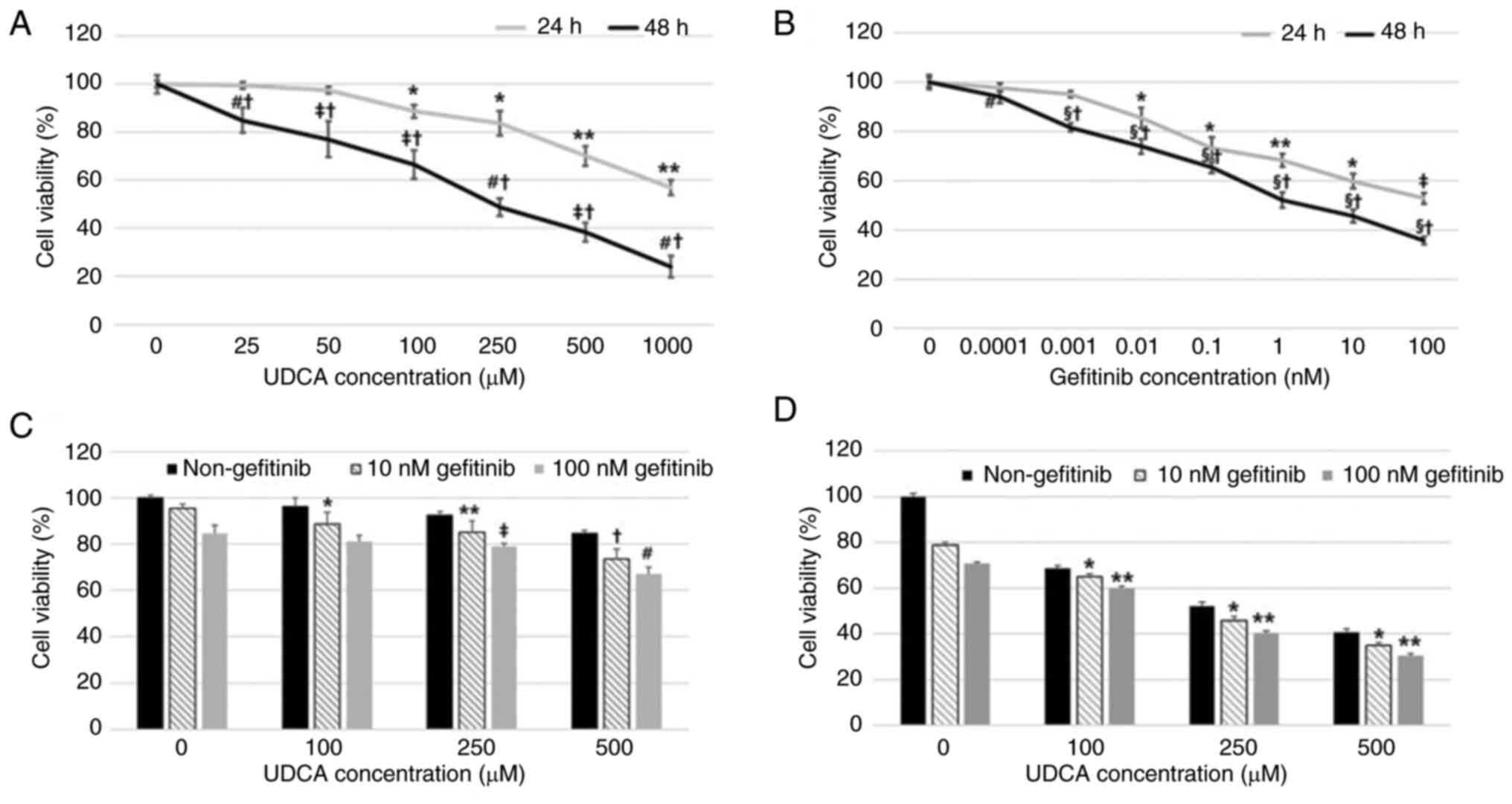
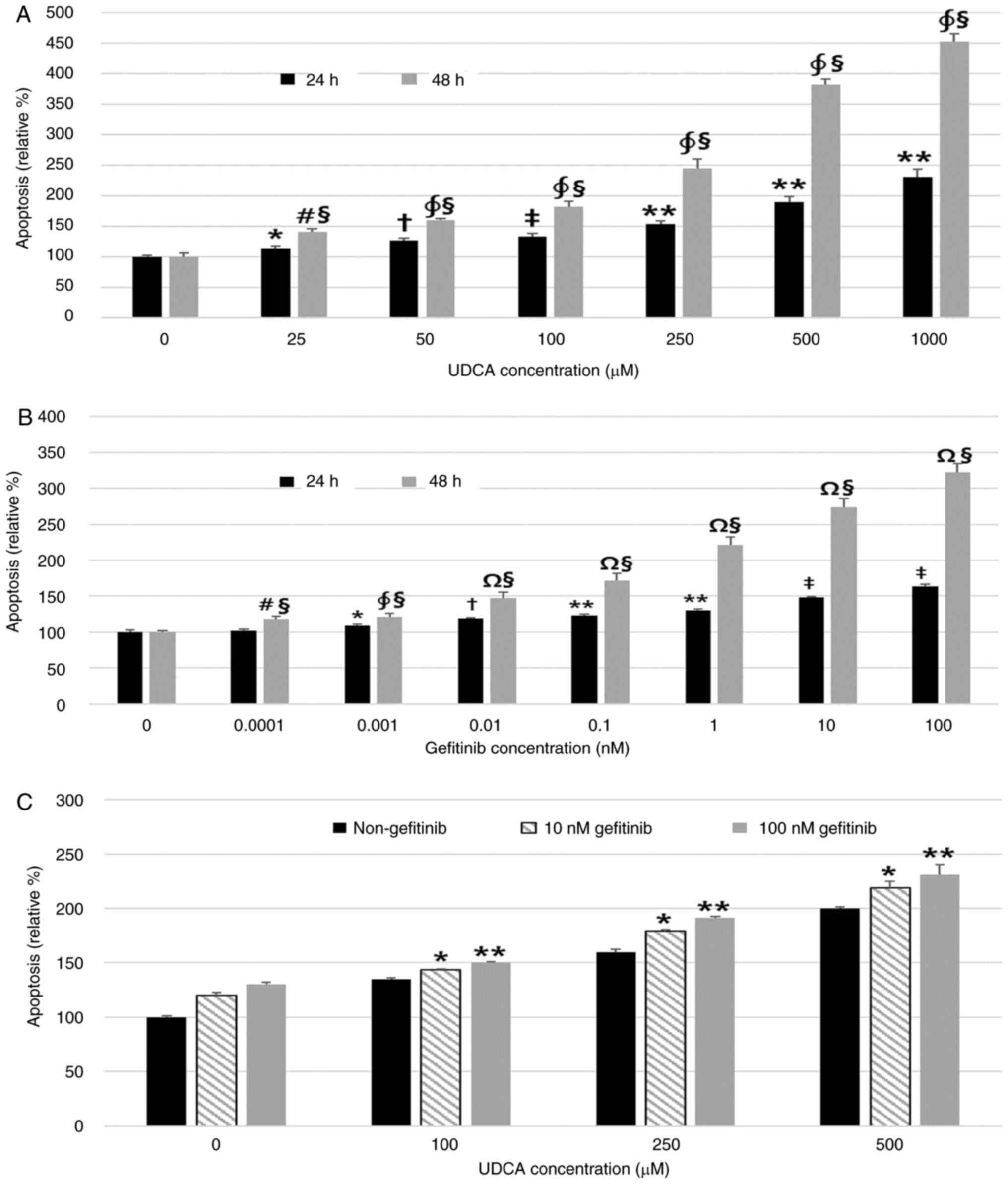
