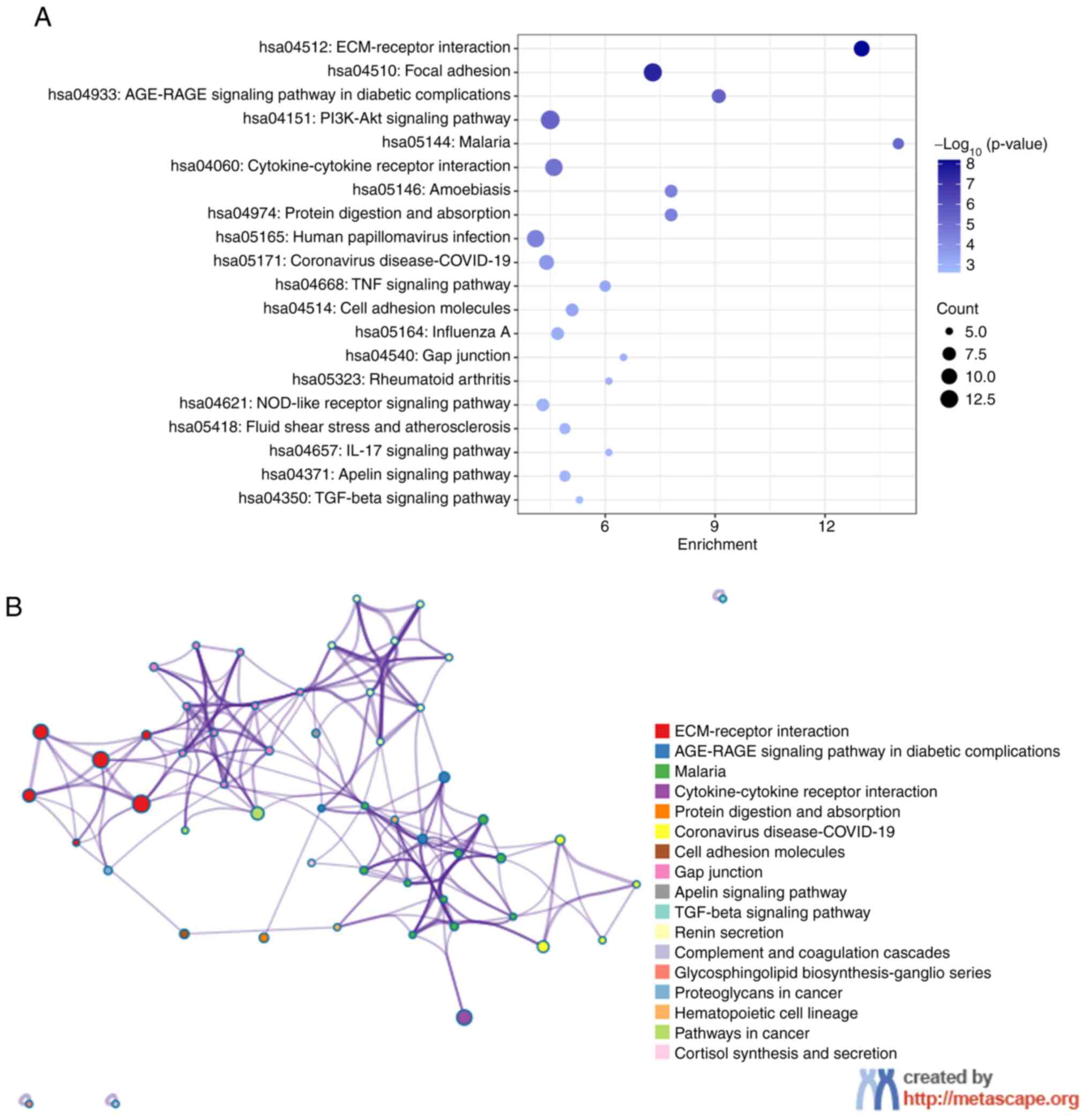
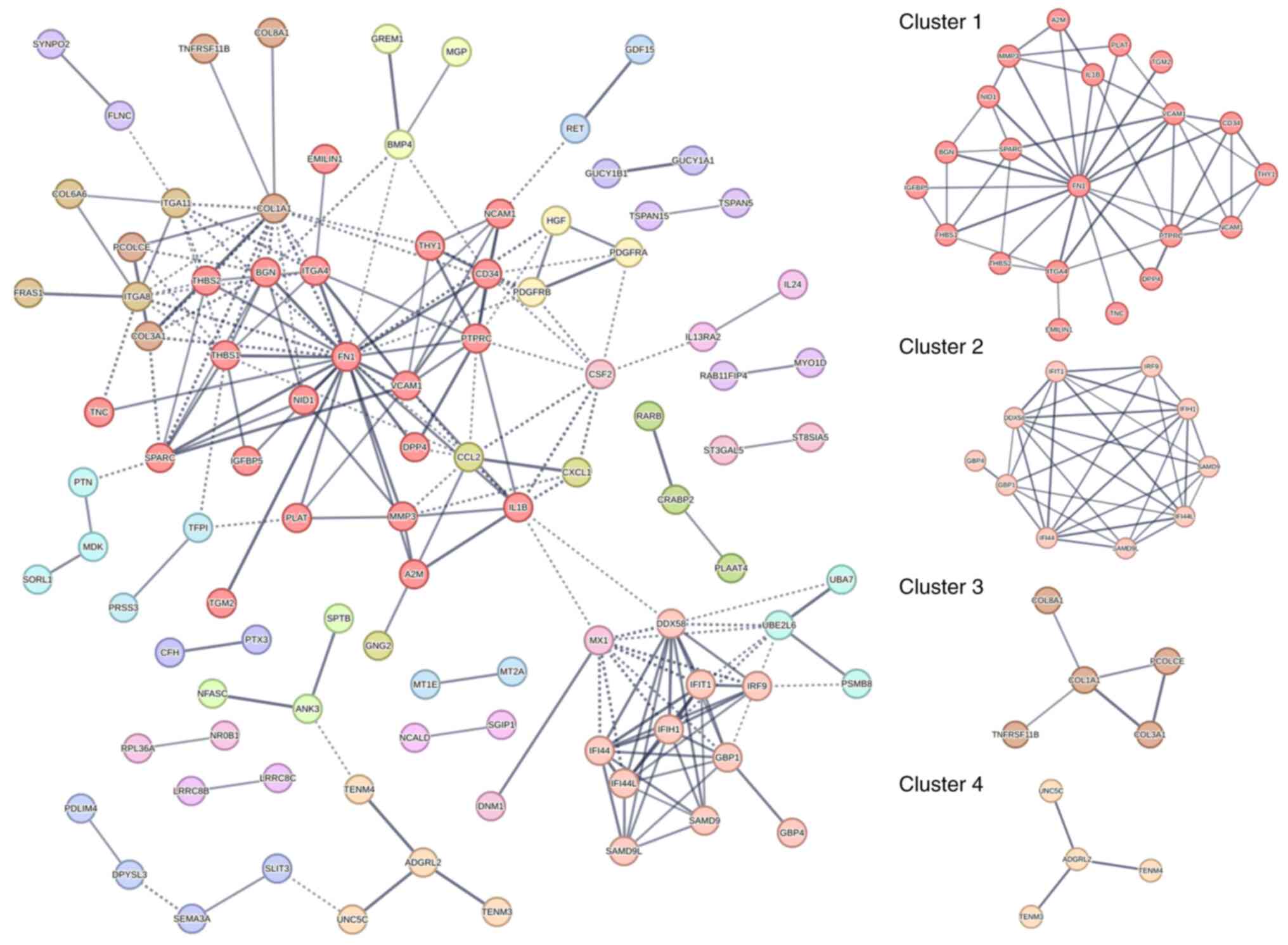
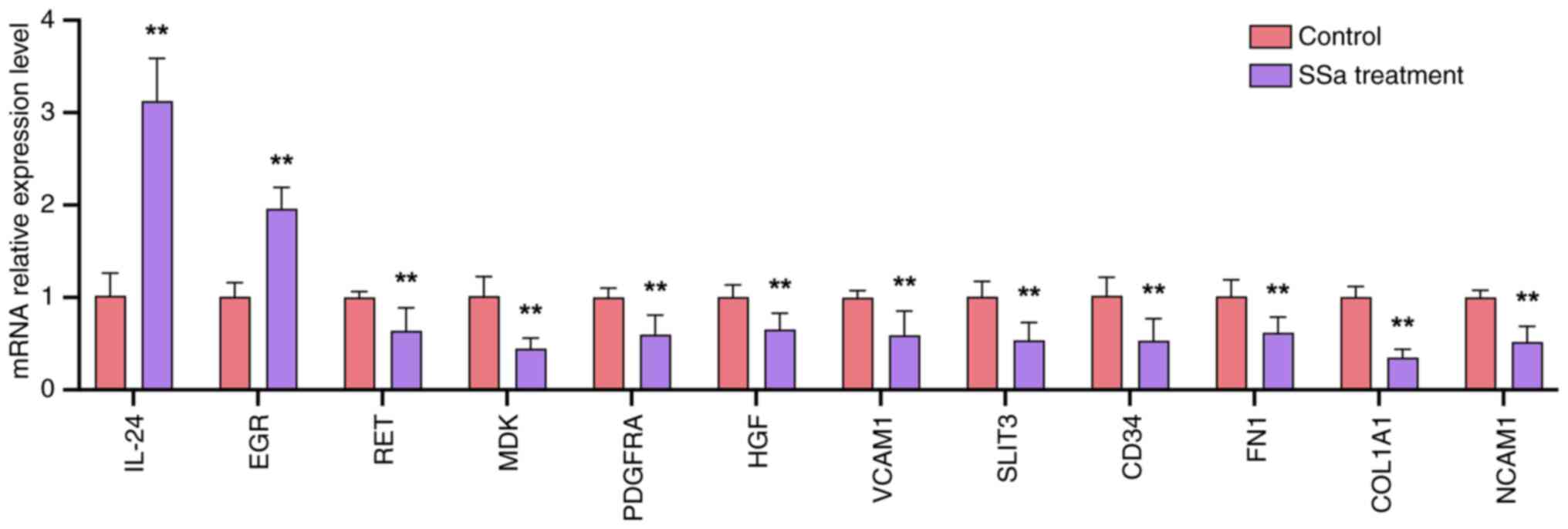
|
1
|
Zafar A, Wang W, Liu G, Xian W, McKeon F,
Zhou J and Zhang R: Targeting the p53-MDM2 pathway for
neuroblastoma therapy: Rays of hope. Cancer Lett. 496:16–29. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bansal M, Gupta A and Ding HF: MYCN and
metabolic reprogramming in neuroblastoma. Cancers (Basel).
14:41132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zafar A, Wang W, Liu G, Wang X, Xian W,
McKeon F, Foster J, Zhou J and Zhang R: Molecular targeting
therapies for neuroblastoma: Progress and challenges. Med Res Rev.
41:961–1021. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lundberg KI, Treis D and Johnsen JI:
Neuroblastoma heterogeneity, plasticity, and emerging therapies.
Curr Oncol Rep. 24:1053–1062. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lin L, Miao L, Lin H, Cheng J, Li M, Zhuo
Z and He J: Targeting RAS in neuroblastoma: Is it possible?
Pharmacol Ther. 236:1080542022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Qiu B and Matthay KK: Advancing therapy
for neuroblastoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 19:515–533. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Whittle SB, Smith V, Doherty E, Zhao S,
McCarty S and Zage PE: Overview and recent advances in the
treatment of neuroblastoma. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 17:369–386.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rivera Z, Escutia C, Madonna MB and Gupta
KH: Biological insight and recent advancement in the treatment of
neuroblastoma. Int J Mol Sci. 24:84702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gao J, Fosbrook C, Gibson J, Underwood TJ,
Gray JC and Walters ZS: Review: Targeting EZH2 in neuroblastoma.
