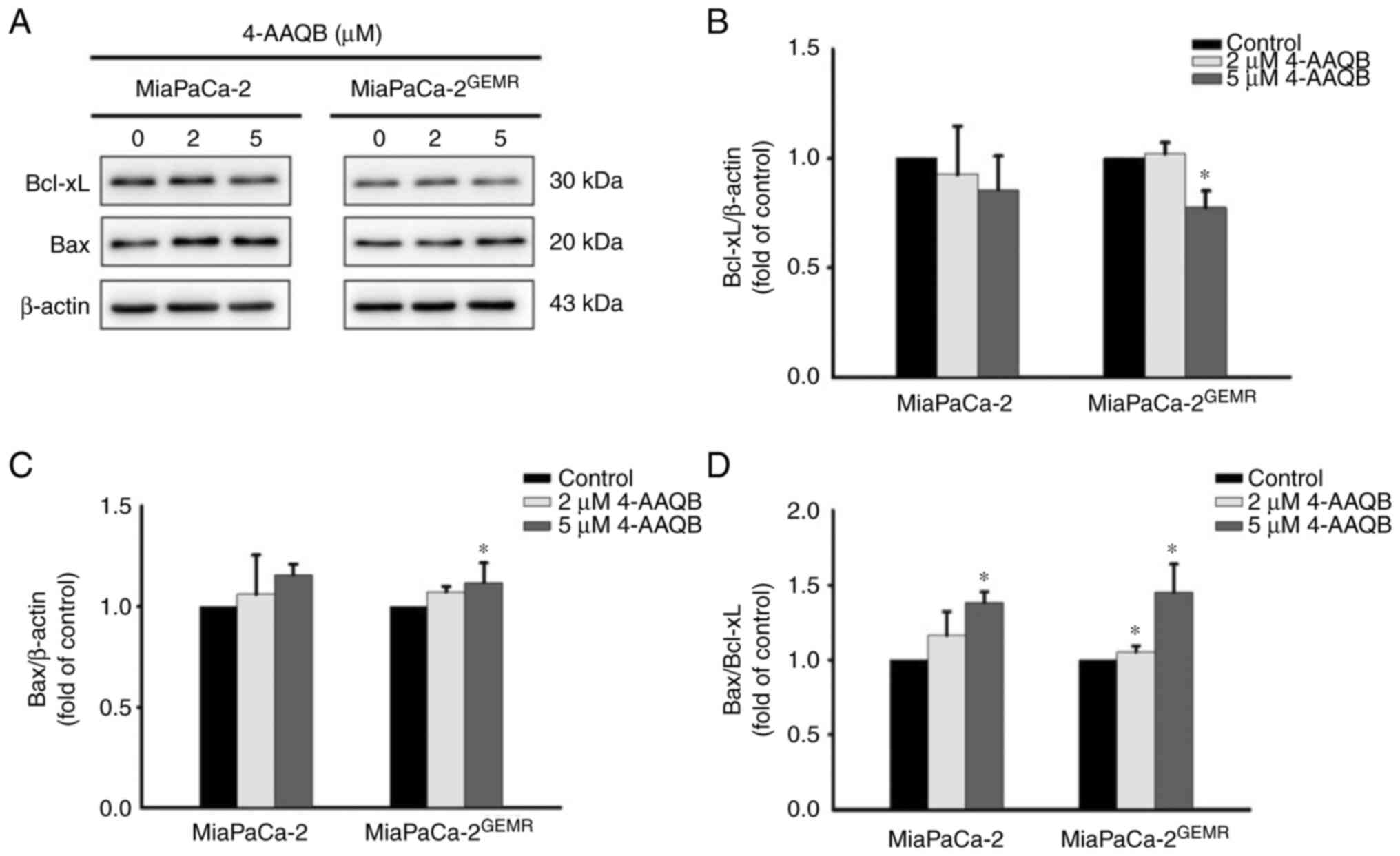
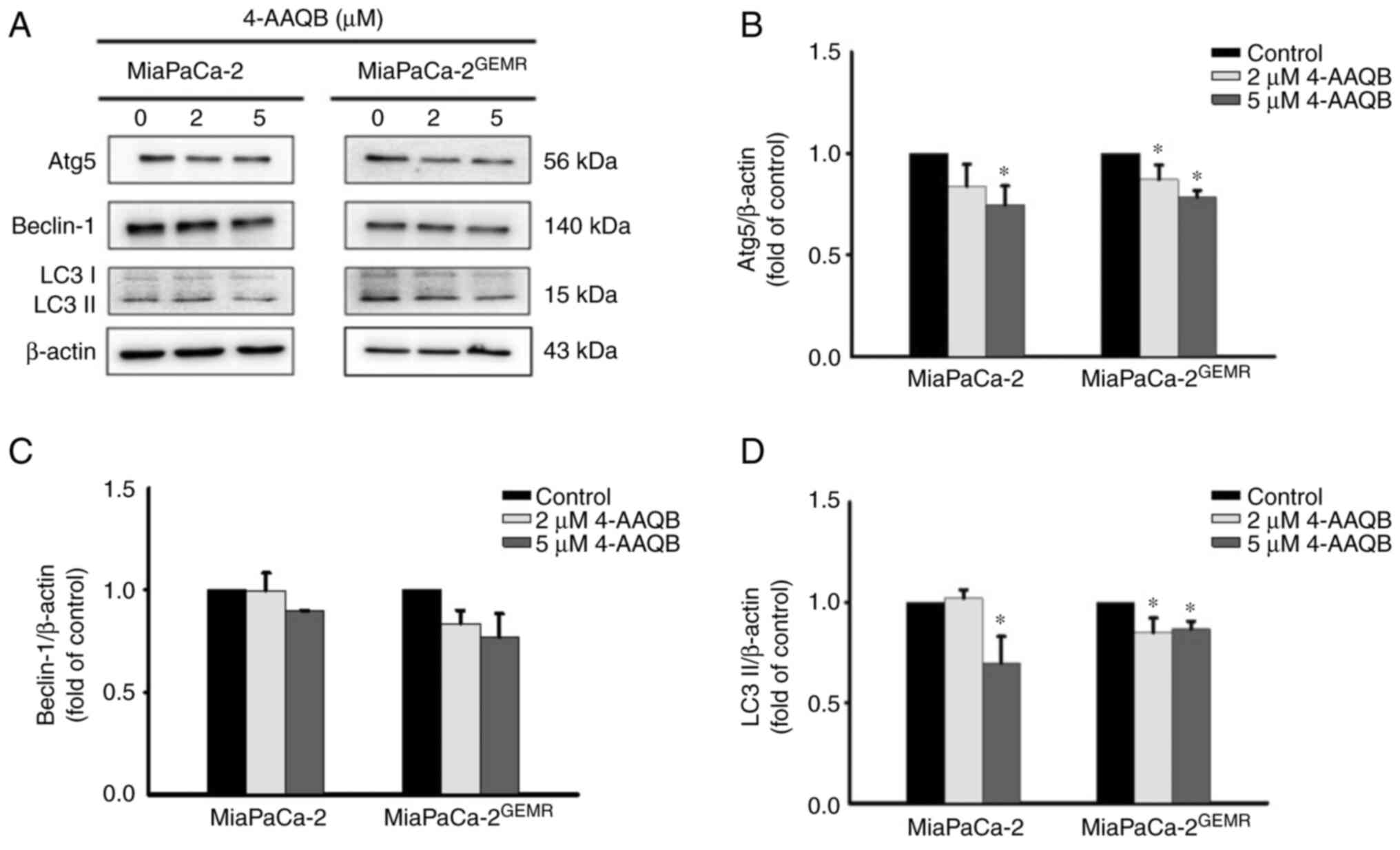
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Traub B, Link KH and Kornmann M: Curing
pancreatic cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 76:232–246. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mizrahi JD, Surana R, Valle JW and Shroff
RT: Pancreatic cancer. Lancet. 395:2008–2020. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Huang J, Lok V, Ngai CH, Zhang L, Yuan J,
Lao XQ, Ng K, Chong C, Zheng ZJ and Wong MCS: Worldwide burden of,
risk factors for, and trends in pancreatic cancer.
