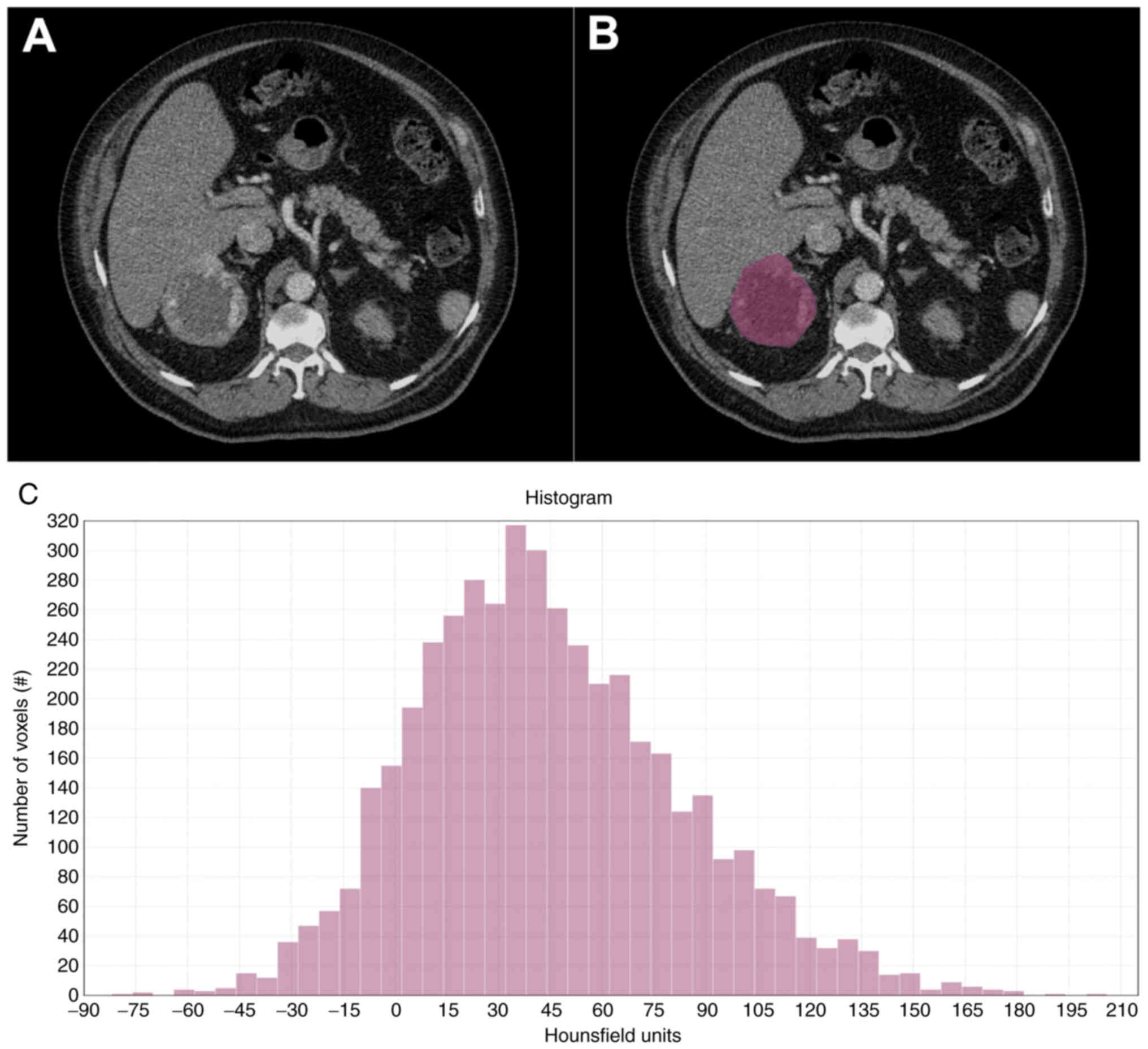
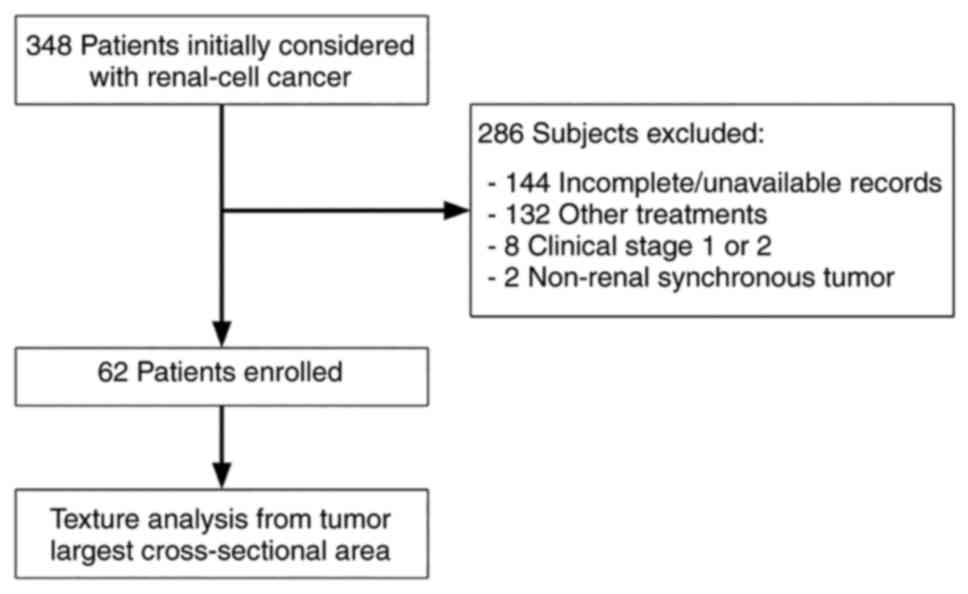
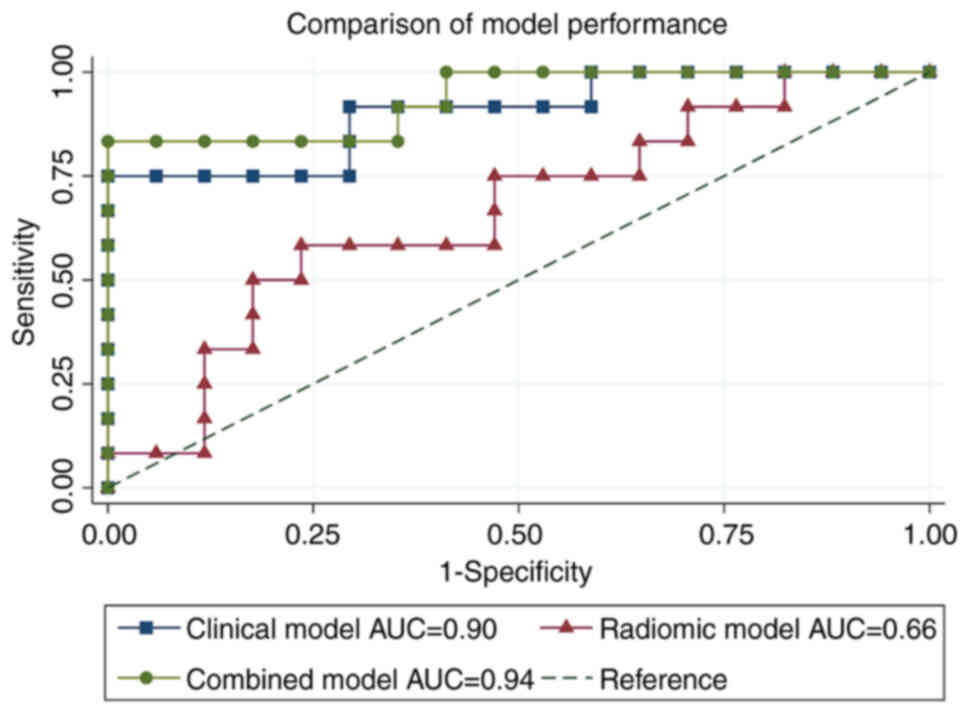
|
1
|
World Health Organization (WHO), . Cancer
Today: GLOBOCAN 2020. International Agency for Research on Cancer.
