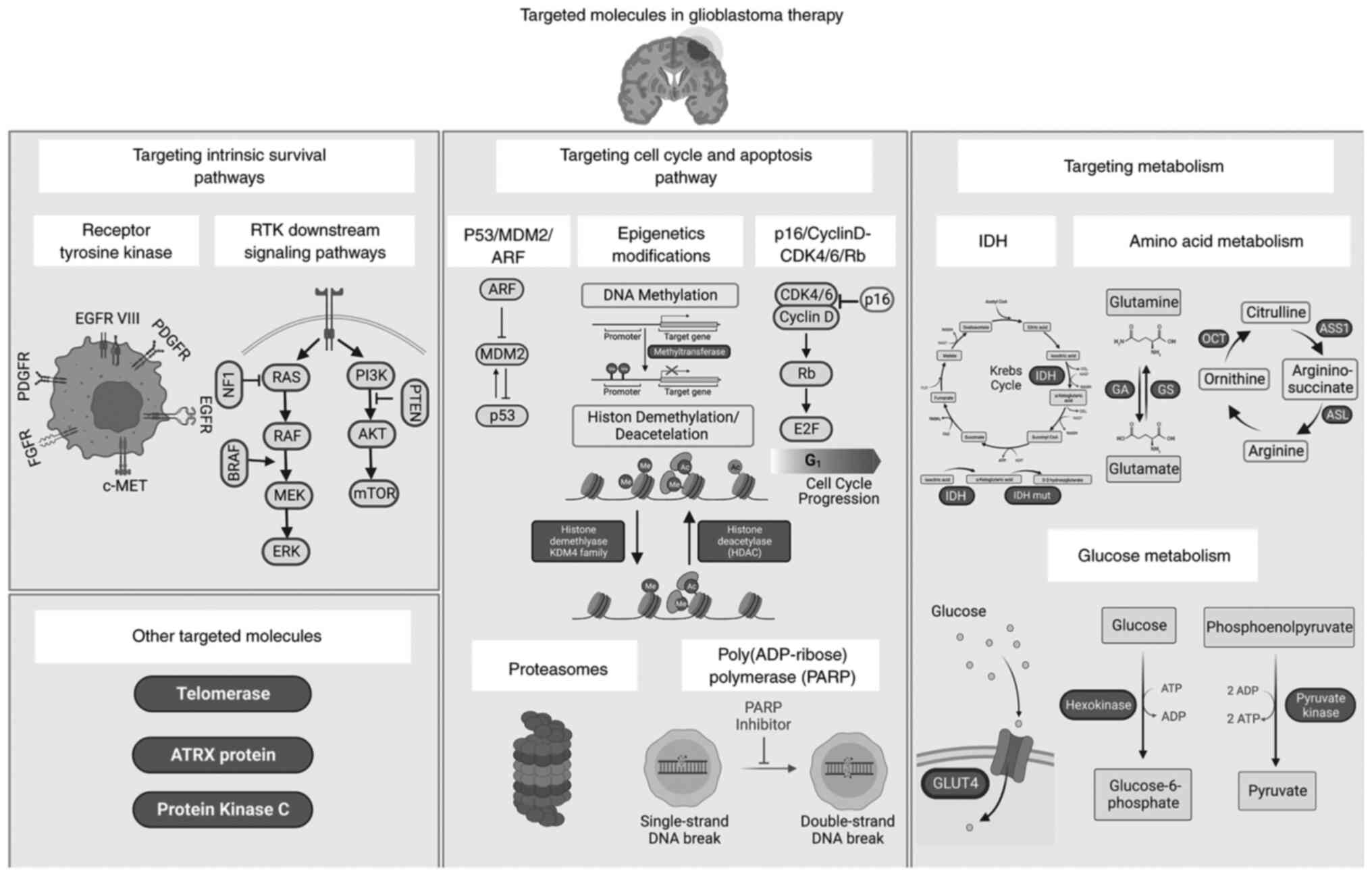
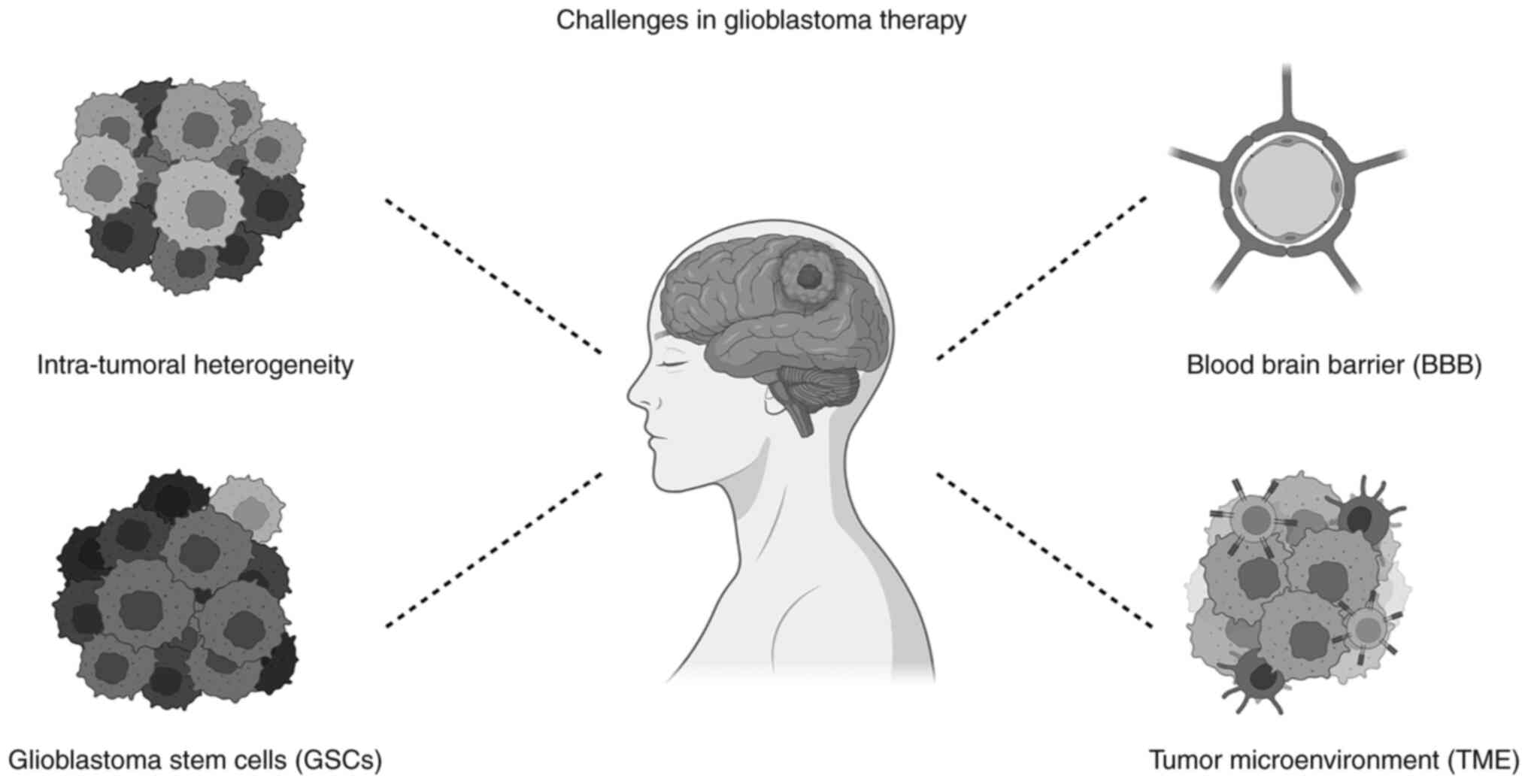
|
1
|
Hanif F, Muzaffar K, Perveen K, Malhi SM
and Simjee SHU: Glioblastoma multiforme: A review of its
epidemiology and pathogenesis through clinical presentation and
treatment. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 18:3–9. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Karachi A, Dastmalchi F, Mitchell DA and
Rahman M: Temozolomide for immunomodulation in the treatment of
glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 20:1566–1572. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Delgado-López PD and Corrales-García EM:
Survival in glioblastoma: A review on the impact of treatment
modalities. Clin Transl Oncol. 18:1062–1071. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tamimi AF and Juweid M: Epidemiology and
outcome of glioblastoma. Glioblastoma. De Vleeschouwer S: Codon
Publications; Brisbane, AU: 2017, Available from:. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470003/
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Verhaak RGW, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V,
Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP, et al:
Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes
of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1,
EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 17:98–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hubbard SR: Structural analysis of
receptor tyrosine kinases. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 71:343–358. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Montor WR, Salas AROSE and Melo FHM:
Receptor tyrosine kinases and downstream pathways as druggable
targets for cancer treatment: The current arsenal of inhibitors.
Mol Cancer. 17:552018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blume-Jensen P and Hunter T: Oncogenic
kinase signalling. Nature. 411:355–365. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hunter T: Tyrosine phosphorylation: Thirty
years and counting. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:140–146. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brennan CW, Verhaak RGW, McKenna A, Campos
B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, Zheng S, Chakravarty D, Sanborn JZ,
Berman SH, et al: The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma.
Cell. 155:462–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chakravarti A, Chakladar A, Delaney MA,
Latham DE and Loeffler JS: The epidermal growth factor receptor
pathway mediates resistance to sequential administration of
radiation and chemotherapy in primary human glioblastoma cells in a
RAS-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 62:4307–4315. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mazzoleni S, Politi LS, Pala M, Cominelli
M, Franzin A, Sergi Sergi L, Falini A, De Palma M, Bulfone A,
Poliani PL and Galli R: Epidermal growth factor receptor expression
identifies functionally and molecularly distinct tumor-initiating
cells in human glioblastoma multiforme and is required for
gliomagenesis. Cancer Res. 70:7500–7513. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li L, Dutra A, Pak E, Labrie JE III,
Gerstein RM, Pandolfi PP, Recht LD and Ross AH: EGFRvIII expression
and PTEN loss synergistically induce chromosomal instability and
glial tumors. Neuro Oncol. 11:9–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hatanpaa KJ, Burma S, Zhao D and Habib AA:
Epidermal growth factor receptor in glioma: Signal transduction,
neuropathology, imaging, and radioresistance. Neoplasia.
12:675–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Talasila KM, Soentgerath A, Euskirchen P,
Rosland GV, Wang J, Huszthy PC, Prestegarden L, Skaftnesmo KO,
Sakariassen PØ, Eskilsson E, et al: EGFR wild-type amplification
and activation promote invasion and development of glioblastoma
independent of angiogenesis. Acta Neuropathol. 125:683–698. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bonavia R, Inda MM, Vandenberg S, Cheng
SY, Nagane M, Hadwiger P, Tan P, Sah DW, Cavenee WK and Furnari FB:
EGFRvIII promotes glioma angiogenesis and growth through the NF-κB,
interleukin-8 pathway. Oncogene. 31:4054–4066. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Katanasaka Y, Kodera Y, Kitamura Y,
Morimoto T, Tamura T and Koizumi F: Epidermal growth factor
receptor variant type III markedly accelerates angiogenesis and
tumor growth via inducing c-myc mediated angiopoietin-like 4
expression in malignant glioma. Mol Cancer. 12:312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Feng H, Hu B, Vuori K, Sarkaria JN,
Furnari FB, Cavenee WK and Cheng SY: EGFRvIII stimulates glioma
growth and invasion through PKA-dependent serine phosphorylation of
Dock180. Oncogene. 33:2504–2512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Eskilsson E, Rosland GV, Talasila KM,
Knappskog S, Keunen O, Sottoriva A, Foerster S, Solecki G, Taxt T,
Jirik R, et al: EGFRvIII mutations can emerge as late and
heterogenous events in glioblastoma development and promote
angiogenesis through Src activation. Neuro Oncol. 18:1644–1655.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Roos A, Dhruv HD, Peng S, Inge LJ, Tuncali
S, Pineda M, Millard N, Mayo Z, Eschbacher JM, Loftus JC, et al:
EGFRvIII-Stat5 signaling enhances glioblastoma cell migration and
survival. Mol Cancer Res. 16:1185–1195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sugawa N, Ekstrand AJ, James CD and
Collins VP: Identical splicing of aberrant epidermal growth factor
receptor transcripts from amplified rearranged genes in human
glioblastomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:8602–8606. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Frederick L, Wang XY, Eley G and James CD:
Diversity and frequency of epidermal growth factor receptor
mutations in human glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 60:1383–1387.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cruz Da Silva E, Mercier MC,
Etienne-Selloum N, Dontenwill M and Choulier L: A systematic review
of glioblastoma-targeted therapies in phases II, III, IV clinical
trials. Cancers (Basel). 13:17952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Van Den Bent M, Eoli M, Sepulveda JM,
Smits M, Walenkamp A, Frenel JS, Franceschi E, Clement PM, Chinot
O, De Vos F, et al: INTELLANCE 2/EORTC 1410 randomized Phase II
study of Depatux-M alone and with temozolomide vs temozolomide or
lomustine in recurrent EGFR amplified glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol.
