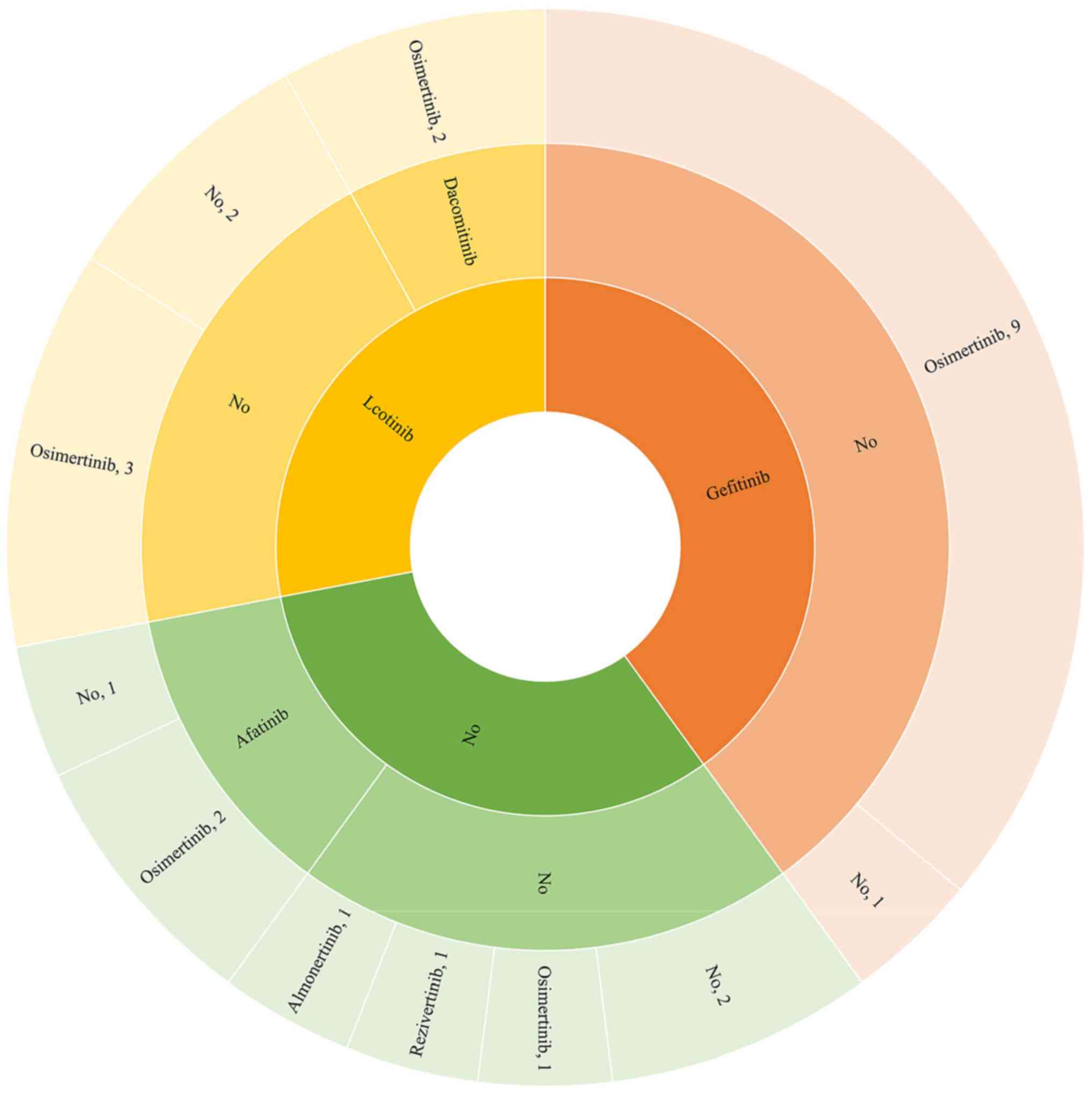
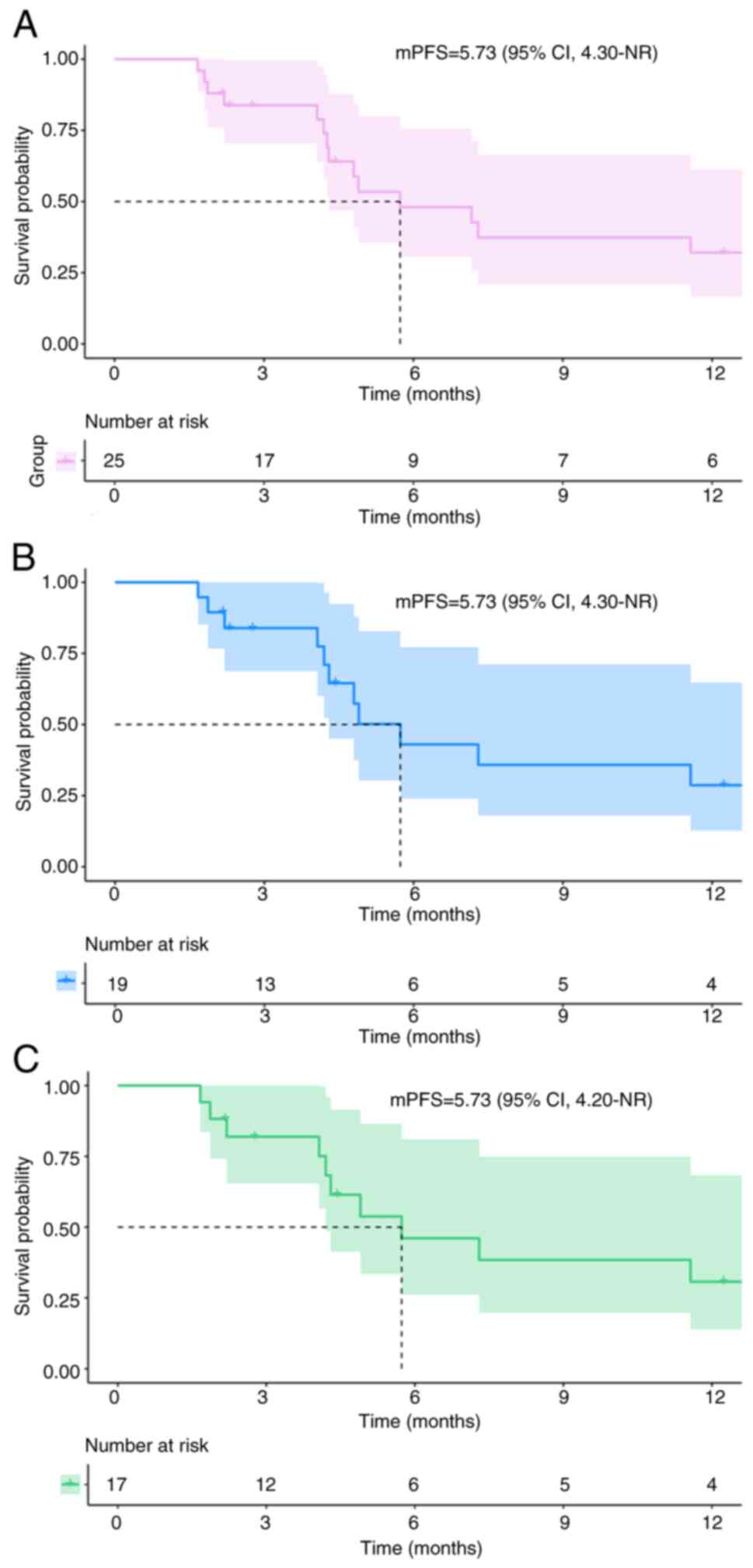
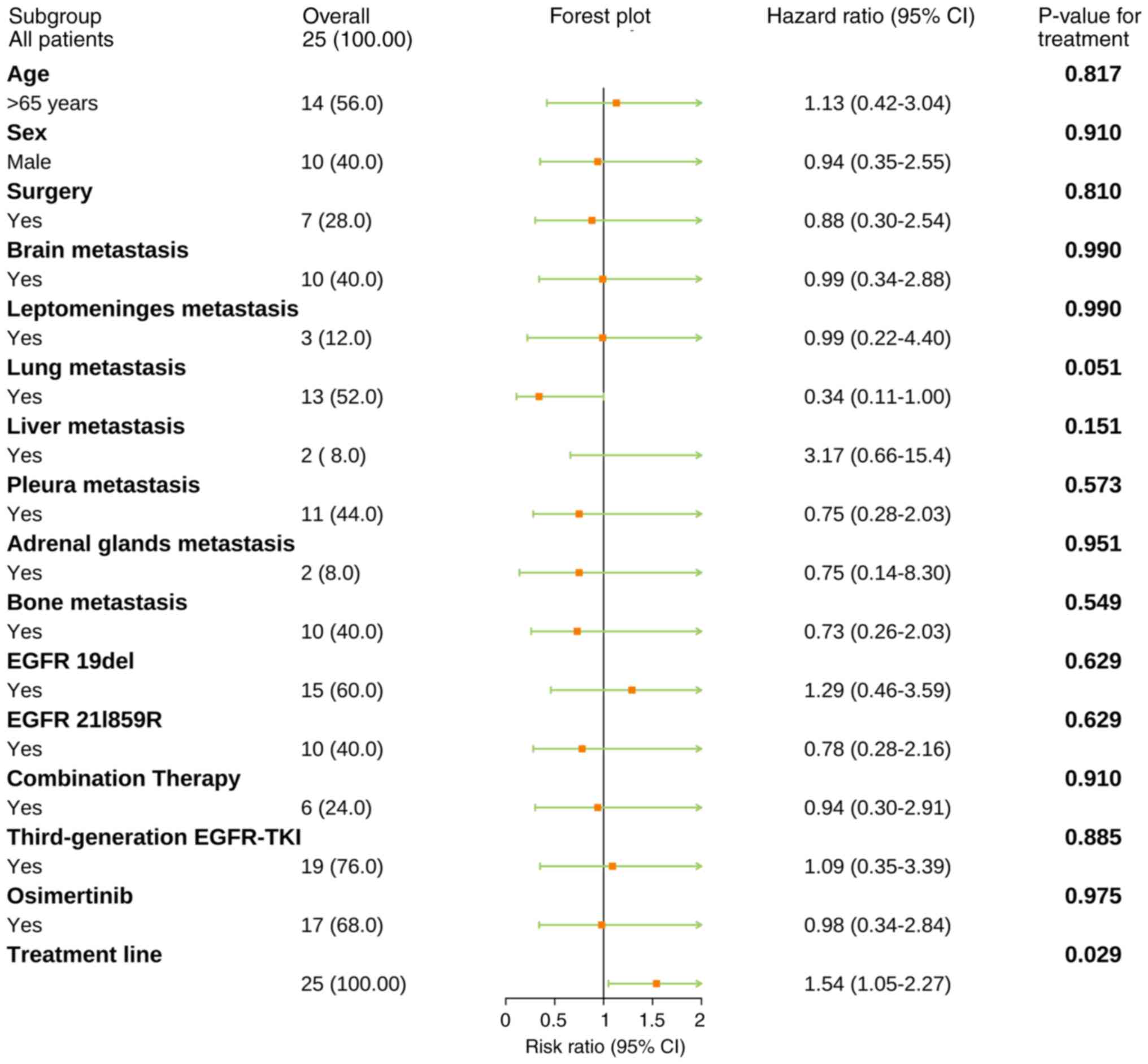
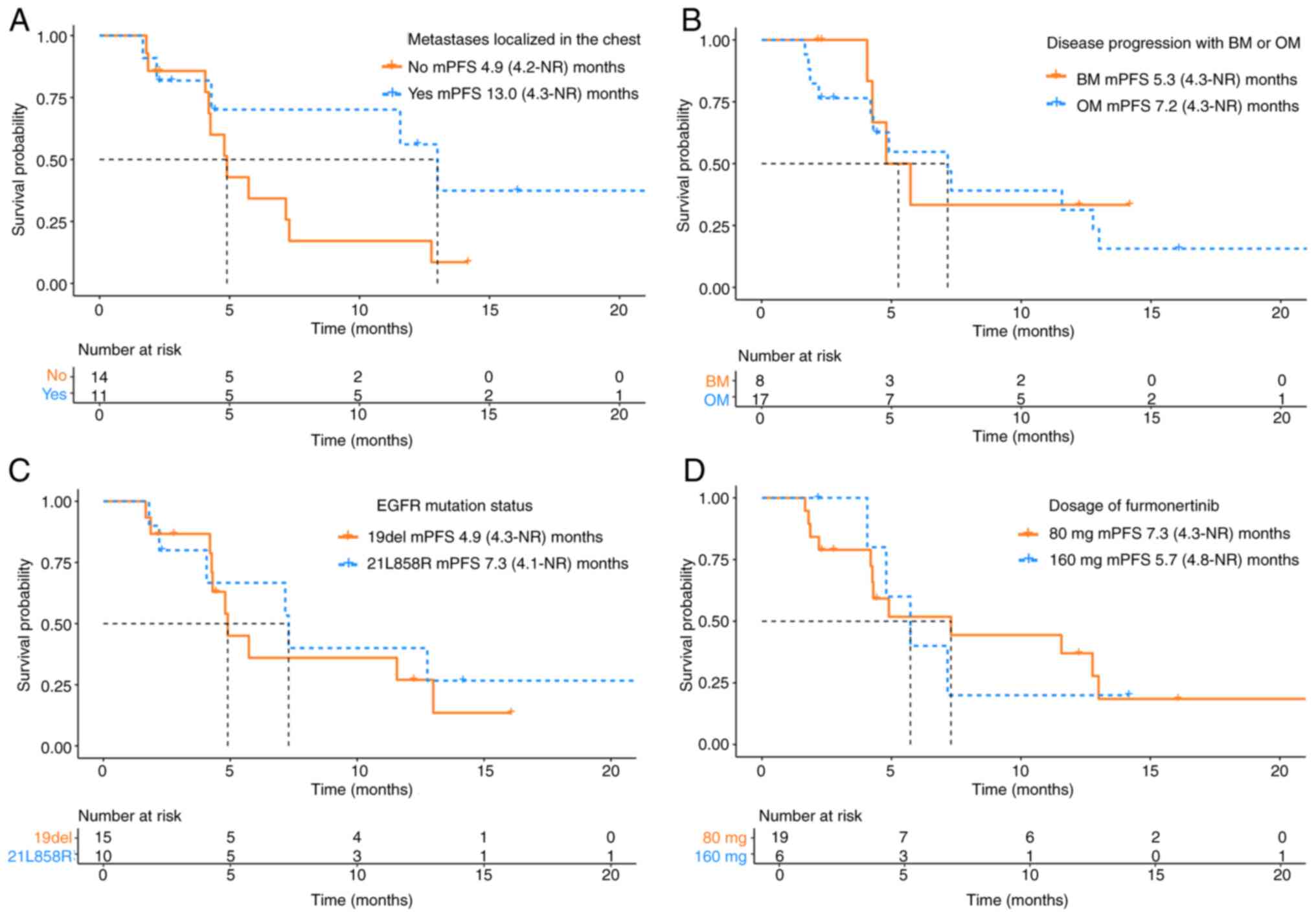
|
1
|
Ding PN, Becker TM, Bray VJ, Chua W, Ma
YF, Lynch D, Po J, Luk AWS, Caixeiro N, de Souza P and Roberts TL:
The predictive and prognostic significance of liquid biopsy in
advanced epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated non-small cell
lung cancer: A prospective study. Lung Cancer. 134:187–193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Shi Y, Au JSK, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan
S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, Heeroma K, Itoh Y, Cornelio G and Yang PC: A
prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in
Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of
adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER). J Thorac Oncol. 9:154–162.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gou LY and Wu YL: Prevalence of driver
mutations in non-small-cell lung cancers in the People's Republic
of China. Lung Cancer (Auckl). 5:1–9. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard
D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, Zhou C, Reungwetwattana T, Cheng Y,
Chewaskulyong B, et al: Overall survival with osimertinib in
untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 382:41–50.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Reckamp KL: Targeted therapy for patients
with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
16((5S)): S601–S604. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhao Y, Wang H and He C: Drug resistance
of targeted therapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
harbored EGFR mutation: From mechanism analysis to clinical
strategy. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 147:3653–3664. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Aisner DL, Akerley
W, Bauman JR, Bharat A, Bruno DS, Chang JY, Chirieac LR, D'Amico
TA, et al: Non-small cell lung cancer, version 3.2022, NCCN
clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
20:497–530. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu C, Xu T, Fang H, Wang X, Liu N, Yang L
and Fang S: High-dose furmonertinib combined with intraventricular
chemotherapy as salvage therapy for leptomeningeal metastasis from
EGFR exon 20 insertion-mutated lung cancer. J Neurooncol.
