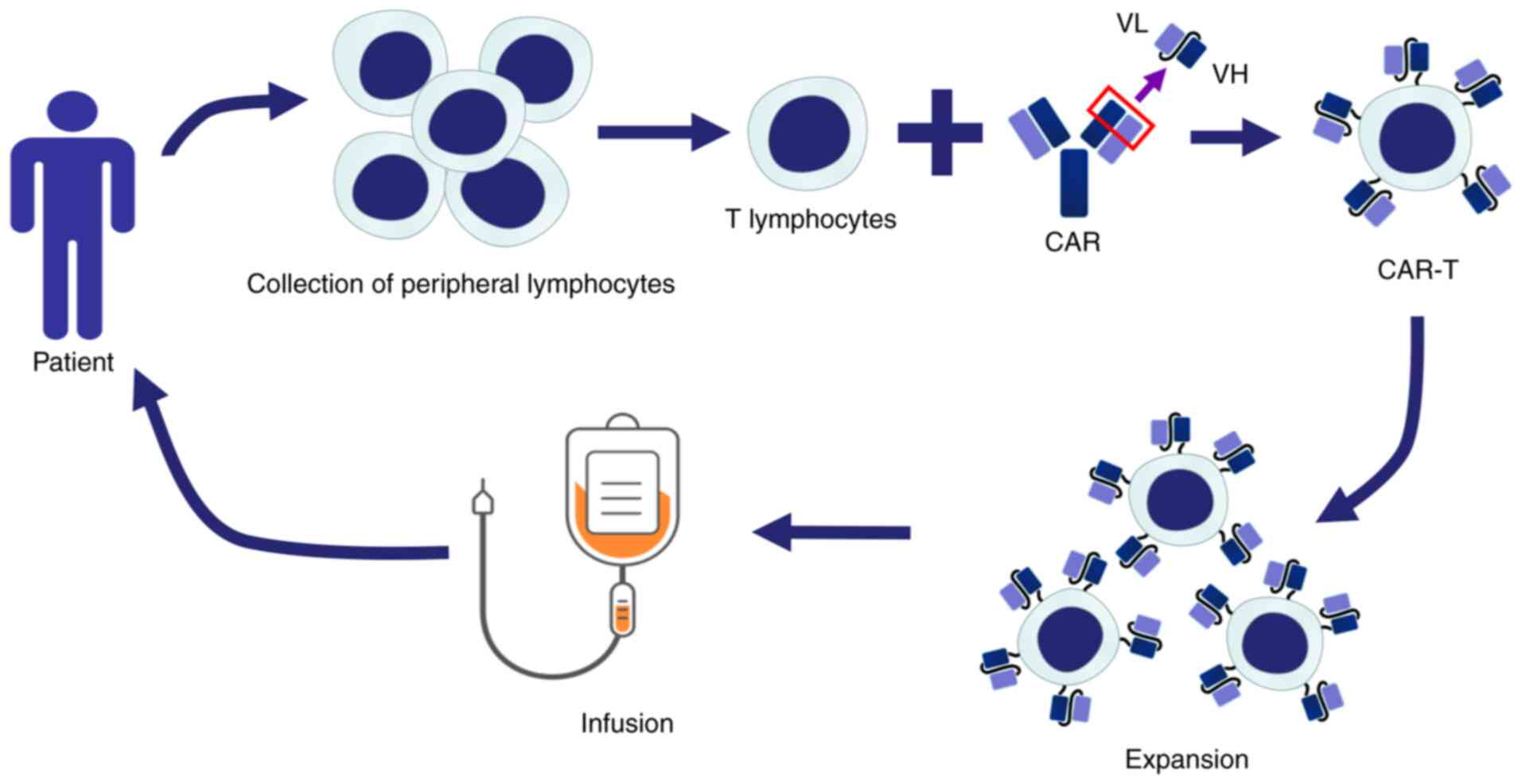
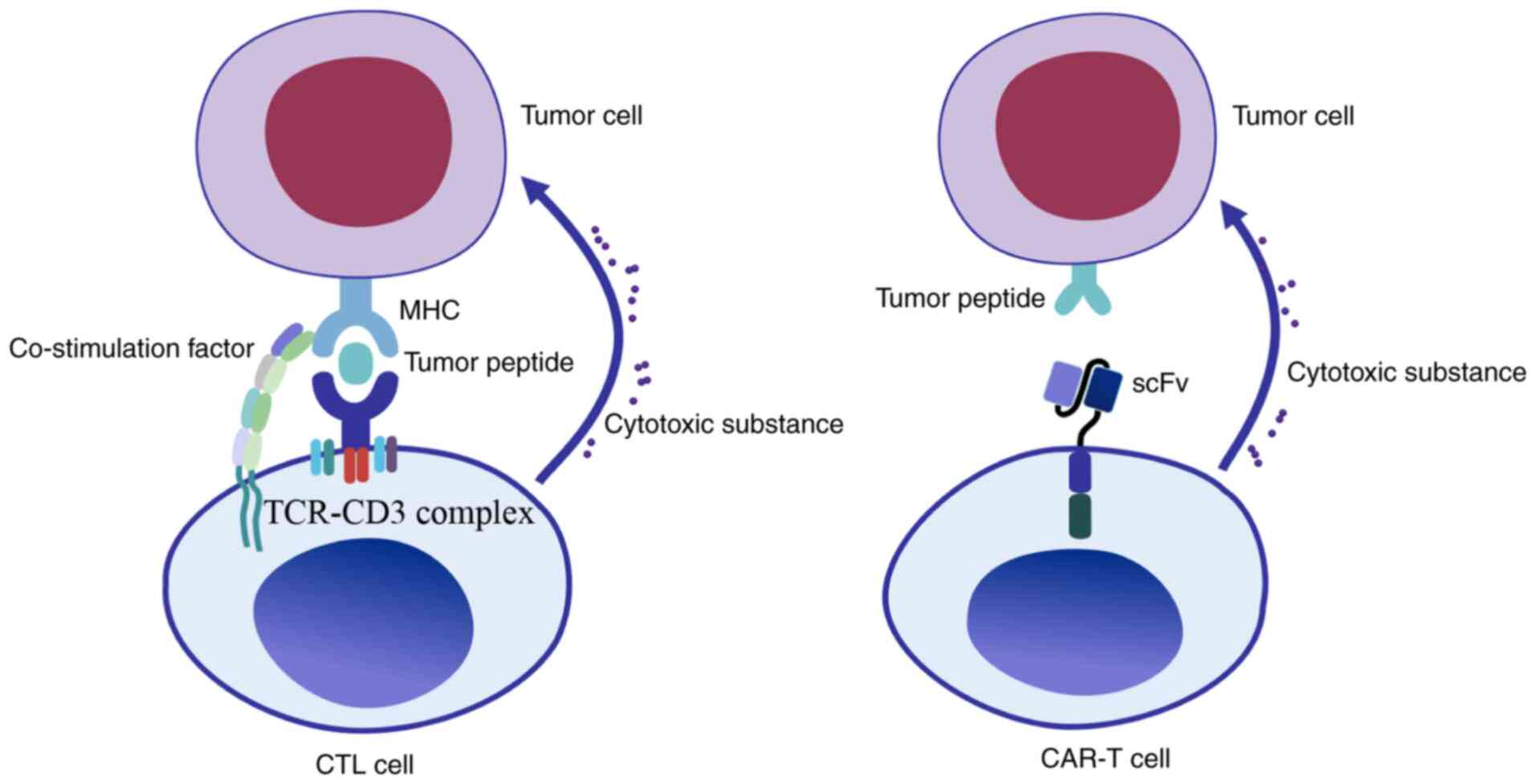
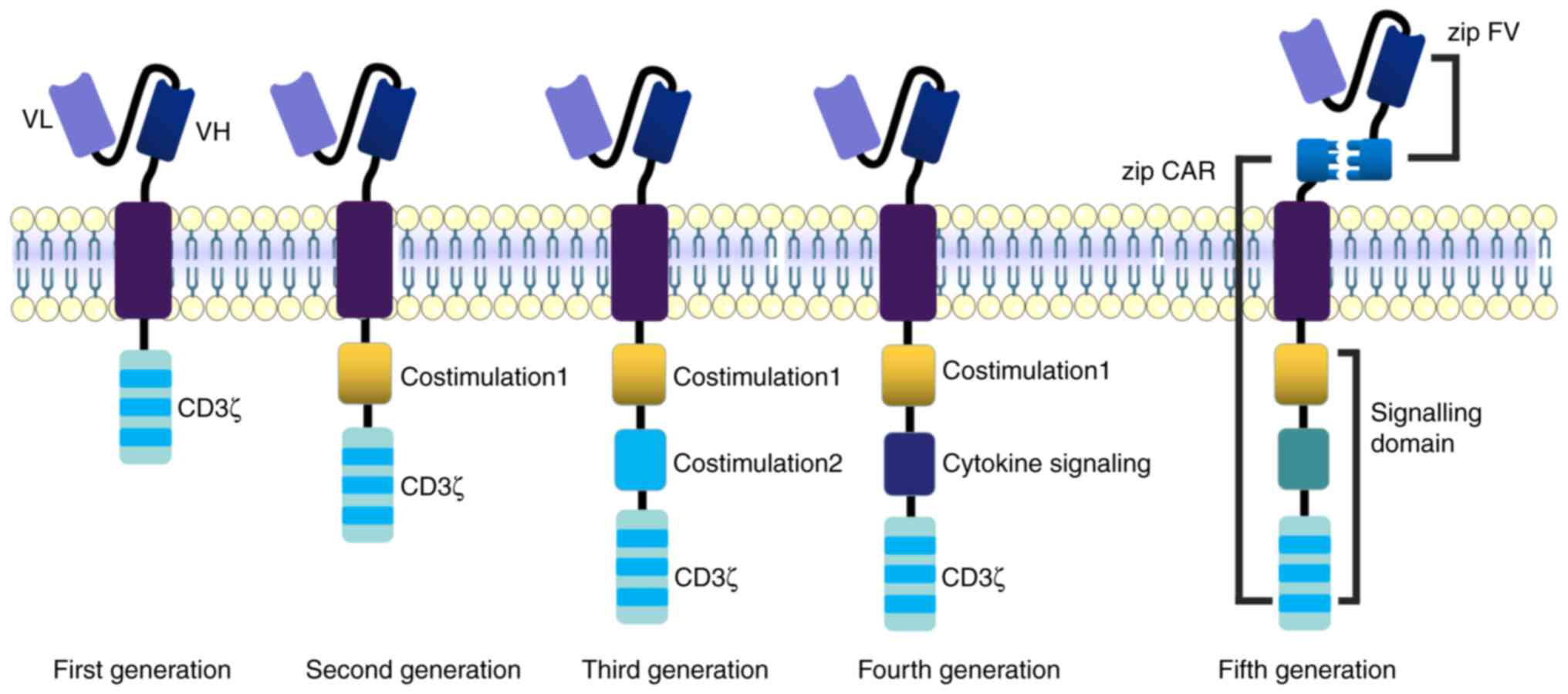
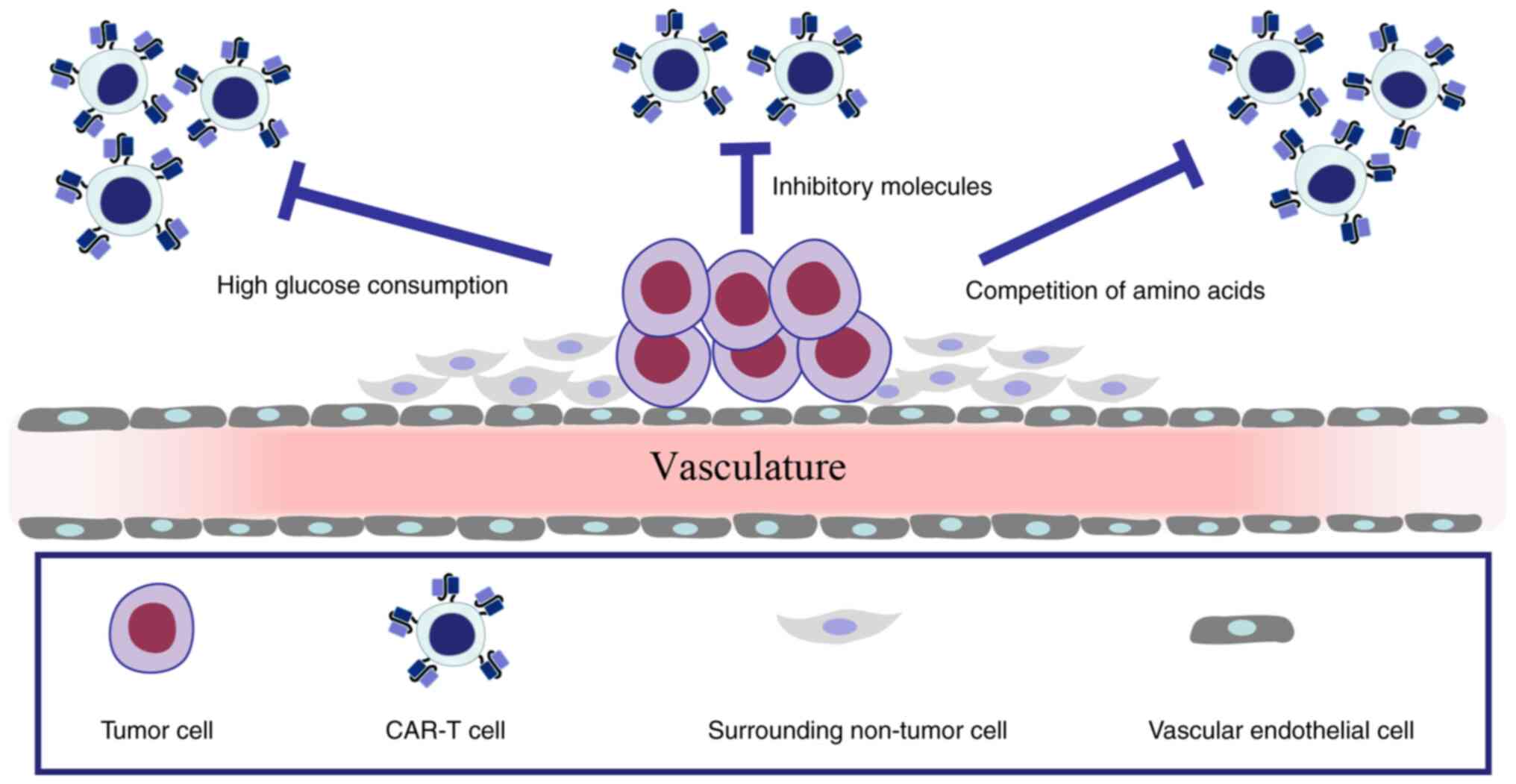
|
1
|
Cao W, Chen HD, Yu YW, Li N and Chen WQ:
Changing profiles of cancer burden worldwide and in China: A
secondary analysis of the global cancer statistics 2020. Chin Med J
(Engl). 134:783–791. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rafei H, Kantarjian HM and Jabbour EJ:
Recent advances in the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
Leuk Lymphoma. 60:2606–2621. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kansagra AJ, Frey NV, Bar M, Laetsch TW,
Carpenter PA, Savani BN, Heslop HE, Bollard CM, Komanduri KV,
Gastineau DA, et al: Clinical utilization of chimeric antigen
receptor T-cells (CAR-T) in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
(ALL)-an expert opinion from the European society for blood and
marrow transplantation (EBMT) and the American society for blood
and marrow transplantation (ASBMT). Bone Marrow Transplant.
54:1868–1880. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Larson RC and Maus MV: Recent advances and