22:684–693. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Solomon MT, Miranda N, Jorrín E, Chon I,
Marinello JJ, Alert J, Lorenzo-Luaces P and Crombet T: Nimotuzumab
in combination with radiotherapy in high grade glioma patients: A
single institution experience. Cancer Biol Ther. 15:504–509. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reardon DA, Nabors LB, Mason WP, Perry JR,
Shapiro W, Kavan P, Mathieu D, Phuphanich S, Cseh A, Fu Y, et al:
Phase I/randomized Phase II study of afatinib, an irreversible ErbB
family blocker, with or without protracted temozolomide in adults
with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 17:430–439.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sampson JH, Aldape KD, Archer GE, Coan A,
Desjardins A, Friedman AH, Friedman HS, Gilbert MR, Herndon JE,
McLendon RE, et al: Greater chemotherapy-induced lymphopenia
enhances tumor-specific immune responses that eliminate
EGFRvIII-expressing tumor cells in patients with glioblastoma.
Neuro Oncol. 13:324–333. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Paulsson J, Lindh MB, Jarvius M, Puputti
M, Nistér M, Nupponen NN, Paulus W, Söderberg O, Dresemann G, von
Deimling A, et al: Prognostic but not predictive role of
platelet-derived growth factor receptors in patients with recurrent
glioblastoma. Int J Cancer. 128:1981–1988. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Plate KH, Breier G, Farrell CL and Risau
W: Platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta is induced during
tumor development and upregulated during tumor progression in
endothelial cells in human gliomas. Lab Invest. 67:529–534.
1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Camorani S, Esposito CL, Rienzo A,
Catuogno S, Iaboni M, Condorelli G, de Franciscis V and Cerchia L:
Inhibition of receptor signaling and of glioblastoma-derived tumor
growth by a novel PDGFRβ aptamer. Mol Ther. 22:828–841. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Vassbotn FS, Ostman A, Langeland N,
Holmsen H, Westermark B, Heldin CH and Nistér M: Activated
platelet-derived growth factor autocrine pathway drives the
transformed phenotype of a human glioblastoma cell line. J Cell
Physiol. 158:381–389. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lokker NA, Sullivan CM, Hollenbach SJ,
Israel MA and Giese NA: Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
autocrine signaling regulates survival and mitogenic pathways in
glioblastoma cells: Evidence that the novel PDGF-C and PDGF-D
ligands may play a role in the development of brain tumors. Cancer
Res. 62:3729–3735. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cattaneo MG, Gentilini D and Vicentini LM:
Deregulated human glioma cell motility: Inhibitory effect of
somatostatin. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 256:34–39. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kwak Y, Kim SI, Park CK, Paek SH, Lee ST
and Park SH: C-MET overexpression and amplification in gliomas. Int
J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:14932–14938. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bender S, Gronych J, Warnatz HJ, Hutter B,
Gröbner S, Ryzhova M, Pfaff E, Hovestadt V, Weinberg F, Halbach S,
et al: Recurrent MET fusion genes represent a drug target in
pediatric glioblastoma. Nat Med. 22:1314–1320. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wen PY, Schiff D, Cloughesy TF, Raizer JJ,
Laterra J, Smitt M, Wolf M, Oliner KS, Anderson A, Zhu M, et al: A
Phase II study evaluating the efficacy and safety of AMG 102
(rilotumumab) in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol.
13:437–446. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li Y, Li A, Glas M, Lal B, Ying M, Sang Y,
Xia S, Trageser D, Guerrero-Cázares H, Eberhart CG, et al: c-Met
signaling induces a reprogramming network and supports the
glioblastoma stem-like phenotype. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
108:9951–9956. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jahangiri A, De Lay M, Miller LM,
Carbonell WS, Hu YL, Lu K, Tom MW, Paquette J, Tokuyasu TA, Tsao S,
et al: Gene expression profile identifies tyrosine kinase c-Met as
a targetable mediator of antiangiogenic therapy resistance. Clin
Cancer Res. 19:1773–1783. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Johnson J, Ascierto ML, Mittal S, Newsome
D, Kang L, Briggs M, Tanner K, Marincola FM, Berens ME, Vande Woude
GF and Xie Q: Genomic profiling of a hepatocyte growth
factor-dependent signature for MET-targeted therapy in
glioblastoma. J Transl Med. 13:3062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cruickshanks N, Zhang Y, Yuan F, Pahuski
M, Gibert M and Abounader R: Role and therapeutic targeting of the
HGF/MET pathway in glioblastoma. Cancers (Basel). 9:872017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang K, Wu Z, Zhang H, Zhang N, Wu W, Wang
Z, Dai Z, Zhang X, Zhang L, Peng Y, et al: Glioma targeted therapy:
Insight into future of molecular approaches. Mol Cancer. 21:392022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cloughesy TF, Mochizuki AY, Orpilla JR,
Hugo W, Lee AH, Davidson TB, Wang AC, Ellingson BM, Rytlewski JA,
Sanders CM, et al: Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 immunotherapy promotes a
survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in
recurrent glioblastoma. Nat Med. 25:477–486. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Torre M, Vasudevaraja V, Serrano J,
DeLorenzo M, Malinowski S, Blandin AF, Pages M, Ligon AH, Dong F,
Meredith DM, et al: Molecular and clinicopathologic features of
gliomas harboring NTRK fusions. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 8:1072020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Jimenez-Pascual A, Mitchell K,
Siebzehnrubl FA and Lathia JD: FGF2: A novel druggable target for
glioblastoma? Expert Opin Ther Targets. 24:311–318. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Feldkamp MM, Lau N and Guha A: The
farnesyltransferase inhibitor L-744,832 inhibits the growth of
astrocytomas through a combination of antiproliferative,
antiangiogenic, and proapoptotic activities. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
886:257–260. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kowalewski A, Durślewicz J, Zdrenka M,
Grzanka D and Szylberg Ł: Clinical relevance of BRAF V600E mutation
status in brain tumors with a focus on a novel management
algorithm. Target Oncol. 15:531–540. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Dischinger PS, Tovar EA, Essenburg CJ,
Madaj ZB, Gardner EE, Callaghan ME, Turner AN, Challa AK, Kempston
T, Eagleson B, et al: NF1 deficiency correlates with estrogen
receptor signaling and diminished survival in breast cancer. NPJ
Breast Cancer. 4:292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Arima Y, Hayashi H, Kamata K, Goto TM,
Sasaki M, Kuramochi A and Saya H: Decreased expression of
neurofibromin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
neurofibromatosis type 1. Exp Dermatol. 19:e136–e141. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Altwairgi AK, Alghareeb WA, AlNajjar FH,
Alhussain H, Alsaeed E, Balbaid AAO, Aldanan S, Orz Y and Alsharm
AA: Atorvastatin in combination with radiotherapy and temozolomide
for glioblastoma: A prospective Phase II study. Invest New Drugs.
39:226–231. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Engelman JA, Luo J and Cantley LC: The
evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth
and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 7:606–519. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Mondin VE, Ben El Kadhi K, Cauvin C,
Jackson-Crawford A, Bélanger E, Decelle B, Salomon R, Lowe M,
Echard A and Carréno S: PTEN reduces endosomal
PtdIns(4,5)P2 in a phosphatase-independent manner via a
PLC pathway. J Cell Biol. 218:2198–2214. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Han F, Hu R, Yang H, Liu J, Sui J, Xiang
X, Wang F, Chu L and Song S: PTEN gene mutations correlate to poor
prognosis in glioma patients: A meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther.
9:3485–3492. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen C, Zhu S, Zhang X, Zhou T, Gu J, Xu
Y, Wan Q, Qi X, Chai Y, Liu X, et al: Targeting the synthetic
vulnerability of PTEN-deficient glioblastoma cells with MCL1
inhibitors. Mol Cancer Ther. 19:2001–2011. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao JJ, Liu Z, Wang L, Shin E, Loda MF
and Roberts TM: The oncogenic properties of mutant p110alpha and
p110beta phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases in human mammary epithelial
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:18443–18448. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Thorpe LM, Yuzugullu H and Zhao JJ: PI3K
in cancer: Divergent roles of isoforms, modes of activation and
therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Cancer. 15:7–24. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
McLendon R, Friedman A, Bigner D, Van Meir
EG, Brat DJ, Mastrogianakis GM, Olson JJ, Mikkelsen T, Lehman N,
Aldape K, et al: Comprehensive genomic characterization defines
human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature. 455:1061–1068.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Parsons DW, Jones S, Zhang X, Lin JCH,
Leary RJ, Angenendt P, Mankoo P, Carter H, Siu IM, Gallia GL, et
al: An integrated genomic analysis of human glioblastoma
multiforme. Science. 321:1807–1812. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Weber GL, Parat MO, Binder ZA, Gallia GL
and Riggins GJ: Abrogation of PIK3CA or PIK3R1 reduces
proliferation, migration, and invasion in glioblastoma multiforme
cells. Oncotarget. 2:833–849. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Quayle SN, Lee JY, Cheung LWT, Ding L,
Wiedemeyer R, Dewan RW, Huang-Hobbs E, Zhuang L, Wilson RK, Ligon
KL, et al: Somatic mutations of PIK3R1 promote gliomagenesis. PLoS
One. 7:e494662012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gallia GL, Rand V, Siu IM, Eberhart CG,
James CD, Marie SKN, Oba-Shinjo SM, Carlotti CG, Caballero OL,
Simpson AJ, et al: PIK3CA gene mutations in pediatric and adult
glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Cancer Res. 4:709–714. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Tanaka S, Batchelor TT, Iafrate AJ,
Dias-Santagata D, Borger DR, Ellisen LW, Yang D, Louis DN, Cahill
DP and Chi AS: PIK3CA activating mutations are associated with more
disseminated disease at presentation and earlier recurrence in
glioblastoma. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 7:662019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
England B, Huang T and Karsy M: Current
understanding of the role and targeting of tumor suppressor p53 in
glioblastoma multiforme. Tumour Biol. 34:2063–2074. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ohgaki H: Genetic pathways to
glioblastomas. Neuropathology. 25:1–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Olafson LR, Gunawardena M, Nixdorf S,
McDonald KL and Rapkin RW: The role of TP53 gain-of-function
mutation in multifocal glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 147:37–47. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fontemaggi G, Dell'Orso S, Trisciuoglio D,
Shay T, Melucci E, Fazi F, Terrenato I, Mottolese M, Muti P, Domany
E, et al: The execution of the transcriptional axis mutant p53,
E2F1 and ID4 promotes tumor neo-angiogenesis. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
16:1086–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Ham SW, Jeon HY, Jin X, Kim EJ, Kim JK,
Shin YJ, Lee Y, Kim SH, Lee SY, Seo S, et al: TP53 gain-of-function
mutation promotes inflammation in glioblastoma. Cell Death Differ.
26:409–425. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pedrote MM, Motta MF, Ferretti GDS,
Norberto DR, Spohr TCLS, Lima FRS, Gratton E, Silva JL and de
Oliveira GAP: Oncogenic gain of function in glioblastoma is linked
to mutant p53 amyloid oligomers. iScience. 23:1008202020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tao W and Levine AJ: P19(ARF) stabilizes
p53 by blocking nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of Mdm2. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 96:6937–6941. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Nakamura M, Watanabe T, Klangby U, Asker
C, Wiman K, Yonekawa Y, Kleihues P and Ohgaki H: p14ARF deletion
and methylation in genetic pathways to glioblastomas. Brain Pathol.