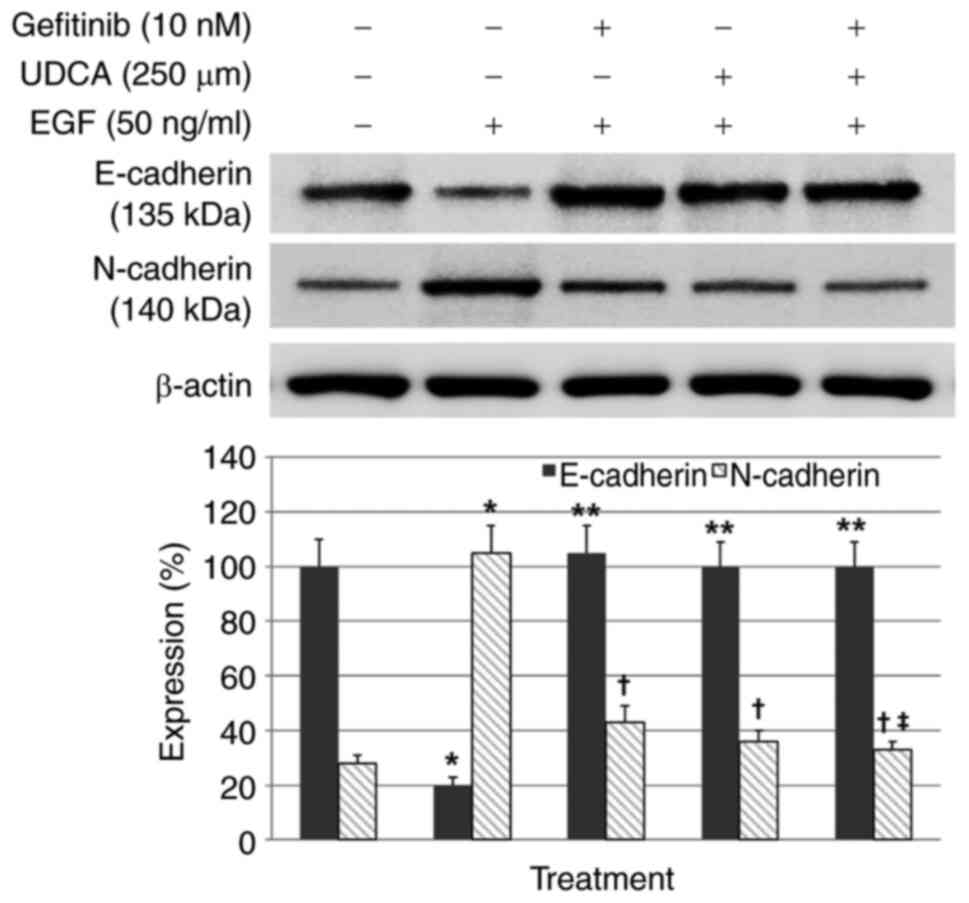
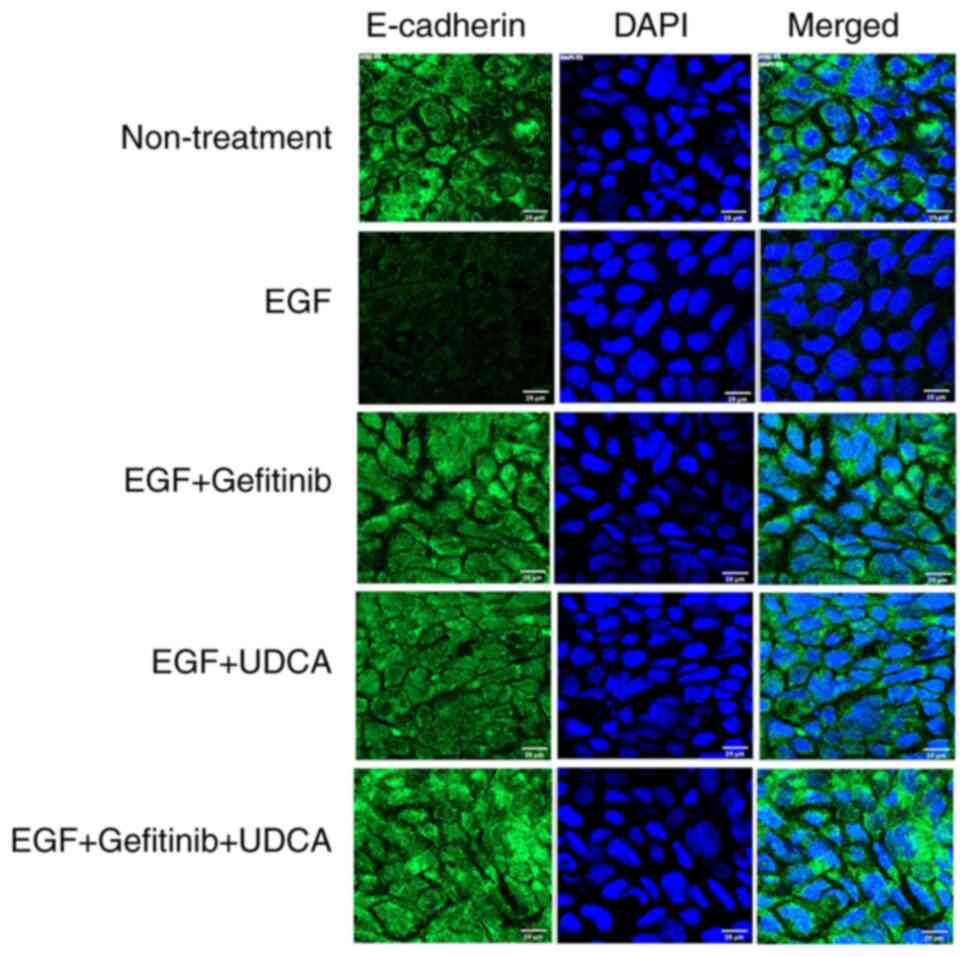
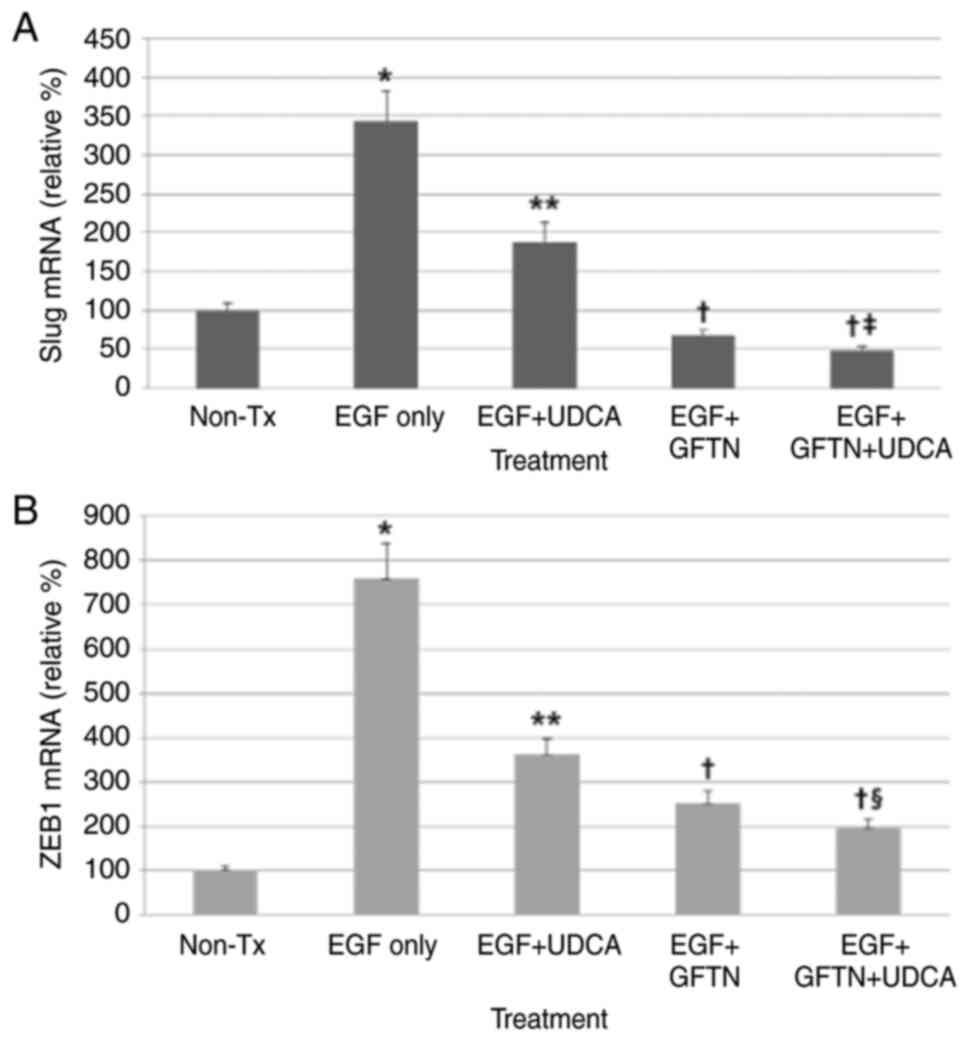
