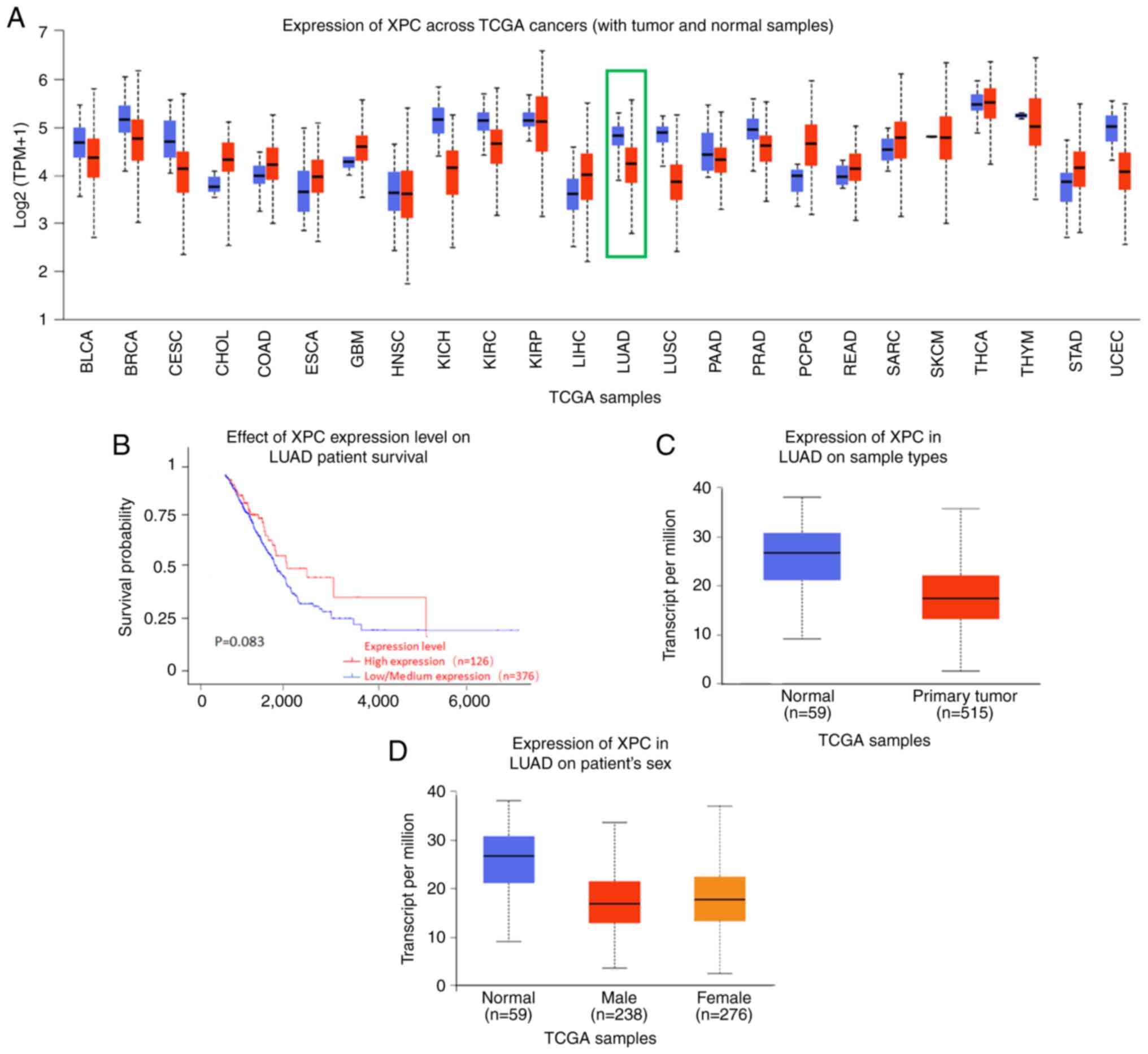
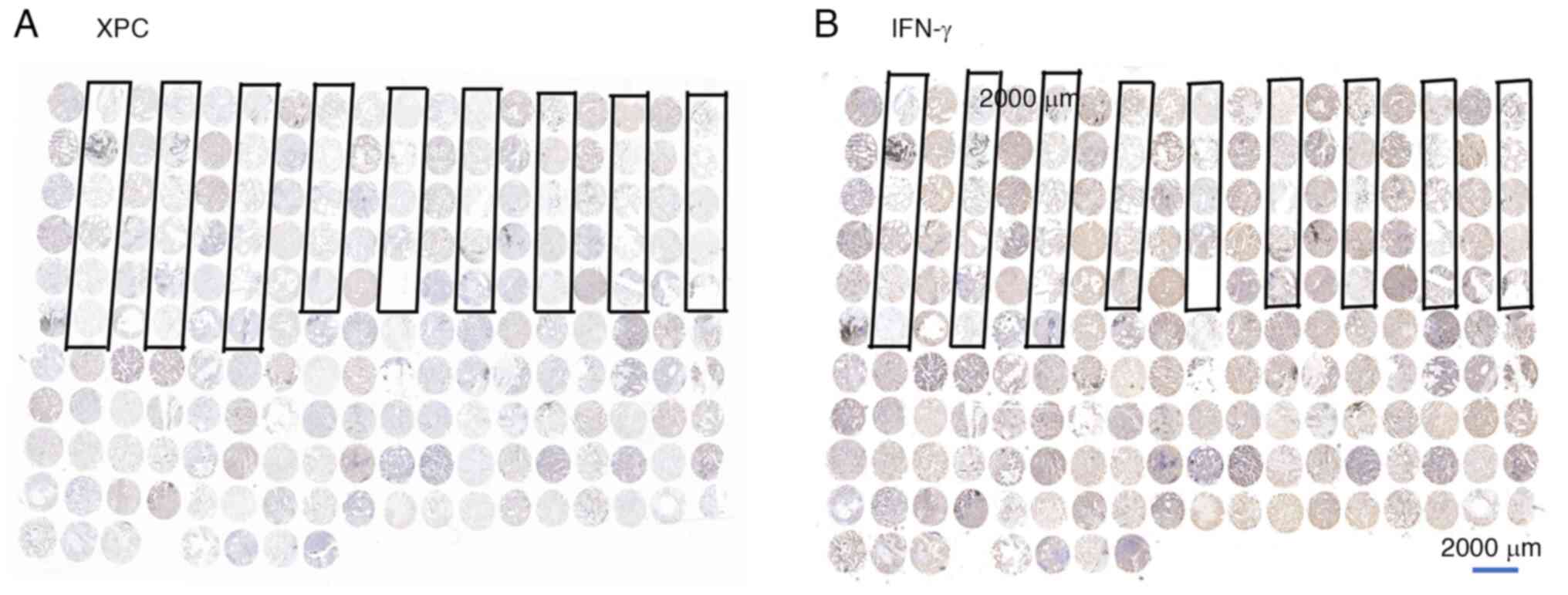
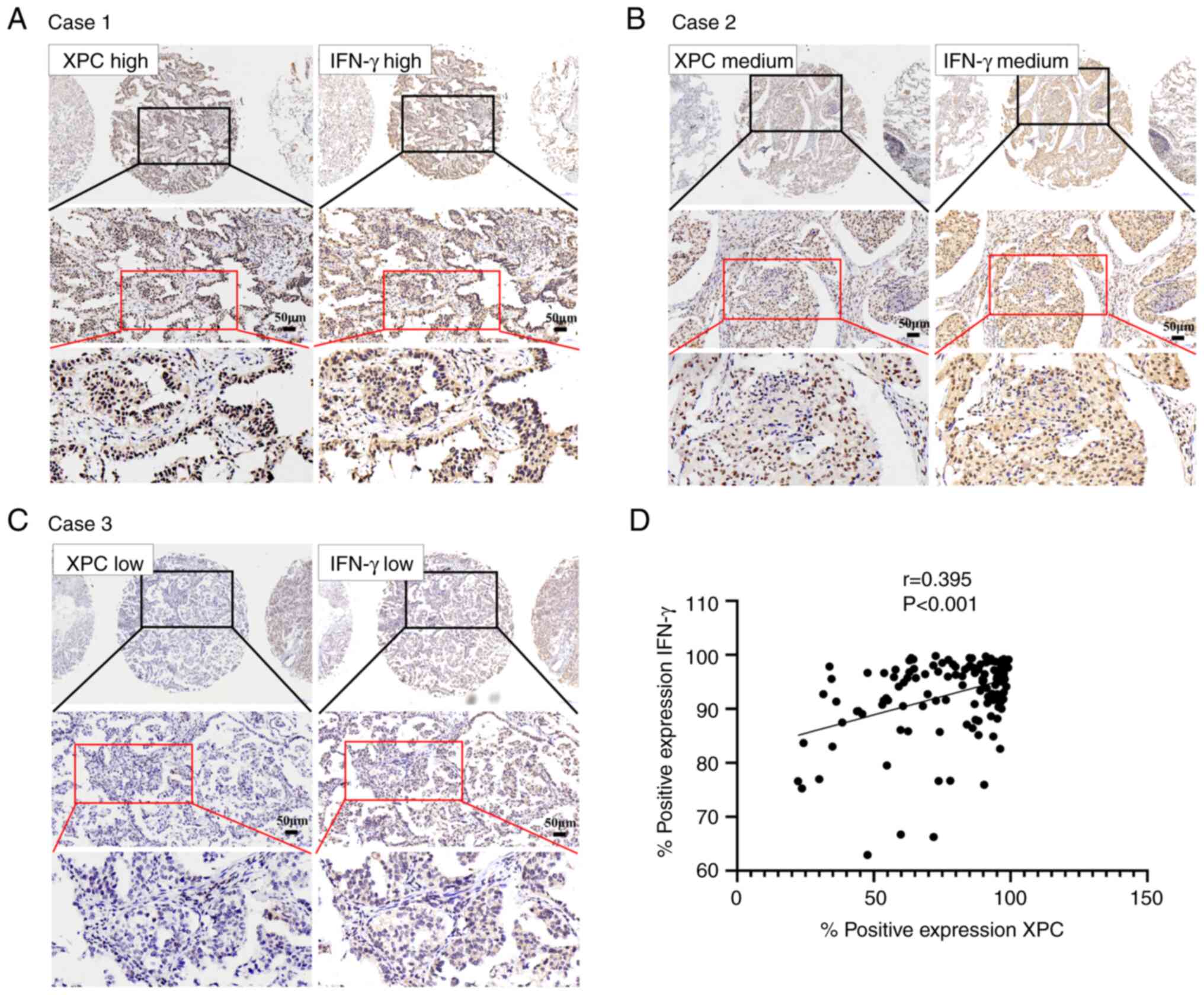
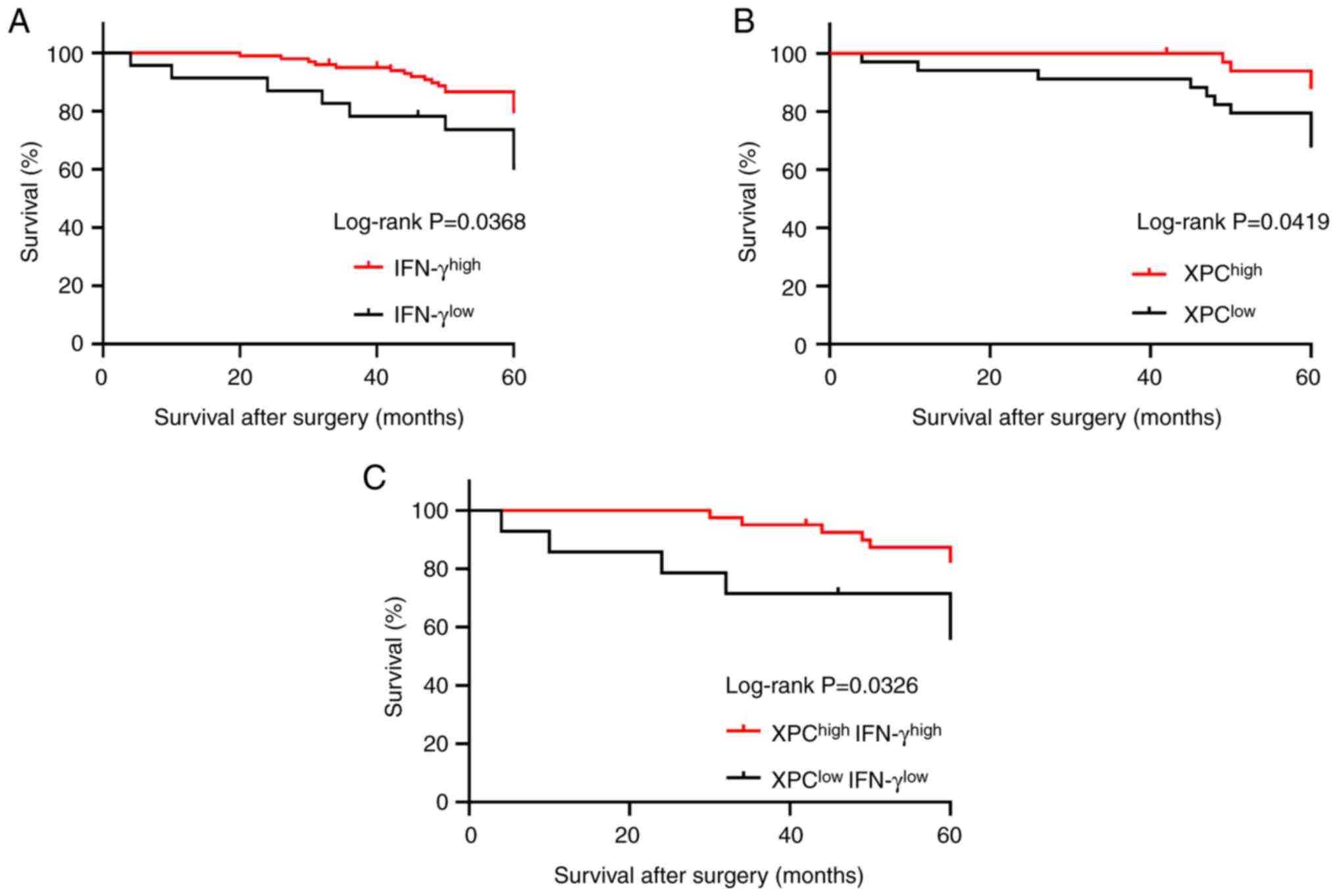
|
1
|
Wu F, Wang L and Zhou C: Lung cancer in
China: Current and prospect. Curr Opin Oncol. 33:40–46. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bade BC and Dela Cruz CS: Lung Cancer
2020: Epidemiology, etiology, and prevention. Clin Chest Med.
41:1–24. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shell SM, Hawkins EK, Tsai MS, Hlaing AS,