11:159–168. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Reifenberger G, Liu L, Ichimura K, Schmidt
EE and Collins VP: Amplification and overexpression of the MDM2
gene in a subset of human malignant gliomas without p53 mutations.
Cancer Res. 53:2736–2739. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Riemenschneider MJ, Büschges R, Wolter M,
Reifenberger J, Boström J, Kraus JA, Schlegel U and Reifenberger G:
Amplification and overexpression of the MDM4 (MDMX) gene from 1q32
in a subset of malignant gliomas without TP53 mutation or MDM2
amplification1. Cancer Res. 59:6091–6096. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xiong Y, Zhang Y, Xiong S and
Williams-Villalobo AE: A glance of p53 functions in brain
development, neural stem cells, and brain cancer. Biology (Basel).
9:2852020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Sherr CJ and McCormick F: The RB and p53
pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell. 2:103–112. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Allen BK, Stathias V, Maloof ME, Vidovic
D, Winterbottom EF, Capobianco AJ, Clarke J, Schurer S, Robbins DJ
and Ayad NG: Epigenetic pathways and glioblastoma treatment:
Insights from signaling cascades. J Cell Biochem. 116:351–363.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Romani M, Pistillo MP and Banelli B:
Epigenetic targeting of glioblastoma. Front Oncol. 8:4482018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Roos WP, Batista LFZ, Naumann SC, Wick W,
Weller M, Menck CFM and Kaina B: Apoptosis in malignant glioma
cells triggered by the temozolomide-induced DNA lesion
O6-methylguanine. Oncogene. 26:186–197. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yu W, Zhang L, Wei Q and Shao A:
O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (MGMT): Challenges and new
opportunities in glioma chemotherapy. Front Oncol. 9:15472020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Zhang J, Chen L, Han L, Shi Z, Zhang J, Pu
P and Kang C: EZH2 is a negative prognostic factor and exhibits
pro-oncogenic activity in glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 356:929–936.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sharma V, Malgulwar PB, Purkait S, Patil
V, Pathak P, Agrawal R, Kulshreshtha R, Mallick S, Julka PK, Suri
A, et al: Genome-wide ChIP-seq analysis of EZH2-mediated H3K27me3
target gene profile highlights differences between low- and
high-grade astrocytic tumors. Carcinogenesis. 38:152–161.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Mohammad F, Weissmann S, Leblanc B, Pandey
DP, Højfeldt JW, Comet I, Zheng C, Johansen JV, Rapin N, Porse BT,
et al: EZH2 is a potential therapeutic target for H3K27M-mutant
pediatric gliomas. Nat Med. 23:483–492. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Lee DH, Kim GW, Yoo J, Lee SW, Jeon YH,
Kim SY, Kang HG, Kim DH, Chun KH, Choi J and Kwon SH: Histone
demethylase KDM4C controls tumorigenesis of glioblastoma by
epigenetically regulating p53 and c-Myc. Cell Death Dis. 12:892021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ceccacci E and Minucci S: Inhibition of
histone deacetylases in cancer therapy: Lessons from leukaemia. Br
J Cancer. 114:605–611. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lee P, Murphy B, Miller R, Menon V, Banik
NL, Giglio P, Lindhorst SM, Varma AK, Vandergrift WA III, Patel SJ
and Das A: Mechanisms and clinical significance of histone
deacetylase inhibitors: Epigenetic glioblastoma therapy. Anticancer
Res. 35:615–625. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Chen R, Zhang M, Zhou Y, Guo W, Yi M,
Zhang Z, Ding Y and Wang Y: The application of histone deacetylases
inhibitors in glioblastoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 39:1382020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Harbour JW, Luo RX, Santi AD, Postigo AA
and Dean DC: Cdk phosphorylation triggers sequential intramolecular
interactions that progressively block Rb functions as cells move
through G1. Cell. 98:859–869. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Matsushime H, Ewen ME, Strom DK, Kato JY,
Hanks SK, Roussel MF and Sherr CJ: Identification and properties of
an atypical catalytic subunit (p34PSK-J3/cdk4) for mammalian D type
G1 cyclins. Cell. 71:323–334. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Cooper S and Shayman JA: Revisiting
retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation during the mammalian cell
cycle. Cell Mol Life Sci. 58:580–595. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Taylor JW, Parikh M, Phillips JJ, James
CD, Molinaro AM, Butowski NA, Clarke JL, Oberheim-Bush NA, Chang
SM, Berger MS and Prados M: Phase-2 trial of palbociclib in adult
patients with recurrent RB1-positive glioblastoma. J Neurooncol.
140:477–483. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Goldberg AL: Protein degradation and
protection against misfolded or damaged proteins. Nature.
426:895–899. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Narayanan S, Cai CY, Assaraf YG, Guo HQ,
Cui Q, Wei L, Huang JJ, Ashby CR Jr and Chen ZS: Targeting the
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway to overcome anti-cancer drug
resistance. Drug Resist Updat. 48:1006632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Kong XT, Nguyen NT, Choi YJ, Zhang G,
Nguyen HN, Filka E, Green S, Yong WH, Liau LM, Green RM, et al:
Phase 2 study of bortezomib combined with temozolomide and regional
radiation therapy for upfront treatment of patients with newly
diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme: safety and efficacy assessment.
Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 100:1195–1203. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Di K, Lloyd GK, Abraham V, MacLaren A,
Burrows FJ, Desjardins A, Trikha M and Bota DA: Marizomib activity
as a single agent in malignant gliomas: Ability to cross the
blood-brain barrier. Neuro Oncol. 18:840–848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Roth P, Mason WP, Richardson PG and Weller
M: Proteasome inhibition for the treatment of glioblastoma. Expert
Opin Investig Drugs. 29:1133–1141. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Quillin J, Patel R, Herzberg E, Alton D,
Bikzhanova G, Geisler L and Olson J: A phase 0 analysis of ixazomib
in patients with glioblastoma. Mol Clin Oncol. 13:432020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Huang J, Campian JL, Gujar AD, Tsien C,
Ansstas G, Tran DD, DeWees TA, Lockhart AC and Kim AH: Final
results of a Phase I dose-escalation, dose-expansion study of
adding disulfiram with or without copper to adjuvant temozolomide
for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 138:105–111. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Huang J, Chaudhary R, Cohen AL, Fink K,
Goldlust S, Boockvar J, Chinnaiyan P, Wan L, Marcus S and Campian
JL: A multicenter Phase II study of temozolomide plus disulfiram
and copper for recurrent temozolomide-resistant glioblastoma. J
Neurooncol. 142:537–544. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Carruthers R and Chalmers AJ: Improving
the therapeutic ratio of radiotherapy by targeting the DNA damage
response. Increasing the Therapeutic Ratio of Radiotherapy. Series:
Cancer Drug Discovery and Development. Tofilon PJ and Camphausen K:
Humana Press; Cham: pp. 1–34. 2017, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Murnyák B, Kouhsari MC, Hershkovitch R,
Kálmán B, Marko-Varga G, Klekner Á and Hortobágyi T: PARP1
expression and its correlation with survival is tumour molecular
subtype dependent in glioblastoma. Oncotarget. 8:46348–46362. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Chalmers AJ: Overcoming resistance of
glioblastoma to conventional cytotoxic therapies by the addition of
PARP inhibitors. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 10:520–533. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Hanna C, Kurian KM, Williams K, Watts C,
Jackson A, Carruthers R, Strathdee K, Cruickshank G, Dunn L,
Erridge S, et al: Pharmacokinetics, safety, and tolerability of
olaparib and temozolomide for recurrent glioblastoma: Results of
the Phase I OPARATIC trial. Neuro Oncol. 22:1840–1850. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Robins HI, Zhang P, Gilbert MR,
Chakravarti A, de Groot JF, Grimm SA, Wang F, Lieberman FS, Krauze
A, Trotti AM, et al: A randomized Phase I/II study of ABT-888 in
combination with temozoflomide in recurrent temozolomide resistant
glioblastoma: An NRG oncology RTOG group study. J Neurooncol.
126:309–316. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Baxter PA, Su JM, Onar-Thomas A, Billups
CA, Li XN, Poussaint TY, Smith ER, Thompson P, Adesina A, Ansell P,
et al: A Phase I/II study of veliparib (ABT-888) with radiation and
temozolomide in newly diagnosed diffuse pontine glioma: A pediatric
brain tumor consortium study. Neuro Oncol. 22:875–885. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 World Health Organi-zation
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Jo SH, Son MK, Koh HJ, Lee SM, Song IH,
Kim YO, Lee YS, Jeong KS, Kim WB, Park JW, et al: Control of
mitochondrial redox balance and cellular defense against oxidative
damage by mitochondrial NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase. J
Biol Chem. 276:16168–16176. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Lee SM, Koh HJ, Park DC, Song BJ, Huh TL
and Park JW: Cytosolic NADP(+)-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase
status modulates oxidative damage to cells. Free Radic Biol Med.
32:1185–1196. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Kim SY and Park JW: Cellular defense
against singlet oxygen-induced oxidative damage by cytosolic
NADP+-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase. Free Radic Res.
37:309–316. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Krell D, Assoku M, Galloway M, Mulholland
P, Tomlinson I and Bardella C: Screen for IDH1, IDH2, IDH3, D2HGDH
and L2HGDH mutations in glioblastoma. PLoS One. 6:e198682011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Arita H, Narita Y, Yoshida A, Hashimoto N,
Yoshimine T and Ichimura K: IDH1/2 mutation detection in gliomas.
Brain Tumor Pathol. 32:79–89. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Yan H, Parsons DW, Jin G, McLendon R,
Rasheed BA, Yuan W, Kos I, Batinic-Haberle I, Jones S, Riggins GJ,
et al: IDH1 and IDH2 mutations in gliomas. N Engl J Med.
360:765–773. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Capper D, Weissert S, Balss J, Habel A,
Meyer J, Jäger D, Ackermann U, Tessmer C, Korshunov A, Zentgraf H,
et al: Characterization of R132H mutation-specific IDH1 antibody
binding in brain tumors. Brain Pathol. 20:245–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Dang L, White DW, Gross S, Bennett BD,
Bittinger MA, Driggers EM, Fantin VR, Jang HG, Jin S, Keenan MC, et
al: Cancer-associated IDH1 mutations produce 2-hydroxyglutarate.
Nature. 462:739–744. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Xu W, Yang H, Liu Y, Yang Y, Wang P, Kim
SH, Ito S, Yang C, Wang P, Xiao MT, et al: Oncometabolite
2-hydroxyglutarate is a competitive inhibitor of
α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases. Cancer Cell. 19:17–30.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Lu C, Ward PS, Kapoor GS, Rohle D, Turcan
S, Abdel-Wahab O, Edwards CR, Khanin R, Figueroa ME, Melnick A, et
al: IDH mutation impairs histone demethylation and results in a
block to cell differentiation. Nature. 483:474–478. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Yalaza C, Ak H, Cagli MS, Ozgiray E, Atay
S and Aydin HH: R132H mutation in IDH1 gene is associated with
increased tumor HIF1-alpha and serum VEGF levels in primary
glioblastoma multiforme. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 47:362–364.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Flavahan WA, Drier Y, Liau BB, Gillespie
SM, Venteicher AS, Stemmer-Rachamimov AO, Suvà ML and Bernstein BE:
Insulator dysfunction and oncogene activation in IDH mutant
gliomas. Nature. 529:110–114. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Fu Y, Zheng S, Zheng Y, Huang R, An N,
Liang A and Hu C: Glioma derived isocitrate dehydrogenase-2
mutations induced up-regulation of HIF-1α and β-catenin signaling:
Possible impact on glioma cell metastasis and chemo-resistance. Int
J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:770–775. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Warburg O: On respiratory impairment in
cancer cells. Science. 124:269–270. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Stern R, Shuster S, Neudecker BA and
Formby B: Lactate stimulates fibroblast expression of hyaluronan
and CD44: The Warburg effect revisited. Exp Cell Res. 276:24–31.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Kroemer G and Pouyssegur J: Tumor cell
metabolism: Cancer's Achilles' heel. Cancer Cell. 13:472–482. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Saier MH Jr: Families of transmembrane
sugar transport proteins. Mol Microbiol. 35:699–710. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Scheepers A, Joost H and Schürmann A: The
glucose transporter families SGLT and GLUT: Molecular basis of
normal and aberrant function. JPEN J Parenter Enteral Nutr.
