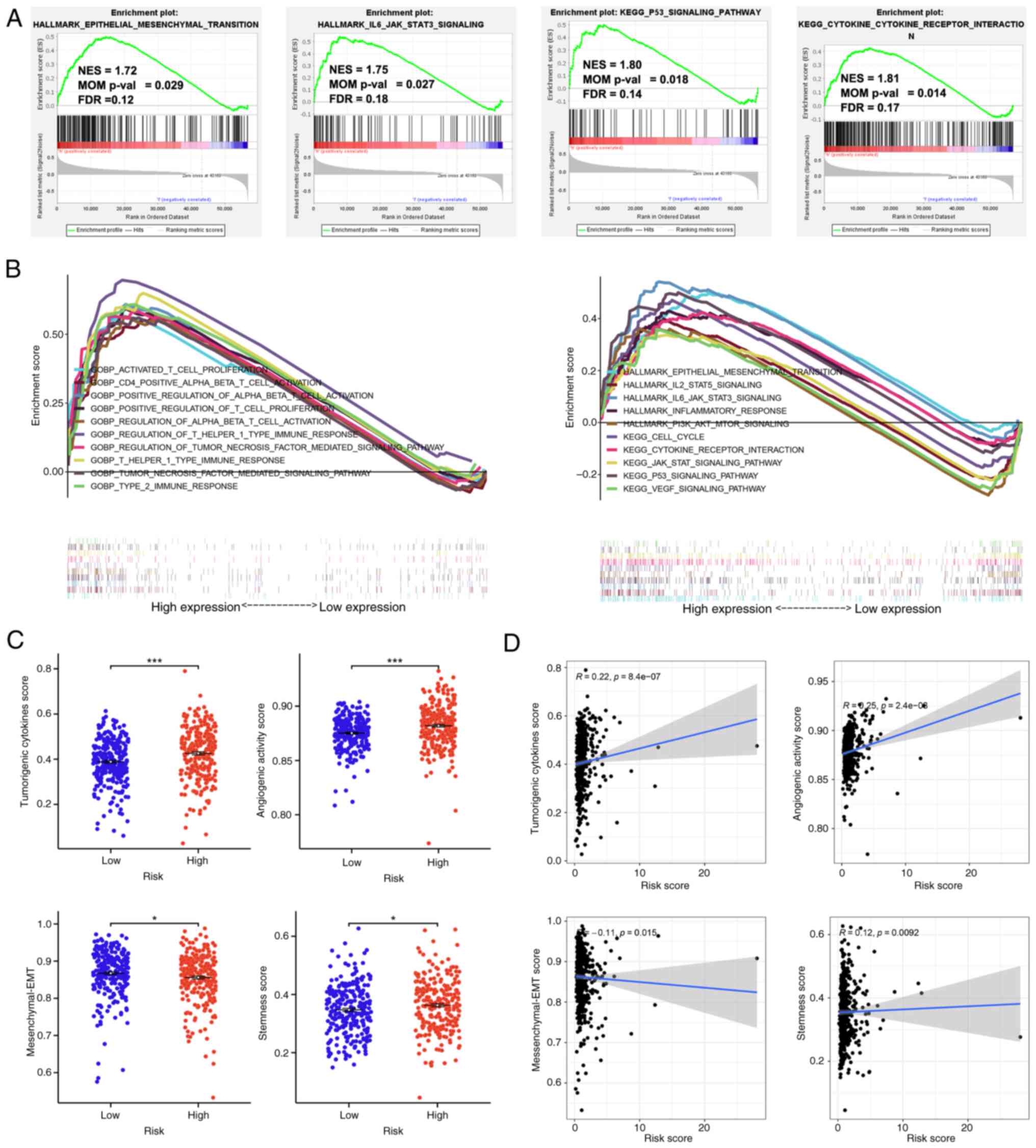
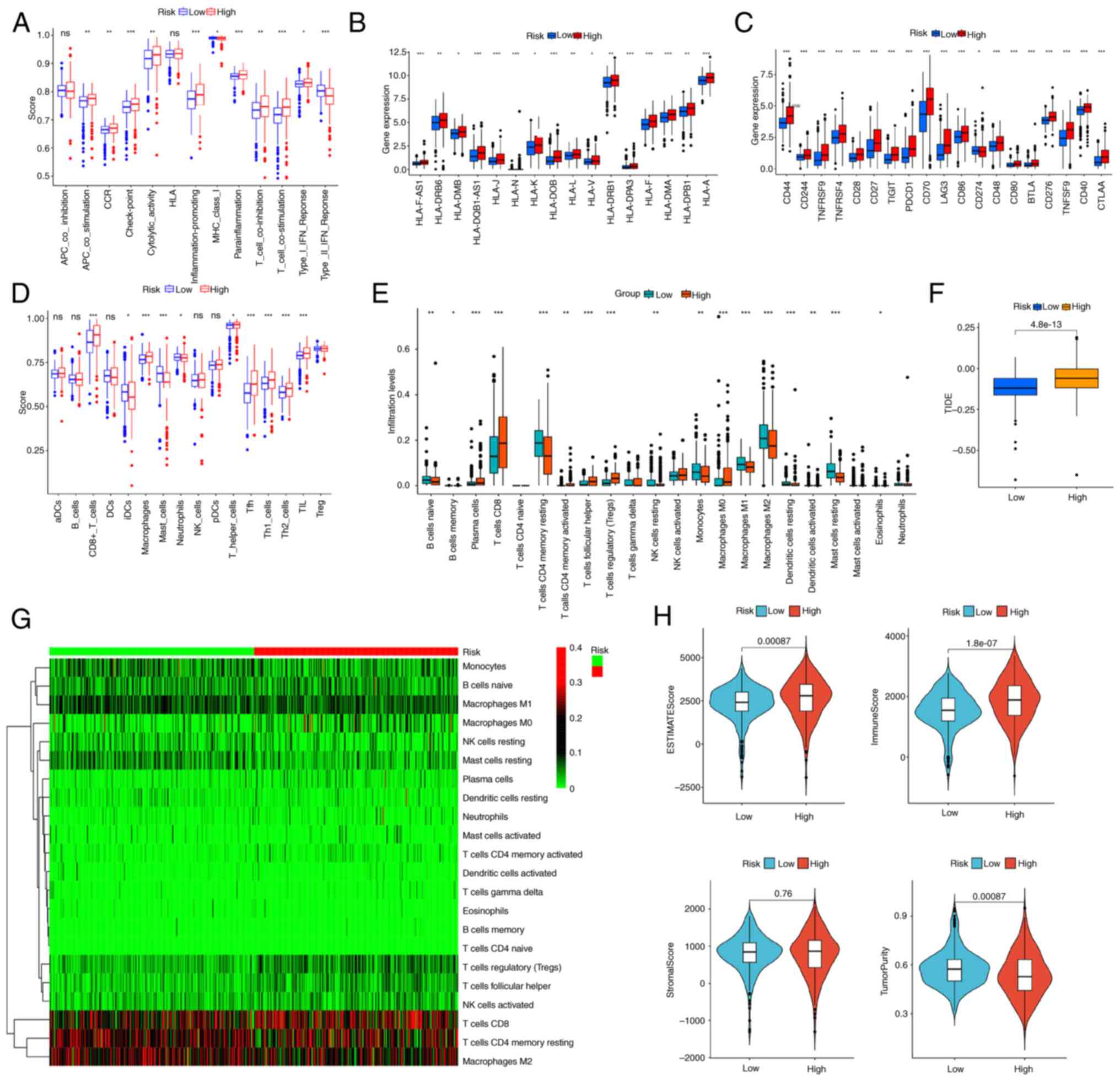
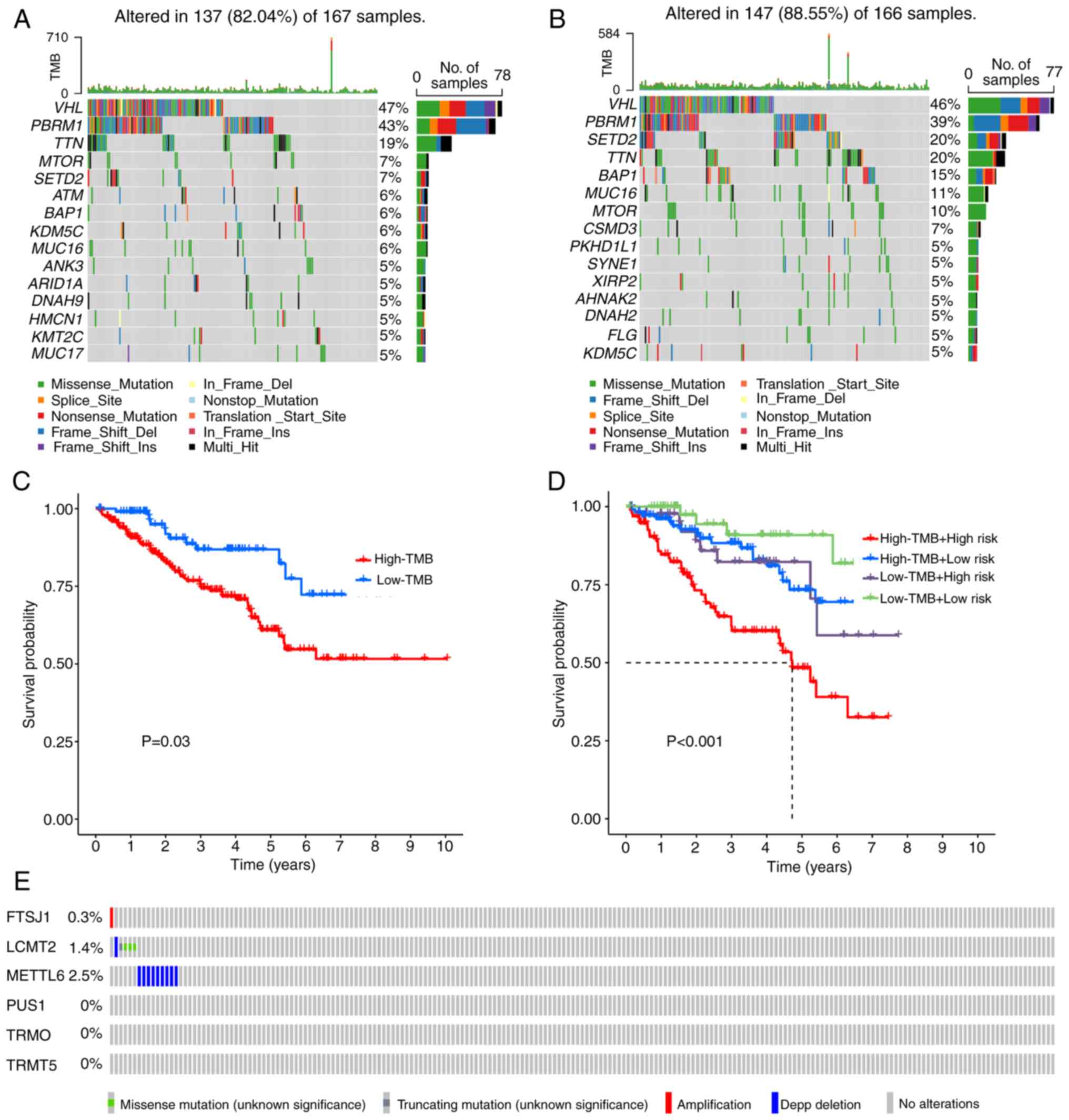
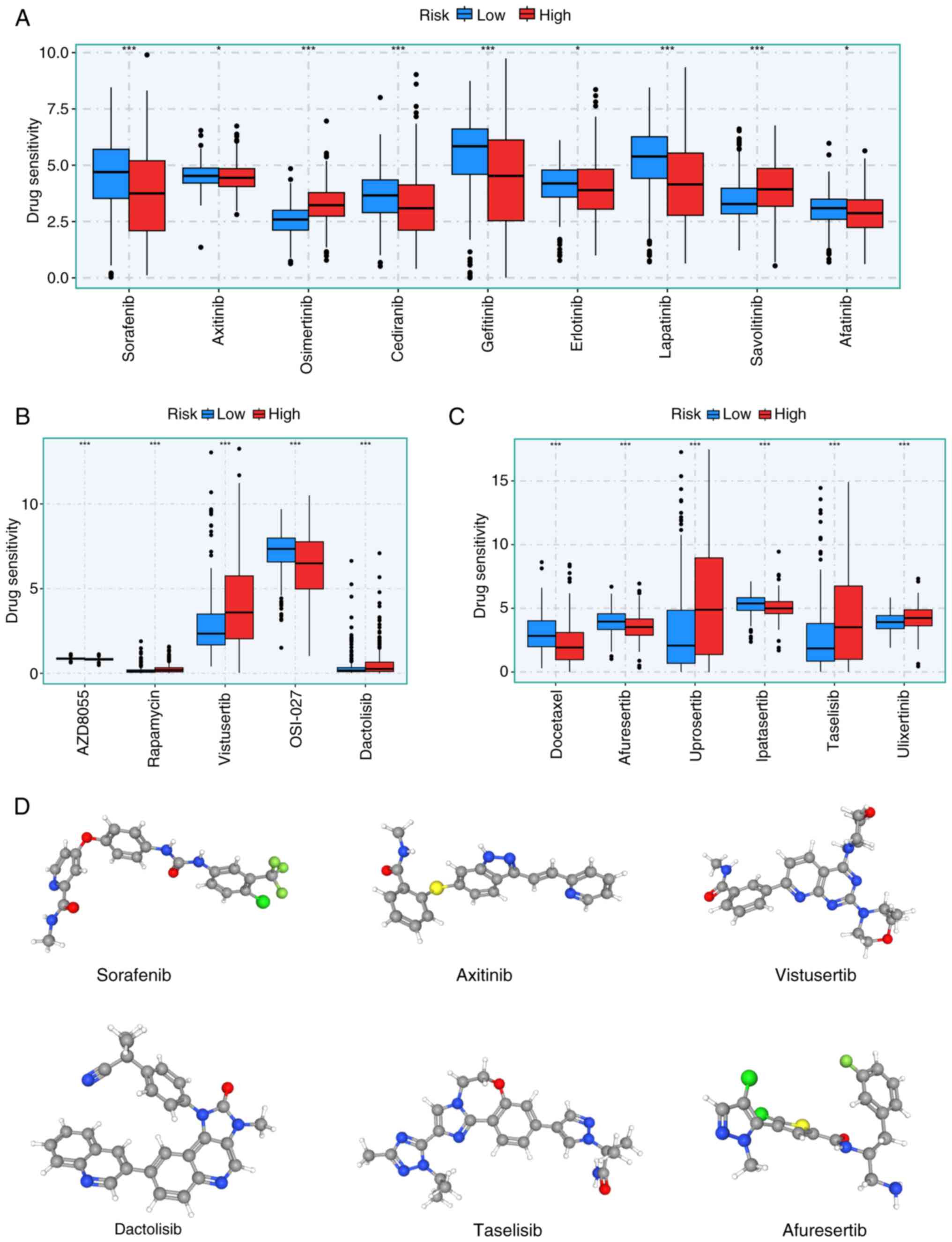
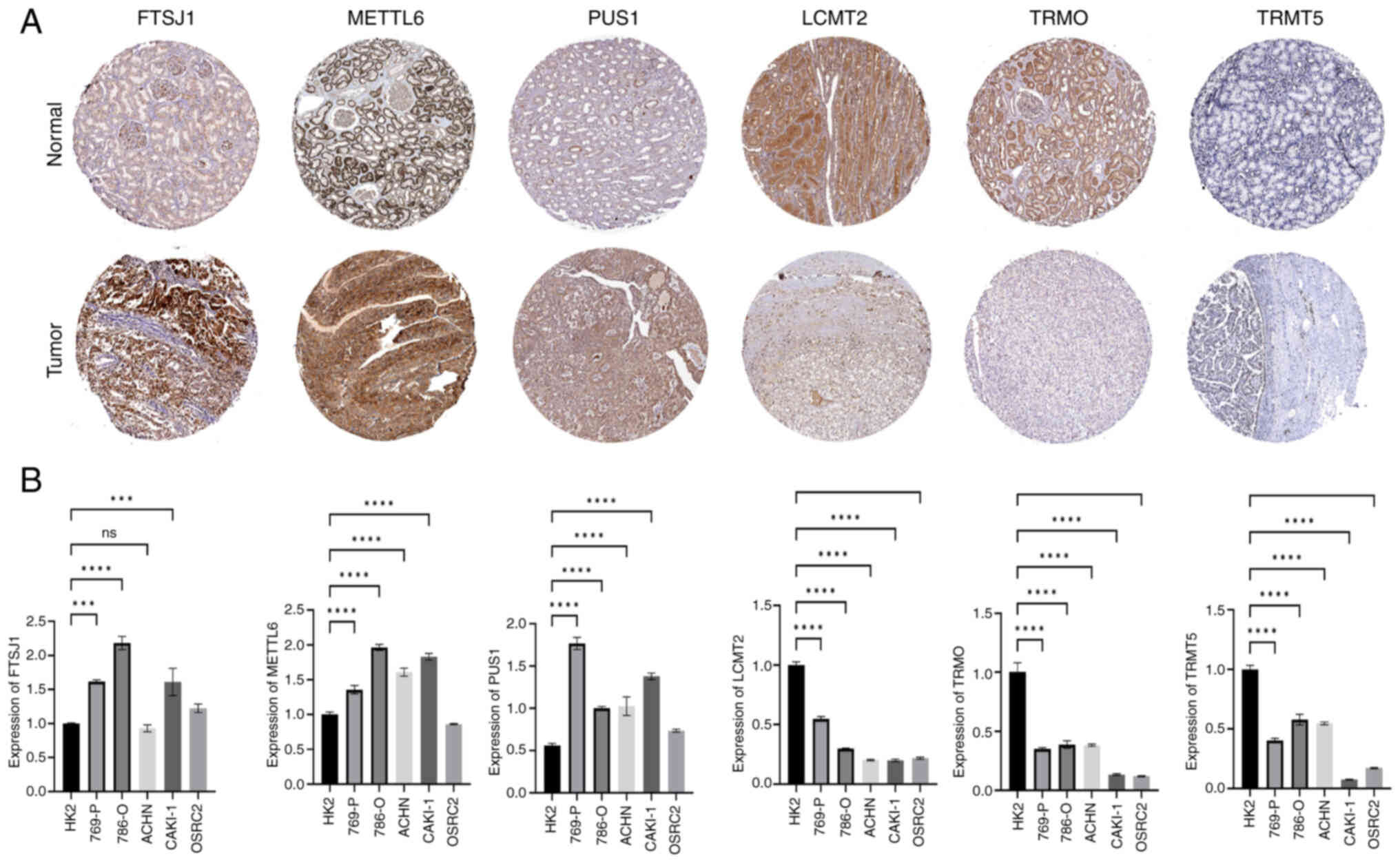
|
1
|
Moch H, Amin MB, Berney DM, Compérat EM,
Gill AJ, Hartmann A, Menon S, Raspollini MR, Rubin MA, Srigley JR,
et al: The 2022 World Health Organization classification of tumours
of the urinary system and male genital organs-part A: Renal,
penile, and testicular tumours. Eur Urol. 82:458–468. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Laversanne M, Sung H, Ferlay J,
Siegel RL, Soerjomataram I and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics
2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for
36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 74:229–263. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB,
Rowland JH, Yabroff KR, Alfano CM, Jemal A, Kramer JL and Siegel
RL: Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J
Clin. 69:363–385. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chujo T and Tomizawa K: Human transfer RNA
modopathies: Diseases caused by aberrations in transfer RNA
modifications. FEBS J. 288:7096–7122. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Suzuki T: The expanding world of tRNA
