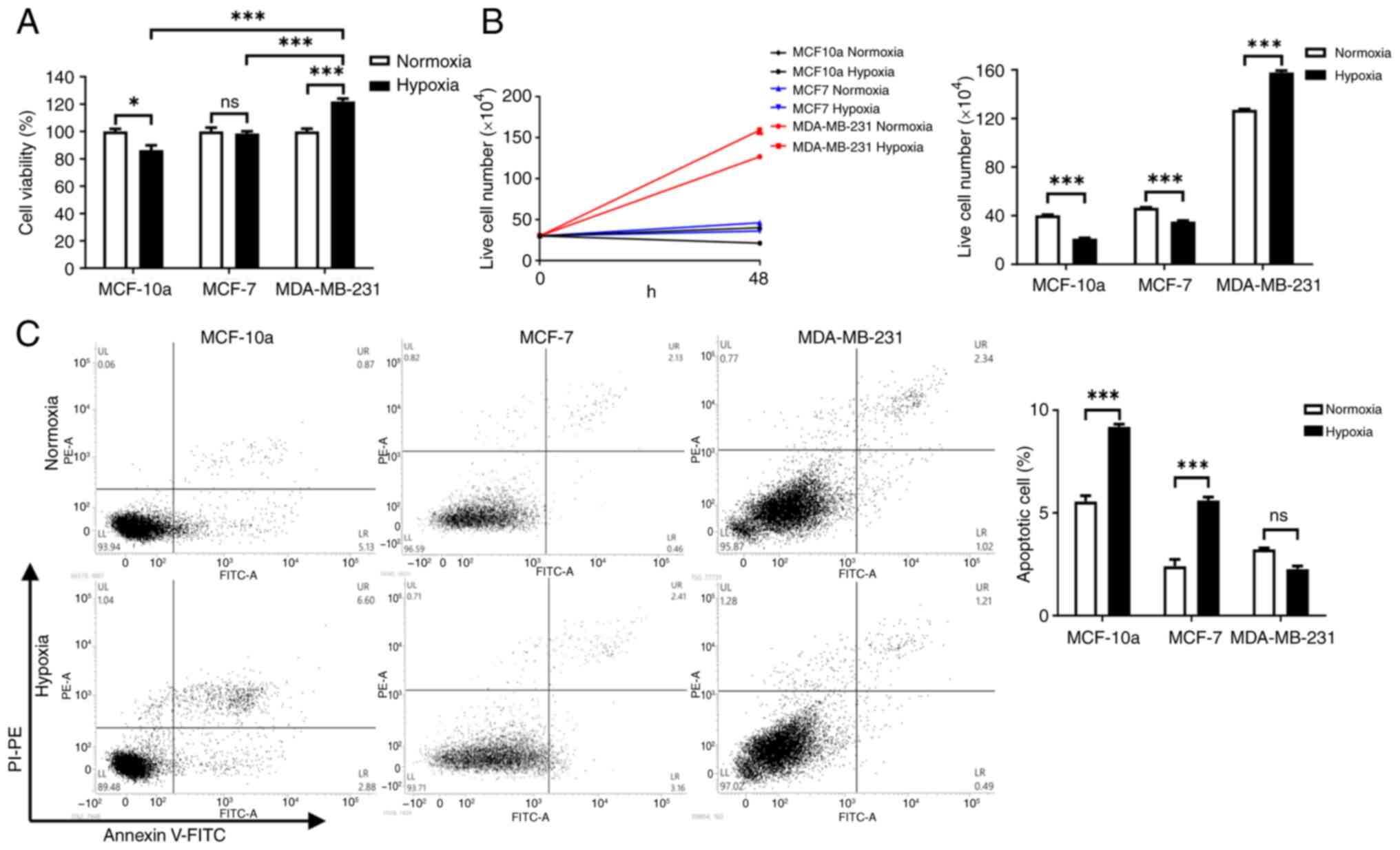
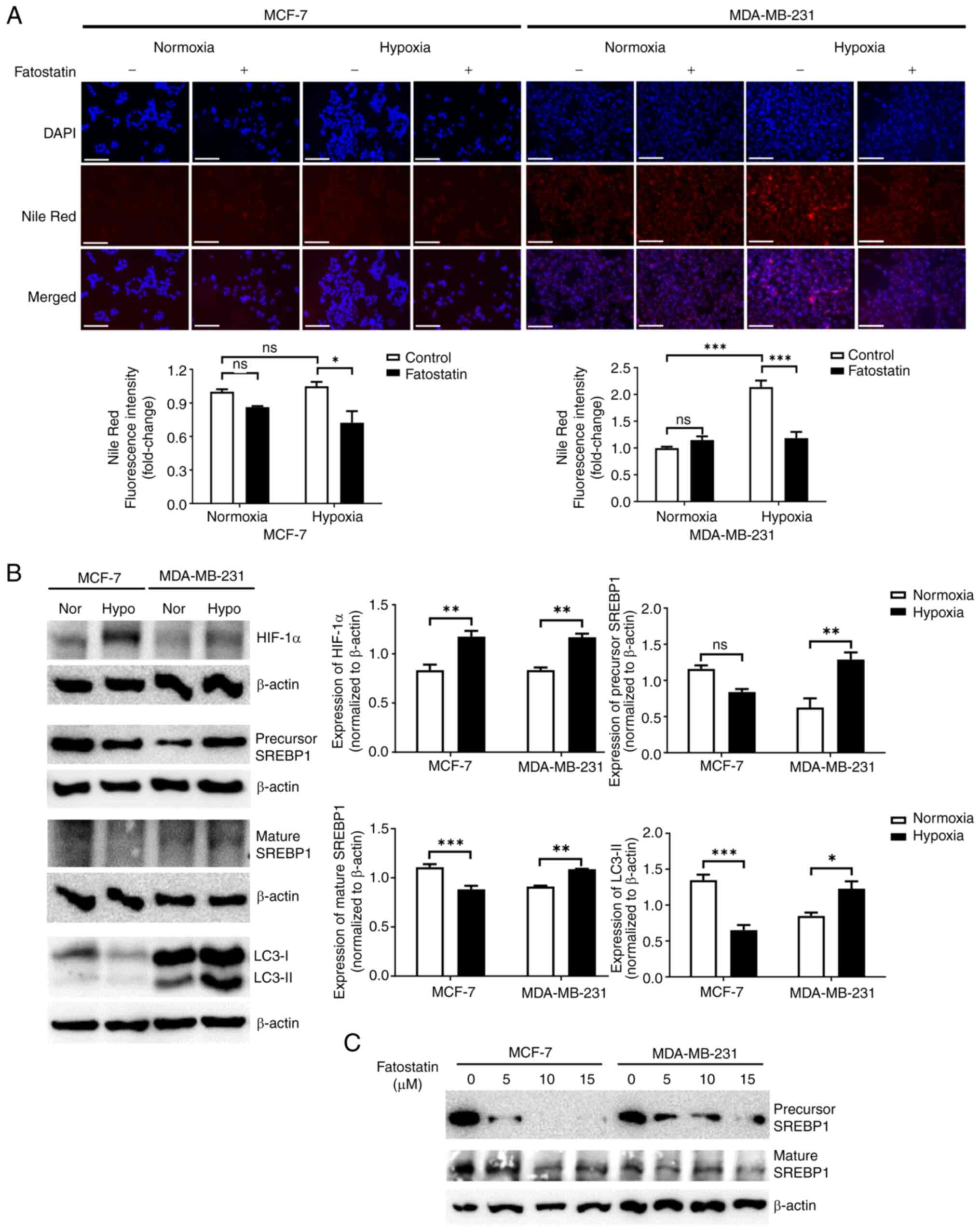
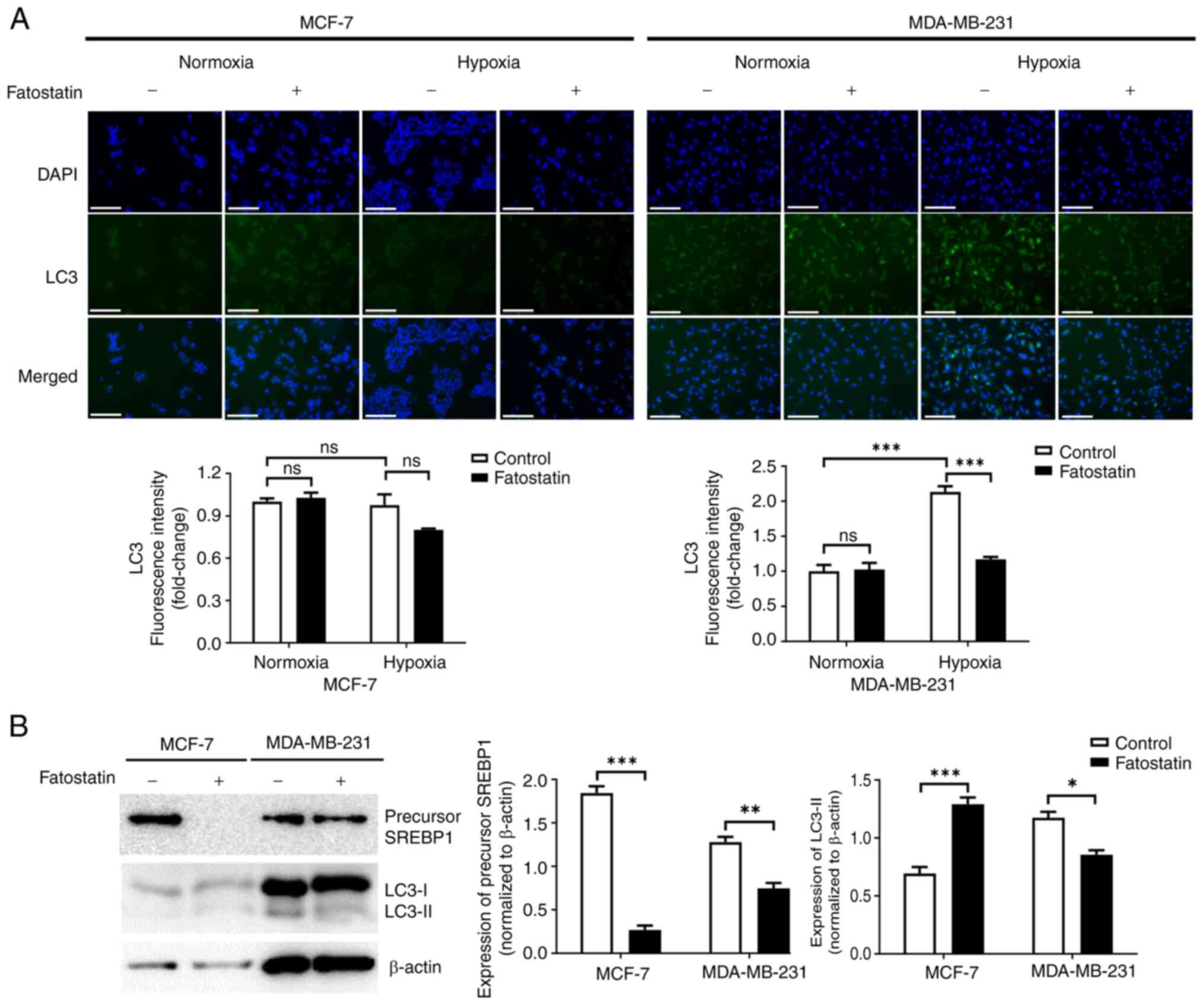
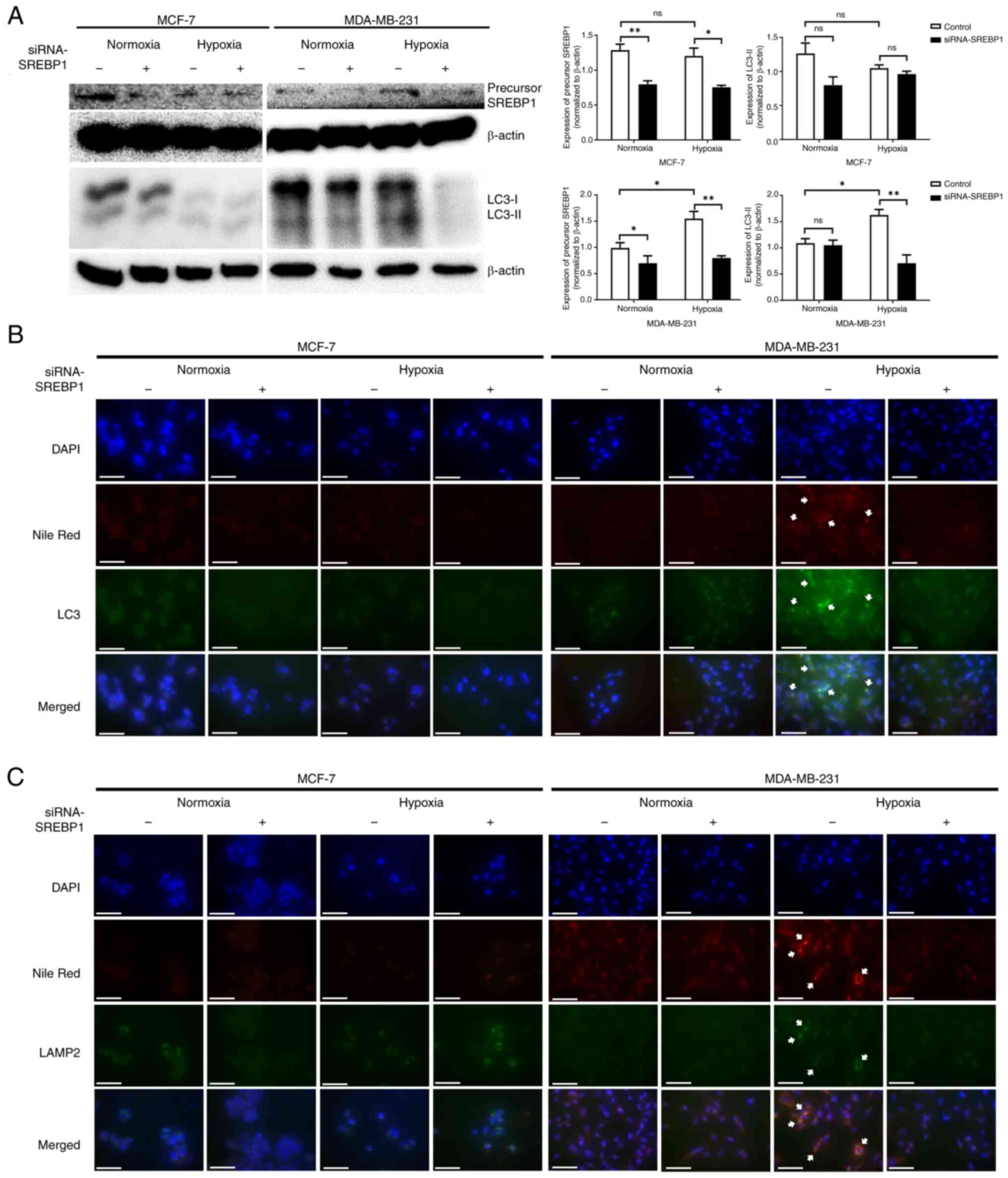
|
1
|
Liu S, Zhang X, Wang W, Li X, Sun X, Zhao
Y, Wang Q, Li Y, Hu F and Ren H: Metabolic reprogramming and
therapeutic resistance in primary and metastatic breast cancer. Mol
Cancer. 23:2612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Munir R, Lisec J, Swinnen JV and Zaidi N:
Lipid metabolism in cancer cells under metabolic stress. Br J
Cancer. 120:1090–1098. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Broadfield LA, Pane AA, Talebi A, Swinnen