discoveries in the mechanisms and functions of CAR T cells. Nat Rev
Cancer. 21:145–161. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bupha-Intr O, Haeusler G, Chee L, Thursky
K, Slavin M and Teh B: CAR-T cell therapy and infection: A review.
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 19:749–758. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Giavridis T, van der Stegen SJC, Eyquem J,
Hamieh M, Piersigilli A and Sadelain M: CAR T cell-induced cytokine
release syndrome is mediated by macrophages and abated by IL-1
blockade. Nat Med. 24:731–738. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gross G, Waks T and Eshhar Z: Expression
of immunoglobulin-T-cell receptor chimeric molecules as functional
receptors with antibody-type specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
86:10024–10028. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eshhar Z, Waks T, Gross G and Schindler
DG: Specific activation and targeting of cytotoxic lymphocytes
through chimeric single chains consisting of antibody-binding
domains and the gamma or zeta subunits of the immunoglobulin and
T-cell receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:720–724. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Siegler EL and Wang P: Preclinical models
in chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T-cell therapy. Hum Gene
Ther. 29:534–546. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Grigor EJM, Fergusson D, Kekre N, Montroy
J, Atkins H, Seftel MD, Daugaard M, Presseau J, Thavorn K, Hutton
B, et al: Risks and benefits of chimeric antigen receptor T-cell
(CAR-T) therapy in cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
Transfus Med Rev. 33:98–110. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roselli E, Frieling JS, Thorner K, Ramello
MC, Lynch CC and Abate-Daga D: CAR-T engineering: Optimizing signal
transduction and effector mechanisms. BioDrugs. 33:647–659. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hu W, Huang X, Huang X, Chen W, Hao L and
Chen Z: Chimeric antigen receptor modified T cell (CAR-T)
co-expressed with ICOSL-41BB promote CAR-T proliferation and tumor
rejection. Biomed Pharmacother. 118:1093332019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ramello MC, Benzaïd I, Kuenzi BM,
Lienlaf-Moreno M, Kandell WM, Santiago DN, Pabón-Saldaña M,
Darville L, Fang B, Rix U, et al: An immunoproteomic approach to
characterize the CAR interactome and signalosome. Sci Signal.
12:eaap97772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Abramson JS: Anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy
for B-cell non-hodgkin lymphoma. Transfus Med Rev. 34:29–33. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chmielewski M and Abken H: TRUCKs: The
fourth generation of CARs. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 15:1145–1154.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kagoya Y, Tanaka S, Guo T, Anczurowski M,
Wang CH, Saso K, Butler MO, Minden MD and Hirano N: A novel
chimeric antigen receptor containing a JAK-STAT signaling domain
mediates superior antitumor effects. Nat Med. 24:352–359. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lin H, Cheng J, Mu W, Zhou J and Zhu L:
Advances in universal CAR-T cell therapy. Front Immunol.