modifications and their disease relevance. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
22:375–392. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ren D, Mo Y, Yang M, Wang D, Wang Y, Yan
Q, Guo C, Xiong W, Wang F and Zeng Z: Emerging roles of tRNA in
cancer. Cancer Lett. 563:2161702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ying X, Liu B, Yuan Z, Huang Y, Chen C,
Jiang X, Zhang H, Qi D, Yang S, Lin S, et al: METTL1-m7
G-EGFR/EFEMP1 axis promotes the bladder cancer development. Clin
Transl Med. 11:e6752021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li T, Chen Z, Wang Z, Lu J and Chen D:
Combined signature of N7-methylguanosine regulators with their
related genes and the tumor microenvironment: a prognostic and
therapeutic biomarker for breast cancer. Front Immunol.
14:12601952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen B, Jiang W, Huang Y, Zhang J, Yu P,
Wu L and Peng H: N7-methylguanosine tRNA modification
promotes tumorigenesis and chemoresistance through WNT/β-catenin
pathway in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncogene. 41:2239–2253. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: The next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quail DF and Joyce JA: Microenvironmental
regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med.
19:1423–1437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kalluri R: The biology and function of
fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 16:582–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan
V, Fearon DF, Merad M, Coussens LM, Gabrilovich DI,
Ostrand-Rosenberg S, Hedrick CC, et al: Understanding the tumor
immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med.
24:541–550. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee SC, Dacheux MA, Norman DD, Balázs L,
Torres RM, Augelli-Szafran CE and Tigyi GJ: Regulation of tumor
immunity by lysophosphatidic acid. Cancers (Basel). 12:12022020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Laplagne C, Domagala M, Le Naour A,
Quemerais C, Hamel D, Fournié JJ, Couderc B, Bousquet C, Ferrand A
and Poupot M: Latest advances in targeting the tumor
microenvironment for tumor suppression. Int J Mol Sci. 20:47192019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Zhou J, Li X, Zhang X, Shi J, Wang
X, Li H, Miao S, Chen H, He X, et al: tRNA-m1A modification
promotes T cell expansion via efficient MYC protein synthesis. Nat
Immunol. 23:1433–1444. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Orellana EA, Liu Q, Yankova E, Pirouz M,
De Braekeleer E, Zhang W, Lim J, Aspris D, Sendinc E, Garyfallos
