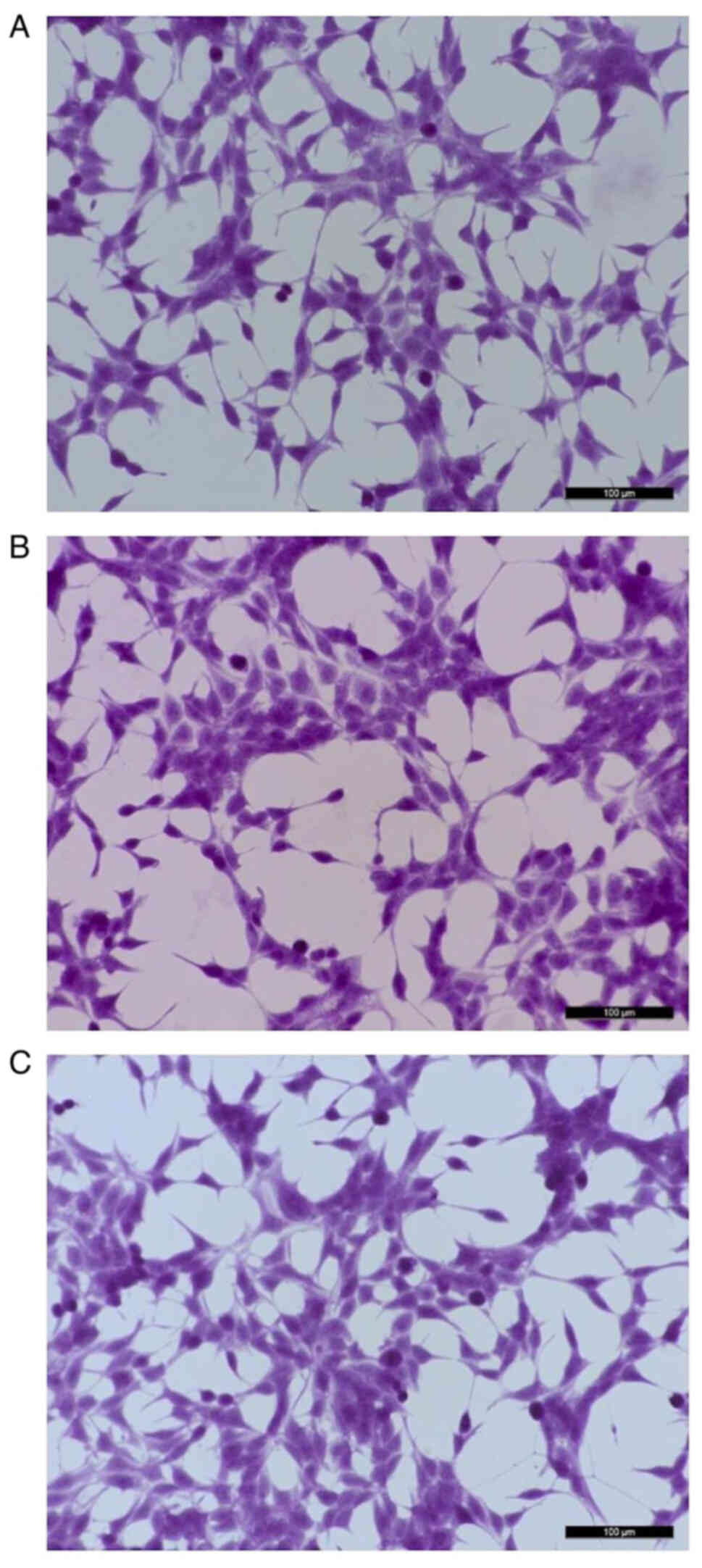
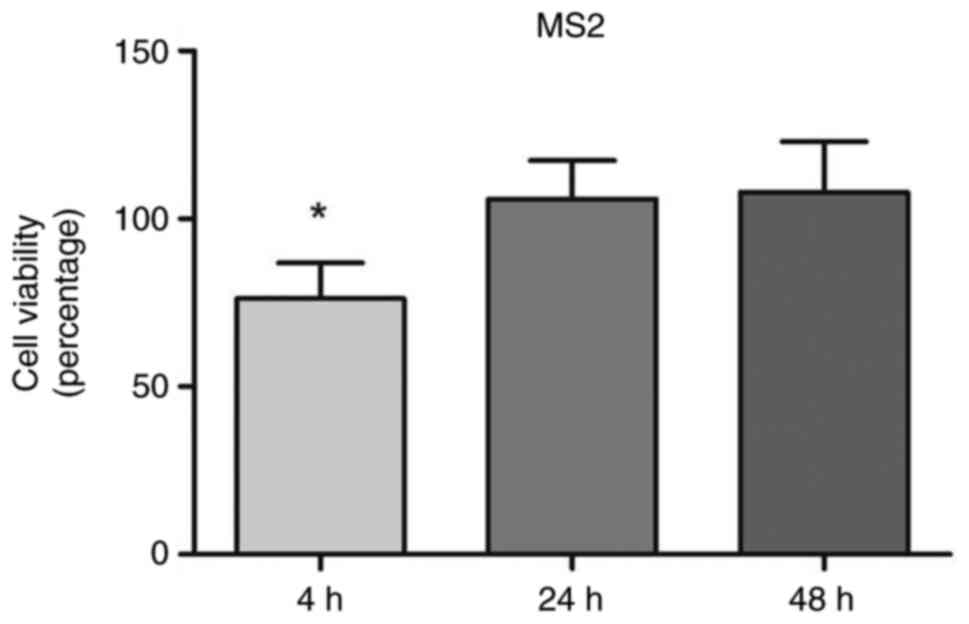
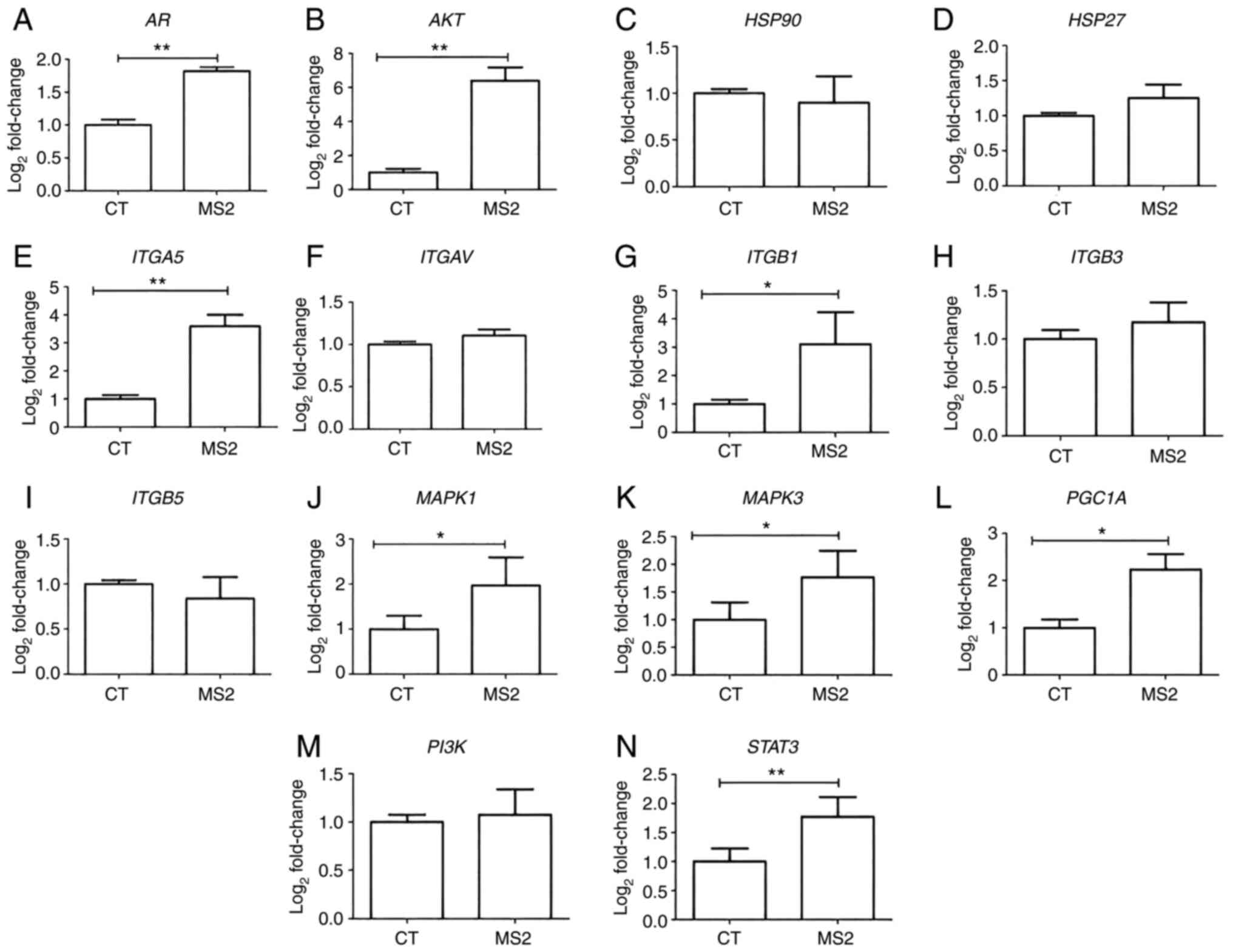
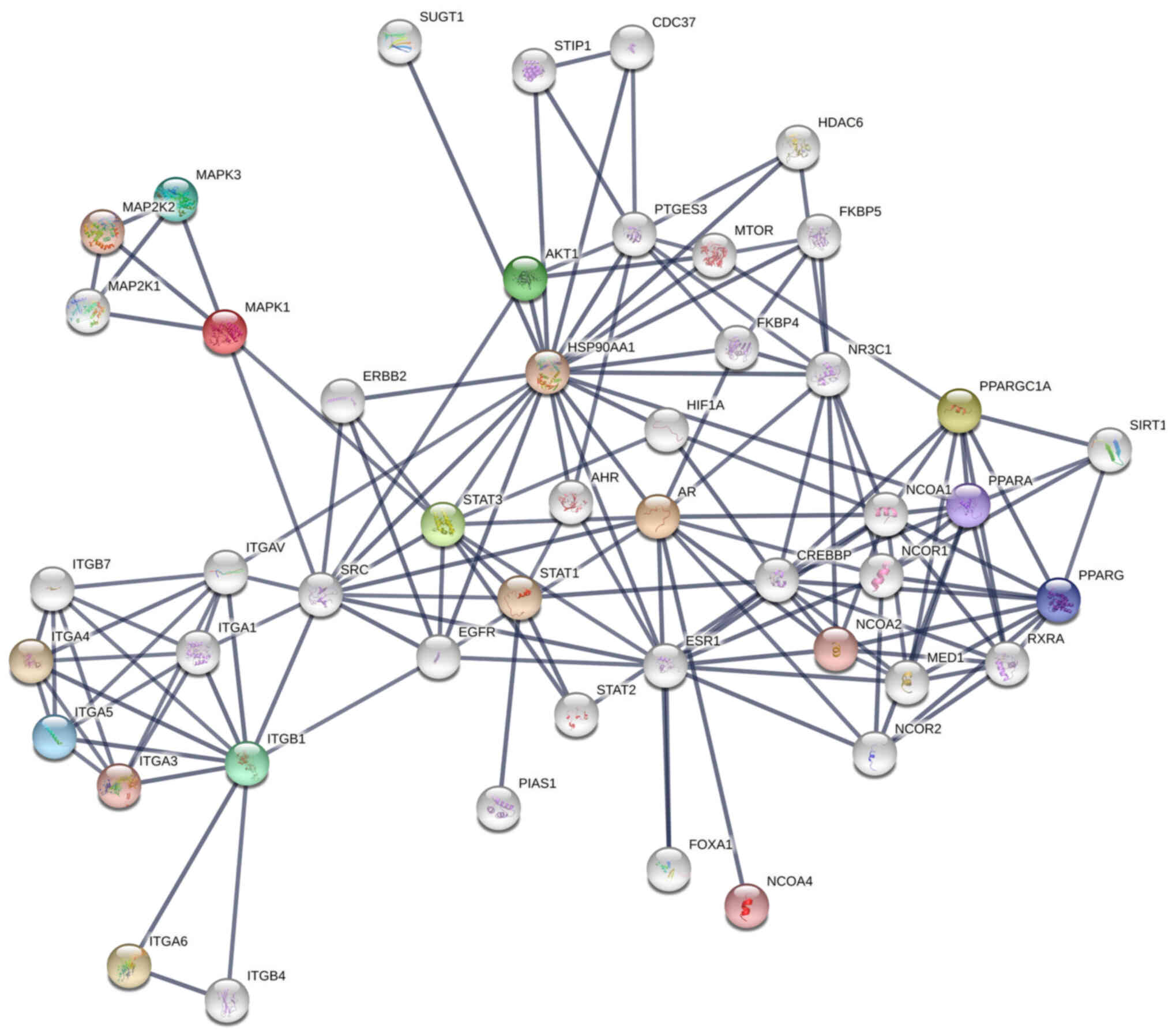
