|
1
|
Shah MH, Goldner WS, Benson AB, Bergsland
E, Blaszkowsky LS, Brock P, Chan J, Das S, Dickson PV, Fanta P, et
al: Neuroendocrine and adrenal tumors, version 2.2021, NCCN
clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
19:839–868. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yao JC, Pavel M, Lombard-Bohas C, Cutsem
EV, Voi M, Brandt U, He W, Chen D, Capdevila J, de Vries EGE, et
al: Everolimus for the treatment of advanced pancreatic
neuroendocrine tumors: Overall survival and circulating biomarkers
from the randomized, phase III RADIANT-3 study. J Clin Oncol.
34:3906–3913. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raymond E, Dahan L, Raoul JL, Bang YJ,
Borbath I, Lombard-Bohas C, Valle J, Metrakos P, Smith D, Vinik A,
et al: Sunitinib malate for the treatment of pancreatic
neuroendocrine tumors. New Engl J Med. 364:501–513. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu Y, Zhao Z, Wang J, Lv W, Lu L, Fu W and
Li W: Safety and efficacy of combining capecitabine and
temozolomide (CAPTEM) to treat advanced neuroendocrine neoplasms: A
meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e127842018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hosaka K, Yang Y, Seki T, Du Q, Jing X, He
X, Wu J, Zhang Y, Morikawa H, Nakamura M, et al: Therapeutic
paradigm of dual targeting VEGF and PDGF for effectively treating
FGF-2 off-target tumors. Nat Commun. 11:37042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Syed YY: Surufatinib: First approval.
Drugs. 81:723–732. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xu JM, Wang Y, Chen YL, Jia R, Li J, Gong
JF, Li J, Qi C, Hua Y, Tan CR, et al: Sulfatinib, a novel kinase
inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors: Results from a
phase I study. Oncotarget. 8:42076–42086. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu J, Shen L, Zhou Z, Li J, Bai C, Chi Y,
Li Z, Xu N, Li E, Liu T, et al: Surufatinib in advanced
extrapancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (SANET-ep): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol.
21:1500–1512. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu J, Bai Y, Sun H, Bai C, Jia R, Li Y,
Zhang W, Liu L, Huang C, Guan M, et al: A single-arm, multicenter,
open-label phase 2 trial of surufatinib in patients with
unresectable or metastatic biliary tract cancer. Cancer.
127:3975–3984. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen J, Ji Q, Bai C, Zheng X, Zhang Y, Shi
F, Li X, Tang P, Xu Z, Huang R, et al: Surufatinib in Chinese
patients with locally advanced or metastatic differentiated thyroid
cancer and medullary thyroid cancer: A multicenter, open-label,
phase II trial. Thyroid. 30:1245–1253. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Oken MM, Creech RH, Tormey DC, Horton J,
Davis TE, McFadden ET and Carbone PP: Toxicity and response
criteria of the Eastern cooperative oncology group. Am J Clin
Oncol. 5:649–655. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
O'Sullivan B, Brierley J, Byrd D, Bosman
F, Kehoe S, Kossary C, Pineros M, Van Eycken E, Weir HK and
Gospodarowicz M: The TNM classification of malignant
tumours-towards common understanding and reasonable expectations.
