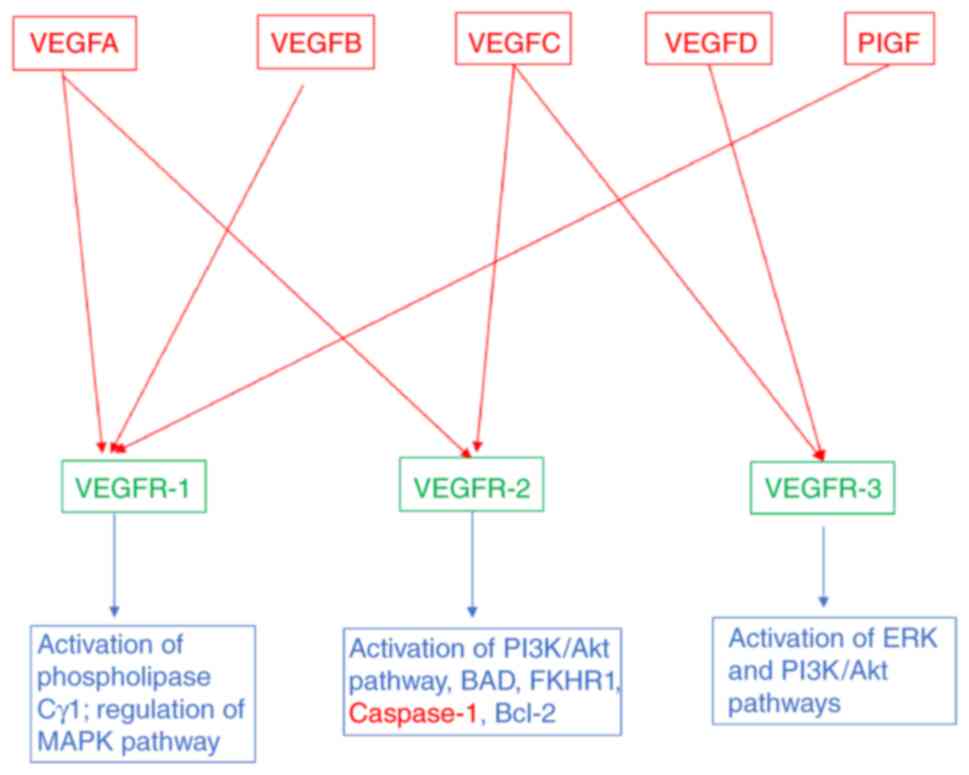
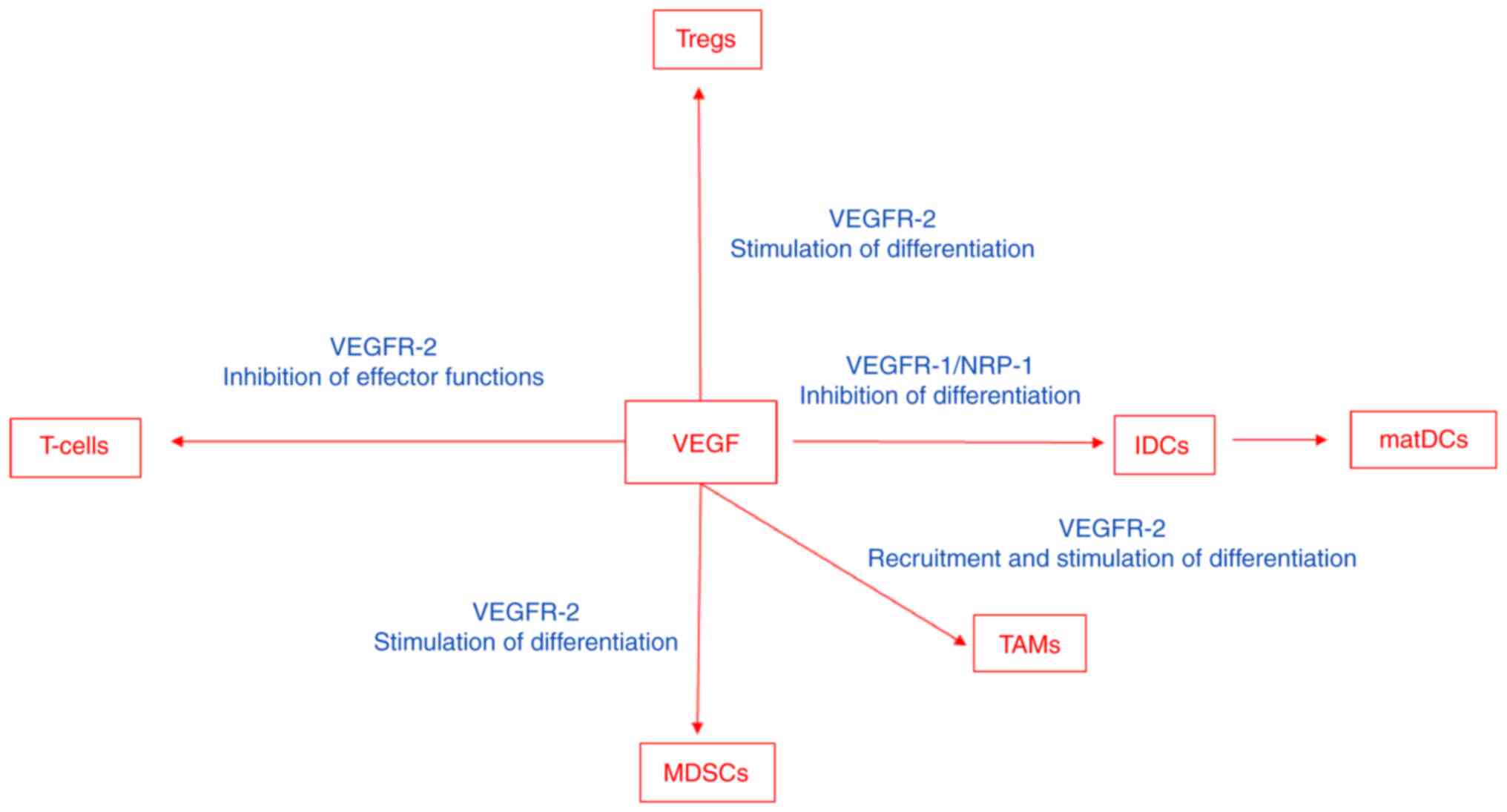
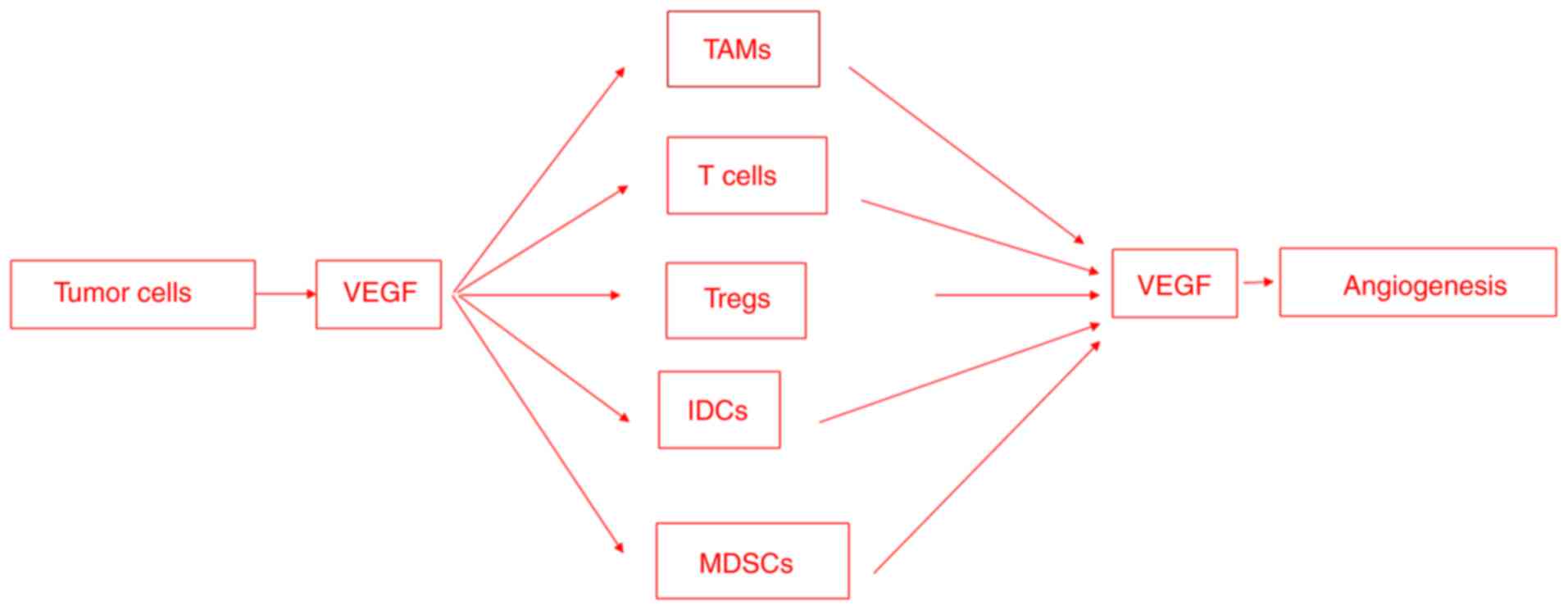
|
1
|
Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi
CA, Harvey VS and Dvorak HF: Tumor cells secrete a vascular
permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid.
