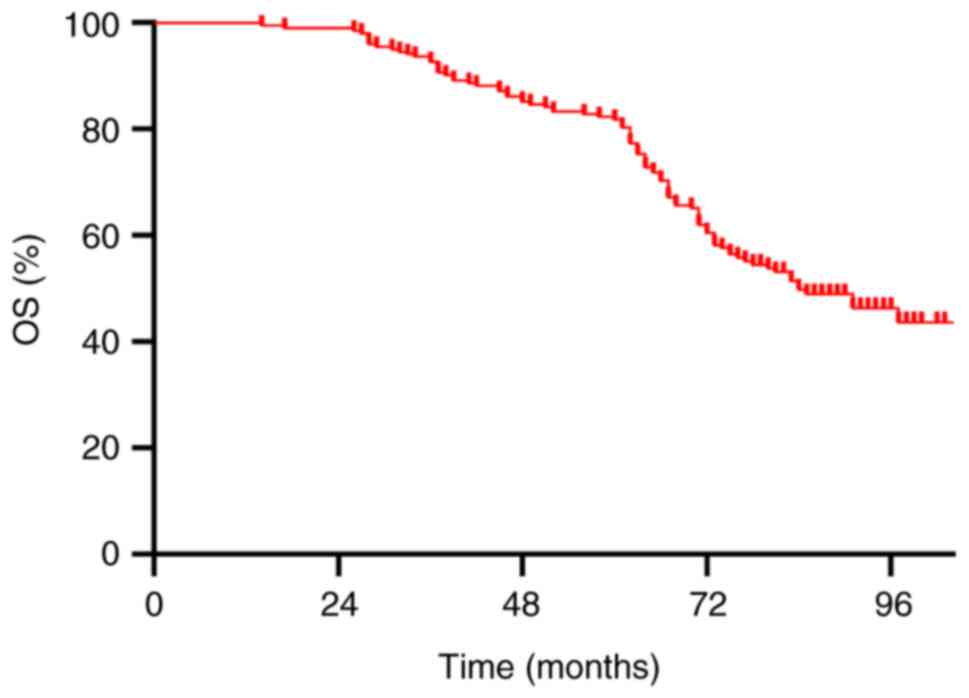
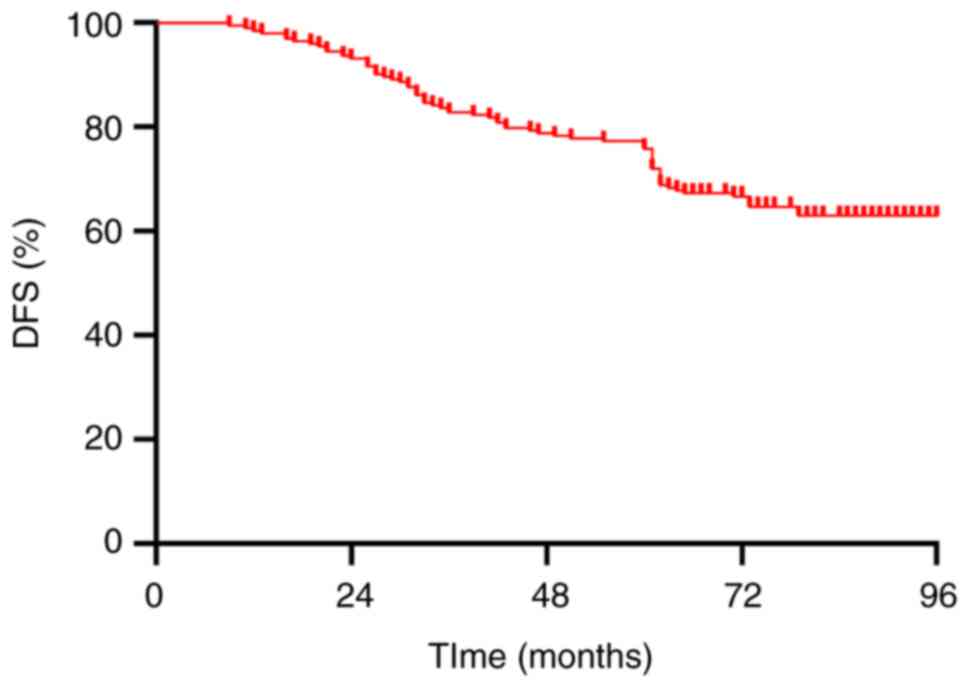
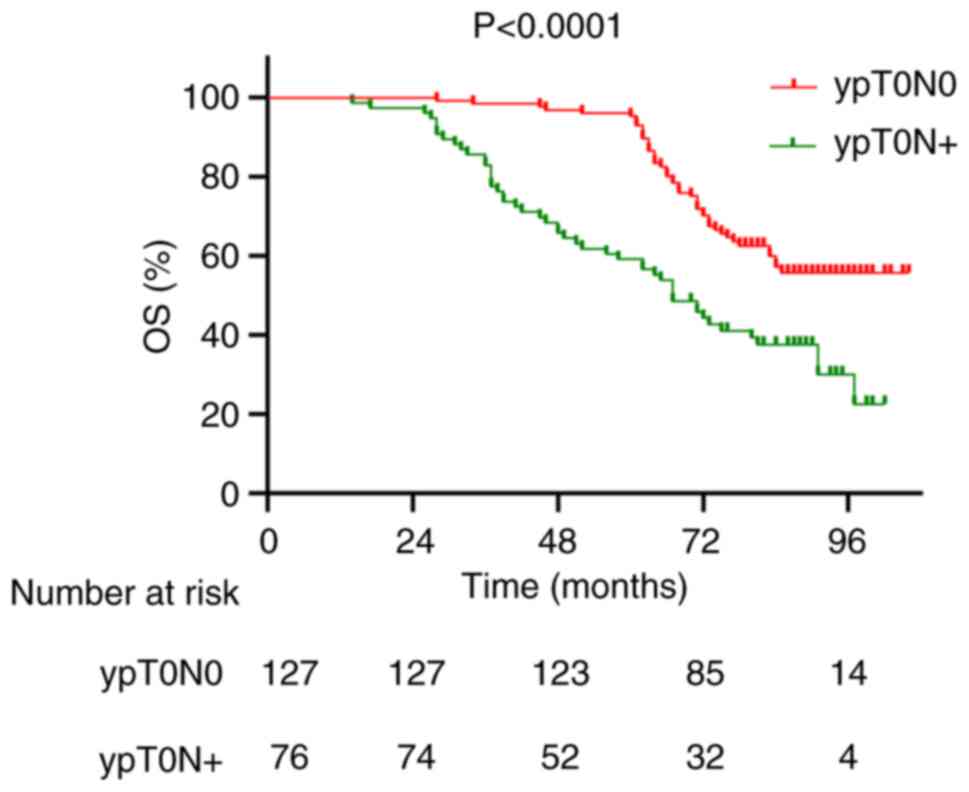
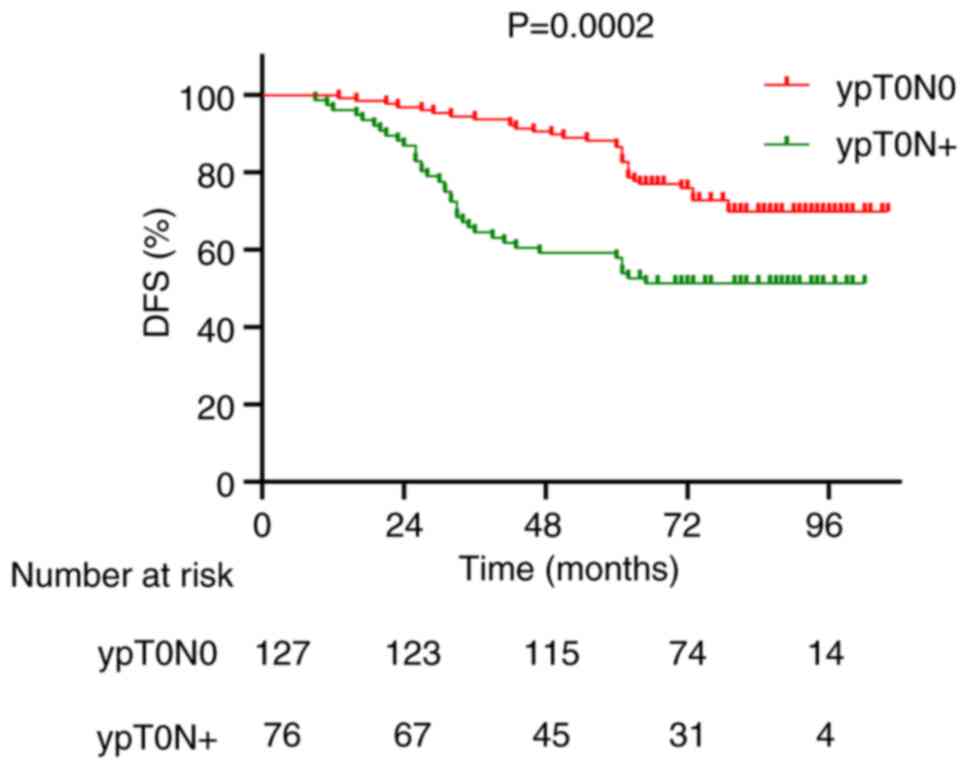
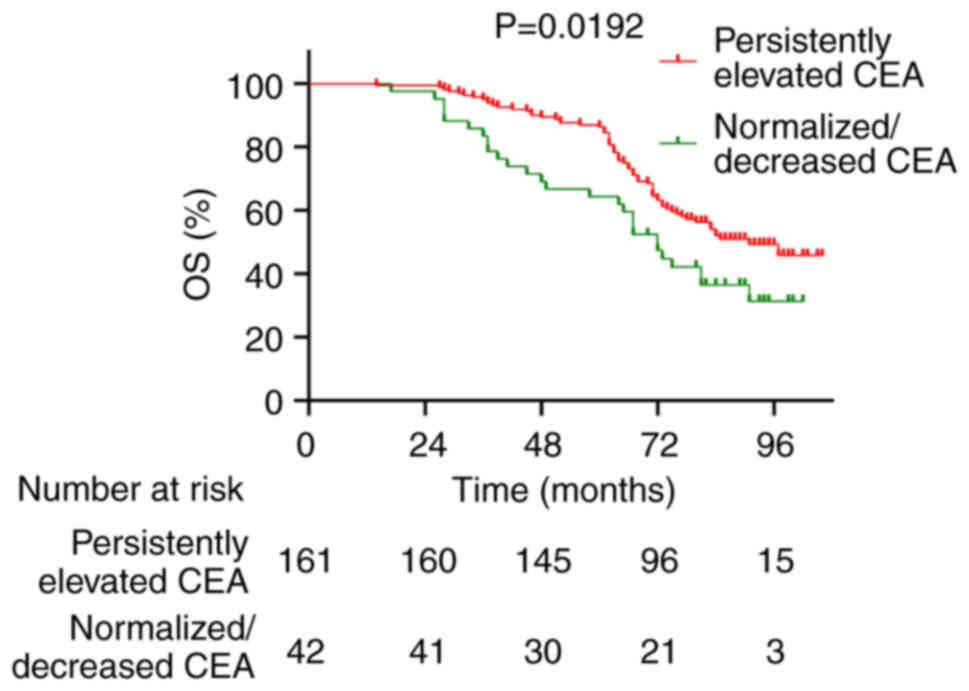
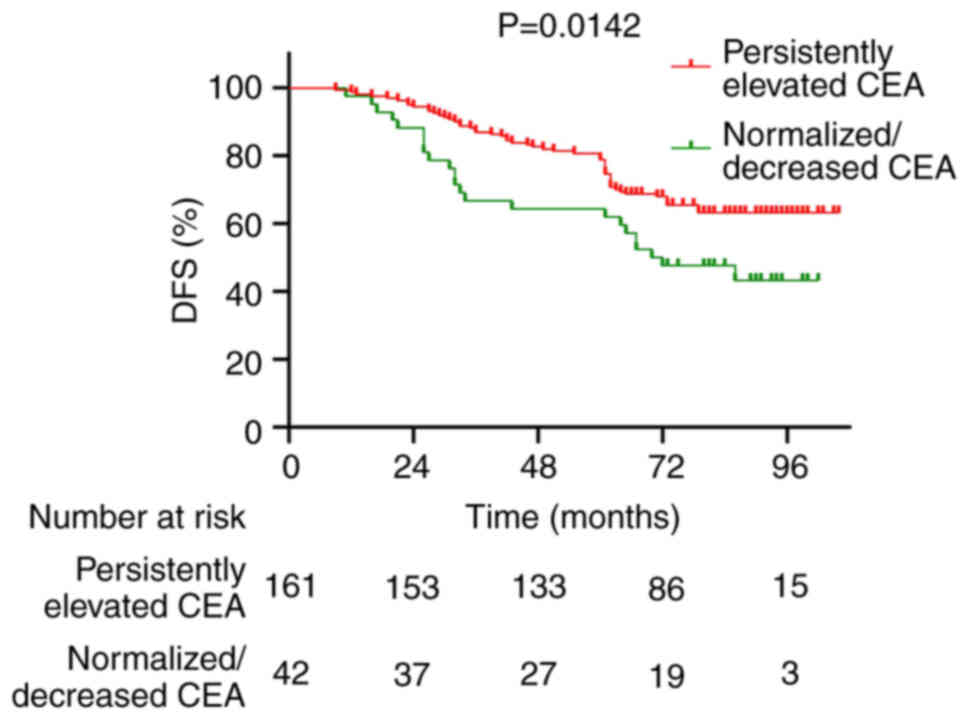
|
1
|
Han B, Zheng R, Zeng H, Wang S, Sun K,
Chen R, Li L, Wei W and He J: Cancer incidence and mortality in
China, 2022. J Natl Cancer Cent. 1:47–53. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lu X, Qi R, Xu Y, Wang X, Cai Y and Wang
C: Tumor regression grade in locally advanced rectal cancer after
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: Influencing factors and prognostic
significance. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 16:124–132. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Glynne-Jones R, Wyrwicz L, Tiret E, Brown
G, Rödel C, Cervantes A and Arnold D; ESMO Guidelines Committee, :
Rectal cancer: ESMO clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 29 (Suppl 4):iv2632018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM,
