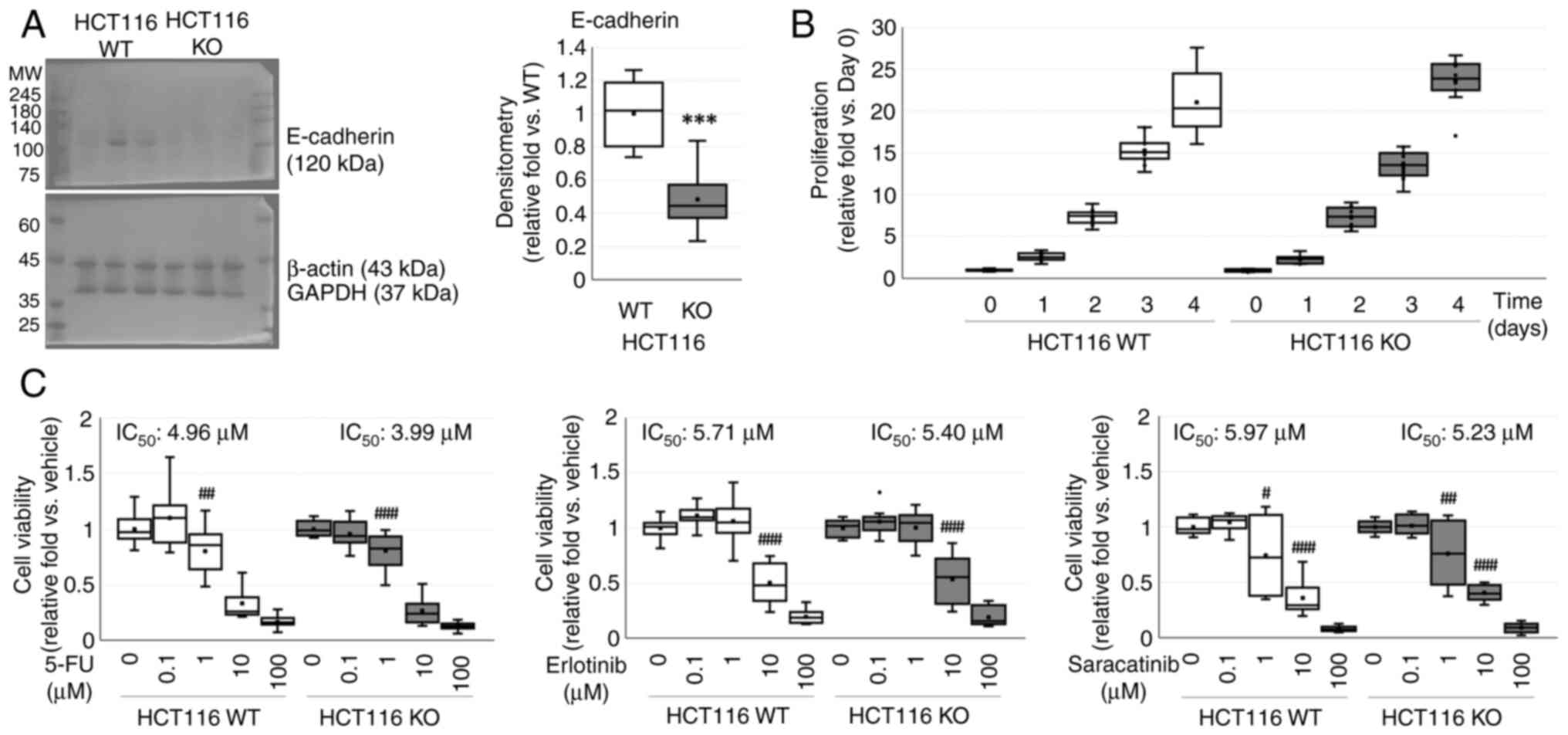
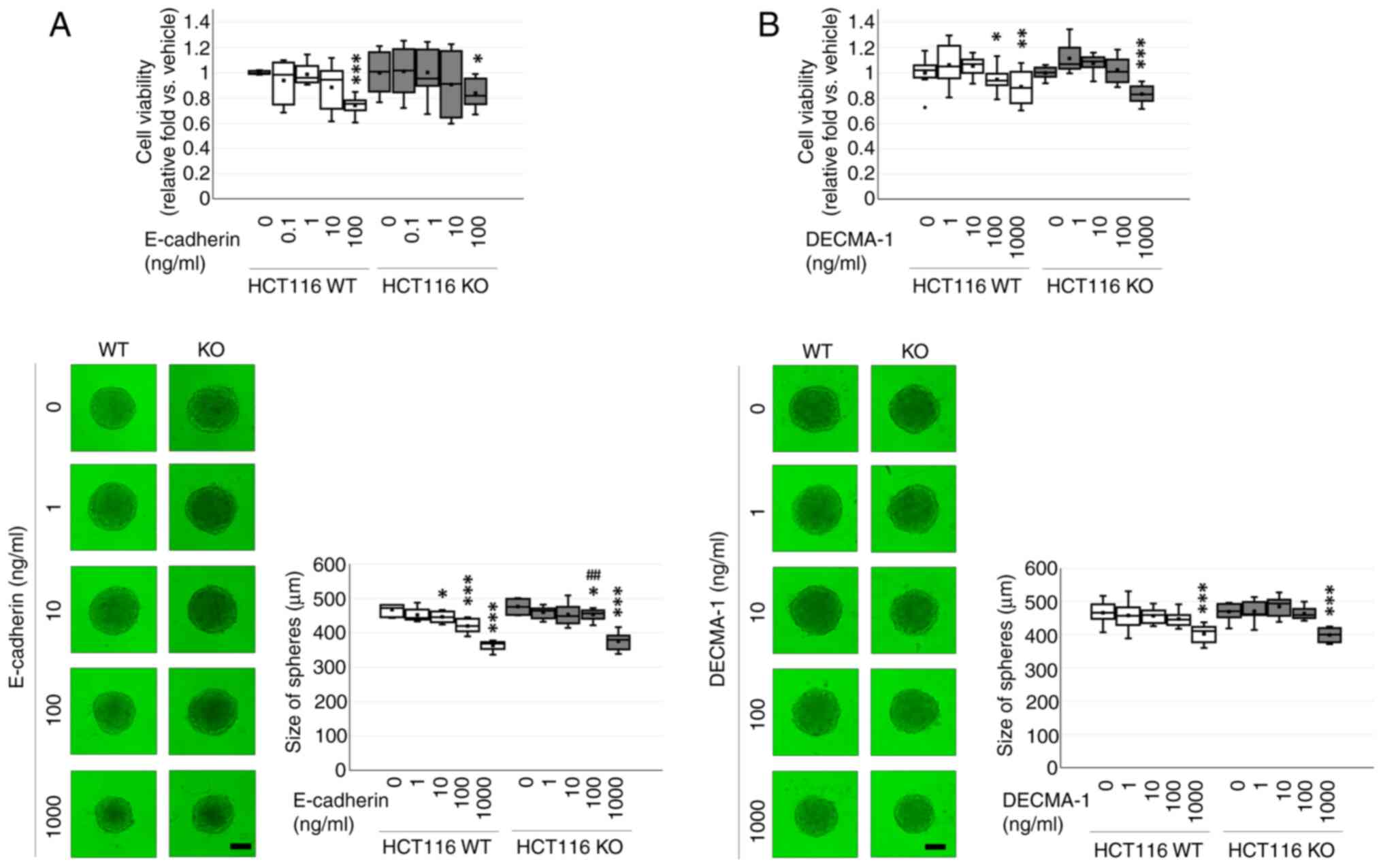
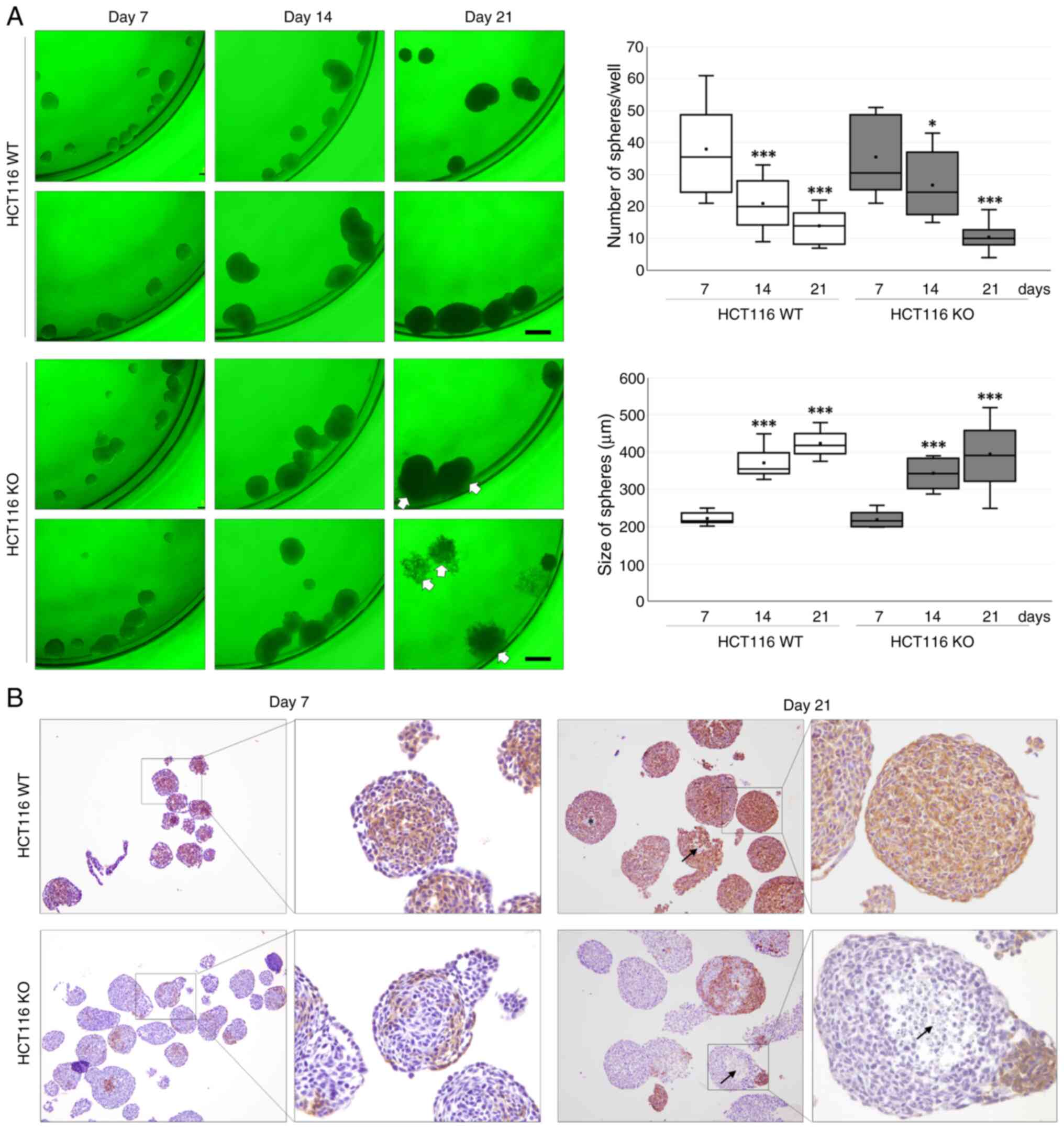
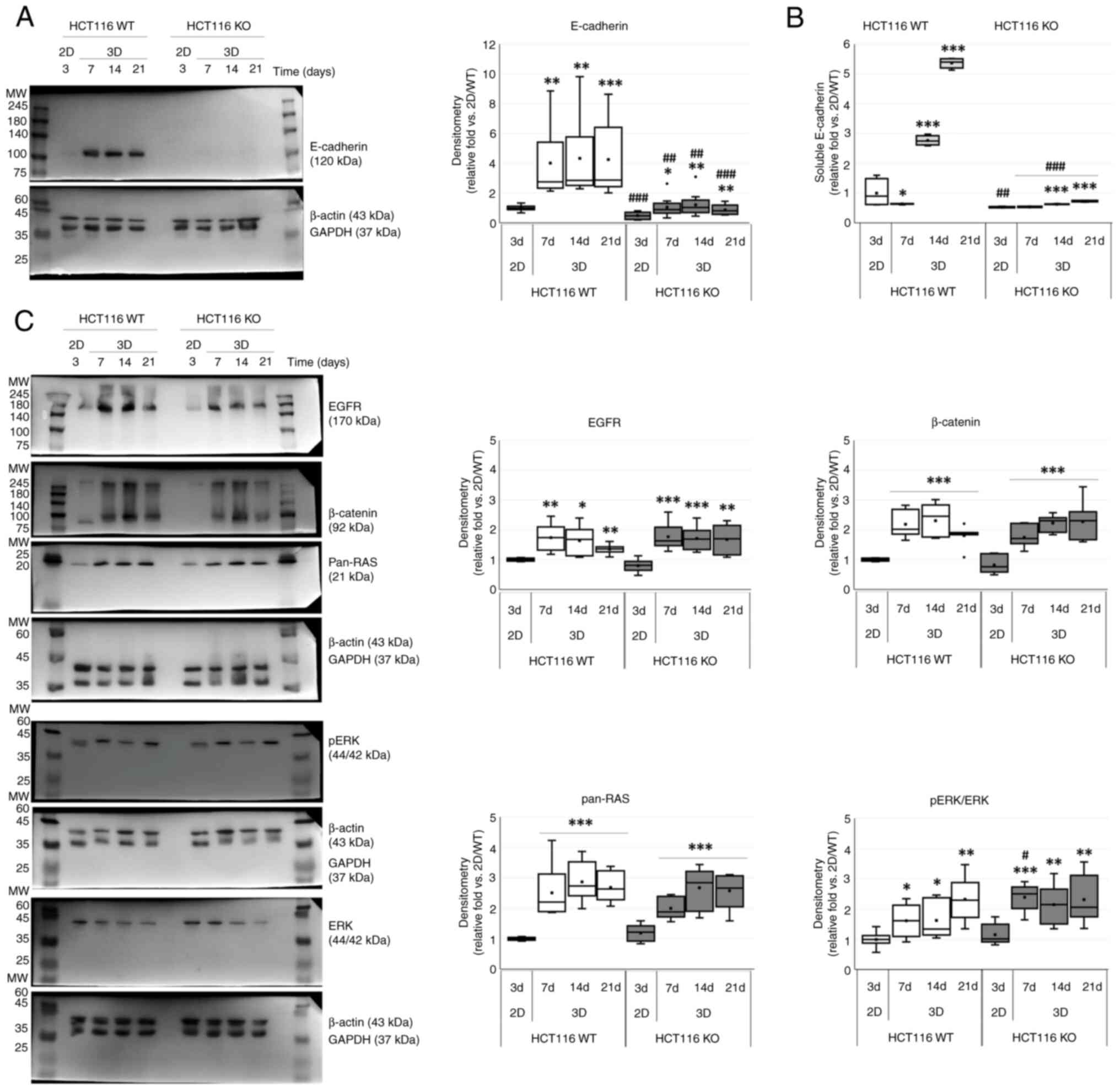
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:12–49. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA
and Jemal A: Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin.
73:233–254. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hecht JR: Current and emerging therapies
for metastatic colorectal cancer: Applying research findings to
clinical practice. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 65 (11 Suppl 4):S15–S21;
quiz S22-4. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Berx G, Becker KF, Höfler H and van Roy F:
Mutations of the human E-cadherin (CDH1) gene. Hum Mutat.