28:364–371. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Flavahan WA, Wu Q, Hitomi M, Rahim N, Kim
Y, Sloan AE, Weil RJ, Nakano I, Sarkaria JN, Stringer BW, et al:
Brain tumor initiating cells adapt to restricted nutrition through
preferential glucose uptake. Nat Neurosci. 16:1373–1382. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Libby CJ, Gc S, Benavides GA, Fisher JL,
Williford SE, Zhang S, Tran AN, Gordon ER, Jones AB, Tuy K, et al:
A role for GLUT3 in glioblastoma cell invasion that is not
recapitulated by GLUT1. Cell Adh Migr. 15:101–115. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Wolf A, Agnihotri S, Micallef J, Mukherjee
J, Sabha N, Cairns R, Hawkins C and Guha A: Hexokinase 2 is a key
mediator of aerobic glycolysis and promotes tumor growth in human
glioblastoma multiforme. J Exp Med. 208:313–326. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Vartanian A, Agnihotri S, Wilson MR,
Burrell KE, Tonge PD, Alamsahebpour A, Jalali S, Taccone MS,
Mansouri S, Golbourn B, et al: Targeting hexokinase 2 enhances
response to radio-chemotherapy in glioblastoma. Oncotarget.
7:69518–69535. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Pastorino JG, Shulga N and Hoek JB:
Mitochondrial binding of hexokinase II inhibits Bax-induced
cytochrome c release and apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:7610–7618.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Agnihotri S, Mansouri S, Burrell K, Li M,
Mamatjan Y, Liu J, Nejad R, Kumar S, Jalali S, Singh SK, et al:
Ketoconazole and posaconazole selectively target HK2-expressing
glioblastoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 25:844–855. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Harada K, Saheki S, Wada K and Tanaka T:
Purification of four pyruvate kinase isozymes of rats by affinity
elution chromatography. Biochim Biophys Acta. 524:327–339. 1978.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Verma H, Cholia RP, Kaur S, Dhiman M and
Mantha AK: A short review on cross-link between pyruvate kinase
(PKM2) and glioblastoma multiforme. Metab Brain Dis. 36:751–765.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Uyeda K: Pyruvate kinase. Encyclopedia of
Biological Chemistry. (2nd edition). Lennarz WJ and Lane MD:
Academic Press; Waltham: pp. 719–721. 2013, Available from:.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780123786302000530
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Mukherjee J, Phillips JJ, Zheng S, Wiencke
J, Ronen SM and Pieper RO: Pyruvate kinase M2 expression, but not
pyruvate kinase activity, is up-regulated in a grade-specific
manner in human glioma. PLoS One. 8:e576102013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Yang W, Xia Y, Hawke D, Li X, Liang J,
Xing D, Aldape K, Hunter T, Alfred Yung WK and Lu Z: PKM2
phosphorylates histone H3 and promotes gene transcription and
tumorigenesis. Cell. 150:685–696. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Jiang Y, Li X, Yang W, Hawke DH, Zheng Y,
Xia Y, Aldape K, Wei C, Guo F, Chen Y and Lu Z: PKM2 regulates
chromosome segregation and mitosis progression of tumor cells. Mol
Cell. 53:75–87. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Cholia RP, Dhiman M, Kumar R and Mantha
AK: Oxidative stress stimulates invasive potential in rat C6 and
human U-87 MG glioblastoma cells via activation and cross-talk
between PKM2, ENPP2 and APE1 enzymes. Metab Brain Dis.
33:1307–1326. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Liang J, Cao R, Wang X, Zhang Y, Wang P,
Gao H, Li C, Yang F, Zeng R, Wei P, et al: Mitochondrial PKM2
regulates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by stabilizing Bcl2.
Cell Res. 27:329–351. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Yang W, Xia Y, Ji H, Zheng Y, Liang J,
Huang W, Gao X, Aldape K and Lu Z: Nuclear PKM2 regulates β-catenin
transactivation upon EGFR activation. Nature. 480:118–122. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Chaneton B and Gottlieb E: Rocking cell
metabolism: Revised functions of the key glycolytic regulator PKM2
in cancer. Trends Biochem Sci. 37:309–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Sizemore ST, Zhang M, Cho JH, Sizemore GM,
Hurwitz B, Kaur B, Lehman NL, Ostrowski MC, Robe PA, Miao W, et al:
Pyruvate kinase M2 regulates homologous recombination-mediated DNA
double-strand break repair. Cell Res. 28:1090–1102. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Rieger J, Bähr O, Maurer GD, Hattingen E,
Franz K, Brucker D, Walenta S, Kämmerer U, Coy JF, Weller M and
Steinbach JP: ERGO: A pilot study of ketogenic diet in recurrent
glioblastoma. Int J Oncol. 44:1843–1852. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Kucharzewska P, Christianson HC and
Belting M: Global profiling of metabolic adaptation to hypoxic
stress in human glioblastoma cells. PLoS One. 10:e01167402015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Ogunrinu TA and Sontheimer H: Hypoxia
increases the dependence of glioma cells on glutathione. J Biol
Chem. 285:37716–37724. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Robertson DS: The physical chemistry of
brain and neural cell membranes: An overview. Neurochem Res.
35:681–687. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Newsholme P, Lima MMR, Procopio J,
Pithon-Curi TC, Doi SQ, Bazotte RB and Curi R: Glutamine and
glutamate as vital metabolites. Braz J Med Biol Res. 36:153–163.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Bak LK, Schousboe A and Waagepetersen HS:
The glutamate/GABA-glutamine cycle: Aspects of transport,
neurotransmitter homeostasis and ammonia transfer. J Neurochem.
98:641–653. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Obara-Michlewska M and Szeliga M:
Targeting glutamine addiction in gliomas. Cancers (Basel).
12:3102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Michalak KP, Maćkowska-Kędziora A,
Sobolewski B and Woźniak P: Key roles of glutamine pathways in
reprogramming the cancer metabolism. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2015:9643212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Rubin H: Deprivation of glutamine in cell
culture reveals its potential for treating cancer. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 116:6964–6968. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Ekici S, Nye JA, Neill SG, Allen JW, Shu
HK and Fleischer CC: Glutamine imaging: A new avenue for glioma
management. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 43:11–18. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
de Groot JF, Liu TJ, Fuller G and Yung
WKA: The excitatory amino acid transporter-2 induces apoptosis and
decreases glioma growth in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res.
65:1934–1940. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Lyons SA, Chung WJ, Weaver AK, Ogunrinu T
and Sontheimer H: Autocrine glutamate signaling promotes glioma
cell invasion. Cancer Res. 67:9463–9471. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Dranoff G, Elion GB, Friedman HS and
Bigner DD: Combination chemotherapy in vitro exploiting glutamine
metabolism of human glioma and medulloblastoma. Cancer Res.
45:4082–4086. 1985.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Seltzer MJ, Bennett BD, Joshi AD, Gao P,
Thomas AG, Ferraris DV, Tsukamoto T, Rojas CJ, Slusher BS,
Rabinowitz JD, et al: Inhibition of glutaminase preferentially
slows growth of glioma cells with mutant IDH1. Cancer Res.
70:8981–8987. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Majewska E, Márquez J, Albrecht J and
Szeliga M: Transfection with GLS2 glutaminase (GAB) sensitizes
human glioblastoma cell lines to oxidative stress by a common
mechanism involving suppression of the PI3K/AKT pathway. Cancers
(Basel). 11:1152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Szeliga M, Obara-Michlewska M, Matyja E,
Łazarczyk M, Lobo C, Hilgier W, Alonso FJ, Márquez J and Albrecht
J: Transfection with liver-type glutaminase cDNA alters gene
expression and reduces survival, migration and proliferation of
T98G glioma cells. Glia. 57:1014–1023. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Szeliga M, Zgrzywa A, Obara-Michlewska M
and Albrecht J: Transfection of a human glioblastoma cell line with
liver-type glutaminase (LGA) down-regulates the expression of
DNA-repair gene MGMT and sensitizes the cells to alkylating agents.
J Neurochem. 123:428–436. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Yin Y, Sun W, Xiang J, Deng L, Zhang B,
Xie P, Qiao W, Zou J and Liu C: Glutamine synthetase functions as a
negative growth regulator in glioma. J Neurooncol. 114:59–69. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Ye ZC, Rothstein JD and Sontheimer H:
Compromised glutamate transport in human glioma cells:
Reduction-mislocalization of sodium-dependent glutamate
transporters and enhanced activity of cystine-glutamate exchange. J
Neurosci. 19:10767–10777. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Chung WJ, Lyons SA, Nelson GM, Hamza H,
Gladson CL, Gillespie GY and Sontheimer H: Inhibition of cystine
uptake disrupts the growth of primary brain tumors. J Neurosci.
25:7101–7110. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Robe PA, Martin DH, Nguyen-Khac MT, Artesi
M, Deprez M, Albert A, Vanbelle S, Califice S, Bredel M and Bours
V: Early termination of ISRCTN45828668, a phase 1/2 prospective,
randomized study of sulfasalazine for the treatment of progressing
malignant gliomas in adults. BMC Cancer. 9:3722009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Sleire L, Skeie BS, Netland IA, Førde HE,
Dodoo E, Selheim F, Leiss L, Heggdal JI, Pedersen PH, Wang J and
Enger PØ: Drug repurposing: Sulfasalazine sensitizes gliomas to
gamma knife radiosurgery by blocking cystine uptake through system
Xc-, leading to glutathione depletion. Oncogene. 34:5951–5959.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Choi YK and Park KG: Targeting glutamine
metabolism for cancer treatment. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 26:19–28.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Morris SM Jr: Enzymes of arginine
metabolism. J Nutr. 134 (Suppl 10):2743S–2747S. 2765S–2767S. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Kuo MT, Savaraj N and Feun LG: Targeted
cellular metabolism for cancer chemotherapy with recombinant
arginine-degrading enzymes. Oncotarget. 1:246–251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Khoury O, Ghazale N, Stone E, El-Sibai M,
Frankel AE and Abi-Habib RJ: Human recombinant arginase I
(Co)-PEG5000 [HuArgI (Co)-PEG5000]-induced arginine depletion is
selectively cytotoxic to human glioblastoma cells. J Neurooncol.
122:75–85. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Choy CT, Wong CH and Loong HHF: Low
expressions of ASS1 and OTC in glioblastoma suggest the potential
clinical use of recombinant human arginase (rhArg). J Neurooncol.
129:579–581. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Bobak Y, Kurlishchuk Y,
Vynnytska-Myronovska B, Grydzuk O, Shuvayeva G, Redowicz MJ,
Kunz-Schughart LA and Stasyk O: Arginine deprivation induces
endoplasmic reticulum stress in human solid cancer cells. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 70:29–38. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Pavlyk I, Rzhepetskyy Y, Jagielski AK,
Drozak J, Wasik A, Pereverzieva G, Olchowik M, Kunz-Schugart LA,
Stasyk O and Redowicz MJ: Arginine deprivation affects glioblastoma
cell adhesion, invasiveness and actin cytoskeleton organization by
impairment of β-actin arginylation. Amino Acids. 47:199–212. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Stasyk OV, Boretsky YR, Gonchar MV and
Sibirny AA: Recombinant arginine-degrading enzymes in metabolic
anticancer therapy and bioanalytics. Cell Biol Int. 39:246–252.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Stone EM, Chantranupong L and Georgiou G:
The second-shell metal ligands of human arginase affect
coordination of the nucleophile and substrate. Biochemistry.
49:10582–10588. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Al-Koussa H, Al-Haddad M, Abi-Habib R and
El-Sibai M: Human recombinant arginase I [HuArgI
(Co)-PEG5000]-induced arginine depletion inhibits colorectal cancer
cell migration and invasion. Int J Mol Sci. 20:60182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Khalil N and Abi-Habib RJ: [HuArgI
(co)-PEG5000]-induced arginine deprivation leads to autophagy
dependent cell death in pancreatic cancer cells. Invest New Drugs.