Cederquist L, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK, Cohen S, Cooper HS, Deming D,
Engstrom PF, et al: Rectal cancer, version 2.2018, NCCN clinical
practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
16:874–901. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jung M, Shin SJ, Koom WS, Jung I, Keum KC,
Hur H, Min BS, Baik SH, Kim NK, Kim H, et al: A randomized phase 2
study of neoadjuvant chemoradiaton therapy with
5-fluorouracil/leucovorin or irinotecan/S-1 in patients with
locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
93:1015–1022. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jung KU, Kim HO, Kim H, Lee D and Cheong
C; on the behalf of Korean Society of Korean Society of
Coloproctology, : Unveiling the profound advantages of total
neoadjuvant therapy in rectal cancer: A trailblazing exploration.
Ann Surg Treat Res. 105:341–352. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu Z, Hao Y, Huang Y, Ling L, Hu X and
Qiao S: Radiotherapy in the preoperative neoadjuvant treatment of
locally advanced rectal cancer. Front Oncol. 13:13005352023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
van der Sluis FJ, van Westreenen HL, van
Etten B, van Leeuwen BL and de Bock GH: Pretreatment identification
of patients likely to have pathologic complete response after
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. Int J Colorectal
Dis. 33:149–157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Latif A, Shirkhoda M, Rouhollahi MR,
Nemati S, Yahyazadeh SH, Zendehdel K, Soroush AR and Yaghoobi
Notash A: Predicting factors of complete pathological response in
locally advanced rectal cancer. Middle East J Dig Dis. 14:443–451.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Smith FM and Winter D: Pathologic complete
response of primary tumor following preoperative chemoradiotherapy
for locally advanced rectal cancer: long-term outcomes and
prognostic significance of pathologic nodal status (KROG 09-01).
Ann Surg. 265:e27–e28. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shin JK, Huh JW, Lee WY, Yun SH, Kim HC,
Cho YB and Park YA: Clinical prediction model of pathological
response following neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer.
Sci Rep. 12:71452022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bosset JF, Calais G, Mineur L, Maingon P,
Radosevic-Jelic L, Daban A, Bardet E, Beny A, Briffaux A and
Collette L: Enhanced tumorocidal effect of chemotherapy with
preoperative radiotherapy for rectal cancer: Preliminary
results-EORTC 22921. J Clin Oncol. 23:5620–5627. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Braendengen M, Tveit KM, Berglund A,
Birkemeyer E, Frykholm G, Påhlman L, Wiig JN, Byström P, Bujko K
and Glimelius B: Randomized phase III study comparing preoperative
radiotherapy with chemoradiotherapy in nonresectable rectal cancer.