Gastroenterology. 160:744–754. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Amrutkar M and Gladhaug IP: Pancreatic
cancer chemoresistance to gemcitabine. Cancers (Basel). 9:1572017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Binenbaum Y, Na'ara S and Gil Z:
Gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Drug
Resist Updat. 23:55–68. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kuang Y, Li B, Wang Z, Qiao X and Ye M:
Terpenoids from the medicinal mushroom Antrodia camphorata:
Chemistry and medicinal potential. Nat Prod Rep. 38:83–102. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lin YW, Pan JH, Liu RH, Kuo YH, Sheen LY
and Chiang BH: The 4-acetylantroquinonol B isolated from mycelium
of Antrodia cinnamomea inhibits proliferation of hepatoma
cells. J Sci Food Agric. 90:1739–1744. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yen IC, Tu QW, Chang TC, Lin PH, Li YF and
Lee SY: 4-Acetylantroquinonol B ameliorates nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis by suppression of ER stress and NLRP3 inflammasome
activation. Biomed Pharmacother. 138:1115042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu CH, Ou CH, Yen IC and Lee SY:
4-Acetylantroquinonol B inhibits osteoclastogenesis by inhibiting
the autophagy pathway in a simulated microgravity model. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:69712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Satriyo PB, Su CM, Ong JR, Huang WC, Fong
IH, Lin CC, Aryandono T, Haryana SM, Deng L, Huang CC, et al:
4-Acetylantroquinonol B induced DNA damage response signaling and
apoptosis via suppressing CDK2/CDK4 expression in triple negative
breast cancer cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 422:1154932021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu HW, Su YK, Bamodu OA, Hueng DY, Lee
WH, Huang CC, Deng L, Hsiao M, Chien MH, Yeh CT and Lin CM: The
disruption of the β-catenin/TCF-1/STAT3 signaling axis by
4-acetylantroquinonol B inhibits the tumorigenesis and cancer
stem-cell-like properties of glioblastoma cells, in vitro and in
vivo. Cancers (Basel). 10:4912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li TY and Chiang BH: 4-Acetylantroquinonol
B from Antrodia cinnamomea enhances immune function of
dendritic cells against liver cancer stem cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:2262–2269. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Tang D, Loze MT, Zeh HJ and Kang R: The
redox protein HMGB1 regulates cell death and survival in cancer
treatment. Autophagy. 6:1181–1183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arumugam T, Ramachandran V, Gomez SB,
Schmidt AM and Logsdon CD: S100P-derived RAGE antagonistic peptide
reduces tumor growth and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 18:4356–4364.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sparvero LJ, Asafu-Adjei D, Kang R, Tang
D, Amin N, Im J, Rutledge R, Lin B, Amoscato AA, Zeh HJ and Lotze
MT: RAGE (receptor for advanced glycation endproducts), RAGE
ligands, and their role in cancer and inflammation. J Transl Med.
7:172009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang R, Tang D, Schapiro NE, Loux T,
Livesey KM, Billiar TR, Wang H, Van Houten BV, Lotze MT and Zeh HJ:
The HMGB1/RAGE inflammatory pathway promotes pancreatic tumor
growth by regulating mitochondrial bioenergetics. Oncogene.
33:567–577. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin JH, Chen SY, Lu CC, Lin JA and Yen GC:
Ursolic acid promotes apoptosis, autophagy, and chemosensitivity in
gemcitabine-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells. Phytother Res.
