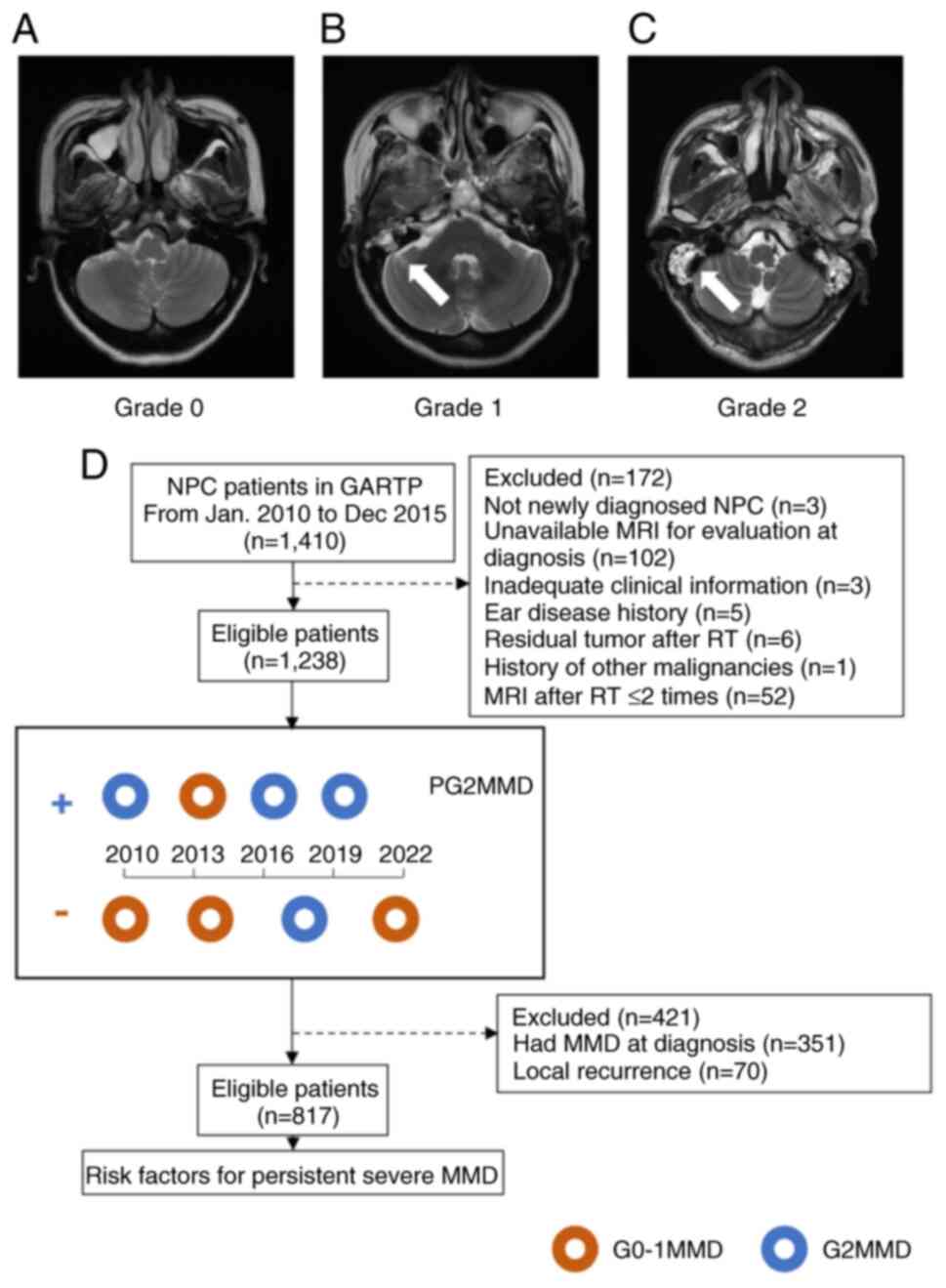
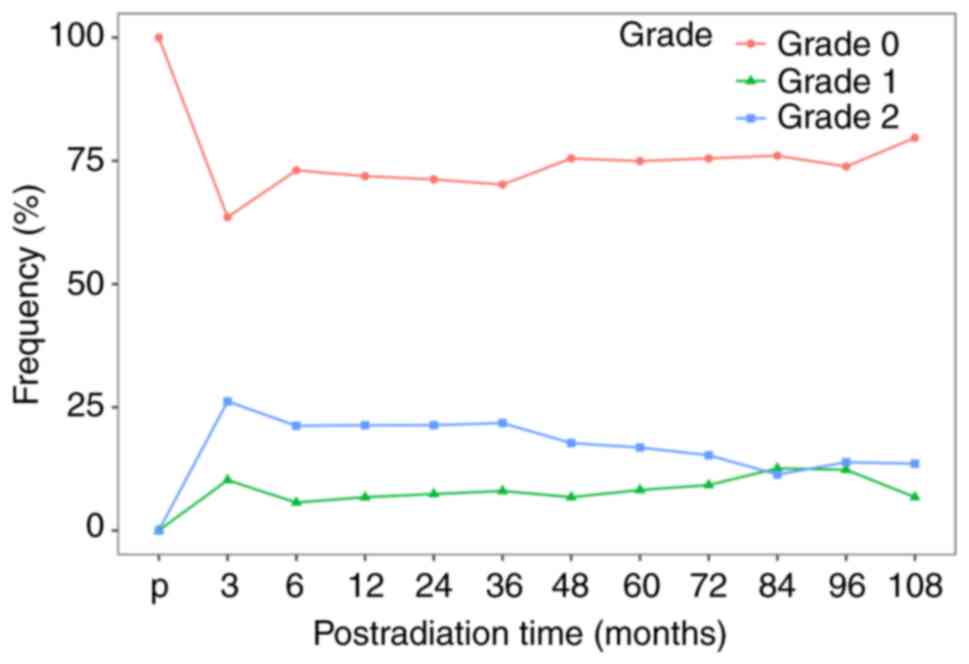
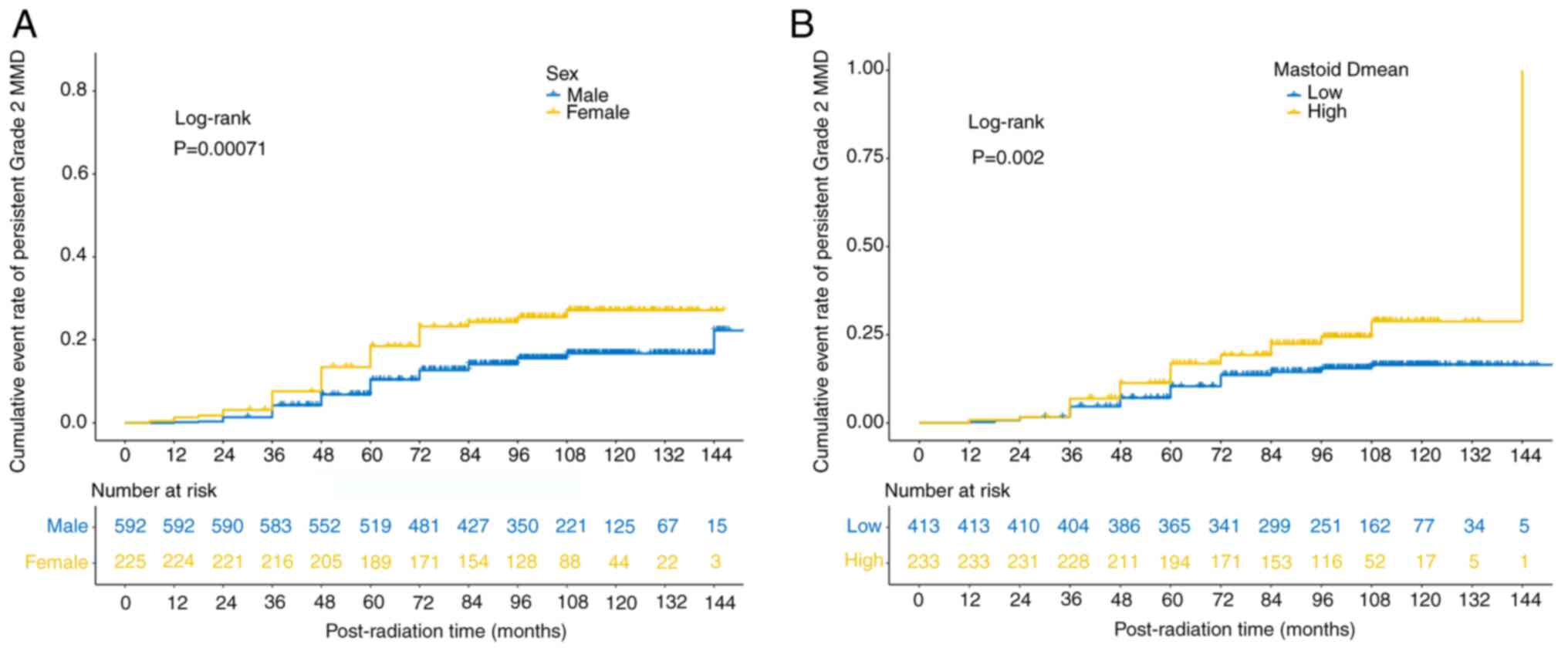
|
1
|
Chen YP, Chan ATC, Le QT, Blanchard P, Sun
Y and Ma J: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 394:64–80. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bhandare N, Antonelli PJ, Morris CG,
Malayapa RS and Mendenhall WM: Ototoxicity after radiotherapy for
head and neck tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 67:469–479.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yao JJ, Zhou GQ, Yu XL, Tang LL, Chen L,
Mao YP, Lin L, Zhang LL, Shao JY, Guo Y, et al: Incidence of and
risk factors for mastoiditis after intensity modulated radiotherapy
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. PLoS One. 10:e01312842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kew J, Tong MC, King AD, Leung SF,
Metreweli C and van Hasselt CA: Magnetic resonance imaging and
audiologic assessment of middle ear effusions in patients with
nasopharyngeal carcinoma before radiation therapy. Am J Otol.