WHO; Geneva, Switzerland: 2020, https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-pieJanuary
05–2022
|
|
2
|
National Cancer Institute (NCI), . Cancer
Stat Facts: Kidney and Renal Pelvis Cancer. Surveilance,
Epidemiology and End Results Program. NCI; https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.htmlJanuary
05–2022
|
|
3
|
Pal S, Gong J, Mhatre SK, Lin SW, Surinach
A, Ogale S, Vohra R, Wallen H and George D: Real-world treatment
patterns and adverse events in metastatic renal cell carcinoma from
a large US claims database. BMC Cancer. 19:5482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Choueiri TK and Motzer RJ: Systemic
therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med.
376:354–366. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
NCCN, . Kidney Cancer version 3.2023,
2022. https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/kidney.pdfOctober
5–2022
|
|
6
|
Escudier B, Porta C, Schmidinger M,
Rioux-Leclercq N, Bex A, Khoo V, Grünwald V, Gillessen S and
Horwich A: Renal cell carcinoma: ESMO clinical practice guidelines
for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 30:706–720.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morais C: Sunitinib resistance in renal
cell carcinoma. J Kidney Cancer VHL. 1:1–11. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Tomczak P,
Michaelson MD, Bukowski RM, Rixe O, Oudard S, Negrier S, Szczylik
C, Kim ST, et al: Sunitinib versus interferon alfa in metastatic
renal-cell carcinoma. N Eng J Med. 356:115–124. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sternberg CN, Davis ID, Mardiak J,
Szczylik C, Lee E, Wagstaff J, Barrios CH, Salman P, Gladkov OA,
Kavina A, et al: Pazopanib in locally advanced or metastatic renal
cell carcinoma: Results of a randomized phase III trial. J Clin
Oncol. 28:1061–1068. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Motzer RJ, Hutson TE, Cella D, Reeves J,
Hawkins R, Guo J, Nathan P, Staehler M, de Souza P, Merchan JR, et
al: Pazopanib versus sunitinib in metastatic renal-cell carcinoma.
N Eng J Med. 369:722–731. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Haralick RM, Shanmugam K and Dinstein I:
Textural features for image classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man
Cybern SMC. 3:610–621. 1973. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ganeshan B, Miles KA, Young RCD and
Chatwin CR: In search of biologic correlates for liver texture on
portal-phase CT. Acad Radiol. 14:1058–1068. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ng F, Ganeshan B, Kozarski R, Miles KA and
Goh V: Assessment of primary colorectal cancer heterogeneity by
using whole-tumor texture analysis: Contrast-enhanced CT texture as
a biomarker of 5-year survival. Radiology. 266:177–184. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Negreros-Osuna AA, Parakh A, Corcoran RB,
Pourvaziri A, Kambadakone A, Ryan DP and Sahani DV: Radiomics
texture features in advanced colorectal cancer: Correlation with
BRAF Mutation and 5-year overall survival. Radiol Imaging
Cancer. 2:e1900842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yip C, Landau D, Kozarski R, Ganeshan B,
Thomas R, Michaelidou A and Goh V: Primary esophageal cancer:
Heterogeneity as potential prognostic biomarker in patients treated
with definitive chemotherapy and radiation therapy. Radiology.
270:141–148. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ganeshan B, Abaleke S, Young RCD, Chatwin
CR and Miles KA: Texture analysis of non-small cell lung cancer on
unenhanced computed tomography: Initial evidence for a relationship
with tumour glucose metabolism and stage. Cancer Imaging.