J Clin Oncol. 26:3687–3694. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Collard MK, Rullier E, Panis Y, Manceau G,
Benoist S, Tuech JJ, Alves A, Laforest A, Mege D, Cazelles A, et
al: Nonmetastatic ypt0 rectal cancer after neoadjuvant treatment
and total mesorectal excision: Lessons from a retrospective
multicentric cohort of 383 patients. Surgery. 171:1193–1199. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park JS, Yoon G, Kim HJ, Park SY, Choi GS,
Kang MK, Kim JG, Jang JS and Seo AN: HER2 status in patients with
residual rectal cancer after preoperative chemoradiotherapy: The
relationship with molecular results and clinicopathologic features.
Virchows Arch. 473:413–423. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
De Roock W, Claes B, Bernasconi D, De
Schutter J, Biesmans B, Fountzilas G, Kalogeras KT, Kotoula V,
Papamichael D, Laurent-Puig P, et al: Effects of KRAS, BRAF, NRAS,
and PIK3CA mutations on the efficacy of cetuximab plus chemotherapy
in chemotherapy-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer: A
retrospective consortium analysis. Lancet Oncol. 11:753–762. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Jo P, Jung K, Grade M, Conradi LC, Wolff
HA, Kitz J, Becker H, Rüschoff J, Hartmann A, Beissbarth T, et al:
CpG island methylator phenotype infers a poor disease-free survival
in locally advanced rectal cancer. Surgery. 151:564–570. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhang S, Li N, Wang F, Liu H, Zhang Y,
Xiao J, Qiu W, Zhang C, Fan X, Qiu M, et al: Characterization of
the tumor microenvironment and identification of spatially
predictive biomarkers associated with beneficial neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy in locally advanced rectal cancer. Pharmacol Res.
197:1069742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mandard AM, Dalibard F, Mandard JC, Marnay
J, Henry-Amar M, Petiot JF, Roussel A, Jacob JH, Segol P, Samama G,
et al: Pathologic assessment of tumor regression after preoperative
chemoradiotherapy of esophageal carcinoma. Clinicopathologic
correlations. Cancer. 73:2680–2686. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Iskander O, Courtot L, Tabchouri N, Artus
A, Michot N, Muller O, Pabst-Giger U, Bourlier P, Kraemer-Bucur A,
Lecomte T, et al: Complete pathological response following
radiochemotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer: Short and
long-term outcome. Anticancer Res. 39:5105–5113. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Capirei C, Valentini V, Cionini L, De
Paoli A, Rodel C, Glynne-Jones R, Coco C, Romano M, Mantello G,
Palazzi S, et al: Prognostic value of pathologic complete response
after neoadjuvant therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer:
Long-term analysis of 566 ypCR patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol
Phys. 72:99–107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li Y, Wang J, Ma X, Tan L, Yan Y, Xue C,
Hui B, Liu R, Ma H and Ren J: A Review of neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Biol
Sci. 12:1022–1031. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sell NM, Qwaider YZ, Goldstone RN, Cauley
CE, Cusack JC, Ricciardi R, Bordeianou LG, Berger DL and Kunitake
H: Ten-year survival after pathologic complete response in rectal
adenocarcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 123:293–298. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
de Campos-Lobato LF, Stocchi L, da Luz
Moreira A, Geisler D, Dietz DW, Lavery IC, Fazio VW and Kalady MF:
Pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant treatment for rectal
cancer decreases distant recurrence and could eradicate local
recurrence. Ann Surg Oneol. 18:1590–1598. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Capirci C, Valentini V, Cionini L, De
Paoli A, Rodel C, Glynne-Jones R, Coco C, Romano M, Mantello G,
Palazzi S, et al: Prognostic value of pathologic complete response
after neoadjuvant therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer:
Long-term analysis of 566 ypCR patients. Int J Radiat Oneol Biol
Phys. 72:99–107. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zeman M, Skałba W, Szymański P, Hadasik G,
Żaworonkow D, Walczak DA and Czarniecka A: Risk factors for
long-term survival in patients with ypN+ M0 rectal cancer after
radical anterior resection. BMC Gastroenterol. 22:1412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Destri G, Maugeri A, Ramistella A, La
Greca G, Conti P, Trombatore G, Vecchio GM, Magro GG, Barchitta M
and Agodi A: The prognostic impact of neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy
on lymph node sampling in patients with locally advanced rectal
cancer. Updates Surg. 72:793–800. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang Q, Liang J, Chen J, Mei S and Wang
Z: Predictive factors for pathologic complete response following
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer
Prev. 22:1607–1611. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu L, Wang L, Gao Z, Zeng Y, Tao K, Wang
Q, Li X, Zhang H, Shen Z, Zhou J, et al: Examined lymph node
numbers influence prognosis in rectal cancer treated with
neoadjuvant therapy. Cancer Pathog Ther. 1:168–176. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ozturk SK, Martinez CG, Mens D, Verhoef C,
Tosetto M, Sheahan K, de Wilt JHW, Hospers GAP, van de Velde CJH,
Marijnen CAM, et al: Lymph node regression after neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Histopathology. 84:935–946.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lu Z, Cheng P, Yang F, Zheng Z and Wang X:
Long-term outcomes in patients with ypT0 rectal cancer after
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and curative resection. Chin J Cancer
Res. 30:272–281. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang H, Sun G, Zheng K, Lou Z, Gao XH,
Meng RG, Furnée EJB and Zhang W: Prognostic factors in patients
with complete response of the tumour (ypT0) after neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy and radical resection of rectal cancer. ANZ J
Surg. 91:E190–E195. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jamal-Hanjani M, Wilson GA, MeGranahan N,
Birkbak NJ, Watkins TBK, Veeriah S, Shafi S, Johnson DH, Mitter R,
Rosenthal R, et al: Trackingthe evolution of non-small-cell lung
cancer. N Engl J Med. 376:2109–2121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Abbosh C, Birkbak NJ, Wilson GA,
Jamal-Hanjani M, Constantin T, Salari R, Le Quesne J, Moore DA,
Veeriah S, Rosenthal R, et al: Corrigendum: Phylogenetic ctDNA
analysis depicts early-stage lung cancer evolution. Nature.
554:2642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Al-Sukhni E, Attwood K, Mattson DM,
Gabriel E and Nurkin SJ: Predictors of pathologic complete response
following neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. Ann Surg
Oncol. 23:1177–1186. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Peng J, Lin J, Qiu M, Wu X, Lu Z, Chen G,
Li L, Ding P, Gao Y, Zeng Z, et al: Clinical factors of
post-chemoradiotherapy as valuable indicators for pathological
complete response in locally advanced rectal cancer. Clinics (Sao
Paulo). 71:449–454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Petrova V, Annicchiarico-Petruzzelli M,
Melino G and Amelio I: The hypoxic tumour microenvironment.
Oncogenesis. 7:102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhou C, Wang K, Zhang X, Xiao Y, Yang C,
Wang J, Qu F, Wang X, Liu M, Gao C, et al: Assessing the predictive
value of clinical factors to pathological complete response for
locally advanced rectal cancer: An analysis of 124 patients. Front
Oncol. 13:11254702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Colloca G, Venturino A and Vitucci P:
Pre-treatment carcinoembryonic antigen and outcome of patients with
rectal cancer receiving neo-adjuvant chemo-radiation and surgical
resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Med Oncol.
34:1772017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Machado Carvalho JV, Dutoit V, Corrò C and
Koessler T: Promises and challenges of predictive blood biomarkers
for locally advanced rectal cancer treated with neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy. Cells. 12:4132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Huang Y, Xu M, Zhuang J, Zhou Z,
Zheng S, Zhu B, Guan G, Chen H and Liu X: Pathomics-based machine
learning models for predicting pathological complete response and
prognosis in locally advanced rectal cancer patients
post-neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy: Insights from two independent
institutional studies. BMC Cancer. 24:15802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu Y, Wu H, Hong L, Qiu J, Wu S, Shao L,
Lin C, Wang Z and Wu J: A large population-based and validated
study on the follow-up management and supportive strategy of
locally advanced rectal cancer patients. Support Care Cancer.
32:6522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bengala C, Bettelli S, Bertolini F,
Sartori G, Fontana A, Malavasi N, Depenni R, Zironi S, Del Giovane
C, Luppi G and Conte PF: Correction to: Prognostic role of EGFR
gene copy number and KRAS mutation in patients with locally
advanced rectal cancer treated with preoperative chemoradiotherapy.