Lancet Oncol. 18:849–851. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carlson EA: Agency for healthcare research
and quality (AHRQ) web site. Orthop Nurs. 27:258–259. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
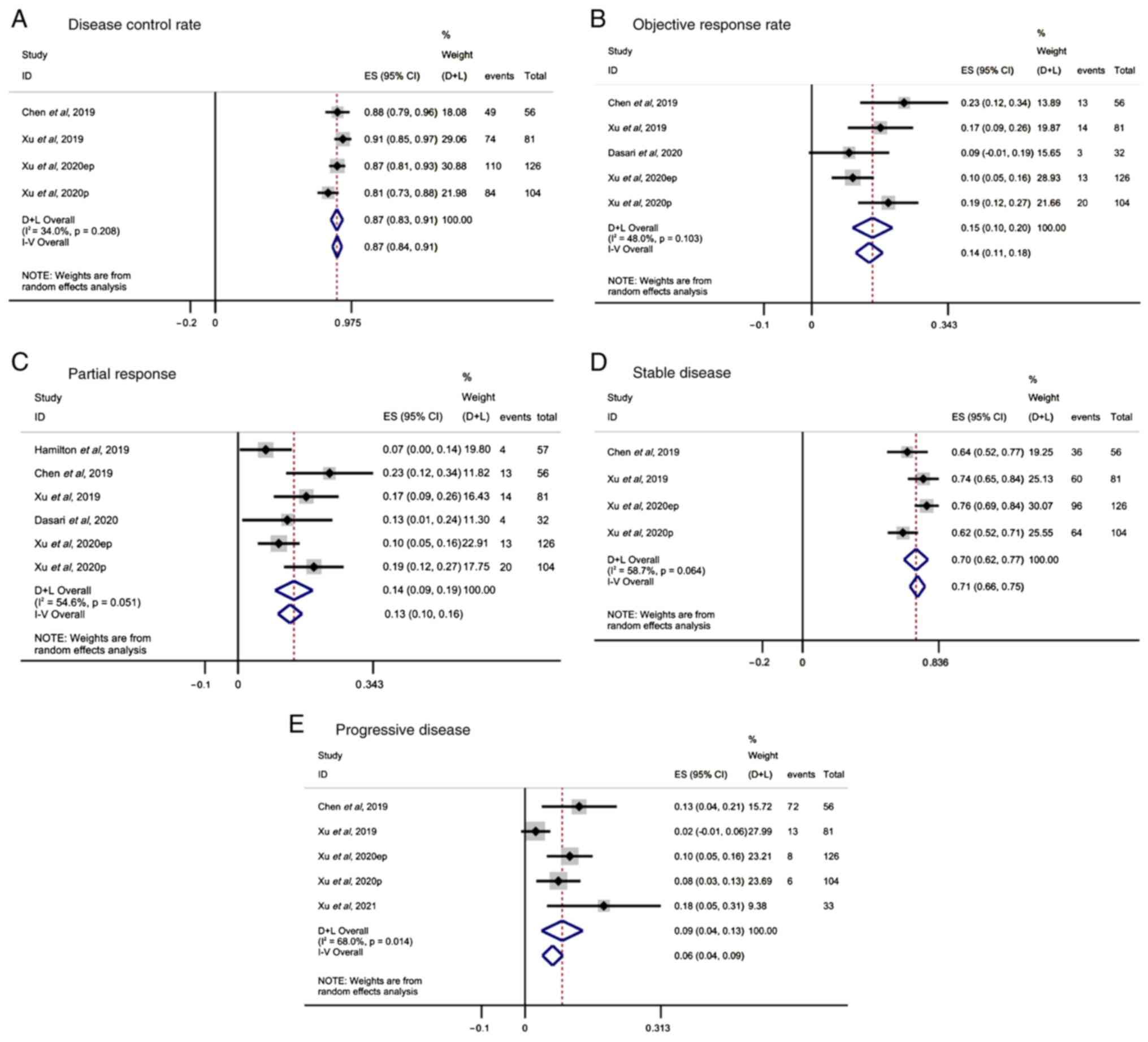
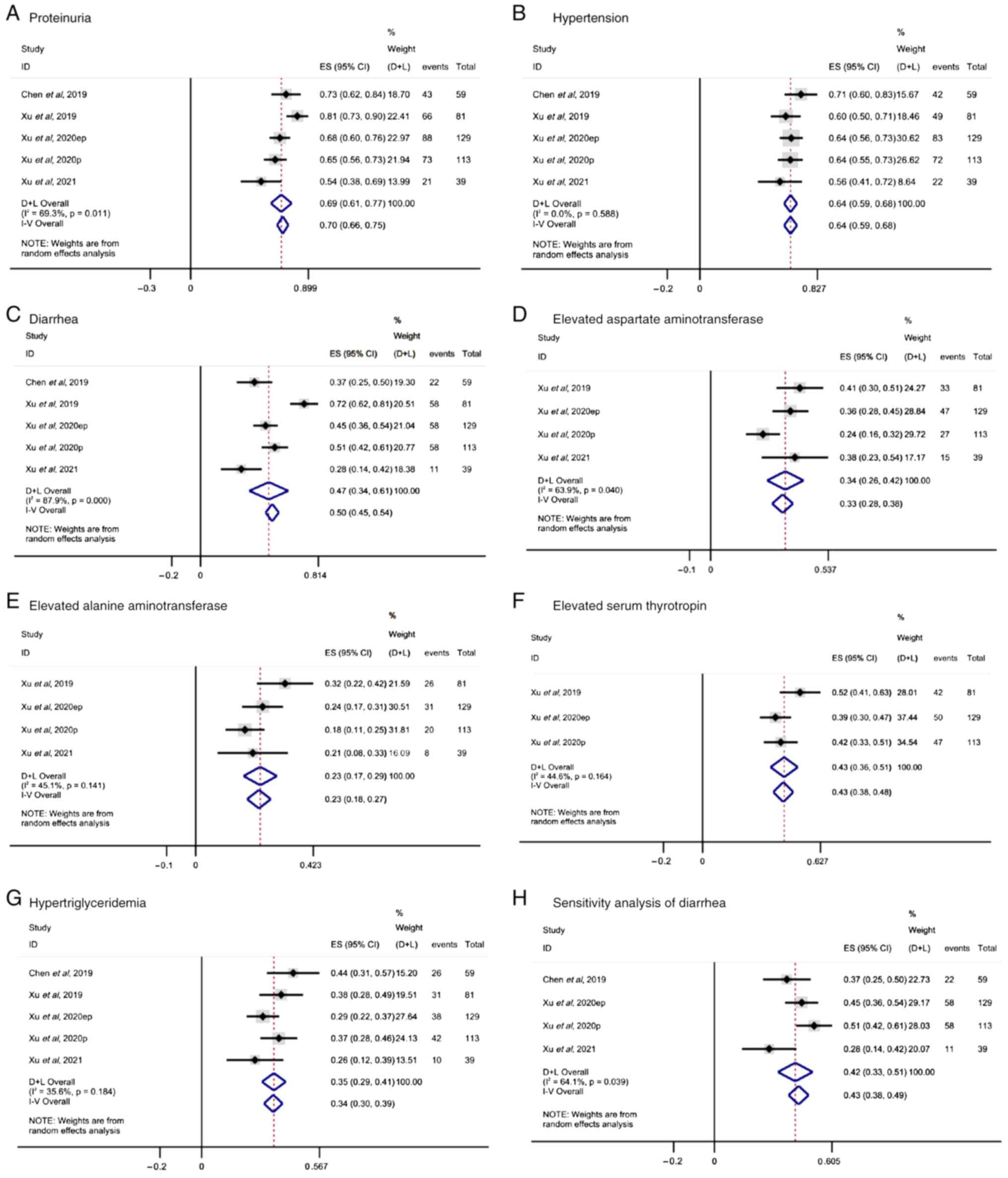
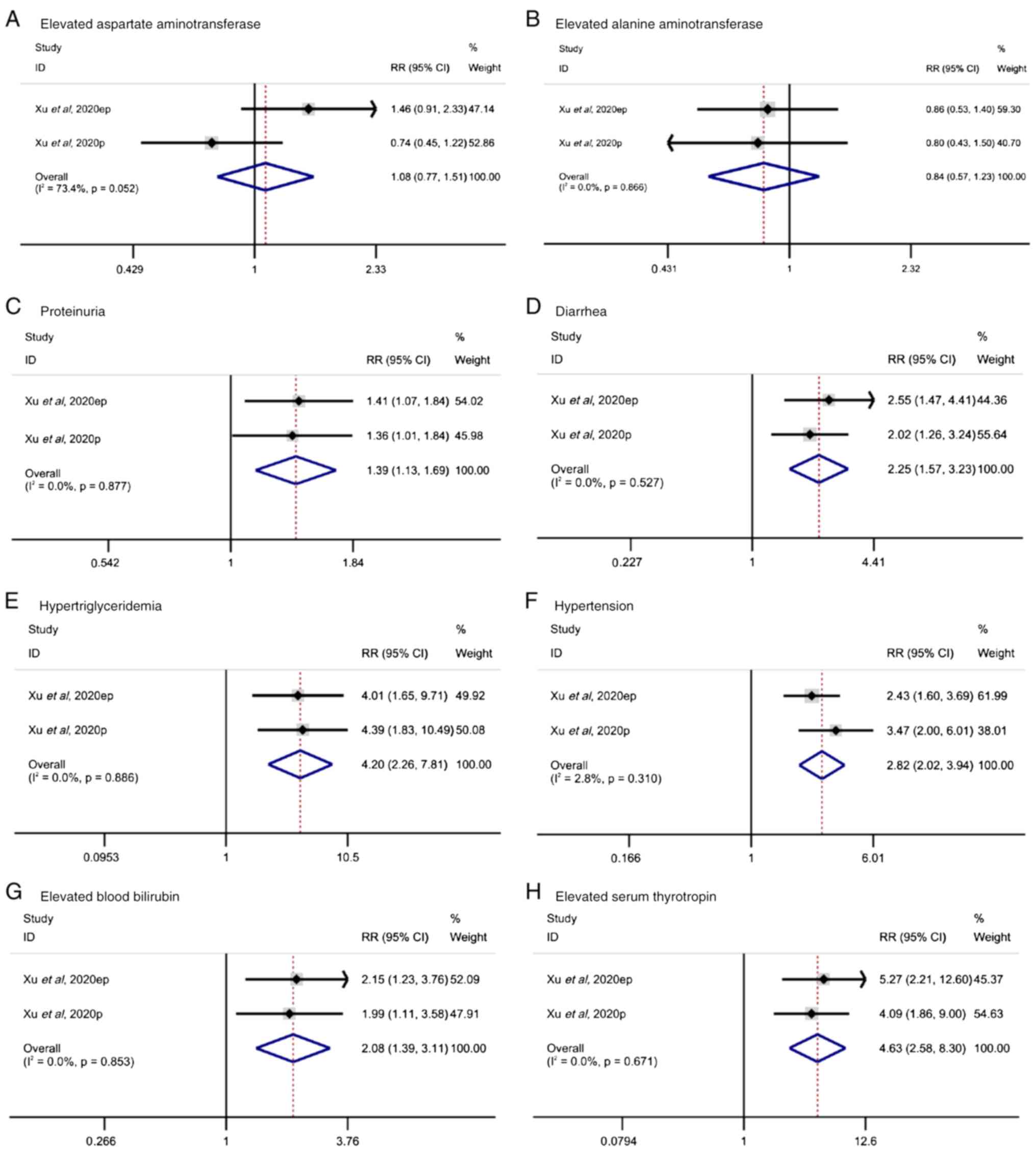
DerSimonian R and Laird N: Meta-analysis
in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 7:177–188. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
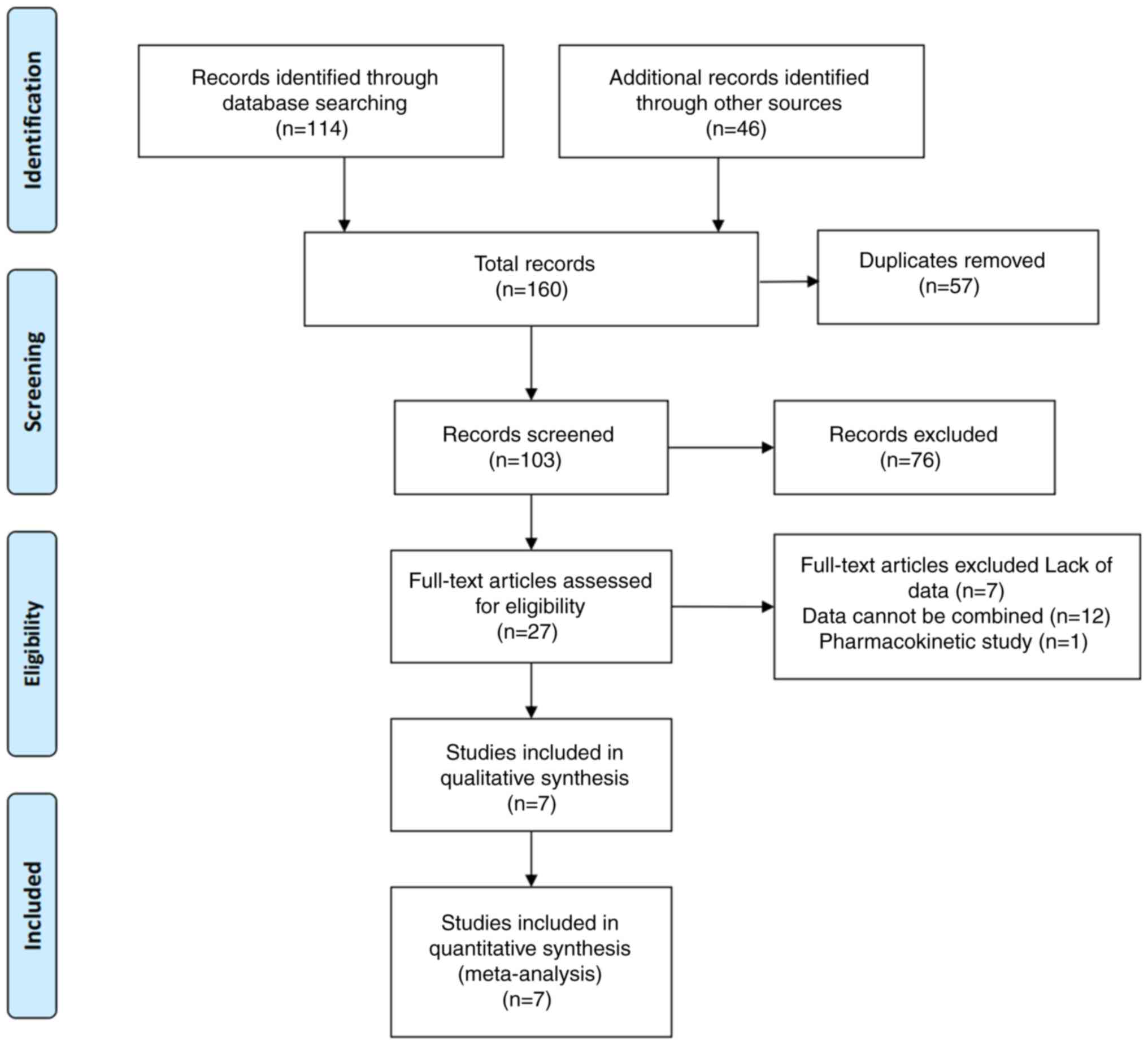