JV and Fendt SM: Lipid metabolism in cancer: New perspectives and
emerging mechanisms. Dev Cell. 56:1363–1393. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Global Burden of Disease 2019 Cancer
Collaboration, . Kocarnik JM, Compton K, Dean FE, Fu W, Gaw BL,
Harvey JD, Henrikson HJ, Lu D, Pennini A, et al: Cancer incidence,
mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and
disability-adjusted life years for 29 cancer groups from 2010 to
2019: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study
2019. JAMA Oncol. 8:420–444. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zipinotti dos Santos D, de Souza JC,
Pimenta TM, da Silva Martins B, Junior RSR, Butzene SMS, Tessarolo
NG, Cilas PML Jr, Silva IV and Rangel LBA: The impact of lipid
metabolism on breast cancer: A review about its role in
tumorigenesis and immune escape. Cell Commun Signal. 21:1612023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harborg S, Zachariae R, Olsen J, Johannsen
M, Cronin-Fenton D, Bøggild H and Borgquist S: Overweight and
prognosis in triple-negative breast cancer patients: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. NPJ Breast Cancer. 7:1192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kaul K, Misri S, Ramaswamy B and Ganju RK:
Contribution of the tumor and obese microenvironment to triple
negative breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 509:115–120. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sun X, Wang M, Wang M, Yu X, Guo J, Sun T,
Li X, Yao L, Dong H and Xu Y: Metabolic reprogramming in
triple-negative breast cancer. Front Oncol. 10:4282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Jiang Q and Dong C: Metabolic
reprogramming in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Biol Med.