169:203–213. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qi R, Fu X, Yu Y, Xu H, Shen M, He S and
Lv D: Efficacy and safety of re-challenging 160 mg furmonertinib
for advanced NSCLC after resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs
targeted agents: A real-world study. Lung Cancer. 184:1073462023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pan X and Shi M: Successful therapy of a
critically ill non-small cell lung cancer patient with compound
mutations in EGFR G719X and S768I genes using furmonertinib: A case
report. Heliyon. 10:e271062024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ding J, Ding X, Zeng J and Liu X:
Furmonertinib for EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer:
A glittering diamond in the rough of EGFR-TKI. Front Pharmacol.
15:13579132024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tsuchida Y and Therasse P: Response
evaluation criteria in solid tumors (RECIST): New guidelines. Med
Pediatr Oncol. 37:1–3. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
National Cancer Institute, . Common
Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). Version 5.0.
2017.https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocoldevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5×7.pdf
|
|
14
|
Xu Z, Hao X, Wang Q, Yang K, Li J and Xing
P: Intracranial efficacy and safety of furmonertinib 160 mg with or
without anti-angiogenic agent in advanced NSCLC patients with BM/LM
as salvage therapy. BMC Cancer. 23:2062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Y, Hu X, Zhang S, Lv D, Wu L, Yu Q,
Zhang Y, Liu L, Wang X, Cheng Y, et al: Efficacy, safety, and
genetic analysis of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR
T790M mutated non-small-cell lung cancer: A phase 2b, multicentre,
single-arm, open-label study. Lancet Respir Med. 9:829–839. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi Y, Chen G, Wang X, Liu Y, Wu L, Hao Y,
Liu C, Zhu S, Zhang X, Li Y, et al: Central nervous system efficacy
of furmonertinib (AST2818) versus gefitinib as first-line treatment
for egfr-mutated NSCLC: Results from the FURLONG study. J Thorac
Oncol. 17:1297–1305. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shi Y, Chen G, Wang X, Liu Y, Wu L, Hao Y,
Liu C, Zhu S, Zhang X, Li Y, et al: Furmonertinib (AST2818) versus
gefitinib as first-line therapy for Chinese patients with locally
advanced or metastatic EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung
cancer (FURLONG): A multicentre, double-blind, randomised phase 3
study. Lancet Respir Med. 10:1019–1028. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan N, Guo S, Huang S, Zhang H and Li X:
The efficacy of furmonertinib in untreated advanced NSCLC patients
with sensitive EGFR mutations in a real-world setting: A single
institutional experience. Front Oncol. 14:13311282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yoshida T, Kuroda H, Oya Y, Shimizu J,
Horio Y, Sakao Y, Hida T and Yatabe Y: Clinical outcomes of
platinum-based chemotherapy according to T790M mutation status in
EGFR-positive non-small cell lung cancer patients after initial
EGFR-TKI failure. Lung Cancer. 109:89–91. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Park S, Keam B, Kim SH, Kim KH, Kim YJ,
Kim JS, Kim TM, Lee SH, Kim DW, Lee JS and Heo DS: Pemetrexed
singlet versus nonpemetrexed-based platinum doublet as second-line
chemotherapy after first-line epidermal growth factor receptor
(EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor failure in non-small cell lung
cancer patients with EGFR mutations. Cancer Res Treat. 47:630–637.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang S, Yang L, Yang Y, Yang G, Xu H, Niu
X and Wang U: The efficacy and safety of chemo-free therapy in
epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase
inhibitor-resistant advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A
single-arm, phase II study. Cancer Med. 12:19438–19448. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Haratani K, Hayashi H, Tanaka T, Kaneda H,
Togashi Y, Sakai K, Hayashi K, Tomida S, Chiba Y, Yonesaka K, et
al: Tumor immune microenvironment and nivolumab efficacy in EGFR
mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer based on T790M status
after disease progression during EGFR-TKI treatment. Ann Oncol.