38:1236–1246. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Tanios R, Bekdash A, Kassab E, Stone E,
Georgiou G, Frankel AE and Abi-Habib RJ: Human recombinant arginase
I(Co)-PEG5000 [HuArgI(Co)-PEG5000]-induced arginine depletion is
selectively cytotoxic to human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Leuk
Res. 37:1565–1571. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Nasreddine G, El-Sibai M and Abi-Habib RJ:
Cytotoxicity of [HuArgI (co)-PEG5000]-induced arginine deprivation
to ovarian cancer cells is autophagy dependent. Invest New Drugs.
38:10–19. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Glazer ES, Stone EM, Zhu C, Massey KL,
Hamir AN and Curley SA: Bioengineered human arginase I with
enhanced activity and stability controls hepatocellular and
pancreatic carcinoma xenografts. Transl Oncol. 4:138–146. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Yoon CY, Sung DJ, Lee JH, Kim AR, Oh CW,
Je JH, Weon BM, Seol SK, Pyun A, Hwu Y, et al: Imaging of renal and
prostate carcinoma with refractive index radiology. Int J Urol.
14:96–103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Hsueh EC, Knebel SM, Lo WH, Leung YC,
Cheng PNM and Hsueh CT: Deprivation of arginine by recombinant
human arginase in prostate cancer cells. J Hematol Oncol. 5:172012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Wang Z, Shi X, Li Y, Fan J, Zeng X, Xian
Z, Wang Z, Sun Y, Wang S, Song P, et al: Blocking autophagy
enhanced cytotoxicity induced by recombinant human arginase in
triple-negative breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e15632014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Hou X, Chen S, Zhang P, Guo D and Wang B:
Targeted arginine metabolism therapy: A dilemma in glioma
treatment. Front Oncol. 12:9388472022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Arita H, Narita Y, Fukushima S, Tateishi
K, Matsushita Y, Yoshida A, Miyakita Y, Ohno M, Collins VP,
Kawahara N, et al: Upregulating mutations in the TERT promoter
commonly occur in adult malignant gliomas and are strongly
associated with total 1p19q loss. Acta Neuropathol. 126:267–276.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Nonoguchi N, Ohta T, Oh JE, Kim YH,
Kleihues P and Ohgaki H: TERT promoter mutations in primary and
secondary glioblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 126:931–937. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Killela PJ, Reitman ZJ, Jiao Y, Bettegowda
C, Agrawal N, Diaz LA Jr, Friedman AH, Friedman H, Gallia GL,
Giovanella BC, et al: TERT promoter mutations occur frequently in
gliomas and a subset of tumors derived from cells with low rates of
self-renewal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:6021–6066. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Arita H, Yamasaki K, Matsushita Y,
Nakamura T, Shimokawa A, Takami H, Tanaka S, Mukasa A, Shirahata M,
Shimizu S, et al: A combination of TERT promoter mutation and MGMT
methylation status predicts clinically relevant subgroups of newly
diagnosed glioblastomas. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 4:792016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Kikuchi Z, Shibahara I, Yamaki T, Yoshioka
E, Shofuda T, Ohe R, Matsuda KI, Saito R, Kanamori M, Kanemura Y,
et al: TERT promoter mutation associated with multifocal phenotype
and poor prognosis in patients with IDH wild-type glioblastoma.
Neurooncol Adv. 2:vdaa1142020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Vuong HG, Nguyen TQ, Ngo TNM, Nguyen HC,
Fung KM and Dunn IF: The interaction between TERT promoter mutation
and MGMT promoter methylation on overall survival of glioma
patients: A meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 20:8972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Patel B, Taiwo R, Kim AH and Dunn GP:
TERT, a promoter of CNS malignancies. Neurooncol Adv.
2:vdaa0252020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Picketts DJ, Higgs DR, Bachoo S, Blake DJ,
Quarrell OW and Gibbons RJ: ATRX encodes a novel member of the SNF2
family of proteins: Mutations point to a common mechanism
underlying the ATR-X syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 5:1899–1907. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Jiao Y, Killela PJ, Reitman ZJ, Rasheed
BA, Heaphy CM, de Wilde RF, Rodriguez FJ, Rosemberg S, Oba-Shinjo
SM, Nagahashi Marie SK, et al: Frequent ATRX, CIC, FUBP1 and IDH1
mutations refine the classification of malignant gliomas.
Oncotarget. 3:709–722. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Koschmann C, Calinescu AA, Nunez FJ,
Mackay A, Fazal-Salom J, Thomas D, Mendez F, Kamran N, Dzaman M,
Mulpuri L, et al: ATRX loss promotes tumor growth and impairs
nonhomologous end joining DNA repair in glioma. Sci Transl Med.
8:328ra282016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
do Carmo A, Balça-Silva J, Matias D and
Lopes MC: PKC signaling in glioblastoma. Cancer Biol Ther.
14:287–294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Steinberg SF: Structural basis of protein
kinase C isoform function. Physiol Rev. 88:1341–1378. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Leirdal M and Sioud M: Protein kinase
Calpha isoform regulates the activation of the MAP kinase ERK1/2 in
human glioma cells: Involvement in cell survival and gene
expression. Mol Cell Biol Res Commun. 4:106–110. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Marquina-Sánchez B, González-Jorge J,
Hansberg-Pastor V, Wegman-Ostrosky T, Baranda-Ávila N, Mejía-Pérez
S, Camacho-Arroyo I and González-Arenas A: The interplay between
intracellular progesterone receptor and PKC plays a key role in
migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cells. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 172:198–206. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Valdés-Rives SA, Arcos-Montoya D, de la
Fuente-Granada M, Zamora-Sánchez CJ, Arias-Romero LE, Villamar-Cruz
O, Camacho-Arroyo I, Pérez-Tapia SM and González-Arenas A: LPA1
receptor promotes progesterone receptor phosphorylation through
PKCα in human glioblastoma cells. Cells. 10:8072021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Yoshiji H, Kuriyama S, Ways DK, Yoshii J,
Miyamoto Y, Kawata M, Ikenaka Y, Tsujinoue H, Nakatani T, Shibuya M
and Fukui H: Protein kinase C lies on the signaling pathway for
vascular endothelial growth factor-mediated tumor development and
angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 59:4413–4418. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Liu Z, Wei Y, Zhang L, Yee PP, Johnson M,
Zhang X, Gulley M, Atkinson JM, Trebak M, Wang HG and Li W:
Induction of store-operated calcium entry (SOCE) suppresses
glioblastoma growth by inhibiting the Hippo pathway transcriptional
coactivators YAP/TAZ. Oncogene. 38:120–139. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Chen Z, Forman LW, Williams RM and Faller
DV: Protein kinase C-δ inactivation inhibits the proliferation and
survival of cancer stem cells in culture and in vivo. BMC Cancer.
14:902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Kim MJ, Kim RK, Yoon CH, An S, Hwang SG,
Suh Y, Park MJ, Chung HY, Kim IG and Lee SJ: Importance of PKCδ
signaling in fractionated-radiation-induced expansion of
glioma-initiating cells and resistance to cancer treatment. J Cell
Sci. 124:3084–3094. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Sarkar S and Yong VW: Reduction of protein
kinase C delta attenuates tenascin-C stimulated glioma invasion in
three-dimensional matrix. Carcinogenesis. 31:311–317. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Lu J, Xu Z, Duan H, Ji H, Zhen Z, Li B,
Wang H, Tang H, Zhou J, Guo T, et al: Tumor-associated macrophage
interleukin-β promotes glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
activation, glycolysis and tumorigenesis in glioma cells. Cancer
Sci. 111:1979–1990. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Sharif TR and Sharif M: Overexpression of
protein kinase C epsilon in astroglial brain tumor derived cell
lines and primary tumor samples. Int J Oncol. 15:237–243.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Okhrimenko H, Lu W, Xiang C, Hamburger N,
Kazimirsky G and Brodie C: Protein kinase C-epsilon regulates the
apoptosis and survival of glioma cells. Cancer Res. 65:7301–7309.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Besson A, Davy A, Robbins SM and Yong VW:
Differential activation of ERKs to focal adhesions by PKC epsilon
is required for PMA-induced adhesion and migration of human glioma
cells. Oncogene. 20:7398–7407. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Besson A, Wilson TL and Yong VW: The
anchoring protein RACK1 links protein kinase cepsilon to integrin
beta chains. Requirements for adhesion and motility. J Biol Chem.
277:22073–22084. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Aeder SE, Martin PM, Soh JW and Hussaini
IM: PKC-eta mediates glioblastoma cell proliferation through the
Akt and mTOR signaling pathways. Oncogene. 23:9062–9069. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Uht RM, Amos S, Martin PM, Riggan AE and
Hussaini IM: The protein kinase C-eta isoform induces proliferation
in glioblastoma cell lines through an ERK/Elk-1 pathway. Oncogene.
26:2885–2893. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Hussaini IM, Carpenter JE, Redpath GT,
Sando JJ, Shaffrey ME and Vandenberg SR: Protein kinase C-eta
regulates resistance to UV- and gamma-irradiation-induced apoptosis
in glioblastoma cells by preventing caspase-9 activation. Neuro
Oncol. 4:9–21. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Phillips E, Lang V, Bohlen J, Bethke F,
Puccio L, Tichy D, Herold-Mende C, Hielscher T, Lichter P and
Goidts V: Targeting atypical protein kinase C iota reduces
viability in glioblastoma stem-like cells via a notch signaling
mechanism. Int J Cancer. 139:1776–1787. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Guo H, Gu F, Li W, Zhang B, Niu R, Fu L,
Zhang N and Ma Y: Reduction of protein kinase C zeta inhibits
migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cells. J Neurochem.
109:203–213. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Baldwin RM, Parolin DA and Lorimer IA:
Regulation of glioblastoma cell invasion by PKC iota and RhoB.
Oncogene. 27:3587–3595. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Odia Y, Iwamoto FM, Moustakas A, Fraum TJ,
Salgado CA, Li A, Kreisl TN, Sul J, Butman JA and Fine HA: A Phase
II trial of enzastaurin (LY317615) in combination with bevacizumab
in adults with recurrent malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol.
127:127–135. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Sevastre AS, Costachi A, Tataranu LG,
Brandusa C, Artene SA, Stovicek O, Alexandru O, Danoiu S, Sfredel V
and Dricu A: Glioblastoma pharmacotherapy: A multifaceted
perspective of conventional and emerging treatments (review). Exp
Ther Med. 22:14082021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Johnson BE, Mazor T, Hong C, Barnes M,
Aihara K, McLean CY, Fouse SD, Yamamoto S, Ueda H, Tatsuno K, et
al: Mutational analysis reveals the origin and therapy-driven
evolution of recurrent glioma. Science. 343:189–193. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Stieber D, Golebiewska A, Evers L,
Lenkiewicz E, Brons NHC, Nicot N, Oudin A, Bougnaud S, Hertel F,
Bjerkvig R, et al: Glioblastomas are composed of genetically
divergent clones with distinct tumourigenic potential and variable
stem cell-associated phenotypes. Acta Neuropathol. 127:203–219.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Neftel C, Laffy J, Filbin MG, Hara T,
Shore ME, Rahme GJ, Richman AR, Silverbush D, Shaw ML, Hebert CM,
et al: An integrative model of cellular states, plasticity, and
genetics for glioblastoma. Cell. 178:835–849.e21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Trapnell C, Williams BA, Pertea G,
Mortazavi A, Kwan G, van Baren MJ, Salzberg SL, Wold BJ and Pachter
L: Transcript assembly and quantification by RNA-Seq reveals
unannotated transcripts and isoform switching during cell
differentiation. Nat Biotechnol. 28:511–515. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Lauko A, Lo A, Ahluwalia MS and Lathia JD:
Cancer cell heterogeneity and plasticity in glioblastoma and brain
tumors. Semin Cancer Biol. 82:162–175. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Snuderl M, Fazlollahi L, Le LP, Nitta M,
Zhelyazkova BH, Davidson CJ, Akhavanfard S, Cahill DP, Aldape KD,
Betensky RA, et al: Mosaic amplification of multiple receptor
tyrosine kinase genes in glioblastoma. Cancer Cell. 20:810–817.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Nobusawa S, Lachuer J, Wierinckx A, Kim
YH, Huang J, Legras C, Kleihues P and Ohgaki H: Intratumoral
patterns of genomic imbalance in glioblastomas. Brain Pathol.