17:44–59. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Marino N, German R, Rao X, Simpson E, Liu
S, Wan J, Liu Y, Sandusky G, Jacobsen M, Stoval M, et al:
Upregulation of lipid metabolism genes in the breast prior to
cancer diagnosis. NPJ Breast Cancer. 6:502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Giró-Perafita A, Palomeras S, Lum DH,
Blancafort A, Viñas G, Oliveras G, Pérez-Bueno F, Sarrats A, Welm
AL and Puig T: Preclinical evaluation of fatty acid synthase and
EGFR inhibition in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
22:4687–4697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu X, Zhang P, Xu J, Lv G and Li Y: Lipid
metabolism in tumor microenvironment: Novel therapeutic targets.
Cancer Cell Int. 22:2242022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo D, Bell EH, Mischel P and Chakravarti
A: Targeting SREBP-1-driven lipid metabolism to treat cancer. Curr
Pharm Des. 20:2619–2626. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng C, Geng F, Cheng X and Guo D: Lipid
metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 38:272018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Griffiths B, Lewis CA, Bensaad K, Ros S,
Zhang Q, Ferber EC, Konisti S, Peck B, Miess H, East P, et al:
Sterol regulatory element binding protein-dependent regulation of
lipid synthesis supports cell survival and tumor growth. Cancer
Metab. 1:32013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lo AKF, Lung RWM, Dawson CW, Young LS, Ko
CW, Yeung WW, Kang W, To KF and Lo KW: Activation of sterol
regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1)-mediated lipogenesis
by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1)
promotes cell proliferation and progression of nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Pathol. 246:180–190. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shi Z, Zhou Q, Gao S, Li W, Li X, Liu Z,
Jin P and Jiang J: Silibinin inhibits endometrial carcinoma via
blocking pathways of STAT3 activation and SREBP1-mediated lipid
accumulation. Life Sci. 217:70–80. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang N, Zhang H, Liu Y, Su P, Zhang J,
Wang X, Sun M, Chen B, Zhao W, Wang L, et al: SREBP1, targeted by
miR-18a-5p, modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast
cancer via forming a co-repressor complex with Snail and HDAC1/2.
Cell Death Differ. 26:843–859. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mahmud I, Tian G, Wang J, Hutchinson TE,
Kim BJ, Awasthee N, Hale S, Meng C, Moore A, Zhao L, et al: DAXX
drives de novo lipogenesis and contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat
Commun. 14:19272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hu P, Zhou P, Sun T, Liu D, Yin J and Liu
L: Therapeutic protein PAK restrains the progression of triple
negative breast cancer through degrading SREBP-1 mRNA. Breast
Cancer Res. 25:1512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Azam A and Sounni NE: Lipid metabolism
heterogeneity and crosstalk with mitochondria functions drive
breast cancer progression and drug resistance. Cancers (Basel).