Science. 219:983–985. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ferrara N: Role of vascular endothelial
growth factor in physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis:
Therapeutic implications. Semin Oncol. 29:10–14. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bouzin C, Brouet A, De Vriese J, DeWever J
and Feron O: Effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on the
lymphocyte-endothelium interactions: Identification of Caveolin-1
and nitric oxide as control points of endothelial cell anergy. J
Immunol. 178:1505–1511. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dirkx AE, Oude Egbrink MG, Castermans K,
van der Schaft DW, Thijssen VL, Dings RP, Kwee L, Mayo KH, Wagstaff
J, Bouma-ter Steege JC and Griffioen AW: Anti-angiogenesis therapy
can overcome endothelial cell anergy and promote
leukocyte-endothelium interactions and infiltration in tumors.
FASEB J. 20:621–630. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Munn LL and Jain RK: Vascular regulation
of antitumor immunity. Science. 365:544–545. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tromp SC, oude Egbrink MG, Dings RP, van
Velzen S, Slaaf DW, Hillen HF, Tangelder GJ, Reneman RS and
Griffioen AW: Tumor angiogenesis factors reduce leukocyte adhesion
in vivo. Int Immunol. 12:671–676. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang J, Yan J and Liu B: Targeting
VEGF/VEGFR to modulate antitumor immunity. Front Immunol. 9:978.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Griffioen AW, Damen CA, Mayo KH,
Barendsz-Janson AF, Martinotti S, Blijham GH and Groenewegen G:
Angiogenesis inhibitors overcome tumor induced endothelial cell
anergy. Int J Cancer. 80:315–319. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shrimali RK, Yu Z, Theoret MR, Chinnasamy
D, Restifo NP and Rosenberg SA: Antiangiogenic agents can increase
lymphocyte infiltration into tumor and enhance the effectiveness of
adoptive immunotherapy of cancer. Cancer Res. 70:6171–6180. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wallin JJ, Bendell JC, Funke R, Sznol M,
Korski K, Jones S, Hernandez G, Mier J, He X, Hodi FS, et al:
Atezolizumab in combination with bevacizumab enhances migration of
antigen-specific T-cells in metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat
Commun. 7:126242016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hegde PS, Wallin JJ and Mancao C:
Predictive markers of anti-VEGF and emerging role of angiogenesis
inhibitors as immunotherapeutics. Semin Cancer Biol. 52:117–124.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Basu A, Hoerning A, Datta D, Edelbauer M,
Stack MP, Calzadilla K, Pal S and Briscoe DM: Cutting edge:
Vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated signaling in human
CD45RO+ CD4+ T cells promotes Akt and ERK activation and
costimulates IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 184:545–549. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wada J, Suzuki H, Fuchino R, Yamasaki A,
Nagai S, Yanai K, Koga K, Nakamura M, Tanaka M, Morisaki T and
Katano M: The contribution of vascular endothelial growth factor to
the induction of regulatory T-cells in malignant effusions.