20:936–944. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Kumar A, Boyle EA, Tokita M, Mikheev AM,
Sanger MC, Girard E, Silber JR, Gonzalez-Cuyar LF, Hiatt JB, Adey
A, et al: Deep sequencing of multiple regions of glial tumors
reveals spatial heterogeneity for mutations in clinically relevant
genes. Genome Biol. 15:5302014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
222
|
Bhaduri A, Di Lullo E, Jung D, Müller S,
Crouch EE, Espinosa CS, Ozawa T, Alvarado B, Spatazza J, Cadwell
CR, et al: Outer radial glia-like cancer stem cells contribute to
heterogeneity of glioblastoma. Cell Stem Cell. 26:48–63.e6. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Pang B, Xu J, Hu J, Guo F, Wan L, Cheng M
and Pang L: Single-cell RNA-seq reveals the invasive trajectory and
molecular cascades underlying glioblastoma progression. Mol Oncol.
13:2588–2603. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Jacob F, Salinas RD, Zhang DY, Nguyen PTT,
Schnoll JG, Wong SZH, Thokala R, Sheikh S, Saxena D, Prokop S, et
al: A patient-derived glioblastoma organoid model and biobank
recapitulates inter- and intra-tumoral heterogeneity. Cell.
180:188–204.e22. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Iwadate Y: Plasticity in glioma stem cell
phenotype and its therapeutic implication. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo).
58:61–70. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Koso H, Takeda H, Yew CCK, Ward JM, Nariai
N, Ueno K, Nagasaki M, Watanabe S, Rust AG, Adams DJ, et al:
Transposon mutagenesis identifies genes that transform neural stem
cells into glioma-initiating cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
109:E2998–E3007. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Wang X, Prager BC, Wu Q, Kim LJY, Gimple
RC, Shi Y, Yang K, Morton AR, Zhou W, Zhu Z, et al: Reciprocal
signaling between glioblastoma stem cells and differentiated tumor
cells promotes malignant progression. Cell Stem Cell.
22:514–528.e5. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Hsu JF, Chu SM, Liao CC, Wang CJ, Wang YS,
Lai MY, Wang HC, Huang HR and Tsai MH: Nanotechnology and
nanocarrier-based drug delivery as the potential therapeutic
strategy for glioblastoma multiforme: An update. Cancers (Basel).
13:1952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Lathia JD, Heddleston JM, Venere M and
Rich JN: Deadly teamwork: Neural cancer stem cells and the tumor
microenvironment. Cell Stem Cell. 8:482–485. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Yuan X, Curtin J, Xiong Y, Liu G,
Waschsmann-Hogiu S, Farkas DL, Black KL and Yu JS: Isolation of
cancer stem cells from adult glioblastoma multiforme. Oncogene.
23:9392–9400. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Brescia P, Ortensi B, Fornasari L, Levi D,
Broggi G and Pelicci G: CD133 is essential for glioblastoma stem
cell maintenance. Stem Cells. 31:857–869. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Carlsson SK, Brothers SP and Wahlestedt C:
Emerging treatment strategies for glioblastoma multiforme. EMBO Mol
Med. 6:1359–1370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Nusse R: Wnt signaling and stem cell
control. Cell Res. 18:523–527. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Sareddy GR, Kesanakurti D, Kirti PB and
Babu PP: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac and
celecoxib attenuates Wnt/β-catenin/Tcf signaling pathway in human
glioblastoma cells. Neurochem Res. 38:2313–2322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Yu JB, Jiang H and Zhan RY: Aberrant Notch
signaling in glioblastoma stem cells contributes to tumor
recurrence and invasion. Mol Med Rep. 14:1263–1268. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Shih IM and Wang TL: Notch signaling,
gamma-secretase inhibitors, and cancer therapy. Cancer Res.
67:1879–1882. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
de la Iglesia N, Puram SV and Bonni A:
STAT3 regulation of glioblastoma pathogenesis. Curr Mol Med.
9:580–590. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Porporato PE, Filigheddu N, Pedro JMBS,
Kroemer G and Galluzzi L: Mitochondrial metabolism and cancer. Cell
Res. 28:265–280. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Sighel D, Notarangelo M, Aibara S, Re A,
Ricci G, Guida M, Soldano A, Adami V, Ambrosini C, Broso F, et al:
Inhibition of mitochondrial translation suppresses glioblastoma
stem cell growth. Cell Rep. 35:1090242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Mai TT, Hamaï A, Hienzsch A, Cañeque T,
Müller S, Wicinski J, Cabaud O, Leroy C, David A, Acevedo V, et al:
Salinomycin kills cancer stem cells by sequestering iron in
lysosomes. Nat Chem. 9:1025–1033. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Sharifzad F, Ghavami S, Verdi J, Mardpour
S, Mollapour Sisakht M, Azizi Z, Taghikhani A, Łos MJ, Fakharian E,
Ebrahimi M and Hamidieh AA: Glioblastoma cancer stem cell biology:
Potential theranostic targets. Drug Resist Updat. 42:35–45. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Saunders NR, Dreifuss JJ, Dziegielewska
KM, Johansson PA, Habgood MD, Møllgård K and Bauer HC: The rights
and wrongs of blood-brain barrier permeability studies: A walk
through 100 years of history. Front Neurosci. 8:4042014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Daneman R and Prat A: The blood-brain
barrier. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 7:a0204122015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Liebner S, Fischmann A, Rascher G, Duffner
F, Grote EH, Kalbacher H and Wolburg H: Claudin-1 and claudin-5
expression and tight junction morphology are altered in blood
vessels of human glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neuropathol.
100:323–331. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
245
|
Wolburg H, Wolburg-Buchholz K, Kraus J,
Rascher-Eggstein G, Liebner S, Hamm S, Duffner F, Grote EH, Risau W
and Engelhardt B: Localization of claudin-3 in tight junctions of
the blood-brain barrier is selectively lost during experimental
autoimmune encephalomyelitis and human glioblastoma multiforme.
Acta Neuropathol. 105:586–592. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Ishihara H, Kubota H, Lindberg RLP,
Leppert D, Gloor SM, Errede M, Virgintino D, Fontana A, Yonekawa Y
and Frei K: Endothelial cell barrier impairment induced by
glioblastomas and transforming growth factor beta2 involves matrix
metalloproteinases and tight junction proteins. J Neuropathol Exp
Neurol. 67:435–448. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
247
|
Rama AR, Alvarez PJ, Madeddu R and Aranega
A: ABC transporters as differentiation markers in glioblastoma
cells. Mol Biol Rep. 41:4847–4851. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Lockman PR, Mittapalli RK, Taskar KS,
Rudraraju V, Gril B, Bohn KA, Adkins CE, Roberts A, Thorsheim HR,
Gaasch JA, et al: Heterogeneous blood-tumor barrier permeability
determines drug efficacy in experimental brain metastases of breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 16:5664–5678. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Taskar KS, Rudraraju V, Mittapalli RK,
Samala R, Thorsheim HR, Lockman J, Gril B, Hua E, Palmieri D, Polli
JW, et al: Lapatinib distribution in HER2 overexpressing
experimental brain metastases of breast cancer. Pharm Res.
29:770–781. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Tiwary S, Morales JE, Kwiatkowski SC, Lang
FF, Rao G and McCarty JH: Metastatic brain tumors disrupt the
blood-brain barrier and alter lipid metabolism by inhibiting
expression of the endothelial cell fatty acid transporter Mfsd2a.
Sci Rep. 8:82672018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
251
|
Elmeliegy MA, Carcaboso AM, Tagen M, Bai F
and Stewart CF: Role of ATP-binding cassette and solute carrier
transporters in erlotinib CNS penetration and intracellular
accumulation. Clin Cancer Res. 17:89–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
de Vries NA, Buckle T, Zhao J, Beijnen JH,
Schellens JHM and van Tellingen O: Restricted brain penetration of
the tyrosine kinase inhibitor erlotinib due to the drug
transporters P-gp and BCRP. Invest New Drugs. 30:443–449. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Oberoi RK, Mittapalli RK and Elmquist WF:
Pharmacokinetic assessment of efflux transport in sunitinib
distribution to the brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 347:755–764. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Lin F, de Gooijer MC, Roig EM, Buil LCM,
Christner SM, Beumer JH, Würdinger T, Beijnen JH and van Tellingen
O: ABCB1, ABCG2, and PTEN determine the response of glioblastoma to
temozolomide and ABT-888 therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 20:2703–2713.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
de Gooijer MC, de Vries NA, Buckle T, Buil
LCM, Beijnen JH, Boogerd W and van Tellingen O: Improved brain
penetration and antitumor efficacy of temozolomide by inhibition of
ABCB1 and ABCG2. Neoplasia. 20:710–720. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Choi YH and Yu AM: ABC transporters in
multidrug resistance and pharmacokinetics, and strategies for drug
development. Curr Pharm Des. 20:793–807. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Tran S, DeGiovanni PJ, Piel B and Rai P:
Cancer nanomedicine: A review of recent success in drug delivery.
Clin Transl Med. 6:442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
Sun T, Zhang YS, Pang B, Hyun DC, Yang M
and Xia Y: Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer
therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 53:12320–12364. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
259
|
Budama-Kilinc Y, Kecel-Gunduz S, Cakir-Koc
R, Aslan B, Bicak B, Kokcu Y, Ozel AE and Akyuz S: Structural
characterization and drug delivery system of natural
growth-modulating peptide against glioblastoma cancer. Int J Pept
Res Ther. 27:2015–2028. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
260
|
Pasut G: Grand challenges in nano-based
drug delivery. Front Med Technol. 1:12019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
261
|
Ambruosi A, Gelperina S, Khalansky A,
Tanski S, Theisen A and Kreuter J: Influence of surfactants,
polymer and doxorubicin loading on the anti-tumour effect of
poly(butyl cyanoacrylate) nanoparticles in a rat glioma model. J
Microencapsul. 23:582–592. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Caraway CA, Gaitsch H, Wicks EE, Kalluri
A, Kunadi N and Tyler BM: Polymeric nanoparticles in brain cancer
therapy: A review of current approaches. Polymers (Basel).
14:29632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Ramalho MJ, Sevin E, Gosselet F, Lima J,
Coelho MAN, Loureiro JA and Pereira MC: Receptor-mediated PLGA
nanoparticles for glioblastoma multiforme treatment. Int J Pharm.
545:84–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Kuang Y, Jiang X, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Ma H, Guo
Y, Zhang Y, An S, Li J, Liu L, et al: Dual functional
peptide-driven nanoparticles for highly efficient glioma-targeting
and drug codelivery. Mol Pharm. 13:1599–1607. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Mathew EN, Berry BC, Yang HW, Carroll RS
and Johnson MD: Delivering therapeutics to glioblastoma: Overcoming
biological constraints. Int J Mol Sci. 23:17112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Wei KC, Chu PC, Wang HYJ, Huang CY, Chen
PY, Tsai HC, Lu YJ, Lee PY, Tseng IC, Feng LY, et al: Focused
ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening to enhance
temozolomide delivery for glioblastoma treatment: A preclinical
study. PLoS One. 8:e589952013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Treat LH, McDannold N, Vykhodtseva N,
Zhang Y, Tam K and Hynynen K: Targeted delivery of doxorubicin to
the rat brain at therapeutic levels using MRI-guided focused
ultrasound. Int J Cancer. 121:901–907. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Coluccia D, Figueiredo CA, Wu MY,
Riemenschneider AN, Diaz R, Luck A, Smith C, Das S, Ackerley C,
O'Reilly M, et al: Enhancing glioblastoma treatment using
cisplatin-gold-nanoparticle conjugates and targeted delivery with
magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound. Nanomedicine.