10:137–143. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Smith AD, Gray MR, del Campo SM, Shlapak
D, Ganeshan B, Zhang X and Carson WE III: Predicting overall
survival in patients with metastatic melanoma on antiangiogenic
therapy and RECIST stable disease on initial posttherapy images
using CT texture analysis. Am J Roentgenol. 205:W283–W293. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Deng Y, Soule E, Samuel A, Shah S, Cui E,
Asare-Sawiri M, Sundaram C, Lall C and Sandrasegaran K: CT texture
analysis in the differentiation of major renal cell carcinoma
subtypes and correlation with Fuhrman grade. Eur Radiol.
29:6922–6929. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Haider MA, Vosough A, Khalvati F, Kiss A,
Ganeshan B and Bjarnason GA: CT texture analysis: A potential tool
for prediction of survival in patients with metastatic clear cell
carcinoma treated with sunitinib. Cancer Imaging. 17:42017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nioche C, Orlhac F, Boughdad S, Reuzé S,
Goya-Outi J, Robert C, Pellot-Barakat C, Soussan M, Frouin F and
Buvat I: LIFEx: A freeware for radiomic feature calculation in
multimodality imaging to accelerate advances in the
characterization of tumor heterogeneity. Cancer Res. 78:4786–4789.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vittinghoff E, Glidden DV, Shiboski SC and
McCulloch CE: Predictor selection. Regression methods in
biostatistics: Linear, logistic, survival, and repeated measures
models. 1st ed. Dietz K, Gail M, Krickeberg K, Samet J and Tsiatis
A: Springer; New York: pp. 133–156. 2005
|
|
23
|
Harada K, Nozawa M, Uemura M, Tatsugami K,
Osawa T, Yamana K, Kimura G, Fujisawa M, Nonomura N, Eto M, et al:
Treatment patterns and outcomes in patients with unresectable or
metastatic renal cell carcinoma in Japan. Int J Urol. 26:202–210.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goh V, Ganeshan B, Nathan P, Juttla JK,
Vinayan A and Miles KA: Assessment of response to tyrosine kinase
inhibitors in metastatic renal cell cancer: CT texture as a
predictive biomarker. Radiology. 261:165–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hutson TE, Liu FX, Dieyi C, Kim R,
Krulewicz S, Kasturi V and Bhanegaonkar A: Effects of early vs
delayed progression on clinical and economic outcomes in patients
with metastatic renal cell carcinoma treated with tyrosine kinase
inhibitors as first-line therapy: Results from the IMPACT RCC
claims data analysis. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 27:1171–1181.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ji Z, Cui Y, Peng Z, Gong J, Zhu H, Zhang
X, Li J, Lu M, Lu Z, Shen L and Sun YS: Use of radiomics to predict
response to immunotherapy of malignant tumors of the digestive
system. Med Sci Monit. 26:e9246712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang B, Zhou L, Zhong J, Lv T, Li A, Ma L,
Zhong J, Yin S, Huang L, Zhou C, et al: Combination of computed
tomography imaging-based radiomics and clinicopathological
characteristics for predicting the clinical benefits of immune
checkpoint inhibitors in lung cancer. Respir Res. 22:1892021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Park KJ, Lee JL, Yoon SK, Heo C, Park BW
and Kim JK: Radiomics-based prediction model for outcomes of
PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy in metastatic urothelial carcinoma. Eur
Radiol. 30:5392–5403. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang H, Yin F, Chen M, Qi A, Lai Z, Yang
L and Wen G: A reliable prediction model for renal cell carcinoma
subtype based on radiomic features from 3D multiphase enhanced CT
images. J Oncol. 2021:65952122021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nazari M, Shiri I and Zaidi H:
Radiomics-based machine learning model to predict risk of death
within 5-years in clear cell renal cell carcinoma patients. Comput
Biol Med. 129:1041352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|