Cancer Treat Rev. 119:1026002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li X, Li X, Huang N, Liu R and Sun R: A
comprehensive review and perspectives on pharmacology and
toxicology of saikosaponins. Phytomedicine. 50:73–87. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li XQ, Song YN, Wang SJ, Rahman K, Zhu JY
and Zhang H: Saikosaponins: A review of pharmacological effects. J
Asian Nat Prod Res. 20:399–411. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xiao LX, Zhou HN and Jiao ZY: Present and
future prospects of the anti-cancer activities of saikosaponins.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 23:2–14. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Motoo Y and Sawabu N: Antitumor effects of
saikosaponins, baicalin and baicalein on human hepatoma cell lines.
Cancer Lett. 86:91–95. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qian L, Murakami T, Kimura Y, Takahashi M
and Okita K: Saikosaponin A-induced cell death of a human hepatoma
cell line (HuH-7): The significance of the ‘sub-G1 peak’ in a DNA
histo. Pathol Int. 45:207–214. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wen-Sheng W: ERK signaling pathway is
involved in p15INK4b/p16INK4a expression and HepG2 growth
inhibition triggered by TPA and saikosaponin A. Oncogene.
22:955–963. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu WS and Hsu HY: Involvement of
p-15(INK4b) and p-16(INK4a) gene expression in saikosaponin a and
TPA-induced growth inhibition of HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 285:183–187. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang SJ, Lee YJ, Kang SG, Cho S, Yoon W,
Lim JH, Min SH, Lee TH and Kim BM: Caspase-4 is essential for
saikosaponin a-induced apoptosis acting upstream of caspase-2 and
γ-H2AX in colon cancer cells. Oncotarget. 8:100433–100448. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim BM and Hong SH: Sequential caspase-2
and caspase-8 activation is essential for saikosaponin a-induced
apoptosis of human colon carcinoma cell lines. Apoptosis.
16:184–197. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen JC, Chang NW, Chung JG and Chen KC:
Saikosaponin-A induces apoptotic mechanism in human breast
MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cancer cells. Am J Chin Med. 31:363–377. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao X, Liu J, Ge S, Chen C, Li S, Wu X,
Feng X, Wang Y and Cai D: Saikosaponin A inhibits breast cancer by
regulating Th1/Th2 balance. Front Pharmacol. 10:6242019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang Y, Dai K, Xu D, Fan H, Ji N, Wang D,
Zhao Y and Liu R: Saikosaponin A alleviates glycolysis of breast
cancer cells through repression of Akt/STAT3 pathway. Chem Biol
Drug Des. 102:115–125. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shi C, Sun L, Fang R, Zheng S, Yu M and Li
Q: Saikosaponin-A exhibits antipancreatic cancer activity by
targeting the EGFR/PI3K/Akt pathway. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.
24:579–588. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cheng T and Ying M: Antitumor effect of
Saikosaponin A on human neuroblastoma cells. Biomed Res Int.
2021:58455542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bolger AM, Lohse M and Usadel B:
Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for illumina sequence data.
Bioinformatics. 30:2114–2120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim D, Paggi JM, Park C, Bennett C and
Salzberg SL: Graph-based genome alignment and genotyping with
HISAT2 and HISAT-genotype. Nat Biotechnol. 37:907–915. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liao Y, Smyth GK and Shi W: featureCounts:
An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads
to genomic features. Bioinformatics. 30:923–930. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Anders S and Huber W: Differential
expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol.