12:226–237. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bustos-Carpinteyro AR, Oliveira C, Sousa
A, Oliveira P, Pinheiro H, Carvalho J, Magaña-Torres MT,
Flores-Miramontes MG, Aguilar-Lemarroy A, Jave-Suárez LF, et al:
CDH1 somatic alterations in Mexican patients with diffuse and mixed
sporadic gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 19:692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bocca C, Bozzo F, Cannito S, Parola M and
Miglietta A: Celecoxib inactivates epithelial-mesenchymal
transition stimulated by hypoxia and/or epidermal growth factor in
colon cancer cells. Mol Carcinog. 51:783–795. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim K, Kim KH, Roh K, Yoo BC, Ku JL, Shin
YK, Cho JY, Kim M, Kwon MH, Goh SH, et al: Antitumor effects of
calgranulin B internalized in human colon cancer cells. Oncotarget.
7:20368–20380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trinh NT, Nguyen TMN, Yook JI, Ahn SG and
Kim SA: Quercetin and quercitrin from Agrimonia pilosa ledeb
inhibit the migration and invasion of colon cancer cells through
the JNK signaling pathway. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 15:3642022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hu MN, Hu SH, Zhang XW, Xiong SM and Deng
H: Overview on new progress of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer
with CDH1 variants. Tumori. 106:346–355. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee Y, Ko D, Yoon J, Lee Y and Kim S:
TMEM52B suppression promotes cancer cell survival and invasion
through modulating E-cadherin stability and EGFR activity. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 40:582021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Manuel Iglesias J, Beloqui I,
Garcia-Garcia F, Leis O, Vazquez-Martin A, Eguiara A, Cufi S, Pavon
A, Menendez JA, Dopazo J and Martin AG: Mammosphere formation in
breast carcinoma cell lines depends upon expression of E-cadherin.
PLoS One. 8:e772812013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han SJ, Kwon S and Kim KS: Challenges of
applying multicellular tumor spheroids in preclinical phase. Cancer
Cell Int. 21:1522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, Yang J,
Lander ES and Weinberg RA: Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis
via multiple downstream transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res.
68:3645–3654. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brouxhon SM, Kyrkanides S, Teng X, Athar
M, Ghazizadeh S, Simon M, O'Banion MK and Ma L: Soluble E-cadherin:
A critical oncogene modulating receptor tyrosine kinases, MAPK and
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling. Oncogene. 33:225–235. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu QP, Kuang JY, Yang QK, Bian XW and Yu
SC: Beyond a tumor suppressor: Soluble E-cadherin promotes the
progression of cancer. Int J Cancer. 138:2804–2812. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Patil PU, D'Ambrosio J, Inge LJ, Mason RW
and Rajasekaran AK: Carcinoma cells induce lumen filling and EMT in
epithelial cells through soluble E-cadherin-mediated activation of
EGFR. J Cell Sci. 128:4366–4379. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ramírez Moreno M and Bulgakova NA: The
cross-talk between EGFR and E-cadherin. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:8286732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Min SO, Lee SW, Bak SY and Kim KS: Ideal
sphere-forming culture conditions to maintain pluripotency in a
hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Cell Int. 15:952015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chang IY and Yoon SP: Increased soluble
E-cadherin of spheroid formation supplemented with fetal bovine
serum in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 25:2072023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Brouxhon SM, Kyrkanides S, Teng X, Raja V,
O'Banion MK, Clarke R, Byers S, Silberfeld A, Tornos C and Ma L:
Monoclonal antibody against the ectodomain of E-cadherin (DECMA-1)
suppresses breast carcinogenesis: Involvement of the
HER/PI3K/Akt/mTOR and IAP pathways. Clin Cancer Res. 19:3234–3246.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stanich PP, Elgindi D, Stoffel E, Koeppe
E, Bansal A, Stetson R, Collins DL, Clark DF, Karloski E, Dudley B,
et al: Colorectal neoplasia in CDH1 pathogenic variant carriers: A
multicenter analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 117:1877–1879. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Han XY, Wei B, Fang JF, Zhang S, Zhang FC,
Zhang HB, Lan TY, Lu HQ and Wei HB: Epithelial-mesenchymal
transition associates with maintenance of stemness in
spheroid-derived stem-like colon cancer cells. PLoS One.
