|
1
|
Wei W, Zeng H, Zheng R, Zhang S, An L,
Chen R, Wang S, Sun K, Matsuda T, Bray F and He J: Cancer
registration in China and its role in cancer prevention and
control. Lancet Oncol. 21:e342–e349. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hu J and Gao D: Recent advances in
aptamer-based microfluidic biosensors for the isolation, signal
amplification and detection of exosomes. Sensors (Basel).
25:8482025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu X, Jiang H and Wang X: Advances in
cancer research: Current and future diagnostic and therapeutic
strategies. Biosensors (Basel). 14:1002024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liu R, Li J, Salena BJ and Li Y: Aptamer
and DNAzyme based colorimetric biosensors for pathogen detection.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 64:e2024187252025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He Y, Zeng X, Xiong Y, Shen C, Huang K and
Chen P: Portable aptasensor based on parallel rolling circle
amplification for tumor-derived exosomes liquid biopsy. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 11:24033712024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin M, Zhang J, Wan H, Yan C and Xia F:
Rationally designed multivalent aptamers targeting cell surface for
biomedical applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 13:9369–9389.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Aiassa LV, Battaglia G and Rizzello L: The
multivalency game ruling the biology of immunity. Biophys Rev
(Melville). 4:0413062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yeldell SB and Seitz O: Nucleic acid