DA, et al: METTL1-mediated m7G modification of Arg-TCT
tRNA drives oncogenic transformation. Mol Cell. 81:3323–3338.e14.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Endres L, Fasullo M and Rose R: tRNA
modification and cancer: Potential for therapeutic prevention and
intervention. Future Med Chem. 11:885–900. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Galon J, Angell HK, Bedognetti D and
Marincola FM: The continuum of cancer immunosurveillance:
Prognostic, predictive, and mechanistic signatures. Immunity.
39:11–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu J, Yao L, Yang Y, Ma J, You R, Yu Z
and Du P: A novel stemness-related lncRNA signature predicts
prognosis, immune infiltration and drug sensitivity of clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. J Transl Med. 23:2382025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wing JB, Tanaka A and Sakaguchi S: Human
FOXP3+ regulatory T cell heterogeneity and function in
autoimmunity and cancer. Immunity. 50:302–316. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu SY, Fu T, Jiang YZ and Shao ZM: Natural
killer cells in cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer. 19:1202020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hong K, Cen K, Chen Q, Dai Y, Mai Y and
Guo Y: Identification and validation of a novel senescence-related
biomarker for thyroid cancer to predict the prognosis and
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 14:11283902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Linehan WM, Srinivasan R and Schmidt LS:
The genetic basis of kidney cancer: A metabolic disease. Nat Rev
Urol. 7:277–285. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Linehan WM, Bratslavsky G, Pinto PA,
Schmidt LS, Neckers L, Bottaro DP and Srinivasan R: Molecular
diagnosis and therapy of kidney cancer. Annu Rev Med. 61:329–343.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hsieh JJ, Purdue MP, Signoretti S, Swanton
C, Albiges L, Schmidinger M, Heng DY, Larkin J and Ficarra V: Renal
cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170092017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Moore LE, Nickerson ML, Brennan P, Toro
JR, Jaeger E, Rinsky J, Han SS, Zaridze D, Matveev V, Janout V, et
al: Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) inactivation in sporadic clear cell
renal cancer: Associations with germline VHL polymorphisms and
etiologic risk factors. PLoS Genet. 7:e10023122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors:
Mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy.