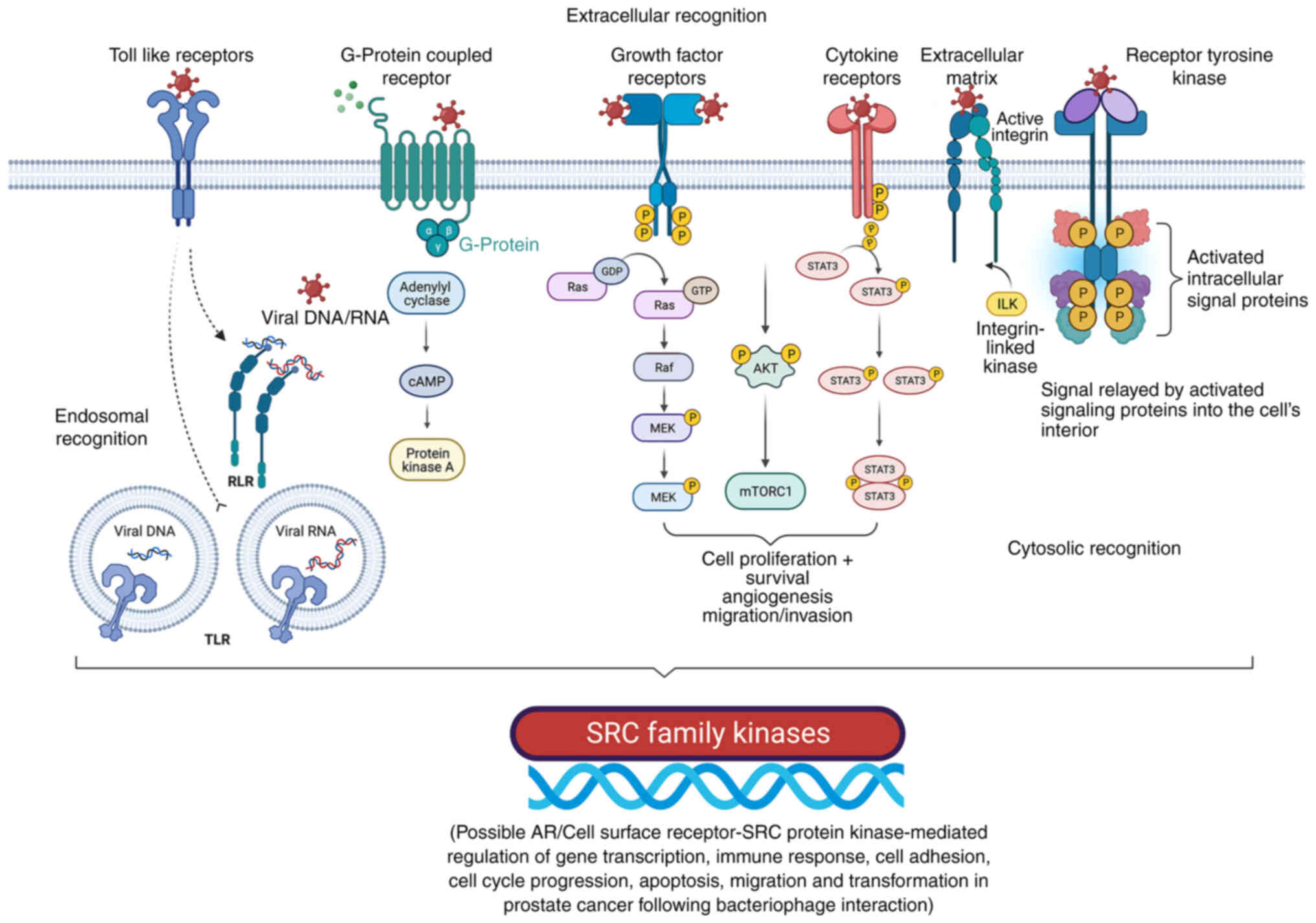
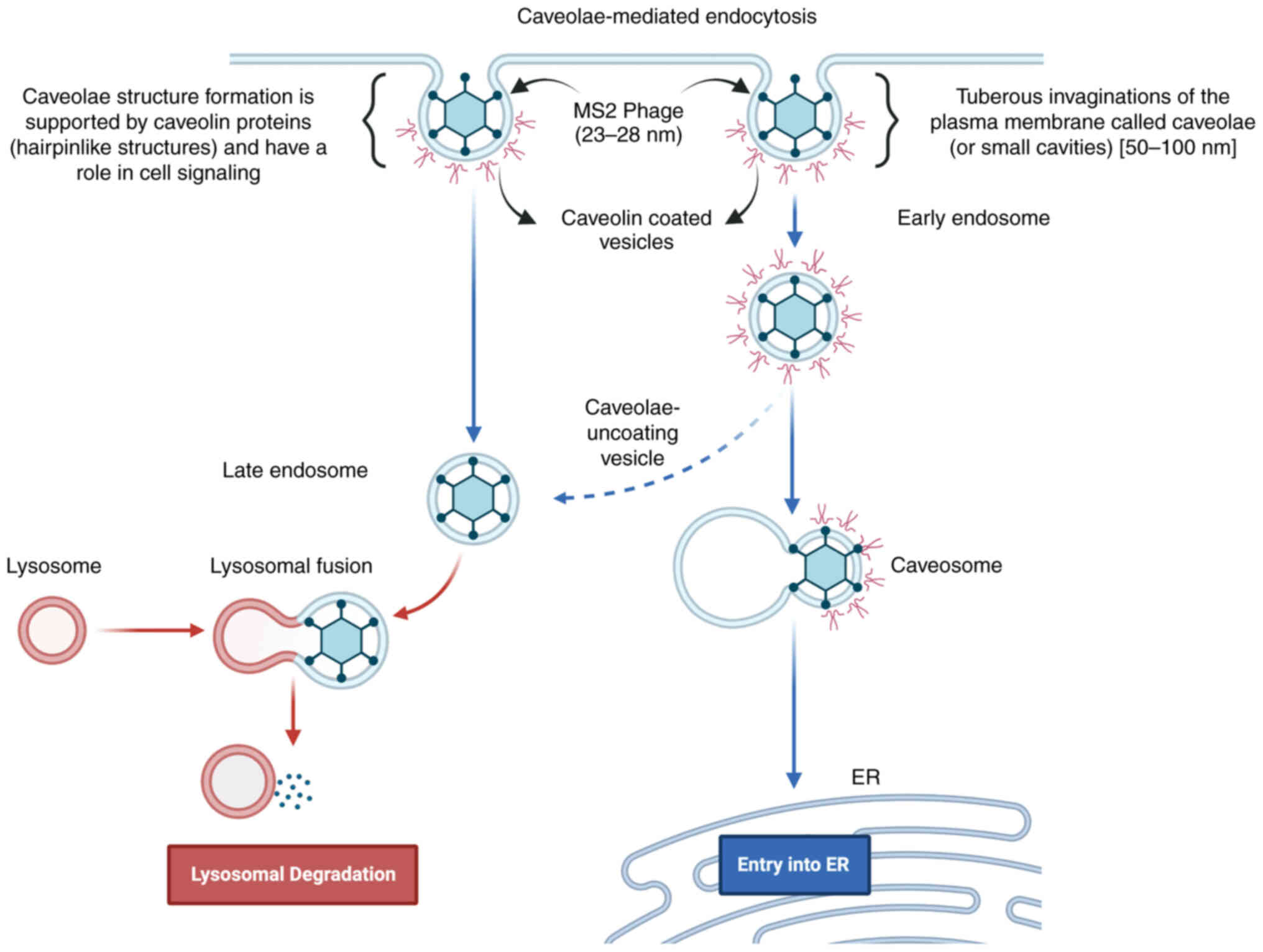
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:7–33. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sakr WA, Grignon DJ, Crissman JD, Heilbrun
LK, Cassin BJ, Pontes JJ and Haas GP: High grade prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN) and prostatic adenocarcinoma
between the ages of 20–69: An autopsy study of 249 cases. In Vivo.