constructs for the interrogation of multivalent protein
interactions. Chem Soc Rev. 49:6848–6865. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Z, Yang X, Lee NZ and Cao X:
Multivalent aptamer approach: Designs, strategies, and
applications. Micromachines (Basel). 13:4362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Moradi Z, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM, Zamanian
J, Moshiri M, Etemad D, Etemad L, Kesharwani P and Sahebkar A:
Designing multivalent aptamers: Recent advancements in diagnostic
and therapeutic approaches for cancer treatment. J Drug Delivery
Sci Technol. 105:1066142025. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
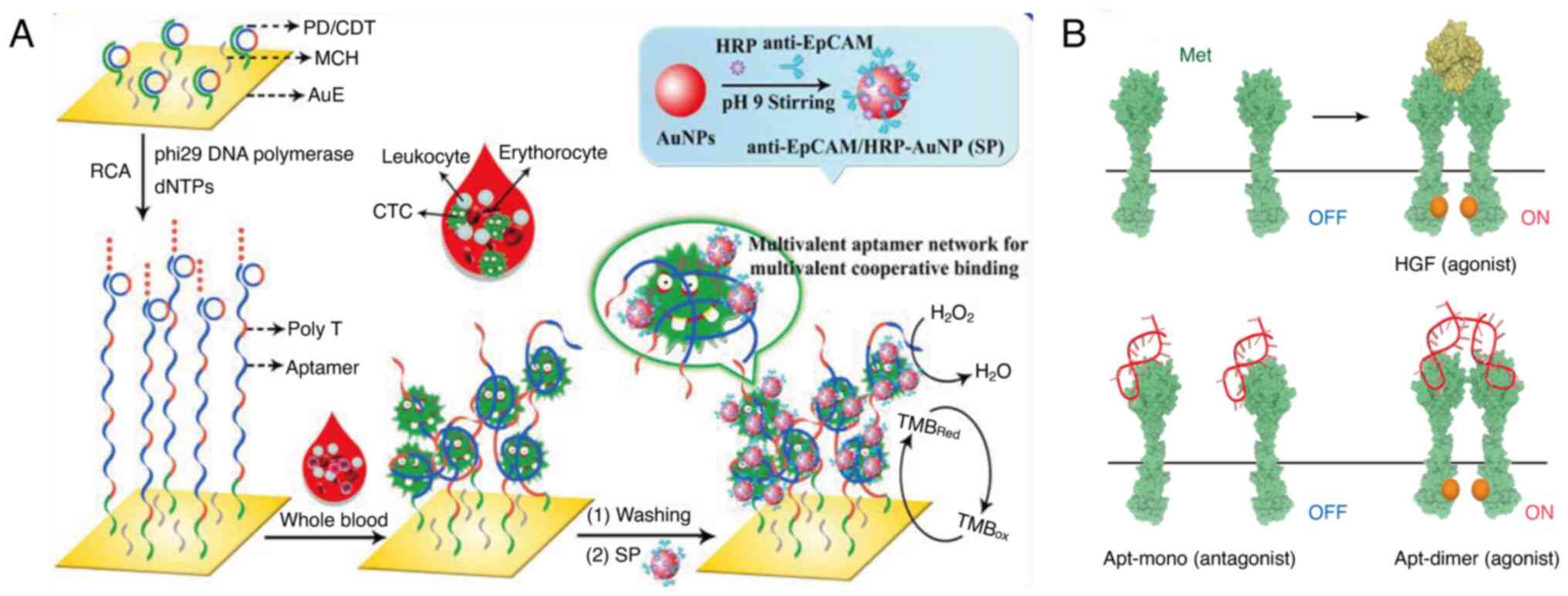
|
Duan Q, Jia H, Chen W, Qin C, Zhang K, Jia
F, Fu T, Wei Y, Fan M, Wu Q and Tan W: Multivalent aptamer-based
lysosome-targeting chimeras (LYTACs) platform for mono- or
dual-targeted proteins degradation on cell surface. Adv Sci
(Weinh). 11:23089242024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang X, Peng Y, Yao L, Shang H, Zheng Z,
Chen W and Xu J: Self-assembly of multivalent aptamer-tethered DNA
monolayers dedicated to a fluorescence polarization-responsive
circular isothermal strand displacement amplification for
salmonella assay. Anal Chem. 95:2570–2578. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
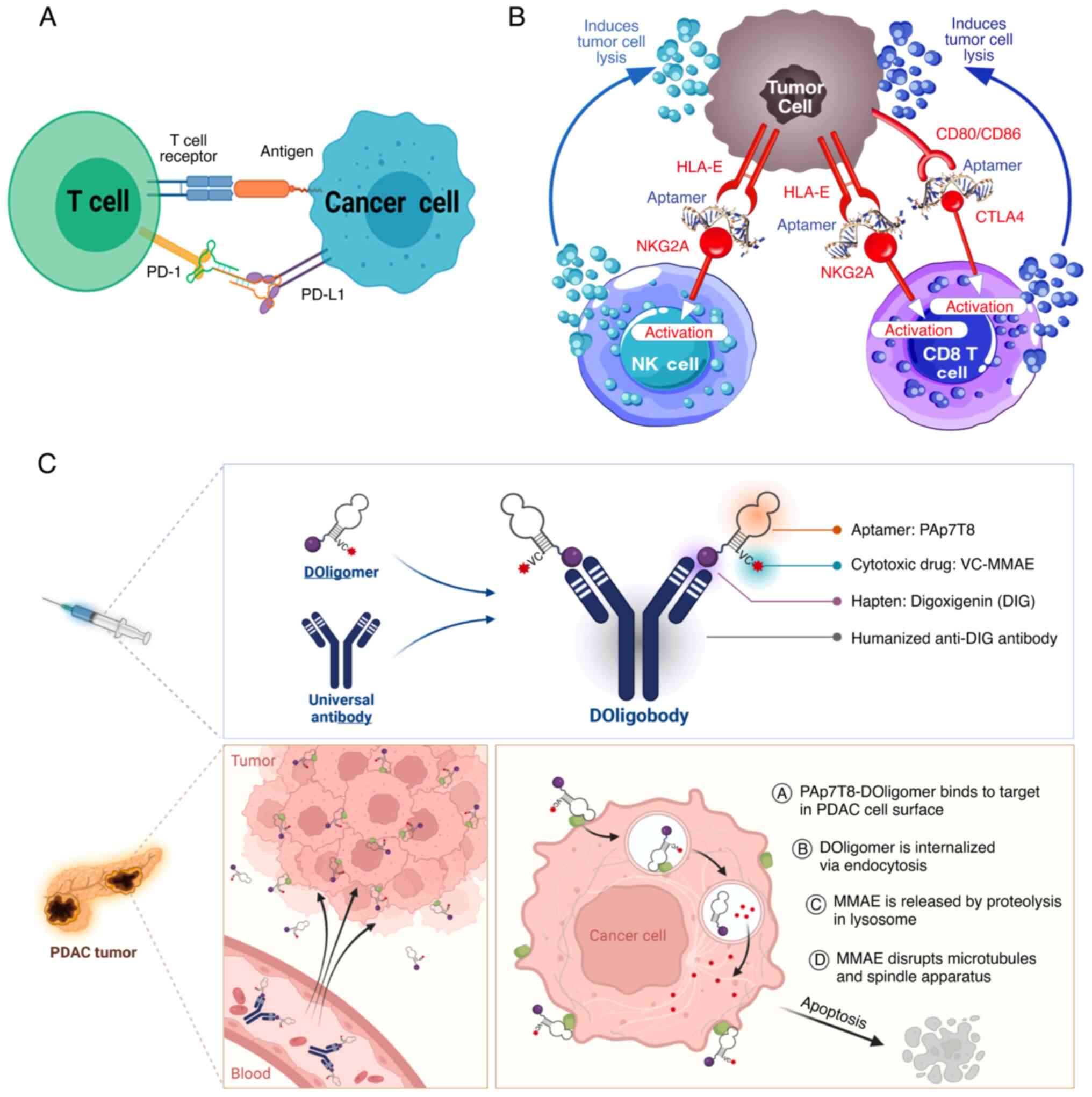
|
13
|
Zhang GQ, Zhong LP, Yang N and Zhao YX:
Screening of aptamers and their potential application in targeted
diagnosis and therapy of liver cancer. World J Gastroenterol.