28:1532–1539. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yu L, Hu Y, Xu J, Qiao R, Zhong H, Han B,
Xia J and Zhong R: Multi-target angiogenesis inhibitor combined
with PD-1 inhibitors may benefit advanced non-small cell lung
cancer patients in late line after failure of EGFR-TKI therapy. Int
J Cancer. 153:635–643. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu X, Li J, Ye L, Zhao J, Xie M, Zhou J,
Shen Y, Zhou F, Wu Y, Han C, et al: Real-world outcomes of
chemo-antiangiogenesis versus chemo-immunotherapy combinations in
EGFR-mutant advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients after
failure of EGFR-TKI therapy. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 10:3782–3792.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang JCH, Xu Y, Huang WT, Su WC, Gao B,
Lee CK, Fang J, Yu W, Wang M and Janne PA: Anti-tumor activity of
sunvozertinib in NSCLC with EGFR sensitizing mutations after
failure of EGFR TKI treatment. J Clin Oncol. 41 (16
Suppl):S91032023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhao Y, He Y, Wang W, Cai Q, Ge F, Chen Z,
Zheng J, Zhang Y, Deng H, Chen Y, et al: Efficacy and safety of
immune checkpoint inhibitors for individuals with advanced
EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer who progressed on EGFR
tyrosine-kinase inhibitors: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and
network meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 25:1347–1356. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shi Y, Zhang S, Hu X, Feng J, Ma Z, Zhou
J, Yang N, Wu L, Liao W, Zhong D, et al: Safety, clinical activity,
and pharmacokinetics of alflutinib (AST2818) in patients with
advanced NSCLC with EGFR T790M mutation. J Thorac Oncol.
15:1015–1026. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu X, Zhang S, Ma Z, Feng J, Wu L, Lv D,
Zhou J, Zhang X, Liu L, Yu Q, et al: Central nervous system
efficacy of furmonertinib (AST2818) in patients with EGFR T790M
mutated non-small cell lung cancer: A pooled analysis from two
phase 2 studies. BMC Med. 21:1642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Meng J, Zhang H, Bao JJ, Chen ZD, Liu XY,
Zhang YF, Jiang Y, Miao LY and Zhong DF: Metabolic disposition of
the EGFR covalent inhibitor furmonertinib in humans. Acta Pharmacol
Sin. 43:494–503. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J,
Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Imamura
F, Nogami N, Kurata T, et al: Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated
advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 378:113–125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jackman DM, Yeap BY, Sequist LV, Lindeman
N, Holmes AJ, Joshi VA, Bell DW, Huberman MS, Halmos B, Rabin MS,
et al: Exon 19 deletion mutations of epidermal growth factor
receptor are associated with prolonged survival in non-small cell
lung cancer patients treated with gefitinib or erlotinib. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:3908–3914. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen H, Yang S, Wang L, Wu Y, Wu Y, Ma S,
He Z, Zhang C, Liu Y, Tang H, et al: High-dose furmonertinib in
patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC and leptomeningeal metastases: A
prospective real-world study. J Thorac Oncol. 20:65–75. 2025.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ang YLE, Zhao X, Reungwetwattana T, Cho
BC, Liao BC, Yeung R, Loong HH, Kim DW, Yang JC, Lim SM, et al: A
phase II study of osimertinib in patients with advanced-stage
non-small cell lung cancer following prior epidermal growth factor
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR TKI) therapy with EGFR and
T790M mutations detected in plasma circulating tumour DNA (PLASMA