8:439–443. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Nelson WG, De Marzo AM and Isaacs WB:
Prostate cancer. N Engl J Med. 349:366–381. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nuhn P, De Bono JS, Fizazi K, Freedland
SJ, Grilli M, Kantoff PW, Sonpavde G, Sternberg CN,
Yegnasubramanian S and Antonarakis ES: Update on systemic prostate
cancer therapies: Management of metastatic castration-resistant
prostate cancer in the era of precision oncology. Eur Urol.
75:88–99. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sumanasuriya S and De Bono J: Treatment of
advanced prostate cancer-a review of current therapies and future
promise. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 8:a0306352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Barquilha CN, Santos NJ, Monção CCD,
Barbosa IC, Lima FO, Justulin LA, Pértega-Gomes N and Felisbino SL:
Sulfiredoxin as a potential therapeutic target for advanced and
metastatic prostate cancer. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020:21485622020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Przystal JM, Waramit S, Pranjol MZI, Yan
W, Chu G, Chongchai A, Samarth G, Olaciregui NG, Tabatabai G,
Carcaboso AM, et al: Efficacy of systemic temozolomide-activated
phage-targeted gene therapy in human glioblastoma. EMBO Mol Med.
11:e84922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ren S, Fengyu Zuo S, Zhao M, Wang X, Wang
X, Chen Y, Wu Z and Ren Z: Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis in lung
cancer by T4 phage surface displaying mVEGFR2 vaccine. Vaccine.
29:5802–5811. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shadidi M, Sørensen D, Dybwad A, Furset G
and Sioud M: Mucosal vaccination with phage-displayed tumour
antigens identified through proteomics-based strategy inhibits the
growth and metastasis of 4T1 breast adenocarcinoma. Int J Oncol.
32:241–247. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ashley CE, Carnes EC, Phillips GK, Durfee
PN, Buley MD, Lino CA, Padilla DP, Phillips B, Carter MB, Willman
CL, et al: Cell-specific delivery of diverse cargos by
bacteriophage MS2 virus-like particles. ACS Nano. 5:5729–5745.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Aanei IL, ElSohly AM, Farkas ME,
Netirojjanakul C, Regan M, Taylor Murphy S, O'Neil JP, Seo Y and
Francis MB: Biodistribution of antibody-MS2 viral capsid conjugates
in breast cancer models. Mol Pharm. 13:3764–3772. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li J, Sun Y, Jia T, Zhang R, Zhang K and
Wang L: Messenger RNA vaccine based on recombinant MS2 virus-like
particles against prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 134:1683–1694.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhai L, Yadav R, Kunda NK, Anderson D,
Bruckner E, Miller EK, Basu R, Muttil P and Tumban E: Oral
immunization with bacteriophage MS2-L2 VLPs protects against oral
and genital infection with multiple HPV types associated with head
& neck cancers and cervical cancer. Antiviral Res. 166:56–65.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lino CA, Caldeira JC and Peabody DS:
Display of single-chain variable fragments on bacteriophage MS2
virus-like particles. J Nanobiotechnology. 15:132017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chang L, Wang G, Jia T, Zhang L, Li Y, Han
Y, Zhang K, Lin G, Zhang R, Li J and Wang L: Armored long
non-coding RNA MEG3 targeting EGFR based on recombinant MS2
bacteriophage virus-like particles against hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:23988–24004. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Briolay T, Petithomme T, Fouet M,
Nguyen-Pham N, Blanquart C and Boisgerault N: Delivery of cancer
therapies by synthetic and bio-inspired nanovectors. Mol Cancer.
20:552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kolesanova EF, Melnikova MV, Bolshakova
TN, Rybalkina EY and Sivov IG: Bacteriophage MS2 as a tool for
targeted delivery in solid tumor chemotherapy. Acta Naturae.
11:98–101. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sanmukh SG and Felisbino SL:
Bacteriophages in cancer biology and therapies. Clin Oncol.