14:62672022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Listenberger LL, Han X, Lewis SE, Cases S,
Farese RV Jr, Ory DS and Schaffer JE: Triglyceride accumulation
protects against fatty acid-induced lipotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 100:3077–3082. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yoon H, Shaw JL, Haigis MC and Greka A:
Lipid metabolism in sickness and in health: Emerging regulators of
lipotoxicity. Mol Cell. 81:3708–3730. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee H, Woo SM, Jang H, Kang M and Kim SY:
Cancer depends on fatty acids for ATP production: A possible link
between cancer and obesity. Semin Cancer Biol. 86:347–357. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ping P, Li J, Lei H and Xu X: Fatty acid
metabolism: A new therapeutic target for cervical cancer. Front
Oncol. 13:11117782023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Miller DM and Shakes DC:
Immunofluorescence microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 48:365–394. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ghosh R, Gilda JE and Gomes AV: The
necessity of and strategies for improving confidence in the
accuracy of western blots. Expert Rev Proteomics. 11:549–560. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mizushima N, Yoshimori T and Levine B:
Methods in mammalian autophagy research. Cell. 140:313–326. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mulcahy Levy JM and Thorburn A: Autophagy
in cancer: Moving from understanding mechanism to improving therapy
responses in patients. Cell Death Differ. 27:843–857. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Daskalaki I, Gkikas I and Tavernarakis N:
Hypoxia and selective autophagy in cancer development and therapy.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 6:1042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Finger EC and Giaccia AJ: Hypoxia,
inflammation, and the tumor microenvironment in metastatic disease.
Cancer Metastasis Rev. 29:285–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Wang M, Schmid T, Xin L,
Kozhuharova L, Yu WK, Huang Y, Cai F and Biskup E: Hypoxia in
breast cancer-scientific translation to therapeutic and diagnostic
clinical applications. Front Oncol. 11:6522662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Network, .
Comprehensive molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
490:61–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Todd BL, Stewart EV, Burg JS, Hughes AL
and Espenshade PJ: Sterol regulatory element binding protein is a
principal regulator of anaerobic gene expression in fission yeast.
Mol Cell Biol. 26:2817–2831. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bensaad K, Favaro E, Lewis CA, Peck B,
Lord S, Collins JM, Pinnick KE, Wigfield S, Buffa FM, Li JL, et al:
Fatty acid uptake and lipid storage induced by HIF-1α contribute to
cell growth and survival after hypoxia-reoxygenation. Cell Rep.
9:349–365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lewis C, Brault C, Peck B, Bensaad K,
Griffiths B, Mitter R, Chakravarty P, East P, Dankworth B, Alibhai
D, et al: SREBP maintains lipid biosynthesis and viability of
cancer cells under lipid- and oxygen-deprived conditions and
defines a gene signature associated with poor survival in
glioblastoma multiforme. Oncogene. 34:5128–5140. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Li W, He P, Huang YF, Li Y, Lu J, Li M,
Kurihara H, Luo Z, Meng T, Onishi M, et al: Selective autophagy of
intracellular organelles: Recent research advances. Theranostics.
11:222–256. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Soto-Avellaneda A and Morrison BE:
Signaling and other functions of lipids in autophagy: A review.
Lipids Health Dis. 19:2142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yan Q, Song Y, Zhang L, Chen Z, Yang C,
Liu S, Yuan X, Gao H, Ding G and Wang H: Autophagy activation
contributes to lipid accumulation in tubular epithelial cells
during kidney fibrosis. Cell Death Discov. 4:22018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhou C, Qian W, Li J, Ma J, Chen X, Jiang
Z, Cheng L, Duan W, Wang Z, Wu Z, et al: High glucose
microenvironment accelerates tumor growth via SREBP1-autophagy axis
in pancreatic cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3022019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Novak
I, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Cuervo AM and Czaja MJ: Autophagy regulates
lipid metabolism. Nature. 458:1131–1135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Pham DV, Tilija Pun N and Park PH:
Autophagy activation and SREBP-1 induction contribute to fatty acid
metabolic reprogramming by leptin in breast cancer cells. Mol
Oncol. 15:657–678. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chandel NS, Budinger GR, Choe SH and
Schumacker PT: Cellular respiration during hypoxia. Role of
cytochrome oxidase as the oxygen sensor in hepatocytes. J Biol
Chem. 272:18808–18816. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ashton TM, McKenna WG, Kunz-Schughart LA
and Higgins GS: Oxidative phosphorylation as an emerging target in
cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res. 24:2482–2490. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|