12:7448232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao J, Lin Q, Song Y and Liu D: Universal
CARs, universal T cells, and universal CAR T cells. J Hematol
Oncol. 11:1322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Qasim W, Zhan H, Samarasinghe S, Adams S,
Amrolia P, Stafford S, Butler K, Rivat C, Wright G, Somana K, et
al: Molecular remission of infant B-ALL after infusion of universal
TALEN gene-edited CAR T cells. Sci Transl Med. 9:eaaj20132017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cho JH, Collins JJ and Wong WW: Universal
chimeric antigen receptors for multiplexed and logical control of T
cell responses. Cell. 173:1426–1438.e11. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Guo Y, Xu B, Wu Z, Bo J, Tong C, Chen D,
Wang J, Wang H, Wang Y and Han W: Mutant B2M-HLA-E and B2M-HLA-G
fusion proteins protects universal chimeric antigen
receptor-modified T cells from allogeneic NK cell-mediated lysis.
Eur J Immunol. 51:2513–2521. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Depil S, Duchateau P, Grupp SA, Mufti G
and Poirot L: ‘Off-the-shelf’ allogeneic CAR T cells: Development
and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 19:185–199. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martino M, Alati C, Canale FA, Musuraca G,
Martinelli G and Cerchione C: A review of clinical outcomes of CAR
T-cell therapies for B-acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int J Mol Sci.
22:21502021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wudhikarn K, Flynn JR, Rivière I, Gönen M,
Wang X, Senechal B, Curran KJ, Roshal M, Maslak PG, Geyer MB, et
al: Interventions and outcomes of adult patients with B-ALL
progressing after CD19 chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
Blood. 138:531–543. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nix MA, Mandal K, Geng H, Paranjape N, Lin
YT, Rivera JM, Marcoulis M, White KL, Whitman JD, Bapat SP, et al:
Surface proteomics reveals CD72 as a target for in vitro-evolved
nanobody-based CAR-T cells in KMT2A/MLL1-rearranged B-ALL. Cancer
Discov. 11:2032–2049. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dai H, Wu Z, Jia H, Tong C, Guo Y, Ti D,
Han X, Liu Y, Zhang W, Wang C, et al: Bispecific CAR-T cells
targeting both CD19 and CD22 for therapy of adults with relapsed or
refractory B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Hematol Oncol.
13:302020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brentjens RJ, Davila ML, Riviere I, Park
J, Wang X, Cowell LG, Bartido S, Stefanski J, Taylor C, Olszewska
M, et al: CD19-targeted T cells rapidly induce molecular remissions
in adults with chemotherapy-refractory acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. Sci Transl Med. 5:177ra382013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Maude SL, Frey N, Shaw PA, Aplenc R,
Barrett DM, Bunin NJ, Chew A, Gonzalez VE, Zheng Z, Lacey SF, et
al: Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in
leukemia. N Engl J Med. 371:1507–1517. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Davila ML, Riviere I, Wang X, Bartido S,
Park J, Curran K, Chung SS, Stefanski J, Borquez-Ojeda O, Olszewska
M, et al: Efficacy and toxicity management of 19-28z CAR T cell
therapy in B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Sci Transl Med.
6:224ra252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hu Y, Zhou Y, Zhang M, Ge W, Li Y, Yang L,
Wei G, Han L, Wang H, Yu S, et al: CRISPR/Cas9-engineered universal
CD19/CD22 dual-targeted CAR-T cell therapy for relapsed/refractory
B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 27:2764–2772.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Raetz EA and Teachey DT: T-cell acute
lymphoblastic leukemia. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program.
2016:580–588. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pan J, Tan Y, Wang G, Deng B, Ling Z, Song
W, Seery S, Zhang Y, Peng S, Xu J, et al: Donor-derived CD7
chimeric antigen receptor T cells for T-cell acute lymphoblastic
leukemia: First-in-human, phase I trial. J Clin Oncol.
39:3340–3351. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu P, Liu Y, Yang J, Zhang X, Yang X, Wang
H, Wang L, Wang Q, Jin D, Li J and Huang X: Naturally selected CD7
CAR-T therapy without genetic manipulations for T-ALL/LBL:
First-in-human phase 1 clinical trial. Blood. 140:321–334.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dai HP, Cui W, Cui QY, Zhu WJ, Meng HM,
Zhu MQ, Zhu XM, Yang L, Wu DP and Tang XW: Haploidentical CD7 CAR
T-cells induced remission in a patient with TP53 mutated relapsed
and refractory early T-cell precursor lymphoblastic
leukemia/lymphoma. Biomark Res. 10:62022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie L, Ma L, Liu S, Chang L and Wen F:
Chimeric antigen receptor T cells targeting CD7 in a child with
high-risk T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int Immunopharmacol.