Anticancer Res. 29:881–888. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ohm JE, Gabrilovich DI, Sempowski GD,
Kisseleva E, Parman KS, Nadaf S and Carbone DP: VEGF inhibits
T-cell development and may contribute to tumor-induced immune
suppression. Blood. 101:4878–4886. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gavalas NG, Tsiatas M, Tsitsilonis O,
Politi E, Ioannou K, Ziogas AC, Rodolakis A, Vlahos G, Thomakos N,
Haidopoulos D, et al: VEGF directly suppresses activation of T
cells from ascites secondary to ovarian cancer via VEGF receptor
type 2. Br J Cancer. 107:1869–1875. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ziogas AC, Gavalas NG, Tsiatas M,
Tsitsilonis O, Politi E, Terpos E, Rodolakis A, Vlahos G, Thomakos
N, Haidopoulos D, et al: VEGF directly suppresses activation of T
cells from ovarian cancer patients and healthy individuals via VEGF
receptor type 2. Int J Cancer. 130:857–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kim CG, Jang M, Kim Y, Leem G, Kim KH, Lee
H, Kim TS, Choi SJ, Kim HD, Han JW, et al: VEGF-A drives
TOX-dependent T cell exhaustion in anti-PD-1-resistant
microsatellite stable colorectal cancers. Science Immunol.
4:eaay05552019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Voron T, Colussi O, Marcheteau E, Pernot
S, Nizard M, Pointet AL, Latreche S, Bergaya S, Benhamouda N,
Tanchot C, et al: VEGF-A modulates expression of inhibitory
checkpoints on CD8+ T cells in tumors. J Exp Med. 212:139–148.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Motz GT, Santoro SP, Wang LP, Garrabrant
T, Lastra RR, Hagemann IS, Lal P, Feldman MD, Benencia F and Coukos
G: Tumor endothelium FasL establishes a selective immune barrier
promoting tolerance in tumors. Nat Med. 20:607–615. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Apte RS, Chen DS and Ferrara N: VEGF in
signaling and disease: beyond discovery and development. Cell.
176:1248–1264. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen DS and Hurwitz H: Combinations of
Bevacizumab with cancer immunotherapy. Cancer J. 24:193–204. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lissoni P, Malugani F, Bonfanti A, Bucovec
R, Secondino S, Brivio F, Ferrari-Bravo A, Ferrante R, Vigoré L,
Rovelli F, et al: Abnormally enhanced blood concentrations of
vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in metastatic cancer
patients and their relation to circulating dendritic cells, IL-12
and endothelin-1. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents. 15:140–144.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boissel N, Rousselot P, Raffoux E, Cayuela
JM, Maarek O, Charron D, Degos L, Dombret H, Toubert A and Rea D:
Defective blood dendritic cells in chronic myeloid leukemia
correlate with high plasmatic VEGF and are not normalized by
imatinib mesylate. Leukemia. 18:1656–1661. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dikov MM, Ohm JE, Ray N, Tchekneva EE,
Burlison J, Moghanaki D, Nadaf S and Carbone DP: Differential roles
of vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1 and 2 in
dendritic cell differentiation. J Immunol. 174:215–222. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Oussa NA, Dahmani A, Gomis M, Richaud M,
Andreev E, Navab-Daneshmand AR, Taillefer J, Carli C, Boulet S,
Sabbagh L, et al: VEGF Requires the receptor NRP-1 to inhibit
lipopolysaccharide-dependent dendritic cell maturation. J Immunol.