11:R1062010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
EdgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, . Aleksander SA,
Balhoff J, Carbon S, Cherry JM, Drabkin HJ, Ebert D, Feuermann M,
Gaudet P, Harris NL, et al: The gene ontology knowledgebase in
2023. Genetics. 224:iyad0312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sherman BT, Hao M, Qiu J, Jiao X, Baseler
MW, Lane HC, Imamichi T and Chang W: DAVID: A web server for
functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene
lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 50:W216–W221. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Kawashima
M and Ishiguro-Watanabe M: KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of
pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 51:D587–D592. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M,
Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C and Chanda SK: Metascape
provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of
systems-level datasets. Nat Commun. 10:15232019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pignatelli M, Luna-Medina R, Pérez-Rendón
A, Santos A and Perez-Castillo A: The transcription factor early
growth response factor-1 (EGR-1) promotes apoptosis of
neuroblastoma cells. Biochem J. 373:739–746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cibelli G, Policastro V, Rössler OG and
Thiel G: Nitric oxide-induced programmed cell death in human
neuroblastoma cells is accompanied by the synthesis of Egr-1, a
zinc finger transcription factor. J Neurosci Res. 67:450–460. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Zhang H, Zhu X, Feng D, Gong J and
Han T: Interleukin-24 induces neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cell
differentiation, growth inhibition, and apoptosis by promoting ROS
production. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 33:709–714. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Skinner MA, Lackey KE and Freemerman AJ:
RET activation inhibits doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in SK-N-MC
cells. Anticancer Res. 28:2019–2025. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kishida S and Kadomatsu K: Involvement of
midkine in neuroblastoma tumourigenesis. Br J Pharmacol.
171:896–904. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Futami H and Sakai R: RET protein promotes
non-adherent growth of NB-39-nu neuroblastoma cell line. Cancer
Sci. 100:1034–1039. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Steen EA, Basilaia M, Kim W, Getz T,
Gustafson JL and Zage PE: Targeting the RET tyrosine kinase in
neuroblastoma: A review and application of a novel selective drug
design strategy. Biochem Pharmacol. 216:1157512023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ishida M, Ichihara M, Mii S, Jijiwa M,
Asai N, Enomoto A, Kato T, Majima A, Ping J, Murakumo Y and
Takahashi M: Sprouty2 regulates growth and differentiation of human
neuroblastoma cells through RET tyrosine kinase. Cancer Sci.
98:815–821. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Erdogan S, Doganlar ZB, Doganlar O,
Turkekul K and Serttas R: Inhibition of midkine suppresses prostate
cancer CD133+ stem cell growth and migration. Am J Med
Sci. 354:299–309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hao H, Maeda Y, Fukazawa T, Yamatsuji T,
Takaoka M, Bao XH, Matsuoka J, Okui T, Shimo T, Takigawa N, et al:
Inhibition of the growth factor MDK/midkine by a novel small
molecule compound to treat non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One.
8:e710932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Han X, Li M, Xu J, Fu J, Wang X, Wang J,
Xia T, Wang S and Ma G: miR-1275 targets MDK/AKT signaling to
inhibit breast cancer chemoresistance by lessening the properties
of cancer stem cells. Int J Biol Sci. 19:89–103. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hou Y, Du W, Wu Q, Chai X, Wang Y, Mi Y,
Tian Y, Tang M, Li J and Yan D: PDGFRA exhibits potential as an
indicator of angiogenesis within the tumor microenvironment and is
up-regulated in BLCA. Microvasc Res. 151:1046142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Daudigeos-Dubus E, LeDret L, Bawa O,
Opolon P, Vievard A, Villa I, Bosq J, Vassal G and Geoerger B: Dual
inhibition using cabozantinib overcomes HGF/MET signaling mediated
resistance to pan-VEGFR inhibition in orthotopic and metastatic
neuroblastoma tumors. Int J Oncol. 50:203–211. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xiang X, Pathak JL, Wu W, Li J, Huang W,
Wu Q, Xin M, Wu Y, Huang Y, Ge L and Zeng S: Human serum-derived
exosomes modulate macrophage inflammation to promote VCAM1-mediated
angiogenesis and bone regeneration. J Cell Mol Med. 27:1131–1143.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yallowitz AR, Shim JH, Xu R and Greenblatt
MB: An angiogenic approach to osteoanabolic therapy targeting the
SHN3-SLIT3 pathway. Bone. 172:1167612023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sasano H and Suzuki T: Pathological
evaluation of angiogenesis in human tumor. Biomed Pharmacother. 59
(Suppl 2):S334–S336. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Lin LH, Lin JS, Yang CC, Cheng HW, Chang
KW and Liu CJ: Overexpression of platelet-derived growth factor and
its receptor are correlated with oral tumorigenesis and poor
prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci.