96:1077312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen D, You F, Xiang S, Wang Y, Li Y, Meng
H, An G, Zhang T, Li Z, Jiang L, et al: Chimeric antigen receptor T
cells derived from CD7 nanobody exhibit robust antitumor potential
against CD7-positive malignancies. Am J Cancer Res. 11:5263–5281.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Png YT, Vinanica N, Kamiya T, Shimasaki N,
Coustan-Smith E and Campana D: Blockade of CD7 expression in T
cells for effective chimeric antigen receptor targeting of T-cell
malignancies. Blood Adv. 1:2348–2360. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Neelapu SS, Locke FL, Bartlett NL, Lekakis
LJ, Miklos DB, Jacobson CA, Braunschweig I, Oluwole OO, Siddiqi T,
Lin Y, et al: Axicabtagene ciloleucel CAR T-cell therapy in
refractory large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 377:2531–2544.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chong EA, Ruella M and Schuster SJ;
Lymphoma Program Investigators at the University of Pennsylvania, :
Five-year outcomes for refractory B-cell lymphomas with CAR T-cell
therapy. N Engl J Med. 384:673–674. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ramos CA, Rouce R, Robertson CS, Reyna A,
Narala N, Vyas G, Mehta B, Zhang H, Dakhova O, Carrum G, et al: In
vivo fate and activity of second-versus third-generation
CD19-specific CAR-T cells in B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphomas. Mol
Ther. 26:2727–2737. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bunse M, Pfeilschifter J, Bluhm J,
Zschummel M, Joedicke JJ, Wirges A, Stark H, Kretschmer V,
Chmielewski M, Uckert W, et al: CXCR5 CAR-T cells simultaneously
target B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and tumor-supportive
follicular T helper cells. Nat Commun. 12:2402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yin Z, Zhang Y and Wang X: Advances in
chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy for B-cell non-Hodgkin
lymphoma. Biomark Res. 9:582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mihăilă RG: Chimeric antigen
receptor-engineered T-cells-a new way and era for lymphoma
treatment. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 14:312–323. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shah NN, Maatman T, Hari P and Johnson B:
Multi targeted CAR-T cell therapies for B-cell malignancies. Front
Oncol. 9:1462019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yu B, Jiang T and Liu D: BCMA-targeted
immunotherapy for multiple myeloma. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1252020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ali SA, Shi V, Maric I, Wang M, Stroncek
DF, Rose JJ, Brudno JN, Stetler-Stevenson M, Feldman SA, Hansen BG,
et al: T cells expressing an anti-B-cell maturation antigen
chimeric antigen receptor cause remissions of multiple myeloma.
Blood. 128:1688–1700. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ferment B and Arnulf B: CAR-T cells
immunotherapy in multiple myeloma: Present and future. Bull Cancer.
108 (10 Suppl):S65–S72. 2021.(In French). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xu J, Chen LJ, Yang SS, Sun Y, Wu W, Liu
YF, Xu J, Zhuang Y, Zhang W, Weng XQ, et al: Exploratory trial of a
biepitopic CAR T-targeting B cell maturation antigen in
relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:9543–9551. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zah E, Nam E, Bhuvan V, Tran U, Ji BY,
Gosliner SB, Wang X, Brown CE and Chen YY: Systematically optimized
BCMA/CS1 bispecific CAR-T cells robustly control heterogeneous
multiple myeloma. Nat Commun. 11:22832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Drent E, Poels R, Ruiter R, van de Donk
NWCJ, Zweegman S, Yuan H, de Bruijn J, Sadelain M, Lokhorst HM,
Groen RWJ, et al: Combined CD28 and 4-1BB costimulation potentiates
affinity-tuned chimeric antigen receptor-engineered T cells. Clin
Cancer Res. 25:4014–4025. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Springuel L, Lonez C, Alexandre B, Van
Cutsem E, Machiels JH, Van Den Eynde M, Prenen H, Hendlisz A, Shaza
L, Carrasco J, et al: Chimeric antigen receptor-T cells for
targeting solid tumors: Current challenges and existing strategies.
Biodrugs. 33:515–537. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jiang X, Xu J, Liu M, Xing H, Wang Z,
Huang L, Mellor AL, Wang W and Wu S: Adoptive CD8+ T
cell therapy against cancer: Challenges and opportunities. Cancer
Lett. 462:23–32. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Irving M, Vuillefroy de Silly R, Scholten
K, Dilek N and Coukos G: Engineering chimeric antigen receptor
T-cells for racing in solid tumors: Don't forget the fuel. Front
Immunol. 8:2672017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Junttila MR and de Sauvage FJ: Influence
of tumour micro-environment heterogeneity on therapeutic response.
Nature. 501:346–354. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hajari Taheri F, Hassani M, Sharifzadeh Z,
Behdani M, Arashkia A and Abolhassani M: T cell engineered with a
novel nanobody-based chimeric antigen receptor against VEGFR2 as a
candidate for tumor immunotherapy. IUBMB Life. 71:1259–1267. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Akbari P, Huijbers EJM, Themeli M,
Griffioen AW and van Beijnum JR: The tumor vasculature an
attractive CAR T cell target in solid tumors. Angiogenesis.