25:3359–3369. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Omer M, Andersen VL, Nielsen JS, Wengel J
and Kjems J: Improved cancer targeting by multimerizing aptamers on
nanoscaffolds. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 22:994–1003. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Sheng W and Fan ZH: An ensemble
of aptamers and antibodies for multivalent capture of cancer cells.
Chem Commun. 50:67222014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu S, Li X, Gao H, Chen J and Jiang H:
Progress in aptamer research and future applications.
ChemistryOpen. e2024004632025.doi: 10.1002/open.202400463 (Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sanjanwala D and Patravale V: Aptamers and
nanobodies as alternatives to antibodies for ligand-targeted drug
delivery in cancer. Drug Discovery Today. 28:1035502023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kovacevic KD, Gilbert JC and Jilma B:
Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of aptamers. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 134:36–50. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vandghanooni S, Eskandani M, Barar J and
Omidi Y: Bispecific therapeutic aptamers for targeted therapy of
cancer: A review on cellular perspective. J Mol Med (Berl).
96:885–902. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu G and Chen X: Aptamer-based targeted
therapy. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 134:65–78. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Herrera M, Pretelli G, Desai J, Garralda
E, Siu LL, Steiner TM and Au L: Bispecific antibodies: Advancing
precision oncology. Trends Cancer. 10:893–919. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Adachi T and Nakamura Y: Aptamers: A
review of their chemical properties and modifications for
therapeutic application. Molecules. 24:42292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kumar Kulabhusan P, Hussain B and Yüce M:
Current perspectives on aptamers as diagnostic tools and
therapeutic agents. Pharmaceutics. 12:6462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mathavan S, Tam YJ, Mustaffa KMF and Tye
GJ: Aptamer based immunotherapy: A potential solid tumor
therapeutic. Front Immunol. 16:15365692025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lauridsen LH, Shamaileh HA, Edwards SL,
Taran E and Veedu RN: Rapid one-step selection method for
generating nucleic acid aptamers: Development of a DNA aptamer
against α-bungarotoxin. PLoS One. 7:e417022012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ferreira D, Barbosa J, Sousa DA, Silva C,
Melo LDR, Avci-Adali M, Wendel HP and Rodrigues LR: Selection of
aptamers against triple negative breast cancer cells using high
throughput sequencing. Sci Rep. 11:86142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hwang CK, Chew EY, Cukras CA, Keenan TDL,
Wong WT, Linehan WM, Chittiboina P, Pacak K and Wiley HE:
Intravitreous treatment of severe ocular von Hippel-Lindau disease
using a combination of the VEGF inhibitor, ranibizumab and PDGF
inhibitor, E10030: Results from a phase 1/2 clinical trial. Clin
Exp Ophthalmol. 49:1048–1059. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Y, Du Y, Zhuo Y and Qiu L:
Functional nucleic acid-based live-cell fluorescence imaging. Front
Chem. 8:5980132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He J, Duan Q, Ran C, Fu T, Liu Y and Tan
W: Recent progress of aptamer-drug conjugates in cancer therapy.