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372:n712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Xu J, Li J, Bai C, Xu N, Zhou Z, Li Z,
Zhou C, Jia R, Lu M, Cheng Y, et al: Surufatinib in advanced
well-differentiated neuroendocrine tumors: A multicenter,
single-arm, open-label, phase Ib/II trial. Clin Cancer Res.
25:3486–3494. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu J, Shen L, Bai C, Wang W, Li J, Yu X,
Li Z, Li E, Yuan X, Chi Y, et al: Surufatinib in advanced
pancreatic neuroendocrine tumours (SANET-p): A randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol.
21:1489–1499. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hamilton E, Wang JS, Li D, Dasari NA,
Paulson S, Cohn AL, Sauter NP, Kania M, Kauh K and Falchook GS:
1393P-Safety and tolerability of surufatinib in western patients
with solid tumours. Ann Oncol. 30 (Suppl 5):v569–v570. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dasari A, Li D, Sung MW, Tucci C, Kauh JS,
Kania MK and Paulson AS: Efficacy and safety of surufatinib in
United States (US) patients (pts) with neuroendocrine tumors
(NETs). J Clin Oncol. 38 (15 Suppl):S46102020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ma Y, Zhang Z, Tang L, Xu YC, Xie ZM, Gu
XF and Wang HX: Cytokine-induced killer cells in the treatment of
patients with solid carcinomas: A systematic review and pooled
analysis. Cytotherapy. 14:483–493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cives M and Strosberg JR:
Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. CA Cancer J Clin.
68:471–487. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hyman DM, Smyth LM, Donoghue MTA, Westin
SN, Bedard PL, Dean EJ, Bando H, El-Khoueiry AB, Pérez-Fidalgo JA,
Mita A, et al: AKT inhibition in solid tumors with AKT1 mutations.