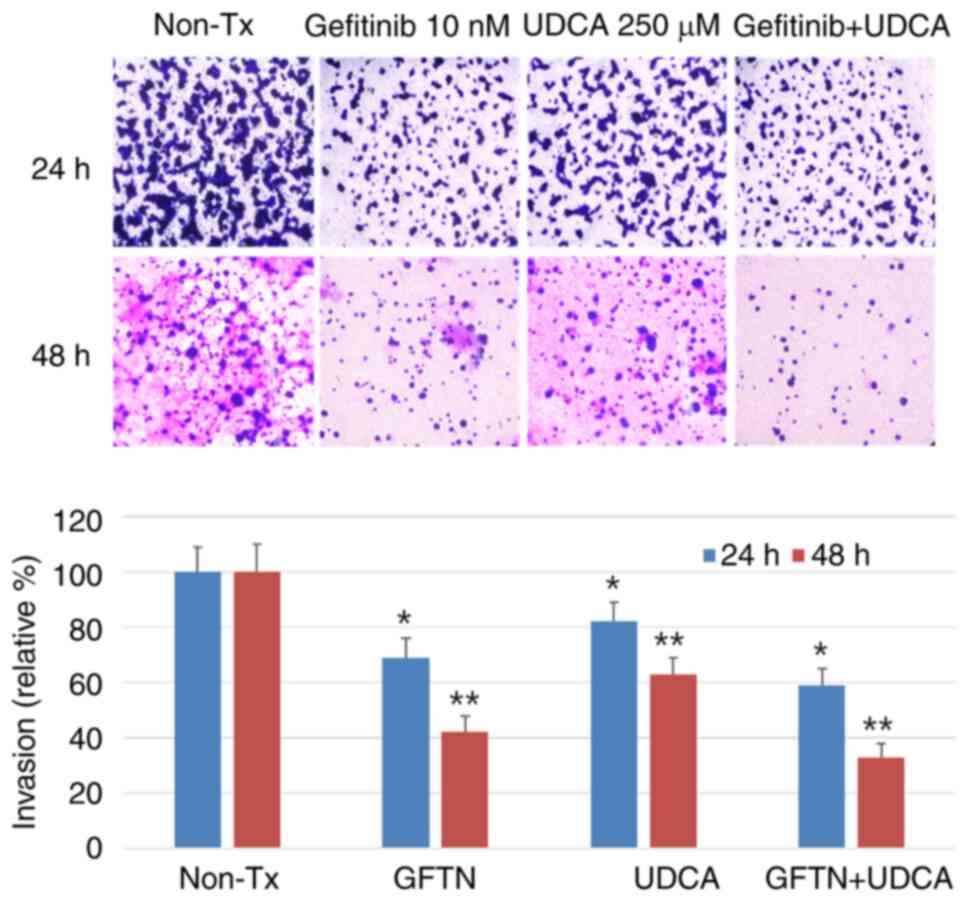
|
1
|
Song GW, Lee SG, Lee YJ, Park KM, Hwang S,
Kim KH, Ahn CS, Moon DB, Ha TY and Jung DH: Analysis of survival
and factors affecting the survival after surgical resection of
peripheral cholangiocarcinoma: 318 Cases in single institute.