14:1137–1148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Timbie KF, Mead BP and Price RJ: Drug and
gene delivery across the blood-brain barrier with focused
ultrasound. J Control Release. 219:61–75. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Burgess A, Shah K, Hough O and Hynynen K:
Focused ultrasound-mediated drug delivery through the blood-brain
barrier. Expert Rev Neurother. 15:477–491. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Dutta D, Heo I and Clevers H: Disease
modeling in stem cell-derived 3D organoid systems. Trends Mol Med.
23:393–410. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Nishida N, Yano H, Nishida T, Kamura T and
Kojiro M: Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc Health Risk Manag.
2:213–219. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Hillen F and Griffioen AW: Tumour
vascularization: Sprouting angiogenesis and beyond. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 26:489–502. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
274
|
Joseph JV, Conroy S, Pavlov K, Sontakke P,
Tomar T, Eggens-Meijer E, Balasubramaniyan V, Wagemakers M, den
Dunnen WF and Kruyt FA: Hypoxia enhances migration and invasion in
glioblastoma by promoting a mesenchymal shift mediated by the
HIF1α-ZEB1 axis. Cancer Lett. 359:107–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
275
|
Huang W, Ding X, Ye H, Wang J, Shao J and
Huang T: Hypoxia enhances the migration and invasion of human
glioblastoma U87 cells through PI3K/Akt/mTOR/HIF-1α pathway.
Neuroreport. 29:1578–1585. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
276
|
Chen JWE, Lumibao J, Blazek A, Gaskins HR
and Harley B: Hypoxia activates enhanced invasive potential and
endogenous hyaluronic acid production by glioblastoma cells.
Biomater Sci. 6:854–862. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
277
|
Rosa P, Catacuzzeno L, Sforna L, Mangino
G, Carlomagno S, Mincione G, Petrozza V, Ragona G, Franciolini F
and Calogero A: BK channels blockage inhibits hypoxia-induced
migration and chemoresistance to cisplatin in human glioblastoma
cells. J Cell Physiol. 233:6866–6877. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Velásquez C, Mansouri S, Gutiérrez O,
Mamatjan Y, Mollinedo P, Karimi S, Singh O, Terán N, Martino J,
Zadeh G and Fernández-Luna JL: Hypoxia can induce migration of
glioblastoma cells through a methylation-dependent control of ODZ1
gene expression. Front Oncol. 9:10362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Huang S, Michalek JE, Reardon DA, Wen PY,
Floyd JR, Fox PT, Clarke GD, Jerabek PA, Schmainda KM, Muzi M, et
al: Assessment of tumor hypoxia and perfusion in recurrent
glioblastoma following bevacizumab failure using MRI and 18F-FMISO
PET. Sci Rep. 11:76322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
280
|
Chédeville AL and Madureira PA: The role
of hypoxia in glioblastoma radiotherapy resistance. Cancers
(Basel). 13:5422021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
281
|
Zhou W, Ke SQ, Huang Z, Flavahan W, Fang
X, Paul J, Wu L, Sloan AE, McLendon RE, Li X, et al: Periostin
secreted by glioblastoma stem cells recruits M2 tumour-associated
macrophages and promotes malignant growth. Nat Cell Biol.
17:170–182. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
282
|
Wei J, Barr J, Kong LY, Wang Y, Wu A,
Sharma AK, Gumin J, Henry V, Colman H, Priebe W, et al:
Glioblastoma cancer-initiating cells inhibit T-cell proliferation
and effector responses by the signal transducers and activators of
transcription 3 pathway. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:67–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
283
|
Yang F, He Z, Duan H, Zhang D, Li J, Yang
H, Dorsey JF, Zou W, Nabavizadeh SA, Bagley SJ, et al: Synergistic
immunotherapy of glioblastoma by dual targeting of IL-6 and CD40.
Nat Commun. 12:34242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
284
|
Banyer JL, Hamilton NH, Ramshaw IA and
Ramsay AJ: Cytokines in innate and adaptive immunity. Rev
Immunogenet. 2:359–373. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
285
|
Conlon KC, Miljkovic MD and Waldmann TA:
Cytokines in the treatment of cancer. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
39:6–21. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
286
|
Zhu VF, Yang J, Lebrun DG and Li M:
Understanding the role of cytokines in glioblastoma multiforme
pathogenesis. Cancer Lett. 316:139–150. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
287
|
Wakabayashi T, Kayama T, Nishikawa R,
Takahashi H, Hashimoto N, Takahashi J, Aoki T, Sugiyama K, Ogura M,
Natsume A and Yoshida J: A multicenter Phase I trial of combination
therapy with interferon-β and temozolomide for high-grade gliomas
(INTEGRA study): The final report. J Neurooncol. 104:573–577. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
288
|
Han MH, Kim JM, Cheong JH, Ryu JI, Won YD,
Nam GH and Kim CH: Efficacy of cytokine-induced killer cell
immunotherapy for patients with pathologically pure glioblastoma.
Front Oncol. 12:8516282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
289
|
Iwami K, Natsume A and Wakabayashi T:
Cytokine therapy of gliomas. Prog Neurol Surg. 32:79–89. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
290
|
Xu S, Tang L, Li X, Fan F and Liu Z:
Immunotherapy for glioma: Current management and future
application. Cancer Lett. 476:1–12. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
291
|
Zhang Y and Zhang Z: The history and
advances in cancer immunotherapy: Understanding the characteristics
of tumor-infiltrating immune cells and their therapeutic
implications. Cell Mol Immunol. 17:807–821. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
292
|
de Mello RA, Veloso AF, Esrom Catarina P,
Nadine S and Antoniou G: Potential role of immunotherapy in
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 10:21–30.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
293
|
Dine J, Gordon R, Shames Y, Kasler MK and
Barton-Burke M: Immune checkpoint inhibitors: An innovation in
immunotherapy for the treatment and management of patients with
cancer. Asia Pac J Oncol Nurs. 4:127–135. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
294
|
Mpakali A and Stratikos E: The role of
antigen processing and presentation in cancer and the efficacy of
immune checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Cancers (Basel).
13:1342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
295
|
Wang J, Toregrosa-Allen S, Elzey BD,
Utturkar S, Lanman NA, Bernal-Crespo V, Behymer MM, Knipp GT, Yun
Y, Veronesi MC, et al: Multispecific targeting of glioblastoma with
tumor microenvironment-responsive multifunctional engineered NK
cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21075071182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
296
|
Rosenberg SA, Restifo NP, Yang JC, Morgan
RA and Dudley ME: Adoptive cell transfer: A clinical path to
effective cancer immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 8:299–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
297
|
Redeker A and Arens R: Improving adoptive
T cell therapy: The particular role of T cell costimulation,
cytokines, and post-transfer vaccination. Front Immunol. 7:3452016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
298
|
Chruściel E, Urban-Wójciuk Z, Arcimowicz
Ł, Kurkowiak M, Kowalski J, Gliwiński M, Marjański T, Rzyman W,
Biernat W, Dziadziuszko R, et al: Adoptive cell therapy-harnessing
antigen-specific T cells to target solid tumours. Cancers (Basel).
12:6832020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
299
|
Staquicini FI, Smith TL, Tang FHF,
Gelovani JG, Giordano RJ, Libutti SK, Sidman RL, Cavenee WK, Arap W
and Pasqualini R: Targeted AAVP-based therapy in a mouse model of
human glioblastoma: A comparison of cytotoxic versus suicide gene
delivery strategies. Cancer Gene Ther. 27:301–310. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
300
|
Vigneswaran K, Neill S and Hadjipanayis
CG: Beyond the World Health Organization grading of infiltrating
gliomas: Advances in the molecular genetics of glioma
classification. Ann Transl Med. 3:952015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
301
|
Goodwin CR, Rath P, Oyinlade O, Lopez H,
Mughal S, Xia S, Xia S, Li Y, Kaur H, Zhou X, et al: Crizotinib and
erlotinib inhibits growth of c-Met+/EGFRvIII+
primary human glioblastoma xenografts. Clin Neurol Neurosurg.
171:26–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
302
|
Sestito S, Runfola M, Tonelli M, Chiellini
G and Rapposelli S: New multitarget approaches in the War against
glioblastoma: A mini-perspective. Front Pharmacol. 9:8742018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
303
|
Lang F, Liu Y, Chou FJ and Yang C:
Genotoxic therapy and resistance mechanism in gliomas. Pharmacol
Ther. 228:1079222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
304
|
Lassman AB, Pugh SL, Gilbert MR, Aldape
KD, Geinoz S, Beumer JH, Christner SM, Komaki R, DeAngelis LM, Gaur
R, et al: Phase 2 trial of dasatinib in target-selected patients
with recurrent glioblastoma (RTOG 0627). Neuro Oncol. 17:992–998.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
305
|
Baratta MG: Glioblastoma is ‘hot’ for
personalized vaccines. Nat Rev Cancer. 19:1292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
306
|
Wiwatchaitawee K, Quarterman JC, Geary SM
and Salem AK: Enhancement of therapies for glioblastoma (GBM) using
nanoparticle-based delivery systems. AAPS PharmSciTech. 22:712021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
307
|
Pearson JRD, Cuzzubbo S, McArthur S,
Durrant LG, Adhikaree J, Tinsley CJ, Pockley AG and McArdle SEB:
Immune escape in glioblastoma multiforme and the adaptation of
immunotherapies for treatment. Front Immunol. 11:5821062020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
308
|
Burger MC, Zhang C, Harter PN, Romanski A,
Strassheimer F, Senft C, Tonn T, Steinbach JP and Wels WS:
CAR-engineered NK cells for the treatment of glioblastoma: Turning
innate effectors into precision tools for cancer immunotherapy.
Front Immunol. 10:26832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
309
|
Granzin M, Wagner J, Köhl U, Cerwenka A,
Huppert V and Ullrich E: Shaping of natural killer cell antitumor
activity by ex vivo cultivation. Front Immunol. 8:4582017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
310
|
Yu MW and Quail DF: Immunotherapy for
glioblastoma: Current progress and challenges. Front Immunol.
12:6763012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
311
|
Dietrich J, Rao K, Pastorino S and Kesari
S: Corticosteroids in brain cancer patients: Benefits and pitfalls.
Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 4:233–242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
312
|
Koyama S, Akbay EA, Li YY, Herter-Sprie
GS, Buczkowski KA, Richards WG, Gandhi L, Redig AJ, Rodig SJ,
Asahina H, et al: Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade
is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints.
Nat Commun. 7:105012016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
313
|
Chan HY, Choi J, Jackson C and Lim M:
Combination immunotherapy strategies for glioblastoma. J
Neurooncol. 151:375–391. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
314
|
Bausart M, Préat V and Malfanti A:
Immunotherapy for glioblastoma: The promise of combination
strategies. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:352022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
315
|
Oh T, Sayegh ET, Fakurnejad S, Oyon D,
Lamano JB, DiDomenico JD, Bloch O and Parsa AT: Vaccine therapies
in malignant glioma. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 15:5082015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
316
|
Hollingsworth RE and Jansen K: Turning the
corner on therapeutic cancer vaccines. NPJ Vaccines. 4:72019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
317
|
Liu J, Fu M, Wang M, Wan D, Wei Y and Wei
X: Cancer vaccines as promising immuno-therapeutics: Platforms and
current progress. J Hematol Oncol. 15:282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
318
|
Keskin DB, Anandappa AJ, Sun J, Tirosh I,
Mathewson ND, Li S, Oliveira G, Giobbie-Hurder A, Felt K, Gjini E,
et al: Neoantigen vaccine generates intratumoral T cell responses
in Phase Ib glioblastoma trial. Nature. 565:234–239. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
319
|
Hilf N, Kuttruff-Coqui S, Frenzel K, Bukur
V, Stevanović S, Gouttefangeas C, Platten M, Tabatabai G, Dutoit V,
van der Burg SH, et al: Actively personalized vaccination trial for
newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Nature. 565:240–245. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
320
|
Inc. AB, . AIVITA biomedical's phase 2
glioblastoma trial shows improved progression free survival. [cited
2022 Aug 5]. Available from:. https://www.prnewswire.com/news-releases/aivita-biomedicals-phase-2-glioblastoma-trial-shows-improved-progression-free-survival-301307757.html
|
|
321
|
Burkhardt JK, Riina H, Shin BJ, Christos
P, Kesavabhotla K, Hofstetter CP, Tsiouris AJ and Boockvar JA:
Intra-arterial delivery of bevacizumab after blood-brain barrier
disruption for the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma:
Progression-free survival and overall survival. World Neurosurg.