8:e733412013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Z, Bu X, Chen H, Wang Q and Sha W:
Bmi-1 promotes the invasion and migration of colon cancer stem
cells through the downregulation of E-cadherin. Int J Mol Med.
38:1199–1207. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qian Y, Wu X, Yokoyama Y, Okuzaki D,
Taguchi M, Hirose H, Wang J, Hata T, Inoue A, Hiraki M, et al:
E-cadherin-Fc chimera protein matrix enhances cancer stem-like
properties and induces mesenchymal features in colon cancer cells.
Cancer Sci. 110:3520–3532. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tay PN, Tan P, Lan Y, Leung CH, Laban M,
Tan TC, Ni H, Manikandan J, Rashid SB, Yan B, et al: Palladin, an
actin-associated protein, is required for adherens junction
formation and intercellular adhesion in HCT116 colorectal cancer
cells. Int J Oncol. 37:909–926. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rao C, Frodyma DE, Southekal S, Svoboda
RA, Black AR, Guda C, Mizutani T, Clevers H, Johnson KR, Fisher KW
and Lewis RE: KSR1- and ERK-dependent translational regulation of
the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Elife. 10:e666082021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Díaz VM, Hurtado M, Kort EJ, Resnati M,
Blasi F, Thomson T and Paciucci R: Requirement of the enzymatic and
signaling activities of plasmin for phorbol-ester-induced
scattering of colon cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 312:2203–2213.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao S, Hu J, Wu X and Liang Z: PMA treated
THP-1-derived-IL-6 promotes EMT of SW48 through STAT3/ERK-dependent
activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
108:618–624. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park YR, Seo SY, Kim SL, Zhu SM, Chun S,
Oh JM, Lee MR, Kim SH, Kim IH, Lee SO, et al: MiRNA-206 suppresses
PGE2-induced colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration, and
invasion by targetting TM4SF1. Biosci Rep. 38:BSR201806642018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dong L, Ding C, Zheng T, Pu Y, Liu J,
Zhang W, Xue F, Kang P, Ma Y, Wang X and Mao C: Extracellular
vesicles from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells treated
with siRNA against ELFN1-AS1 suppress colon adenocarcinoma
proliferation and migration. Am J Transl Res. 11:6989–6999.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang X, Zheng YT and Rong W: Sevoflurane
induces apoptosis and inhibits the growth and motility of colon
cancer in vitro and in vivo via inactivating Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK
signaling. Life Sci. 239:1169162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cheng B, Rong A, Zhou Q and Li W: LncRNA
LINC00662 promotes colon cancer tumor growth and metastasis by
competitively binding with miR-340-5p to regulate CLDN8/IL22
co-expression and activating ERK signaling pathway. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 39:52020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jun JH, Oh JE, Shim JK, Kwak YL and Cho
JS: Effects of bisphenol A on the proliferation, migration, and
tumor growth of colon cancer cells: In vitro and in vivo evaluation
with mechanistic insights related to ERK and 5-HT3. Food Chem
Toxicol. 158:1126622021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Minelli R, Serpe L, Pettazzoni P, Minero
V, Barrera G, Gigliotti C, Mesturini R, Rosa AC, Gasco P, Vivenza
N, et al: Cholesteryl butyrate solid lipid nanoparticles inhibit
the adhesion and migration of colon cancer cells. Br J Pharmacol.