Korean J Hepatol. 13:208–221. 2007.(In Korean). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blechacz B: Cholangiocarcinoma: Current
knowledge and new developments. Gut Liver. 11:13–26. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Amaral JD, Viana RJ, Ramalho RM, Steer CJ
and Rodrigues CM: Bile acids: Regulation of apoptosis by
ursodeoxycholic acid. J Lipid Res. 50:1721–1734. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guicciardi ME and Gores GJ:
Ursodeoxycholic acid cytoprotection: Dancing with death receptors
and survival pathways. Hepatology. 35:971–973. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Amaral JD, Castro RE, Solá S, Steer CJ and
Rodrigues CM: p53 is a key molecular target of ursodeoxycholic acid
in regulating apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 282:34250–34259. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu H, Qin CY, Han GQ, Xu HW, Meng M and
Yang Z: Mechanism of apoptotic effects induced selectively by
ursodeoxycholic acid on human hepatoma cell lines. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:1652–1658. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu H, Xu HW, Zhang YZ, Huang Y, Han GQ,
Liang TJ, Wei LL, Qin CY and Qin CK: Ursodeoxycholic acid induces
apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts in mice. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:10367–10374. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Serfaty L, Bissonnette M and Poupon R:
Ursodeoxycholic acid and chemoprevention of colorectal cancer.
Gastroenterol Clin Biol. 34:516–522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Khare S, Mustafi R, Cerda S, Yuan W,
Jagadeeswaran S, Dougherty U, Tretiakova M, Samarel A, Cohen G,
Wang J, et al: Ursodeoxycholic acid suppresses Cox-2 expression in
colon cancer: Roles of Ras, p38, and CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein. Nutr Cancer. 60:389–400. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pang L, Zhao X, Liu W, Deng J, Tan X and
Qiu L: Anticancer effect of ursodeoxycholic acid in human oral
squamous carcinoma HSC-3 cells through the caspases. Nutrients.
7:3200–3218. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Olsson R, Boberg KM, de Muckadell OS,
Lindgren S, Hultcrantz R, Folvik G, Bell H, Gangsøy-Kristiansen M,
Matre J, Rydning A, et al: High-dose ursodeoxycholic acid in
primary sclerosing cholangitis: A 5-year multicenter, randomized,
controlled study. Gastroenterology. 129:1464–1472. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rudolph G, Kloeters-Plachky P, Rost D and
Stiehl A: The incidence of cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing
cholangitis after long-time treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid.
Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 19:487–491. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nieto MA and Cano A: The
epithelial-mesenchymal transition under control: Global programs to
regulate epithelial plasticity. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:361–368.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guarino M, Rubino B and Ballabio G: The
role of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer pathology.
Pathology. 39:305–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thiery JP, Acloque H, Huang RY and Nieto
MA: Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
Cell. 139:871–890. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lamouille S, Subramanyam D, Blelloch R and
Derynck R: Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal and
mesenchymal-epithelial transitions by microRNAs. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 25:200–207. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Puisieux A, Brabletz T and Caramel J:
Oncogenic roles of EMT-inducing transcription factors. Nat Cell
Biol. 16:488–494. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Firrincieli D, Boissan M and Chignard N:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the liver. Gastroenterol Clin
Biol. 34:523–528. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ryu HS, Chung JH, Lee K, Shin E, Jing J,
Choe G, Kim H, Xu X, Lee HE, Kim DG, et al: Overexpression of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition-related markers according to cell
dedifferentiation: Clinical implications as an independent
predictor of poor prognosis in cholangiocarcinoma. Hum Pathol.