Trends Pharmacol Sci. 33:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gnarra JR, Tory K, Weng Y, Schmidt L, Wei
MH, Li H, Latif F, Liu S, Chen F, Duh FM, et al: Mutations of the
VHL tumour suppressor gene in renal carcinoma. Nat Genet. 7:85–90.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Maas M, Kurcz A, Hennenlotter J, Scharpf
M, Fend F, Walz S, Stühler V, Todenhöfer T, Stenzl A, Bedke J and
Rausch S: Differential expression and clinical relevance of C-X-C
motif chemokine receptor 4 (CXCR4) in renal cell carcinomas, benign
renal tumors, and metastases. Int J Mol Sci. 24:52272023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Massari F, Ciccarese C, Santoni M,
Brunelli M, Piva F, Modena A, Bimbatti D, Fantinel E, Santini D,
Cheng L, et al: Metabolic alterations in renal cell carcinoma.
Cancer Treat Rev. 41:767–776. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Choueiri TK, Hessel C, Halabi S, Sanford
B, Michaelson MD, Hahn O, Walsh M, Olencki T, Picus J, Small EJ, et
al: Cabozantinib versus sunitinib as initial therapy for metastatic
renal cell carcinoma of intermediate or poor risk (Alliance A031203
CABOSUN randomised trial): Progression-free survival by independent
review and overall survival update. Eur J Cancer. 94:115–125. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Porta C, Procopio G, Cartenì G, Sabbatini
R, Bearz A, Chiappino I, Ruggeri EM, Re GL, Ricotta R, Zustovich F,
et al: Sequential use of sorafenib and sunitinib in advanced
renal-cell carcinoma (RCC): An Italian multicentre retrospective
analysis of 189 patient cases. BJU Int. 108:E250–E257. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Q, Gao S, Shou Y, Jia Y, Wei Z, Liu
Y, Shi J, Miao D, Miao Q, Zhao C, et al: AIM2 promotes renal cell
carcinoma progression and sunitinib resistance through FOXO3a-ACSL4
axis-regulated ferroptosis. Int J Biol Sci. 19:1266–1283. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Liu X, Gong L, Ding W, Hao W, Peng
Y, Zhang J, Cai W and Gao Y: Mechanisms of sunitinib resistance in
renal cell carcinoma and associated opportunities for therapeutics.
Br J Pharmacol. 180:2937–2955. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sun H, Zheng J, Xiao J, Yue J, Shi Z, Xuan
Z, Chen C, Zhao Y, Tang W, Ye S, et al: TOPK/PBK is phosphorylated
by ERK2 at serine 32, promotes tumorigenesis and is involved in
sorafenib resistance in RCC. Cell Death Dis. 13:4502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li J, Zhang L, Ge T, Liu J, Wang C and Yu
Q: Understanding sorafenib-induced cardiovascular toxicity:
Mechanisms and treatment implications. Drug Des Devel Ther.
18:829–843. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Li Y, Li S, Zhu Y, Liang X, Meng H, Chen
J, Zhang D, Guo H and Shi B: Incidence and risk of
sorafenib-induced hypertension: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich). 16:177–185. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yang Y and Bu P: Progress on the
cardiotoxicity of sunitinib: Prognostic significance, mechanism and
protective therapies. Chem Biol Interact. 257:125–131. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cui W, Zhao D, Jiang J, Tang F, Zhang C
and Duan C: tRNA modifications and modifying enzymes in disease,
the potential therapeutic targets. Int J Biol Sci. 19:1146–1162.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang H, Li H, Pan R, Wang S and Liu X:
tRNA modifications and their potential roles in pancreatic cancer.