22:473–475. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Balakrishnan A, Rajan A, Salter AI,
Kosasih PL, Wu Q, Voutsinas J, Jensen MC, Plückthun A and Riddell
SR: Multispecific targeting with synthetic ankyrin repeat motif
chimeric antigen receptors. Clin Cancer Res. 25:7506–7516. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Rodriguez-Garcia A, Lynn RC, Poussin M,
Eiva MA, Shaw LC, O'Connor RS, Minutolo NG, Casado-Medrano V, Lopez
G, Matsuyama T and Powell DJ: J: CAR-T cell-mediated depletion of
immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages promotes endogenous
antitumor immunity and augments adoptive immunotherapy. Nat Commun.
12:8772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang H, Li F, Cao J, Wang X, Cheng H, Qi
K, Wang G, Xu K, Zheng J, Fu YX and Yang X: A chimeric antigen
receptor with antigen-independent OX40 signaling mediates potent
antitumor activity. Sci Transl Med. 13:eaba73082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Santoro SP, Kim S, Motz GT, Alatzoglou D,
Li C, Irving M, Powell DJ Jr and Coukos G: T cells bearing a
chimeric antigen receptor against prostate-specific membrane
antigen mediate vascular disruption and result in tumor regression.
Cancer Immunol Res. 3:68–84. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Byrd TT, Fousek K, Pignata A, Szot C,
Samaha H, Seaman S, Dobrolecki L, Salsman VS, Oo HZ, Bielamowicz K,
et al: TEM8/ANTXR1-specific CAR T cells as a targeted therapy for
triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res. 78:489–500. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Nishida T and Kataoka H: Glypican
3-targeted therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
11:13392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Wang P, Qin W, Liu T, Jiang D, Cui L, Liu
X, Fang Y, Tang X, Jin H and Qian Q: PiggyBac-engineered T cells
expressing a glypican-3-specific chimeric antigen receptor show
potent activities against hepatocellular carcinoma. Immunobiology.
225:1518502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sun B, Yang D, Dai H, Liu X, Jia R, Cui X,
Li W, Cai C, Xu J and Zhao X: Eradication of hepatocellular
carcinoma by NKG2D-based CAR-T cells. Cancer Immunol Res.
7:1813–1823. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yazdanifar M, Zhou R, Grover P, Williams
C, Bose M, Moore LJ, Wu ST, Maher J, Dreau D and Mukherjee AP:
Overcoming immunological resistance enhances the efficacy of a
novel anti-tMUC1-CAR T cell treatment against pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Cells. 8:10702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Cui J, Zhang Q, Song Q, Wang H, Dmitriev
P, Sun MY, Cao X, Wang Y, Guo L, Indig IH, et al: Targeting hypoxia
downstream signaling protein, CAIX, for CAR T-cell therapy against
glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 21:1436–1446. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Mao Y, Fan W, Hu H, Zhang L, Michel J, Wu
Y, Wang J, Jia L, Tang X, Xu L, et al: MAGE-A1 in lung
adenocarcinoma as a promising target of chimeric antigen receptor T
cells. J Hematol Oncol. 12:1062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Zhang C, Wang Z, Yang Z, Wang M, Li S, Li
Y, Zhang R, Xiong Z, Wei Z, Shen J, et al: Phase I escalating-dose
trial of CAR-T therapy targeting CEA+ metastatic
colorectal cancers. Mol Ther. 25:1248–1258. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Abbott RC, Verdon DJ, Gracey FM,
Hughes-Parry HE, Iliopoulos M, Watson KA, Mulazzani M, Luong K,
D'Arcy C, Sullivan LC, et al: Novel high-affinity EGFRvIII-specific
chimeric antigen receptor T cells effectively eliminate human
glioblastoma. Clin Transl Immunology. 10:e12832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
O'Rourke DM, Nasrallah MP, Desai A,
Melenhorst JJ, Mansfield K, Morrissette JJD, Martinez-Lage M, Brem
S, Maloney E, Shen A, et al: A single dose of peripherally infused
EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces
adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci
Transl Med. 9:eaaa09842017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Choi BD, Yu X, Castano AP, Bouffard AA,
Schmidts A, Larson RC, Bailey SR, Boroughs AC, Frigault MJ, Leick
MB, et al: CAR-T cells secreting BiTEs circumvent antigen escape
without detectable toxicity. Nat Biotechnol. 37:1049–1058. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Moghimi B, Muthugounder S, Jambon S,
Tibbetts R, Hung L, Bassiri H, Hogarty MD, Barrett DM, Shimada H
and Asgharzadeh S: Preclinical assessment of the efficacy and
specificity of GD2-B7H3 SynNotch CAR-T in metastatic neuroblastoma.