43:2360–2370. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fabris L, Cadamuro M, Moserle L, Dziura J,
Cong X, Sambado L, Nardo G, Sonzogni A, Colledan M, Furlanetto A,
et al: Nuclear expression of S100A4 calcium-binding protein
increases cholangiocarcinoma invasiveness and metastasization.
Hepatology. 54:890–899. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yao X, Wang X, Wang Z, Dai L, Zhang G, Yan
Q and Zhou W: Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of
epithelial mesenchymal transition-related protein expression in
intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 5:255–261.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Korita PV, Wakai T, Ajioka Y, Inoue M,
Takamura M, Shirai Y and Hatakeyama K: Aberrant expression of
vimentin correlates with dedifferentiation and poor prognosis in
patients with intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Anticancer Res.
30:2279–2285. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang KJ, Zhang BY, Zhang KP, Tang LM, Liu
SS, Zhu DM and Zhang DL: Clinicopathologic significance of slug
expression in human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:2554–2557. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dos Santos A, Court M, Thiers V, Sar S,
Guettier C, Samuel D, Bréchot C, Garin J, Demaugre F and Masselon
CD: Identification of cellular targets in human intrahepatic
cholangiocarcinoma using laser microdissection and accurate mass
and time tag proteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics. 9:1991–2004. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sebastian S, Settleman J, Reshkin SJ,
Azzariti A, Bellizzi A and Paradiso A: The complexity of targeting
EGFR signalling in cancer: From expression to turnover. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1766:120–139. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Barr S, Thomson S, Buck E, Russo S, Petti
F, Sujka-Kwok I, Eyzaguirre A, Rosenfeld-Franklin M, Gibson NW,
Miglarese M, et al: Bypassing cellular EGF receptor dependence
through epithelial-to-mesenchymal-like transitions. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 25:685–693. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yoshikawa D, Ojima H, Iwasaki M, Hiraoka
N, Kosuge T, Kasai S, Hirohashi S and Shibata T:
Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of EGFR, VEGF, and
HER2 expression in cholangiocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 98:418–425.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yoon JH, Gwak GY, Lee HS, Bronk SF,
Werneburg NW and Gores GJ: Enhanced epidermal growth factor
receptor activation in human cholangiocarcinoma cells. J Hepatol.
41:808–814. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Clapéron A, Guedj N, Mergey M, Vignjevic
D, Desbois-Mouthon C, Boissan M, Saubaméa B, Paradis V, Housset C
and Fouassier L: Loss of EBP50 stimulates EGFR activity to induce
EMT phenotypic features in biliary cancer cells. Oncogene.
31:1376–1388. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ito Y, Takeda T, Sasaki Y, Sakon M, Yamada
T, Ishiguro S, Imaoka S, Tsujimoto M, Higashiyama S, Monden M and
Matsuura N: Expression and clinical significance of the erbB family
in intrahepatic cholangiocellular carcinoma. Pathol Res Pract.
197:95–100. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Harder J, Waiz O, Otto F, Geissler M,
Olschewski M, Weinhold B, Blum HE, Schmitt-Graeff A and Opitz OG:
EGFR and HER2 expression in advanced biliary tract cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:4511–4517. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Clapéron A, Mergey M, Nguyen Ho-Bouldoires
TH, Vignjevic D, Wendum D, Chrétien Y, Merabtene F, Frazao A,
Paradis V, Housset C, et al: EGF/EGFR axis contributes to the
progression of cholangiocarcinoma through the induction of an
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Hepatol. 61:325–332. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lee J, Hong EM, Kim JH, Kim JH, Jung JH,
Park SW, Koh DH and Jang HJ: Ursodeoxycholic acid shows
antineoplastic effects in bile duct cancer cells via apoptosis
induction; p53 activation; and EGFR-ERK, COX-2, and PI3K-AKT
pathway inhibition. Mol Biol Rep. 48:6231–6240. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ku JL, Yoon KA, Kim IJ, Kim WH, Jang JY,
Suh KS, Kim SW, Park YH, Hwang JH, Yoon YB and Park JG:
Establishment and characterisation of six human biliary tract
cancer cell lines. Br J Cancer. 87:187–193. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lee J, Hong EM, Kim JH, Jung JH, Park SW,
Koh DH, Choi MH, Jang HJ and Kae SH: Metformin induces apoptosis
and inhibits proliferation through the AMP-activated protein kinase
and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor pathways in the bile duct
cancer cells. J Cancer. 10:1734–1744. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee BY, Timpson P, Horvath LG and Daly RJ:
FAK signaling in human cancer as a target for therapeutics.