Acta Pharm Sin B. 13:1358–1370. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Hu B, Pei X, Li J, Qi D, Xu Y, Ou
H, Wu Y, Xue L, Huang JH, et al: A non-G-quadruplex DNA aptamer
targeting NCL for diagnosis and therapy in bladder cancer. Adv
Healthc Mater. 12:e23007912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang LF, Ling M, Kacherovsky N and Pun SH:
Aptamers 101: Aptamer discovery and in vitro applications in
biosensors and separations. Chem Sci. 14:4961–4978. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen X, Ma Y, Luo H, Abdullah R, Pan Y,
Zhang Y, Zhong C, Zhang B and Zhang G: Peptide aptamer-paclitaxel
conjugates for tumor targeted therapy. Pharmaceutics. 17:402024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lyu C, Khan IM and Wang Z: Capture-SELEX
for aptamer selection: A short review. Talanta. 229:1222742021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cossu J, Ravelet C, Martel-Frachet V,
Peyrin E and Boturyn D: Peptide-based CE-SELEX enables convenient
isolation of aptamers specifically recognizing CD20-expressing
cells. Bioorg Med Chem. 110:1178312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li Q, Zhao X, Liu H and Qu F: Low pH
capillary electrophoresis application to improve capillary
electrophoresis-systematic evolution of ligands by exponential
enrichment. J Chromatogr A. 1364:289–294. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhu C, Zhao XY, Yang G and Qu F: Capillary
electrophoresis involving in high efficiency screening for
aptamers. Chin J Analytical Chemistry. 48:583–589. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Tam WW, Yu Y, Zhuo Z, Xue Z, Tsang
C, Qiao X, Wang X, Wang W, Li Y, et al: The application of aptamer
in biomarker discovery. Biomark Res. 11:702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lam SY, Lau HL and Kwok CK: Capture-SELEX:
Selection strategy, aptamer identification, and biosensing
application. Biosensors (Basel). 12:11422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Meng X, Wen K, Citartan M and Lin Q: A
comparative study of aptamer isolation by conventional and
microfluidic strategies. Analyst. 148:787–798. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kubo T, Koike T, Ouchi T, Khaliq N, Sasaki
E, Kuroda K, Ueda M, Hanaoka K and Nemoto N: In vitro selection of
dye-fluorescence-enhancing peptide aptamer by cDNA display. Anal
Biochem. 698:1157222025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Jeddi I and Saiz L: Computational design
of single-stranded DNA hairpin aptamers immobilized on a biosensor
substrate. Sci Rep. 11:109842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fan R, Tao X, Zhai X, Zhu Y, Li Y, Chen Y,
Dong D, Yang S and Lv L: Application of aptamer-drug delivery
system in the therapy of breast cancer. Biomed Pharmacother.
161:1144442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang Y, Lai BS and Juhas M: Recent
advances in aptamer discovery and applications. Molecules.
24:9412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Vorobyeva M, Vorobjev P and Venyaminova A:
Multivalent aptamers: Versatile tools for diagnostic and
therapeutic applications. Molecules. 21:16132016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li PC, Guo J, Huo F, Yang
J, Jia R, Wang J, Huang Q, Theodorescu D, et al: Development of
novel aptamer-based targeted chemotherapy for bladder cancer.
Cancer Res. 82:1128–1139. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lakshmipriya T, Fujimaki M, Gopinath SCB,
Awazu K, Horiguchi Y and Nagasaki Y: A high-performance
waveguide-mode biosensor for detection of factor IX using PEG-based
blocking agents to suppress non-specific binding and improve
sensitivity. Analyst. 138:2863–2870. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Moreira D, Leitão D, Lopes-Nunes J, Santos
T, Figueiredo J, Miranda A, Alexandre D, Tomaz C, Mergny JL and
Cruz C: G-quadruplex aptamer-ligand characterization. Molecules.
27:67812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schmidt C, Kammel A, Tanner JA, Kinghorn
AB, Khan MM, Lehmann W, Menger M, Schedler U, Schierack P and
Rödiger S: A multiparametric fluorescence assay for screening
aptamer-protein interactions based on microbeads. Sci Rep.