34:2053–2066. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lan CY, Chen SY, Kuo CW, Lu CC and Yen GC:
Quercetin facilitates cell death and chemosensitivity through
RAGE/PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis in human pancreatic cancer cells. J Food
Drug Anal. 27:887–896. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lia ZY, Chen SY, Weng MH and Yen GC:
Ursolic acid restores sensitivity to gemcitabine through the
RAGE/NF-κB/MDR1 axis in pancreatic cancer cells and in a mouse
xenograft model. J Food Drug Anal. 29:262–274. 2021.
|
|
21
|
Hsu YH, Chen SY, Wang SY, Lin JA and Yen
GC: Pterostilbene enhances cytotoxicity and chemosensitivity in
human pancreatic cancer cells. Biomolecules. 10:7092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chang HY, Chen SY, Wu CH, Lu CC and Yen
GC: Glycyrrhizin attenuates the process of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by modulating HMGB1 initiated
novel signaling pathway in prostate cancer cells. J Agric Food
Chem. 67:3323–3332. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Connolly P, Garcia-Carpio I and Villunger
A: Cell-cycle cross talk with caspases and their substrates. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 12:a0364752020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bedoui S, Herold MJ and Strasser A:
Emerging connectivity of programmed cell death pathways and its
physiological implications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:678–695.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gil J, Ramsey D, Szmida E, Leszczynski P,
Pawlowski P, Bebenek M and Sasiadek MM: The BAX gene as a candidate
for negative autophagy-related genes regulator on mRNA levels in
colorectal cancer. Med Oncol. 34:162017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zeh HJ, Bahary N, Boone BA, Singhi AD,
Miller-Ocuin JL, Normolle DP, Zureikat AH, Hogg ME, Bartlett DL,
Lee KK, et al: A randomized phase II preoperative study of
autophagy inhibition with high-dose hydroxychloroquine and
gemcitabine/nab-paclitaxel in pancreatic cancer patients. Clin
Cancer Res. 26:3126–3134. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu L, Wei J and Liu P: Attacking the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway for targeted therapeutic treatment
in human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. S1044-579X(21)00188-7. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bernard M, Cardin GB, Cahuzac M, Ayad T,
Bissada E, Guertin L, Bahig H, Nguyen-Tan PF, Filion E, Ballivy O,
et al: Dual inhibition of autophagy and PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway as a
therapeutic strategy in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Cancers (Basel). 12:23712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Su H, Yang F, Wang Q, Shen Q, Huang J,
Peng C, Zhang Y, Wan W, Wong CCL, Sun Q, et al: VPS34 acetylation
controls its lipid kinase activity and the initiation of canonical
and non-canonical autophagy. Mol Cell. 67:907–921.e7. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jaber N, Dou Z, Chen JS, Catanzaro J,
Jiang YP, Ballou LM, Selinger E, Ouyang X, Lin RZ, Zhang J and Zong
WX: Class III PI3K Vps34 plays an essential role in autophagy and
in heart and liver function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:2003–2008.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wen C, Wang H, Wu X, He L, Zhou Q, Wang F,
Chen S, Huang L, Chen J, Wang H, et al: ROS-mediated inactivation
of the PI3K/AKT pathway is involved in the antigastric cancer
effects of thioredoxin reductase-1 inhibitor chaetocin. Cell Death
Dis. 10:8092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ju HQ, Gocho T, Aguilar M, Wu M, Zhuang
ZN, Fu J, Yanaga K, Huang P and Chiao PJ: Mechanisms of overcoming
intrinsic resistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma through the redox modulation. Mol Cancer Ther.
14:788–798. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Aiello NM, Brabletz T, Kang Y, Nieto MA,
Weinberg RA and Stanger BZ: Upholding a role for EMT in pancreatic
cancer metastasis. Nature. 547:E7–E8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zheng X, Carstens JL, Kim J, Scheible M,
Kaye J, Sugimoto H, Wu CC, LeBleu VS and Kalluri R:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis
but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature.