Pharmacol Ther. 146:132–149. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Citri A and Yarden Y: EGF-ERBB signalling:
Towards the systems level. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 7:505–516. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hubbard SR: EGF receptor activation: Push
comes to shove. Cell. 125:1029–1031. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yarden Y and Sliwkowski MX: Untangling the
ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2:127–137. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Quon H, Liu FF and Cummings BJ: Potential
molecular prognostic markers in head and neck squamous cell
carcinomas. Head Neck. 23:147–159. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pawlowski V, Révillion F, Hebbar M, Hornez
L and Peyrat JP: Prognostic value of the type I growth factor
receptors in a large series of human primary breast cancers
quantified with a real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain
reaction assay. Clin Cancer Res. 6:4217–4225. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mayer A, Takimoto M, Fritz E, Schellander
G, Kofler K and Ludwig H: The prognostic significance of
proliferating cell nuclear antigen, epidermal growth factor
receptor, and mdr gene expression in colorectal cancer. Cancer.
71:2454–2460. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yamanaka Y, Friess H, Kobrin MS, Buchler
M, Beger HG and Korc M: Coexpression of epidermal growth factor
receptor and ligands in human pancreatic cancer is associated with
enhanced tumor aggressiveness. Anticancer Res. 13:565–569.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Nakazawa K, Dobashi Y, Suzuki S, Fujii H,
Takeda Y and Ooi A: Amplification and overexpression of c-erbB-2,
epidermal growth factor receptor, and c-met in biliary tract
cancers. J Pathol. 206:356–365. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Altimari A, Fiorentino M, Gabusi E,
Gruppioni E, Corti B, D'Errico A and Grigioni WF: Investigation of
ErbB1 and ErbB2 expression for therapeutic targeting in primary
liver tumours. Dig Liver Dis. 35:332–338. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lee CS and Pirdas A: Epidermal growth
factor receptor immunoreactivity in gallbladder and extrahepatic
biliary tract tumours. Pathol Res Pract. 191:1087–1091. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pais-Costa SR, Farah JF, Artigiani-Neto R,
Martins SJ and Goldenberg A: Evaluation of P53, E-cadherin, Cox-2,
and EGFR protein immunoexpression on prognostic of resected
gallbladder carcinoma. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 27:126–132. 2014.(In
English, Portuguese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Gwak GY, Yoon JH, Shin CM, Ahn YJ, Chung
JK, Kim YA, Kim TY and Lee HS: Detection of response-predicting
mutations in the kinase domain of the epidermal growth factor
receptor gene in cholangiocarcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
131:649–652. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Baselga J and Arteaga CL: Critical update
and emerging trends in epidermal growth factor receptor targeting
in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 23:2445–2459. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Rocha-Lima CM, Soares HP, Raez LE and
Singal R: EGFR targeting of solid tumors. Cancer Control.
14:295–304. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xiong HQ, Rosenberg A, LoBuglio A, Schmidt
W, Wolff RA, Deutsch J, Needle M and Abbruzzese JL: Cetuximab, a
monoclonal antibody targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor,
in combination with gemcitabine for advanced pancreatic cancer: A
multicenter phase II Trial. J Clin Oncol. 22:2610–2616. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Henson ES and Gibson SB: Surviving cell
death through epidermal growth factor (EGF) signal transduction
pathways: Implications for cancer therapy. Cell Signal.
18:2089–2097. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhou J, Yi Q and Tang L: The roles of
nuclear focal adhesion kinase (FAK) on cancer: A focused review. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:2502019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|