2:12952017.
|
|
20
|
Sanmukh SG, Dos Santos SAA and Felisbino
SL: Natural bacteriophages T4 and M13 down-regulates Hsp90 gene
expression in human prostate cancer cells (PC-3) representing a
potential nanoparticle against cancer. Virol Res J. 1:21–23.
2017.
|
|
21
|
Sanmukh SG and Felisbino SL: Development
of pipette tip gap closure migration assay (s-ARU method) for
studying semi-adherent cell lines. Cytotechnology. 70:1685–1695.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sanmukh SG, Santos NJ, Barquilha CN, dos
Santos SAA, Duran BOS, Delella FK, Moroz A, Justulin LA, Carvalho
HF and Felisbino SL: Exposure to bacteriophages T4 and M13
increases integrin gene expression and impairs migration of human
PC-3 prostate cancer cells. Antibiotics (Basel). 10:12022021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sanmukh SG, Dos Santos NJ, Barquilha CN,
Cucielo MS, de Carvalho M, Dos Reis PP, Delella FK, Carvalho HF and
Felisbino SL: Bacteriophages M13 and T4 increase the expression of
anchorage-dependent survival pathway genes and down regulate
androgen receptor expression in LNCaP prostate cell line. Viruses.
13:17542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mosmann T: Rapid colorimetric assay for
cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and
cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods. 65:55–63. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Berridge MV and Tan AS: Characterization
of the cellular reduction of
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT):
Subcellular localization, substrate dependence, and involvement of
mitochondrial electron transport in MTT reduction. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 303:474–482. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie Z, Bailey A, Kuleshov MV, Clarke DJB,
Evangelista JE, Jenkins SL, Lachmann A, Wojciechowicz ML,
Kropiwnicki E, Jagodnik KM, et al: Gene set knowledge discovery
with enrichr. Curr Protoc. 1:e902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Nastou KC, Lyon D,
Kirsch R, Pyysalo S, Doncheva NT, Legeay M, Fang T, Bork P, et al:
The STRING database in 2021: Customizable protein-protein networks,
and functional characterization of user-uploaded gene/measurement
sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 49(D1): D605–D612. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Langer I, Jeandriens J, Couvineau A,
Sanmukh S and Latek D: Signal transduction by VIP and PACAP
receptors. Biomedicines. 10:4062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peterson YK and Luttrell LM: The diverse
roles of arrestin scaffolds in G protein-coupled receptor
signaling. Pharmacol Rev. 69:256–297. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gad AA and Balenga N: The Emerging Role of
adhesion GPCRs in cancer. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 3:29–42. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liscano Y, Oñate-Garzón J and Delgado JP:
Peptides with Dual antimicrobial-anticancer activity: Strategies to
overcome peptide limitations and rational design of anticancer
peptides. Molecules. 25:42452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hwang JS, Kim SG, Shin TH, Jang YE, Kwon
DH and Lee G: Development of anticancer peptides using artificial
intelligence and combinational therapy for cancer therapeutics.
Pharmaceutics. 14:9972022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ripa I, Andreu S, López-Guerrero JA and
Bello-Morales R: Membrane rafts: Portals for viral entry. Front
Microbiol. 12:6312742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim A, Shin TH, Shin SM, Pham CD, Choi DK,
Kwon MH and Kim YS: Cellular internalization mechanism and
intracellular trafficking of filamentous M13 phages displaying a
cell-penetrating transbody and TAT peptide. PLoS One. 7:e518132012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peterziel H, Mink S, Schonert A, Becker M,
Klocker H and Cato AC: Rapid signalling by androgen receptor in
prostate cancer cells. Oncogene. 18:6322–6329. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liao RS, Ma S, Miao L, Li R, Yin Y and Raj
GV: Androgen receptor-mediated non-genomic regulation of prostate
cancer cell proliferation. Transl Androl Urol. 2:187–196.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Heinlein CA and Chang C: The roles of
androgen receptors and androgen-binding proteins in nongenomic
androgen actions. Mol Endocrinol. 16:2181–2187. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Siu MK, Chen WY, Tsai HY, Yeh HL, Yin JJ,
Liu SY and Liu YN: Androgen receptor regulates SRC expression
through microRNA-203. Oncotarget. 7:25726–25741. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Taheri M, Khoshbakht T, Jamali E,
Kallenbach J, Ghafouri-Fard S and Baniahmad A: Interaction between
non-coding RNAs and androgen receptor with an especial focus on
prostate cancer. Cells. 10:31982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kim KH, Dobi A, Shaheduzzaman S, Gao CL,
Masuda K, Li H, Drukier A, Gu Y, Srikantan V, Rhim JS and
Srivastava S: Characterization of the androgen receptor in a benign
prostate tissue-derived human prostate epithelial cell line:
RC-165N/human telomerase reverse transcriptase. Prostate Cancer
Prostatic Dis. 10:30–38. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang J, Li D, Zhang R, Peng R and Li J:
Delivery of microRNA-21-sponge and pre-microRNA-122 by MS2
virus-like particles to therapeutically target hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 246:2463–2472. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Foglizzo V and Marchiò S: Bacteriophages
as therapeutic and diagnostic vehicles in cancer. Pharmaceuticals
(Basel). 14:1612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Echarri A and Del Pozo MA: Caveolae
internalization regulates integrin-dependent signaling pathways.