study). Cancers (Basel). 15:49992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Leonetti A, Verzè M, Minari R, Perrone F,
Gnetti L, Bordi P, Pluchino M, Nizzoli R, Azzoni C, Bottarelli L,
et al: Resistance to osimertinib in advanced EGFR-mutated NSCLC: A
prospective study of molecular genotyping on tissue and liquid
biopsies. Br J Cancer. 130:135–142. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Esagian SM, Grigoriadou GI, Nikas IP,
Boikou V, Sadow PM, Won JK and Economopoulos KP: Comparison of
liquid-based to tissue-based biopsy analysis by targeted next
generation sequencing in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A
comprehensive systematic review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
146:2051–2066. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lin LH, Allison DHR, Feng Y, Jour G, Park
K, Zhou F, Moreira AL, Shen G, Feng X, Sabari J, et al: Comparison
of solid tissue sequencing and liquid biopsy accuracy in
identification of clinically relevant gene mutations and
rearrangements in lung adenocarcinomas. Mod Pathol. 34:2168–2174.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Vatrano S, Righi L, Vavalá T, Rapa I,
Busso M, Izzo S, Cappia S, Veltri A, Papotti M, Scagliotti GV and
Novello S: Molecular and histological changes in post-treatment
biopsies of non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer: A
retrospective study. Target Oncol. 11:157–166. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Han B, Zhou C, Wu L, Yu X, Li Q, Liu F and
Shen C: 1210P Preclinical and preliminary clinical investigations
of furmonertinib in NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertions (20ins). Ann
Oncol. 32 (Suppl 5):S9642021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sa H, Shi Y, Ding C and Ma K: A real-world
study of the efficacy and safety of furmonertinib for patients with
non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:7729–7742. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hu S, Ming H, He Q, Ding M, Ding H and Li
C: A study of high dose furmonertinib in EGFR exon 20 insertion
mutation-positive advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Front Oncol.
14:13143012024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Spira A, Cho BC, Felip E, Garon EB, Goto
K, Johnson M, Leighl N, Passaro A, Planchard D, Popat S, et al:
FURVENT: Phase 3 trial of firmonertinib vs chemotherapy as
first-line treatment for advanced NSCLC with EGFR exon 20 insertion
mutations (FURMO-004). Lung Cancer. 199:1080662025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu G, Chen Q, Lv D, Lin L and Huang J:
Pulmonary adenocarcinoma patient with complex mutations on EGFR
benefits from furmonertinib after acquiring gefitinib resistance: A
case report. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 19:247–252. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin H, Yang Z, Li Z, Chen J, Wang H and
Lin Y: EGFR kinase domain duplication in lung adenocarcinoma with
systemic and intracranial response to a double-dose of
furmonertinib: A case report and literature review. Front Oncol.
14:13215872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Jia G, Bashir S, Ye M, Li Y, Lai M, Cai L
and Xu: Furmonertinib and intrathecal pemetrexed chemotherapy
rechallenges osimertinib-refractory leptomeningeal metastasis in a
non-small cell lung cancer patient harboring EGFR20 R776S, C797S,
and EGFR21 L858R compound EGFR mutations: A case report. Anticancer
Drugs. 35:542–547. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ni C, Zhang L, Yu X, Pang Y and Xu J:
Response to furmonertinib in a patient with non-small cell lung
cancer harboring HER2 exon 21 insertion mutation: A case report.
Front Oncol. 14:14403792024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|