12:29612022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
O'Connell GC and Smothers CG: Optimized
methodology for product recovery following emulsion PCR:
Applications for amplification of aptamer libraries and other
complex templates. J Biol Methods. 7:e1282020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zheng X, Gao S, Wu J and Hu X: Recent
advances in aptamer-based biosensors for detection of pseudomonas
aeruginosa. Front Microbiol. 11:6052292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Salunkhe S, Dheeraj, Basak M, Chitkara D
and Mittal A: Surface functionalization of exosomes for
target-specific delivery and in vivo imaging & tracking:
Strategies and significance. J Control Release. 326:599–614. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Park NJ, Wang X, Diaz A, Goos-Root DM,
Bock C, Vaught JD, Sun W and Strom CM: Measurement of cetuximab and
panitumumab-unbound serum EGFR extracellular domain using an assay
based on slow off-rate modified aptamer (SOMAmer) reagents. PLoS
One. 8:e717032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kelly L, Maier KE, Yan A and Levy M: A
comparative analysis of cell surface targeting aptamers. Nat
Commun. 12:62752021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen Z, Hu L, Zhang BT, Lu A, Wang Y, Yu Y
and Zhang G: Artificial intelligence in aptamer-target binding
prediction. Int J Mol Sci. 22:36052021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Stuber A and Nakatsuka N: Aptamer
renaissance for neurochemical biosensing. ACS Nano. 18:2552–2563.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Gao S, Zheng X, Jiao B and Wang L:
Post-SELEX optimization of aptamers. Anal Bioanal Chem.
408:4567–4573. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wu L, Wang Y, Xu X, Liu Y, Lin B, Zhang M,
Zhang J, Wan S, Yang C and Tan W: Aptamer-based detection of
circulating targets for precision medicine. Chem Rev.
121:12035–12105. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Miao Y, Fu C, Yu Z, Yu L, Tang Y and Wei
M: Current status and trends in small nucleic acid drug
development: Leading the future. Acta Pharm Sin B. 14:3802–3817.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tabuchi Y, Yang J and Taki M: Relative
nuclease resistance of a DNA aptamer covalently conjugated to a
target protein. Int J Mol Sci. 23:77782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang Y, Dong Q, Xiao J, Fang X, Huang W,
Li Q, Chen Z, Liu H and Tan W: In-vivo polyvalent simpleaptamer@protein-based
nanocarrier with synergistic charge effect for high drug loading,
high nuclease resistance, and high receptor accessibility. CCS
Chem. 1–13. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Zhang Y, Zhang H, Chan DWH, Ma Y, Lu A, Yu
S, Zhang B and Zhang G: Strategies for developing long-lasting
therapeutic nucleic acid aptamer targeting circulating protein: The
present and the future. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10:10481482022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yu Y, Wang L, Ni S, Li D, Liu J, Chu HY,
Zhang N, Sun M, Li N, Ren Q, et al: Targeting loop3 of sclerostin
preserves its cardiovascular protective action and promotes bone
formation. Nat Commun. 13:42412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Camorani S, Caliendo A, Morrone E, Agnello
L, Martini M, Cantile M, Cerrone M, Zannetti A, La Deda M, Fedele
M, et al: Bispecific aptamer-decorated and light-triggered
nanoparticles targeting tumor and stromal cells in breast cancer
derived organoids: Implications for precision phototherapies. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 43:922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Zhang N, Wang J, Bing T, Liu X and
Shangguan D: Transferrin receptor-mediated internalization and
intracellular fate of conjugates of a DNA aptamer. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 27:1249–1259. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xiao Y, Pan T, Da W, Liu Y, Chen S, Chen
D, Liu K, Zheng Y, Xie D, Gao Y, et al: Aptamer-drug
conjugates-loaded bacteria for pancreatic cancer synergistic
therapy. Sig Transduct Target Ther. 9:2722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Safarkhani M, Ahmadi S, Ipakchi H, Saeb
MR, Makvandi P, Ebrahimi Warkiani M, Rabiee N and Huh Y:
Advancements in aptamer-driven DNA nanostructures for precision
drug delivery. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e24016172024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Papaefthymiou A, Doukatas A and
Galanopoulos M: Pancreatic cancer and oligonucleotide therapy:
Exploring novel therapeutic options and targeting chemoresistance.
Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 46:1019112022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Wang J, Tan M, Wang Y, Liu X and Lin A:
Advances in modification and delivery of nucleic acid drugs.
Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 52:417–428. 2023.(In English,
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pfeiffer F, Rosenthal M, Siegl J, Ewers J
and Mayer G: Customised nucleic acid libraries for enhanced aptamer
selection and performance. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 48:111–118. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Peng Y, Lu B, Deng Y, Yang N and Li G: A
dual-recognition-controlled electrochemical biosensor for accurate
and sensitive detection of specific circulating tumor cells.