20:74–76. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nishimura R, Baba Y, Murakami R, Baba T,
Furusawa M, Ishikawa T, Ushio Y and Takahashi M: MR evaluation of
radiation otomastoiditis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 39:155–160.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McDonald MH, Hoffman MR and Gentry LR:
When is fluid in the mastoid cells a worrisome finding? J Am Board
Fam Med. 26:218–220. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jose J, Coatesworth AP, Anthony R and
Reilly PG: Life threatening complications after partially treated
mastoiditis. BMJ. 327:41–42. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen JF and Lee ST: Nasopharyngeal
carcinoma presenting as an intracranial abscess. Surg Neurol.
49:553–557. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
King AD, Kew J, Tong M, Leung SF, Lam WW,
Metreweli C and van Hasselt CA: Magnetic resonance imaging of the
eustachian tube in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: Correlation of
patterns of spread with middle ear effusion. Am J Otol. 20:69–73.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao JJ, Zhou GQ, Lin L, Zhang WJ, Peng YL,
Chen L, Tang LL, Mao YP, Ma J and Sun Y: Dose-volume factors
associated with ear disorders following intensity modulated
radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Sci Rep. 5:135252015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Walker GV, Ahmed S, Allen P, Gidley PW,
Woo SY, DeMonte F, Chang EL and Mahajan A: Radiation-induced middle
ear and mastoid opacification in skull base tumors treated with
radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:e819–e823. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yao JJ, Zhou GQ, Jin YN, Zhang WJ, Lin L,
Yu XL, Shao JY, Ma J and Sun Y: Predictors of mastoiditis after
intensity-modulated radiotherapy in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A
dose-volume analysis. J Cancer. 7:276–282. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang TM, Shen GP, Chen MY, Zhang JB, Sun
Y, He J, Xue WQ, Li XZ, Huang SY, Zheng XH, et al: Genome-wide
association study of susceptibility loci for radiation-induced
brain injury. J Natl Cancer Inst. 111:620–628. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Amin MB, Edge SB, Greene FL, Byrd DR,
Brookland RK, Washington MK, Gershenwald JE, Compton CC, Hess KR,
Sullivan DC, et al: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. Springer;
Heidelberg: 2017
|
|
15
|
Saat R, Mahmood G, Laulajainen-Hongisto A,
Lempinen L, Aarnisalo AA, Jero J and Markkola A: Comparison of MR
imaging findings in paediatric and adult patients with acute
mastoiditis and incidental intramastoid bright signal on
T2-weighted images. Eur Radiol. 26:2632–2639. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Halperin E, Wazer D, Perez C and Brady L:
Perez & Brady's Principles and Practice of Radiation Oncology.
Lippincott Williams & Wilkins (LWW); Philadelphia, PA: 2018
|
|
17
|
Boussaid M, Brahim O, Bouanen I, Kenani M,
Limem H, Mahjoub Y, Mesrati MA and Aissaoui A: Sex determination by
Ct -scan analysis of the mastoid bone: A cross-sectional study.
Heliyon. 10:e337122024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yalcinkaya A, Yalcinkaya R, Sardh F and
Landegren N: Immune dynamics throughout life in relation to sex
hormones and perspectives gained from gender-affirming hormone
therapy. Front Immunol. 15:15013642025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kaiser M, Semeraro MD, Herrmann M,
Absenger G, Gerger A and Renner W: Immune aging and immunotherapy
in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 22:70162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Popescu C, Ioniţă E, Mogoantă CA,
Simionescu C and Pătru E: Clinical and histopathological aspects in
otomastoiditis. Rom J Morphol Embryol. 50:453–460. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mullin S, Smith L, Lee K, D'Souza G,
Woodgate P, Elflein J, Hällqvist J, Toffoli M, Streeter A, Hosking
J, et al: Ambroxol for the treatment of patients with parkinson
disease with and without glucocerebrosidase gene mutations: A
nonrandomized, noncontrolled trial. JAMA Neurol. 77:427–434. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou X, Jin X, Yang L and Wei X: Efficacy
and safety of ambroxol hydrochloride in the treatment of secretory
otitis media: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Transl
Med. 10:1422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yan JJ, Guo SS, Lin DF, Liu LT, Liu SL,
Xiao BB, Yang JH, Wen DX, Yang ZC, Liang YJ, et al: Development and
validation of a normal tissue complication probability model for
acquired nasal cavity stenosis and atresia after radical
radiotherapy for nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Radiother Oncol.
160:9–17. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|