J Clin Oncol. 35:2251–2259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ukidve A, Cu K, Kumbhojkar N, Lahann J and
Mitragotri S: Overcoming biological barriers to improve solid tumor
immunotherapy. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 11:2276–2301. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xiao WY, Wang Y, An HW, Hou D, Mamuti M,
Wang MD, Wang J, Xu W, Hu L and Wang H: Click Reaction-Assisted
Peptide Immune Checkpoint Blockade for Solid Tumor Treatment. ACS
Appl Mater Interfaces. 12:40042–40051. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Heery CR, O'Sullivan-Coyne G, Madan RA,
Cordes L, Rajan A, Rauckhorst M, Lamping E, Oyelakin I, Marté JL,
Lepone LM, et al: Avelumab for metastatic or locally advanced
previously treated solid tumours (JAVELIN Solid Tumor): A phase 1a,
multicohort, dose-escalation trial. Lancet Oncol. 18:587–598. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Speck T, Heidbuechel JPW, Veinalde R,
Jaeger D, von Kalle C, Ball CR, Ungerechts G and Engeland CE:
Targeted BiTE expression by an oncolytic vector augments
therapeutic efficacy against solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res.
24:2128–2137. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cébe-Suarez S, Zehnder-Fjällman A and
Ballmer-Hofer K: The role of VEGF receptors in angiogenesis;
complex partnerships. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:601–615. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Daniele G, Corral J, Molife LR and de Bono
JS: FGF receptor inhibitors: Role in cancer therapy. Curr Oncol
Rep. 14:111–119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Al-Ostoot FH, Sherapura A, V V, Basappa G,
H K V, B T P and Khanum SA: Targeting HIF-1α by newly synthesized
Indolephenoxyacetamide (IPA) analogs to induce
anti-angiogenesis-mediated solid tumor suppression. Pharmacol Rep.
73:1328–1343. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu J: Current treatments and future
potential of surufatinib in neuroendocrine tumors (NETs). Ther Adv
Med Oncol. 13:175883592110426892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lu X, Yan S, Koral KA and Chen Z:
Surufatinib for the treatment of advanced extrapancreatic
neuroendocrine tumors. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 21:917–926.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bodei L, Kwekkeboom DJ, Kidd M, Modlin IM
and Krenning EP: Radiolabeled somatostatin analogue therapy of
gastroenteropancreatic cancer. Semin Nucl Med. 46:225–238. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rao Q, Li M, Xu W, Pang K, Guo X, Wang D,
Liu J, Guo W and Zhang Z: Clinical benefits of PD-1/PD-L1
inhibitors in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Hepatol Int. 14:765–775. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang J, Song Q, Cai L, Xie Y and Chen Y:
The efficacy of 177Lu-DOTATATE peptide receptor
radionuclide therapy (PRRT) in patients with metastatic
neuroendocrine tumours: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 146:1533–1543. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yin X, Yin Y, Shen C, Chen H, Wang J, Cai
Z, Chen Z and Zhang B: Adverse events risk associated with
regorafenib in the treatment of advanced solid tumors:
Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Onco Targets Ther.
11:6405–6414. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Feng G, Luo Y, Zhang Q, Zeng F, Xu J and
Zhu J: Sorafenib and radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid
cancer (RR-DTC): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocrine.
68:56–63. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Santoni M, Conti A, De Giorgi U, Iacovelli
R, Pantano F, Burattini L, Muzzonigro G, Berardi R, Santini D and
Cascinu S: Risk of gastrointestinal events with sorafenib,
sunitinib and pazopanib in patients with solid tumors: A systematic
review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Int J Cancer.
135:763–773. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
HUTCHMED, . Chi-Med announces the NMPA
approval of surufatinib (Sulanda® in China) for
non-pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. https://www.hutch-med.com/chi-med-announces-the-nmpa-approval-of-surufatinib-sulanda-in-china-for-epnet/December
30–2020
|
|
40
|
HUTCHMED, . Surufatinib (Sulanda): Chinese
prescribing information. https://www.hutch-med.com/sc/pipeline-and-products/our-products/#sulanda-scDecember
29–2020
|
|
41
|
HUTCHMED, . Chi-Med announces second NDA
acceptance in China for surufatinib in pancreatic neuroendocrine
tumors. https://www.hutch-med.com/chi-med-announces-second-nda-acceptance-in-china-for-surufatinib-in-pancreatic-net/September
17–2020
|
|
42
|
HUTCHMED, . Chi-Med initiates rolling
submission of NDA to U.S. FDA for surufatinib for the treatment of
advanced neuroendocrine tumors. https://www.hutch-med.com/chi-med-initiates-rolling-submission-of-nda-to-us-fda-for-surufatinib-for-the-treatment-of-advanced-net/December
28–2020
|