527:525–530. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Parveen A, Subedi L, Kim HW, Khan Z, Zahra
Z, Farooqi MQ and Kim SY: Phytochemicals targeting VEGF and
VEGF-related multifactors as anticancer therapy. J Clin Med.
8:3502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hosein AN, Brekken RA and Maitra A:
Pancreatic cancer stroma: An update on therapeutic targeting
strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:487–505. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhao H, Wu S, Li H, Duan Q, Zhang Z, Shen
Q, Wang C and Yin T: ROS/KRAS/AMPK signaling contributes to
gemcitabine-induced stem-like cell properties in pancreatic cancer.
Mol Ther Oncolytics. 14:299–312. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu W, Liu Q, Pan J and Sui Z: miR-373-3p
enhances the chemosensitivity of gemcitabine through cell cycle
pathway by targeting CCND2 in pancreatic carcinoma cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 105:887–898. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lin YW and Chiang BH:
4-acetylantroquinonol B isolated from Antrodia cinnamomea
arrests proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cell
by affecting p53, p21 and p27 levels. J Agric Food Chem.
59:8625–8631. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kang R, Tang D, Lotze MT and Zeh HJ III:
RAGE regulates autophagy and apoptosis following oxidative injury.
Autophagy. 7:442–444. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kang R, Tang D, Livesey KM, Schapiro NE,
Lotze MT and Zeh HJ III: The receptor for advanced glycation
end-products (RAGE) protects pancreatic tumor cells against
oxidative injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 15:2175–2184. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liu M, Bamodu OA, Huang WC, Zucha MA, Lin
YK, Wu ATH, Huang CC, Lee WH, Yuan CC, Hsiao M, et al:
4-Acetylantroquinonol B suppresses autophagic flux and improves
cisplatin sensitivity in highly aggressive epithelial cancer
through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 325:48–60. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Piffoux M, Eriau E and Cassier PA:
Autophagy as a therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Br J
Cancer. 124:333–344. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Liu PF, Tsai KL, Hsu CJ, Tsai WL, Cheng
JS, Chang HW, Shiau CW, Goan YG, Tseng HH, Wu CH, et al: Drug
repurposing screening identifies tioconazole as an ATG4 inhibitor
that suppresses autophagy and sensitizes cancer cells to
chemotherapy. Theranostics. 8:830–845. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shao S, Li S, Qin Y, Wang X, Yang Y, Bai
H, Zhou L, Zhao C and Wang C: Spautin-1, a novel autophagy
inhibitor, enhances imatinib-induced apoptosis in chronic myeloid
leukemia. Int J Oncol. 44:1661–1668. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tam C, Rao S, Waye MMY, Ng TB and Wang CC:
Autophagy signals orchestrate chemoresistance of gynecological
cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 1875:1885252021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Larue L and Bellacosa A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: Role
of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene.
24:7443–7454. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chang TC, Yeh CT, Adebayo BO, Lin YC, Deng
L, Rao YK, Huang CC, Lee WH, Wu AT, Hsiao M, et al:
4-Acetylantroquinonol B inhibits colorectal cancer tumorigenesis
and suppresses cancer stem-like phenotype. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
288:258–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bamodu OA, Yang CK, Cheng WH, Tzeng DTW,
Kuo KT, Huang CC, Deng L, Hsiao M, Lee WH and Yeh CT:
4-Acetyl-antroquinonol B suppresses SOD2-enhanced cancer stem
cell-like phenotypes and chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells
by inducing hsa-miR-324 re-expression. Cancers (Basel). 10:2692018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Friedl P and Wolf K: Tumour-cell invasion
and migration: Diversity and escape mechanisms. Nat Rev Cancer.
3:362–374. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Jin H, Yu Y, Hu Y, Lu C, Li J, Gu J, Zhang
L, Huang H, Zhang D, Wu XR, et al: Divergent behaviors and
underlying mechanisms of cell migration and invasion in
non-metastatic T24 and its metastatic derivative T24T bladder
cancer cell lines. Oncotarget. 6:522–536. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|