Rizzo CJ and Chazin WJ: Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group
C protein (XPC) serves as a general sensor of damaged DNA. DNA
Repair (Amst). 12:947–953. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhou H, Saliba J, Sandusky GE and Sears
CR: XPC protects against smoking- and carcinogen-induced lung
adenocarcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 40:403–411. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kobaisi F, Sulpice E, Barette C, Fayyad N,
Fauvarque MO, Badran B, Fayyad-Kazan M, Fayyad-Kazan H, Gidrol X
and Rachidi W: Isoconazole and clemizole hydrochloride partially
reverse the xeroderma pigmentosum C phenotype. Int J Mol Sci.
22:81562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
D'Errico M, Parlanti E, Teson M, de Jesus
BM, Degan P, Calcagnile A, Jaruga P, Bjørås M, Crescenzi M, Pedrini
AM, et al: New functions of XPC in the protection of human skin
cells from oxidative damage. EMBO J. 25:4305–4315. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fayyad N, Kobaisi F, Beal D, Mahfouf W,
Ged C, Morice-Picard F, Fayyad-Kazan M, Fayyad-Kazan H, Badran B,
Rezvani HR and Rachidi W: Xeroderma pigmentosum C (XPC) mutations
in primary fibroblasts impair base excision repair pathway and
increase oxidative DNA damage. Front Genet. 11:5616872020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang W, Ma S, Ding Z, Yang Y, Wang H, Yang
K, Cai X, Li H, Gao Z and Qu M: XPC protein improves lung
adenocarcinoma prognosis by inhibiting lung cancer cell stemness.