Cell Cycle. 5:2179–2182. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shi F and Sottile J: Caveolin-1-dependent
beta1 integrin endocytosis is a critical regulator of fibronectin
turnover. J Cell Sci. 121:2360–2371. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Tahir SA, Yang G, Ebara S, Timme TL, Satoh
T, Li L, Goltsov A, Ittmann M, Morrisett JD and Thompson TC:
Secreted caveolin-1 stimulates cell survival/clonal growth and
contributes to metastasis in androgen-insensitive prostate cancer.
Cancer Res. 61:3882–3885. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xing Y, Wen Z, Gao W, Lin Z, Zhong J and
Jiu Y: Multifaceted functions of host cell caveolae/caveolin-1 in
virus infections. Viruses. 12:4872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schaffner F, Ray AM and Dontenwill M:
Integrin α5β1, the fibronectin receptor, as a pertinent therapeutic
target in solid tumors. Cancers (Basel). 5:27–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hou J, Yan D, Liu Y, Huang P and Cui H:
The roles of integrin α5β1 in human cancer. Onco Targets Ther.
13:13329–13344. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Pantano F, Croset M, Driouch K,
Bednarz-Knoll N, Iuliani M, Ribelli G, Bonnelye E, Wikman H, Geraci
S, Bonin F, et al: Integrin alpha5 in human breast cancer is a
mediator of bone metastasis and a therapeutic target for the
treatment of osteolytic lesions. Oncogene. 40:1284–1299. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hou S, Isaji T, Hang Q, Im S, Fukuda T and
Gu J: Distinct effects of β1 integrin on cell proliferation and
cellular signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Sci Rep.
6:184302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Morozevich GE, Kozlova NI, Ushakova NA,
Preobrazhenskaya ME and Berman AE: Integrin α5β1 simultaneously
controls EGFR-dependent proliferation and Akt-dependent
pro-survival signaling in epidermoid carcinoma cells. Aging (Albany
NY). 4:368–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Butler DE, Marlein C, Walker HF, Frame FM,
Mann VM, Simms MS, Davies BR, Collins AT and Maitland NJ:
Inhibition of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway activates autophagy and
compensatory Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK signalling in prostate cancer.
Oncotarget. 8:56698–56713. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
DuShane JK and Maginnis MS: Human DNA
virus exploitation of the MAPK-ERK cascade. Int J Mol Sci.
20:34272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mukherjee R, McGuinness DH, McCall P,
Underwood MA, Seywright M, Orange C and Edwards J: Upregulation of
MAPK pathway is associated with survival in castrate-resistant
prostate cancer. Br J Cancer. 104:1920–1928. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Bluemn EG, Coleman IM, Lucas JM, Coleman
RT, Hernandez-Lopez S, Tharakan R, Bianchi-Frias D, Dumpit RF,
Kaipainen A, Corella AN, et al: Androgen receptor
pathway-independent prostate cancer is sustained through FGF
signaling. Cancer Cell. 32:474–489.e6. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Liang H and Ward WF: PGC-1alpha: A key
regulator of energy metabolism. Adv Physiol Educ. 30:145–151. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Abdulghani J, Gu L, Dagvadorj A, Lutz J,
Leiby B, Bonuccelli G, Lisanti MP, Zellweger T, Alanen K, Mirtti T,
et al: Stat3 promotes metastatic progression of prostate cancer. Am
J Pathol. 172:1717–1728. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Barton BE, Karras JG, Murphy TF, Barton A
and Huang HF: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3
(STAT3) activation in prostate cancer: Direct STAT3 inhibition
induces apoptosis in prostate cancer lines. Mol Cancer Ther.
3:11–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Bishop JL, Thaper D and Zoubeidi A: The
multifaceted roles of STAT3 signaling in the progression of
prostate cancer. Cancers (Basel). 6:829–859. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zhao M, Gao FH, Wang JY, Liu F, Yuan HH,
Zhang WY and Jiang B: JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway activation
mediates tumor angiogenesis by upregulation of VEGF and bFGF in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 73:366–374. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kujawski M, Kortylewski M, Lee H, Herrmann
A, Kay H and Yu H: Stat3 mediates myeloid cell-dependent tumor
angiogenesis in mice. J Clin Invest. 118:3367–3377. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Molek P, Strukelj B and Bratkovic T:
Peptide phage display as a tool for drug discovery: Targeting
membrane receptors. Molecules. 16:857–887. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Agu CA, Klein R, Schwab S, König-Schuster
M, Kodajova P, Ausserlechner M, Binishofer B, Bläsi U, Salmons B,
Günzburg WH and Hohenadl C: The cytotoxic activity of the
bacteriophage lambda-holin protein reduces tumour growth rates in
mammary cancer cell xenograft models. J Gene Med. 8:229–241. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
David M, Ribeiro J, Descotes F, Serre CM,
Barbier M, Murone M, Clézardin P and Peyruchaud O: Targeting
lysophosphatidic acid receptor type 1 with Debio 0719 inhibits
spontaneous metastasis dissemination of breast cancer cells
independently of cell proliferation and angiogenesis. Int J Oncol.