Br J Cancer. 131:9542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zheng S, You Z, Guo G, Lin Z, Wang S and
Yang G: Effect of KRAS mutation status on clinicopathological
characteristics and overall survival in patients with rectal
cancer. BMC Gastroenterol. 25:372025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
De Mattia E, Polesel J, Mezzalira S,
Palazzari E, Pollesel S, Toffoli G and Cecchin E: Predictive and
prognostic value of oncogene mutations and microsatellite
instability in locally-advanced rectal cancer treated with
neoadjuvant radiation-based therapy: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). 15:14692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Swets M, Graham Martinez C, van Vliet S,
van Tilburg A, Gelderblom H, Marijnen CAM, van de Velde CJH and
Nagtegaal ID: Microsatellite instability in rectal cancer: What
does it mean? A study of two randomized trials and a systematic
review of the literature. Histopathology. 81:352–362. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Li C, Liu T, Liu Y, Zhang J and Zuo D:
Prognostic value of tumour microenvironment-related genes by TCGA
database in rectal cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 25:5811–5822. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schrag D, Shi Q, Weiser MR, Gollub MJ,
Saltz LB, Musher BL, Goldberg J, Al Baghdadi T, Goodman KA,
McWilliams RR, et al: Preoperative treatment of locally advanced
rectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 389:322–334. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Scott AJ, Kennedy EB, Berlin J, Brown G,
Chalabi M, Cho MT, Cusnir M, Dorth J, George M, Kachnic LA, et al:
Management of locally advanced rectal cancer: ASCO guideline. J
Clin Oncol. 42:3355–3375. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sobrero A, Lonardi S, Rosati G, Di
Bartolomeo M, Ronzoni M, Pella N, Scartozzi M, Banzi M, Zampino MG,
Pasini F, et al: FOLFOX or CAPOX in stage II to III colon cancer:
Efficacy results of the Italian three or six colon adjuvant trial.
J Clin Oncol. 36:1478–1485. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Bond MJG, Bolhuis K, Loosveld OJL, de
Groot JWB, Droogendijk H, Helgason HH, Hendriks MP, Klaase JM,
Kazemier G, Liem MSL, et al: First-line systemic treatment
strategies in patients with initially unresectable colorectal
cancer liver metastases (CAIRO5): An open-label, multicentre,
randomised, controlled, phase 3 study from the Dutch colorectal
cancer group. Lancet Oncol. 24:757–771. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ciardiello F, Ciardiello D, Martini G,
Napolitano S, Tabernero J and Cervantes A: Clinical management of
metastatic colorectal cancer in the era of precision medicine. CA
Cancer J Clin. 72:372–401. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kajiwara Y and Ueno H: Essential updates
2022–2023: Surgical and adjuvant therapies for locally advanced
colorectal cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Surg. 8:977–986. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Grothey A: Pembrolizumab in MSI-H-dMMR
advanced colorectal cancer-A new standard of care. N Engl J Med.
383:2283–2285. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tie J, Wang Y, Tomasetti C, Li L, Springer
S, Kinde I, Silliman N, Tacey M, Wong HL, Christie M, et al:
Circulating tumor DNA analysis detects minimal residual disease and
predicts recurrence in patients with stage II colon cancer. Sci
Transl Med. 8:346ra922016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Reinert T, Schøler LV, Thomsen R, Tobiasen
H, Vang S, Nordentoft I, Lamy P, Kannerup AS, Mortensen FV,
Stribolt K, et al: Analysis of circulating tumour DNA to monitor
disease burden following colorectal cancer surgery. Gut.
65:625–634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Linders D, Deken M, van der Valk M,
Tummers W, Bhairosingh S, Schaap D, van Lijnschoten G, Zonoobi E,
Kuppen P, van de Velde C, et al: CEA, EpCAM, αvβ6 and uPAR
expression in rectal cancer patients with a pathological complete
response after neoadjuvant therapy. Diagnostics (Basel).
11:5162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Boogerd LS, van der Valk MJ, Boonstra MC,
Prevoo HA, Hilling DE, van de Velde CJ, Sier CF, Fariña Sarasqueta
A and Vahrmeijer AL: Biomarker expression in rectal cancer tissue
before and after neoadjuvant therapy. Onco Targets Ther.
11:1655–1664. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wu L, Zhu JJ, Liang XH, Tong H and Song Y:
Predictive value of magnetic resonance imaging parameters combined
with tumor markers for rectal cancer recurrence risk after surgery.
World J Gastrointest Surg. 17:1018972025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
De Palma FDE, Luglio G, Tropeano FP,
Pagano G, D'Armiento M, Kroemer G, Maiuri MC and De Palma GD: The
role of Micro-RNAs and circulating tumor markers as predictors of
response to neoadjuvant therapy in locally advanced rectal cancer.