197:3927–3935. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Curiel TJ, Wei S, Dong H, Alvarez X, Cheng
P, Mottram P, Krzysiek R, Knutson KL, Daniel B, Zimmermann MC, et
al: Blockade of B7-H1 improves myeloid dendritic cell-mediated
antitumor immunity. Nat Med. 9:562–567. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mimura K, Kono K, Takahashi A, Kawaguchi Y
and Fujii H: Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits the
function of human mature dendritic cells mediated by VEGF
receptor-2. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 56:761–770. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oyama T, Ran S, Ishida T, Nadaf S, Kerr L,
Carbone DP and Gabrilovich DI: Vascular endothelial growth factor
affects dendritic cell maturation through the inhibition of nuclear
factor-kappa B activation in hemopoietic progenitor cells. J
Immunol. 160:1224–1232. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Crawford Y and Ferrara N: Tumor and
stromal pathways mediating refractoriness/resistance to
anti-angiogenic therapies. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 30:624–630. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang Y, Chen X, Dikov MM, Novitskiy SV,
Mosse CA, Yang L and Carbone DP: Distinct roles of VEGFR-1 and
VEGFR-2 in the aberrant hematopoiesis associated with elevated
levels of VEGF. Blood. 110:624–631. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Karakhanova S, Link J, Heinrich M,
Shevchenko I, Yang Y, Hassenpflug M, Bunge H, von Ahn K, Brecht R,
Mathes A, et al: Characterization of myeloid leukocytes and soluble
mediators in pancreatic cancer: Importance of myeloid-derived
suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology. 4:e9985192015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shojaei F, Wu X, Malik AK, Zhong C,
Baldwin ME, Schanz S, Fuh G, Gerber HP and Ferrara N: Tumor
refractoriness to anti-VEGF treatment is mediated by CD11b+Gr1+
myeloid cells. Nat Biotechnol. 25:911–920. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mantovani A and Locati M: Tumor-associated
macrophages as a paradigm of macrophage plasticity, diversity, and
polarization: Lessons and open questions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 33:1478–1483. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Linde N, Lederle W, Depner S, van Rooijen
N, Gutschalk CM and Mueller MM: Vascular endothelial growth
factor-induced skin carcinogenesis depends on recruitment and
alternative activation of macrophages. J Pathol. 227:17–28. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Movahedi K, Laoui D, Gysemans C, Baeten M,
Stangé G, Van den Bossche J, Mack M, Pipeleers D, In't Veld P, De
Baetselier P and Van Ginderachter JA: Different tumor
microenvironments contain functionally distinct subsets of
macrophages derived from Ly6C(high) monocytes. Cancer Res.
70:5728–5739. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gabrusiewicz K, Liu D, Cortes-Santiago N,
Hossain MB, Conrad CA, Aldape KD, Fuller GN, Marini FC, Alonso MM,
Idoate MA, et al: Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor
therapy-induced glioma invasion is associated with accumulation of
Tie2-expressing monocytes. Oncotarget. 5:2208–2220. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bhowmick NA, Neilson EG and Moses HL:
Stromal fibroblasts in cancer initiation and progression. Nature.
432:332–337. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Raredon MSB, Adams TS, Suhail Y, Schupp
JC, Poli S, Neumark N, Leiby KL, Greaney AM, Yuan Y, Horien C, et
al: Single-cell connectomic analysis of adult mammalian lungs. Sci
Adv. 5:eaaw38512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Barratt SL, Flower VA, Pauling JD and
Millar AB: VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) and fibrotic
lung disease. Int J Mol Med. 19:12692018.
|
|
40
|
Manzoni M, Rovati B, Ronzoni M, Loupakis
F, Mariucci S, Ricci V, Gattoni E, Salvatore L, Tinelli C, Villa E
and Danova M: Immunological effects of Bevacizumab-based treatment
in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncology. 79:187–196. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Martino EC, Misso G, Pastina P, Costantini
S, Vanni F, Gandolfo C, Botta C, Capone F, Lombardi A, Pirtoli L,
et al: Immune-modulating effects of bevacizumab in metastatic
non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Cell Death Discov. 2:16025.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Alfaro C, Suarez N, Gonzalez A, Solano S,
Erro L, Dubrot J, Palazon A, Hervas-Stubbs S, Gurpide A,
Lopez-Picazo JM, et al: Influence of bevacizumab, sunitinib and
sorafenib as single agents or in combination on the inhibitory
effects of VEGF on human dendritic cell differentiation from
monocytes. Br J Cancer. 100:1111–1119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Osada T, Chong G, Tansik R, Hong T,
Spector N, Kumar R, Hurwitz HI, Dev I, Nixon AB, Lyerly HK, et al:
The effect of anti-VEGF therapy on immature myeloid cell and
dendritic cells in cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother.