166:587–601. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Satow R, Hirano T, Batori R, Nakamura T,
Murayama Y and Fukami K: Phospholipase Cδ1 induces E-cadherin
expression and suppresses malignancy in colorectal cancer cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:13505–13510. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peng C, Li Z, Niu Z, Niu W, Xu Z, Gao H,
Niu W, Wang J, He Z, Gao C, et al: Norcantharidin suppresses colon
cancer cell epithelial-mesenchymal transition by inhibiting the
αvβ6-ERK-Ets1 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 6:205002016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li X, Zhang G, Wang Y, Elgehama A, Sun Y,
Li L, Gu Y, Guo W and Xu Q: Loss of periplakin expression is
associated with the tumorigenesis of colorectal carcinoma. Biomed
Pharmacother. 87:366–374. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chang YF, Wang HH, Shu CW, Tsai WL, Lee
CH, Chen CL and Liu PF: TMEM211 promotes tumor progression and
metastasis in colon cancer. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 45:4529–4543.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li Y, Zhu G, Zhai H, Jia J, Yang W, Li X
and Liu L: Simultaneous stimulation with tumor necrosis factor-α
and transforming growth factor-β1 induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in colon cancer cells via the NF-κB pathway. Oncol Lett.
15:6873–6880. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lin MC, Wang FY, Kuo YH and Tang FY:
Cancer chemopreventive effects of lycopene: Suppression of MMP-7
expression and cell invasion in human colon cancer cells. J Agric
Food Chem. 59:11304–11318. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bartucci M, Svensson S, Ricci-Vitiani L,
Dattilo R, Biffoni M, Signore M, Ferla R, De Maria R and Surmacz E:
Obesity hormone leptin induces growth and interferes with the
cytotoxic effects of 5-fluorouracil in colorectal tumor stem cells.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 17:823–833. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hashimoto K, Nishimura S, Shinyashiki Y,
Ito T and Akagi M: Characterizing inflammatory markers in highly
aggressive soft tissue sarcomas. Medicine (Baltimore).
101:e306882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kleer CG, van Golen KL, Braun T and
Merajver SD: Persistent E-cadherin expression in inflammatory
breast cancer. Mod Pathol. 14:458–464. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Cohen EN, Gao H, Anfossi S, Mego M, Reddy
NG, Debeb B, Giordano A, Tin S, Wu Q, Garza RJ, et al: Inflammation
mediated metastasis: Immune induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition in inflammatory breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
10:e01327102015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Shirahama S, Furukawa F, Wakita H and
Takigawa M: E- and P-cadherin expression in tumor tissues and
soluble E-cadherin levels in sera of patients with skin cancer. J
Dermatol Sci. 13:30–36. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Devaux CA, Mezouar S and Mege JL: The
E-cadherin cleavage associated to pathogenic bacteria infections
can favor bacterial invasion and transmigration, dysregulation of
the immune response and cancer induction in humans. Front
Microbiol. 10:25982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Katayama M, Hirai S, Yasumoto M, Nishikawa
K, Nagata S, Otsuka M, Kamihagi K and Kato I: Soluble fragments of
e-cadherin cell-adhesion molecule increase in urinary-excretion of
cancer-patients, potentially indicating its shedding from
epithelial tumor-cells. Int J Oncol. 5:1049–1057. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Repetto O, De Paoli P, De Re V, Canzonieri
V and Cannizzaro R: Levels of soluble E-cadherin in breast,
gastric, and colorectal cancers. Biomed Res Int. 2014:4080472014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Weiss JV, Klein-Scory S, Kübler S,
Reinacher-Schick A, Stricker I, Schmiegel W and Schwarte-Waldhoff
I: Soluble E-cadherin as a serum biomarker candidate: Elevated
levels in patients with late-stage colorectal carcinoma and FAP.
Int J Cancer. 128:1384–1392. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Okugawa Y, Toiyama Y, Inoue Y, Iwata T,
Fujikawa H, Saigusa S, Konishi N, Tanaka K, Uchida K and Kusunoki
M: Clinical significance of serum soluble E-cadherin in colorectal
carcinoma. J Surg Res. 175:e67–e73. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|