77:130–134. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
322
|
Patel AP, Tirosh I, Trombetta JJ, Shalek
AK, Gillespie SM, Wakimoto H, Cahill DP, Nahed BV, Curry WT,
Martuza RL, et al: Single-cell RNA-seq highlights intratumoral
heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma. Science. 344:1396–1401.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
323
|
Wang Q, Hu B, Hu X, Kim H, Squatrito M,
Scarpace L, deCarvalho AC, Lyu S, Li P, Li Y, et al: Tumor
evolution of glioma-intrinsic gene expression subtypes associates
with immunological changes in the microenvironment. Cancer Cell.
32:42–56.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
324
|
Petroni G, Buqué A, Zitvogel L, Kroemer G
and Galluzzi L: Immunomodulation by targeted anticancer agents.
Cancer Cell. 39:310–345. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
325
|
Song Y, Fu Y, Xie Q, Zhu B, Wang J and
Zhang B: Anti-angiogenic agents in combination with immune
checkpoint inhibitors: A promising strategy for cancer treatment.
Front Immunol. 11:19562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
326
|
Selek L, Seigneuret E, Nugue G, Wion D,
Nissou MF, Salon C, Seurin MJ, Carozzo C, Ponce F, Roger T and
Berger F: Imaging and histological characterization of a human
brain xenograft in pig: The first induced glioma model in a large
animal. J Neurosci Methods. 221:159–165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
327
|
Khoshnevis M, Carozzo C, Bonnefont-Rebeix
C, Belluco S, Leveneur O, Chuzel T, Pillet-Michelland E, Dreyfus M,
Roger T, Berger F and Ponce F: Development of induced glioblastoma
by implantation of a human xenograft in Yucatan minipig as a large
animal model. J Neurosci Methods. 282:61–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
328
|
Tora MS, Texakalidis P, Neill S, Wetzel J,
Rindler RS, Hardcastle N, Nagarajan PP, Krasnopeyev A, Roach C,
James R, et al: Lentiviral vector induced modeling of high-grade
spinal cord glioma in minipigs. Sci Rep. 10:52912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
329
|
Khoshnevis M, Carozzo C, Brown R, Bardiès
M, Bonnefont-Rebeix C, Belluco S, Nennig C, Marcon L, Tillement O,
Gehan H, et al: Feasibility of intratumoral 165Holmium siloxane
delivery to induced U87 glioblastoma in a large animal model, the
Yucatan minipig. PLoS One. 15:e02347722020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
330
|
Hicks WH, Bird CE, Pernik MN, Haider AS,
Dobariya A, Abdullah KG, Aoun SG, Bentley RT, Cohen-Gadol AA,
Bachoo RM, et al: Large animal models of glioma: Current status and
future prospects. Anticancer Res. 41:5343–5353. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
331
|
Zhao CY, Cheng R, Yang Z and Tian ZM:
Nanotechnology for cancer therapy based on chemotherapy. Molecules.
23:8262018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
332
|
Zaimy MA, Saffarzadeh N, Mohammadi A,
Pourghadamyari H, Izadi P, Sarli A, Moghaddam LK, Paschepari SR,
Azizi H, Torkamandi S and Tavakkoly-Bazzaz J: New methods in the
diagnosis of cancer and gene therapy of cancer based on
nanoparticles. Cancer Gene Ther. 24:233–243. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
333
|
Geletneky K, Hajda J, Angelova AL, Leuchs
B, Capper D, Bartsch AJ, Neumann JO, Schöning T, Hüsing J, Beelte
B, et al: Oncolytic H-1 parvovirus shows safety and signs of
immunogenic activity in a first Phase I/IIa glioblastoma trial. Mol
Ther. 25:2620–2634. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
334
|
Angelova AL, Barf M, Geletneky K,
Unterberg A and Rommelaere J: Immunotherapeutic potential of
oncolytic H-1 parvovirus: Hints of glioblastoma microenvironment
conversion towards immunogenicity. Viruses. 9:3822017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
335
|
Suryawanshi YR and Schulze AJ: Oncolytic
viruses for malignant glioma: On the verge of success? Viruses.
13:12942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
336
|
Li J, Wang W, Wang J, Cao Y, Wang S and
Zhao J: Viral gene therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: A promising
hope for the current dilemma. Front Oncol. 11:6782262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
337
|
Clement PMJ, Dirven L, Eoli M,
Sepulveda-Sanchez JM, Walenkamp AME, Frenel JS, Franceschi E,
Weller M, Chinot O, De Vos FYFL, et al: Impact of depatuxizumab
mafodotin on health-related quality of life and neurological
functioning in the Phase II EORTC 1410/INTELLANCE 2 trial for
EGFR-amplified recurrent glioblastoma. Eur J Cancer. 147:1–12.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
338
|
Sathornsumetee S, Desjardins A,
Vredenburgh JJ, McLendon RE, Marcello J, Herndon JE, Mathe A,
Hamilton M, Rich JN, Norfleet JA, et al: Phase II trial of
bevacizumab and erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant
glioma. Neuro Oncol. 12:1300–1310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
339
|
Mellinghoff IK, Wang MY, Vivanco I,
Haas-Kogan DA, Zhu S, Dia EQ, Lu KV, Yoshimoto K, Huang JH, Chute
DJ, et al: Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas
to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N Engl J Med. 353:2012–2024. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
340
|
Raizer JJ, Abrey LE, Lassman AB, Chang SM,
Lamborn KR, Kuhn JG, Yung WK, Gilbert MR, Aldape KD, Wen PY, et al:
A Phase I trial of erlotinib in patients with nonprogressive
glioblastoma multiforme postradiation therapy, and recurrent
malignant gliomas and meningiomas. Neuro Oncol. 12:87–94. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
341
|
Lucas JT Jr, Knapp BJ, Uh J, Hua CH,
Merchant TE, Hwang SN, Patay Z and Broniscer A: Posttreatment
DSC-MRI is predictive of early treatment failure in children with
supratentorial high-grade glioma treated with erlotinib. Clin
Neuroradiol. 28:393–400. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
342
|
Prados MD, Chang SM, Butowski N, DeBoer R,
Parvataneni R, Carliner H, Kabuubi P, Ayers-Ringler J, Rabbitt J,
Page M, et al: Phase II study of erlotinib plus temozolomide during
and after radiation therapy in patients with newly diagnosed
glioblastoma multiforme or gliosarcoma. J Clin Oncol. 27:579–54.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
343
|
Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Bady P, Kamoshima Y,
Kouwenhoven MCM, Delorenzi M, Lambiv WL, Hamou MF, Matter MS, Koch
A, et al: Pathway analysis of glioblastoma tissue after
preoperative treatment with the EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor
gefitinib-a Phase II trial. Mol Cancer Ther. 10:1102–1112. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
344
|
Wang Y, Liang D, Chen J, Chen H, Fan R,
Gao Y, Gao Y, Tao R and Zhang H: Targeted therapy with anlotinib
for a patient with an oncogenic FGFR3-TACC3 fusion and recurrent
glioblastoma. Oncologist. 26:173–177. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
345
|
Hainsworth JD, Ervin T, Friedman E, Priego
V, Murphy PB, Clark BL and Lamar RE: Concurrent radiotherapy and
temozolomide followed by temozolomide and sorafenib in the
first-line treatment of patients with glioblastoma multiforme.
Cancer. 116:3663–3669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
346
|
Shahid S, Kushner BH, Modak S, Basu EM,
Rubin EM, Gundem G, Papaemmanuil E and Roberts SS: Association of
BRAF V600E mutations with vasoactive intestinal peptide syndrome in
MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 68:e292652021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
347
|
Rahman MA, Brekke J, Arnesen V, Hannisdal
MH, Navarro AG, Waha A, Herfindal L, Rygh CB, Bratland E, Brandal
P, et al: Sequential bortezomib and temozolomide treatment promotes
immunological responses in glioblastoma patients with positive
clinical outcomes: A phase 1B study. Immun Inflamm Dis. 8:342–359.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
348
|
Morin A, Soane C, Pierce A, Sanford B,
Jones KL, Crespo M, Zahedi S, Vibhakar R and Mulcahy Levy JM:
Proteasome inhibition as a therapeutic approach in atypical
teratoid/rhabdoid tumors. Neurooncol Adv. 2:vdaa0512020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
349
|
Gupta SK, Kizilbash SH, Carlson BL, Mladek
AC, Boakye-Agyeman F, Bakken KK, Pokorny JL, Schroeder MA, Decker
PA, Cen L, et al: Delineation of MGMT hypermethylation as a
biomarker for veliparib-mediated temozolomide-sensitizing therapy
of glioblastoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 108:djv3692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
350
|
Xiong Y, Guo Y, Liu Y, Wang H, Gong W, Liu
Y, Wang X, Gao Y, Yu F, Su D, et al: Pamiparib is a potent and
selective PARP inhibitor with unique potential for the treatment of
brain tumor. Neoplasia. 22:431–440. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
351
|
Lowery MA, Burris HA III, Janku F, Shroff
RT, Cleary JM, Azad NS, Goyal L, Maher EA, Gore L, Hollebecque A,
et al: Safety and activity of ivosidenib in patients with
IDH1-mutant advanced cholangiocarcinoma: A phase 1 study. Lancet
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:711–720. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
352
|
DiNardo CD, Hochhaus A, Frattini MG, Yee
K, Zander T, Krämer A, Chen X, Ji Y, Parikh N, Choi J and Wei AH: A
phase 1 study of IDH305 in patients with IDH1R132-mutant acute
myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndrome. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. Mar 30–2022.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
353
|
Penas-Prado M, Hess KR, Fisch MJ, Lagrone
LW, Groves MD, Levin VA, De Groot JF, Puduvalli VK, Colman H,
Volas-Redd G, et al: Randomized Phase II adjuvant factorial study
of dose-dense temozolomide alone and in combination with
isotretinoin, celecoxib, and/or thalidomide for glioblastoma. Neuro
Oncol. 17:266–273. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
354
|
Kesari S, Schiff D, Henson JW, Muzikansky
A, Gigas DC, Doherty L, Batchelor TT, Longtine JA, Ligon KL, Weaver
S, et al: Phase II study of temozolomide, thalidomide, and
celecoxib for newly diagnosed glioblastoma in adults. Neuro Oncol.
10:300–308. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
355
|
Halatsch ME, Dwucet A, Schmidt CJ,
Mühlnickel J, Heiland T, Zeiler K, Siegelin MD, Kast RE and
Karpel-Massler G: In vitro and clinical compassionate use
experiences with the drug-repurposing approach CUSP9v3 in
glioblastoma. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 14:12412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
356
|
Morgan RA, Johnson LA, Davis JL, Zheng Z,
Woolard KD, Reap EA, Feldman SA, Chinnasamy N, Kuan CT, Song H, et
al: Recognition of glioma stem cells by genetically modified T
cells targeting EGFRvIII and development of adoptive cell therapy
for glioma. Hum Gene Ther. 23:1043–1053. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
357
|
Liau LM, Ashkan K, Tran DD, Campian JL,
Trusheim JE, Cobbs CS, Heth JA, Salacz M, Taylor S, D'Andre SD, et
al: First results on survival from a large Phase 3 clinical trial
of an autologous dendritic cell vaccine in newly diagnosed
glioblastoma. J Transl Med. 16:1422018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
358
|
Weller M, Butowski N, Tran DD, Recht LD,
Lim M, Hirte H, Ashby L, Mechtler L, Goldlust SA, Iwamoto F, et al:
Rindopepimut with temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed,
EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ACT IV): A randomised,
double-blind, international phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol.
18:1373–1385. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
359
|
Reardon DA, Desjardins A, Vredenburgh JJ,
O'Rourke DM, Tran DD, Fink KL, Nabors LB, Li G, Bota DA, Lukas RV,
et al: Rindopepimut with bevacizumab for patients with relapsed
EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ReACT): Results of a double-blind
randomized Phase II trial. Clin Cancer Res. 26:1586–1594. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|