Arch Biochem Biophys. 714:1090832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Begley U, Sosa MS, Avivar-Valderas A,
Patil A, Endres L, Estrada Y, Chan CTY, Su D, Dedon PC,
Aguirre-Ghiso JA and Begley T: A human tRNA methyltransferase
9-like protein prevents tumour growth by regulating LIN9 and
HIF1-α. EMBO Mol Med. 5:366–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Brazane M, Dimitrova DG, Pigeon J,
Paolantoni C, Ye T, Marchand V, Da Silva B, Schaefer E, Angelova
MT, Stark Z, et al: The ribose methylation enzyme FTSJ1 has a
conserved role in neuron morphology and learning performance. Life
Sci Alliance. 6:e2022018772023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
He Q, Yang L, Gao K, Ding P, Chen Q, Xiong
J, Yang W, Song Y, Wang L, Wang Y, et al: FTSJ1 regulates tRNA
2′-O-methyladenosine modification and suppresses the malignancy of
NSCLC via inhibiting DRAM1 expression. Cell Death Dis. 11:3482020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pruitt KD, Tatusova T, Klimke W and
Maglott DR: NCBI reference sequences: Current status, policy and
new initiatives. Nucleic Acids Res. 37((Database Issue)): D32–D36.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sun Y, Liu Q, Zhong S, Wei R and Luo JL:
Triple-negative breast cancer intrinsic FTSJ1 favors tumor
progression and attenuates CD8+ T cell infiltration. Cancers
(Basel). 16:5972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Suzuki Y, Noma A, Suzuki T, Ishitani R and
Nureki O: Structural basis of tRNA modification with CO2 fixation
and methylation by wybutosine synthesizing enzyme TYW4. Nucleic
Acids Res. 37:2910–2925. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yeon SY, Jo YS, Choi EJ, Kim MS, Yoo NJ
and Lee SH: Frameshift mutations in repeat sequences of ANK3,
HACD4, TCP10L, TP53BP1, MFN1, LCMT2, RNMT, TRMT6, METTL8 and
METTL16 genes in colon cancers. Pathol Oncol Res. 24:617–622. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ignatova VV, Kaiser S, Ho JSY, Bing X,
Stolz P, Tan YX, Lee CL, Gay FPH, Lastres PR, Gerlini R, et al:
METTL6 is a tRNA m3C methyltransferase that regulates
pluripotency and tumor cell growth. Sci Adv. 6:eaaz45512020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gatza ML, Silva GO, Parker JS, Fan C and
Perou CM: An integrated genomics approach identifies drivers of
proliferation in luminal-subtype human breast cancer. Nat Genet.
46:1051–1059. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Grünberg S, Doyle LA, Wolf EJ, Dai N,
Corrêa IR Jr, Yigit E and Stoddard BL: The structural basis of mRNA
recognition and binding by yeast pseudouridine synthase PUS1. PLoS
One. 18:e02912672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Martinez NM, Su A, Burns MC, Nussbacher
JK, Schaening C, Sathe S, Yeo GW and Gilbert WV: Pseudouridine
synthases modify human pre-mRNA co-transcriptionally and affect
pre-mRNA processing. Mol Cell. 82:645–659.e9. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hu YX, Diao LT, Hou YR, Lv G, Tao S, Xu
WY, Xie SJ, Ren YH and Xiao ZD: Pseudouridine synthase 1 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma through mRNA pseudouridylation to enhance
the translation of oncogenic mRNAs. Hepatology. 80:1058–1073. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Li L, Zhu C, Xu S, Xu Q, Xu D, Gan S, Cui
X and Tang C: PUS1 is a novel biomarker for evaluating malignancy
of human renal cell carcinoma. Aging (Albany NY). 15:5215–5227.
2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Fang Z, Shen HY, Xu Q, Zhou HL, Li L, Yang
SY, Zhu Z and Tang JH: PUS1 is a novel biomarker for predicting
poor outcomes and triple-negative status in breast cancer. Front
Oncol. 12:10305712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kimura S, Miyauchi K, Ikeuchi Y, Thiaville
PC, Crécy-Lagard Vd and Suzuki T: Discovery of the β-barrel-type
RNA methyltransferase responsible for N6-methylation of
N6-threonylcarbamoyladenosine in tRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res.
42:9350–9365. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kulkarni O, Sugier PE, Guibon J,
Boland-Augé A, Lonjou C, Bacq-Daian D, Olaso R, Rubino C, Souchard
V, Rachedi F, et al: Gene network and biological pathways
associated with susceptibility to differentiated thyroid carcinoma.
Sci Rep. 11:89322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Argente-Escrig H, Vílchez JJ, Frasquet M,
Muelas N, Azorín I, Vílchez R, Millet-Sancho E, Pitarch I,
Tomás-Vila M, Vázquez-Costa JF, et al: A novel TRMT5 mutation
causes a complex inherited neuropathy syndrome: The role of nerve
pathology in defining a demyelinating neuropathy. Neuropathol Appl
Neurobiol. 48:e128172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhao Q, Zhang L, He Q, Chang H, Wang Z,
Cao H, Zhou Y, Pan R and Chen Y: Targeting TRMT5 suppresses
hepatocellular carcinoma progression via inhibiting the HIF-1α
pathways. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 24:50–63. 2023.(In English,
Chinese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang Y, Suarez ER, Kastrunes G, de Campos
NSP, Abbas R, Pivetta RS, Murugan N, Chalbatani GM, D'Andrea V and
Marasco WA: Evolution of cell therapy for renal cell carcinoma. Mol
Cancer. 23:82024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Pal SK, Tran B, Haanen JBAG, Hurwitz ME,
Sacher A, Tannir NM, Budde LE, Harrison SJ, Klobuch S, Patel SS, et
al: CD70-targeted allogeneic CAR T-cell therapy for advanced clear
cell renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 14:1176–1189. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Xu Z, Jiang W, Liu L, Qiu Y, Wang J, Dai
S, Guo J and Xu J: Dual-loss of PBRM1 and RAD51 identifies
hyper-sensitive subset patients to immunotherapy in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 73:952024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Hinshaw DC and Shevde LA: The tumor
microenvironment innately modulates cancer progression. Cancer Res.