57:1115–1124. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Kusmartsev S, Eruslanov E, Kübler H, Tseng
T, Sakai Y, Su Z, Kaliberov S, Heiser A, Rosser C, Dahm P, et al:
Oxidative stress regulates expression of VEGFR1 in myeloid cells:
link to tumor-induced immune suppression in renal cell carcinoma. J
Immunol. 181:346–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Terme M, Pernot S, Marcheteau E, Sandoval
F, Benhamouda N, Colussi O, Dubreuil O, Carpentier AF, Tartour E
and Taieb J: VEGFA-VEGFR pathway blockade inhibits tumor-induced
regulatory T-cell proliferation in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res.
73:539–549. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Garon EB, Ciuleanu TE, Arrieta O, Prabhash
K, Syrigos KN, Goksel T, Park K, Gorbunova V, Kowalyszyn RD, Pikiel
J, et al: Ramucirumab plus docetaxel versus placebo plus docetaxel
for second-line treatment of stage IV non-small-cell lung cancer
after disease progression on platinum-based therapy (REVEL): A
multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet.
384:665–673. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
van Hooren L, Georganaki M, Huang H,
Mangsbo SM and Dimberg A: Sunitinib enhances the antitumor
responses of agonistic CD40-antibody by reducing MDSCs and
synergistically improving endothelial activation and T-cell
recruitment. Oncotarget. 7:50277–50289. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ozao-Choy J, Ma G, Kao J, Wang GX, Meseck
M, Sung M, Schwartz M, Divino CM, Pan PY, Chen SH, et al: The novel
role of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the reversal of immune
suppression and modulation of tumor microenvironment for
immune-based cancer therapies. Cancer Res. 69:2514–2522. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ko JS, Zea AH, Rini BI, Ireland JL, Elson
P, Cohen P, Golshayan A, Rayman PA, Wood L, Garcia J, et al:
Sunitinib mediates reversal of myeloid-derived suppressor cell
accumulation in renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res.
15:2148–2157. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Finke J, Ko J, Rini B, Rayman P, Ireland J
and Cohen P: MDSC as a mechanism of tumor escape from sunitinib
mediated anti-angiogenic therapy. Int Immunopharmacol. 11:856–861.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Guislain A, Gadiot J, Kaiser A, Jordanova
ES, Broeks A, Sanders J, van Boven H, de Gruijl TD, Haanen JB, Bex
A and Blank CU: Sunitinib pretreatment improves tumor-infiltrating
lymphocyte expansion by reduction in intratumoral content of
myeloid-derived suppressor cells in human renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 64:1241–1250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Marasco M, Berteotti A, Weyershaeuser J,
Thorausch N, Sikorska J, Krausze J, Brandt HJ, Kirkpatrick J, Rios
P, Schamel WW, et al: Molecular mechanism of SHP2 activation by
PD-1 stimulation. Sci Adv. 6:eaay44582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sharpe AH, Wherry EJ, Ahmed R and Freeman
GJ: The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in
regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat Immunol. 8:239–245.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wei SC, Duffy CR and Allison JP:
Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
Cancer Discov. 8:1069–1086. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen PL, Roh W, Reuben A, Cooper ZA,
Spencer CN, Prieto PA, Miller JP, Bassett RL, Gopalakrishnan V,
Wani K, et al: Analysis of immune signatures in longitudinal tumor
samples yields insight into biomarkers of response and mechanisms
of resistance to immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer Discov.
6:827–837. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Huang Y, Yuan J, Righi E, Kamoun WS,
Ancukiewicz M, Nezivar J, Santosuosso M, Martin JD, Martin MR,
Vianello F, et al: Vascular normalizing doses of antiangiogenic
treatment reprogram the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment
and enhance immunotherapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:17561–17566.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Allen E, Jabouille A, Rivera LB,
Lodewijckx I, Missiaen R, Steri V, Feyen K, Tawney J, Hanahan D,
Michael IP and Bergers G: Combined antiangiogenic and anti-PD-L1
therapy stimulates tumor immunity through HEV formation. Sci Transl
Med. 9:eaak96792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Mayoux M, Roller A, Pulko V, Sammicheli S,
Chen S, Sum E, Jost C, Fransen MF, Buser RB, Kowanetz M, et al:
Dendritic cells dictate responses to PD-L1 blockade cancer
immunotherapy. Sci Transl Med. 12:5342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|