Biosens Bioelectron. 201:1139732022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Li J, Zhang Z, Gu J, Amini R, Mansfield
AG, Xia J, White D, Stacey HD, Ang JC, Panesar G, et al: Three on
three: Universal and high-affinity molecular recognition of the
symmetric homotrimeric spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 with a symmetric
homotrimeric aptamer. J Am Chem Soc. 144:23465–23473. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ge Z, Guo L, Wu G, Li J, Sun Y, Hou Y, Shi
J, Song S, Wang L, Fan C, et al: DNA origami-enabled engineering of
ligand-drug conjugates for targeted drug delivery. Small.
16:e19048572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang S, Liu X, Wei D, Zhou H, Zhu J, Yu Q,
Luo L, Dai X, Jiang Y, Yu L, et al: Polyvalent aptamer nanodrug
conjugates enable efficient tumor cuproptosis therapy through
copper overload and glutathione depletion. J Am Chem Soc.
146:30033–30045. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Eilers A, Witt S and Walter J:
Aptamer-modified nanoparticles in medical applications. Aptamers in
Biotechnology. vol. 174. Urmann K and Walter JG: Springer
International Publishing; Cham: pp. 161–193. 2020, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Diao W, Yang B, Sun S, Wang A, Kou R, Ge
Q, Shi M, Lian B, Sun T, Wu J, et al: PNA-modified liposomes
improve the delivery efficacy of CAPIRI for the synergistic
treatment of colorectal cancer. Front Pharmacol. 13:8931512022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang X, Wei X, Wu CX, Men X, Wang J, Bai
JJ, Sun XY, Wang Y, Yang T, Lim CT, et al: Multiplex profiling of
biomarker and drug uptake in single cells using microfluidic flow
cytometry and mass spectrometry. ACS Nano. 18:6612–6622. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Amini R, Ma J, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Gu J,
Soleymani L and Li Y: Dimeric DNA aptamers for the spike protein of
SARS-CoV-2 derived from a structured library with dual random
domains. Small Methods. Dec 20;e24016002024.doi:
10.1002/smtd.202401600 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Yang J, Li X, Jiang B, Yuan R and Xiang Y:
In situ-generated multivalent aptamer network for efficient capture
and sensitive electrochemical detection of circulating tumor cells
in whole blood. Anal Chem. 92:7893–7899. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Su N, Zhang J, Liu W, Zheng H, Li M, Zhao
J, Gao M and Zhang X: Specific isolation and quantification of
PD-L1 positive tumor derived exosomes for accurate breast cancer
discrimination via aptamer-functionalized magnetic composites and
SERS immunoassay. Talanta. 281:1269562025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Song Z, Zhou Y, Shen M, Zhao D, Hu H, Zeng
S, Sun L and Cai S: MUC1 detection and in situ imaging method based
on aptamer conformational switch and hybridization chain reaction.
Talanta. 239:1231292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chen Y, Tyagi D, Lyu M, Carrier AJ, Nganou
C, Youden B, Wang W, Cui S, Servos M, Oakes K, et al: Regenerative
NanoOctopus based on multivalent-aptamer-functionalized magnetic
microparticles for effective cell capture in whole blood. Anal
Chem. 91:4017–4022. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Liu Y, Zhang B, Wu X, Wang F, Yang Z, Li
M, Sheng K, Yan Y, Zhu L, Jing H, et al: A facile liquid biopsy
assay for highly efficient CTCs capture and reagent-less monitoring
of immune checkpoint PD-L1 expression on CTCs with non-small cell
lung cancer patients. Biosens Bioelectron. 275:1172362025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ueki R, Uchida S, Kanda N, Yamada N, Ueki
A, Akiyama M, Toh K, Cabral H and Sando S: A chemically unmodified
agonistic DNA with growth factor functionality for in vivo
therapeutic application. Sci Adv. 6:eaay28012020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lei Y, Qiao Z, Tang J, He X, Shi H, Ye X,
Yan L, He D and Wang K: DNA nanotriangle-scaffolded activatable
aptamer probe with ultralow background and robust stability for
cancer theranostics. Theranostics. 8:4062–4071. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Menon AP, Villanueva H,
Meraviglia-Crivelli D, van Santen HM, Hellmeier J, Zheleva A,
Nonateli F, Peters T, Wachsmann TLA, Hernandez-Rueda M, et al: CD3
aptamers promote expansion and persistence of tumor-reactive T