79:4557–4566. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Gajewski TF, Schreiber H and Fu YX: Innate
and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat
Immunol. 14:1014–1022. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Boutilier AJ and Elsawa SF: Macrophage
polarization states in the tumor microenvironment. Int J Mol Sci.
22:69952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Tao JH, Cheng M, Tang JP, Liu Q, Pan F and
Li XP: Foxp3, regulatory T cell, and autoimmune diseases.
Inflammation. 40:328–339. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gao Y, You M, Fu J, Tian M, Zhong X, Du C,
Hong Z, Zhu Z, Liu J, Markowitz GJ, et al: Intratumoral stem-like
CCR4+ regulatory T cells orchestrate the immunosuppressive
microenvironment in HCC associated with hepatitis B. J Hepatol.
76:148–159. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
De Serres SA, Sayegh MH and Najafian N:
Immunosuppressive drugs and Tregs: A critical evaluation! Clin J Am
Soc Nephrol. 4:1661–1669. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chen ML, Pittet MJ, Gorelik L, Flavell RA,
Weissleder R, von Boehmer H and Khazaie K: Regulatory T cells
suppress tumor-specific CD8 T cell cytotoxicity through TGF-beta
signals in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:419–424. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Fu J, Xu D, Liu Z, Shi M, Zhao P, Fu B,
Zhang Z, Yang H, Zhang H, Zhou C, et al: Increased regulatory T
cells correlate with CD8 T-cell impairment and poor survival in
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Gastroenterology. 132:2328–2339.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Shan F, Somasundaram A, Bruno TC, Workman
CJ and Vignali DAA: Therapeutic targeting of regulatory T cells in
cancer. Trends Cancer. 8:944–961. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Li C, Jiang P, Wei S, Xu X and Wang J:
Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: New mechanisms,
potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol Cancer.
19:1162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Rak R, Polonsky M, Eizenberg-Magar I, Mo
Y, Sakaguchi Y, Mizrahi O, Nachshon A, Reich-Zeliger S,
Stern-Ginossar N, Dahan O, et al: Dynamic changes in tRNA
modifications and abundance during T cell activation. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 118:e21065561182021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lu S, Wei X, Tao L, Dong D, Hu W, Zhang Q,
Tao Y, Yu C, Sun D and Cheng H: A novel tRNA-derived fragment
tRF-3022b modulates cell apoptosis and M2 macrophage polarization
via binding to cytokines in colorectal cancer. J Hematol Oncol.
15:1762022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Vesely MD, Zhang T and Chen L: resistance
mechanisms to anti-PD cancer immunotherapy. Annu Rev Immunol.
40:45–74. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nishimura H and Honjo T: PD-1: An
inhibitory immunoreceptor involved in peripheral tolerance. Trends
Immunol. 22:265–268. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cui JW, Li Y, Yang Y, Yang HK, Dong JM,
Xiao ZH, He X, Guo JH, Wang RQ, Dai B and Zhou ZL: Tumor
immunotherapy resistance: Revealing the mechanism of
PD-1/PD-L1-mediated tumor immune escape. Biomed Pharmacother.
171:1162032024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Rotte A: Combination of CTLA-4 and PD-1
blockers for treatment of cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:2552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Palmeri M, Mehnert J, Silk AW, Jabbour SK,
Ganesan S, Popli P, Riedlinger G, Stephenson R, de Meritens AB,
Leiser A, et al: Real-world application of tumor mutational
burden-high (TMB-high) and microsatellite instability (MSI)
confirms their utility as immunotherapy biomarkers. ESMO Open.
7:1003362022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Klempner SJ, Fabrizio D, Bane S, Reinhart
M, Peoples T, Ali SM, Sokol ES, Frampton G, Schrock AB, Anhorn R
and Reddy P: Tumor mutational burden as a predictive biomarker for
response to immune checkpoint inhibitors: A review of current
evidence. Oncologist. 25:e147–e159. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhang Q, Lin B, Chen H, Ye Y, Huang Y,
Chen Z and Li J: Lipid metabolism-related gene expression in the
immune microenvironment predicts prognostic outcomes in renal cell
carcinoma. Front Immunol. 14:13242052023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|