Front Pharmacol. 12:7079402021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang X, He N, Gu D, Wickliffe J, Salazar
J, Boldogh I and Xie J: Genetic Evidence for XPC-KRAS interactions
during lung cancer development. J Genet Genomics. 42:589–596. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abolfathi H, Sheikhpour M, Shahraeini SS,
Khatami S and Nojoumi SA: Studies in lung cancer cytokine
proteomics: A review. Expert Rev Proteomics. 18:49–64. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marrugal A, Ojeda L, Paz-Ares L,
Molina-Pinelo S and Ferrer I: Proteomic-Based approaches for the
study of cytokines in lung cancer. Dis Markers. 2016:21386272016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao Y, Yang J, Cai Y, Fu S, Zhang N, Fu X
and Li L: IFN-ү-mediated inhibition of lung cancer correlates with
PD-L1 expression and is regulated by PI3K-AKT signaling. Int J
Cancer. 143:931–943. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang X, Zeng Y, Qu Q, Zhu J, Liu Z, Ning
W, Zeng H, Zhang N, Du W, Chen C and Huang JA: PD-L1 induced by
IFN-ү from tumor-associated macrophages via the JAK/STAT3 and
PI3K/AKT signaling pathways promoted progression of lung cancer.
Int J Clin Oncol. 22:1026–1033. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fang C, Weng T, Hu S, Yuan Z, Xiong H,
Huang B, Cai Y, Li L and Fu X: IFN-ү-induced ER stress impairs
autophagy and triggers apoptosis in lung cancer cells.
Oncoimmunology. 10:19625912021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nasim F, Sabath BF and Eapen GA: Lung
cancer. Med Clin North Am. 103:463–473. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kgokolo MCM, Anderson K, Siwele SC, Steel
HC, Kwofie LLI, Sathekge MM, Meyer PWA, Rapoport BL and Anderson R:
Elevated levels of soluble CTLA-4, PD-1, PD-L1, LAG-3 and TIM-3 and
systemic inflammatory stress as potential contributors to immune
suppression and generalized tumorigenesis in a cohort of South
African xeroderma pigmentosum patients. Front Oncol. 12:8197902022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu YH, Wu TC, Liao JW, Yeh KT, Chen CY and
Lee H: p53 dysfunction by xeroderma pigmentosum group c defects
enhance lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via increased Mmp1
expression. Cancer Res. 70:10422–10432. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ahn SS, Kwon M, Sung M, Jung SM, Lee SW,
Park YB, Kim ST and Song JJ: Ex Vivo Interferon gamma production by
peripheral immune cells predicts survival in lung adenocarcinoma.
Clin Lung Cancer. 20:e299–e308. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Carrot-Zhang J, Yao X, Devarakonda S,
Deshpande A, Damrauer JS, Silva TC, Wong CK, Choi HY, Felau I,
Robertson AG, et al: Whole-genome characterization of lung
adenocarcinomas lacking alterations in the RTK/RAS/RAF pathway.
Cell Rep. 34:1087842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Akoglu H: User's guide to correlation
coefficients. Turk J Emerg Med. 18:91–93. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Asamura H, Nishimura KK, Giroux DJ,
Chansky K, Hoering A, Rusch V and Rami-Porta R; Members of the
IASLC Staging and Prognostic Factors Committee of the Advisory
Boards, and Participating Institutions, : IASLC lung cancer staging
project: The new database to inform revisions in the Ninth Edition
of the TNM classification of lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol.
18:564–575. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Villalobos P and Wistuba II: Lung cancer
biomarkers. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 31:13–29. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao C, Kong N, Zhang F, Zhou L, Xu M and
Wu L: Development and validation of the potential biomarkers based
on m6A-related lncRNAs for the predictions of overall survival in
the lung adenocarcinoma and differential analysis with cuproptosis.