cells for adoptive T cell therapy in cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 35:1021982024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zlinska V, Feketova Z, Czyrek A, Chudzian
J, Zivkovic ML, Ursachi VC, Dudeja P, Fafilek B, Rynes J,
Rico-Llanos G, et al: Specific inhibition of fibroblast growth
factor receptor 1 signaling by a DNA aptamer. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 36:1024052025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zschäbitz S and Grüllich C: Lenvantinib: A
tyrosine kinase inhibitor of VEGFR 1–3, FGFR 1–4, PDGFRα, KIT and
RET. Small Molecules in Oncology. vol. 211. Martens UM: Springer
International Publishing; Cham: pp. 187–198. 2018, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Shapir Itai Y, Barboy O, Salomon R,
Bercovich A, Xie K, Winter E, Shami T, Porat Z, Erez N, Tanay A, et
al: Bispecific dendritic-T cell engager potentiates anti-tumor
immunity. Cell. 187:375–389.e18. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
De Assis LH, Fassi DE and Hutchings M:
Bispecific antibody therapies. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ
Program. 2023:216–222. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Thomas BJ, Porciani D and Burke DH: Cancer
immunomodulation using bispecific aptamers. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
27:894–915. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sun Y, Mo L, Hu X, Yu D, Xie S, Li J, Zhao
Z, Fang X, Ye M, Qiu L, et al: Bispecific aptamer-based
recognition-then-conjugation strategy for PD1/PDL1 axis blockade
and enhanced immunotherapy. ACS Nano. 16:21129–21138. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Shalata W, Weissmann S, Itzhaki Gabay S,
Sheva K, Abu Saleh O, Jama AA, Yakobson A and Rouvinov K: A
retrospective, single-institution experience of bullous pemphigoid
as an adverse effect of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Cancers
(Basel). 14:54512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ji P, Gong Y, Jin ML, Wu HL, Guo LW, Pei
YC, Chai WJ, Jiang YZ, Liu Y, Ma XY, et al: In vivo
multidimensional CRISPR screens identify Lgals2 as an immunotherapy
target in triple-negative breast cancer. Sci Adv. 8:eabl82472022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ayass MA, Tripathi T, Griko N, Okyay T,
Ramankutty Nair R, Zhang J, Zhu K, Melendez K, Pashkov V and
Abi-Mosleh L: Dual checkpoint aptamer immunotherapy: Unveiling
tailored cancer treatment targeting CTLA-4 and NKG2A. Cancers
(Basel). 16:10412024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Chen G, Mao D, Wang X, Chen J, Gu C, Huang
S, Yang Y, Zhang F and Tan W: Aptamer-based self-assembled
nanomicelle enables efficient and targeted drug delivery. J
Nanobiotechnol. 21:4152023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Choi SI, Lee YS, Lee YM, Kim HJ, Kim WJ,
Jung S, Im JE, Lee MR, Kim JK, Jeon AR, et al: Complexation of drug
and hapten-conjugated aptamer with universal hapten antibody for
pancreatic cancer treatment. J Control Release. 360:940–952. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Szymanowski W, Szymanowska A, Bielawska A,
Lopez-Berestein G, Rodriguez-Aguayo C and Amero P: Aptamers as
potential therapeutic tools for ovarian cancer: Advancements and
challenges. Cancers (Basel). 15:53002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Xie S, Wang Z, Fu T, Zheng L, Wu H, He L,
Huang H, Yang C, Wang R, Qian X, et al: Engineering aptamers with
selectively enhanced biostability in the tumor microenvironment.
Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 61:e2022012202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Mojarad-Jabali S, Farshbaf M, Walker PR,
Hemmati S, Fatahi Y, Zakeri-Milani P, Sarfraz M and Valizadeh H: An
update on actively targeted liposomes in advanced drug delivery to
glioma. Int J Pharm. 602:1206452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Rosenberg JE, Bambury RM, Van Allen EM,
Drabkin HA, Lara PN Jr, Harzstark AL, Wagle N, Figlin RA, Smith GW,
Garraway LA, et al: A phase II trial of AS1411 (a novel
nucleolin-targeted DNA aptamer) in metastatic renal cell carcinoma.
Invest New Drugs. 32:178–187. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Giordano FA, Layer JP, Leonardelli S,
Friker LL, Turiello R, Corvino D, Zeyen T, Schaub C, Müller W,
Sperk E, et al: L-RNA aptamer-based CXCL12 inhibition combined with
radiotherapy in newly-diagnosed glioblastoma: Dose escalation of
the phase I/II GLORIA trial. Nat Commun. 15:42102024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|