21:23602020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wei T, Zhang LN, Lv Y, Ma XY, Zhi L, Liu
C, Ma F and Zhang XF: Overexpression of platelet-derived growth
factor receptor alpha promotes tumor progression and indicates poor
prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 5:10307–10317.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hecht M, Papoutsi M, Tran HD, Wilting J
and Schweigerer L: Hepatocyte growth factor/c-Met signaling
promotes the progression of experimental human neuroblastomas.
Cancer Res. 64:6109–6118. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Paul JD, Coulombe KLK, Toth PT, Zhang Y,
Marsboom G, Bindokas VP, Smith DW, Murry CE and Rehman J:
SLIT3-ROBO4 activation promotes vascular network formation in human
engineered tissue and angiogenesis in vivo. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
64:124–131. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Liu H and Zhao KY: Application of CD34
expression combined with three-phase dynamic contrast-enhanced
computed tomography scanning in preoperative staging of gastric
cancer. World J Gastrointest Surg. 15:2513–2524. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mei Y, Wang Z, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Li X, Liu
H, Ye J and You H: Regulation of neuroblastoma differentiation by
forkhead transcription factors FOXO1/3/4 through the receptor
tyrosine kinase PDGFRA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:4898–4903.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Moosavi F, Giovannetti E, Peters GJ and
Firuzi O: Combination of HGF/MET-targeting agents and other
therapeutic strategies in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol.
160:1032342021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
An Q, Liu T, Wang MY, Yang YJ, Zhang ZD,
Lin ZJ and Yang B: CircKRT7-miR-29a-3p-COL1A1 axis promotes ovarian
cancer cell progression. Onco Targets Ther. 13:8963–8976. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Dehghan MH, Ashrafi MR, Hedayati M,
Shivaee S and Rajabi S: Oral contraceptive steroids promote
papillary thyroid cancer metastasis by targeting angiogenesis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Int J Mol Cell Med. 10:219–226.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Li X, Sun X, Kan C, Chen B, Qu N, Hou N,
Liu Y and Han F: COL1A1: A novel oncogenic gene and therapeutic
target in malignancies. Pathol Res Pract. 236:1540132022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Li J, Yang R, Yang H, Chen S, Wang L, Li
M, Yang S, Feng Z and Bi J: NCAM regulates the proliferation,
apoptosis, autophagy, EMT, and migration of human melanoma cells
via the Src/Akt/mTOR/cofilin signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
121:1192–1204. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhou Y, Cao G, Cai H, Huang H and Zhu X:
The effect and clinical significance of FN1 expression on
biological functions of gastric cancer cells. Cell Mol Biol
(Noisy-le-grand). 66:191–198. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Cao M, Xiao D and Ding X: The anti-tumor
effect of ursolic acid on papillary thyroid carcinoma via
suppressing fibronectin-1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 84:2415–2424.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ding Y, Zhang M, Hu S, Zhang C, Zhou Y,
Han M, Li J, Li F, Ni H, Fang S and Chen Q: MiRNA-766-3p inhibits
gastric cancer via targeting COL1A1 and regulating PI3K/AKT
signaling pathway. J Cancer. 15:990–998. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Markovsky E, Eldar-Boock A, Ben-Shushan D,
Baabur-Cohen H, Yeini E, Pisarevsky E, Many A, Aviel-Ronen S,
Barshack I and Satchi-Fainaro R: Targeting NCAM-expressing
neuroblastoma with polymeric precision nanomedicine. J Control
Release. 249:162–172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Heinly BE and Grant CN: Cell adhesion
molecules in neuroblastoma: Complex roles, therapeutic potential.
Front Oncol. 12:7821862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|