40:1133–1141. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chaudhary PK and Kim S: An insight into
GPCR and G-proteins as cancer drivers. Cells. 10:32882021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Bar-Shavit R, Maoz M, Kancharla A, Nag JK,
Agranovich D, Grisaru-Granovsky S and Uziely B: G protein-coupled
receptors in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 17:13202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yang J, Mapelli C, Wang Z, Sum CS, Hua J,
Lawrence RM, Ni Y and Seiffert DA: An optimized agonist peptide of
protease-activated receptor 4 and its use in a validated
platelet-aggregation assay. Platelets. 33:979–986. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hu Y, Ma A, Lin S, Yang Y and Hong G:
Novel peptide screened from a phage display library antagonizes the
activity of CC chemokine receptor 9. Oncol Lett. 14:6471–6476.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Nickho H, Younesi V, Aghebati-Maleki L,
Motallebnezhad M, Majidi Zolbanin J, Movassagh Pour A and Yousefi
M: Developing and characterization of single chain variable
fragment (scFv) antibody against frizzled 7 (Fzd7) receptor.
Bioengineered. 8:501–510. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Pavlovic Z, Adams JJ, Blazer LL, Gakhal
AK, Jarvik N, Steinhart Z, Robitaille M, Mascall K, Pan J, Angers
S, et al: A synthetic anti-frizzled antibody engineered for
broadened specificity exhibits enhanced anti-tumor properties.
MAbs. 10:1157–1167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tobia C, Chiodelli P, Nicoli S, Dell'era
P, Buraschi S, Mitola S, Foglia E, van Loenen PB, Alewijnse AE and
Presta M: Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-1 controls venous
endothelial barrier integrity in zebrafish. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 32:e104–e116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Dąbrowska K, Kaźmierczak Z, Majewska J,
Miernikiewicz P, Piotrowicz A, Wietrzyk J, Lecion D, Hodyra K,
Nasulewicz-Goldeman A, Owczarek B and Górski A: Bacteriophages
displaying anticancer peptides in combined antibacterial and
anticancer treatment. Future Microbiol. 9:861–869. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hart SL, Knight AM, Harbottle RP, Mistry
A, Hunger HD, Cutler DF, Williamson R and Coutelle C: Cell binding
and internalization by filamentous phage displaying a cyclic
Arg-Gly-Asp-containing peptide. J Biol Chem. 269:12468–12474. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Kantoch M and Mordarski M: Binding of
bacterial viruses by cancer cells in vitro. Postepy Hig Med Dosw.
12:191–192. 1958.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Porayath C, Salim A, Palillam Veedu A,
Babu P, Nair B, Madhavan A and Pal S: Characterization of the
bacteriophages binding to human matrix molecules. Int J Biol
Macromol. 110:608–615. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Lehti TA, Pajunen MI, Skog MS and Finne J:
Internalization of a polysialic acid-binding Escherichia coli
bacteriophage into eukaryotic neuroblastoma cells. Nat Commun.
8:19152017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kantoch M: Studies on phagocytosis of
bacterial viruses. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. 6:63–84. 1958.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Bloch H: Experimental investigation on the
relationships between bacteriophages and malignant tumors. Arch
Virol. 1:481–496. 1940.(In German).
|
|
80
|
Szczaurska-Nowak K, Dabrowska K, Celka M,
Kurzepa A, Nevozhay D, Wietrzyk J, Switala-Jelen K, Syper D,
Pozniak G, Opolski A, et al: Antitumor effect of combined treatment
of mice with cytostatic agents and bacteriophage T4. Anticancer
Res. 29:2361–2370. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Dabrowska K, Skaradziński G, Jończyk P,
Kurzepa A, Wietrzyk J, Owczarek B, Zaczek M, Switała-Jeleń K,
Boratyński J, Poźniak G, et al: The effect of bacteriophages T4 and
HAP1 on in vitro melanoma migration. BMC Microbiol. 9:132009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kurzepa-Skaradzinska A, Skaradzinski G,
Weber-Dabrowska B, Zaczek M, Maj T, Slawek A, Switalska M,
Maciejewska M, Wietrzyk J, Rymowicz W and Gorski A: Influence of
bacteriophage preparations on migration of HL-60 leukemia cells in
vitro. Anticancer Res. 33:1569–1574. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Merril CR, Friedman TB, Attallah AF, Geier
MR, Krell K and Yarkin R: Isolation of bacteriophages from
commercial sera. In Vitro. 8:91–93. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Eriksson F, Tsagozis P, Lundberg K, Parsa
R, Mangsbo SM, Persson MA, Harris RA and Pisa P: Tumor-specific
bacteriophages induce tumor destruction through activation of
tumor-associated macrophages. J Immunol. 182:3105–3111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|