Int J Mol Sci. 21:70402020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Chatila WK, Kim JK, Walch H, Marco MR,
Chen CT, Wu F, Omer DM, Khalil DN, Ganesh K, Qu X, et al: Genomic
and transcriptomic determinants of response to neoadjuvant therapy
in rectal cancer. Nat Med. 28:1646–1655. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Yang J, Lin Y, Huang Y, Jin J, Zou S,
Zhang X, Li H, Feng T, Chen J, Zuo Z, et al: Genome landscapes of
rectal cancer before and after preoperative chemoradiotherapy.
Theranostics. 9:6856–6866. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Davies H, Bignell GR, Cox C, Stephens P,
Edkins S, Clegg S, Teague J, Woffendin H, Garnett MJ, Bottomley W,
et al: Mutations of the BRAF gene in human cancer. Nature.
417:949–954. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hammarström K, Nunes L, Mathot L,
Mezheyeuski A, Lundin E, Korsavidou Hult N, Imam I, Osterlund E,
Sjöblom T and Glimelius B: Clinical and genetic factors associated
with tumor response to neoadjuvant (chemo)radiotherapy, survival
and recurrence risk in rectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 155:40–53.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Corcoran RB, André T, Atreya CE, Schellens
JHM, Yoshino T, Bendell JC, Hollebecque A, McRee AJ, Siena S,
Middleton G, et al: Combined BRAF, EGFR, and MEK inhibition in
patients with BRAFV600E-mutant colorectal cancer. Cancer
Discov. 4:428–443. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Hasan S, Renz P, Wegner RE, Finley G, Raj
M, Monga D, McCormick J and Kirichenko A: Microsatellite
instability (MSI) as an independent predictor of pathologic
complete response (PCR) in locally advanced rectal cancer: A
national cancer database (NCDB) analysis. Ann Surg. 271:716–723.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Koopman M, Kortman GAM, Mekenkamp L,
Ligtenberg MJL, Hoogerbrugge N, Antonini NF, Punt CJA and van
Krieken JHJM: Deficient mismatch repair system in patients with
sporadic advanced colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 100:266–273.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Acar T, Acar N, Kamer E, Tekindal MA,
Cengiz F, Kar H, Atahan K and Haciyanli M: Do microsatellite
instability (MSI) and deficient mismatch repair (dMMR) affect the
pathologic complete response (pCR) in patients with rectal cancer
who received neoadjuvant treatment? Updates Surg. 72:73–82. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yu JH, Liao LE, Xiao BY, Zhang X, Wu AW,
Cheng Y, Tang JH, Jiang W, Kong LH, Han K, et al: Long-term
outcomes of dMMR/MSI-H rectal cancer treated with anti-PD-1-based
immunotherapy as curative-intent treatment. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
22:e2370962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Langman G, Patel A and Bowley DM: Size and
distribution of lymph nodes in rectal cancer resection specimens.
Dis Colon Rectum. 4:406–414. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Achilli P, Ferrari D, Calini G, Bertoglio
CL, Magistro C, Origi M, Carnevali P, Alampi BD, Giusti I, Ferrari
G, et al: Preoperative lateral lymph node features and impact on
local recurrence after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and total
mesorectal excision for locally advanced rectal cancer: Results
from a multicentre international cohort study. Colorectal Dis.
26:466–475. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Beppu N, Matsubara N, Noda M, Yamano T,
Kakuno A, Doi H, Kamikonya N, Yamanaka N, Yanagi H and Tomita N:
Pathologic evaluation of the response of mesorectal positive nodes
to preoperative chemoradiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer.
Surgery. 157:743–751. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Kokaine L, Gardovskis A and Gardovskis J:
Evaluation and predictive factors of complete response in rectal
cancer after neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy. Medicina (Kaunas).
57:10442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Yuhara H, Steinmaus C, Cohen SE, Corley
DA, Tei Y and Buffler PA: Is diabetes mellitus an independent risk
factor for colon cancer and rectal cancer? Am J Gastroenterol.
106:1911–1922. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Cai Z, Xie X, Chen Y, Chen Z, Cao W, Saad
KSS, Zou Y, Lan P and Wu X: Risk factor analysis for inaccurate
pre-operative MRI staging in rectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 20:2532020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|