Nat Commun. 12:5112021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Porter D, Frey N, Wood PA, Weng Y and
Grupp SA: Grading of cytokine release syndrome associated with the
CAR T cell therapy tisagenlecleucel. J Hematol Oncol. 11:352018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nagle SJ, Murphree C, Raess PW, Schachter
L, Chen A, Hayes-Lattin B, Nemecek E and Maziarz RT: Prolonged
hematologic toxicity following treatment with chimeric antigen
receptor T cells in patients with hematologic malignancies. Am J
Hematol. 96:455–461. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Schubert ML, Schmitt M, Wang L, Ramos CA,
Jordan K, Müller-Tidow C and Dreger P: Side-effect management of
chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy. Ann Oncol.
32:34–48. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Wang Z and Han W: Biomarkers of cytokine
release syndrome and neurotoxicity related to CAR-T cell therapy.
Biomark Res. 6:42018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Szenes V and Curran KJ: Utilization of CAR
T cell therapy in pediatric patients. Semin Oncol Nurs.
35:1509292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Koristka S, Ziller-Walter P, Bergmann R,
Arndt C, Feldmann A, Kegler A, Cartellieri M, Ehninger A, Ehninger
G, Bornhäuser M and Bachmann MP: Anti-CAR-engineered T cells for
epitope-based elimination of autologous CAR T cells. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 68:1401–1415. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bonini C, Ferrari G, Verzeletti S, Servida
P, Zappone E, Ruggieri L, Ponzoni M, Rossini S, Mavilio F,
Traversari C and Bordignon C: HSV-TK gene transfer into donor
lymphocytes for control of allogeneic graft-versus-leukemia.
Science. 276:1719–1724. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Straathof KC, Pulè MA, Yotnda P, Dotti G,
Vanin EF, Brenner MK, Heslop HE, Spencer DM and Rooney CM: An
inducible caspase 9 safety switch for T-cell therapy. Blood.
105:4247–4254. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gerber HP, Sibener LV, Lee LJ and Gee M:
Intracellular targets as source for cleaner targets for the
treatment of solid tumors. Biochem Pharmacol. 168:275–284. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Morgan RA, Yang JC, Kitano M, Dudley ME,
Laurencot CM and Rosenberg SA: Case report of a serious adverse
event following the administration of T cells transduced with a
chimeric antigen receptor recognizing ERBB2. Mol Ther. 18:843–851.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Fedorov VD, Themeli M and Sadelain M:
PD-1- and CTLA-4-based inhibitory chimeric antigen receptors
(iCARs) divert off-target immunotherapy responses. Sci Transl Med.
5:215ra1722013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kloss CC, Condomines M, Cartellieri M,
Bachmann M and Sadelain M: Combinatorial antigen recognition with
balanced signaling promotes selective tumor eradication by
engineered T cells. Nat Biotechnol. 31:71–75. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Feng Y, Liu X, Li X, Zhou Y, Song Z, Zhang
J, Shi B and Wang J: Novel BCMA-OR-CD38 tandem-dual chimeric
antigen receptor T cells robustly control multiple myeloma.
Oncoimmunology. 10:19591022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Wilson FP and Berns JS: Tumor lysis
syndrome: New challenges and recent advances. Adv Chronic Kidney
Dis. 21:18–26. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Miao L, Zhang Z, Ren Z and Li Y: Reactions
related to CAR-T cell therapy. Front Immunol. 12:6632012021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Gust J, Ponce R, Liles WC, Garden GA and
Turtle CJ: Cytokines in CAR T cell-associated neurotoxicity. Front
Immunol. 11:5770272020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Newrzela S, Cornils K, Li Z, Baum C,
Brugman MH, Hartmann M, Meyer J, Hartmann S, Hansmann ML, Fehse B
and von Laer D: Resistance of mature T cells to oncogene
transformation. Blood. 112:2278–2286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Fraietta JA, Nobles CL, Sammons MA, Lundh
S, Carty SA, Reich TJ, Cogdill AP, Morrissette JJD, Denizio JE,
Reddy S, et al: Disruption of TET2 promotes the therapeutic
efficacy of CD19-targeted T cells. Nature. 558:307–312. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ruella M, Xu J, Barrett DM, Fraietta JA,
Reich TJ, Ambrose DE, Klichinsky M, Shestova O, Patel PR,
Kulikovskaya I, et al: Induction of resistance to chimeric antigen
receptor T cell therapy by transduction of a single leukemic B
cell. Nat Med. 24:1499–1503. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Smith TT, Stephan SB, Moffett HF, McKnight
LE, Ji W, Reiman D, Bonagofski E, Wohlfahrt ME, Pillai SPS and
Stephan MT: In situ programming of leukaemia-specific T cells using
synthetic DNA nanocarriers. Nat Nanotechnol. 12:813–820. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Zhang Z, Qiu S, Zhang X and Chen W:
Optimized DNA electroporation for primary human T cell engineering.
Bmc Biotechnol. 18:42018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|