BMC Bioinformatics. 23:3272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ruiz-Cordero R and Devine WP: Targeted
therapy and checkpoint immunotherapy in lung cancer. Surg Pathol
Clin. 13:17–33. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rodriguez-Canales J, Parra-Cuentas E and
Wistuba II: Diagnosis and molecular classification of lung cancer.
Cancer Treat Res. 170:25–46. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Luo C, Lei M and Zhang Y, Zhang Q, Li L,
Lian J, Liu S, Wang L, Pi G and Zhang Y: Systematic construction
and validation of an immune prognostic model for lung
adenocarcinoma. J Cell Mol Med. 24:1233–1244. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lundin A and Driscoll B: Lung cancer stem
cells: Progress and prospects. Cancer Lett. 338:89–93. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sugasawa K: XPC: Its Product and
Biological Roles. Molecular Mechanisms of Xeroderma Pigmentosum.
Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Ahmad SI and Hanaoka
F: Volume 637. Springer; New York, NY: 2008, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nemzow L, Lubin A, Zhang L and Gong F:
XPC: Going where no DNA damage sensor has gone before. DNA Repair
(Amst). 36:19–27. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cui T, Srivastava AK, Han C, Yang L, Zhao
R, Zou N, Qu M, Duan W, Zhang X and Wang Q-E: XPC inhibits NSCLC
cell proliferation and migration by enhancing E-Cadherin
expression. Oncotarget. 6:10060–10072. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Teng X, Fan XF, Li Q, Liu S, Wu DY, Wang
SY, Shi Y and Dong M: XPC inhibition rescues cisplatin resistance
via the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in A549/DDP lung adenocarcinoma
cells. Oncol Rep. 41:1875–1882. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nasrallah NA, Wiese BM and Sears CR:
Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group C (XPC): Emerging roles
in non-dermatologic malignancies. Front Oncol. 12:8469652022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Medler TR, Murugan D, Horton W, Kumar S,
Cotechini T, Forsyth AM, Leyshock P, Leitenberger JJ, Kulesz-Martin
M, Margolin AA, et al: Complement C5a fosters squamous
carcinogenesis and limits T cell response to chemotherapy. Cancer
Cell. 34:561–578.e6. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Weichselbaum RR, Liang H, Deng L and Fu
YX: Radiotherapy and immunotherapy: A beneficial liaison? Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 14:365–379. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Burke F, East N, Upton C, Patel K and
Balkwill FR: Interferon gamma induces cell cycle arrest and
apoptosis in a model of ovarian cancer: Enhancement of effect by
batimastat. EJC. 33:1114–1121. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schoenborn JR and Wilson CB: Regulation of
interferon-gamma during innate and adaptive immune responses. Adv
Immunol. 96:41–101. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Shin EC, Ahn JM, Kim CH, Choi Y, Ahn YS,
Kim H, Kim SJ and Park JH: IFN-gamma induces cell death in human
hepatoma cells through a TRAIL/death receptor-mediated apoptotic
pathway. Int J Cancer. 93:262–268. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Minn AJ and Wherry EJ: Combination cancer
therapies with immune checkpoint blockade: Convergence on
interferon signaling. Cell. 165:272–275. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Galani V, Kastamoulas M, Varouktsi A,
Lampri E, Mitselou A and Arvanitis DL: IFNs-signaling effects on
lung cancer: An up-to-date pathways-specific review. Clin Exp Med.
17:281–289. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lee KS, Chung WY, Park JE, Jung YJ, Park
JH, Sheen SS and Park KJ: Interferon-ү-Inducible chemokines as
prognostic markers for lung cancer. Int J Environ Res Public
Health. 18:93452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Song M, Ping Y, Zhang K, Yang L, Li F,
Zhang C, Cheng S, Yue D, Maimela NR, Qu J, et al: Low-Dose IFNү
induces tumor cell stemness in tumor microenvironment of non-small
cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 79:3737–3748. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|